Abstract
When heterogeneous joints are created, problems with the formation of intermetallic phases arise. There are various ways to reduce the formation of intermetallics. One of the ways that is discussed in this article is to use a suitable interlayer of appropriate thickness when forming the joint. A too-thin interlayer does not protect against the formation of brittle intermetallic phases. On the other hand, a too-thick interlayer increases the heterogeneity of the joint and, thus, decreases its useful properties. Within this paper, the formation of diffusion joints between the base material (AISI 304 steel, duplex steel, AISI 316L steel, or titanium grade 2) and the 0.2 mm thick intermediate layer (nickel or vanadium) was studied. Initial diffusion joints were prepared in a Gleeble 3500 machine, and samples for the study of diffusion kinetics were subsequently heat-treated in a vacuum furnace. The result of the research was the determination of specific diffusion parameters of nickel and vanadium into all four tested base materials. The initial diffusion depth (simple heating to the target temperature without holding at this temperature) of nickel was 4.46 µm into duplex steel and 5.48 µm into Ti Gr. 2 at 950 °C. At the same temperature, the initial diffusion depth of vanadium was 14.54 µm into duplex steel and 14.32 µm into Ti Gr. 2. In addition, general equations for the calculation of diffusion coefficients for the mentioned materials in the temperature range of 850 to 1150 °C were established.
Keywords:
diffusion coefficient; nickel; vanadium; titanium; stainless steel; duplex steel; diffusion bonding 1. Introduction
Diffusion bonding creates heterogeneous joints that often cannot be formed by conventional fusion methods. Ti alloys and stainless steels are examples of such diffusion-bonded materials. This combination of advanced alloys has achieved significant popularity in the aerospace, petrochemical, nuclear, and medical industries, for example. These joints have found their use mainly due to their high specific strength, low weight, and also the saving of precious metals. Joining of these materials is generally difficult, and during the process intermetallic phases can be formed, which are undesirable in the joint [1,2].
The formation of intermetallic phases can be eliminated by adding an interlayer to the diffusion joint, but quality joints can also be formed without an interlayer. The joining of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy with duplex stainless steel without an interlayer has been investigated by several researchers [3,4]. The joints were formed in the temperature range 650–800 °C, and the kinetics of interlayer formation and the activation energy were evaluated according to the Arrhenius equation. The joining of titanium or titanium alloys with AISI 304 stainless steel is discussed in [5,6,7]. The authors of [5] reported that the highest strength was achieved at a joining temperature of 800 °C because of the smaller width of the intermetallic phase formation area. In the case of joining of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy and AISI 304 steel, [7] reported that the highest strength was achieved at 900 °C.
As already mentioned, during the formation of heterogeneous joints, fragile intermetallic phases can be formed for specific concentrations of elements, which especially decrease the fracture properties of the joint. Thus, the formation of intermetallic compounds is most often eliminated by using an interlayer of different materials. The joining of pseudo-α-Ti alloy with Ti-stabilized stainless steel (SS321) was studied in [8]. The authors investigated the formation of joints both without an interlayer and with a nickel interlayer. The joints were created at temperatures of 800–940 °C, with an interlayer thickness of 5 ± 2 µm being determined as optimal. The joining of titanium or titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V and stainless steel AISI 304 with the use of different interlayers is described in [9,10,11,12], where it is shown that, in addition to a nickel interlayer, a silver or copper interlayer can also be used, and the optimal temperature of joining is stated to be 900 °C in all cases. Similar conclusions were also reached when investigating diffusion joints between titanium alloy and a micro-duplex stainless steel [13] or AISI 316L steel [14].
In diffusion bonding, a combination of different metals can be used as an interlayer to create a multilayer. The creation of joints made of titanium alloy TC4/Ti-6Al-4V and AISI 316L/AISI 321 steel with a multilayer was published in [15,16,17,18]. Various combinations of interlayers (V, Cu, Co, Ni, Nb) were used in the tests. However, in all cases, the highest bond strengths were achieved around 900 °C. Above 950 °C, intermetallic phases are already formed.
The microstructure and strength properties of the joint are affected not only by the interlayer used but also by the process parameters of the joining. Research on the effects of individual process parameters (the effects of different pressures and times used) is described in [19,20,21,22].
In addition to a suitably selected interlayer, it is also necessary to correctly determine the layer thickness. Some papers [17,23] show that, at higher temperatures or longer holding times, the elements can diffuse through the interlayer and intermetallic phases are formed. In order to prevent this, it is useful to have an idea of how quickly the elements will diffuse into a specific type of alloy at specific process parameters—temperature and bonding time.
Therefore, this paper focuses on the determination of the diffusion coefficients of Ni and V into the stainless austenitic steels AISI 304 and AISI 316L, duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1, and Ti grade 2 for the temperature range 850 to 1150 °C. For heterogeneous joints that include Ni and vanadium interlayers, the determination of diffusion coefficients can be complicated. Some authors [23,24,25,26] have presented diffusion coefficients for titanium at 800 and 900 °C (DTi = 5.5 × 10−14 m2·s−1 at 900 °C and DTi = 9 × 10−14 m2·s−1 at 800 °C), for iron α at 900 °C (DFe-α = 5 × 10−15 m2·s−1), and for nickel at 800 °C (DNi = 3 × 10−17 m2·s−1). However, diffusion coefficients in the temperature range 850–1150 °C have not been published anywhere before.
