Abstract
In this work, a Mg-5Nb metal–metal composite was reinforced with nano SiC (SiCn) ceramic reinforcement of varying volume fractions, using the disintegrated melt deposition technique. The extruded Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites were characterized for their microstructure and mechanical properties. Based on the results obtained, it was observed that the volume fraction of nano-SiC reinforcement played an important role in determining the grain size and improving the mechanical properties. A comparison of properties with those of pure Mg and Mg-5Nb composite showed that while the improvement in hardness occurred at all volume fractions, a minimum volume fraction of ~0.27% SiCn was required to increase the tensile and compressive strengths. The observed mechanical response of the composites were investigated in terms of the effect of SiCn volume fraction, processing, distribution of metallic and ceramic reinforcements and the inherent properties of the matrix and reinforcements. The influences of these factors on the mechanical behavior of the composites are understood based on the structure–property relationship.
1. Introduction
The depletion of earth’s oil reserves and the simultaneous requirement of fuel efficiency and emission reduction (especially in the transportation sector) have resulted in a multifold increase in the research and development of light weight materials. Amongst the light metals, magnesium (Mg) and its alloys with its low density, fuel efficiency and recyclability, is an excellent choice for weight-critical applications. Mg-alloys also exhibit good dimensional stability, machinability and damping capacity [1]. The commonly used Mg-alloy systems usually contain Al, Mn, Zn, Zr and rare-earth elements as alloying constituents and are designated as AZ31 (Mg-3Al-1Zn), AM50 (Mg-5Al-0.1Mn), ZK60 (Mg-5.5Zn-0.7Zr), etc. [2]. However, the relatively low strength and poor ductility of these alloys limits their use for critical applications. Most of these limitations can be overcome by the addition of high strength and high modulus micron-scale ceramic reinforcements (such as Al2O3 and SiC) into Mg-matrix (metal matrix composites, Mg-MMCs). The introduction of such reinforcements into the Mg-matrix significantly improves specific mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, elastic modulus and yield strength, at the expense of ductility [3,4,5].
Unlike conventional alloying elements such as those mentioned above, which usually form Mg-based intermetallic compounds in the Mg-material (such as Mg17Al12, MgZn2, etc.), unconventional alloying elements based on metals such as Ti, Mo etc. which are insoluble or have negligible solubility in Mg, do not form any phase with Mg. These are considered as metallic reinforcements [6,7]. Recently, addition of varying weight fractions of Nb in pure Mg was studied [8]. It was reported that the addition of 5 wt.% Nb to pure Mg significantly improved the failure strain, with little/no improvement in the strength properties. Increasing the Nb content (wt. %) to 10% and 15% enhanced the strength but drastically reduced the fracture strain [8].
Based on recent research works [9,10,11,12], the addition of ceramic particles at nano-meter scale length, especially nano-Al2O3 and CNTs, to pure/alloyed Mg have improved both the strength and ductility of the resulting Mg-composites. The additional advantage of using nano-sized particles include the utilization of low volume fractions of reinforcements, when compared to the high volume fractions required in micron-scale particle reinforced MMCs. A literature review on Mg-nanocomposites indicates that research work on the incorporation of other nano-scale ceramic particles, such as nano-SiC, have not been attempted, except in a few works [13,14].
Taking into consideration the high ductility reported for Mg-5Nb metal–metal composite [8], the aim of this study is to investigate the effect of nano-SiC reinforcements on its microstructure and mechanical properties. Mg-5 wt.% Nb metal–metal composite reinforced with four volume fractions (0.13%, 0.27%, 0.55% and 1.1% Vf) of nano-scale SiC particles (SiCn) were prepared using the disintegrated melt deposition technique (DMD) [9], followed by hot extrusion. The extruded Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites were investigated for their microstructural and mechanical properties. The influence of nanoparticle volume fraction, effect of processing, distribution of metallic/ceramic particles and secondary phases and the inherent properties of the constituent elements on the mechanical response of Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites have been discussed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Macrostructure and Density
The macrostructural examination of the Mg-5Nb-SiCn as-cast billets and extruded rods indicated that the surface of the materials were smooth and did not show any presence of macropores, blowholes and/or shrinkage cavities. The absence of macro-defects in the samples indicated the suitability of the processing parameters that result in sound, defect-free castings.
Table 1 shows the results of the density and porosity measurements made on the extruded sections. From the table, it is seen that the density values increase with increasing content of SiCn, which is due to the higher density of SiC (3.21 g/cc) when compared to that of pure Mg. It can also be observed that the experimentally measured density values of the Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites are comparable to those of their theoretically estimated values. This indicates very low levels of porosity (<0.1 %) and is in agreement with macroscopic observations.

Table 1.
Results of Density and Porosity Measurements in Mg-5Nb-SiCn Composites.
| Composition | Theoretical Density/(g/cm3) | Experimental Density/(g/cm3) | Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf) | 1.8142 | 1.813 ± 0.014 | 0.066 |
| Mg-5Nb-0.50SiCn (0.27% Vf) | 1.8162 | 1.8154 ± 0.009 | 0.044 |
| Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf) | 1.820 | 1.8186 ± 0.014 | 0.077 |
| Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf) | 1.828 | 1.8273 ± 0.003 | 0.048 |
2.2. Microstructure
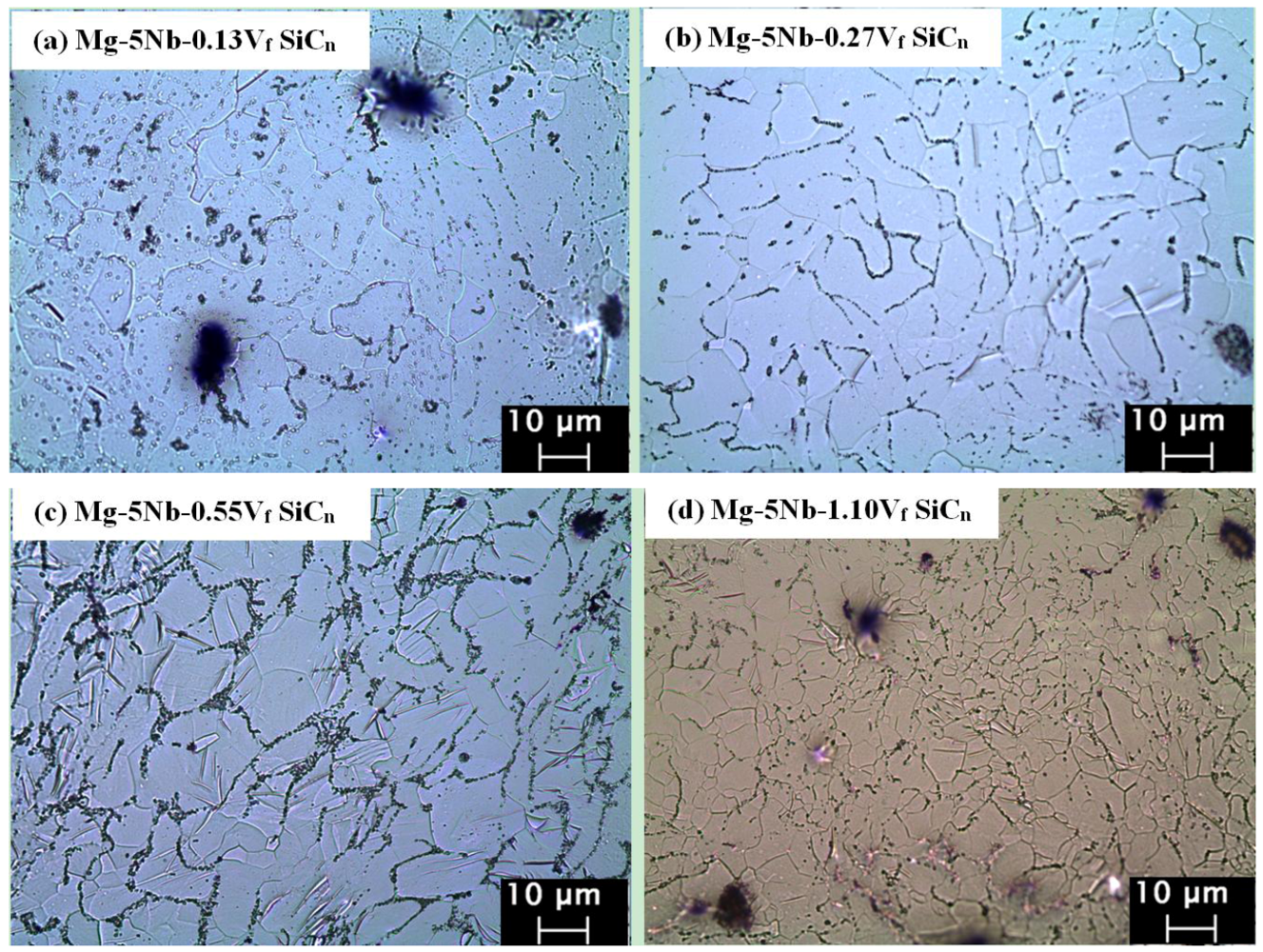
Table 2 and Figure 1 show the results of the microstructural investigations conducted on the extruded materials. It can be observed that when compared to pure Mg, fine and near-equiaxed grains are observed in all the materials, with the average grain size <10 μm (Table 1, Figure 1a–d). The observed refined microstructure is due to the presence of reinforcement particles (both Nb and SiCn), which act as heterogeneous sites for grain nucleation [15]. Further, as the hot extrusion was carried out at 350 °C (>0.5 Tm), it results in recrystallization, thereby leading to the formation of fine and nearly-equiaxed grains [9]. It can also be seen from Table 1 that when compared to Mg-5Nb, the additions of SiCn up to 0.27 Vf did not contribute to grain size reduction. On the contrary, for Vf > 0.27% grain refinement can be observed. This indicates that at these SiCn contents, the nanoparticles act as an obstacle for grain growth [9], thus resulting in a fine-grained structure.
