Microstructure and Phase Composition of Novel Crossover Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Y(Er) Alloys with Equal Zn/Mg/Cu Ratio and Cr Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alloys Preparation
2.2. Microstructure and Phase Composition Analyses
2.3. Preparation of the Specimens for Microstructure Investigation
2.4. Heat Treatment and Rolling Processing
2.5. Mechanical Properties’ Measurements and Calculations
2.6. Electro-Chemical Corrosion Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermodynamic Calculation of the Phase Composition
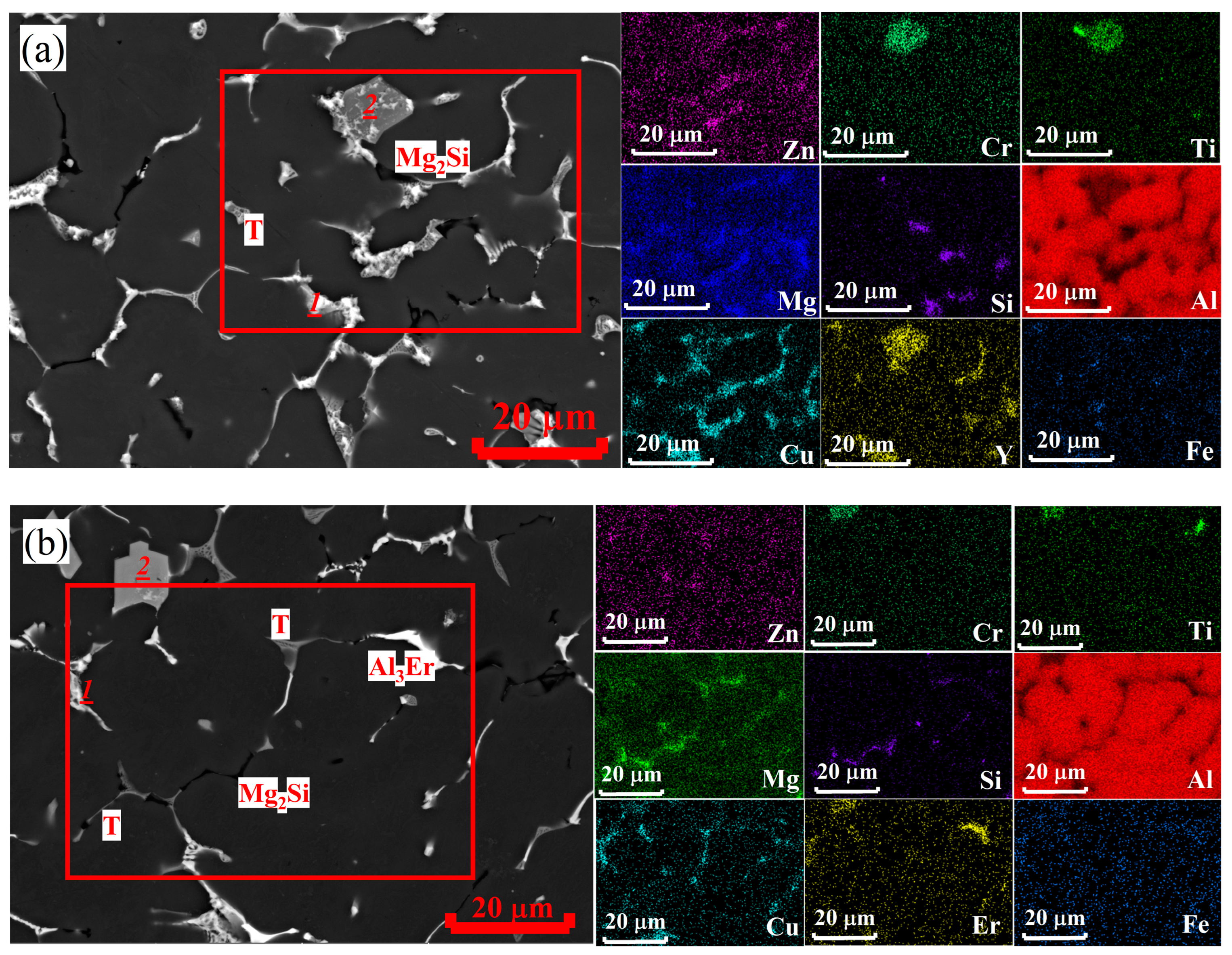
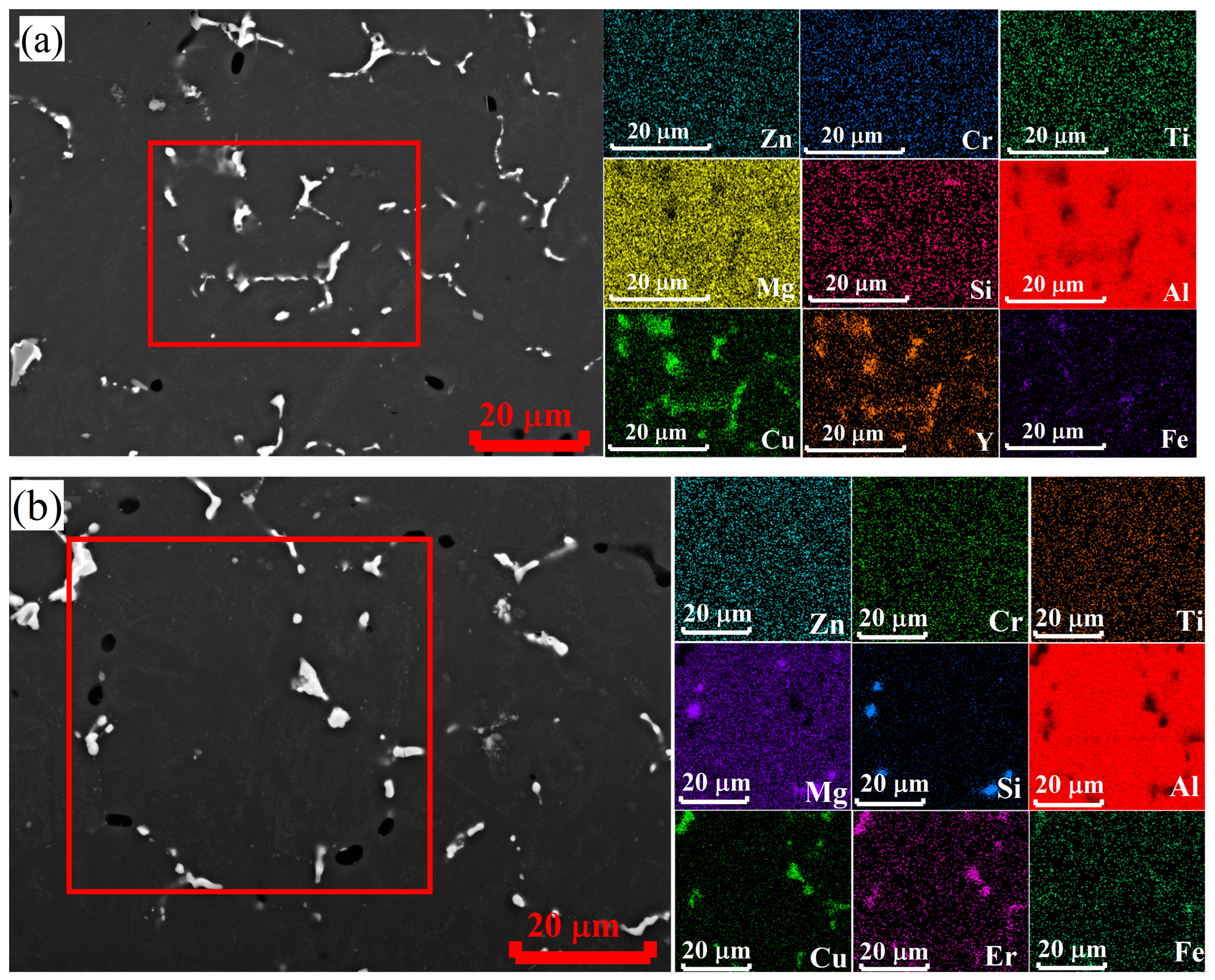
3.2. As-Cast Microstructure and Phase Composition
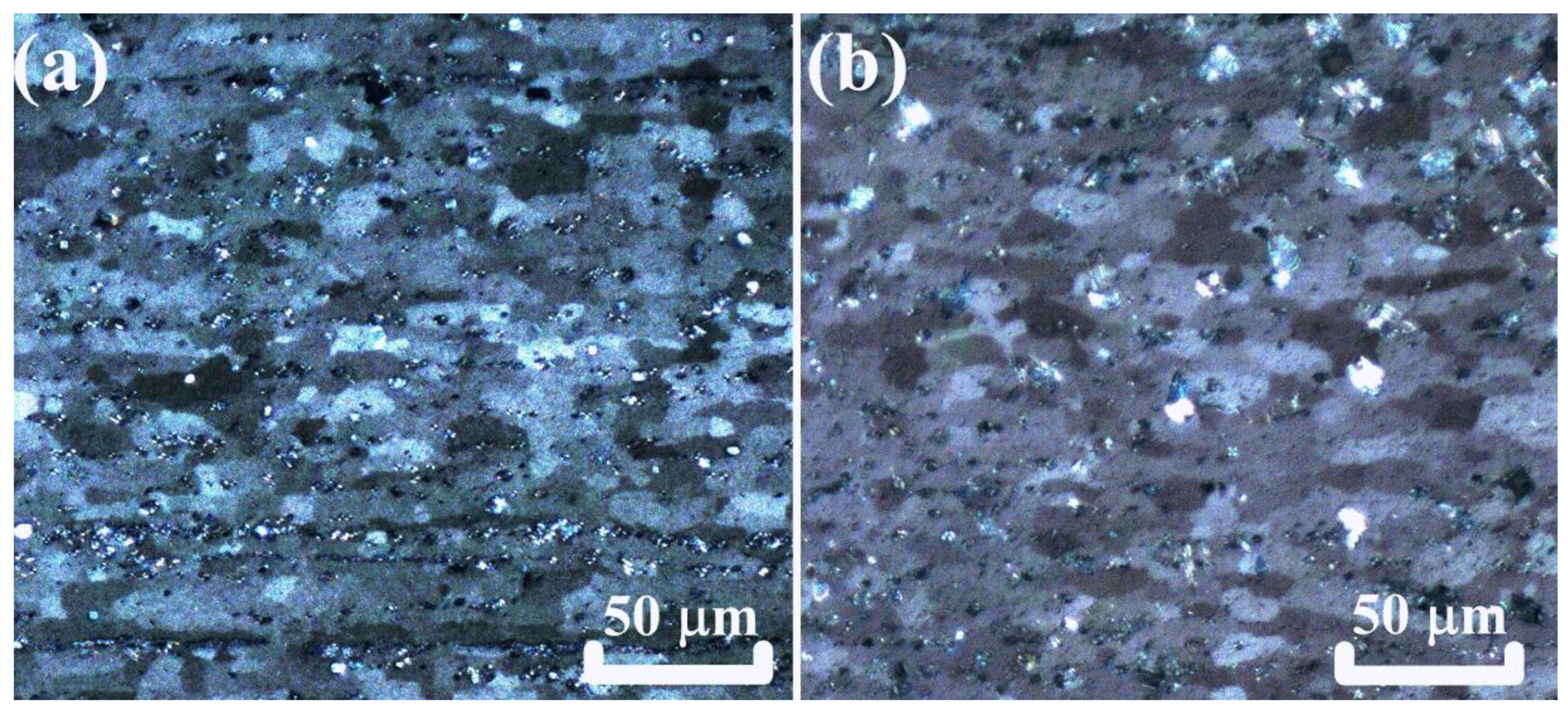
3.3. Evaluation of the Microstructure under Solution Treatment
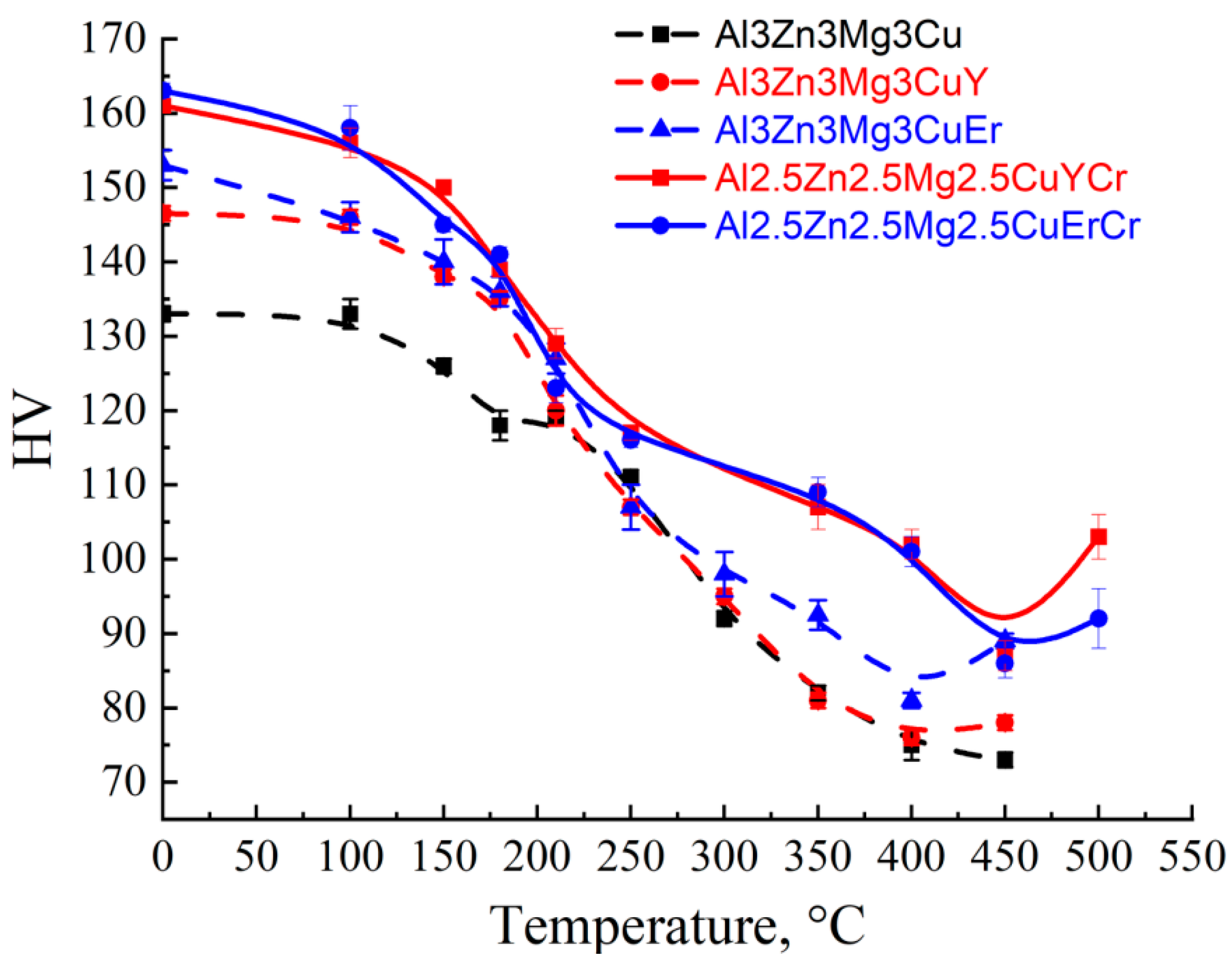
3.4. Aging Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Cast Alloy
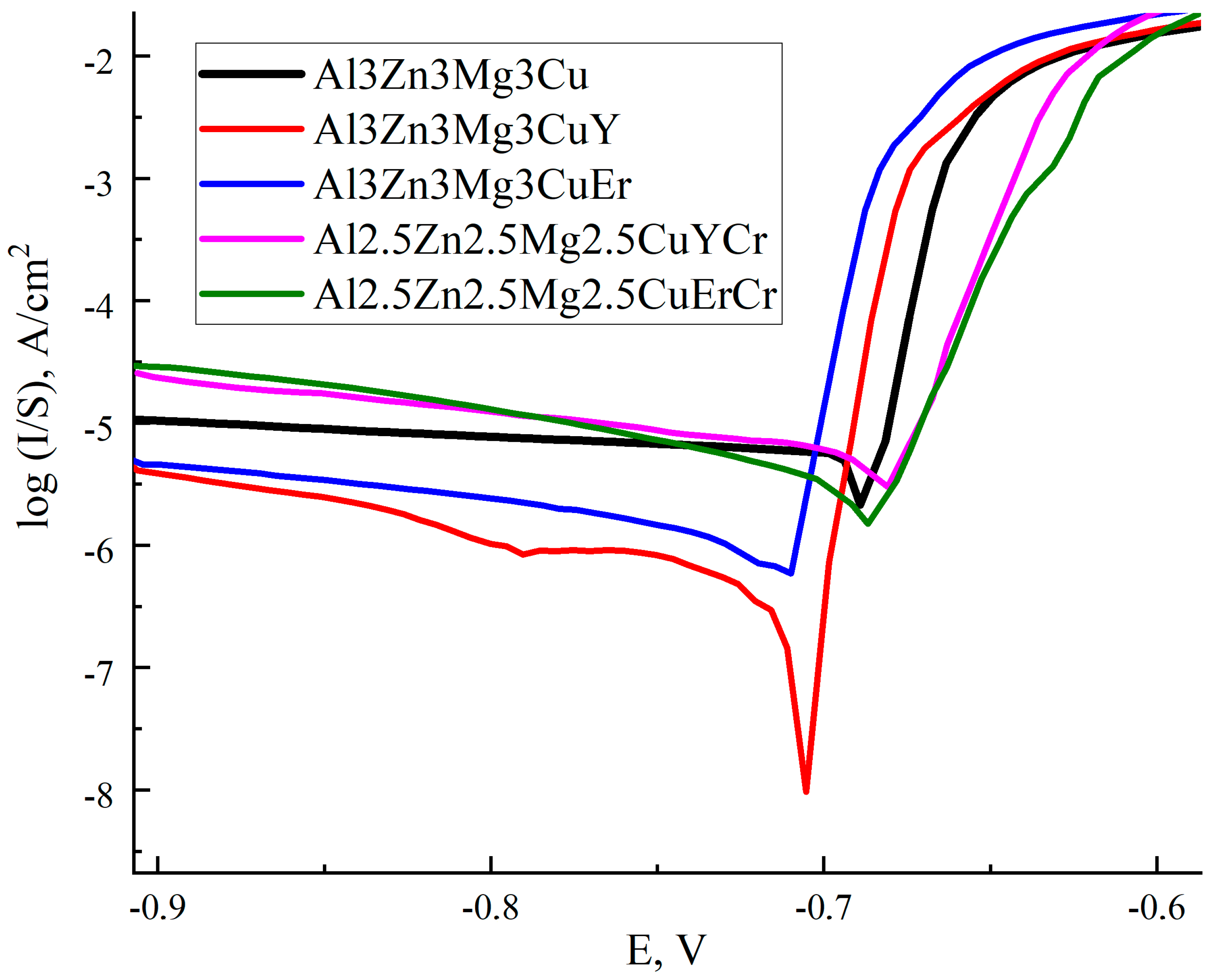
3.5. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior
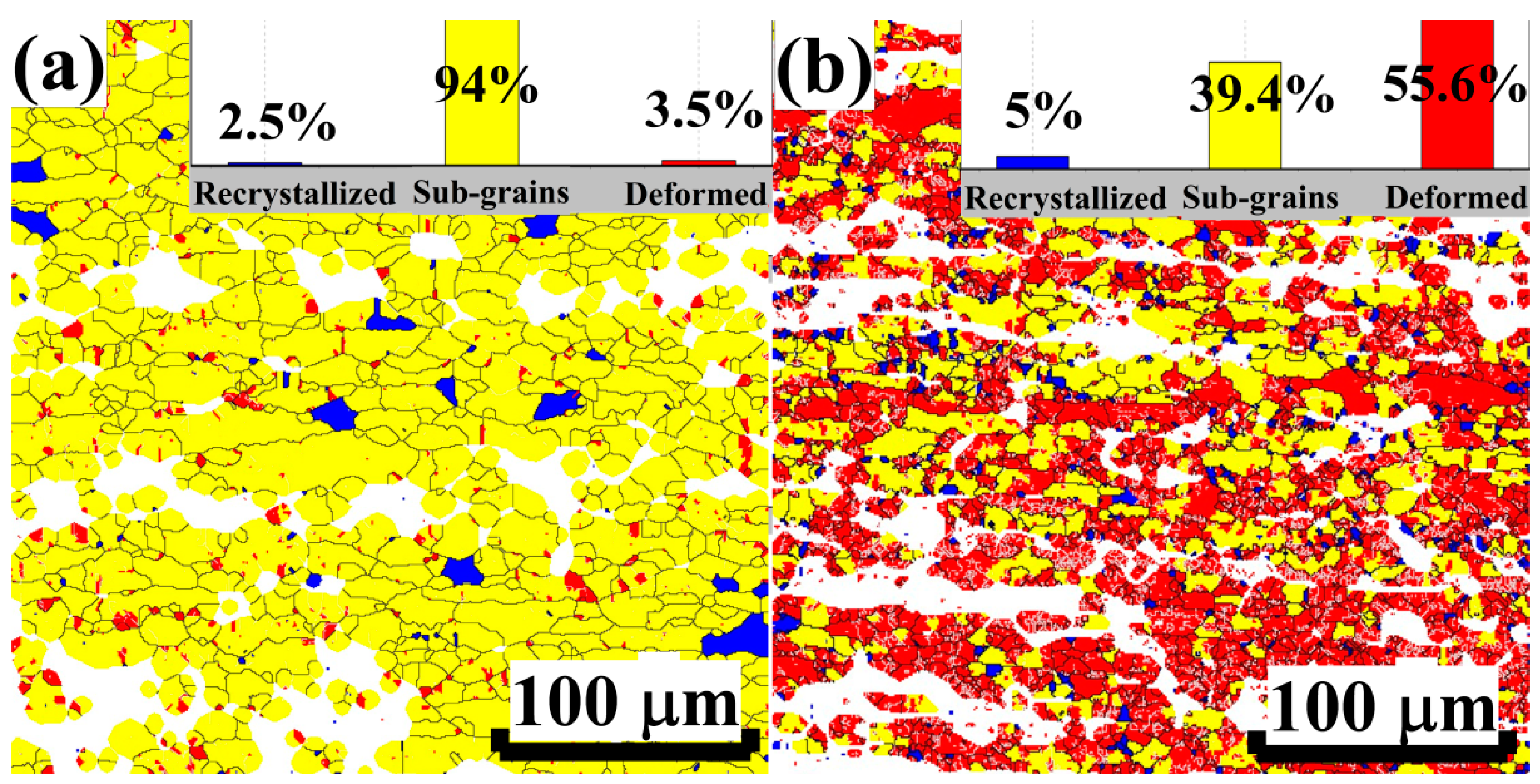
3.6. Recovery and Recrystallization Behavior of Rolled Sheets
3.7. Aging Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Wrought Alloy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASM International Handbook Committee. Properties and selection–nonferrous alloys and special-purpose materials. In ASM Handbook; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 2001; Volume 2, ISBN 0871700077. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotorevsky, V.S.; Belov, N.A.; Glazoff, M.V. Casting Aluminum Alloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 9780080453705. [Google Scholar]
- Eskin, D.G.; Suyitno; Katgerman, L. Mechanical properties in the semi-solid state and hot tearing of aluminium alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2004, 49, 629–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdniakov, A.V.; Zolotorevskiy, V.S. Determining hot cracking index of Al–Si–Cu–Mg casting alloys calculated using effective solidification range. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2014, 27, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdniakov, A.V.; Zolotorevskiy, V.S.; Mamzurina, O.I. Determining hot cracking index of Al–Mg–Zn casting alloys calculated using effective solidification range. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2015, 28, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.D.; Foley, R.D.; Griffin, J.A.; Monroe, C.A. Microstructural Characterization and Thermodynamic Simulation of Cast Al–Zn–Mg–Cu Alloys. Int. J. Met. 2016, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyan, T.K.; Belov, N.A.; Alabin, A.N.; Zlobin, G.S. Calculation-experimental study of the aging of casting high-strength Al-Zn-Mg-(Cu)-Ni-Fe aluminum alloys. Russ. Metall. 