The paper “Determination of diffusion coefficients of nickel and vanadium in stainless and duplex steels and titanium” builds on and significantly extends the knowledge gained in the authors’ previous paper [27]. The previous article focused on the study of nickel’s diffusion from the nickel interlayer into AISI 304 and AISI 316L steels. In the literature, it is possible to find diffusion coefficients for the individual chemical elements, but it turns out that the diffusion rate depends not only on the element that diffuses but also on the alloy into which the diffusion takes place, and in this case it is already very difficult or almost impossible to find reliable data for specific metal couples. The aim of this work is to provide a dataset that will be useful to other experimenters. It follows from the above that attention should also be paid to other metals that are widely commercially used (duplex steels, titanium), and that suitable interlayers should be sought for these metals that would allow the formation of heterogeneous joints without the formation of intermetallic phases. For this reason, we carried out further experiments in which (in addition to AISI 304 and AISI 316L steels) duplex steels and titanium grade 2 were studied, and a vanadium interlayer was also used as further extension of the previous experiments (only a nickel interlayer was used in the previous paper).
2. Materials and Methods
The diffusion coefficients for the pure vanadium and nickel interlayer were determined as part of the experimental work. For vanadium, the diffusion coefficients into two austenitic stainless steels (AISI 304 and 316L), duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1, and titanium grade 2 were determined. For nickel, the diffusion coefficients into duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 and titanium grade 2 were determined. The test samples of all materials were made from a 12 mm diameter rolled circular bar. The first used material was AISI 304 (X5CrNi18-10) steel I. The second used material was austenitic stainless steel with the specification AISI 316L (X2CrNiMo17-3-2). Furthermore, duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1 was tested. The chemical composition of all tested materials was measured using a Bruker Q4 Tasmann spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, Karlsruhe, Germany). The chemical compositions shown in Table 1 are the average of 7 measurements.

Table 1.
Chemical composition (wt%) of the AISI 304, AISI 316L, and duplex (1.4162) steel.
Another tested material was commercially pure titanium Grade 2 (3.7035). The chemical composition was measured at 7 places using a Bruker Q4 Tasmann spectrometer, and the average values from these measurements are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical composition (wt%) of the titanium grade 2.
The temperature regime was applied to the samples in a Reetz vacuum furnace (HTM Reetz GmbH, Berlin, Germany).
For the determination of diffusion coefficients, test samples in the shape of a cylinder with a length of 50 mm and a diameter of 12 mm were used, and their front contact surfaces were ground to achieve specified surface roughness and parallel surfaces. The experiment had two phases: In the first phase, diffusion bonding of the samples was carried out in a Gleeble 3500 thermal–mechanical simulator (Dynamic System Inc., New York, NY, USA). The aim of the process was to create only initial diffusion bonds between the materials and the interlayer, so that the sample would not fracture during further process and could be used for phase 2. Samples of AISI 316L, AISI 304, and duplex steel with nickel or vanadium interlayers were bonded in the Gleeble 3500 at 1000 °C with a clamping force of 2.5 kN and a holding time of 1 min. A titanium grade 2 heterogeneous joint with a nickel interlayer was bonded at 850 °C with a clamping force of 0.5 kN and a holding time of 5 min. For titanium grade 2 with a vanadium interlayer, the bonding parameters were as follows: 950 °C, 0.5 kN clamping force, and a holding time of 1 min. The reason for using lower temperatures for grade 2 titanium was to eliminate deformation of the pure titanium during joining.
In addition to the monitoring of the main process parameters, surface roughness was also measured for the contact surfaces of the test samples of all tested materials, as well as for the nickel and vanadium foils. The roughness on the contact surfaces of the samples was measured with a MITUTOYO SV-2000N2 SURFTEST contact profilometer (Mitutoyo, Kawasaki, Japan), and the roughness of the foils was measured on a KEYENCE VK-X1100 3D confocal microscope (Keyence, Itasca, IL, USA)—for results, see Table 3. Control of the device and evaluation of the results were realized by the MultiFileAnalyser VK-H1XMD 2019 software (Keyence, Itasca, IL, USA).

Table 3.
Roughness of samples and foils.
The second phase of the experiments was focused on the determination of the diffusion intensity of Ni and V into the tested materials. The experiments were conducted in a Reetz vacuum furnace with temperature regimes with maximum temperatures of 850 °C, 950 °C, 1050 °C, and 1150 °C. The heating rate was graded and the same for all experiments. The course of the temperature regime with a holding temperature of 950 °C is shown for illustration in Figure 1. During the thermal activation of diffusion, the vacuum in the furnace was 7 × 10−5 mbar. No additional pressure was applied to the samples with initial diffusion bonds from experimental phase 1.
