The Influence of Insertion Depth of Inorganic Materials on Solidification Microstructure and Segregation of 2.5-ton 42CrMo Ingot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Experimental Design
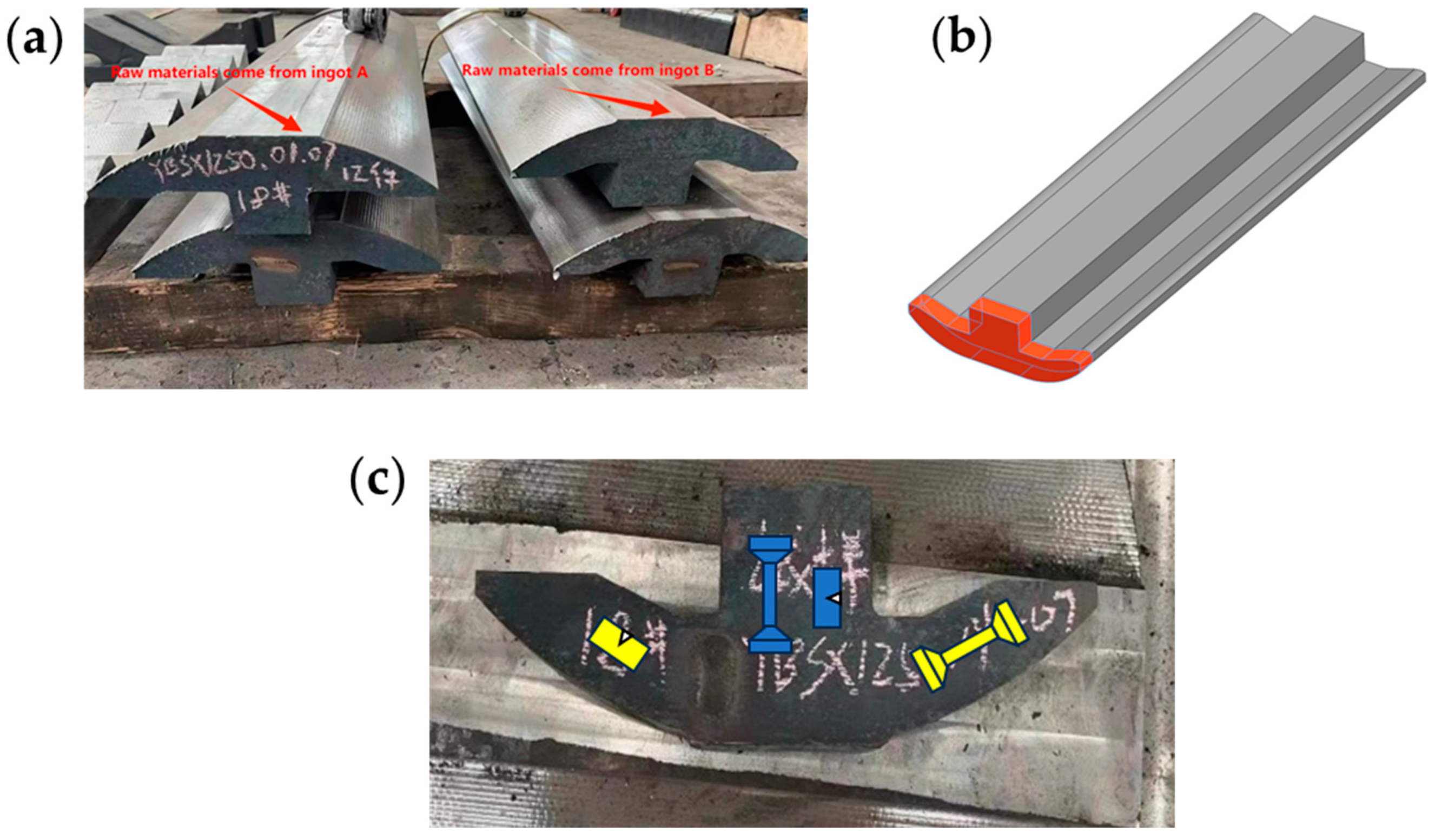
