N-Atom Doping of ω–Fe, α–Fe, and γ–Fe Compounds: A First-Principle Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
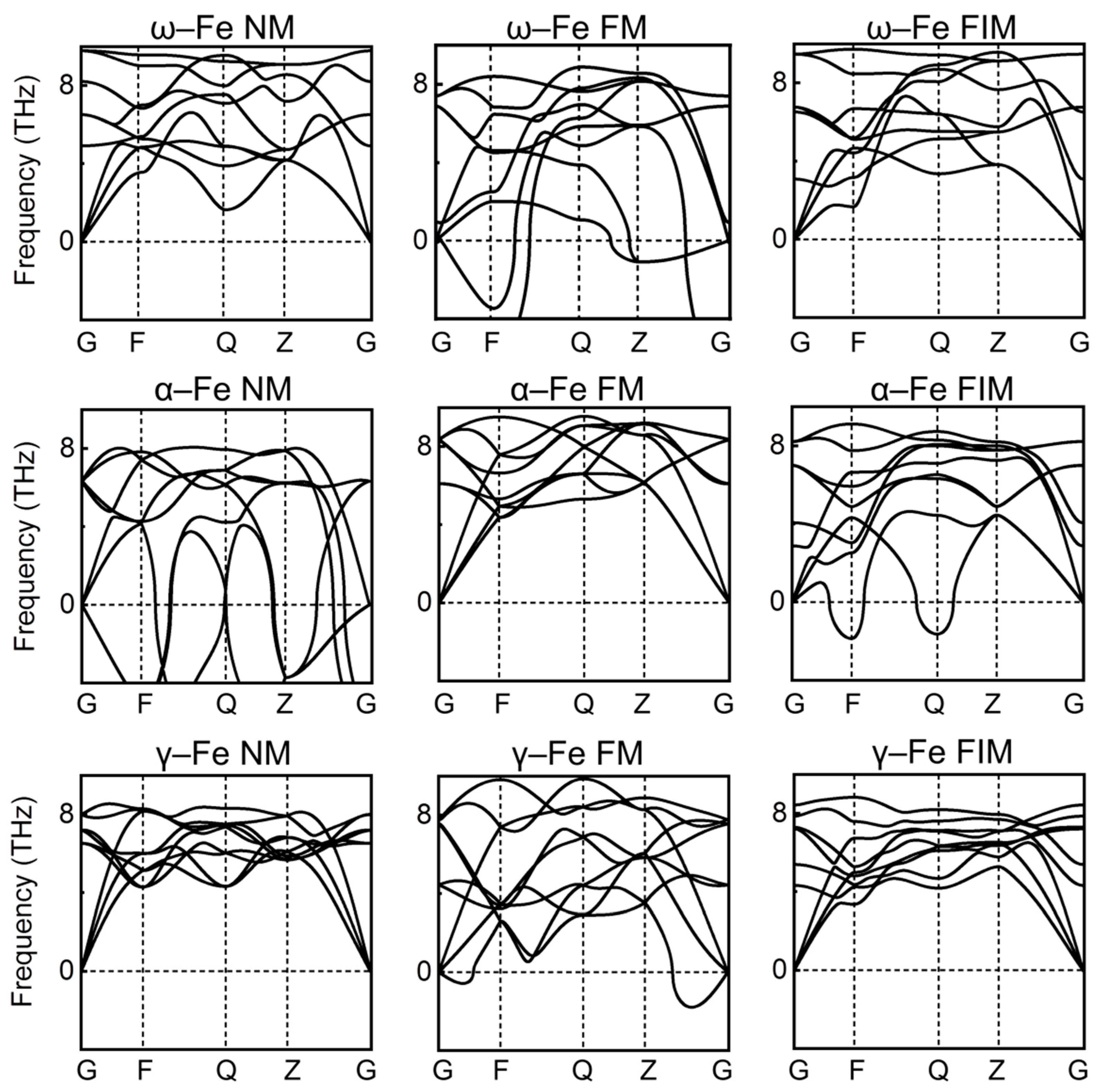
3.1. Pure Fe Phases
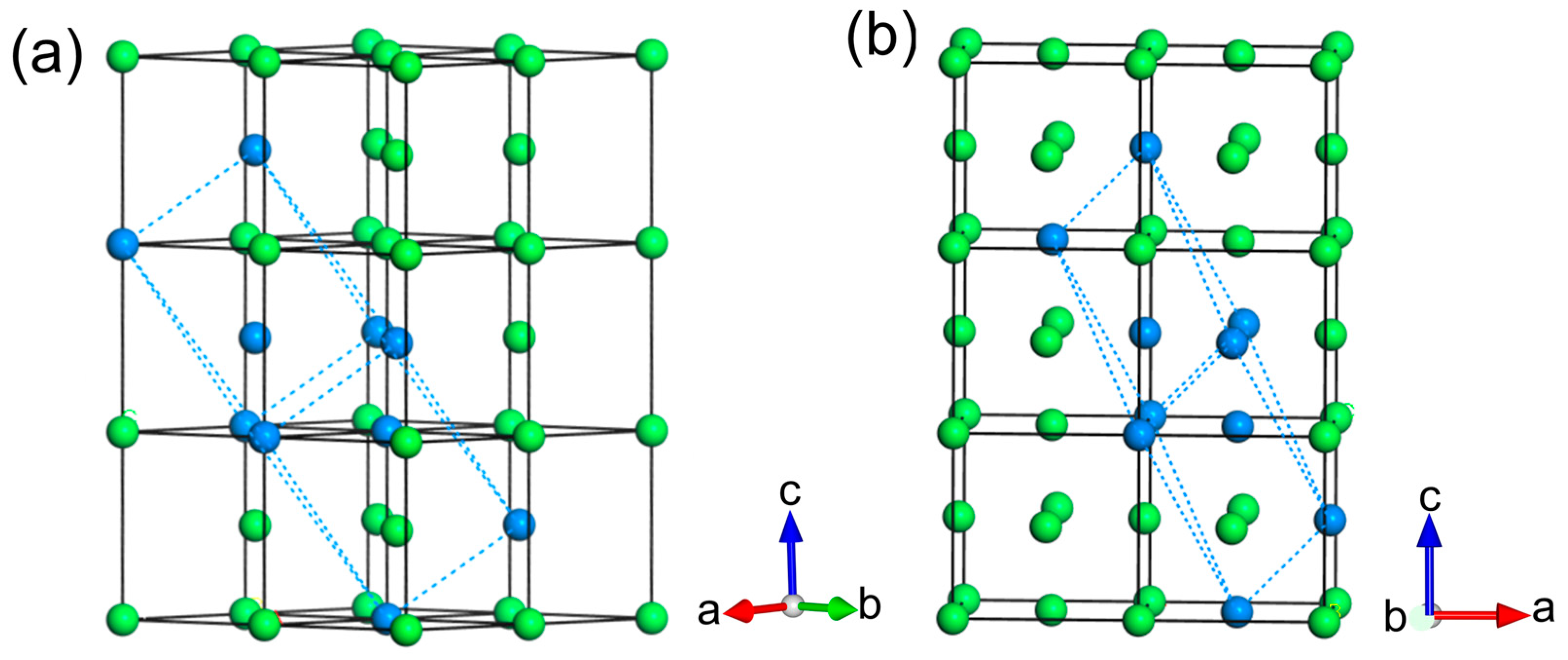
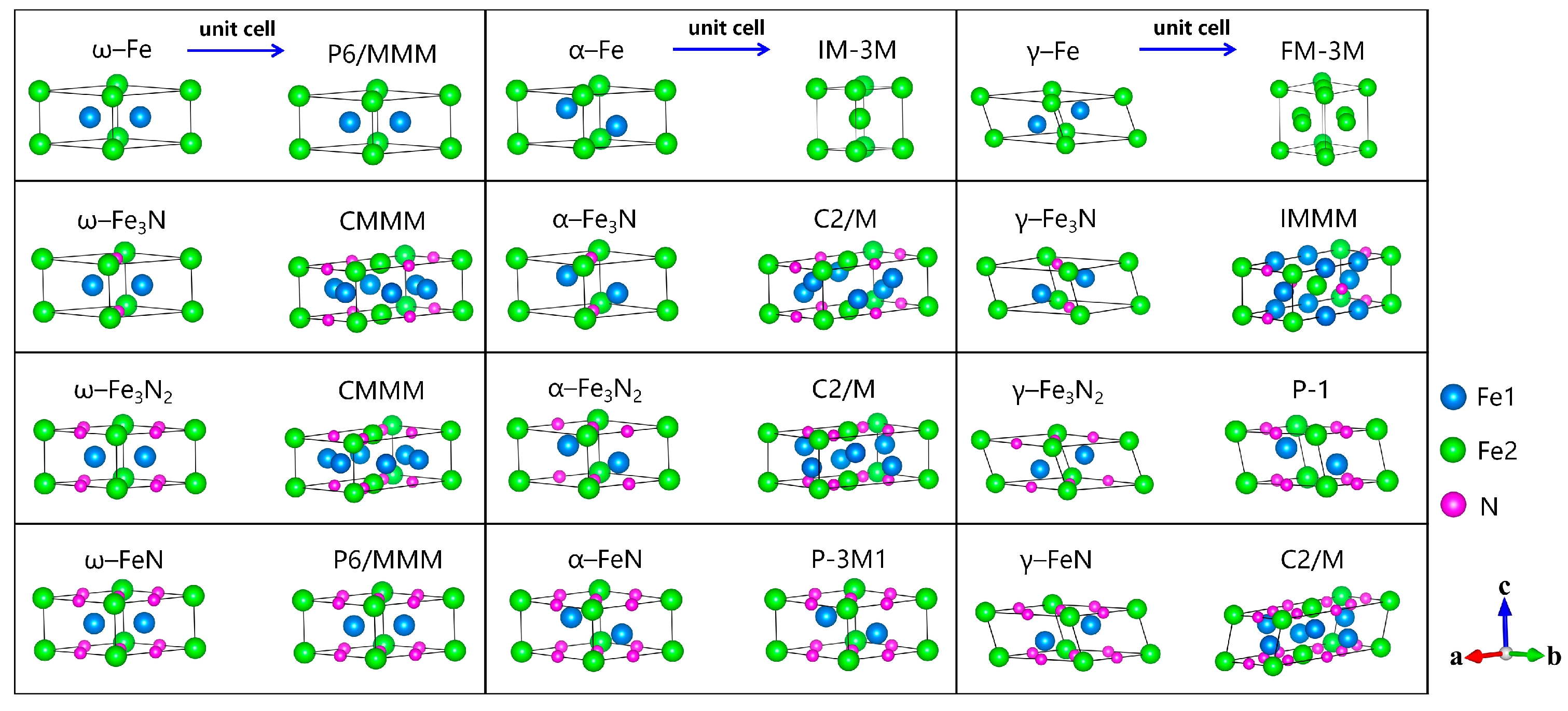
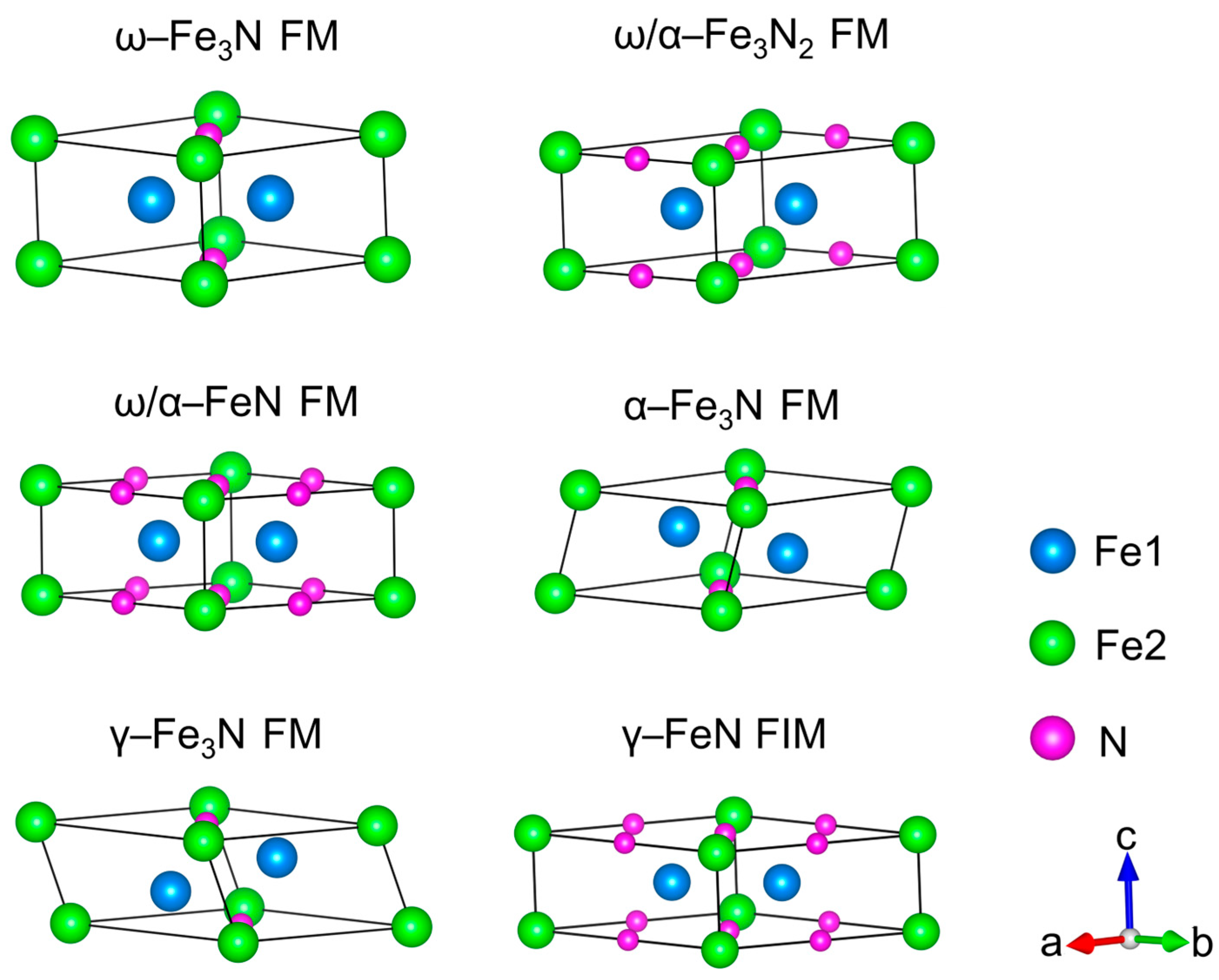
3.2. N-Doping ω–Fe, α–Fe, and γ–Fe Phases
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Byrnes, M.L.G.; Grujicic, M.; Owen, W.S. Nitrogen strengthening of a stable austenitic stainless steel. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, G.; Menzel, J. Nitrogen alloyed steels—A new generation of materials with extraordinary properties. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 1995, 10, 290–302. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, J.W. Overview: High–nitrogen alloying of stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1996, 207, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, H. Manufacture and application of high nitrogen steels. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Bell, T. Corrosion properties of plasma nitride AISI 410 martensitic stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl and 1% HCl aqueous solutions. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2036–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.; Falleiros, N.A.; Tschiptschin, A.P. Corrosion erosion behavior of austenitic and martensitic high nitrogen stainless steels. Wear 2007, 263, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.A.; Alonso, N.; Tschiptschin, A.P. The corrosion resistance of nitrogen bearing martensitic stainless steels. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Oh, C.S.; Kim, S.J.; Takaki, S. Deformation twinning in high–nitrogen austenitic stainless steel. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3649–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.P.; Wang, L.J.; Qin, B.; Liu, C.M.; Subramanian, S.V. Effect of N on microstructure and mechanical properties of 16Cr5Ni1Mo martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onomoto, T.; Terazawa, Y.