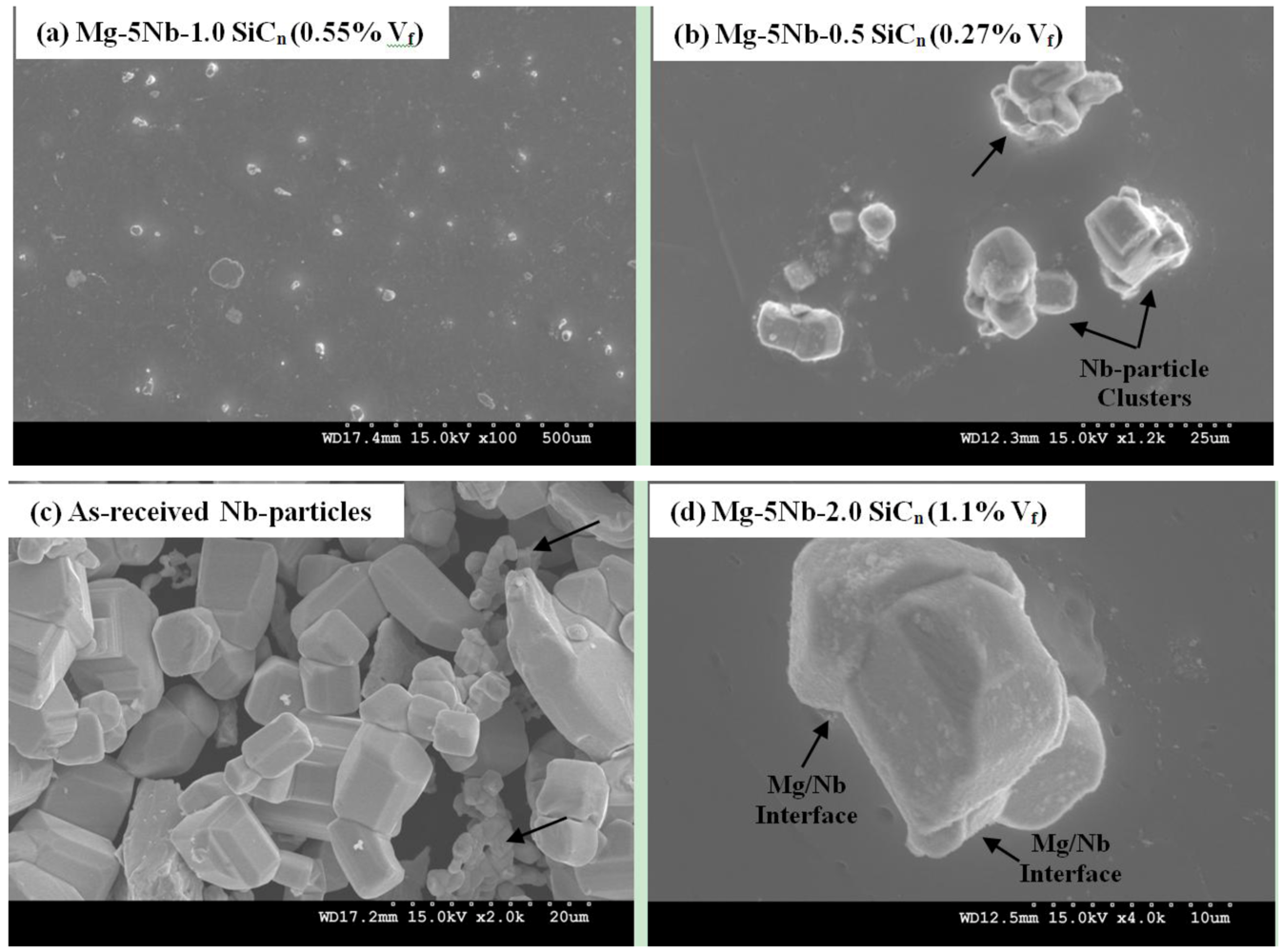
Figure 2 shows the distribution of Nb and SiCn particulates in the Mg-matrix. Microstructural observations indicated that the Nb particles were distributed uniformly throughout the matrix, while higher magnification images showed clustering of Nb particles that were present in all the composites. Representative images showing these features are given in Figure 2a, b. It should be noted that there are several factors that can contribute to particle clustering (often referred to as “particle local inhomogenity” [16], that include: (i) processing parameters such as insufficient melt stirring time, low melt temperature or low solidification rate; (ii) poor wettability between the particle/matrix; (iii) irregular shape of the particle and (iv) chemical incompatibility between the particle/matrix [16,17,18].

Table 2.