2.2. Industrial Experimental Procedure
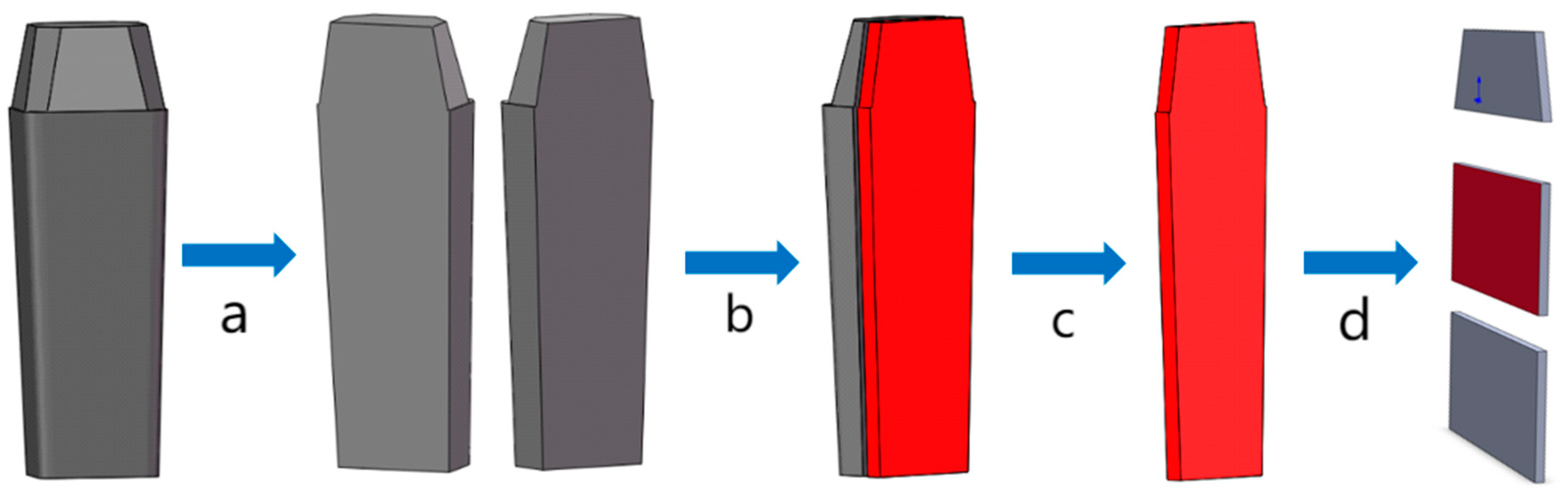
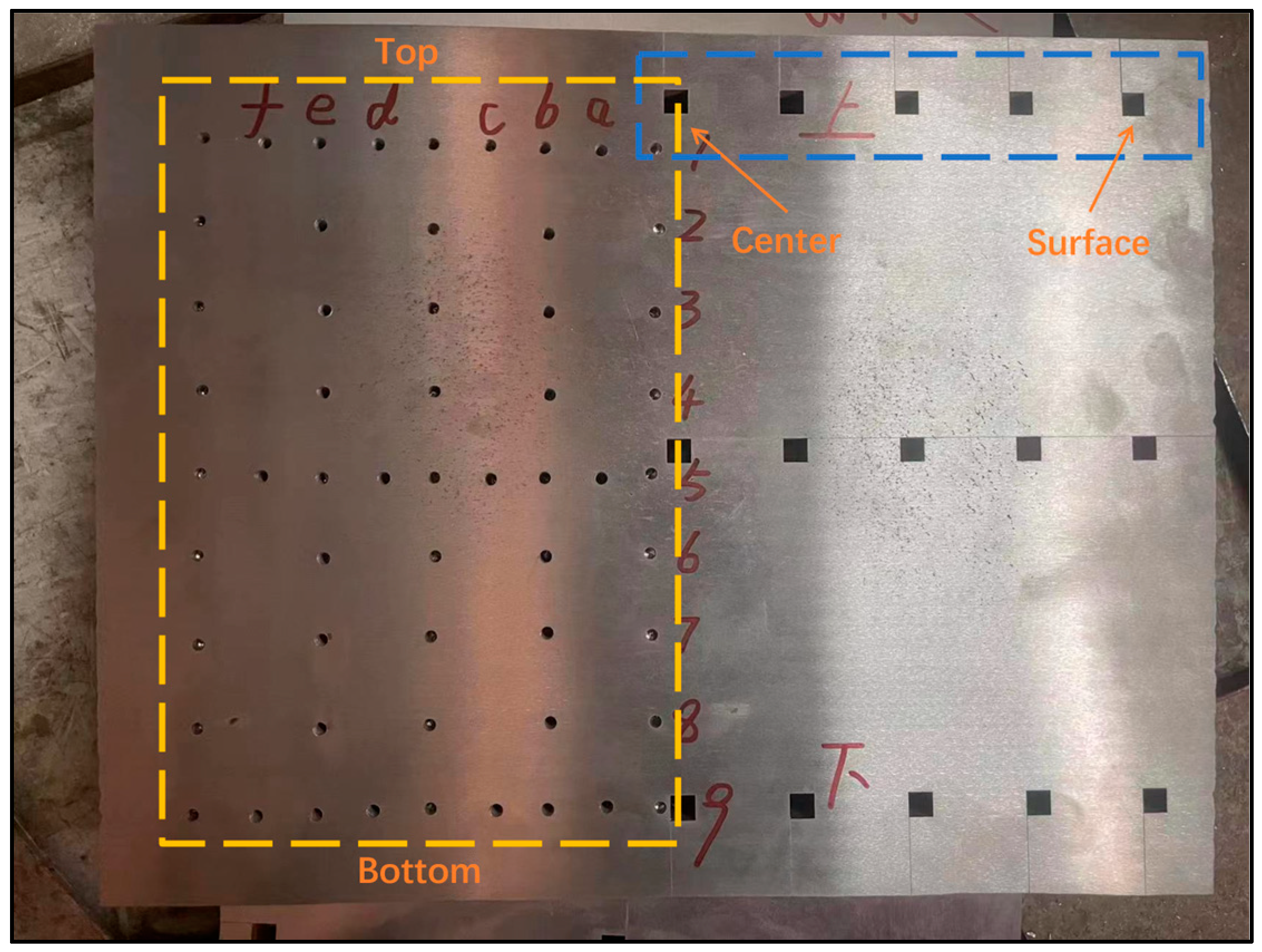
2.3. Sampling Characterization Methods
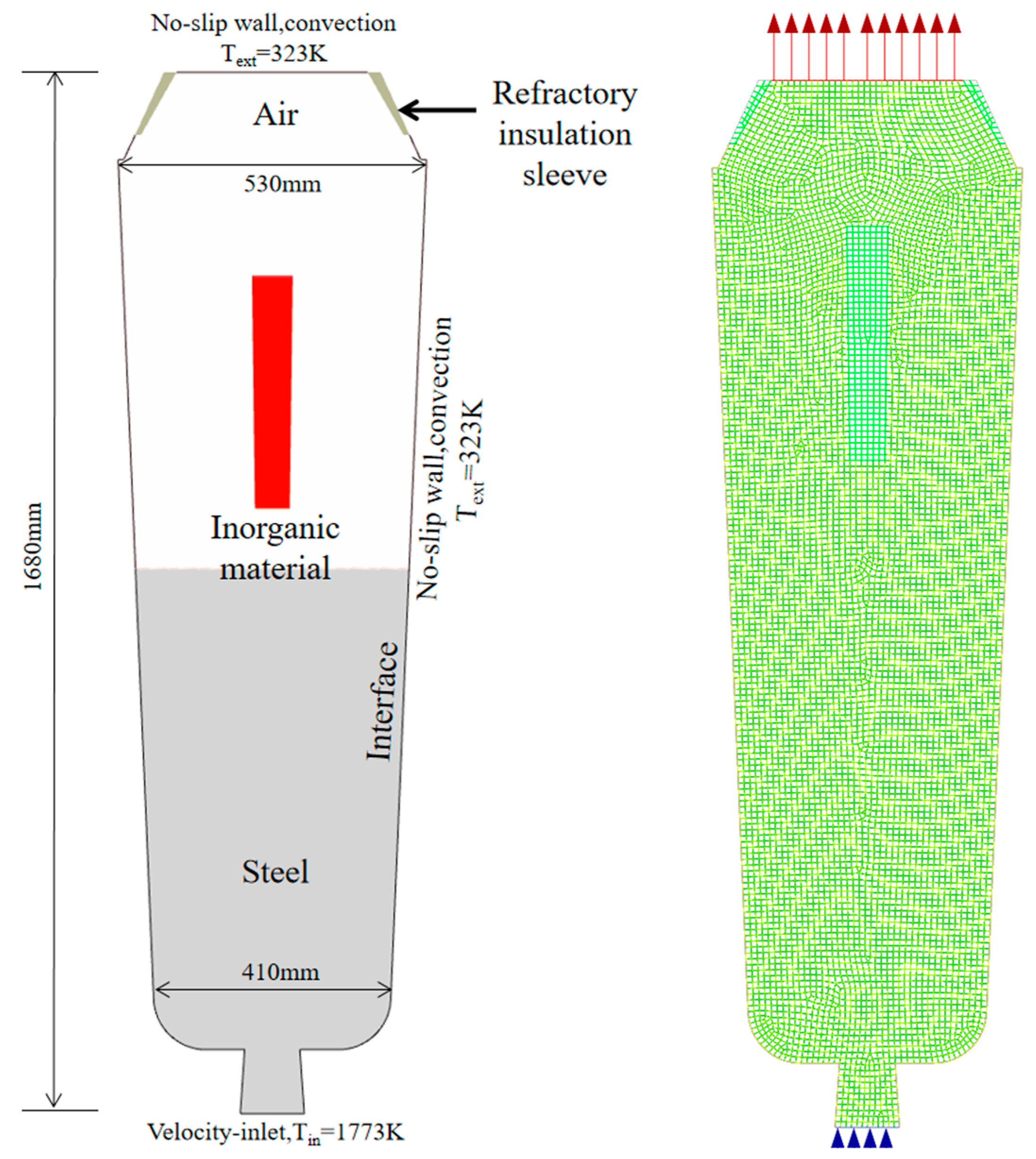
3. Numerical Simulation Model
