Effect of Laser Welding on Performance of the B1500HS/340LA High-Strength Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
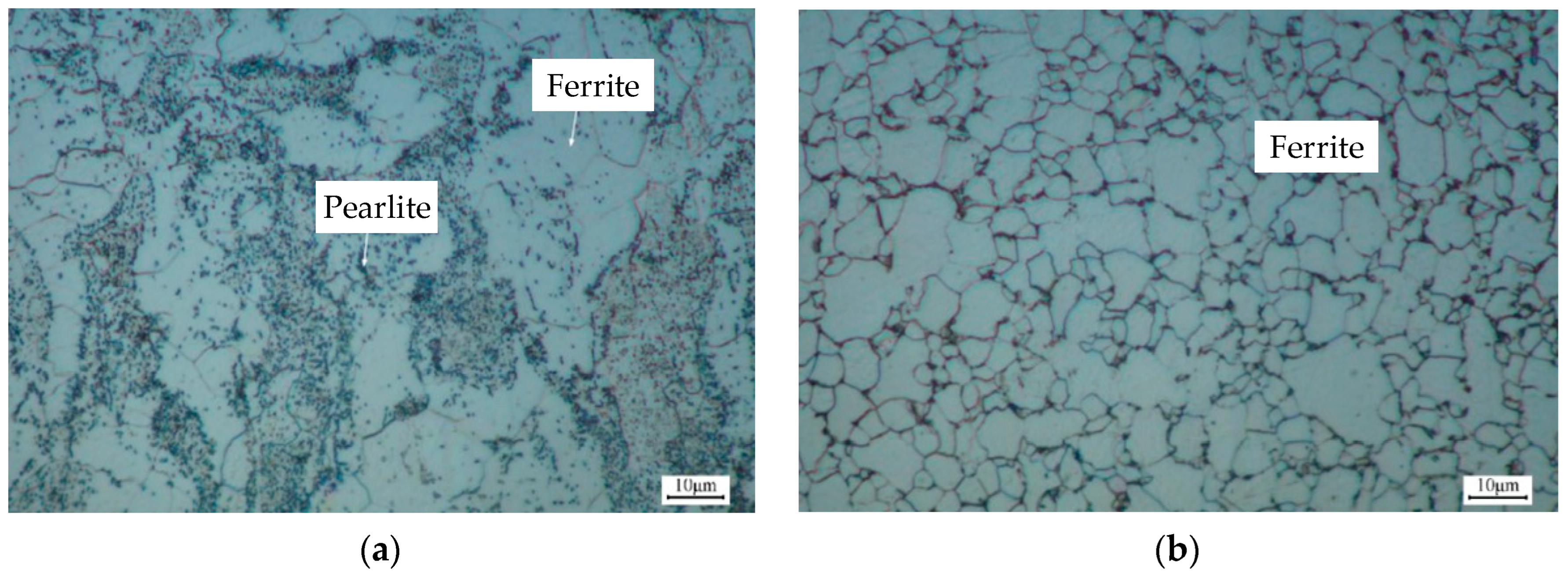
2.1. Base Materials
2.2. Laser Welding Experiments
2.3. Microstructure and Microhardness Testing
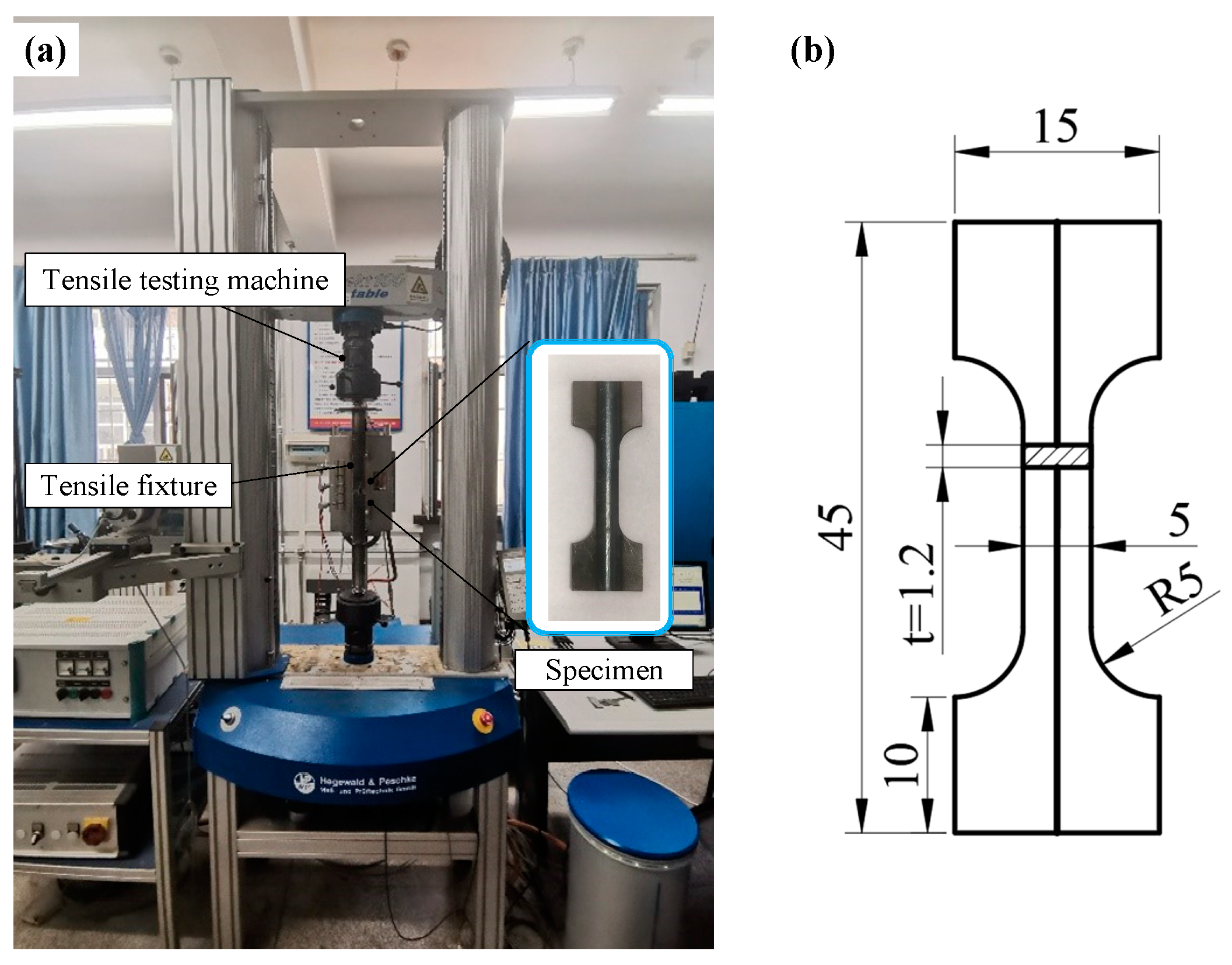
2.4. Mechanical Properties Testing
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
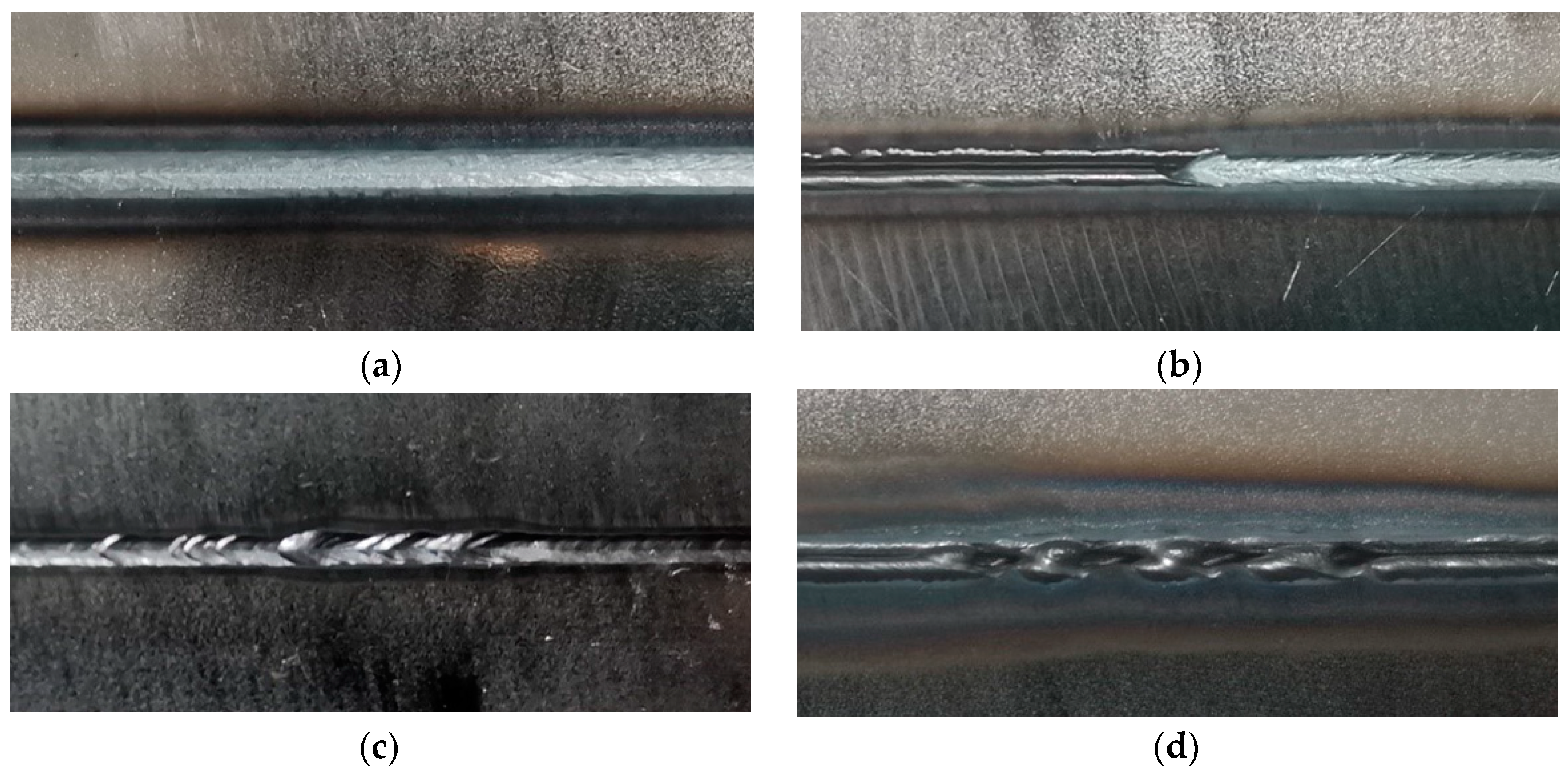
3.1. Macroscopic Weld Quality of TWBs
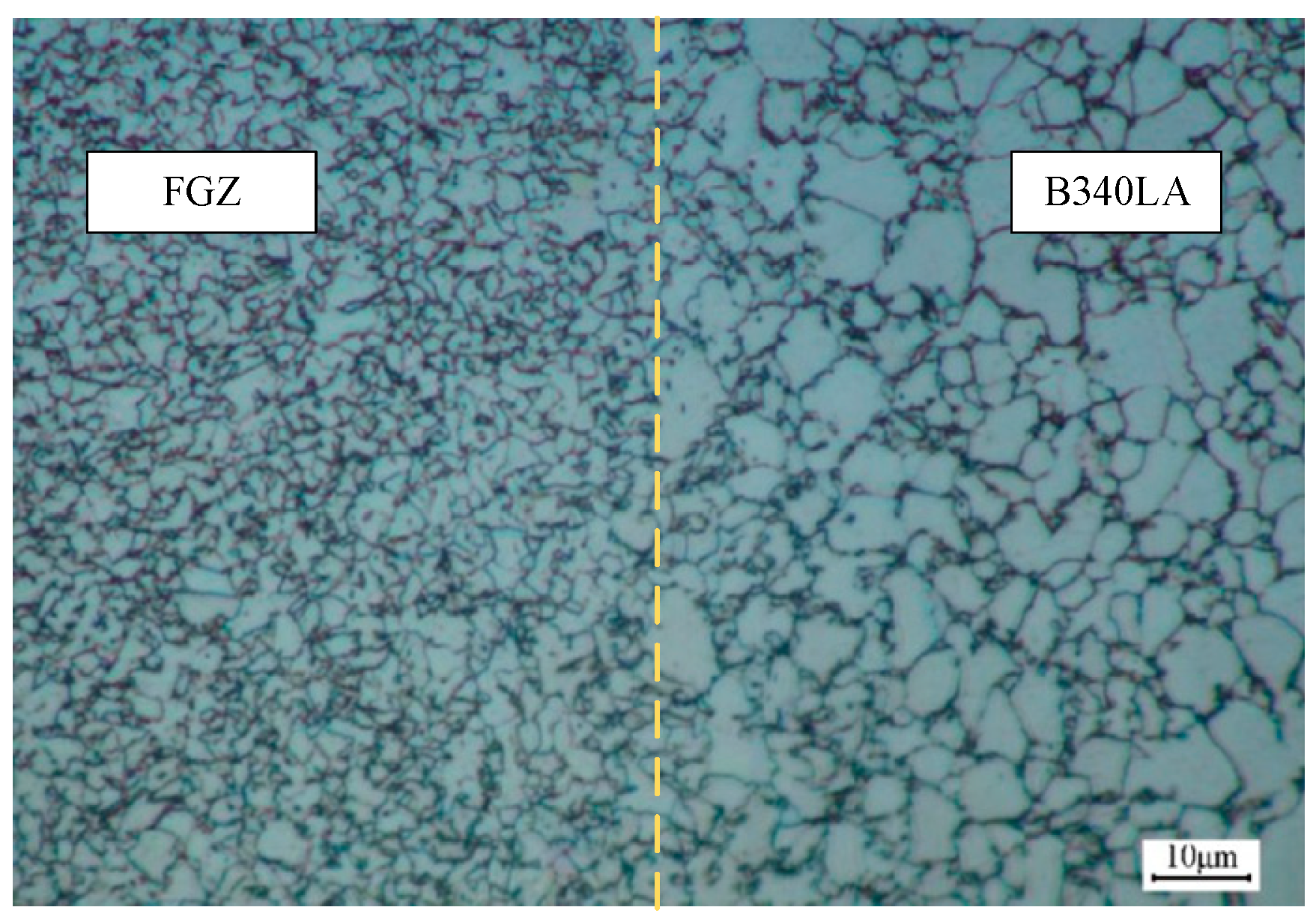
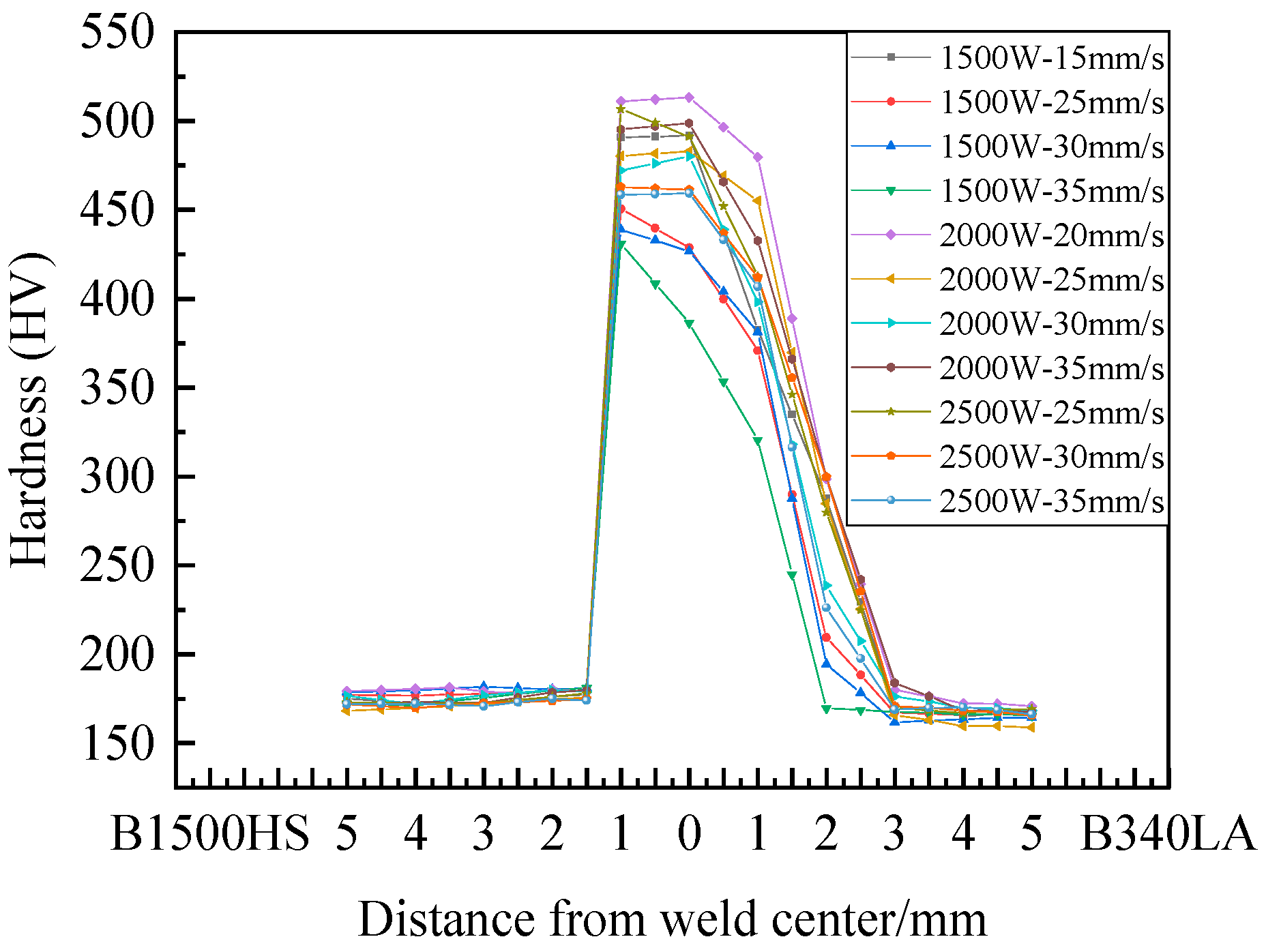
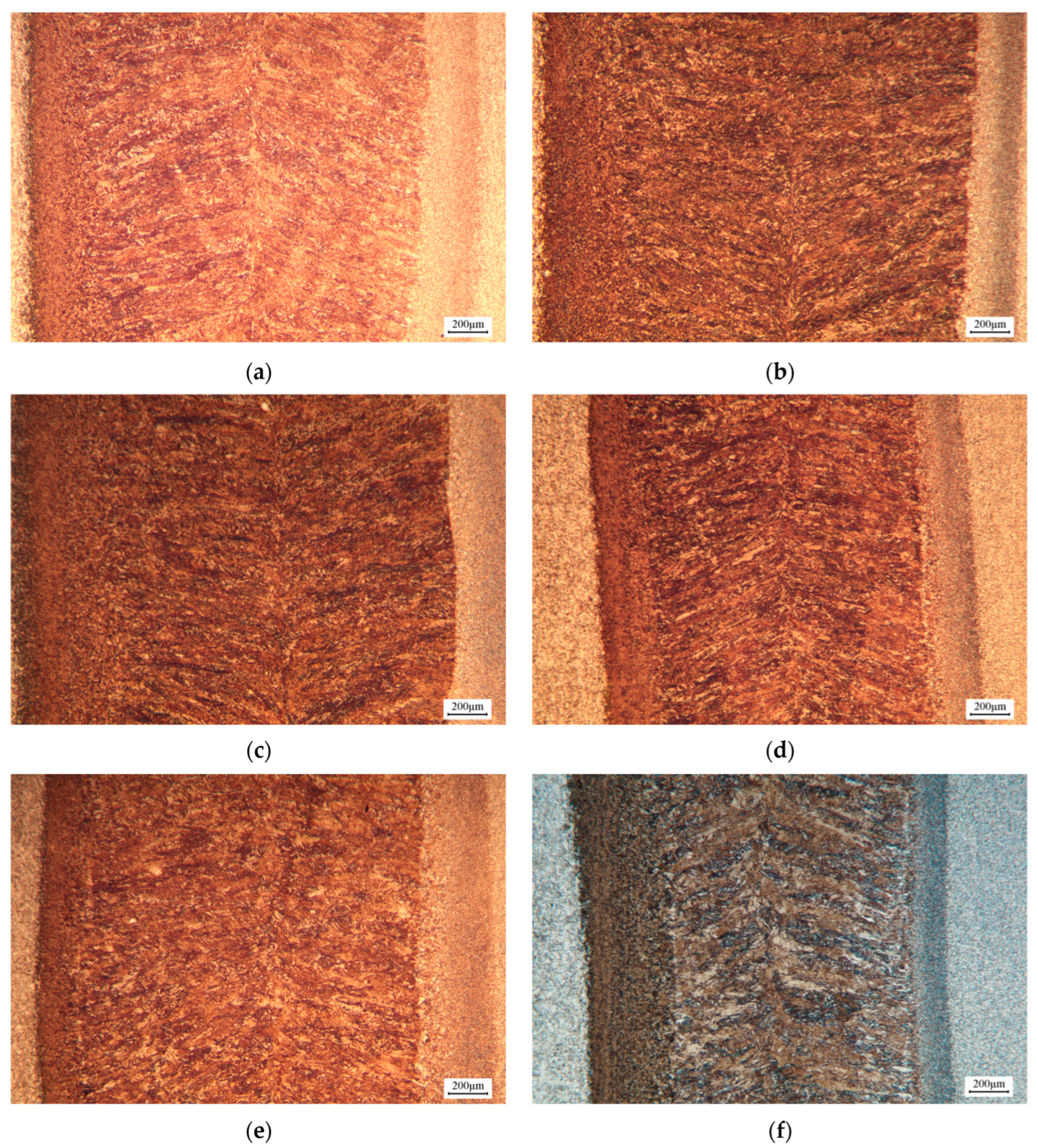
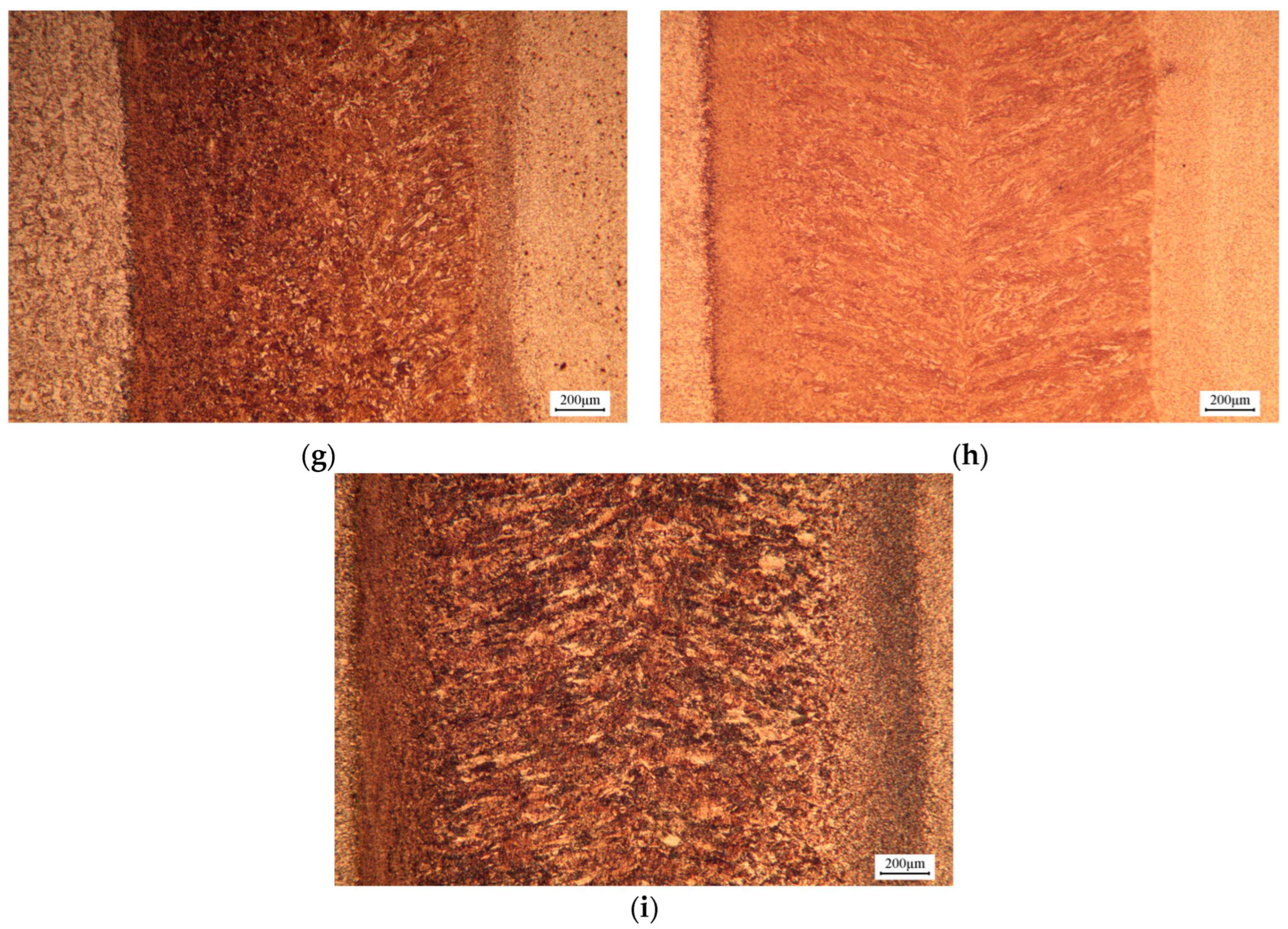
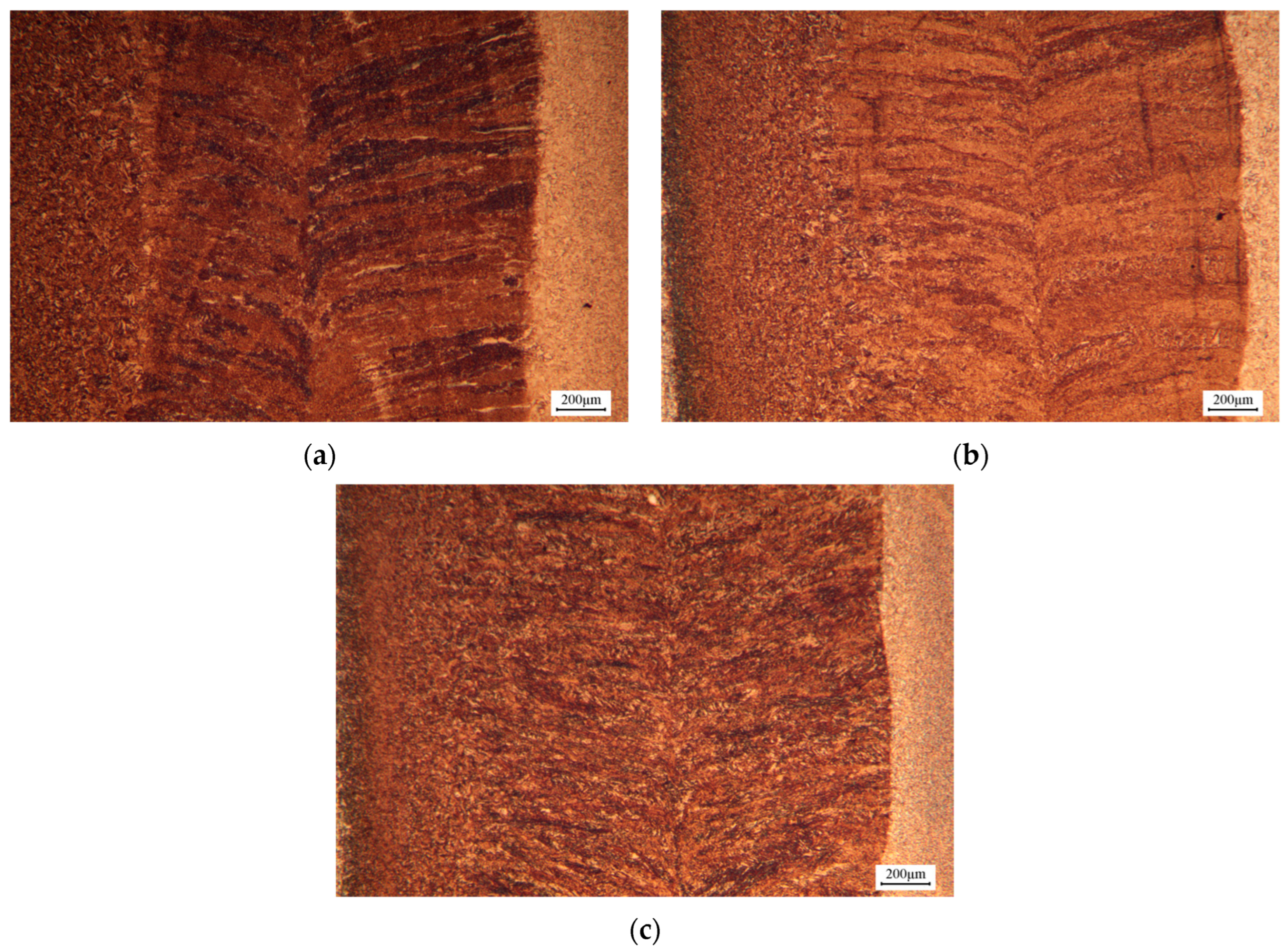
3.2. Microstructure and Hardness
3.3. Effect of Different Laser Welding Parameters on Microstructure and Hardness
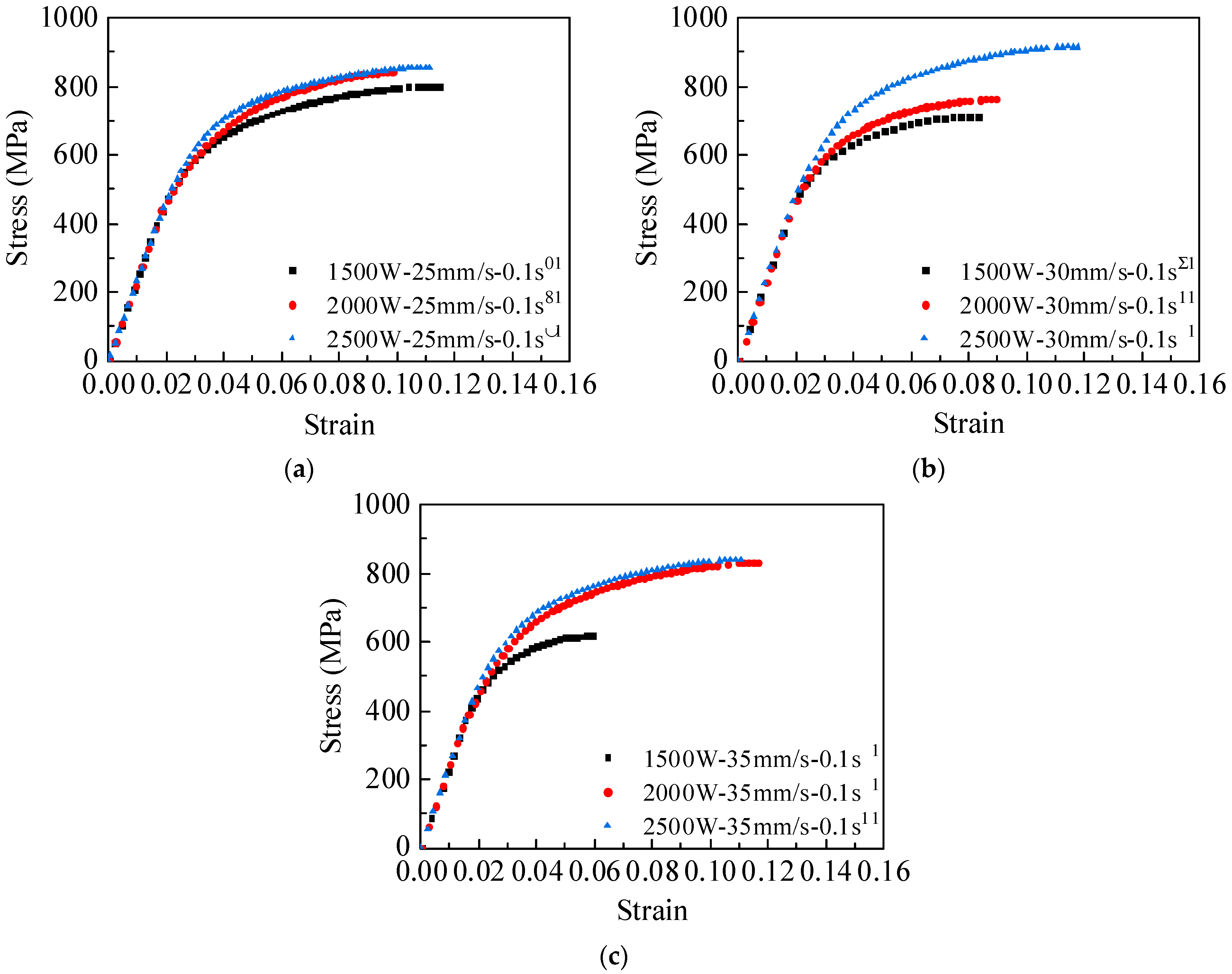
3.4. Effect of Different Welding Process Parameters on Mechanical Properties
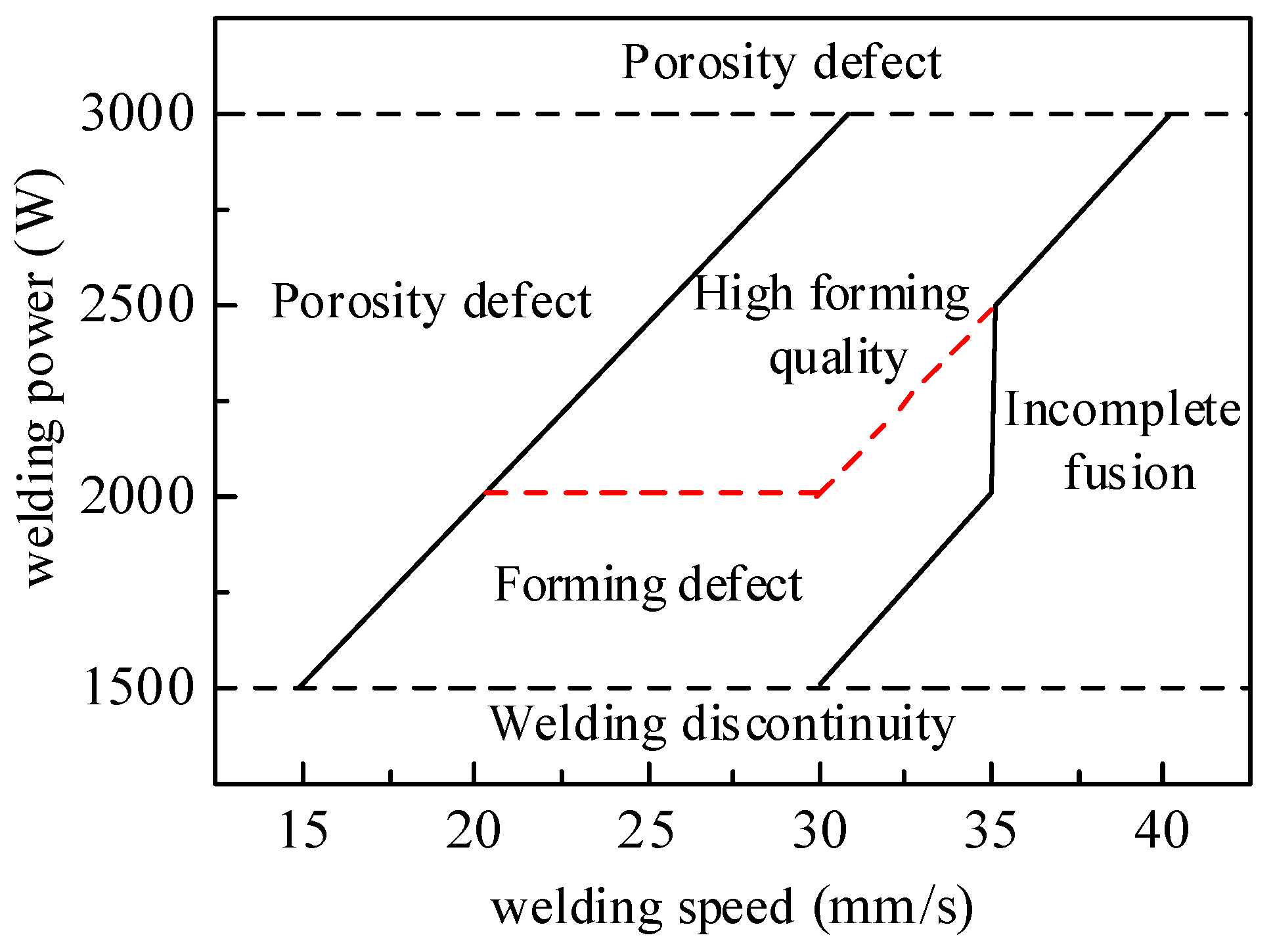
3.5. Optimal Welding Parameter Range for High-Quality Welds
4. Forming Quality Evaluation of TWBs
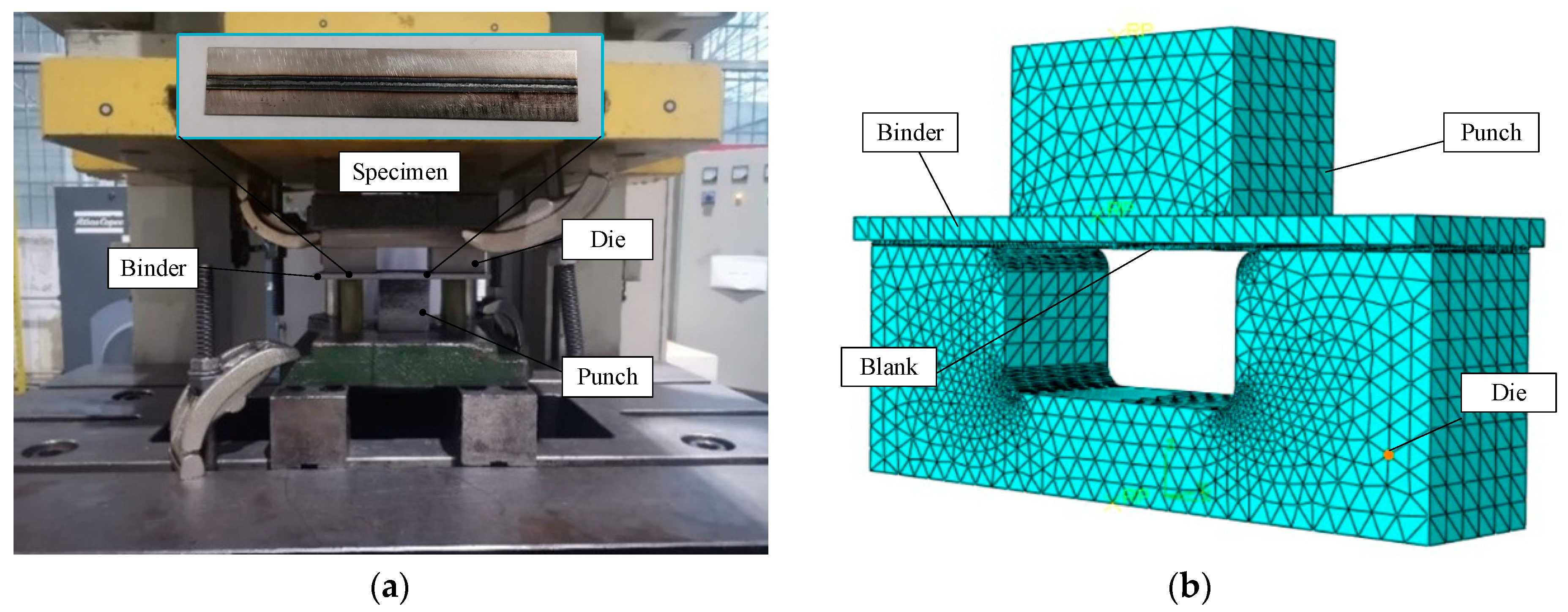
4.1. Bend-Forming Tests and Finite Element Modeling
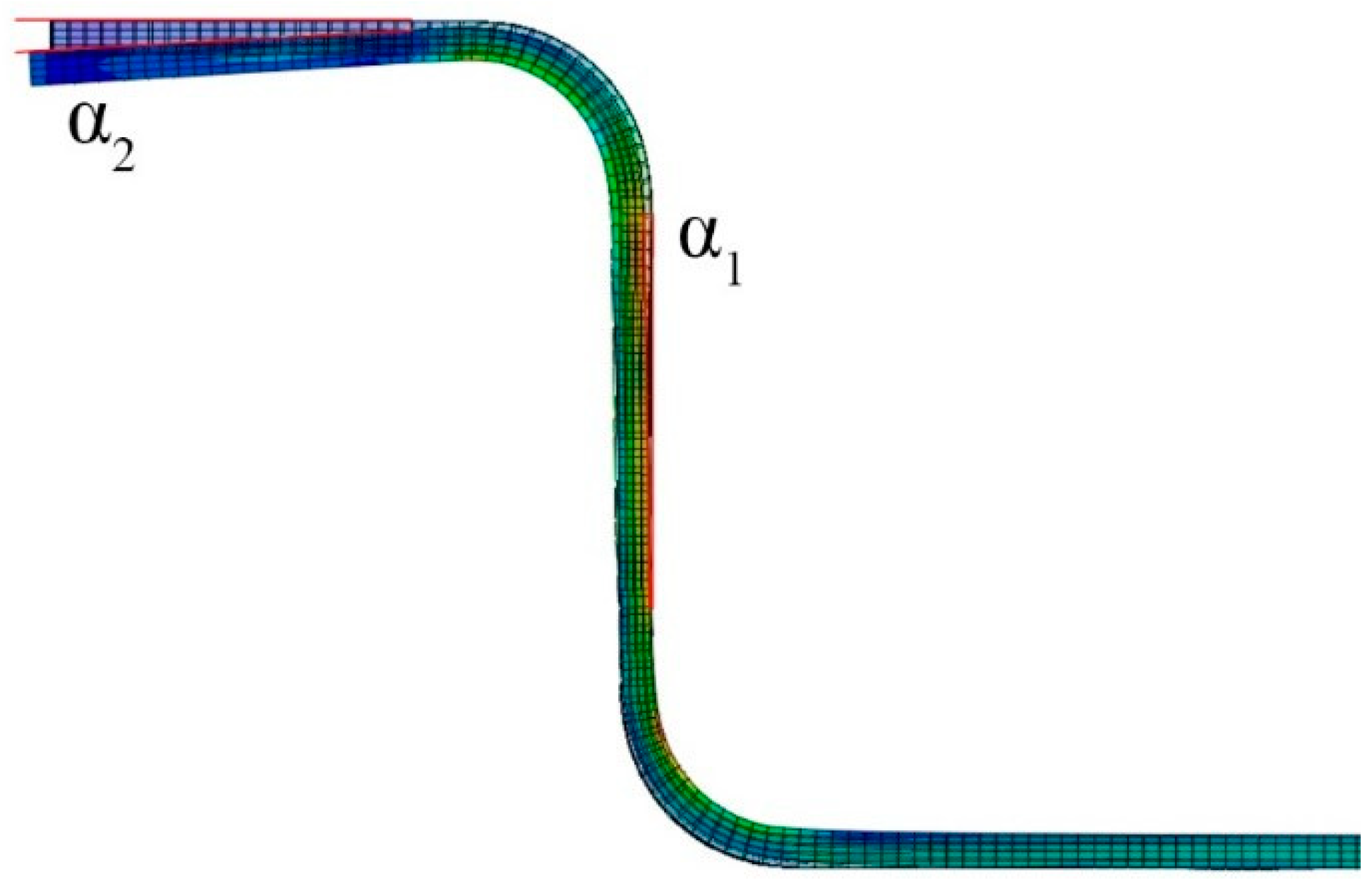
4.2. Results of Bending Tests and Finite Element Analysis
5. Conclusions
- At a constant welding speed, increasing the welding power expanded the widths of the FZ and HAZ, resulting in a more uniform microstructural distribution and an increase in hardness.
- The effect of welding speed on the quality of high-strength steel TWBs was less pronounced than that of welding power; however, an unsuitable welding speed often caused defects such as porosity and discontinuities in the weld seam.