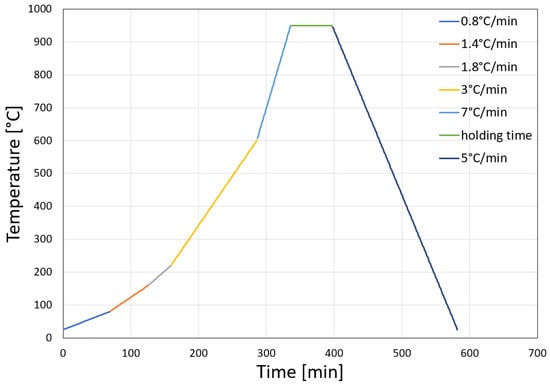
Figure 1.
Temperature regime in the vacuum furnace—maximum temperature 950 °C and holding time 1 h.
A Tescan Mira 3 scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Tescan Orsay holding a.s., Brno, Czech Republic) equipped with an Oxford UltimMax65 detector (Oxford Instruments plc, Oxfordshire, England) for energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis was used for the study of diffusion kinetics. The concentration of each element as a function of distance from the diffusion contact area for each type of thermal activation was measured by EDX. An accelerating voltage of 10 kV was set for all measurements.
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Diffusion Bonding in the Gleeble 3500
For the first phase of bonding (formation of diffusion bridges), a K-type thermocouple was always welded to the sample using a capacitor welder. Because the maximum welding temperature was 1000 °C, K-type thermocouples could be used without any problems. After welding the thermocouples, the samples were placed in full-contact copper jaws and placed in the chamber of the Gleeble device, as shown in Figure 2. All contact surfaces and foil surfaces were degreased and cleaned, and then two layers of foil were clamped between the two base materials. Two 0.1 mm thick foils were always used as the interlayer so that a sufficient interlayer thickness was achieved for the experiment, where diffusion through the entire layer would not be possible even at longer holding times.
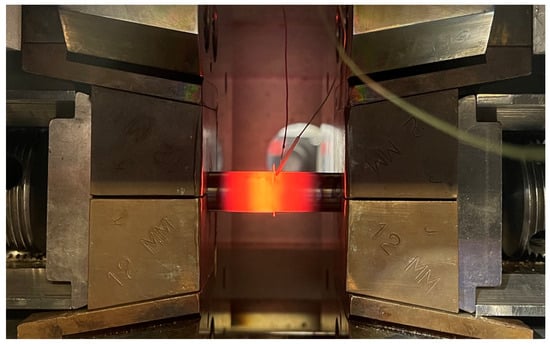
Figure 2.
Clamped and heated sample in the Gleeble chamber.
After the samples were clamped, the chamber was evacuated and the samples and foils were bonded using heating cycles. The welding parameters are detailed in Section 2. The finished samples were then cut using a metallographic saw and polished for analysis on a scanning electron microscope. The initial diffusion bonds were observed using SEM. An example of the appearance of a diffusion weld of the duplex steel with a nickel interlayer (left part of the joint) and AISI 304 steel with a nickel interlayer (right part of the joint) is shown in Figure 3. Based on the energy-dispersive analysis, the minimal diffusion depth into the base material was confirmed. In the case of duplex steel, the initial diffusion of Ni was 2.24 µm, and for Ti grade 2 it was 5.02 µm. The initial diffusion of vanadium into the base material was slightly higher: for AISI 304 steel it was 8.98 µm, for AISI 316L steel it was 7.43 µm, for duplex steel it was 5.61 µm, and for titanium grade 2 it was 1.47 µm.
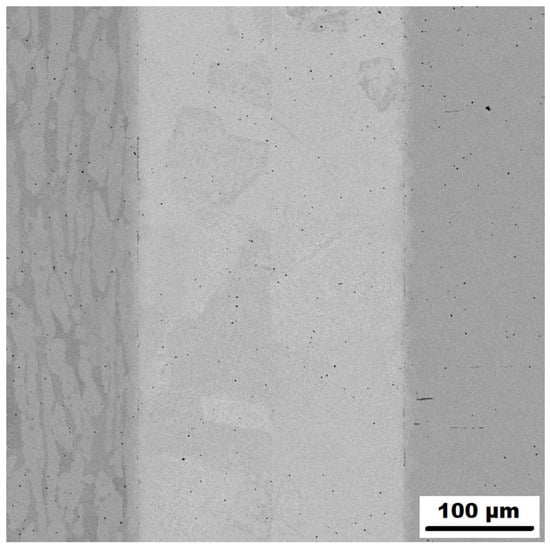
Figure 3.
The appearance of a diffusion weld of the duplex steel with a nickel interlayer (left part of the joint) and AISI 304 steel with a nickel interlayer (right part of the joint).
3.2. Evaluation of Diffusion Kinetics
The other half of the welded samples were placed in a vacuum furnace, where thermal activation of diffusion was applied under defined boundary conditions. The following temperatures were chosen for the experimental testing: 850 °C, 950 °C, 1050 °C, and 1150 °C. Two holding times (1 h and 5 h) were applied for each of these temperatures. Each sample was individually placed in the vacuum furnace and treated under the specific conditions.