4. Results and Discussions
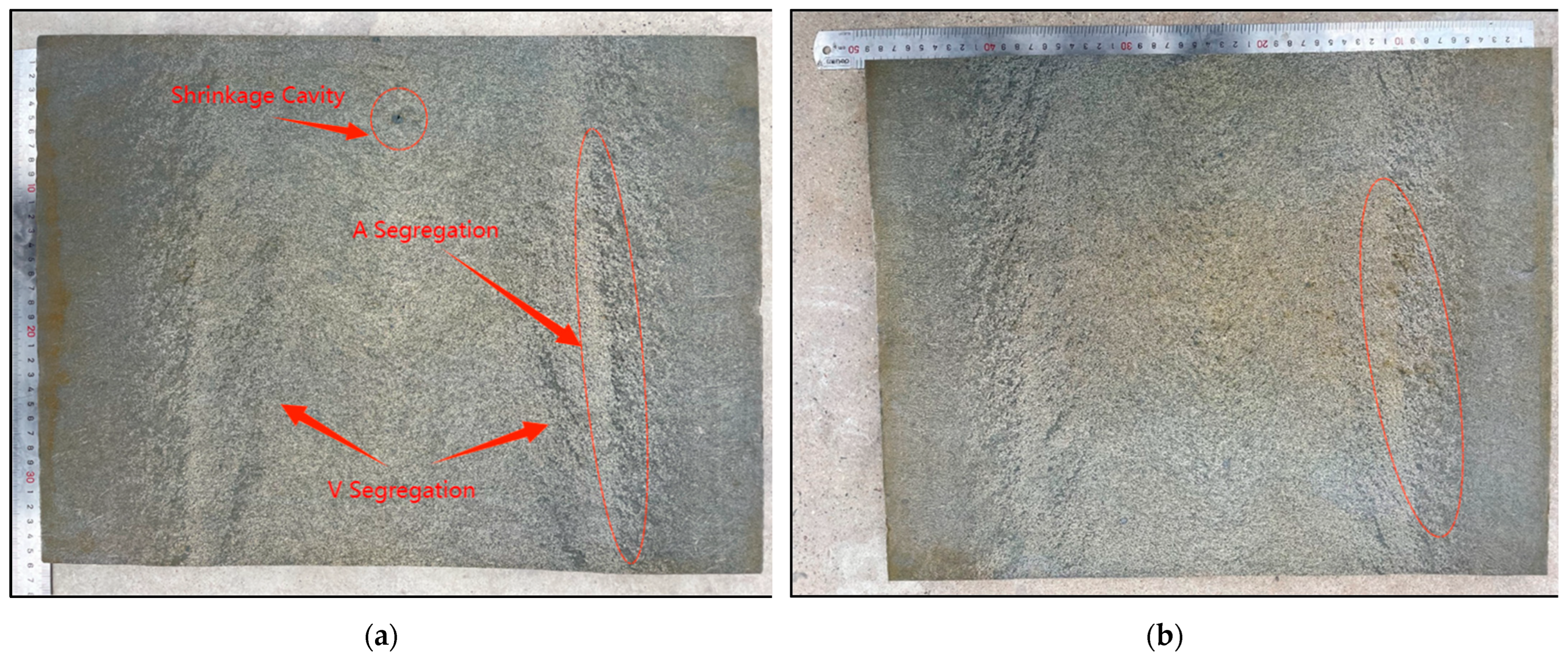
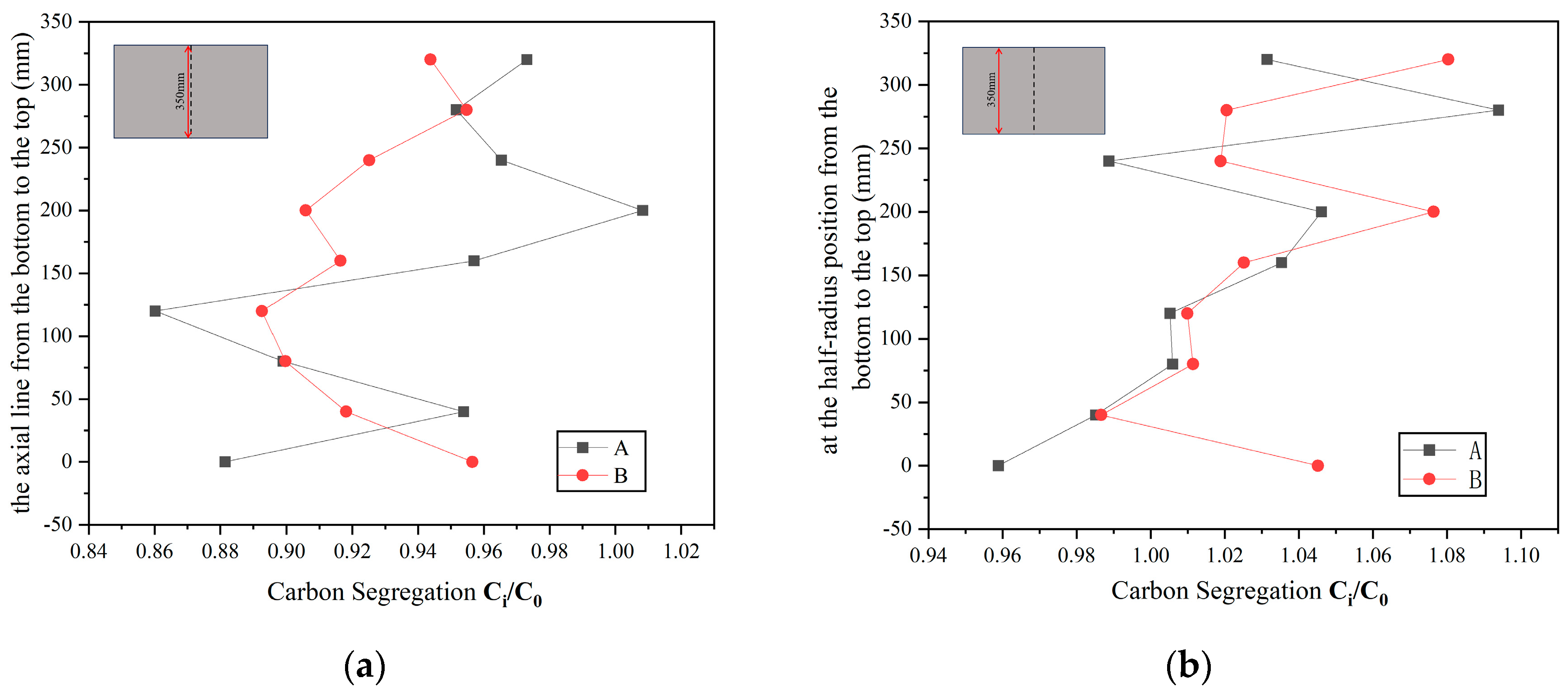
4.1. Macrosegregation Analysis
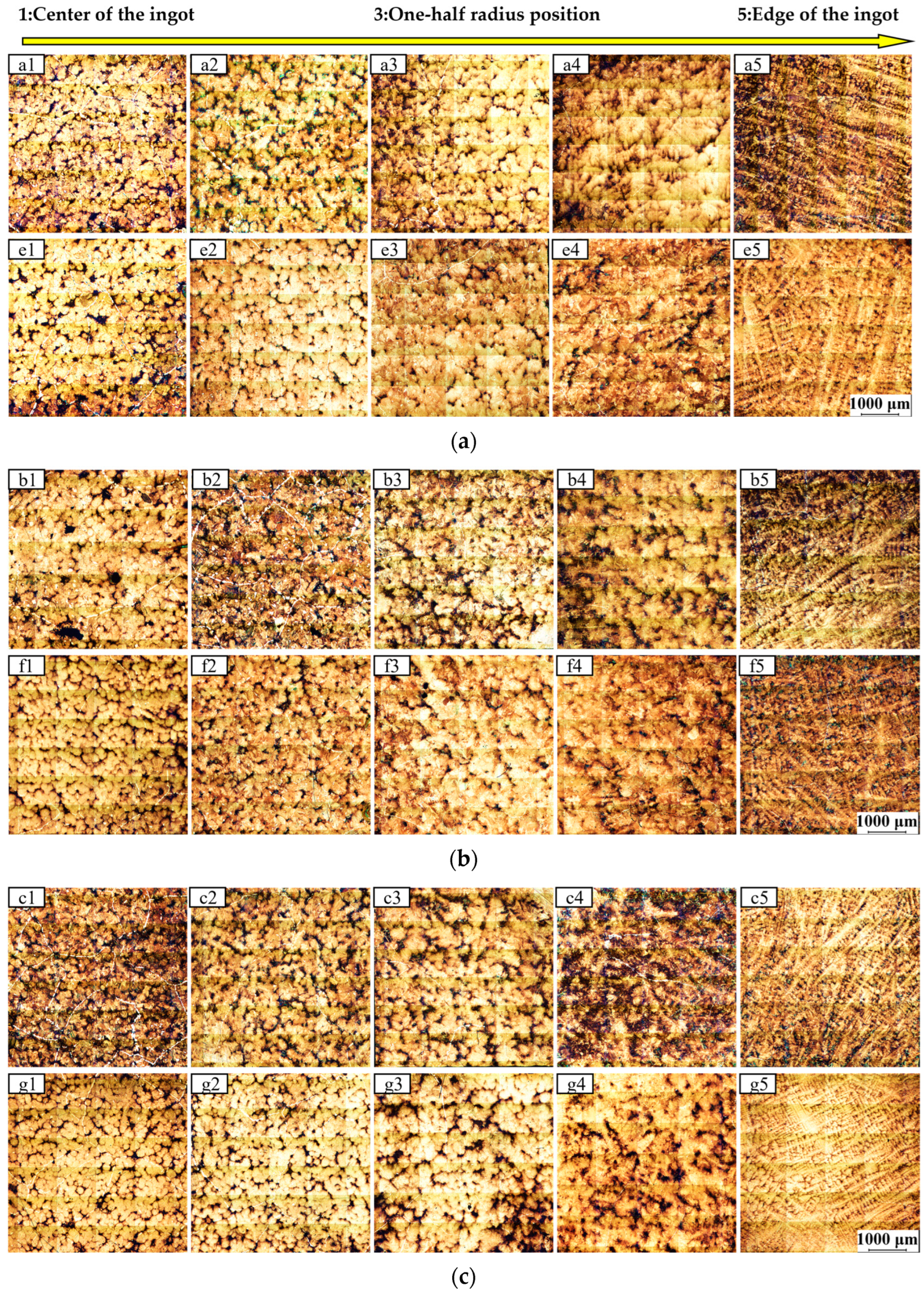
4.2. Metallographic Analysis
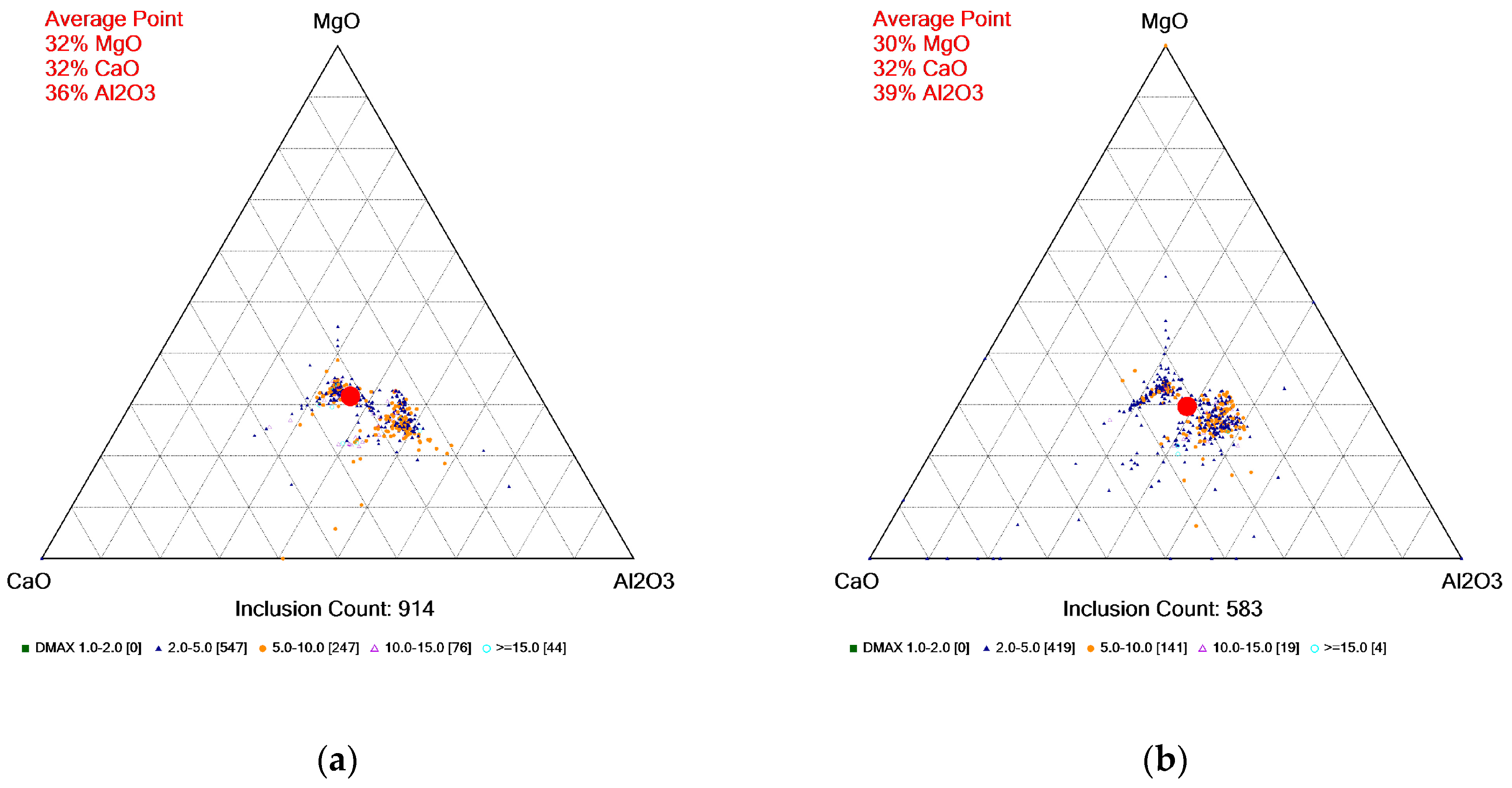