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S. Effect of grain refinement on tensile properties in Fe–25Cr–1N alloy. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, H.; Kurihana, S. Solution nitriding treatment of Fe–Cr alloys under pressurized nitrogen gas. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Habara, Y.; Kuroda, K. Efforts to save nickel in austenitic stainless steels. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluba, W.J.; Kaluba, T.; Taillard, R. The austenitizing behavior of high–nitrogen martensitic stainless steels. Scr. Mater. 1999, 41, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneteau, A.; Aeby–Gautier, E.; Geandier, G.; Weisbecker, P.; Rediaimia, A.; Appolaire, B. Tempering of a martensitic stainless steel: Investigation by in situ synchrotron X–ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behjati, P.; Kermanpur, A.; Najafizadeh, A.; Baghbadorani, H.S.; Karjalainen, L.P.; Jung, J.G.; Lee, Y.K. Effect of nitrogen content on grain refinement and mechanical properties of a reversion–treated Ni–free 18Cr–12Mn austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45A, 6317–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, P.; Ye, Z.F.; Li, D.Z. Effect of N on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high Si martensitic heat–resistance steels. Acta Metall. Sin. 2014, 27, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.H.; Ohnuma, M. ω–Fe particle size and distribution in high–nitrogen martensitic steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 5339–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Shu, D.; Zhu, G.; Wang, D.; Sun, B. Mechanical instability and tensile properties of tizrhfnbta high entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mater. 