- With laser welding parameters of 2500 W-30 mm/s, the weld joint exhibited an elongation of 12% and an ultimate strength of 915 MPa, demonstrating superior mechanical properties compared to other parameter combinations.
- With laser welding parameters of 2500 W-30 mm/s, the springback angle of the sidewall of the hat-shaped part was 2.71°, while the flange springback angle was 3.98°. The weld joint exhibited high strength, and the stress distribution at the weld-to-base material interface was more uniform compared to other welding conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merklein, M.; Johannes, M.; Lechner, M.; Kuppert, A. A review on tailored blanks-Production, applications and evaluation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, L. Numerical investigation of pore defect formation in the weld during high speed laser welding. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 022066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, L. Numerical analysis of the influence of molten pool instability on the weld formation during the high speed fiber laser welding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 160, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Shahabad, S.I.; Yavuz, M.; Duley, W.W.; Biro, E.; Zhou, Y. Numerical modelling and experimental validation of the effect of laser beam defocusing on process optimization during fiber laser welding of automotive press-hardened steels. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 67, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmpoosh, M.H.; Khan, M.S.; Kalashami, A.G.; Macwan, A.; Biro, E.; Zhou, Y. Effects of laser beam defocusing on high-strain-rate tensile behavior of press-hardened Zn-coated 22MnB5 steel welds. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 141, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orturk, E.; Arikan, H. Investigation of mechanical properties of laser welded dual-phase steels at macro and micro levels. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wan, Z.; Peng, P.; Jia, Q.; Zou, G.; Peng, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fiber laser welded QP980 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 256, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Guo, W.; Peng, P.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, G. Microstructure- and Strain Rate -Dependent Tensile Behavior of Fiber Laser-Welded DP980 Steel Joint. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Qin, Y.Q.; Jiang, W.X. Effect of welding parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded Al-Si coated 22MnB5 hot stamping steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 270, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.S.; Sun, Q.; Nie, X.K.; Wang, X.N.; Chen, X.M. Mirostructure and properties of laser welded joints of dual phase and press-hardened steels. Int. Conf. Technol. Plast. (ICTP) 2017, 207, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, O.; Aydin, H.; Davut, K. Effect of heat input on HAZ softening in fiber laser