4.3. Inclusion Analysis
4.4. Mechanical Properties of Final Products
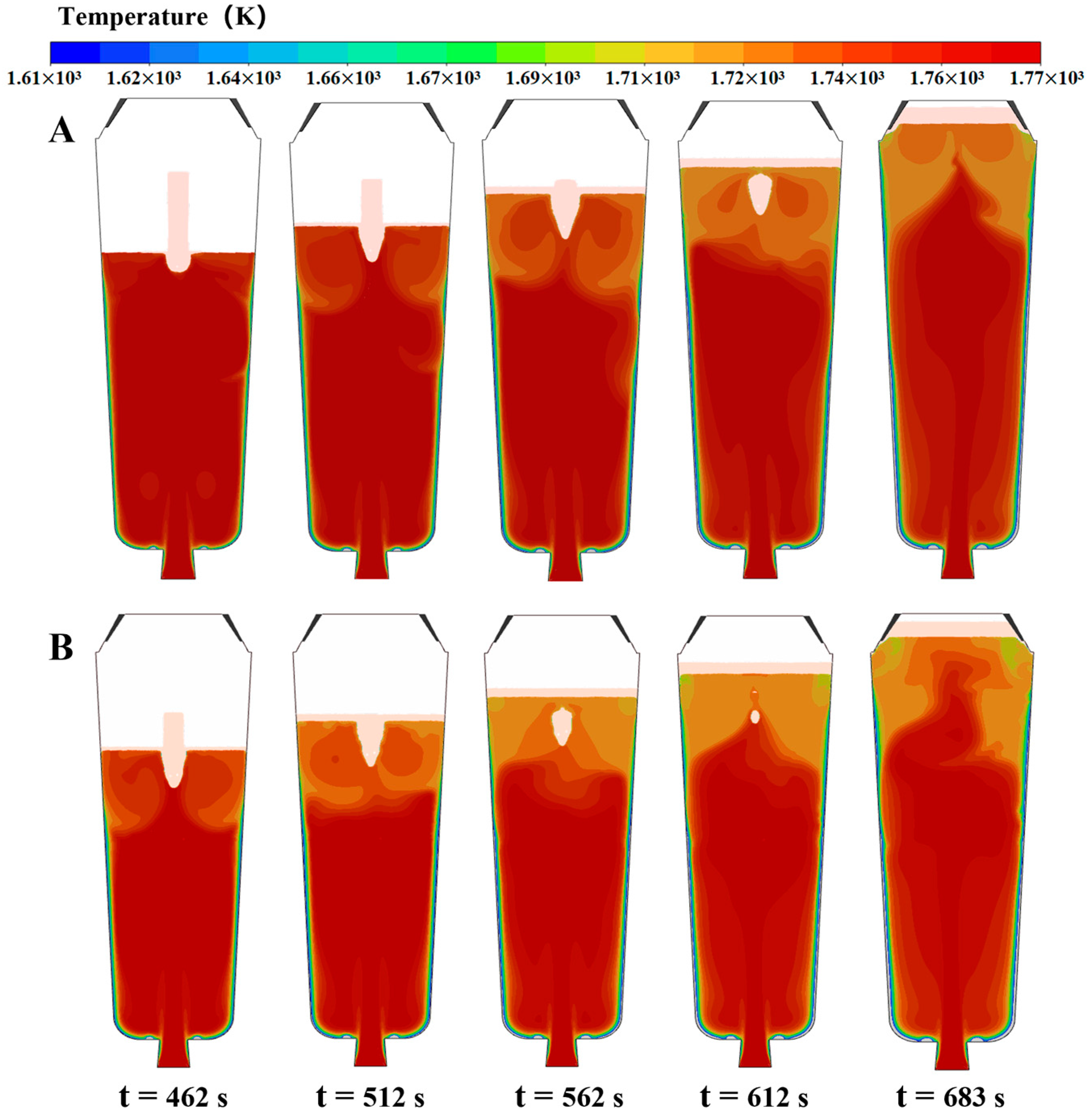
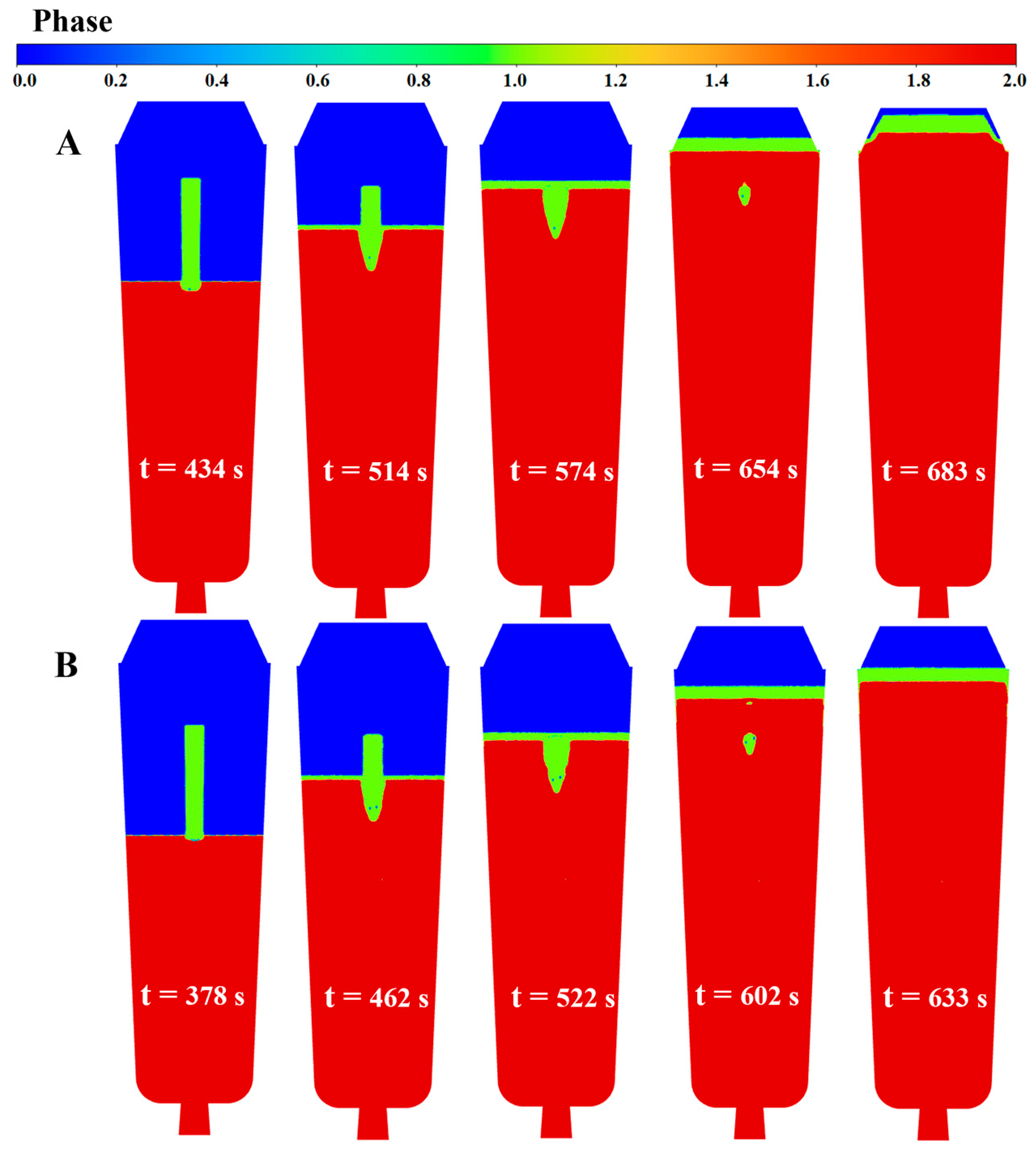
4.5. Numerical Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
- After altering the process parameter of the placement depth of inorganic materials, we have identified better process windows through a series of comparative studies. Industrial trial results demonstrate that Ingot B, with deeper placement of inorganic materials, exhibits a significantly refined solidification microstructure, resulting in a significant reduction in equiaxed grain size at the ingot center, with fewer coarse columnar grains and a smaller spacing between secondary dendrite arms.
