The Interplay between Nucleation and the Rates of Chemical Reduction in the Synthesis of Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Microemulsions: A Computer Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
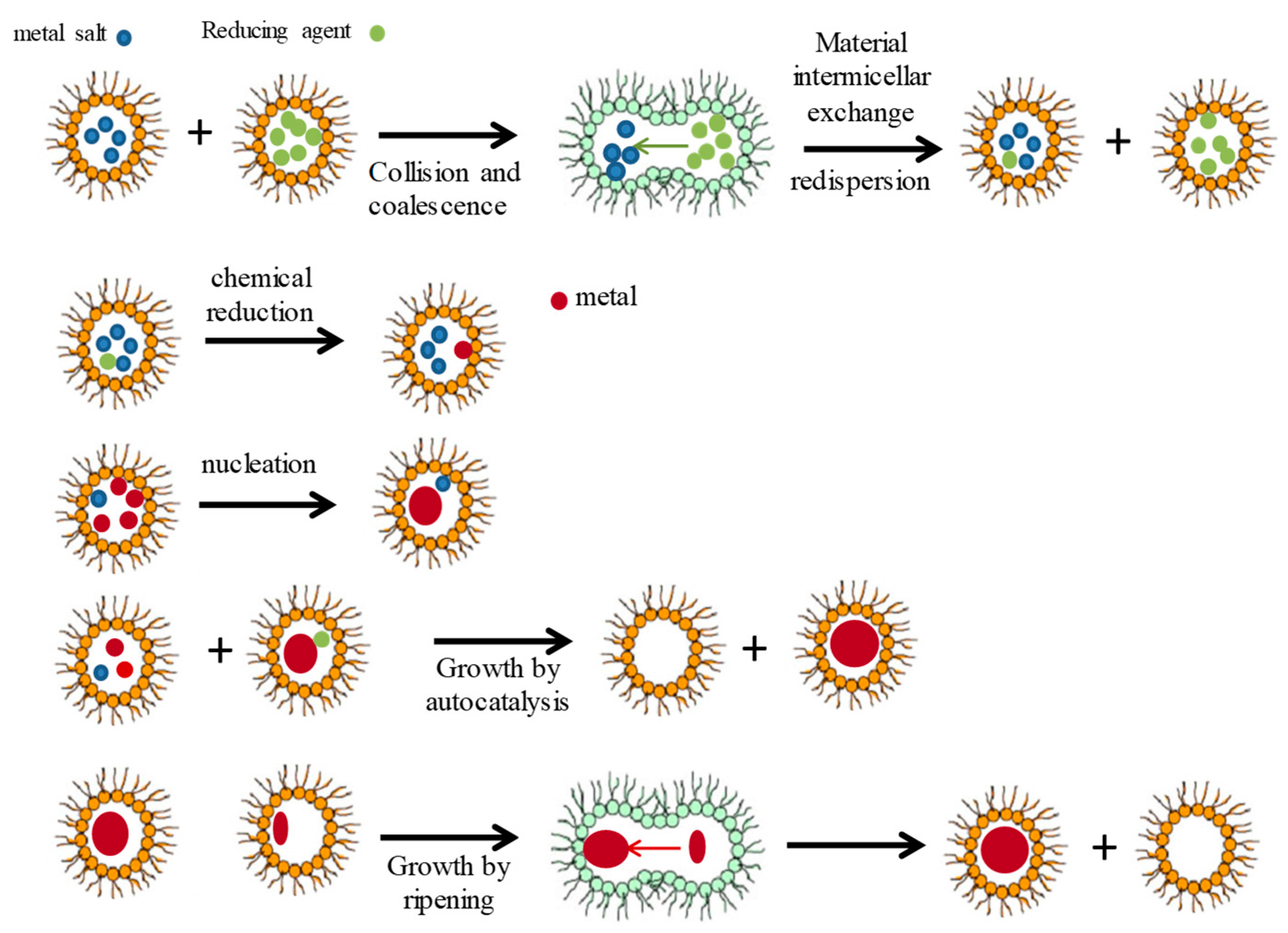
2. Simulation Procedure
2.1. Microemulsion as Nanoreactor
2.2. Feeding Solution (〈c〉 Parameter)
2.3. Droplet Size
2.4. Criteria for Interdroplet Exchange of Reactants and Non-Aggregated Products (Exchange Parameter kex)
2.5. Chemical Reduction Rates (Reduction Rates Parameters, vAu and vM)
2.6. Nucleation (n* Parameter)
2.7. Growth by Autocatalysis
2.8. Growth by Ripening
2.9. Criteria for Interdroplet Exchange of Growing Particles (Flexibility Parameter f): Interdroplet Channel Size
2.10. Characterization of the Microemulsion by the Material Interdroplet Exchange Criteria
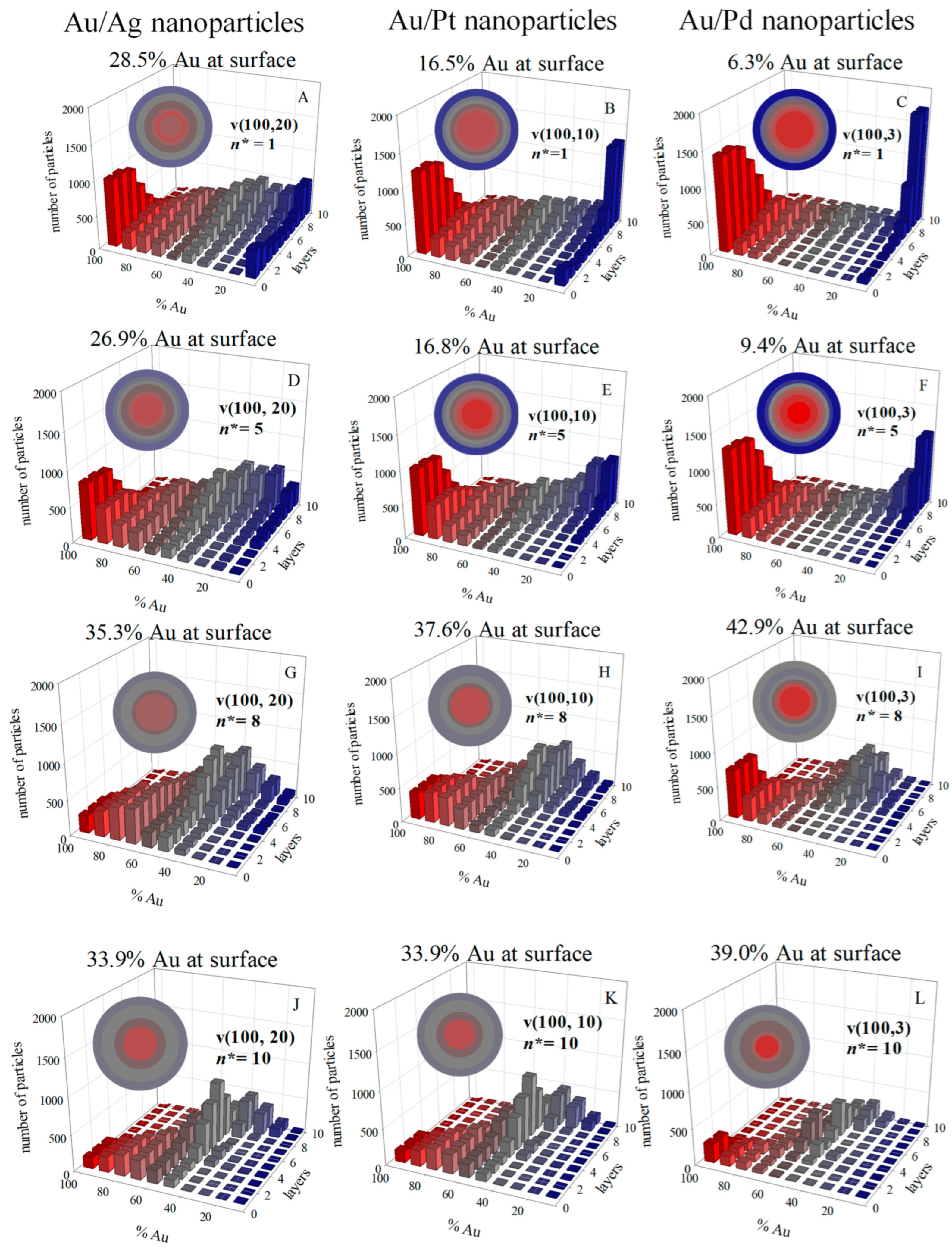
2.11. Nanoparticle Characterization
2.12. Model Validation
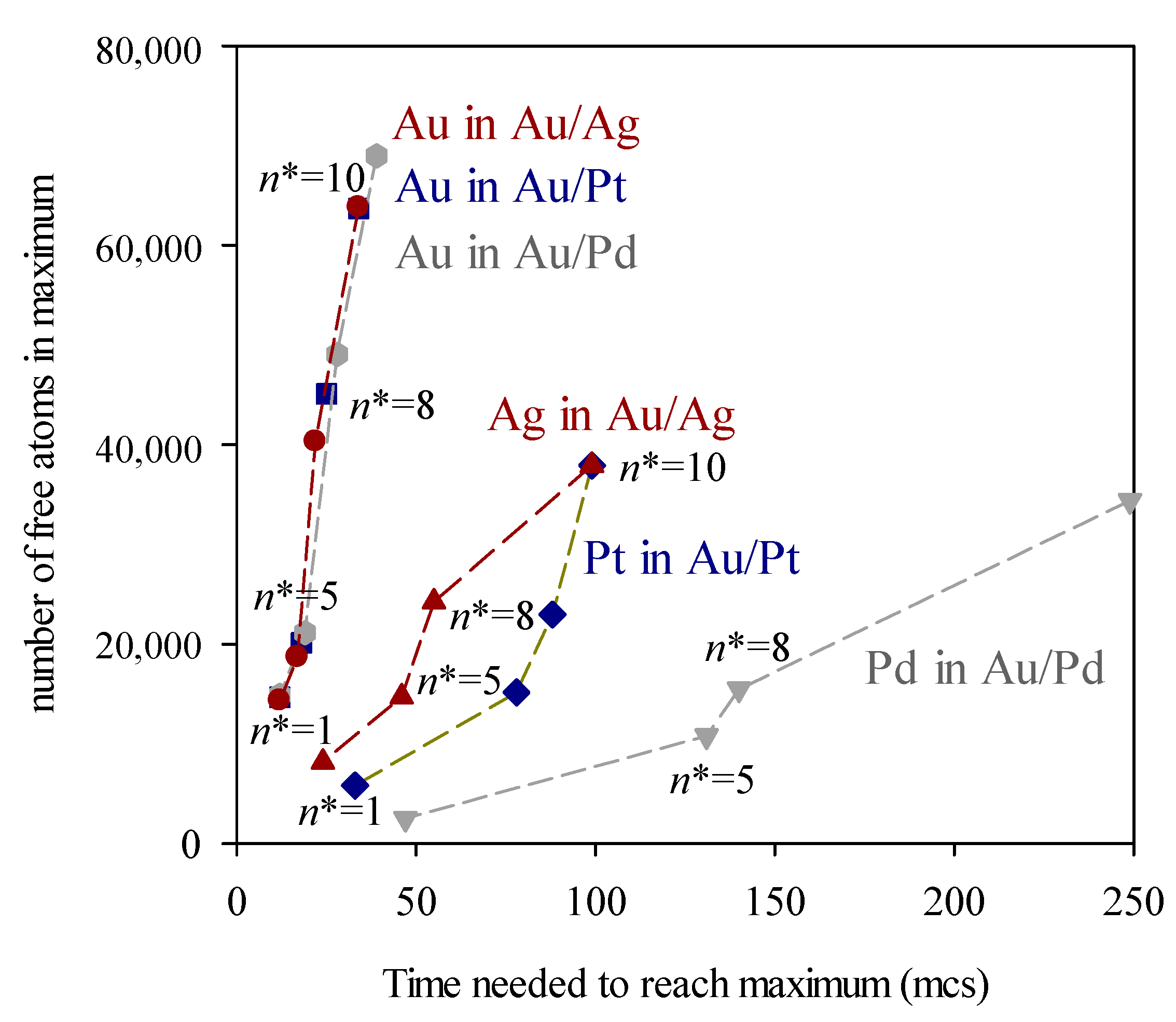
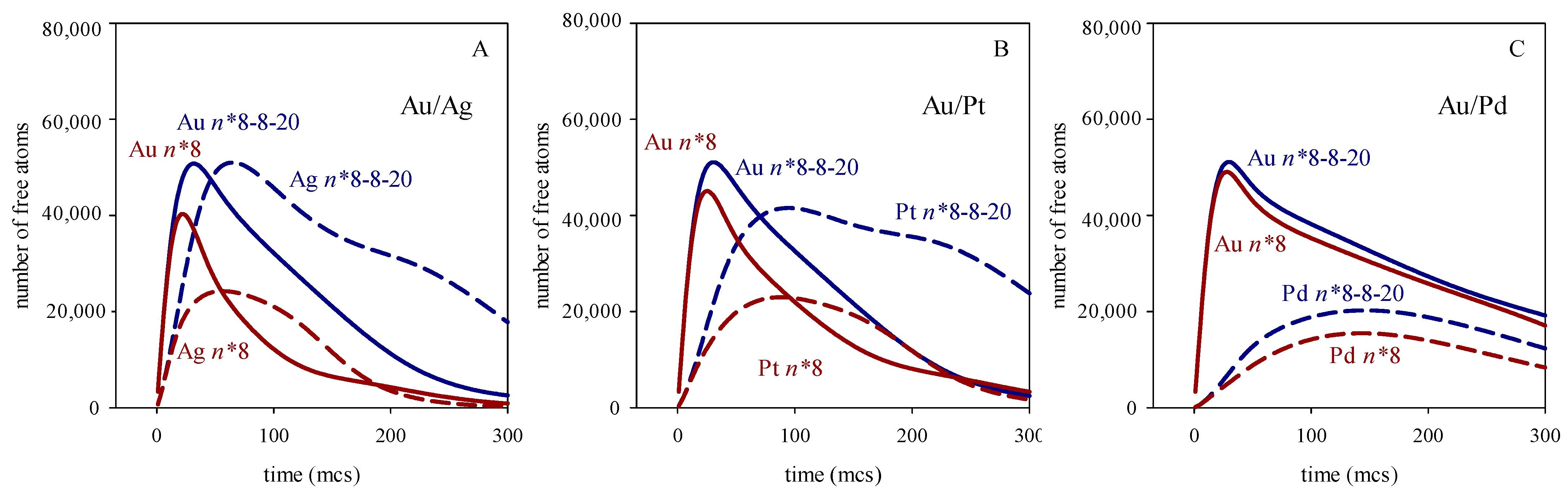
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suntivich, J.; Xu, Z.; Carlton, C.E.; Kim, J.; Han, B.; Lee, S.W.; Bonnet, N.; Marzari, N.; Allard, L.F.; Gasteiger, H.A.; et al. Surface composition tuning of Au-Pt bimetallic nanoparticles for enhanced carbon monoxide and methanol electro-oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7985–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Qian, D.; Xu, G.; Xu, H.; Dai, J.; Du, Y. Magnetic Fe3O4 supported PdAu bimetallic nanoparticles with the enhanced catalytic activity for Heck and Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 573, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutonnet, M.; Lögdberg, S.; Svensson, E.E. Recent developments in the aplication of nanoparticles prepared from w/o microemulsions in heterogeneous catalysis. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 13, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinfelt, J.H. Catalysis by alloys and bimetallic clusters. Acc. Chem. Res. 1977, 10, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, R.Y.G.; Schwarze, M.; Schomäker, R.; Stubenrauch, C. Catalytic activity of mono- and bi-metallic nanoparticles synthesized via microemulsions. Catalysts 2014, 4, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Murray, C.B.; Weller, D.; Folks, L.; Moser, A. Monodisperse FePt nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 2000, 287, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, P.V. Quantum Dot Solar Cells. Semiconductor Nanocrystals as Light Harvesters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 18737–18753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-M.; Rhee, H.-K. Dendrimer-templated AgPd bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 271, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutonnet, M.; Sánchez-Domínguez, M. Microemulsion droplets to catalytically active nanoparticles. How the application of colloidal tools in catalysis aims to well designed and efficient catalysts. Catal. Today 2017, 285, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, H.; Isaksson, S.; Altskaer, A.; Holmberg, K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with controllable morphology prepared from oil-in-water emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 467, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, C. Preparation of Cu-Ni alloy nanocrystallites in water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, R.; Jellinek, J.; Johnston, R.L. Nanoalloys: From theory to applications of alloy clusters and nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 845–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelescu, D.G.; Magno, L.; Stubenrauch, C. Monte Carlo simulation of the size and composition of bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized in water in oil microemulsions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 22069–22078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, C.; Buceta, D.; López-Quintela, M.A. On metal segregation of bimetallic nanocatalysts prepared by a one-pot method in microemulsions. Catalysts 2017, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Hu, X.; Kang, X.; Zhao, H.; Sun, M.; Cihen, X. A one-step facile synthesis of Ag-Ni core-shell nanoparticles in water-in-oil microemulsions. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 367, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumelda, T.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Kosydar, R.; Góral-Kurbiel, M.; Gurgul, J.; Duraczynska, D. Formation of Pd-group VIII bimetallic nanoparticles by the “water-in-oil” microemulsion method. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 529, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumelda, T.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Kosydar, R.; Gurgul, J. Synthesis of carbon-supported bimetallic palladium-iridium catalysts by microemulsion: Characterization and electrocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 392–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla-Gullón, J.; Vidal-Iglesias, F.J.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Electrochemical characterization of platinum-ruthenium nanoparticles prepared by water-in-oil microemulsion. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 5079–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, S.; García-García, F.J.; Jaeras, S.; Martínez-Huerta, M.V.; García Fierro, J.L.; Boutonnet, M. Preparation of carbon supported Pt and PtRu nanoparticles from microemulsion. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 285, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Koboyashi, K.; Nagai, M. Preparation and characterization of platinum-ruthenium bimetallic nanoparticles using reverse microemulsions for fuel cell catalyst. J. Oleo Sci. 2007, 56, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chan, K.Y. Water-in-oil microemulsion synthesis of platinum-ruthenium nanoparticles, their characterization and electrocatalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, D.; Huang, T. Preparation of Au/Pt bimetallic nanoparticles in water-in-oil microemulsions. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fernández, P.; Rojas, S.; Ocón, P.; Gómez de la Fuente, J.L.; San Fabián, J.; Sanza, J.; Peña, M.A.; García-García, F.J.; Terreros, P.; Fierro, J.L.G. Influence of the preparation route of bimetallic Pt-Au nanoparticle electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2913–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A. Gold–platinum alloy nanoparticles through water-in-oil microemulsion. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2015, 5, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmatpour, F.; Abazari, R. Formation of dispersed palladium-nickel bimetallic nanoparticles in microemulsions: Synthesis, characterization, and their use as efficient heterogeneous recyclable catalysts for the amination reactions of aryl chlorides under mild conditions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55815–55826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethayaraja, M.; Bandyopadhyaya, R. Population balance models and Monte Carlo simulations for nanoparticle formation in water-in-oil microemulsions: Implications for CdS synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 17102–17113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, B.; Veit, P.; Sundmacher, K. Nanoparticle Precipitation in Reverse Microemulsions: Particle Formation Dynamics and Tailoring of Particle Size Distributions. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4320–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, B.; Rauscher, F.; Adityawarman, D.; Voigt, A.; Sundmacher, K. Microemulsion-assisted precipitation of particles: Experimental and model-based process analysis. Chem. Eng. Process. 2006, 45, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwe, R.P.; Khilar, K.C. Effects of the Intermicellar Exchange Rate and Cations on the Size of Silver Chloride Nanoparticles formed in Reverse Micelles of AOT. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6432–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadh, B.; Tikku, S.; Khilar, K.C. Modeling core–shell nanoparticle formation using three reactive microemulsions. Colloids Surf. A 2007, 298, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Shukla, D.; Mehra, A. Coagulation of Nanoparticles in Reverse Micellar Systems: A Monte Carlo Model. Langmuir 2005, 21, 11528–11533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ström, L.; Ström, H.; Carlsson, P.; Skoglundh, M.; Härelind, H. Catalytically active Pd-Ag Alloy nanoparticles synthesized in microemulsion template. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9754–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojo, C.; Buceta, D.; López-Quintela, M.A. On the minimum reactant concentration required to prepare Au/M core-shell nanoparticles by the one-pot microemulsion route. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2019, 5, 20180045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buceta, D.; Tojo, C.; Vukmirovik, M.; Deepak, F.L.; López-Quintela, M.A. Controlling bimetallic nanostructures by the microemulsion method with sub-nanometer resolution using a prediction model. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7435–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojo, C.; de Dios, M.; López-Quintela, M.A. On the structure of bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized in microemulsions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19145–19154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, F.; Tojo, C. Modelling of nano-alloying and structural evolution of bimetallic core-shell nanoparticle obtained via the microemulsion route. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, F.; Tojo, C. Designing Bimetallic Nanoparticle Structures Prepared from Microemulsions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 17801–17813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapantulu, A.; Bandyopadhyaya, R. Formation of Gold Nanoparticles in Water-in-Oil Microemulsions: Experiment, Mechanism, and Simulation. Langmuir 2021, 37, 6623–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, C.; Buceta, D.; López-Quintela, M.A. Synthesis of Pt/M (M = Au, Rh) Nanoparticles in Microemulsions: Controlling the Metal Distribution in Pt/M Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 2503–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towey, T.F.; Khan-Lodhi, A.; Robinson, B.H. Kinetics and mechanism of formation of quantum-sized cadmium sulfide particles in water-aerosol OT-oil microemulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 3757–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares-Baez, J.