Influencing Factors and Mechanisms of Zinc Recovery from Electric Arc Furnace Dust via Microwave-Assisted Carbothermic Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
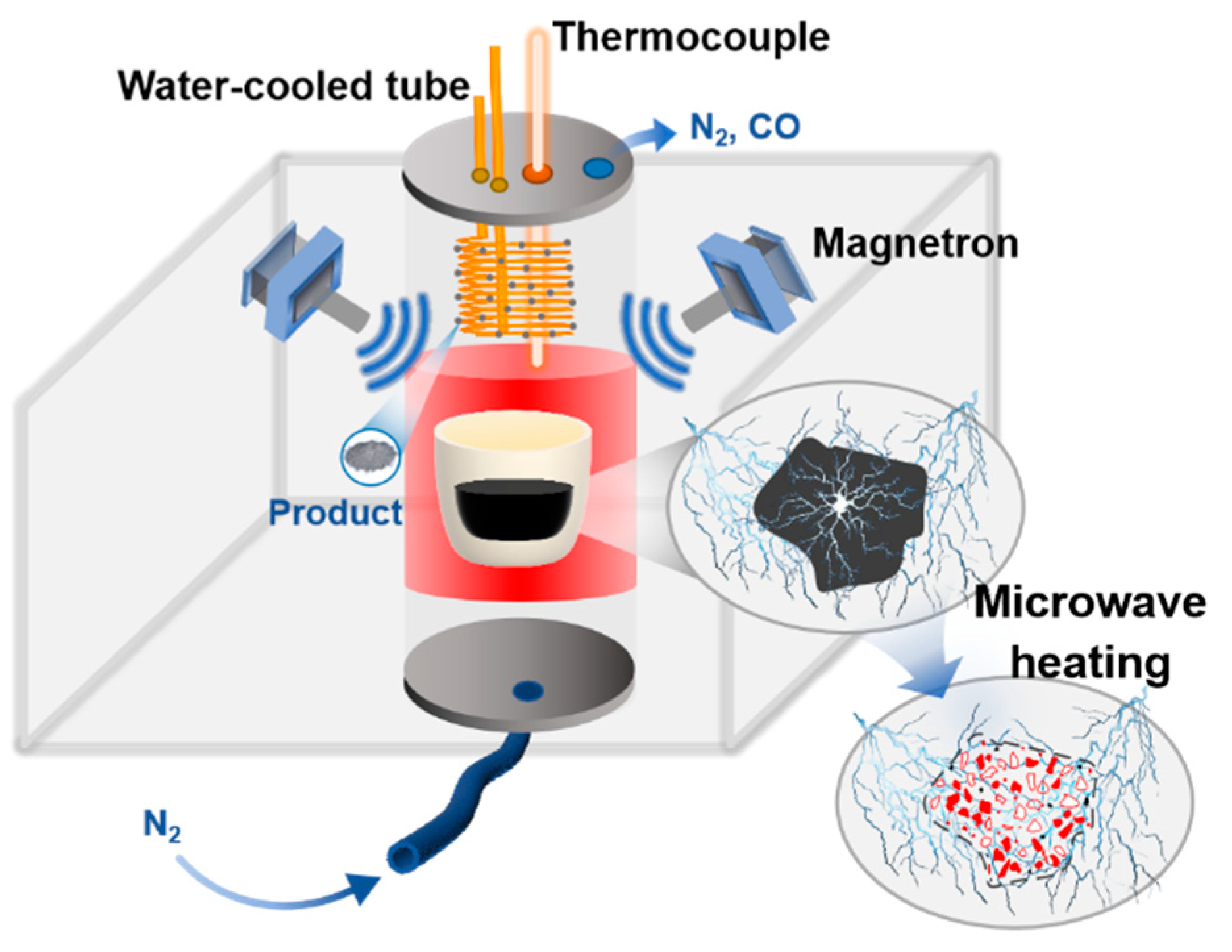
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
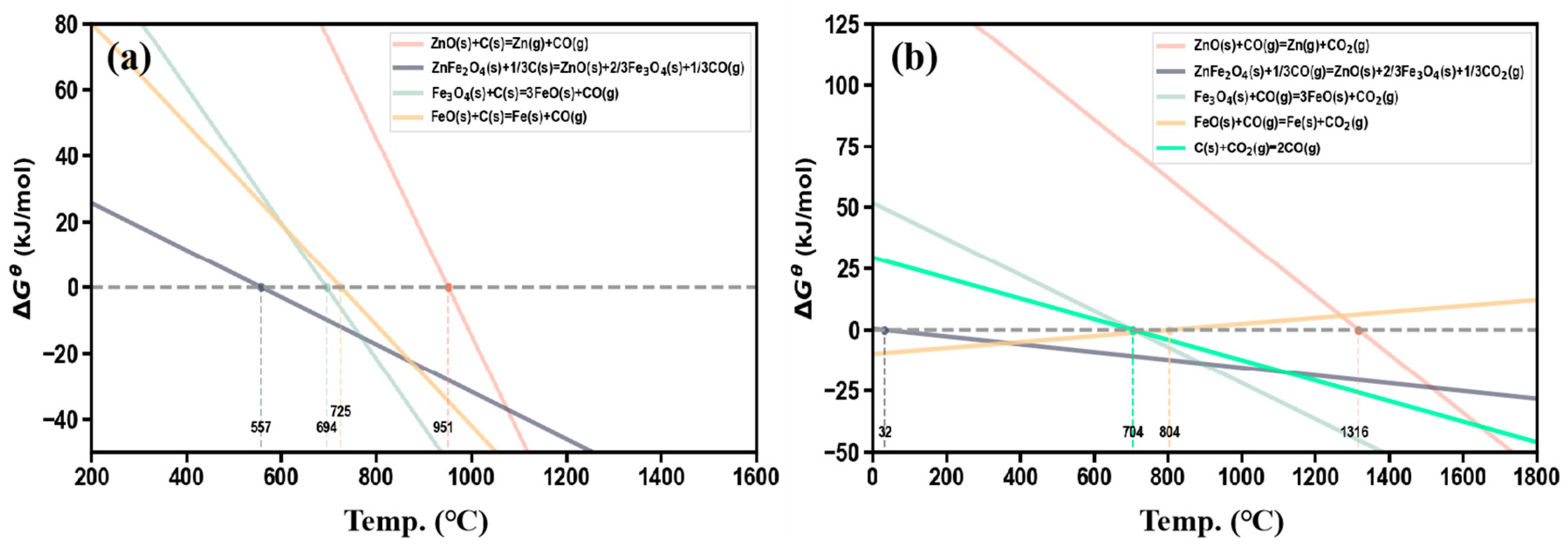
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis
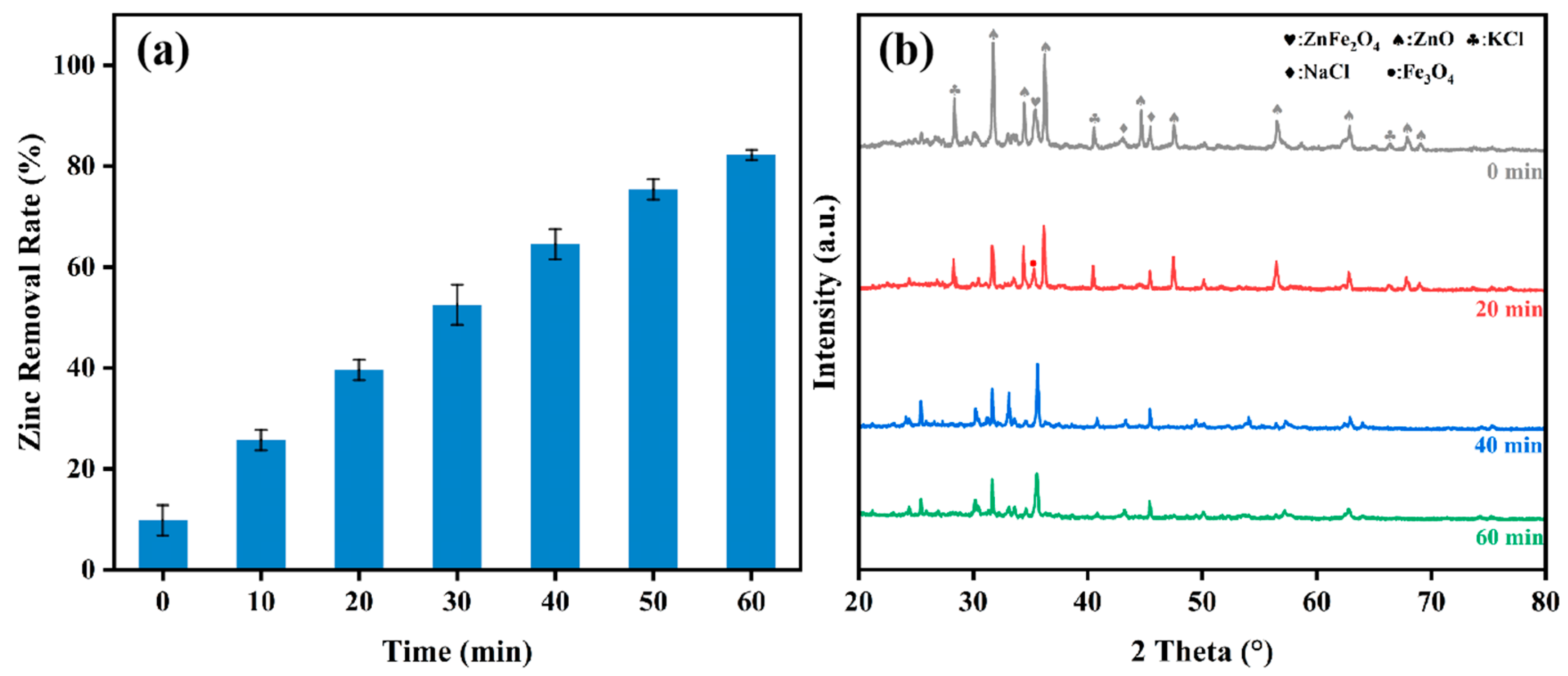
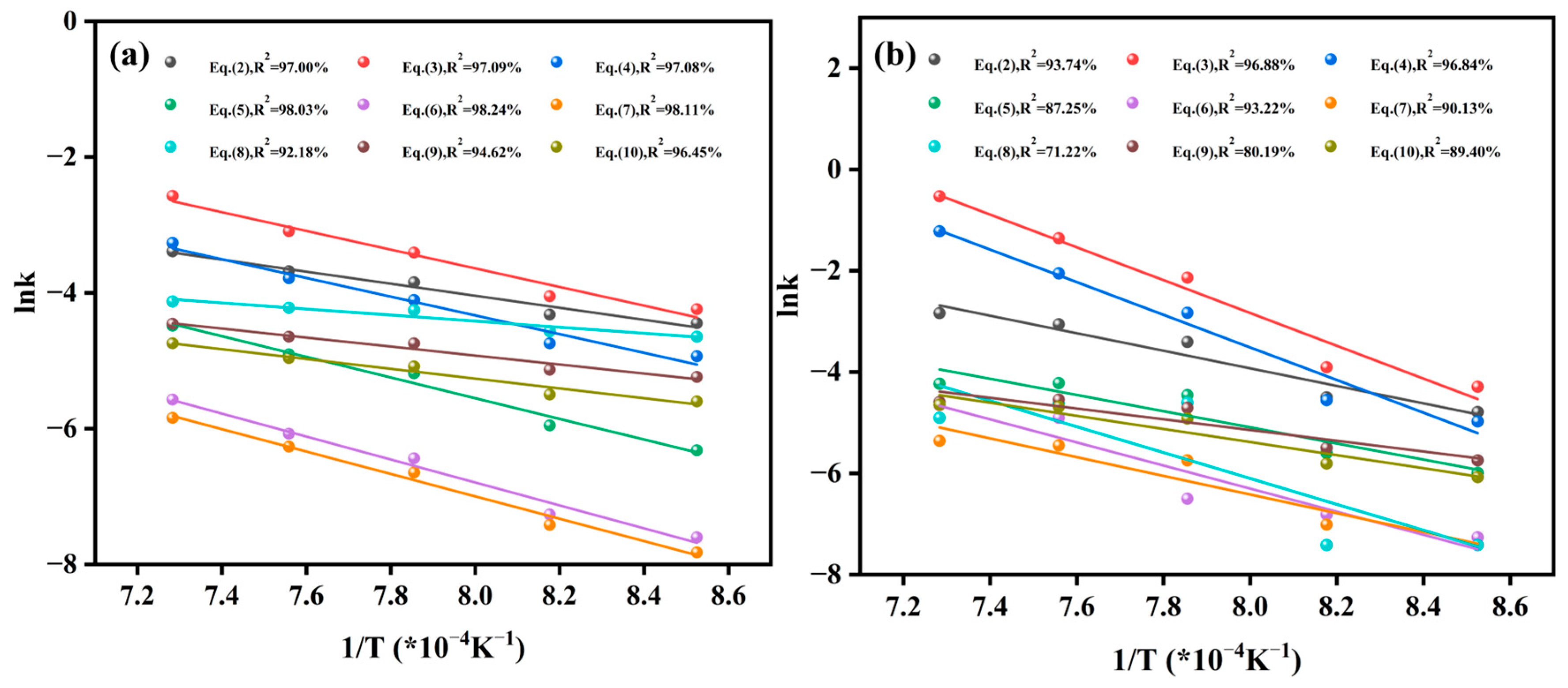
3.2. Effect of Holding Time on Zinc Removal Rate
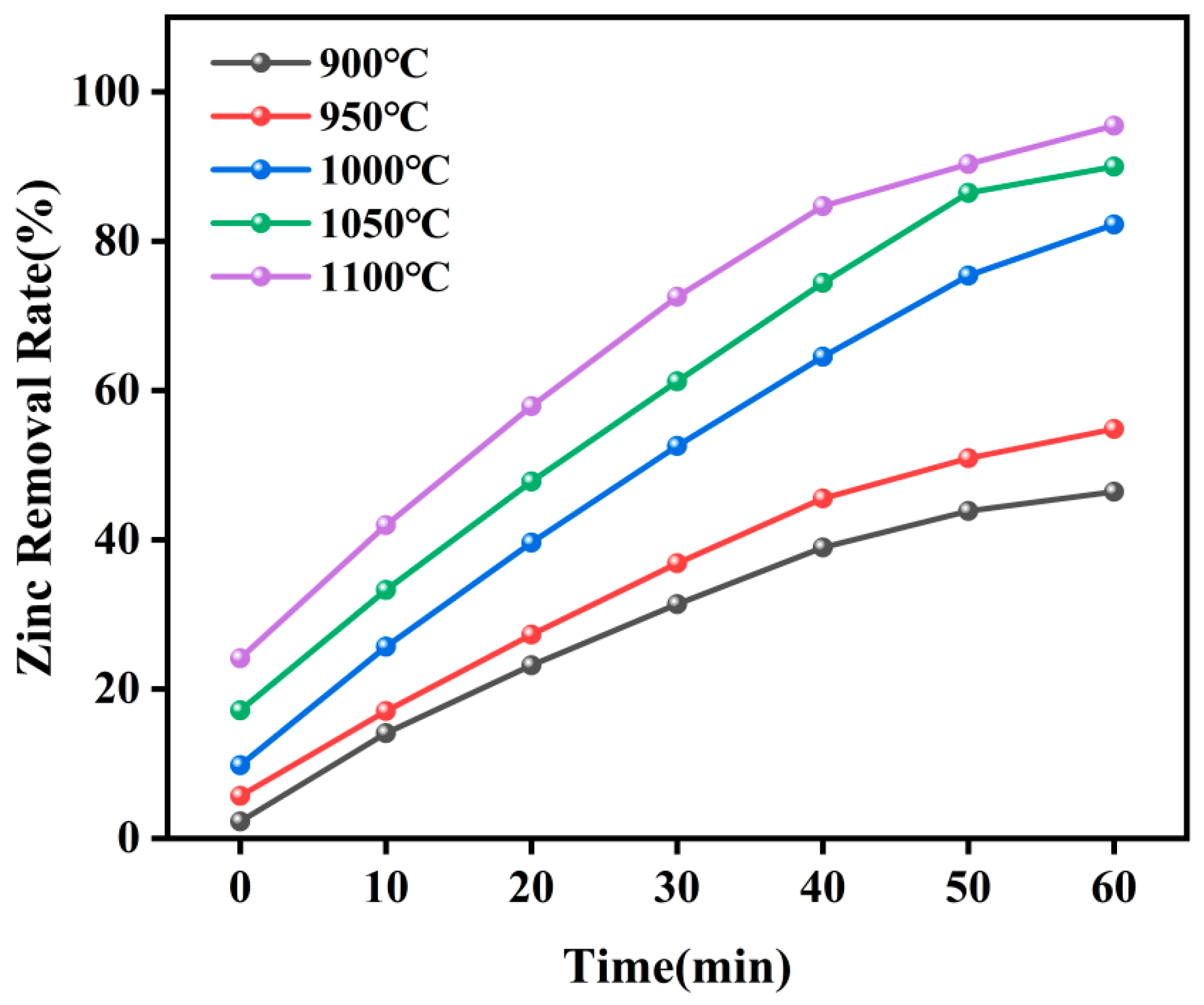
3.3. Effect of Temperature on Zinc Removal Rate
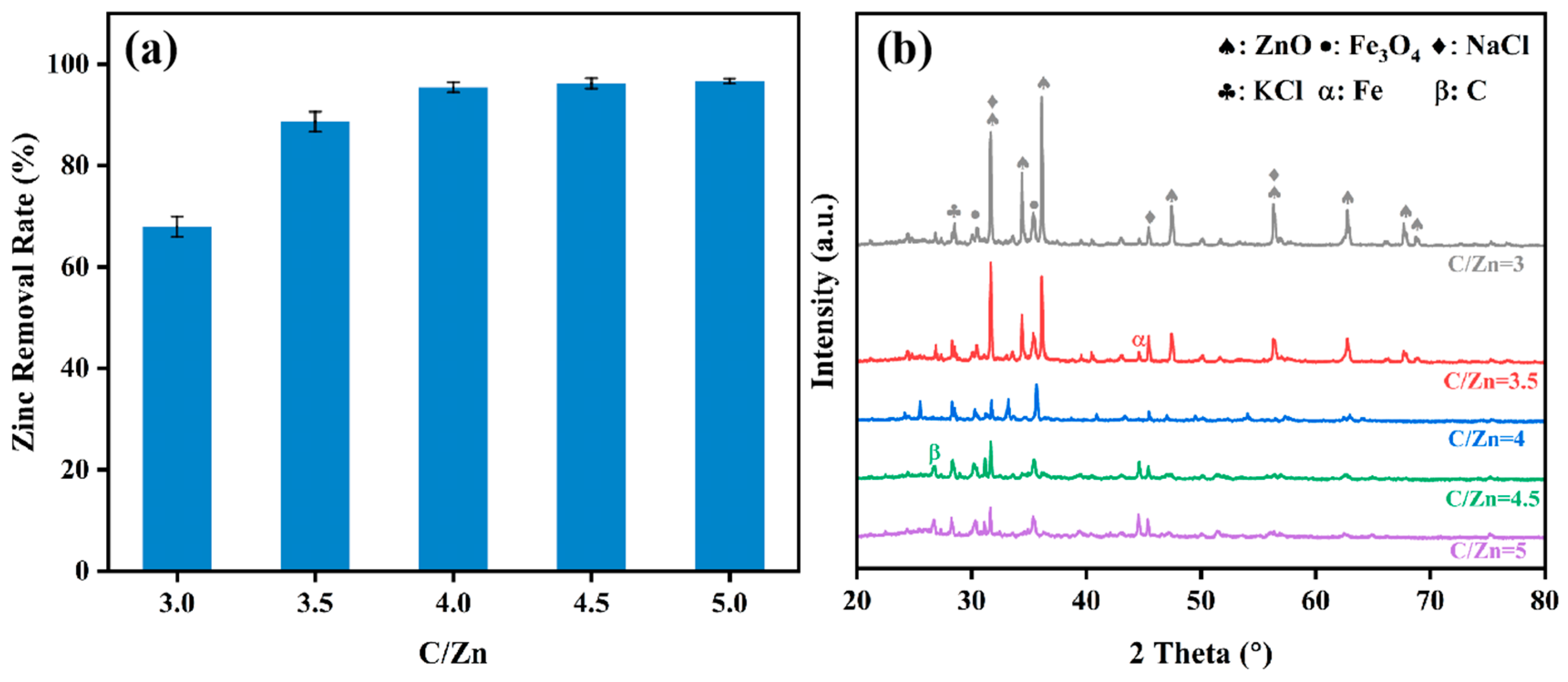
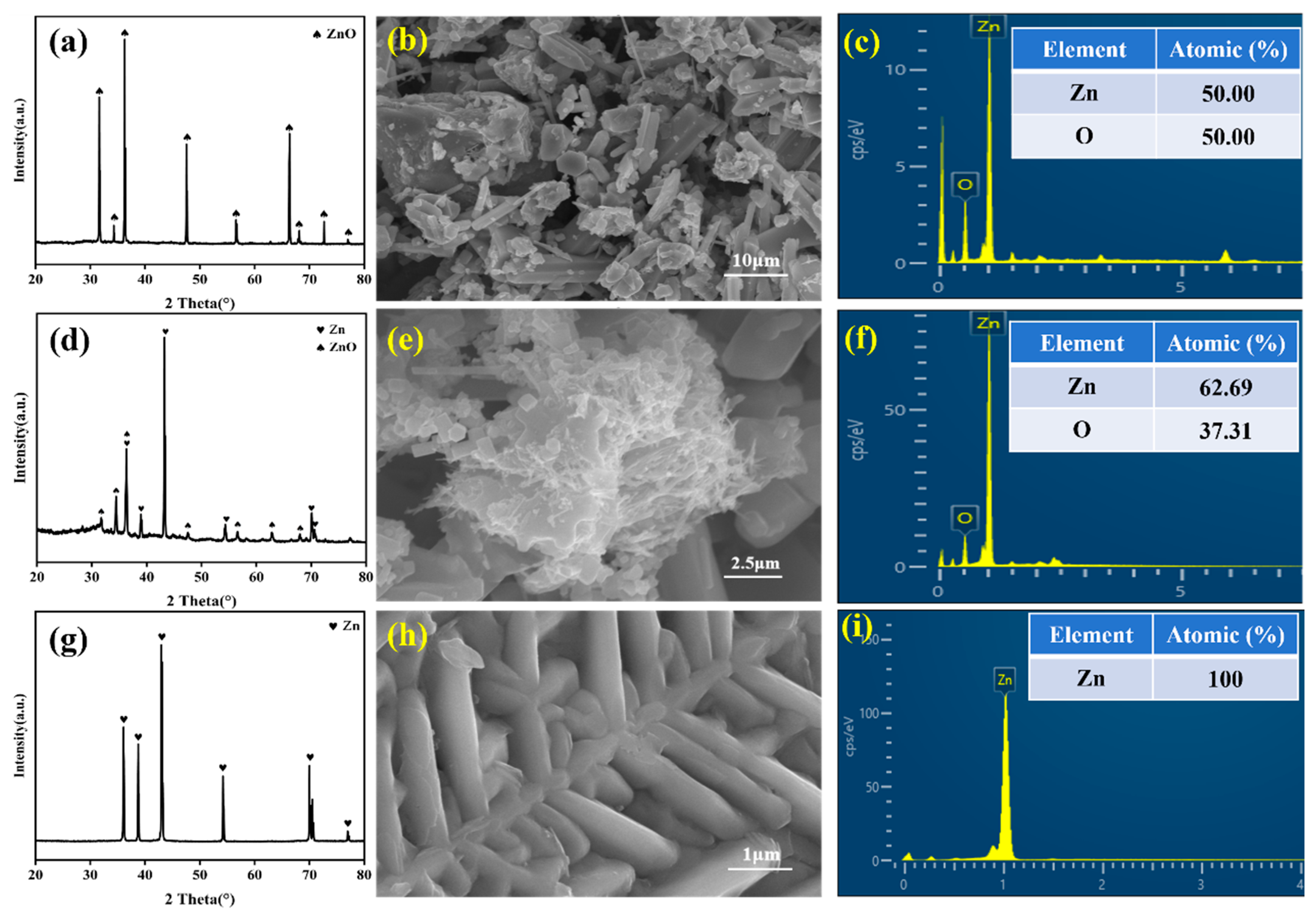
3.4. Effect of C/Zn Ratio on Zinc Removal Rate and Product
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, H.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Guo, Y. Development and assessment of an integrated wind energy system for green steelmaking based on electric arc furnace route. Energy 2024, 302, 131783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worldsteel Association. World Steel in Figures 2024. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/data/world-steel-in-figures-2024/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Al-Negheimish, A.I.; Al-Mutlaq, F.M.; Fares, G.; Alhozaimy, A.M.; Iqbal Khan, M. Characterization of chemical accelerators for sustainable recycling of fresh electric-arc furnace dust in cement pastes. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 3046–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza, A.; Cifuentes, S.; Colorado, H.A. Asphalt modified with superfine electric arc furnace steel dust (EAF dust) with high zinc oxide content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Lunar, A.; Barbudo, A.; Fernández, J.M.; Jiménez, J.R. Promotion of circular economy: Steelwork dusts as secondary raw material in conventional mortars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.S.; Silva, J.S.; Costa, B.D.S.; Labes, C.; Oliveira, R.M.P.B. Preparation of glaze using electric-arc furnace dust as raw material. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5504–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, V.N.; Papandreou, A.; Kanellopoulou, D.; Stournaras, C.J. Structural ceramics containing electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheyab, M.A.T.; Khedaywi, T.S. Effect of electric arc furnace dust (EAFD) on properties of asphalt cement mixture. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 70, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, I.; Đurović, D.; Marković, S.; Veselinović, L.; Janković-Častvan, I.; Radmilović, V.V.; Radmilović, V.R. Alkali activated slag cement doped with Zn-rich electric arc furnace dust. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12783–12794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Al-Homidy, A.A.; Maslehuddin, M.; Saleh, T.A. Method and Mechanisms of Soil Stabilization Using Electric Arc Furnace Dust. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Fiotakis, K.; Vlachogianni, T. Airborne particulate matter and human health: Toxicological assessment and importance of size and composition of particles for oxidative damage and carcinogenic mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2008, 26, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-M.; Huang, W.