2014, 2014, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodova, I.G.; Shirinkina, I.G.; Rasposienko, D.Y.; Akopyan, T.K. Structural Evolution in the Quenched Al–Zn–Mg–Fe–Ni Alloy during Severe Plastic Deformation and Annealing. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2020, 121, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C.; Olivetti, E.A. Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals. Nature 2019, 575, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemper, L.; Tunes, M.A.; Tosone, R.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Pogatscher, S. On the potential of aluminum crossover alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 124, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J. Effect of high Cu concentration on the mechanical property and precipitation behavior of Al–Mg–Zn-(Cu) crossover alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 4585–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, G.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, J. Composition optimization and mechanical properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Si–Mn crossover alloys by orthogonal design. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 307, 128216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J. A novel Al-Mg-Zn(-Cu) crossover alloy with ultra-high strength. Mater. Lett. 2023, 347, 134640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Meng, L.; Chen, Z.; Gong, W.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D. The influence of precipitation on plastic deformation in a high Mg-containing AlMgZn-based crossover alloy: Slip localization and strain hardening. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 173, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trink, B.; Weißensteiner, I.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Strobel, K.; Hofer-Roblyek, A.; Pogatscher, S. Processing and microstructure–property relations of Al-Mg-Si-Fe crossover alloys. Acta Mater. 2023, 257, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hao, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J. Modifying the microstructure and stress distribution of crossover Al-Mg-Zn alloy for regulating stress corrosion cracking via retrogression and re-aging treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 884, 145564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Liu, Z.; Qin, J.; Wei, Q.; Wang, B.; Yi, D. Enhanced corrosion performance by controlling grain boundary precipitates in a novel crossover Al-Cu-Zn-Mg alloy by optimizing Zn content. Mater. Charact. 