welding of 22MnB5 steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 164, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Darabi, R.; Ghabussi, A.; Habibi, M.; Foong, L.K. Weld orientation effects on the formability of tailor welded thin steel sheets. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 149, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, S.; Knysh, P.; Korkolis, Y.P. Experimental investigation of the mechanical response of laser-welded dissimilar blanks from advanced- and ultra-high-strength steels. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdarian, R.; Sheikhi, M.; Torkamany, M.J. An investigation on the laser welding process parameter effects on the failure mode of tailor welded blanks during the formability testing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojek, J.; Hyrcza-Michalska, M.; Bokota, A.; Piekarska, W. Determination of mechanical properties of the weld zone in tailor-welded blanks. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2012, 12, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y. Development of Precise Spring-back Control System of Tailor Welded Blanks Air Bending Process. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 50, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Yamagishi, D.; Igi, S.; Ikeda, R. Development of double-sided friction stir welding of advanced high strength steel sheets. Weld. World. 2023, 67, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadian, P.; O’Keeffe, C.; Butcher, C.; Worswick, M.J. Fracture Response in Hot-Stamped Tailor-Welded Blanks of Ductibor® 500-AS and Usibor® 1500-AS: Experiments and Modelling. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 253, 107864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attique, U.; Butt, S.I.; Mubashar, A.; Ali, L.; Hussain, G. Numerical analysis of stress & strain and thickness variation in single point incremental forming of tailor welded steel blanks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 1791–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.-Q.; Xiang, N.; Wang, H.-R.; Yang, M.-H.; Wang, P.-Y.; Huang, T.; Guo, J.-Q.; Chen, F.-X. Numerical investigation of controllable non-uniform deformation of tailor-welded blanks using heterogeneous pressure-carrying medium. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 186, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Lee, P.-K.; Chiuhuang, C.-K.; Chen, F.-K. A Study on Hot Stamping of Tailor Welded Blanks. J. Chin. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2022, 43, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Luo, Z.; Ao, S.S.; Cai, Y.C. Effect of Laser Welding Parameters on Weld Bowing Distortion of Thin Plates. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2018, 37, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Tang, J.J.; Sun, Z.; Sui, Y.; Han, X. Irreversible hydrogen embrittlement study of B1500HS high strength boron steel. Mater. Des. 2021, 199, 109404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, G.; Huang, L.; Zheng, W.; Xie, H. Experimental verification of tailor welded joining partners for hot stamping and analytical modeling of TWBs rheological constitutive in austenitic state. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 585, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1-2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Li, M.; Yao, D.; Guan, Y.; Duan, Y.; Yang, L. Effect of Welding Speed and Post Quenching on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded B1500HS Joints. Materials 2020, 13, 4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.P.; Jiang, R.; He, L.F.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.Z. Influence of Deformation Degree and Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Phase Transformation Temperature of B1500HS Steel. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. Lett. 2018, 31, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wan, Z.; Jia, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Tan, C.; Peng, P. Laser weldability of TWIP980 with DP980/B1500HS/QP980 steels: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 124, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Paes, L.E.; Pereira, M.; Pinto Pereira, A.d.S.; Niño Borhóquez, C.E.; Weingaertner, W.L. Power and welding speed influence on bead quality for overlapped joint laser welding. J. Laser Appl. 2019, 31, 022403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| C | Si | Mn | Al | B | S | P | Cr | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.23 | 0.25 | 1.35 | 0.046 | 0.0026 | 0.002 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.016 | Bal |
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.072 | 0.036 | 0.78 | 0.023 | 0.0115 | 0.048 | Bal |
| Test Num. | Laser Power/(W) | Welding Speed/(mm/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 15 |
| 2 | 1500 | 25 |
| 3 | 1500 | 30 |
| 4 | 1500 | 35 |
| 5 | 2000 | 20 |
| 6 | 2000 | 25 |
| 7 | 2000 | 30 |
| 8 | 2000 | 35 |
| 9 | 2500 | 25 |
| 10 | 2500 | 30 |
| 11 | 2500 | 35 |
| 12 | 3000 | 30 |
| Test Num. | Laser Power /W | Welding Speed /(mm/s) | Macroscopic Surface Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 15 | complete fusion * |
| 2 | 1500 | 25 | complete fusion |
| 3 | 1500 | 30 | complete fusion |
| 4 | 1500 | 35 | incomplete fusion * |
| 5 | 2000 | 20 | complete fusion |
| 6 | 2000 | 25 | complete fusion |
| 7 | 2000 | 30 | complete fusion |
| 8 | 2000 | 35 | welding discontinuity |
| 9 | 2500 | 25 | complete fusion |
| 10 | 2500 | 30 | complete fusion |
| 11 | 2500 | 35 | complete fusion |
| 12 | 3000 | 30 | porosity defect |
| Young’s Modulus/GPa | B1500HS | B340LA | Weld Seam |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | 212 | 212 | 215 |
| Test Num. | laser Welding Parameters | α1 /° | α2 /° |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 W-25 mm/s | 2.10° | 3.32° |
| 2 | 1500 W-30 mm/s | 1.99° | 3.13° |
| 3 | 1500 W-35 mm/s | 1.82° | 3.02° |
| 4 | 2000 W-25 mm/s | 2.48° | 4.01° |
| 5 | 2000 W-30 mm/s | 2.41° | 3.99° |
| 6 | 2000 W-35 mm/s | 2.36° | 4.01° |
| 7 | 2500 W-25 mm/s | 3.10° | 4.37° |
| 8 | 2500 W-30 mm/s | 2.71° | 3.98° |
| 9 | 2500 W-35 mm/s | 2.98° | 4.12° |