2020, 201, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikka, S.K.; Vohra, Y.K.; Chidambaram, R. Omega phase in materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1982, 27, 245–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinkle, D.R.; Hennig, R.G.; Srinivasan, S.G.; Hatch, D.M.; Jones, M.D.; Stokes, H.T.; Albers, R.C.; Wilkins, J.W. New mechanism for the α to ω martensitic transformation in pure titanium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 025701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Tanaka, I. Evolution of crystal structures in metallic elements. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 184104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.H. Review on ω phase in body–centered cubic metals and alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 2014, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.R.; Dolin, P.; Van der Ven, A. Crystallography, thermodynamics and phase transitions in refractory binary alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 200, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ping, D.H.; Zhao, X. Twin structure of the lath martensite in low carbon steel. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2016, 26, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.W.; Ping, D.H.; Ohmura, T.; Ohnuma, M. Electron diffraction analysis of quenched fe–c martensite. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.H.; Geng, W.T. A popular metastable omega phase in body–centered cubic steels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.H. Understanding solid–solid (fcc → ω + bcc) transition at atomic scale. Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 28, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cui, J.; Rong, L. In situ heating TEM observations of a novel microstructure evolution in a low carbon martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 165, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Hu, G.J.; Jing, B.; Zhao, Q.; Su, S.L.; He, M.Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.D.; Ping, D.H. Dependence of {112}<111>–type twin density on carbon content in Fe–C martensite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.H.; Singh, A.; Guo, S.Q.; Ohmura, T.; Ohnuma, M.; Abe, T.; Onodera, H. A simple method for observing ω–Fe electron diffraction spots from < 112> α–Fe directions of quenched Fe–C twinned martensite. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Silcock, J.M. An X–ray examination of the omegaphase in TiV, TiMo and TiCr alloys. Acta Metall. 1958, 6, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, S.L. Omega phase in a Zr–25 at.% Ti alloy. Acta Metall. 1969, 17, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fontaine, D. Mechanical instabilities in the B.C.C. lattice and the beta to omega phase transformation. Acta Metall. 1970, 18, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tanaka, I. Stability of the ω structure of transition elements. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 094108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tanaka, I. ω structure in steel: A first-principles study. J. Alloy. Comp. 2016, 684, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.A.S.; Pallaspuro, S.; Cao, W.; Somani, M.; Alatalo, M.; Huttula, M.; Kömi, J. Density functional theory study of ω phase in steel with varied alloying elements. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2020, 120, e26223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, F.; Hendry, A. Microstructure and mechanical–behavior of nitrogen alloyed martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1995, 11, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriljuk, V.G.; Berns, H. High Nitrogen Steels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Toro, A.; Misiolek, W.Z.; Tschiptschin, A.P. Correlations between microstructure and surface properties in a high nitrogen martensitic stainless steel. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 3363–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, J.; De Cooman, B.C. Quenching and partitioning (Q&P) processing of martensitic stainless steels. Metal Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 946–967. [Google Scholar]
- Böttger, A.; Van Genderen, M.J.; Sijbrandij, S.J.; Mittemeijer, E.J.; Smith, G.D.W. Atom–probe and X–ray diffraction analysis of the composition and structure of precipitates formed on tempering of ternary iron–carbon–nitrogen martensites. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.H.; Xiang, H.P. Simulated electron diffraction patterns of ω–Fe in Fe–C martensite. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 045105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, L.; Nie, X.; Wang, D. Electronic structure of fcc iron in metastable magnetic phases. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1997, 167, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmuller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total–energy calculations using a plane–wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented–wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented–wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methfessel, M.; Paxton, A.T. High–precision sampling for brillouin–zone integration in metals. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 40, 3616–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, P.; Lewandowski, M. Iron nitride thin films: Growth, structure, and properties. Crys. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 4618–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Tanaka, I. First principles phonon calculations in materials science. Scr. Mater. 2015, 108, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Oba, F.; Tanaka, I. First–principles calculations of the ferroelastic transition between rutile–type and CaCl2–type SiO2 at high pressures. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 134106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerny, M.; Pokluda, J.; Sob, M.; Friák, M.; Sandera, P. Ab initio calculations of elastic and magnetic properties of Fe, Co, Ni, and Cr crystals under isotropic deformation. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 035116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbach, M.; Nicholson, D.M.; Rusanu, A.; Brown, G. First principles calculation of finite temperature magnetism in Fe and Fe3C. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07E138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulairol, R.; Fu, C.C.; Barreteau, C. Structure and magnetism of bulk Fe and Cr: From plane waves to LCAO methods. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2010, 22, 295502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, M.A.M.; Hsiao, C.L.; Santos, R.B.; Hultman, L.; Birch, J.; Gueorguiev, G.K. Self-induced core–shell InAlN nanorods: Formation and stability unraveled by ab initio simulations. ACS Nanosci. Au. 2023, 3, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, M.A.M.; Farmer, W.; Hsiao, C.L.; Santos, R.B.; Hultman, L.; Birch, J.; Ankit, K.; Gueorguiev, G.K. Density functional theory-fed phase field model for semiconductor nanostructures: The case of self-induced core–shell InAlN nanorods. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 4717–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
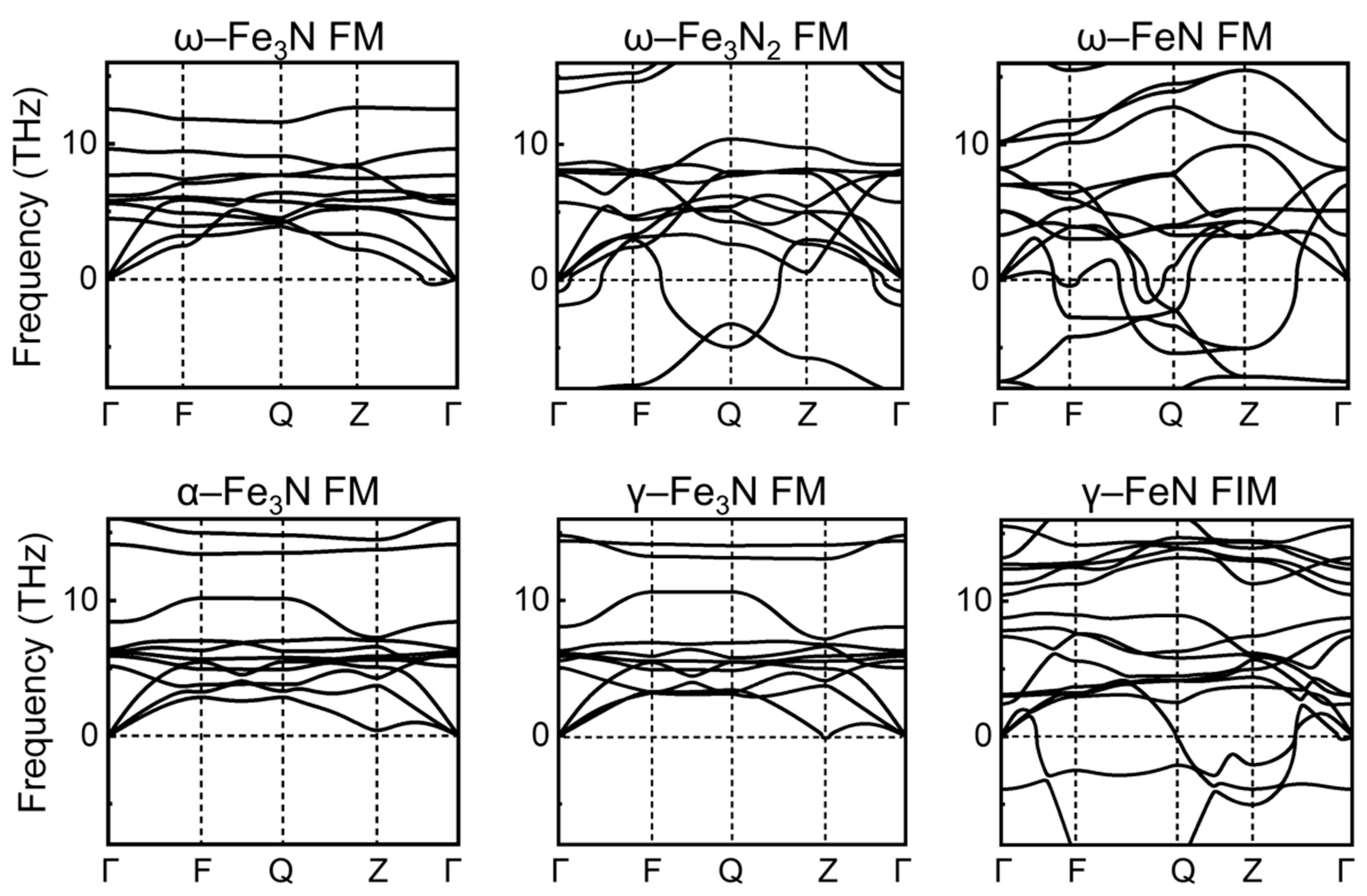
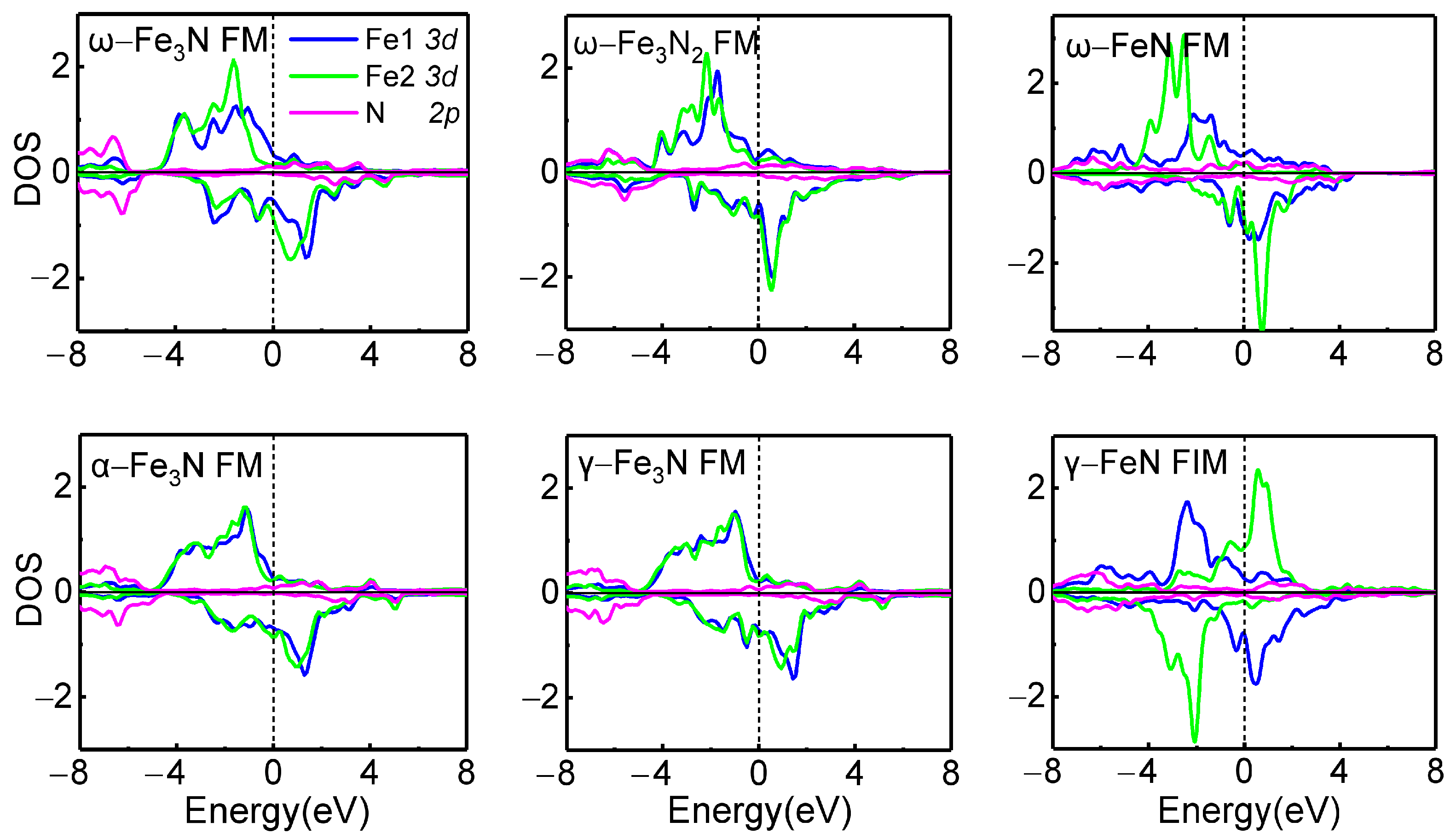
| ω–Fe | α–Fe | γ–Fe | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | |
| ΔE | 762 | 594 | 522 | 1422 | 0 | 531 | 486 | 444 | 369 |
| α | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 107 | 107 | 106 |
| β | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 107 | 107 | 106 |