2024, 208, 113615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerchikova, N.S.; Fridlyander, I.N.; Zaitseva, N.I.; Kirkina, N.N. Change in the structure and properties of Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 1972, 14, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Song, H.; Guo, M.; Cao, L. Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with various Zn/Mg ratios. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J. Precipitation hardening and intergranular corrosion behavior of novel Al–Mg–Zn(-Cu) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavatskikh, M.V.; Barkov, R.Y.; Gorlov, L.E.; Khomutov, M.G.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Novel Cast and Wrought Al-3Zn-3Mg-3Cu-Zr-Y(Er) Alloys with Improved Heat Resistance. Metals 2023, 13, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.M.; Barkov, R.Y.; Prosviryakov, A.S.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Structure and Properties of New Heat-Resistant Cast Alloys Based on the Al–Cu–Y and Al–Cu–Er Systems. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2021, 122, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Structural and compositional evolution of Al3(Zr,Y) precipitates in Al-Zr-Y alloy. Mater. Charact. 2016, 121, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.P.; Gao, K.Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Nie, Z.R. Synergetic effect of Er and Zr on the precipitation hardening of Al–Er–Zr alloy. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bin, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Lu, X. Precipitation evolution and coarsening resistance at 400 °C of Al microalloyed with Zr and Er. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.P.; Gao, K.Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.R. Precipitation evolution in Al-Er-Zr alloys during aging at elevated temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 574, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, H.; Lai, Y.; Ou, Y.; Li, D. Effects of minor Zr and Er on microstructure and mechanical properties of pure aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Yin, H.; Jiang, H.; Su, X.; Bin, J. Effects of Er and Zr additions on precipitation and recrystallization of pure aluminum. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wen, S.P.; Gao, K.Y.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.R. Age hardening behavior and corresponding microstructure of dilute Al-Er-Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2013, 44, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokhrin, A.V.; Nagicheva, G.S.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Kopylov, V.I.; Bobrov, A.A.; Tabachkova, N.Y. Effect of Er, Si, Hf and Nb Additives on the Thermal Stability of Microstructure, Electrical Resistivity and Microhardness of Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloys of Al-0.25%Zr. Materials 2023, 16, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Microstructure and stress corrosion cracking resistance of Al-6.5Zn-2Cu-1.5Mg-0.05Ti alloy modified by Cr addition. Mater. Charact. 