Results of Grain Size and Grain Morphology of Mg-5Nb-SiCn Composites.
| Composition | Grain Size/μm | Aspect Ratio | Roundness/μm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Mg [19] | 16.3 ± 9.9 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.9 | |
| Mg-5Nb [8] | 9.1 ± 3.2 | 1.8 ± 0.63 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | |
| Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf) | 9.9 ± 4.4 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | |
| Mg-5Nb-0.50SiCn (0.27% Vf) | 9.4 ± 4.2 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | |
| Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf) | 6.1 ± 3.2 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | |
| Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf) | 5.9 ± 2.6 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | |
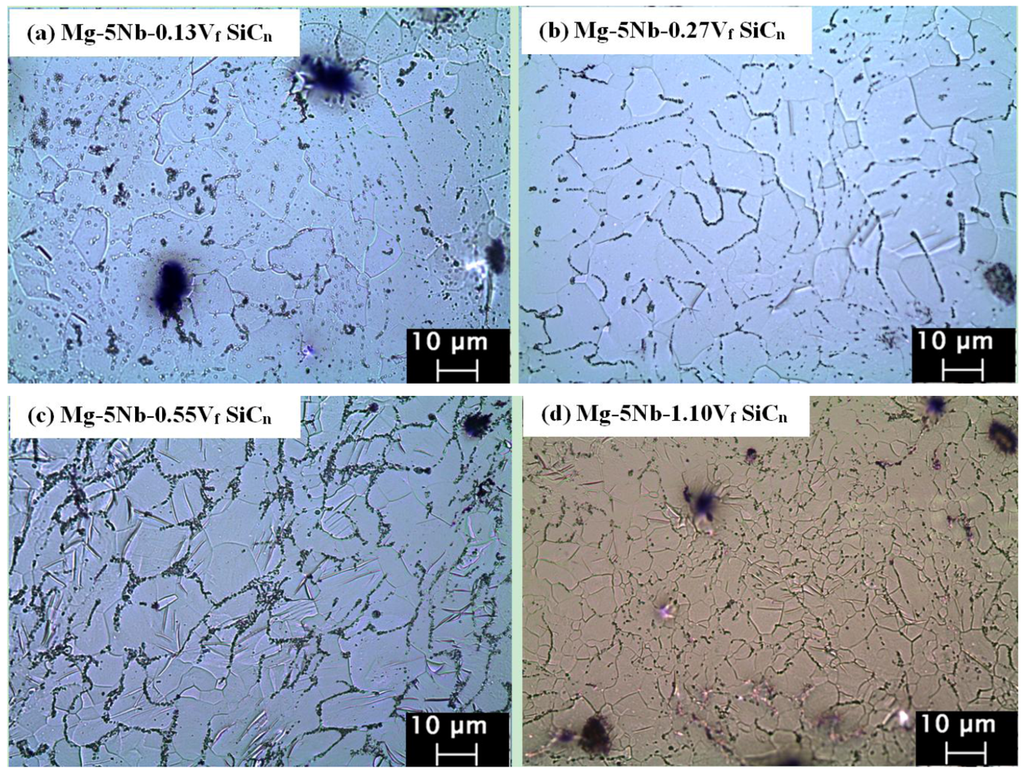
Figure 1.
Optical micrographs of (a) Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf); (b) Mg-5Nb-0.50SiCn (0.27% Vf); (c) Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf); (d) Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf).
Figure 1.
Optical micrographs of (a) Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf); (b) Mg-5Nb-0.50SiCn (0.27% Vf); (c) Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf); (d) Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf).
In the current work, standardized process parameters were employed. Further, the DMD technique has a relatively high solidification rate when compared to conventional die casting processes. Regarding the particle shape, the Nb-particles were dominantly cuboidal in shape of varying sizes and in the as-received condition, the relatively smaller-sized particles are found to be clustered (arrow, Figure 2c). While the wettability value of Mg/Nb is not known, the high magnification image shown in Figure 2d shows good interface bonding (arrow), indicating good wettability. However, it should be noted that based on the Mg-Nb phase diagram [20], Nb and Mg has no solubility (mutually insoluble) and does not form any intermetallic phase. Hence, considering the relatively high density of Nb (8.57 g/cc) and the lack of chemical compatibility (i.e., absence of chemical bonding due to no solubility) between Nb-particles and Mg-matrix, the Nb particles will tend to agglomerate during processing, thereby forming Nb-clusters. Earlier works on Mg-Ti and AZ31-Cr also showed similar agglomerations containing Ti and Cr [19,21]. In these works, Ti showed good wettability with the Mg-matrix, while the wettability of Cr with Mg was not known. However, not only was there no solubility between the Ti/Cr particles and Mg, but also that the particles were irregular in shape, such that it resulted in particle segregation/clustering [19,21].
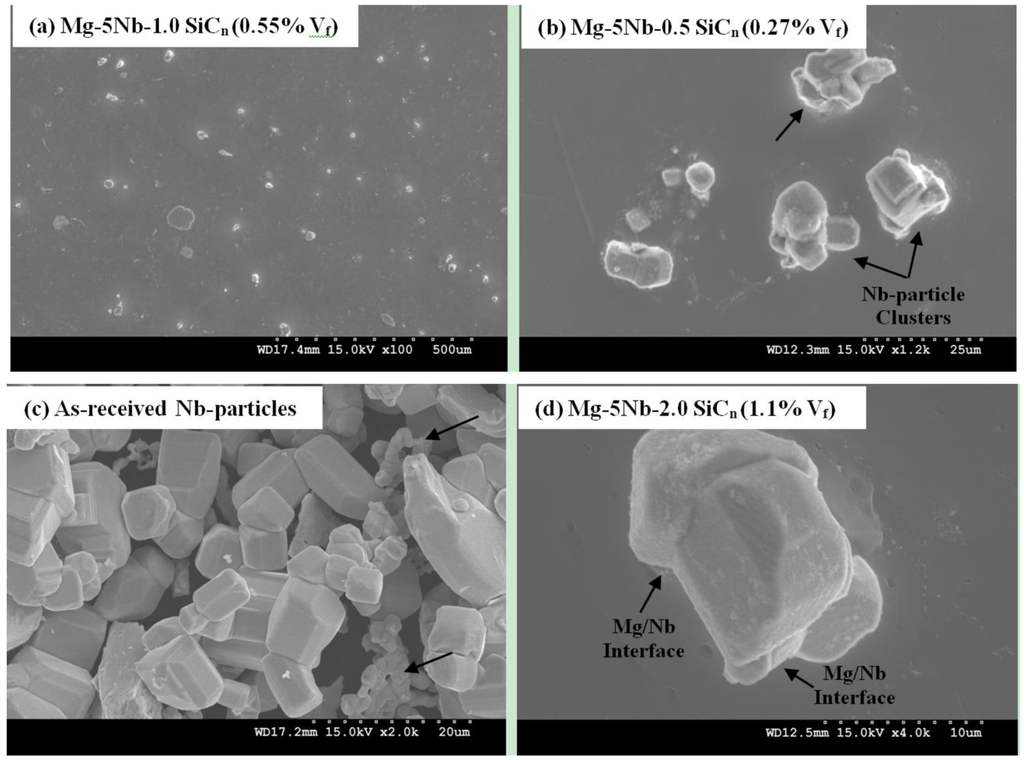
Figure 2.
Representative SEM micrographs showing: (a) uniform distribution of Nb particles in Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf); (b) high magnification image of clustered Nb-particles (arrow) in Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.27% Vf); (c) image of as-received Nb particles that are cuboidal in shape with varying sizes; (d) high magnification image of Nb particle in Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf) showing good interfacial bonding between Mg and Nb (arrow) with no interfacial reaction products.
Figure 2.
Representative SEM micrographs showing: (a) uniform distribution of Nb particles in Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf); (b) high magnification image of clustered Nb-particles (arrow) in Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.27% Vf); (c) image of as-received Nb particles that are cuboidal in shape with varying sizes; (d) high magnification image of Nb particle in Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf) showing good interfacial bonding between Mg and Nb (arrow) with no interfacial reaction products.
For the distribution of SiCn particles, EDX analysis was conducted on the polished samples. From Figure 3 that shows the x-ray mapping of Si, C, Nb and Mg, it can be seen that while the SiCn particles were uniformly distributed in the matrix, they were also seen to be preferentially located on the Nb-clusters (arrows). These observations suggest that the distribution of the micron-particles in the Mg-matrix strongly control the dispersion of the nano-reinforcements.