| Test Num. | Laser Power /W | Welding Speed /(mm/s) | Macroscopic Surface Quality | Forming Quality of TWBs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 15 | complete fusion | forming defect * |
| 2 | 1500 | 25 | complete fusion | forming defect |
| 3 | 1500 | 30 | complete fusion | forming defect |
| 4 | 1500 | 35 | incomplete fusion | \ |
| 5 | 2000 | 20 | complete fusion | forming defect |
| 6 | 2000 | 25 | complete fusion | forming defect |
| 7 | 2000 | 30 | complete fusion | good formation * |
| 8 | 2000 | 35 | welding discontinuity | \ |
| 9 | 2500 | 25 | complete fusion | forming defect |
| 10 | 2500 | 30 | complete fusion | good formation |
| 11 | 2500 | 35 | complete fusion | forming defect |
| 12 | 3000 | 30 | porosity defect | \ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Duan, Y.; Hao, S.; Guan, Y. Effect of Laser Welding on Performance of the B1500HS/340LA High-Strength Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040393
Wang H, Duan Y, Hao S, Guan Y. Effect of Laser Welding on Performance of the B1500HS/340LA High-Strength Steel. Metals. 2025; 15(4):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040393
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Heyuan, Yongchuan Duan, Shijun Hao, and Yingping Guan. 2025. "Effect of Laser Welding on Performance of the B1500HS/340LA High-Strength Steel" Metals 15, no. 4: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040393
APA StyleWang, H., Duan, Y., Hao, S., & Guan, Y. (2025). Effect of Laser Welding on Performance of the B1500HS/340LA High-Strength Steel. Metals, 15(4), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040393