2022, 183, 111621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, L.; Weng, Y.; Schryvers, D.; Liu, Q.; Idrissi, H. Atomic-scale investigation of the heterogeneous precipitation in the E (Al18Mg3Cr2) dispersoid of 7075 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 851, 156890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Chen, K.H.; Chen, X.; Chao, H.; Peng, G.S. Effect of Cr, Yb and Zr additions on localized corrosion of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2872–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Chao, H.; Chen, K.H. Effect of Zr, Er and Cr additions on microstructures and properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 610, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, L.; Chen, K.; Liu, W. Influence of minor combined addition of Cr and Pr on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviors of an ultrahigh strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy. Micron 2018, 104, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.H.; Fang, H.C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Effect of of Yb, Cr and Zr additions on recrystallization and corrosion resistance of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 497, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, X.; Lin, X.; Yao, T.; Peng, L. Multi-alloying effect of Ti, Mn, Cr, Zr, Er on the cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Mater. Charact. 2023, 201, 112984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zheng, X.; Yang, W.; Feng, D.; Peng, D. Study on the hot deformation behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Cr aluminum alloy during multi-stage hot compression. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2009, 22, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Chen, K.H.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.P.; Peng, G.S.; Huang, B.Y. Effect of Zr, Cr and Pr additions on microstructures and properties of ultra-high strength Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7606–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Chen, K.; Fang, H.; Chen, S. Effect of Cr and Yb additions on microstructure and properties of low copper Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Zr alloy. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2012, 36, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Luo, F.H.; Chen, K.H. Effect of intermetallic phases and recrystallization on the corrosion and fracture behavior of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Yb-Cr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 684, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Zhang, H.; Peng, D.S.; Zhou, J. Study on the hot deformation behaviors of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Cr aluminum alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2008, 21, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Z. Effect of Minor Cr, Mn, Zr, Ti and B on Grain Refinement of As-Cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2010, 39, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhan, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, Q.; Matsumura, S.; Sha, G. On the strengthening effect of Al-Cr-Si dispersoid in an Al-Si-Mg-Cu casting alloy with Cr addition. Mater. Charact. 2020, 166, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriaga-Benitez, R.I.; Pekguleryuz, M. The synergistic effects of nano-sized α-Al(Mn,Cr,Fe)Si and Al–Si–Zr dispersoids on the creep behavior Al–Si–Mg–Cu (Mn, Cr, Zr) diesel engine alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Shang, P.J.; Huang, L.P.; Chen, K.H.; Liu, G.; Xiong, X. Precipitates and precipitation behavior in Al–Zr–Yb–Cr alloys. Mater. Lett. 2012, 75, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.M.; Glavatskikh, M.V.; Barkov, R.Y.; Loginova, I.S.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Effect of chromium on microstructure and mechanical properties of the Al-Cu-Er-Zr alloy. Metallurgist 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.M.; Glavatskikh, M.V.; Barkov, R.Y.; Loginova, I.S.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Effect of Mn substitution on Cr in the Al-Cu-Er-Mg-Zr-Fe-Si-Ti cast alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 983, 173958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xue, C.; Yang, X.; Tian, G.; Liu, X.; Tang, H. Quantifying the Effects of Grain Refiners Al-Ti-B and La on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of W319 Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhan, Y. Phase-Equilibrium Investigation of the Al-Cr-Er Ternary System at 773 K (500 °C). Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 2956–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Al-Cr-Cu (Aluminum-Chromium-Copper). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2012, 33, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Al-Er-Mg (Aluminum-Erbium-Magnesium). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2007, 28, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogl, P.; Stiltz, S.; Hayes, F.H. The Al-Cr-Mg system alumum-chromium-magnesium). JPE 1992, 13, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lv, J.; Tang, H.; Huang, D. Phase equilibria and solidification characteristics in the Al-rich region of the Al-Ti-Er system. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 980, 173667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishchik, M.S.; Mochugovskiy, A.G.; Cuda, M.; Kishchik, A.A.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V. Particle Stimulated Nucleation Effect for Al-Mg-Zr-Sc Alloys with Ni Addition during Multidirectional Forging. Metals 2023, 13, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, A.O.; Yakovtseva, O.A.; Kishchik, A.A.; Kotov, A.D.; Moustafa, E.B.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V. Effect of Coarse Eutectic-Originated Particles on the Microstructure and Properties of the Friction Stir-Processed Al-Mg-Zr-Sc-Based Alloys. JOM 2023, 75, 2989–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishchik, A.A.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V.; Kotov, A.D.; Rofman, O.V.; Portnoy, V.K. Al-Mg-Fe-Ni based alloy for high strain rate superplastic forming. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 718, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.M.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V.; Barkov, R.Y.; Kotov, A.D.; Mochugovskiy, A.G.; Yakovtseva, O.A.; Glavatskikh, M.V.; Loginova, I.S.; Medvedeva, S.V.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Effect of Homogenization Treatment Regime on Microstructure, Recrystallization Behavior, Mechanical Properties, and Superplasticity of Al-Cu-Er-Zr Alloy. JOM 2021, 73, 3092–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylovskaya, A.V.; Kotov, A.D.; Barkov, R.Y.; Yakovtseva, O.A.; Glavatskikh, M.V.; Loginova, I.S.; Pozdniakov, A.V. The Influence of Y and Er on the Grain Structure and Superplasticity of Al-Cu-Mg-Based Alloys. JOM 2024, 76, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochugovskiy, A.G.; Prosviryakov, A.S.; Tabachkova, N.Y.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V. The Effect of Ce on the Microstructure, Superplasticity, and Mechanical Properties of Al-Mg-Si-Cu Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
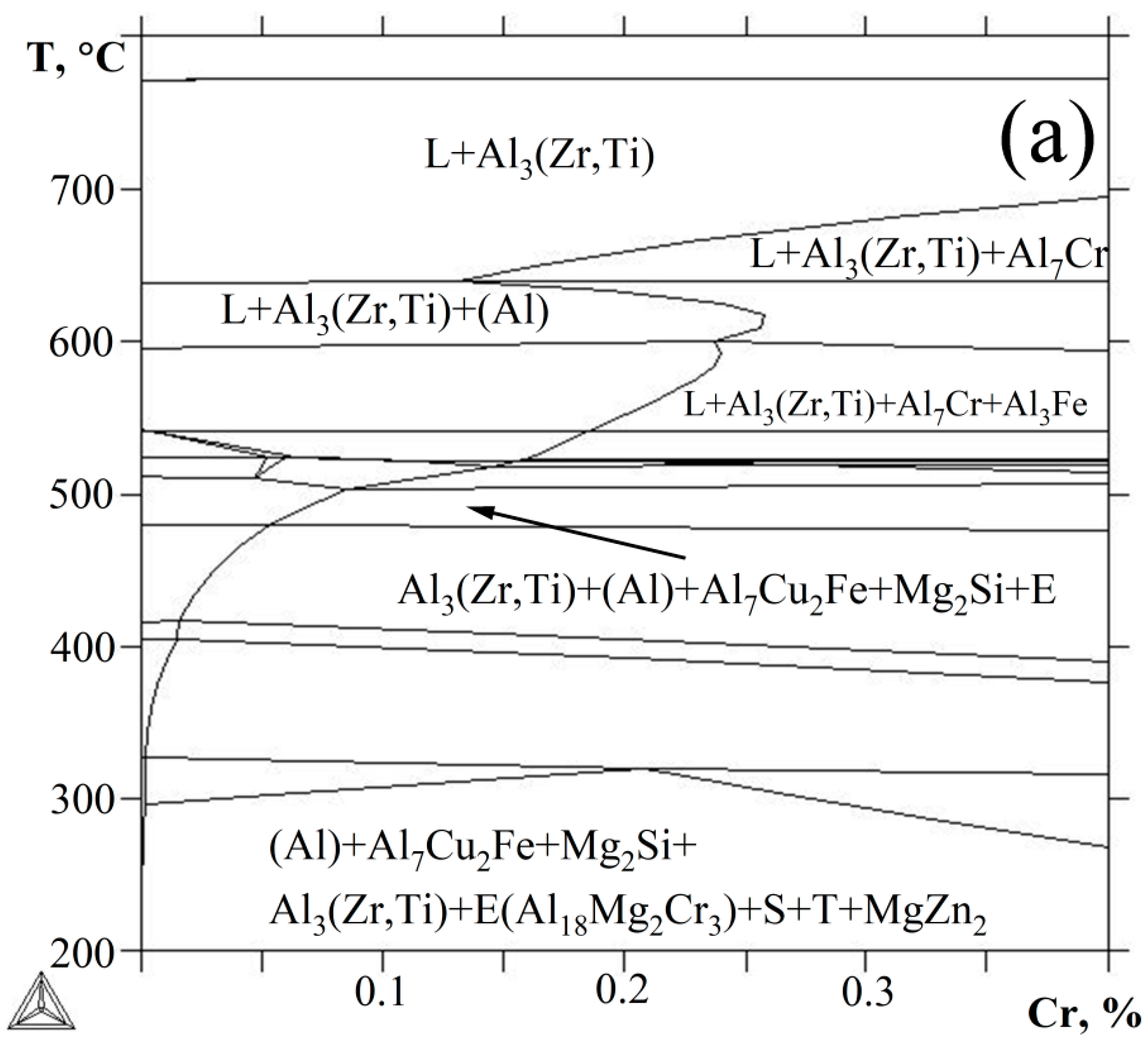
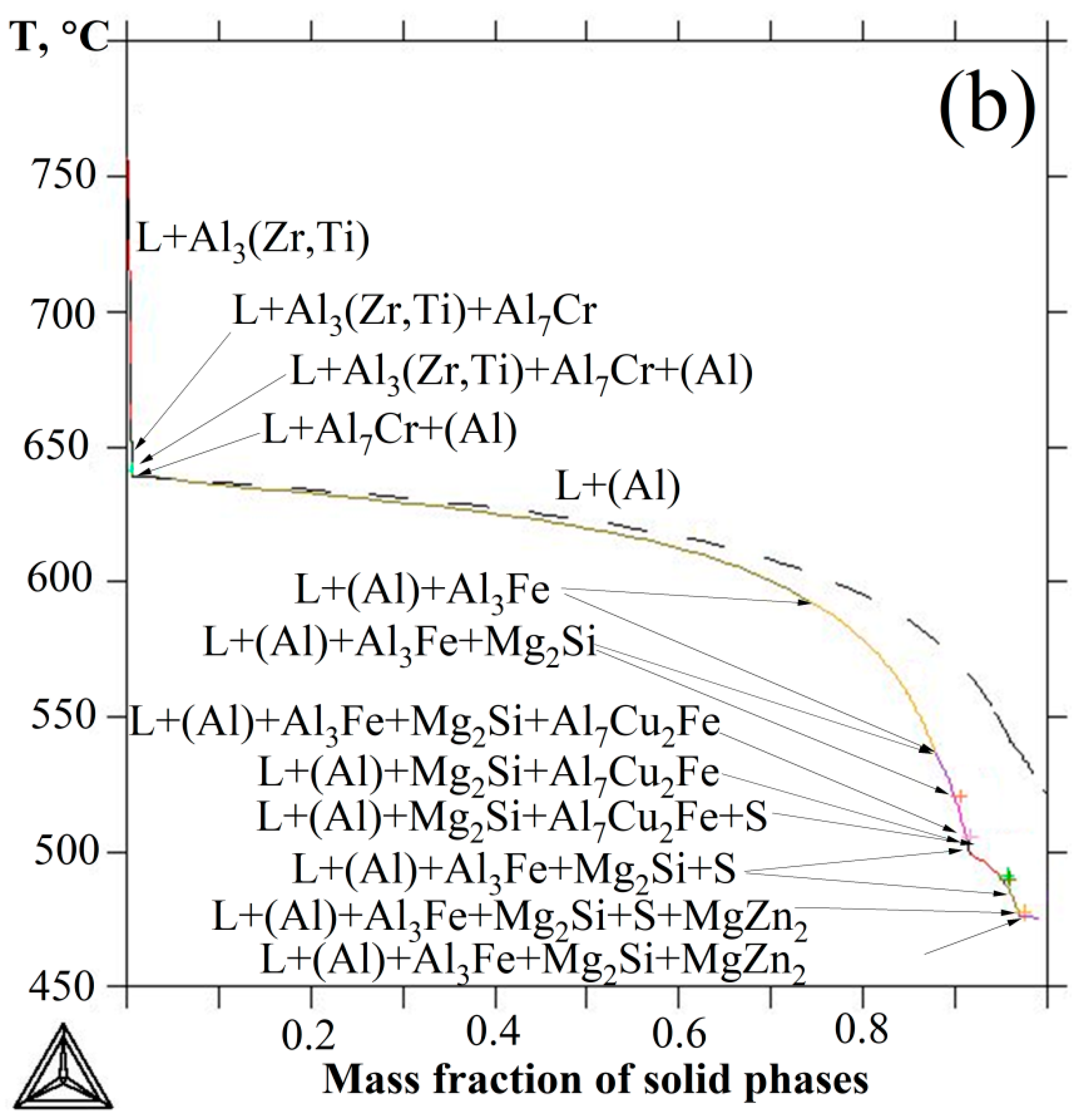
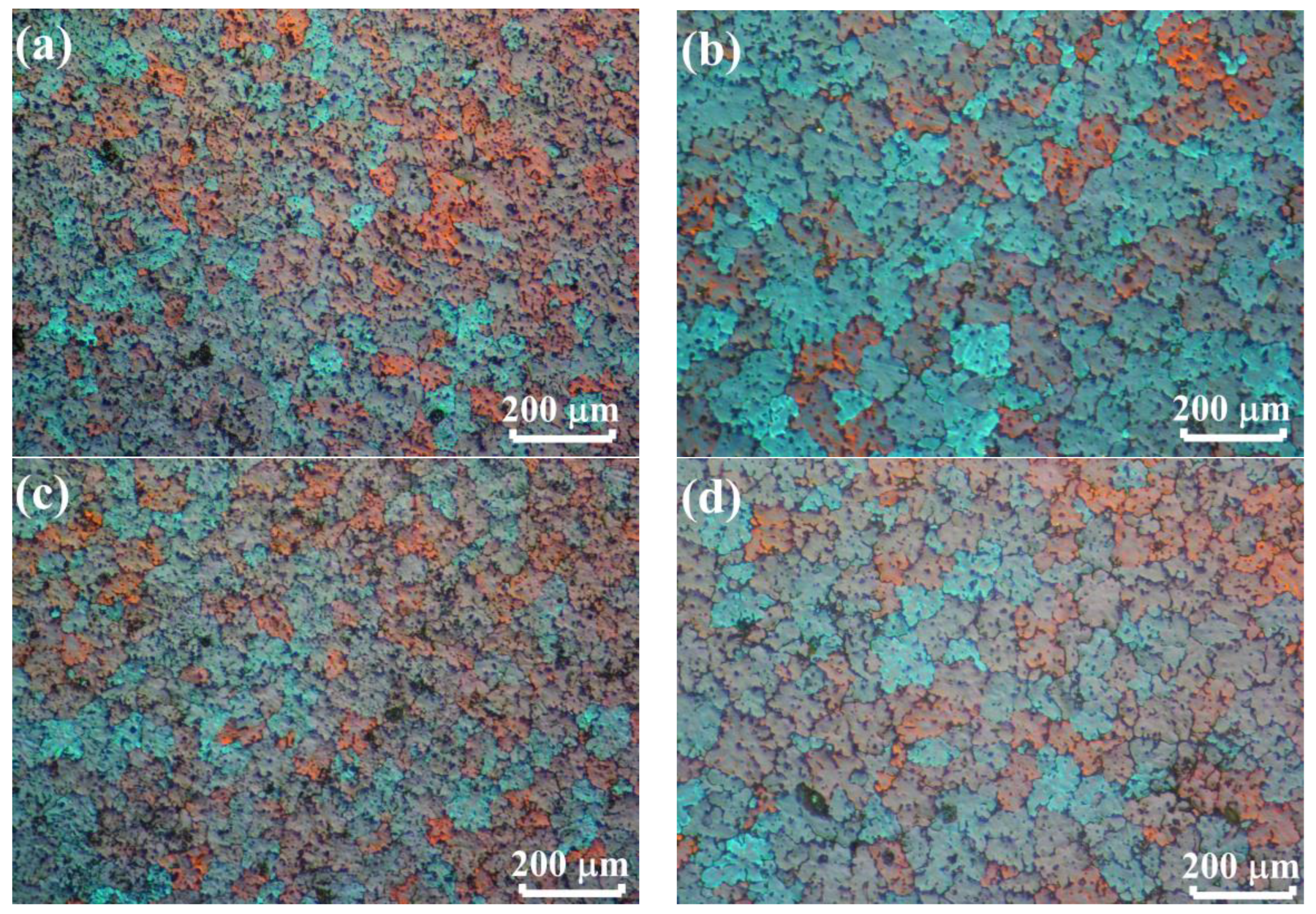




| Alloy | Al | Zn | Mg | Cu | Zr | Ti | Fe and Si | Y or Er | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuY | bal. | 3.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | - |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | bal. | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuEr | bal. | 2.9 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.4 | - |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | bal. | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| TL, °C | TS, °C | T65%, °C | TNS, °C | ESR, °C | HCIc, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 756 | 521 | 606 | 475 | 131 | 14 |