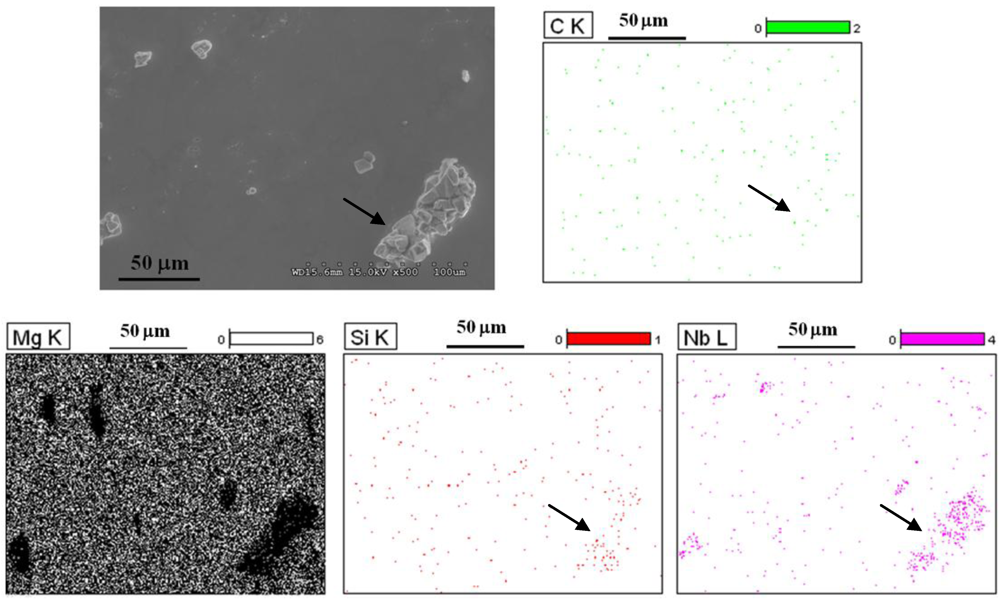
Figure 3.
EDX analyses showing the x-ray mapping of C, Mg, Si and Nb in Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf) composite. SiCn (Si and C) is seen to be uniformly distributed in the Mg-matrix and also preferentially present within the Nb-particle cluster (arrows).
Figure 3.
EDX analyses showing the x-ray mapping of C, Mg, Si and Nb in Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf) composite. SiCn (Si and C) is seen to be uniformly distributed in the Mg-matrix and also preferentially present within the Nb-particle cluster (arrows).
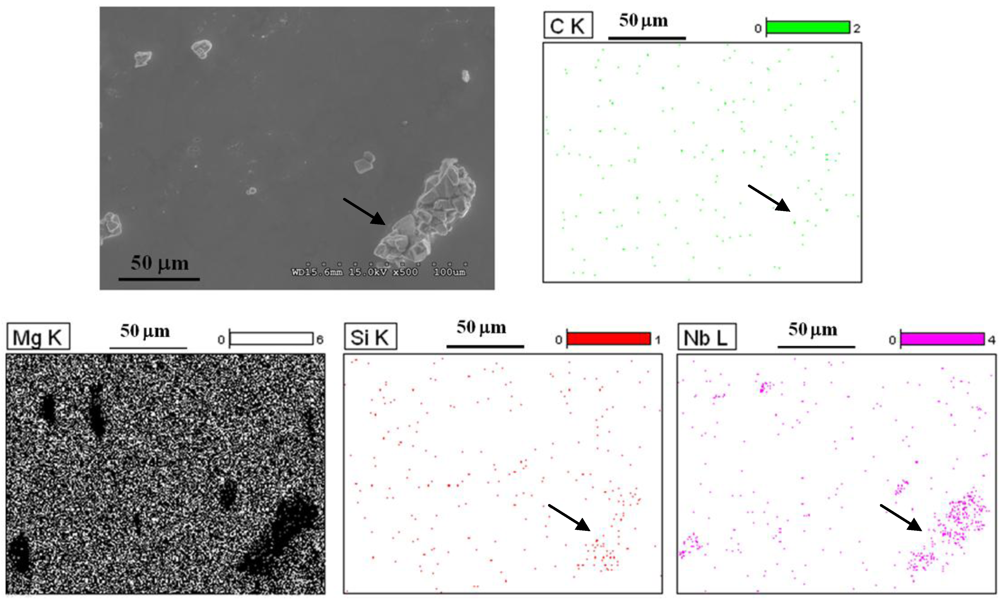
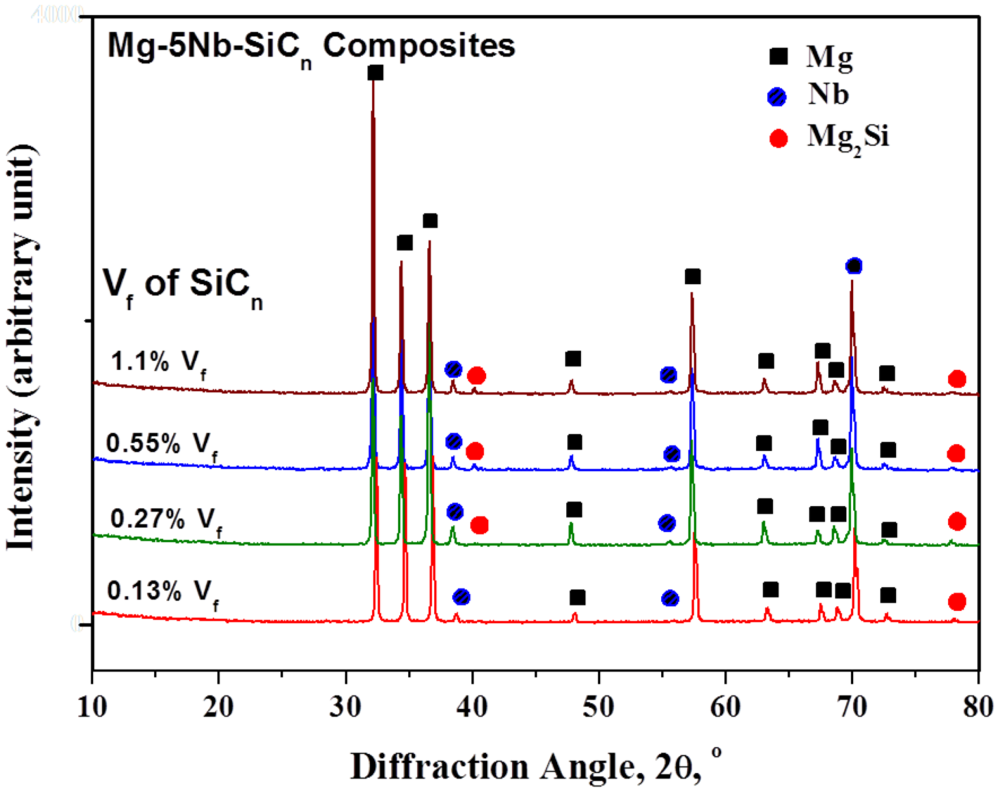
Figure 4 shows the x-ray diffraction patterns of the developed Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites. It can be seen that in all the composites, Mg and Nb peaks were prominent. As mentioned above, no secondary phase formation occurs between Mg and Nb due to the lack of mutual solubility. While SiC peaks could not be identified due to its very low volume fraction, low intensity peak corresponding to Mg2Si has been observed. It is well-known that the interaction of Mg and SiC results in the instantaneous formation of Mg2Si and has been reported in Mg-based micron SiC reinforced composites [15].