- From the perspective of the macrosegregation degree, Ingot B, with inorganic material rods placed deeper, is superior to Ingot A. This is demonstrated by a 10.35% reduction in the area percentage of the positive segregation zone on the test surface and a 15.32% decrease in the area of the negative segregation zone. Additionally, the fluctuation degree and range of carbon segregation values at two specific positions in the vertical direction are smaller in Ingot B compared to Ingot A.
- The mechanical performance analysis of rough processed products from ingots A and B indicates a slight increase in various properties in the impact and tensile strength specimens of Ingot B. The transverse position mechanical properties are significantly improved, with tensile strength increased by 41 MPa and yield strength increased by 46 MPa.
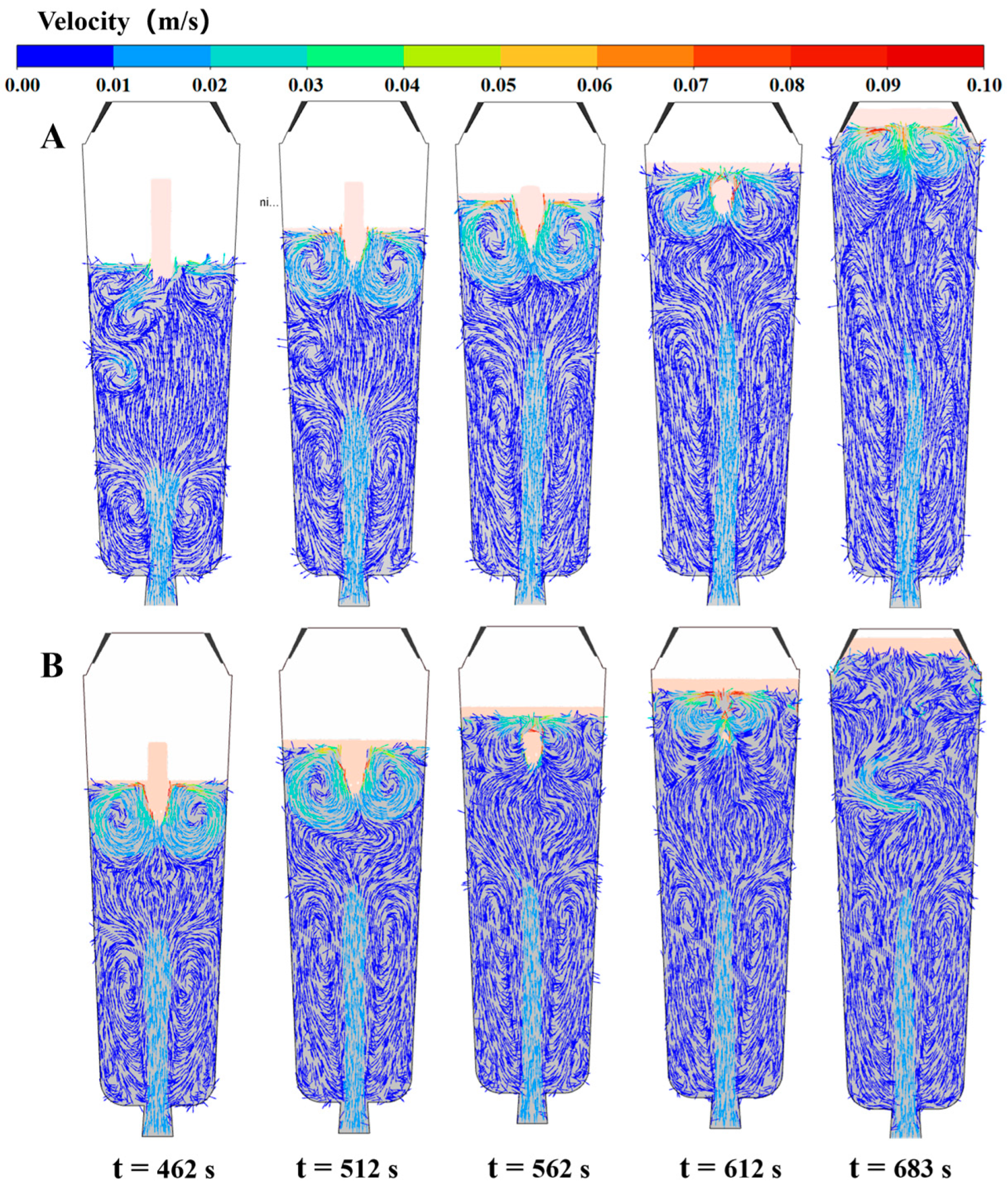
- The simulation results reveal a series of coupling effects generated by the inorganic material internal heat absorption technology during the solidification of the ingot, specifically including an increase in temperature gradient and the induction of forced convection. When the placement depth of the inorganic materials within the ingot mold is increased, the cooling effect becomes more significant, the flow area of molten steel induced by the inorganic materials expands, and the linear velocity of the double-circle flow increases. This further explains why the solidification quality of the ingot improves with an increase in the placement depth of the inorganic materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Cheng, G.G.; Wang, G.B.; Qiao, T.; Shi, R.X. Formation mechanism of inspection defects in hundred-ton class 55NiCrMoV7 die steel forging. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2024, 51, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Research progress and prospects on the formation mechanism of macrosegregation and shrinkage porosity in large steel ingots. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.F.; Liu, H.W.; Fu, P.X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Miao, Y.Y.; Liu, H.H.; Sun, C.; Li, D.Z. Distinct Mechanisms for Channel Segregation in Ultra-Heavy Advanced Steel Ingots Numerical Simulation and Experimental Characterization. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 2771–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesoult, G. Macrosegregation in steel strands and ingots: Characterisation, formation and consequences. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 413–414, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Chesman, C.; Al-Bermani, S.; Holland, M.; Davies, P.; Talamantes-Silva, J. A Comprehensive Case Study of Macrosegregation in a Steel Ingot. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1860–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, E.; Delannoy, Y.; Fautrelle, Y.; Budenkova, O. Numerical Simulation of Macrosegregation Formation in a 2.45 ton Steel Ingot Using a Three-Phase Equiaxed Solidification Model. Metals 2021, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.C. Our Understanding of Macrosegregation. Past and Present. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Kishimoto, A.; Tani, K.; Saito, T. Development of 3D Macrosegregation Analysis Technique for a 19-Ton Steel Ingot with Complex Shape. Int. J. Met. 2023, 17, 2958–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.C.; Li, H.B.; Ni, Z.W.; Luo, H.X.; Feng, H.; Zhang, S.C.; Jiang, Z.H. Carbon Macrosegregation Pattern in 30Cr15Mo1N Ingot: Impact of Pouring Rate. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 2300908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati, N.; Champliaud, H.; Morin, J.B.; Jahazi, M. Influence of the Hot-Top Thermal Regime on the Severity and Extent of Macrosegregation in Large-Size Steel Ingots. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sato, I. Development of high purity large forgings for nuclear power plants. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 417, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.T.; Shen, H.F.; Liu, B.C. Modelling of macrosegregation in a 231-ton steel ingot with multi-pouring process. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, S59–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Li, J.; Ge, H.; Cai, D.; Hu, Q.; Li, J. A comprehensive study of layer casting process by a four-phase filling-solidification model. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 284, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Ren, N.; Zhang, W.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, M.; Li, J. Experimental and simulation studies of layer casting on industrial-scale Al-4.5 wt Pct Cu ingot: Effect, defect, and optimization. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 322, 118205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayev, O.; Hress, O.; Hu, C.Y.; Xin, R.; Wu, K.M. The Development of Steel Band Feeding for HSLA Heavy Plates. Metallurgist 2016, 59, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Xiao, L.; Gan, Y. Effect of steel strip feeding on the columnar-equiaxed solidification in a large continuous casting round bloom. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 1770–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Li, B.-k.; Liu, Z.-q.; Li, X.-l. Effect of strip feeding into mold on fluid flow and heat transfer in continuous casting process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, B.; Kang, X.; Li, D. A novel technique for reducing macrosegregation in heavy steel ingots. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-h.; Yu, S.; Xu, Y.-j.; Jiang, D.-q.; Shuai, S.-s.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.-m. Melting and floating processes of inorganic materials in molten steel: Visualization physical simulation and mathematical modelling. China Foundry 2023, 20, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Shuai, S.; Yu, S.; Jiang, D.; Chen, C.; Hu, T.; Ren, Z. Improving microstructure and segregation of steel ingot by inorganic heat absorption method. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 2544–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhu, L.; Lai, J.; Pan, M.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, W.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Ren, Z. Application of heat absorption method to reduce macrosegregation during solidification of bearing steel ingot. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.; Nenchev, B.; Dong, H. On Directional Dendritic Growth and Primary Spacing—A Review. Crystals 2020, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tsukamoto, S.; Nagai, K. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure evolution of rapidly cooled high-impurity steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 403, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandersluis, E.; Ravindran, C. Comparison of Measurement Methods for Secondary Dendrite Arm Spacing. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2017, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.-H.; Decterov, S.A.; Pelton, A.D. Critical Thermodynamic Evaluation and Optimization of the MgO-Al2O3 CaO-MgO-Al2O3, and MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 Systems. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2004, 25, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engh, T.A.; Sigworth, G.K.; Kvithyld, A.; Engh, T.A.; Sigworth, G.K.; Kvithyld, A. Principles of Metal Refining and Recycling; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 303–364. [Google Scholar]
- Petch, N.J. The Cleavage Strength of Polycrystals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 174, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.O. The Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: III Discussion of Results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 1951, B64, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.63 | 0.068 | 0.009 | 1.10 | 0.18 | Balance |
| Position | KV2 J |
|---|---|
| Transverse Direction of A | 66.6 |
| Transverse Direction of B | 71.9 |
| Radial Direction of A | 70.9 |
| Radial Direction of B | 75.8 |
| Position | Rm MPa | Rp0.2 MPa | A % | Z % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transverse Direction of A | 1116 | 1017 | 13.5 | 53 |
| Transverse Direction of B | 1157 | 1063 | 15.5 | 58 |
| Radial Direction of A | 1015 | 927 | 16.2 | 43 |
| Radial Direction of B | 1028 | 959 | 18.5 | 49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Xu, S.; Ren, Z. The Influence of Insertion Depth of Inorganic Materials on Solidification Microstructure and Segregation of 2.5-ton 42CrMo Ingot. Metals 2024, 14, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14070753
Sun S, Du Y, Zhang Z, Jiang D, Xu S, Ren Z. The Influence of Insertion Depth of Inorganic Materials on Solidification Microstructure and Segregation of 2.5-ton 42CrMo Ingot. Metals. 2024; 14(7):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14070753
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shujian, Yonglong Du, Zhenqiang Zhang, Danqing Jiang, Songzhe Xu, and Zhongming Ren. 2024. "The Influence of Insertion Depth of Inorganic Materials on Solidification Microstructure and Segregation of 2.5-ton 42CrMo Ingot" Metals 14, no. 7: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14070753
APA StyleSun, S., Du, Y., Zhang, Z., Jiang, D., Xu, S., & Ren, Z. (2024). The Influence of Insertion Depth of Inorganic Materials on Solidification Microstructure and Segregation of 2.5-ton 42CrMo Ingot. Metals, 14(7), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14070753