| Phase | Al | Zn | Mg | Cu | Ti | Fe | Y or Er | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Figure 3a) | bal. | 4.5 | 2.7 | 27 | - | 1.9 | 11.2 | - |
| 2 (Figure 3a) | bal. | 3.7 | 2.8 | 3.7 | 5.8 | - | 11.6 | 6.8 |
| (Al) (Figure 3a) | bal. | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.0 | - | 0.3Zr | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 1 (Figure 3b) | bal. | 2.8 | 1.6 | 26.5 | - | 1.6 | 11.2 | - |
| 2 (Figure 3b) | bal. | 3.4 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.7 | - | 16.2 | 5.7 |
| (Al) (Figure 3b) | bal. | 1.8 | 1.5 | 0.9 | - | 0.3Zr | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| (Al) | Al3Fe | E (Al18Mg3Cr2) | Mg2Si | Al3(Zr,Ti) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bal. (2.5Zn-2.4Mg-2.5Cu-0.1Cr) | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Alloy | As-Cast State | 480 °C, 3 h + 520 °C, 6 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Mg | Cu | Zn | Mg | Cu | |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 1.6 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuY [22] | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 1.3 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | 1.8 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 1.4 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuEr [22] | 2.2 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.2 |
| Alloy | Composition of (Al) | Phase Composition at 120–210 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Mg | Cu | η | S | T | |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | 2.9 | 2.9 | 1.6 | 1.4–0 | 0–0.8 | 8.9–8.4 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | 2.8 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 0.7–0 | 0–0.3 | 9.1–8.3 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuEr(Y) [22] | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.2 | - | - | 9.9–8.7 |
| Alloy | YS, MPa | UTS, MPa | El., % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | |||
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | 257 ± 4 | 298 ± 1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | 260 ± 1 | 310 ± 5 | 2 ± 0.3 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuEr(Y) | 270–280 | 330–340 | 2–3 |
| 200 °C | |||
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | 233 ± 5 | 245 ± 4 | 7 ± 0.6 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | 215 ± 3 | 228 ± 5 | 5 ± 0.5 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuEr(Y) | 225–230 | 237–250 | 3.5–5.2 |
| Alloy | Ecor, V | Icor, µA/sm2 |
|---|---|---|
| Al3Zn3Mg3Cu | −0.689 | 4.81 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuY | −0.705 | 0.23 |