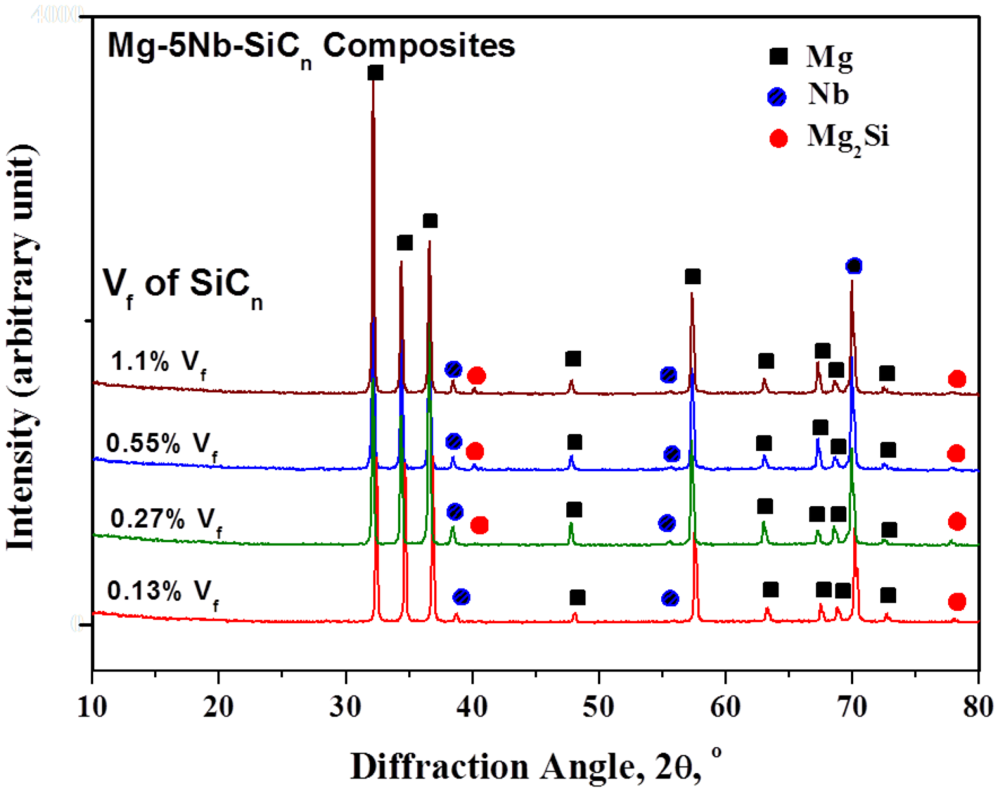
Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the developed Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites.
Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the developed Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites.
2.3. Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of the developed Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites with varying SiCn volume fractions are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. The properties are also compared with those of pure Mg and Mg-5Nb metal–metal composite. From Table 3, it can be seen that the addition of SiCn increases the hardness significantly. The hardness increases with increasing Vf of SiCn such that at 1.10% Vf, the value is almost 2.5 times more than that of pure Mg and Mg-5Nb.
From Table 3 it can be seen that unlike the hardness, the strength properties do not increase with increase in SiCn content. Rather, for Vf ≤ 0.27%, there is a decrease in strength properties. For Vf > 0.27%, there is a significant improvement in both the yield strength and tensile strength, however at the expense of ductility. The Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf) composite shows the highest values of strength amongst all the materials, with ~50% increase in yield strength and ~33% increase in tensile strength. Comparatively, the increment in strength in Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.1% Vf) composite is slightly lower. However, among these two composites, 1.1% Vf shows improved ductility.
Table 4 shows the results of the compression tests. It can be seen from the table that, similar to that observed under tension, no improvement in yield strength occurs until ~0.27% Vf and the values are similar or lower than that of pure Mg and Mg-5Nb. In comparison, for composites with 0.55% Vf and 1.1% Vf of SiCn, an increase of ~25% and ~30% in compressive yield strength can be observed. Further, for SiCn Vf ≥ 0.27%, nominal increase in the ultimate compressive strength values are also seen, with little variation in the compressive ductility.

Table 3.
Hardness and Tensile Properties of Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites with varying SiCn contents.
| Materials | Micro Hardness, Hv | Tensile Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2% Tensile Yield Strength (TYS)/MPa | Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) /MPa | Failure Strain/% | ||
| Pure Mg [19] | 46 | 129 ± 4 | 174 ± 8 | 7.8 ± 0.9 |
| Mg-5Nb [8] | 45 ± 2 | 129 ± 5 | 186 ± 5 | 13.0 ± 1.1 |
| Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf) | 63 ± 5.7 | 116 ± 7 | 164 ± 6 | 2.2 ± 0.3 |
| Mg-5Nb-0.50SiCn (0.27% Vf) | 73 ± 4.6 | 116 ± 17 | 176 ± 15 | 4.3 ± 0.1 |
| Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf) | 100 ± 4.1 | 182 ± 10 | 240 ± 6 | 2.1 ± 0.2 |
| Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf) | 117 ± 3.4 | 156 ± 8 | 208 ± 4 | 5.1 ± 0.6 |

Table 4.
Compressive Properties of Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites with varying SiCn contents.
| Materials | Compressive Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2% Compressive Yield Strength (CYS) /MPa | Ultimate Compressive Strength (UCS)/MPa | Failure Strain /% | |
| Pure Mg [19] | 74 ± 3 | 273 ± 11 | 22.7 ± 4.9 |
| Mg-5Nb | 75 ± 2 | 290 ± 5 | 22.4 ± 1.2 |
| Mg-5Nb-0.25SiCn (0.13% Vf) | 62 ± 6 | 287 ± 5 | 22.8 ± 0.4 |
| Mg-5Nb-0.50SiCn (0.27% Vf) | 72 ± 3 | 306 ± 1 | 23.6 ± 0.6 |
| Mg-5Nb-1.0 SiCn (0.55% Vf) | 95 ± 1 | 310 ± 2 | 19.4 ± 1.3 |
| Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn (1.10% Vf) | 106 ± 8 | 315 ± 3 | 20.9 ± 4.1 |
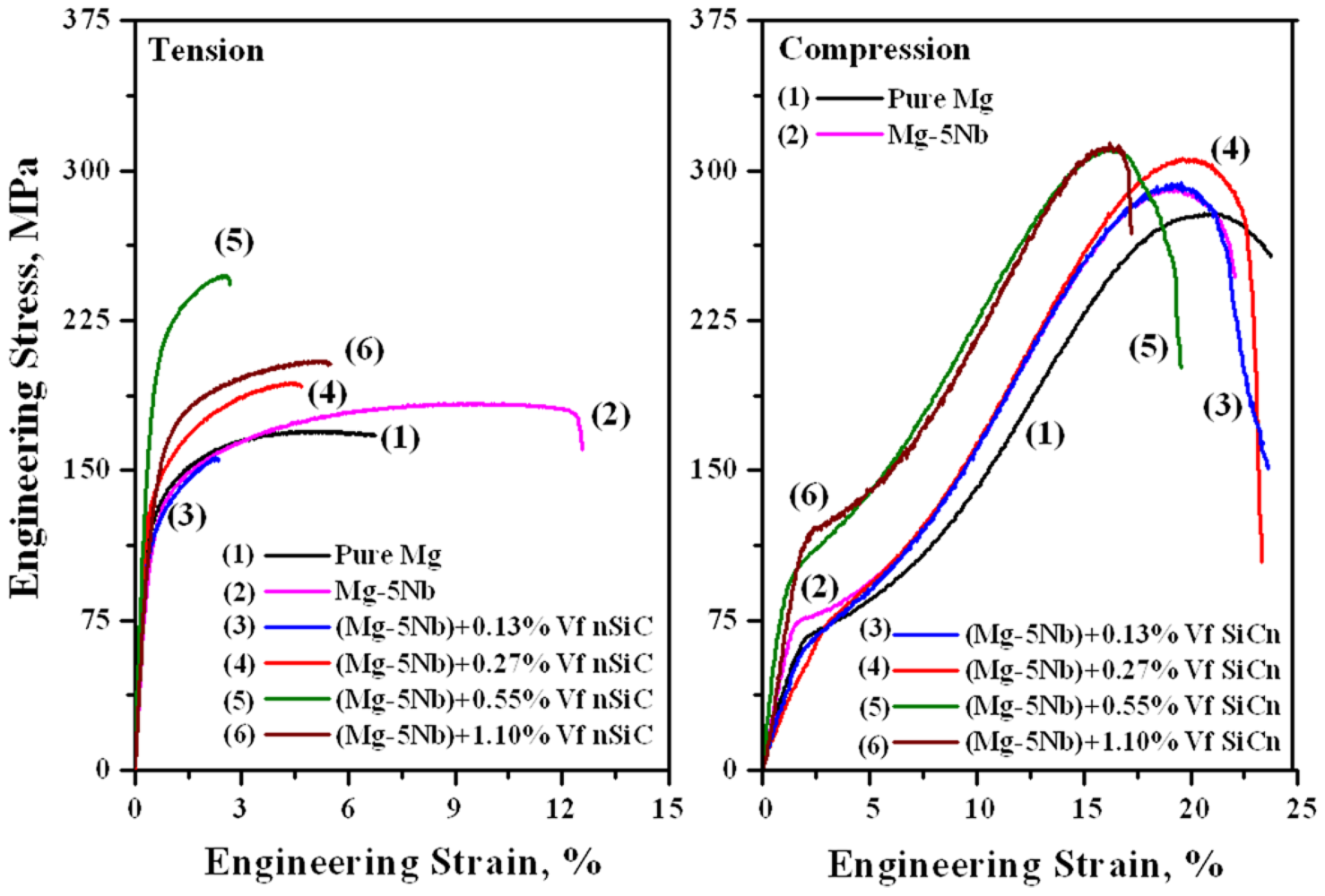
Figure 5 shows the representative engineering stress-strain curves of pure Mg, Mg-5Nb and Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites under tensile and compressive loading conditions.