-P.; Panizon, E.; Ferrando, R. Nanoscale Effects on Phase Separation. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5394–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, T.; Sato, H.; Komasawa, I. Mechanism of formation of Titanium dioxide ultrafine particles in reverse micelles by hydrolysis of Titaniumtetrabutoxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 3014–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, H.; Braun, J.; Behm, R.J. Direct Identification of Critical Clusters in Chemical Vapor Deposition. J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zana, R.; Lang, J. Dynamics of microemulsions. In Microemulsions: Structure and Dynamics; Freiberg, S.E., Bothorel, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987; p. 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tojo, C. The Interplay between Nucleation and the Rates of Chemical Reduction in the Synthesis of Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Microemulsions: A Computer Study. Metals 2024, 14, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14090987
Tojo C. The Interplay between Nucleation and the Rates of Chemical Reduction in the Synthesis of Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Microemulsions: A Computer Study. Metals. 2024; 14(9):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14090987
Chicago/Turabian StyleTojo, Concha. 2024. "The Interplay between Nucleation and the Rates of Chemical Reduction in the Synthesis of Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Microemulsions: A Computer Study" Metals 14, no. 9: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14090987
APA StyleTojo, C. (2024). The Interplay between Nucleation and the Rates of Chemical Reduction in the Synthesis of Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Microemulsions: A Computer Study. Metals, 14(9), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14090987