| Al3Zn3Mg3CuEr | −0.710 | 1.00 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | −0.681 | 0.98 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | −0.687 | 0.68 |
| State | YS, MPa | UTS, MPa | El., % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuYCr | |||
| As rolled | 455 ± 10 | 476 ± 4 | 3.2 ± 1.0 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/natural aging | 300 ± 1 | 470 ± 10 | 17 ± 2 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/120 °C for 72 h | 302 ± 1 | 437 ± 4 | 12 ± 2 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/150 °C for 24 h | 295 ± 1 | 440 ± 5 | 16 ± 2 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/180 °C for 7 h | 280 ± 2 | 422 ± 3 | 14 ± 0.2 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/210 °C for 2 h | 300 ± 3 | 406 ± 5 | 9 ± 0.3 |
| Al2.5Zn2.5Mg2.5CuErCr | |||
| As rolled | 467 ± 10 | 490 ± 10 | 3.4 ± 0.8 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/natural aging | 280 ± 5 | 454 ± 4 | 16 ± 1 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/120 °C for 72 h | 312 ± 2 | 446 ± 1 | 15 ± 0.3 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/150 °C for 24 h | 292 ± 2 | 439 ± 4 | 16.2 ± 0.2 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/180 °C for 7 h | 293 ± 2 | 420 ± 3 | 14 ± 1.0 |
| 520 °C for 15 min/210 °C for 2 h | 299 ± 3 | 414 ± 3 | 12.3 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glavatskikh, M.V.; Barkov, R.Y.; Gorlov, L.E.; Khomutov, M.G.; Pozdniakov, A.V. Microstructure and Phase Composition of Novel Crossover Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Y(Er) Alloys with Equal Zn/Mg/Cu Ratio and Cr Addition. Metals 2024, 14, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050547
Glavatskikh MV, Barkov RY, Gorlov LE, Khomutov MG, Pozdniakov AV. Microstructure and Phase Composition of Novel Crossover Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Y(Er) Alloys with Equal Zn/Mg/Cu Ratio and Cr Addition. Metals. 2024; 14(5):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050547
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlavatskikh, Maria V., Ruslan Yu. Barkov, Leonid E. Gorlov, Maxim G. Khomutov, and Andrey V. Pozdniakov. 2024. "Microstructure and Phase Composition of Novel Crossover Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Y(Er) Alloys with Equal Zn/Mg/Cu Ratio and Cr Addition" Metals 14, no. 5: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050547
APA StyleGlavatskikh, M. V., Barkov, R. Y., Gorlov, L. E., Khomutov, M. G., & Pozdniakov, A. V. (2024). Microstructure and Phase Composition of Novel Crossover Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-Y(Er) Alloys with Equal Zn/Mg/Cu Ratio and Cr Addition. Metals, 14(5), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050547