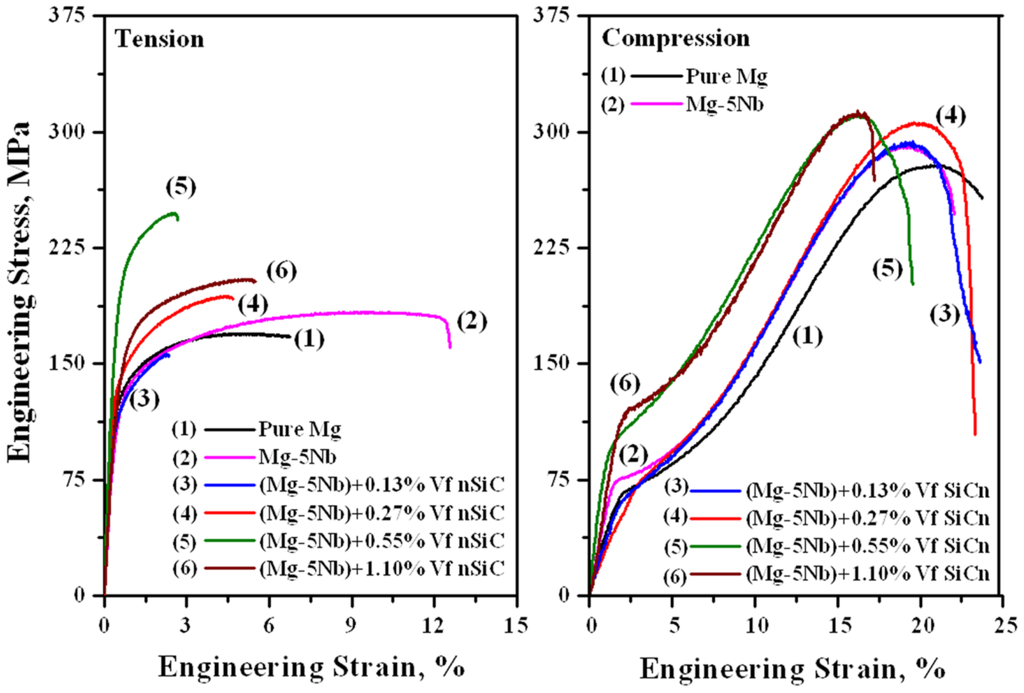
Figure 5.
Representative engineering stress-strain curves of pure Mg, Mg-5Nb and Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites under tensile and compressive loading conditions.
Figure 5.
Representative engineering stress-strain curves of pure Mg, Mg-5Nb and Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites under tensile and compressive loading conditions.
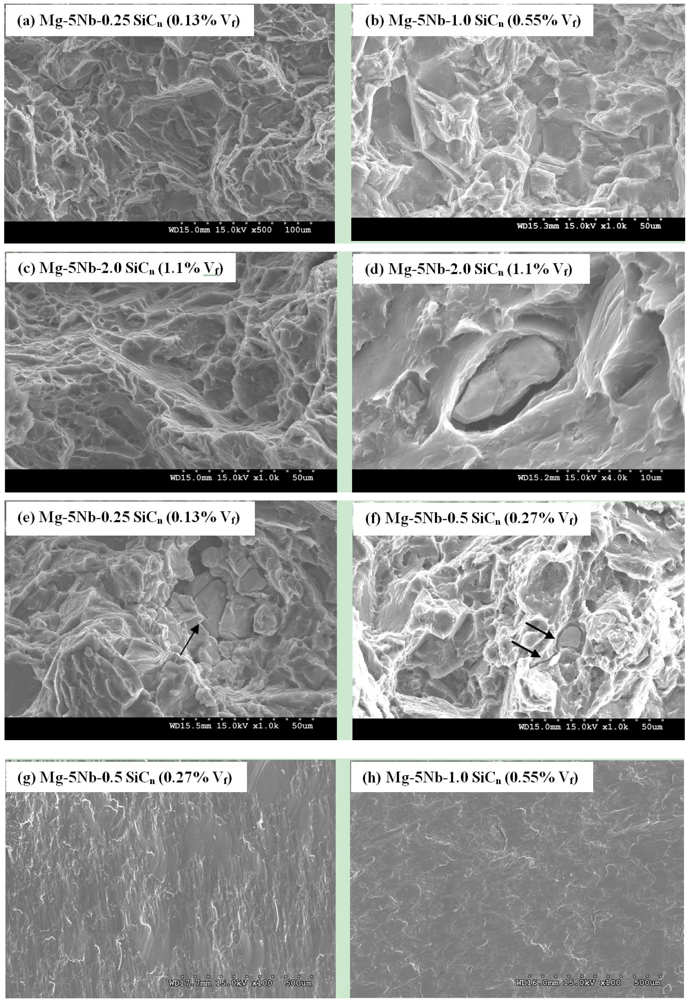
The fracture surface analyses of the tensile and compressive tested samples were conducted and representative images are shown in Figure 6a–h. Under tensile loading, pure Mg exhibits dominant cleavage fracture due to its h.c.p. structure [19], whereas dimple-like ductile features were reported in Mg-5Nb [8]. In the Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites, dominant cleavage fracture with brittle morphology is seen (Figure 6a, c). Regions showing dimple-like ductile features were also observed, particularly in Mg-5Nb-2.0 SiCn composite (Figure 6c). The brittle mode of fracture is largely due to the presence of hard SiC particles, Nb/SiCn clusters and the formation of Mg2Si, which is a brittle intermetallic. Further, the good interfacial bonding between Mg/(Nb/SiCn) contributes only to mechanical bonding, but has low shear strength across the interface due to the absence of chemical bonding (no intermetallic phase formation) [21,22]. This would result in particle debonding due to increasing applied loads (Figure 6d). While a crack extending into the matrix near the Nb/SiCn cluster is seen in Figure 6e, f shows an Nb-particle that is perfectly embedded in the matrix. However, voids coalescing around the particle (arrow) can also be seen, which would eventually result in debonding and/or matrix cracking. These consequently lead to low fracture strains (Table 3). Under compressive loads, fracture occurs by dominant shear fracture in all the materials (Figure 6g, h).