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-K.; Kuo, Y.-L. Utilization of electric arc furnace dust as regenerable sorbents for the removal of hydrogen sulfide. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S694–S699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A. Recycling of electric arc furnace dust through dissolution in deep eutectic ionic liquids and electrowinning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-harahsheh, M.; Al-Nu’airat, J.; Al-Otoom, A.; Al-hammouri, I.A.; Al-jabali, H.; Al-zoubi, M.; Abu Al’asal, S.A. Treatments of electric arc furnace dust and halogenated plastic wastes: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcai, Z.; Stanforth, R. Integrated hydrometallurgical process for production of zinc from electric arc furnace dust in alkaline medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 80, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Han, Y. Hydrometallurgical detoxification and recycling of electric arc furnace dust. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 2076–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, D.; Pan, J.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y. A study on the zinc removal kinetics and mechanism of zinc-bearing dust pellets in direct reduction. Powder Technol. 2021, 380, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetens, T.; Klaasen, B.; Van Acker, K.; Blanpain, B. Comparison of electric arc furnace dust treatment technologies using exergy efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-harahsheh, M.; Kingman, S.; Al-Makhadmah, L.; Hamilton, I.E. Microwave treatment of electric arc furnace dust with PVC: Dielectric characterization and pyrolysis-leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, K.; Fu, T.; Gao, J.; Hussain, S.; AlGarni, T.S. Pyrometallurgical recovery of zinc and valuable metals from electric arc furnace dust—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleti, J.L.; Manfredi, G.V.P.; Junca, E.; Grillo, F.F.; de Oliveira, J.R.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Tenório, J.A.S. Kinetic Investigation of Self-reducing Briquettes of Electric Arc Furnace Dust Produced with Charcoals. JOM 2022, 74, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Yoo, J.-M.; Park, J.-T.; Lee, J.-C. A Kinetic Study of the Carbothermic Reduction of Zinc Oxide with Various Additives. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, A.; Bäckström, D.; Johansson, R.; Fredriksson, C.; Andersson, K. Radiative Heat Transfer Conditions in a Rotary Kiln Test Furnace Using Coal, Biomass, and Cofiring Burners. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7482–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Peng, Z.; Li, G.; Lee, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Rao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. Microwave-Assisted Reduction of Electric Arc Furnace Dust with Biochar: An Examination of Transition of Heating Mechanism. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9515–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzulevich, A.P.; Kalganov, D.A.; Anzulevich, S.N.; Bychkov, I.V.; Peng, Z. Optimal microwave heating of biochar containing iron ore pellets. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1461, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Li, G.; Peng, Z.; Lee, J.; Lin, X.; Rao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. Microwave-assisted self-reduction of composite briquettes of zinc ferrite and carbonaceous materials. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Fu, J.; Mao, X.; Kang, Q.; Ran, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Microwave assisted preparation of activated carbon from biomass: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 958–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, K.; Qiu, D.; Omran, M.; Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Khan, I.U.; Zhang, D.; Ahmed, A.; et al. Recent developments on the removal of zinc from electric arc furnace dust by using microwave heating. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 16274–16290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Baños, B.; Catalá-Civera, J.M.; Sánchez, J.R.; Navarrete, L.; López-Buendía, A.M.; Schmidt, L. High Temperature Dielectric Properties of Iron- and Zinc-Bearing Products during Carbothermic Reduction by Microwave Heating. Metals 2020, 10, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T.; Heikkinen, E.-P.; Chen, G. Dielectric properties and carbothermic reduction of zinc oxide and zinc ferrite by microwave heating. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T. Utilization of blast furnace sludge for the removal of zinc from steelmaking dusts using microwave heating. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 867–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikalidis, C.; Mitrakas, M.; Tsitouridou, R. Immobilization of electric arc furnace dust toxic elements within the matrix of concrete based products. Glob. Nest J. 2010, 12, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Li, G.-F.; Sun, Y.-S.; He, M.-Z. Reduction behavior of hematite in the presence of coke. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Luo, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D. Comparative Study on the Kinetics of the Isothermal Reduction of Iron Ore Composite Pellets Using Coke, Charcoal, and Biomass as Reducing Agents. Metals 2021, 11, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Zhang, G.-H.; Chou, K.-C. Kinetics and mechanism of hydrogen reduction of ilmenite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y.-L.; Hua, H.-J.; Deng, Y.; Sun, Z.-Z.; Liu, L.-H. Isothermal reduction kinetics and reduction prediction for iron ore pellets. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2025, 32, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Ma, S.-H.; Yang, S.-T.; Zhou, M. Kinetics and mechanism of coal-based direct reduction of high-chromium vanadium–titanium magnetite. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, Q.; Xie, H.; Qin, Q.; Wang, K. CO2 Gasification Rate Analysis of Datong Coal Using Slag Granules as Heat Carrier for Heat Recovery from Blast Furnace Slag by Using a Chemical Reaction. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 4810–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Xia, J.; Chen, Z. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the carbothermal reduction of aluminum sulfate. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2021, 196, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yu, S.; Shao, J.; Zhu, K.; Ju, D.; Chen, C.; Qi, D.; Wang, F.; Bai, N.; Mao, R.; et al. Mechanisms and kinetics of zinc and iron separation enhanced by calcified carbothermal reduction for electric arc furnace dust. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 40, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
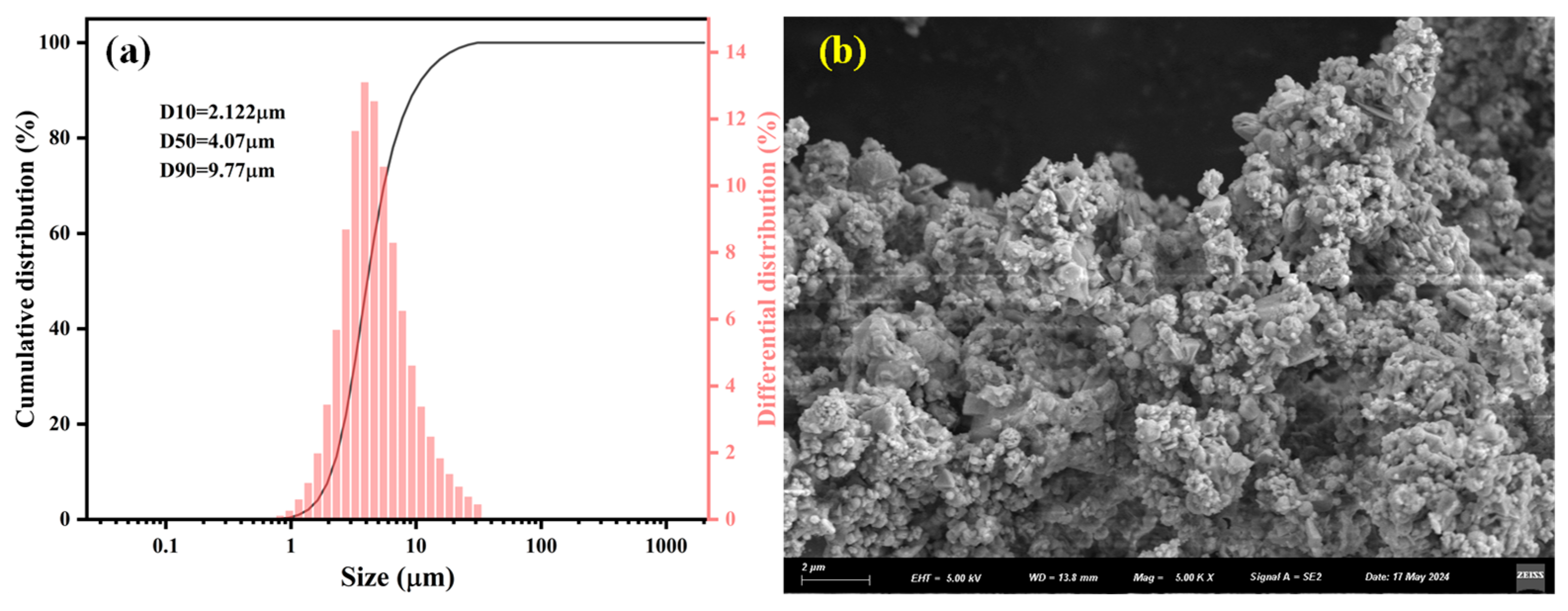


| Element | C | H | O | N | S | Cl | F | Fe | Zn | Si | Al | Ca | Pb | Mg | Mn | Na | K | Ni | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.9 | 0.6 | 21.5 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 13.0 | 27.2 | 18.9 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 0.2 |
| Mechanism | 0~30 min | 30~60 min | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ea/kJ·mol−1 | R2 | Ea/kJ·mol−1 | R2 | ||
| Chemical reaction | Equation (2) | 73.57 | 97.00% | 145.18 | 93.74% |
| Equation (3) | 114.62 | 97.09% | 267.32 | 96.88% | |
| Equation (4) | 114.50 | 97.08% | 267.29 | 96.84% | |
| Diffusion | Equation (5) | 126.68 | 98.03% | 133.27 | 87.25% |
| Equation (6) | 146.50 | 98.24% | 190.34 | 93.22% | |
| Equation (7) | 133.26 | 98.11% | 152.87 | 90.13% | |
| Phase-boundary reaction | Equation (8) | 37.05 | 92.18% | 36.67 | 71.22% |
| Equation (9) | 54.76 | 94.62% | 89.26 | 80.19% | |