| γ | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| a | 3.85 | 4.18 | 3.97 | 3.89 | 4.00 | 4.01 | 4.22 | 4.43 | 4.31 |
| b | 3.85 | 4.18 | 3.97 | 3.89 | 4.00 | 4.01 | 4.22 | 4.43 | 4.31 |
| c | 2.42 | 2.37 | 2.40 | 2.38 | 2.45 | 2.40 | 2.43 | 2.58 | 2.41 |
| V | 31.11 | 36.05 | 32.80 | 31.39 | 34.06 | 33.50 | 30.69 | 35.99 | 32.49 |
| µFe1 | – | 2.59 | 1.66 | – | 2.19 | 1.92 | – | 2.60 | 1.57 |
| µFe2 | – | 2.47 | −1.59 | – | 2.19 | −1.95 | – | 2.60 | −1.79 |
| ω–Fe3N | ω–Fe3N2 | ω–FeN | |||||||
| NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | |
| ΔHf | 0.95 | 0.18 | 0.53 | 2.00 | 1.20 | 1.27 | 5.69 | 4.47 | 4.73 |
| α | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| γ | 125 | 124 | 127 | 127 | 127 | 128 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| a | 4.14 | 4.25 | 4.39 | 5.02 | 5.08 | 5.10 | 4.71 | 4.94 | 4.95 |
| b | 4.14 | 4.25 | 4.39 | 4.18 | 4.17 | 4.17 | 4.71 | 4.94 | 4.95 |
| c | 2.82 | 2.76 | 2.69 | 2.64 | 2.82 | 2.84 | 2.73 | 2.66 | 2.61 |
| V | 39.47 | 41.48 | 41.70 | 44.49 | 47.56 | 47.94 | 52.75 | 56.35 | 55.56 |
| µFe1 | – | 1.95 | 1.94 | – | 1.90 | 2.19 | – | 1.74 | 0.88 |
| µFe2 | – | 2.38 | −2.37 | – | 2.35 | −2.39 | – | 3.09 | −3.11 |
| µN | – | −0.04 | −0.01 | – | 0.03 | 0.04 | – | 0.05 | −0.02 |
| α–Fe3N | α–Fe3N2 | α–FeN | |||||||
| NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | |
| ΔHf | 0.74 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 2.00 | 1.20 | 1.27 | 5.69 | 4.47 | 4.68 |
| α | 105 | 102 | 103 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β | 105 | 103 | 103 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| γ | 48 | 50 | 50 | 127 | 127 | 128 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| a | 4.51 | 4.48 | 4.48 | 4.18 | 4.17 | 4.17 | 4.71 | 4.94 | 4.92 |
| b | 4.51 | 4.48 | 4.48 | 5.02 | 5.08 | 5.10 | 4.71 | 4.94 | 4.92 |
| c | 2.54 | 2.67 | 2.67 | 2.64 | 2.82 | 2.84 | 2.74 | 2.66 | 2.71 |
| V | 37.19 | 40.19 | 40.19 | 44.49 | 47.56 | 47.94 | 52.75 | 56.34 | 57.00 |