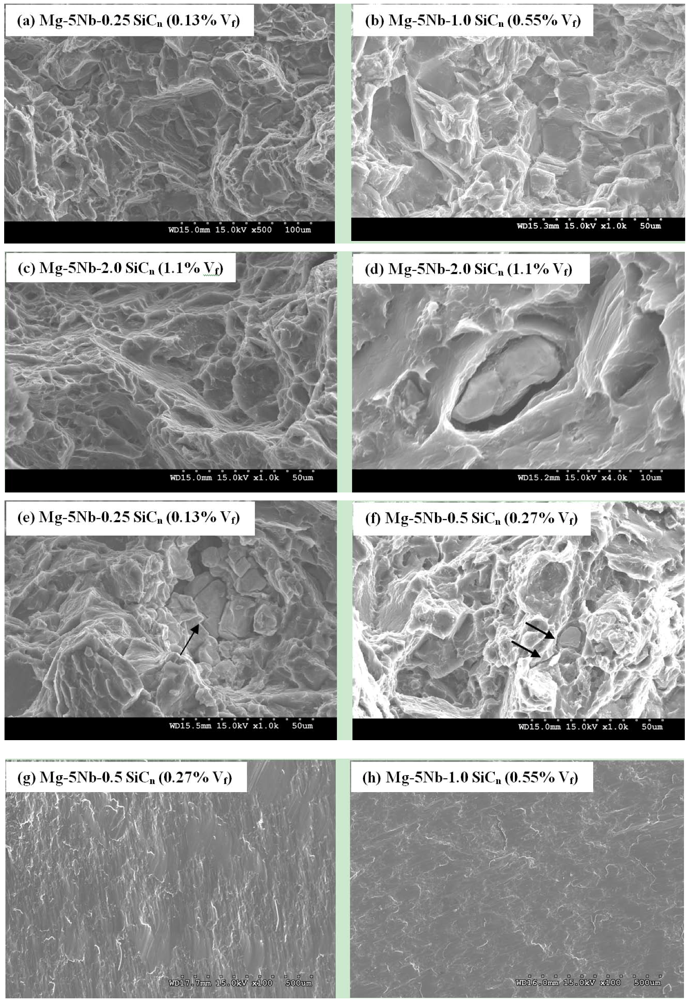
Figure 6.
Representative tensile fracture surfaces showing (a,b) Brittle fracture features in Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites with Vf: 0.13% and 0.55%; (c) regions showing ductile dimples in Mg-5Nb-2.0SiCn (1.1% Vf) composite; (d) particle debonding in of Mg-5Nb-2.0SiCn (1.1% Vf) composite; (e) crack extension into matrix around debonded Nb/SiCn clusters; (f) void coalescence around Nb-particle. Representative compressive fracture surfaces showing (g,h) dominant shear fracture.
Figure 6.
Representative tensile fracture surfaces showing (a,b) Brittle fracture features in Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites with Vf: 0.13% and 0.55%; (c) regions showing ductile dimples in Mg-5Nb-2.0SiCn (1.1% Vf) composite; (d) particle debonding in of Mg-5Nb-2.0SiCn (1.1% Vf) composite; (e) crack extension into matrix around debonded Nb/SiCn clusters; (f) void coalescence around Nb-particle. Representative compressive fracture surfaces showing (g,h) dominant shear fracture.
Based on the experimental results, it is observed that the addition of nano-sized SiC particles have significantly altered the mechanical properties of Mg-5Nb. The effect of SiCn volume fraction, processing, distribution of metallic and ceramic reinforcements and their inherent properties in influencing the mechanical behavior of the composites are discussed in the following sections.
2.3.1. Effect of SiCn Volume Fraction
From Table 3 and Table 4, it can be observed that the volume fraction of the reinforcement play an important role in determining the mechanical properties of the composites. As can be seen from the tables, for Vf ≤ 0.27%, the strength properties under both tensile and compressive loading conditions are either similar to or lower than that of pure Mg and Mg-5Nb composite. Considerable improvement in strength values (both yield strength and ultimate strength) are observed for Vf > 0.27%. These results indicate that there exists a minimum volume fraction of reinforcement that is required for strength improvement to occur.
Conventionally, composites are usually considered advantageous over the base matrix for the reason that they provide improved strength properties at both room and elevated temperatures. Most of the research works [23,24,25] have reported such behavior in Al- and Mg-based micron/nano-reinforced composites. On the other hand, several authors have reported the anomalous behavior of Al- andMg-composites, wherein the room temperature strength (ultimate strength) of the composites is lower than that of the base alloy [24,26,27,28], similar to those observed in the present case. This was attributed to various factors, such as the properties of the alloy matrix, critical volume fraction of reinforcement and residual stresses [24,25,27,28]. Friend [26] observed such a behavior in Al-MMCs with different alloy matrices. He observed that a critical volume fraction (Vcrit) should be exceeded for significant strength improvement to occur and that the composites with volume fraction less than Vcrit exhibited strength much lower than that of the unreinforced alloy. Further, it was suggested that the value of Vcrit depended largely on the matrix properties such as the ultimate tensile strength and yield strength, and the difference between them (rate of work-hardening), as it would affect the plastically induced load transfer [26]. Jayalakshmi et al. observed low room temperature properties of Mg-MMCs when compared to unreinforced alloy in tension [27], while Milliere and Suery reported such a behavior under compression in Al-MMCs [28].
In the current work, Mg-5Nb is the base material and based on the above-mentioned factors, it can be deduced that Vf ≤ 0.27% are too low (i.e., less than Vcrit) for any strength improvement to occur. Hence, due to low Vf and insufficient matrix-to-particle load transfer, failure occurs at low strengths and strains. In contrast, for Vf > 0.27%, significant strength enhancement is evident under tension as well as compression (both YS and US). The improvement in strength properties can be attributed to the following combined effects of: (i) grain refinement, given the finer grain size observed (Table 2), the increase in strength due to the piling up of dislocations at grain boundaries (Hall-Petch effect [29]); (ii) Orowan strengthening [29,30], that occurs due to the impeding of dislocation motion by the nanoparticles; (iii) increase in the dislocation density due to thermal mismatch (difference in thermal expansion coefficients of the reinforcements and Mg matrix) [19,21]; and (iv) effective load transfer from matrix to hard nanoparticles [9,30].
2.3.2. Effect of Processing
In the present work, the hot extrusion process carried out at temperatures greater than the recrystallization temperature has ensured fine and equi-axed grains. From Table 3 and Table 4, it can be seen that the tensile yield strength (TYS) is higher than that under compression (CYS), while the ultimate strength values are significantly high under compression (UCS) than under tension (UTS). This yield asymmetry between tension-compression is attributed to the extrusion process [31]. It should be noted that unlike f.c.c or b.c.c metals, the properties of h.c.p metals such as Mg, are strongly governed by texture (orientation of the grains). It is well-established that in contrast to the behavior observed in cast Mg-alloys, in extruded Mg-rods, the basal planes of the grains tend to strongly align parallel to the loading direction (i.e., c-axis of the grains is nearly perpendicular to the loading direction). This leads to the observed tension-compression yield asymmetry, and can be seen from the difference in the shape of the stress-strain curve [31]. As seen from Figure 5a, under tension, the high stress and low work hardening is slip-dominant, as twinning is not a favorable deformation process under tension [32]. Under compression, the significant work hardening observed is indicative of twinning and the evolution of crystallographic texture, that result in high compressive strength with large strains [33,34,35] (Figure 5b). A comparison between the shapes of the curves does not show much difference with increasing SiCn, indicating that the operating tensile/compressive deformation mechanisms does not change with increasing volume fraction.