After thermal activation of diffusion, the concentration of each element was determined by EDX analysis. By analyzing the concentration profiles of nickel and vanadium, the influence of temperature and time on the diffusion ability could be assessed. The changes in the concentrations of individual elements in the interface area were measured by linear EDX analysis. Seven lines were measured for each sample. Based on the measured EDX analyses, the diffusion coefficients were calculated. The diffusion depths of nickel/vanadium into individual materials at different temperatures and holding times were also determined experimentally (see Figure 4 and Figure 5).
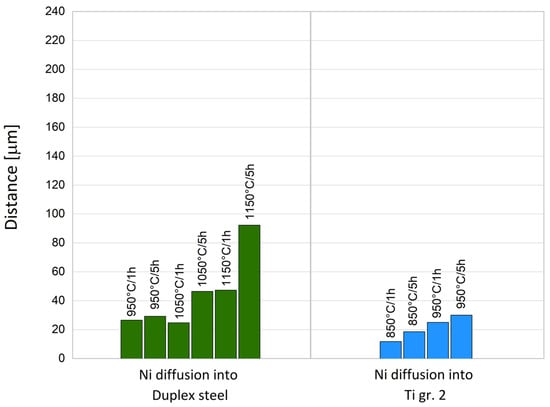
Figure 4.
The maximum diffusion depth of nickel into duplex steel and Ti Gr. 2 at different temperatures and holding times.
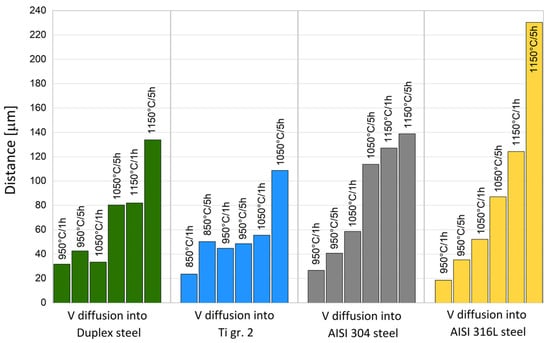
Figure 5.
The maximum diffusion depth of vanadium into AISI 304, AISI 316L, duplex steel, and Ti Gr. 2 at different temperatures and holding times.
The measured data (Figure 4 and Figure 5) show that nickel diffuses into the duplex steel to a smaller depth than it does into Ti gr. 2 at the same temperature and holding time. For the diffusion of vanadium, the results are similar, with the largest diffusion depths reached for Ti gr. 2 at the same temperature regime. In addition, a comparison of the boundary thermal exposures for the individual materials (950 °C_1 h and 1150 °C_5 h for AISI 304, AISI 316L, and duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1, and 850 °C_1 h and 1050 °C_5 h for titanium) was carried out. The comparison of nickel’s diffusion is summarized in Figure 6, and the same comparison for vanadium’s diffusion is shown in Figure 7. The significant differences in heat regimes are clearly visible from the graphs (Figure 6 and Figure 7); a higher temperature and a longer holding time will allow nickel and vanadium to diffuse to a greater depth.
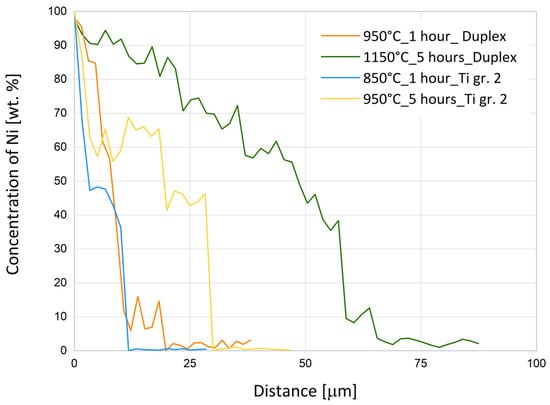
Figure 6.
Comparison of Ni concentration gradients for extreme temperature exposures.
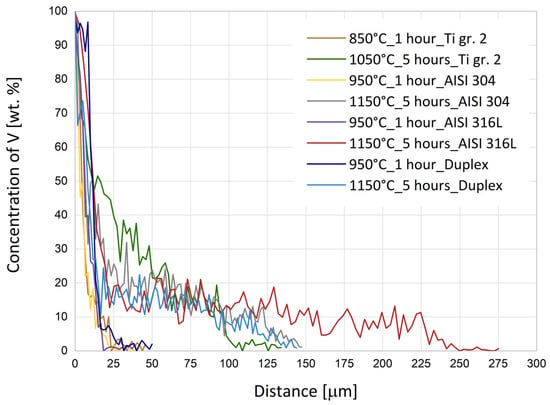
Figure 7.
Comparison of vanadium concentration gradients for extreme temperature exposures.