| µFe1 | – | 2.05 | 2.05 | – | 1.90 | 2.19 | – | 1.74 | 2.01 |
| µFe2 | – | 2.08 | 2.08 | – | 2.35 | −2.39 | – | 3.09 | −3.07 |
| µN | – | −0.05 | −0.05 | – | 0.03 | 0.04 | – | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| γ–Fe3N | γ–Fe3N2 | γ–FeN | |||||||
| NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | NM | FM | FIM | |
| ΔHf | 0.65 | −0.04 | 0.24 | – | – | – | 4.71 | – | 4.04 |
| α | 106 | 107 | 106 | – | – | – | 90 | – | 90 |
| β | 106 | 107 | 106 | – | – | – | 90 | – | 90 |
| γ | 48 | 48 | 47 | – | – | – | 40 | – | 41 |
| a | 4.56 | 4.60 | 4.66 | – | – | – | 5.50 | – | 5.57 |
| b | 4.56 | 4.60 | 4.66 | – | – | – | 5.50 | – | 5.57 |
| c | 2.55 | 2.68 | 2.65 | – | – | – | 2.64 | – | 2.70 |
| V | 37.45 | 40.43 | 40.41 | – | – | – | 51.82 | – | 55.24 |
| µFe1 | – | 2.11 | 2.04 | – | – | – | – | – | 2.21 |
| µFe2 | – | 1.99 | −2.03 | – | – | – | – | – | −2.51 |
| µN | – | −0.05 | −0.003 | – | – | – | – | – | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Xiang, H.; Xu, L.; Qu, S.; Feng, A.; Li, N.; Ping, D. N-Atom Doping of ω–Fe, α–Fe, and γ–Fe Compounds: A First-Principle Study. Metals 2025, 15, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020098
Tang J, Xiang H, Xu L, Qu S, Feng A, Li N, Ping D. N-Atom Doping of ω–Fe, α–Fe, and γ–Fe Compounds: A First-Principle Study. Metals. 2025; 15(2):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020098
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jing, Hongping Xiang, Lin Xu, Shoujiang Qu, Aihan Feng, Na Li, and Dehai Ping. 2025. "N-Atom Doping of ω–Fe, α–Fe, and γ–Fe Compounds: A First-Principle Study" Metals 15, no. 2: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020098
APA StyleTang, J., Xiang, H., Xu, L., Qu, S., Feng, A., Li, N., & Ping, D. (2025). N-Atom Doping of ω–Fe, α–Fe, and γ–Fe Compounds: A First-Principle Study. Metals, 15(2), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020098