| Equation (10) | 60.84 | 96.45% | 107.54 | 89.40% | |
| Reductant | Heating Form | Controlling Mechanism | Ea (kJ/mol) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charcoal | Electric heating | Phase-boundary | 137.6–200.3 | [21] |
| diffusion | 360.5–378.8 | |||
| Graphite | Electric heating | One-dimensional diffusion | 305.01 | [40] |
| Chemical reaction | 315.67 | |||
| Chemical reaction | 288.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Lu, C.; Wei, T.; Xiong, Y.; Ren, J.; Qiu, D.; Yu, Y. Influencing Factors and Mechanisms of Zinc Recovery from Electric Arc Furnace Dust via Microwave-Assisted Carbothermic Reduction. Metals 2025, 15, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040437
Wang K, Lu C, Wei T, Xiong Y, Ren J, Qiu D, Yu Y. Influencing Factors and Mechanisms of Zinc Recovery from Electric Arc Furnace Dust via Microwave-Assisted Carbothermic Reduction. Metals. 2025; 15(4):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040437
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kai, Chunyang Lu, Taida Wei, Yuandong Xiong, Jie Ren, Dejin Qiu, and Yaowei Yu. 2025. "Influencing Factors and Mechanisms of Zinc Recovery from Electric Arc Furnace Dust via Microwave-Assisted Carbothermic Reduction" Metals 15, no. 4: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040437
APA StyleWang, K., Lu, C., Wei, T., Xiong, Y., Ren, J., Qiu, D., & Yu, Y. (2025). Influencing Factors and Mechanisms of Zinc Recovery from Electric Arc Furnace Dust via Microwave-Assisted Carbothermic Reduction. Metals, 15(4), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040437