The diffusion welds are produced at high temperatures. The heating rate to this temperature can be very fast if induction or resistance heating is used. Rapid heating helps to limit the effect of heating on the width of the diffusion area. However, in industry, available devices with indirect heating of the material are most often used. In the case of indirect heating, the heating rate to the maximum temperature (and the speed of cooling to room temperature) is significantly lower—in the order of units of °C/s. The experiments carried out as part of this research aimed to get as close as possible to the conditions of industrial applications. Therefore, a vacuum furnace with slow heating and cooling rates was used. It is clear that diffusion already takes place during heating and also continues during cooling. This was the reason why the separate experiments were performed to verify the effects of heating and cooling in the vacuum furnace on the total width of the diffusion zone. For these tests, the samples that were produced were only heated to the maximum temperature and then cooled without holding at the temperature. The heating and cooling rates were the same as in the other cases (see the heating and cooling ramps in Figure 1). Therefore, Table 4 shows the experimentally determined diffusion depths of Ni and V into each material only after heating and cooling in the vacuum furnace.

Table 4.
Diffusion depths (h) without dwell time on temperature (determined on real samples).
3.3. Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients
The diffusion coefficients were determined from Equation (1) and are shown in Table 5 for the diffusion of Ni into selected base materials and in Table 6 for the diffusion of V. The detailed calculation process has already been presented in a previous publication [27]; therefore, only the final equation for the calculation of the diffusion coefficient D is presented here. The median of the seven calculated D values from the seven measured line data for each temperature exposure is then presented in the tables.
where D is the diffusion coefficient, k is the line directive, and t is the time.

Table 5.
Calculated diffusion coefficients (D) of Ni into the base materials.

Table 6.
Calculated diffusion coefficients (D) of V into the base materials.
For completeness, it was necessary to verify that temperature and time were variables that had a statistically significant influence on the diffusion kinetics. A two-factor ANOVA with repetition was used for this. For a more accurate statistical evaluation, ANOVA was not applied to the summary median D value, but it was applied to each of the seven calculated D values (see Table 5 and Table 6). Table 7 shows the results of the two-factor analysis of variance for nickel diffusion into each of the base materials studied. Table 8 summarizes the same for the vanadium interlayer. The significance level of the test was considered to be β = 5% for all calculations. Statistical evaluation confirmed that both temperature and time have a statistically significant effect. Only for the diffusion of vanadium into AISI 304 steel did the statistical evaluation show a non-significant effect of time. These results will be further verified by more experiments.

Table 7.
Results of two-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repetition for a nickel interlayer.

Table 8.
Results of two-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repetition for a vanadium interlayer.
Since it was confirmed that the diffusion rate increases with increasing temperature, this dependence can be expressed mathematically by Equation (2):
where D is the diffusion coefficient, D0 is a partial factor depending on the state of the crystal lattice and the frequency of diffusing atoms, Qm is the activation energy, Rm is the molar gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature. Equation (2) and Figure 8 (for nickel) and Figure 9 (for vanadium) show an exponential dependence of D on −1/T. Figure 8 and Figure 9 also show specific calculation equations for individual curves.
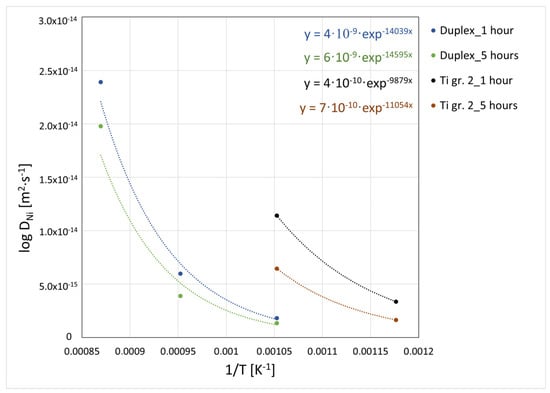
Figure 8.
Dependence of log DNi on 1/T for duplex and Ti gr. 2 and both 1 h and 5 h.
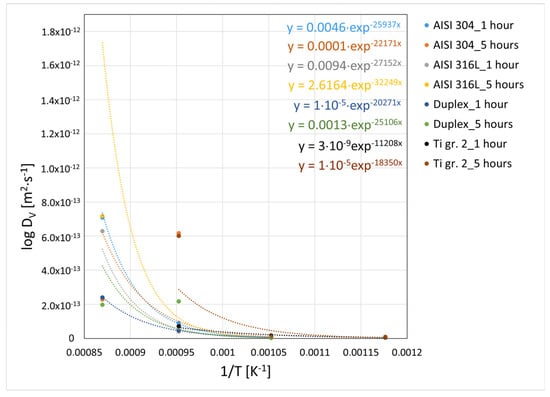
Figure 9.
Dependence of log DV on 1/T for AISI 304, AISI 316L, duplex steel, and Ti gr. 2 and both 1 h and 5 h.
For investigation of the diffusion kinetics, nickel and vanadium interlayers of greater thicknesses than would be needed in practice were used. Due to this experiment’s arrangement, there was always a band unaffected by diffusion in the middle of the interlayer, in which the concentration of nickel or vanadium was measured to be 100%. Therefore, the diffusion joint could be theoretically divided into two halves for the calculation of diffusion coefficients. If the diffusion coefficient is already known, another case of diffusion calculation can be used to represent the real case of a diffusion joint. This case is shown in Figure 10.
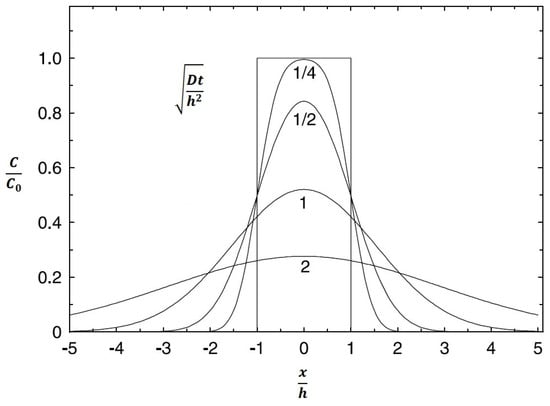
Figure 10.
Diffusion from a 2 h wide sheet for different values of [27].
In the case shown in Figure 10, it is assumed that a sheet (interlayer) with a thickness of 2 h with the same initial concentration is connected to two half-spaces, which in practice are two rods of pure material. For curve 1/4 of Figure 10, the nickel concentration in the interlayer is c0 = 100%, and then Equation (3) can be used:
The relevance of the calculated diffusion coefficients DNi and DV can be determined from Equation (3). This equation was used to calculate the diffusion depth for the selected process conditions (temperature and time). The calculated values can be compared with the values obtained by experimental measurement of chemical concentrations using EDX analysis to predict the accuracy of the diffusion coefficients obtained by calculation from the mathematical model. The effects of heating and cooling are presented in the previous section in Table 4.
4. Discussion
The main goal of the present paper was to establish the diffusion kinetics of nickel and vanadium into austenitic stainless steels (AISI 304 and AISI 316L), duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1, and commercially pure titanium (titanium grade 2), and then to determine the diffusion coefficients of nickel and vanadium into each material for a defined range of temperatures and holding times.
Based on the performed experiments and calculations, it can be concluded that the kinetics of diffusion and the depth to which nickel and vanadium diffuse are significantly affected by the applied temperature, as was shown in the case of the studied base materials. In Ref. [6,7,10], the authors reached similar conclusions and showed the effect of temperature on the example of the formation of intermetallic phases. The area of existence of these intermetallic phases occurs at higher concentrations of the given element. It is therefore clear that diffusion has to occur faster at higher temperatures to reach the regions where intermetallic phases exist. For duplex steel, nickel diffusion occurred at 1150 °C to a depth 3.3× greater than at 950 °C and 2× greater than at 1050 °C. For titanium grade 2, diffusion of Ni occurred at 950 °C to a depth 2× greater than at 850 °C. Diffusion kinetics was also evaluated for vanadium. For AISI 304 steel, V diffusion occurred at 1150 °C to a depth 3.5× greater than at 950 °C and 1.3× greater than at 1050 °C. For AISI 316L steel, at 1150 °C, V diffusion occurred up to an 8× greater depth compared to 950 °C and a 2.8× greater depth compared to 1050 °C. For duplex steel, the differences were not as large. At 1150 °C, V diffusion occurred to a 3.4× greater depth than at 950 °C and a 1.7× greater depth than at 1050 °C. For titanium grade 2, at 1050 °C, vanadium diffused to 2× greater depths compared to 850 and 950 °C.
There are two factors that influence the diffusion kinetics of nickel and vanadium into the studied base materials—temperature, and dwell time on temperature. Figure 6 compares the two limit cases of Ni diffusion into duplex steel and the two limit cases for Ti grade 2. Figure 7 compares all limit cases of V diffusion into all studied materials. From the performed experiments and from the results of the two-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repetition, it was confirmed that both the temperature and the dwell time at the temperature have a significant effect on the formation of diffusion joints.
The intensity of diffusion, which already starts when heating to the bonding temperature and continues when cooling down from this temperature, depends on the value of the maximum temperature (850, 950, 1050, and 1150 °C). Currently, industrial companies most often use indirect radiation heating for the creation of diffusion joints, which only provides slow heating rates. In such a case, it must be taken into account that diffusion already occurs during the heating and cooling of the products, as can be seen from Table 8. The diffusion of Ni is slower than that of V. For austenitic stainless steels, the diffusion of V is very similar, but vanadium diffuses slightly slower into AISI 316L steel. The reason for this slower diffusion may be due to the Mo content. AISI 316L steel has up to 2.5% more Mo, and this can inhibit diffusion.
In Ref. [23], the authors present diffusion coefficients for nickel (DNi = 3 × 10−17 m2·s−1 at 800 °C) and diffusion coefficients for titanium at 800 and 900 °C (DTi = 5.5 × 10−14 m2·s−1 at 900 °C and DTi = 9 × 10−14 m2·s−1 at 800 °C). However, the values of the diffusion coefficients for individual elements are not sufficient for application use, since the diffusion coefficients for a given pair of materials must be taken into account. According to Equation (2), the diffusion coefficients are exponentially dependent on the mathematical relationship −1/T. For that reason, the calculation of the diffusion coefficients for the base materials and nickel or vanadium was based on the temperature dependence according to the Arrhenius equation. Equation (4) would therefore be sufficient for the calculation of D0 and Q. On the other hand, the aim of this paper was not only to provide simple values of diffusion coefficients but also to show other researchers a method for determining diffusion coefficients at a specific temperature for arbitrary combinations of base material and interlayer. Moreover, Equation (5) shows how to correctly determine the thickness of interlayers for heterogeneous joints.
The results of the experiments (Figure 8 and Figure 9) were used to determine the general Equation (4) for calculating the diffusion coefficients of nickel and vanadium into the studied base materials in the specific temperature ranges. The values of the coefficients k and x for individual combinations of base materials and Ni or V interlayers are summarized in Table 9. This table also shows (see explanations of individual colors) the temperature range of the applicability of Equations (4) and (5) for specific combinations of materials. T is the diffusion process temperature in K.

Table 9.
The values of the coefficients k and x for calculation into Equations (4) and (5).
The depth of the diffusion area between the base material and the used interlayer must also be known for practical use. This depth is determined on the basis of the diffusion kinetics of nickel and vanadium into base materials (DNi, DV) and is determined by Equation (3). The modified Equation (5) can be used to calculate the specific diffusion depth for individual combinations of base materials and Ni or V interlayers over a range of temperatures (T) and for times (t) in the range of 1 to 5 h, where h is the width of the diffusion zone (m), T is the temperature at which diffusion occurs (K), and t is the holding time at temperature (s). The values of the coefficients k and x for individual combinations of base materials and Ni or V interlayers are summarized in Table 9.
When preparing diffusion joints using interlayers, it is necessary to know the diffusion coefficients and the width of the diffusion zone for the pairs of metals to be joined, so that it is possible to correctly design the process parameters and, thus, avoid the formation of inhomogeneities in the joint. The quality of the diffusion joint subsequently affects the mechanical properties of the joint, as well as other properties (e.g., physical properties or residual stresses in the joint). A number of interlayers (e.g., nickel, vanadium, niobium, copper, or silver) [17,18] can be used for diffusion joining of austenitic steels, as well as duplex steels or titanium alloys. In further research, our team would therefore like to devote itself to a detailed study focused on the use of other suitable interlayers—niobium, copper, and silver.
5. Conclusions
The diffusion kinetics of nickel and vanadium into austenitic stainless steels AISI 304 and AISI 316L, duplex steel X2CrMnNiN21-5-1, and commercially pure titanium (Ti gr. 2) was studied. The result of this research was the determination of specific diffusion coefficients for the given materials in the range of the most commonly applied temperatures and holding times. The following can be stated:
- Diffusion takes place not only after reaching the test temperature but also during heating and cooling. The diffusion of Ni was slower than the diffusion of V. For austenitic stainless steels, the diffusion of V was very similar, but vanadium diffused into AISI 316L steel slightly more slowly. The reason for this slower diffusion may be due to the Mo content, which, because of its size, is used to strengthen the solid solution of the steels. AISI 316L steel has a significantly higher Mo content compared to AISI 304 steel.
- To determine DNi and DV for specific materials, the generalized Equation (4) was formulated in the range of applied temperatures (T) 1223.15–1423.15 K (for steel) and 1123.15–1323.15 K (for titanium). This equation can be used in the indicated temperature range to calculate the specific depth of the diffusion area at the interface between the base material and the used interlayer.
- Equation (5) was used to calculate the depth of the diffusion area in the range of applied temperatures (T) 1223.15–1423.15 K (for steel) and 1123.15–1323.15 K (for titanium), while dwell times (t) can be inserted into the equation from 1 up to 5 h. The specific results obtained by calculating Equation (5) also serve to optimize the thickness of the used interlayer. The initial diffusion depth (simple heating to the target temperature without holding at this temperature) of nickel was 4.46 µm into duplex steel and 5.48 µm into Ti Gr. 2 at 950 °C. At the same temperature, the initial diffusion depth of vanadium was 14.54 µm into duplex steel and 14.32 µm into Ti Gr. 2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Š.V. and J.M.; methodology, Š.V. and J.M.; validation, J.M., M.Š. and D.K.; formal analysis, Š.V.; investigation, Š.V.; resources, Š.V., M.Š. and D.K.; data curation, Š.V. and M.Š.; writing—original draft preparation, Š.V.; writing—review and editing, M.Š., J.M. and D.K.; visualization, Š.V.; supervision, J.M.; project administration, Š.V.; funding acquisition, Š.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Student Grant Competition of the Technical University of Liberec under the project No. SGS-2023-5329 “Kinetics of diffusion processes and optimization of heterogeneous diffusion joint formation”, and by the project of the Ministry of Education, Youth, and Sports of the Czech Republic and the European Union—European Structural and Investment Funds in the frame of Operational Programme Research, Development, and Education—project Hybrid Materials for Hierarchical Structures, grant HyHi, Reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000843.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Sun, D.; Li, H. Research Progress on Control Strategy of Intermetallic Compounds in Welding Process of Heterogeneous Materials. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, K.O.; Atieh, A.M. Current Trends in Dissimilar Diffusion Bonding of Titanium Alloys to Stainless Steels, Aluminium and Magnesium. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, C.; Senthilkumar, V.; Sarala, S.; Arivarasan, J. Low Temperature Diffusion Bonding of Ti-6Al-4V and Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 234, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, N.; Khan, T.; Eroğlu, M. Diffusion Bonding of a Microduplex Stainless Steel to Ti–6Al–4V. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Bhanumurthy, K.; GB, K.; Krishnan, J.; Chatterjee, S. Strength of the Diffusion Bonded Joints between CP Ti and 304 Stainless Steel Processed below and above β-Transus. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Negemiya, A.; Selvarajan, R.; Sonar, T. Effect of Diffusion Bonding Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy and AISI 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel Joints. Mater. Test. 2023, 65, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigraman, T.; Ravindran, D.; Narayanasamy, R. Effect of Phase Transformation and Intermetallic Compounds on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength Properties of Diffusion-Bonded Joints between Ti–6Al–4V and AISI 304L. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2012, 36, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Keskar, N.A. Solid-State Diffusion Bonding of Pseudo-α-Ti Alloy to Ti-Stabilized Stainless Steel: With and Without Interlayer. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 7527–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, M. Development of Processing Windows for Diffusion Bonding of Ti–6Al–4V Titanium Alloy and 304 Stainless Steel with Silver as Intermediate Layer. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Ghosh, M.; Laik, A.; Bhanumurthy, K.; Kale, G.; Chatterjee, S. Diffusion Bonding of Commercially Pure Titanium to 304 Stainless Steel Using Copper Interlayer. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 407, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S. Interfacial Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Diffusion-Bonded Titanium–Stainless Steel Joints Using a Nickel Interlayer. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 425, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-L.; Sheng, G.-M.; Deng, Y.-Q. Impulse Pressuring Diffusion Bonding of Titanium to 304 Stainless Steel Using Pure Ni Interlayer. Rare Met. 2016, 35, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Sam, S.; Chatterjee, S. Interfacial Reactions and Strength Properties in Dissimilar Titanium Alloy/Ni Alloy/Microduplex Stainless Steel Diffusion Bonded Joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Song, T.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Luo, C.Q.; Simpson, M.D.; Luo, Z. A Review on Diffusion Bonding between Titanium Alloys and Stainless Steels. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8701890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Paidar, M.; Kumar, N.K.; ElDin, H.M.S.; Kannan, S.; Abdullaev, S.; Mehrez, S. Influence of Bonding Time during Diffusion Bonding of Ti–6Al–4V to AISI 321 Stainless Steel on Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties. Vacuum 2024, 222, 113072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, X.; Sun, H.; Song, T.; Mo, D.; Li, X.; Luo, Z. Interfacial Reaction and Microstructure Investigation of TC4/V/Cu/Co/316L Diffusion-Bonded Joints. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 127140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Jiang, X.; Shao, Z.; Fang, Y.; Mo, D.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, M. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Vacuum Diffusion Bonded Joints between Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy and AISI316L Stainless Steel Using Cu/Nb Multi-Interlayer. Vacuum 2017, 145, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, F.; Raza, S.H. Diffusion Bonding Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Nb/Cu/Ni Multi-Interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2012, 68, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Negemiya, A.; Rajakumar, S.; Sonar, T.; Ivanov, M. Influence of Diffusion Bonding Pressure on Microstructural Features and Strength Performance of Dissimilar Ti–6Al–4V Alloy and AISI 304 Steel Joints Developed Using Copper Interlayer. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2023, 145, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Negemiya, A.; Rajakumar, S.; Balasubramanian, V. Diffusion Bonding of a Titanium Alloy to Austenitic Stainless Steel Using Copper as an Interlayer. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, K.O.; Richardson, A.; Khan, T.I.; Shar, M.A. High-Temperature Diffusion Bonding of Ti–6Al–4V and Super-Duplex Stainless Steel Using a Cu Interlayer Embedded with Alumina Nanoparticles. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, C.; Dong, H.; Wu, B.; Ma, Y.; Zou, C.; Yang, Y. Vacuum Diffusion Bonding of TC4 Titanium Alloy to 316L Stainless Steel with AlCoCrCuNi2 High-Entropy Alloy Interlayer. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S. Characterization of Diffusion Bonded Joint between Titanium and 304 Stainless Steel Using a Ni Interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mishra, B. Influence of Interface Microstructure on the Strength of the Transition Joint between Ti-6Al-4V and Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, B.; Gutiérrez, I.; Urcola, J.J. The Use of Kirkendall Effect for Calculating Intrinsic Diffusion Coefficients in a 316L/Ti6242 Diffusion Bonded Couple. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, B.; Gutiérrez, L.; Urcola, J. Interface Microstructures in Diffusion Bonding of Titanium Alloys to Stainless and Low Alloy Steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1993, 9, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovská, Š.; Moravec, J.; Švec, M. Kinetics of Nickel Diffusion into Austenitic Stainless Steels AISI 304 and 316L and Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients. Materials 2023, 16, 6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).