2.3.3. Effect of Inherent Properties of Matrix/Metallic/Ceramic Reinforcements
The inherent properties of the matrix and the reinforcements largely determine the behavior of micro/nano composites. As discussed in the previous section, the inherent matrix properties such as yield strength, tensile strength and rate of work hardening determine the critical volume fraction of reinforcement required for property enhancement to occur at room temperature. Stronger and stiffer reinforcements (both metallic/ceramic) are considered to impart high hardness and high modulus, coupled with improved room and elevated temperature strength properties [23].
In the present work, micron-scale Nb is used as the metallic reinforcement which forms the base Mg-5Nb matrix for SiCn reinforcement. Nb metal is a ductile b.c.c. metal with relatively low mechanical properties. The yield and ultimate strengths of Nb (e.g. under tension) are ~175 MPa and 275 MPa respectively [36], which is similar to the properties of several commercial Mg-alloys [23]. However, Nb exhibits an extremely high room temperature ductility of ~50% [36]. Hence, the making of Mg-Nb metal–metal composite has improved the ductility but with little/no improvement in strength (Table 3 and Table 4). In contrast, SiC is one of the hardest materials, but possesses poor ductility (<2%). In most of the micron-SiC reinforced MMCs, high strength properties with poor ductility were observed [15,23]. While nano-sized particles are reported to have simultaneously improved both strength and ductility, most of them were based on nano-Al2O3 added to relatively brittle Mg-matrices [9,19,23]. In the current work, the addition of hard SiCn to a relatively softer Mg-5Nb has resulted in the lowering of ductility. While the inherent brittleness of SiC is a major controlling factor, other factors that contribute to reduced ductility include the distribution of reinforcing elements, interface properties and the formation of intermetallic phases.
2.3.4. Effect of Reinforcement Distribution and Intermetallic Formation
The distribution of both micro-Nb and nano-SiCn, as seen in Figure 2 and Figure 3, play an important role in influencing the mechanical properties of the Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites. The incorporation of SiCn particles has refined the grain size and has increased both the yield and ultimate strength for Vf > 0.27%. As discussed in Section 2.2, Nb particles though are distributed uniformly in the Mg-matrix, agglomeration/clustering are also observed. It should be noted that clustering is generally considered to aid in particle-to-particle load transfer [18] and increase the strength. However, unlike other hard metallic reinforcements in Mg, such as Ti or Cr [19,21], in the present case, the addition of softer Nb (with strength comparable to Mg) [36] does not contribute towards increasing the strength. In addition, the SiCn particles are also preferentially located on the Nb-agglomerates. A major drawback associated with such particle clustering is the tendency of the clusters to promote void nucleation/growth/coalescence [37]. This is due to the fact that the clustered particles are local regions with high volume fraction of particles with high stress concentration (‘particle local inhomogenity’ [16]), which can initiate voids on the application of loads. Hence, for uniform deformation to occur, the clusters at these local regions must activate more slip systems in the matrix to accommodate the same amount of deformation. This would result in the fracture/debonding of clusters at an early stage [38,39]. Such features (void coalescence/debonding) are observed in the tensile fractographs shown in Figure 6. Further, in the present case, the lack of interfacial chemical bonding (weak interface) between Nb and (Nb/SiCn) agglomerates with Mg, would also aid crack formation at the particle/matrix interface (Figure 6). In addition, the formation of brittle Mg2Si intermetallic phase, while increasing the mechanical properties, would also contribute to the reduction in the ductility [15] (Table 3 and Table 4).
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Processing
Mg-5Nb (Mg-turnings, Acros Organics, Singapore; Nb-powder of average particle size <10 μm, Prochem, Rockford Illinois) were used as the base materials to produce Mg-5Nb metal–metal composite. The Mg-5Nb composite was reinforced with 0.25 to 2 wt.% nano-SiC particles (average particle size ~50 nm, Nanostructured and Amorphous, US). The disintegrated melt deposition (DMD) technique which employs bottom pouring of the melt was used to produce the Mg-nanocomposites. The DMD technique adopts the simultaneous vortex stirring of the melt and its disintegration, with argon (Ar) gas for inert atmosphere and for melt disintegration, resulting in a high yield process which offers finer grain size [9]. The Ar gas was purged into the Mg-5Nb-nSiC molten metal at ~3 L/min at a super-heat temperature of ~750 °C, with intermittent stirring for 5 min. The melt was released through an orifice of diameter ~10 mm, situated at the bottom of the crucible and was disintegrated with two Ar gas jets maintained at ~25 L/min (oriented in the direction normal to the melt stream) before its deposition onto the steel mould.
Cylindrical billets of 36 mm diameter cut from the deposited ingots and soaked at ~400 °C for 1 h, were extruded at ~350 °C using a 150 ton hydraulic press at an extrusion ratio of 20.25:1 to produce rods of 8 mm diameter that were used for further characterizations.
3.2. Materials Characterization
Density measurements were performed on the extruded samples using the Archimedean Principle [2]. Microstructural characterization of finely polished and etched samples taken from the extruded rods were conducted using optical microscope (Olympus) and field emission scanning electron microscope (Hitachi FESEM-S4300) coupled with energy dispersion analysis (EDS). The grain size of the developed materials was determined using the Scion image analysis software. X-ray diffraction analyses were conducted on the samples using an automated Shimadzu LAB-XRD-6000 x-ray diffractometer (Cu, Kα; λ = 1.54056 Ǻ), with a scanning speed of ~2 min−1. Phase identification was carried out by matching the Bragg angle and the intensity of the peaks with the standard peaks of Mg, Al and other related phases.
Microhardness measurements were performed on polished flat specimens using a Shimadzu HMV automatic digital microhardness tester with a Vickers indenter (load: ~25 gf and dwell time: ~15 sec). More than ten measurements were performed for each specimen. Uniaxial tensile tests and compression tests were performed at room temperature using a Materials Test System (MTS 810). Tensile tests were conducted on smooth bar tensile specimens (ASTM Standard E8M-08) with diameter ~5 mm and gauge length ~25 mm, at a constant strain rate of ~1.69 × 10−4 s−1. A strain gauge (MTS extensometer) was used to measure the strain during the test. Compression tests were conducted on cylindrical samples of length ~8 mm and diameter ~8 mm (aspect ratio, l/d = 1) in accordance with ASTM E9-89a guidelines, at a constant strain rate of ~8.3 × 10−4 s−1. A minimum of 5 tests were conducted for each composition to obtain repeatable values. Fractographic analysis was performed using Hitachi FESEM-S4300.
4. Conclusions
Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites of varying SiCn volume fractions were produced using the disintegrated melt deposition technique. The composites after extrusion were evaluated for their microstructure and mechanical properties. The main results can be summarized as follows:
(i) The Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites produced by DMD technique provided sound castings with minimum porosity.
(ii) The addition of nano-size SiC reinforcements to the Mg-5Nb metal-metal composite altered the microstructure and resulted in fine and equi-axed grains. The presence of nano-sized reinforcements and the hot extrusion process contributed to the refinement in grains by providing sites for grain nucleation and inhibiting grain growth. The agglomeration/clustering of Nb and SiCn reinforcements observed in the microstructural analyses were attributed to chemical incompatibility between Mg and Nb.
(iii) The addition of SiCn significantly improved the hardness, which increased with increasing volume fraction.
(iv) Based on the tensile and compressive properties, the requirement of a critical volume fraction of SiCn was essential for strength improvement to occur. While Vf ≤ 0.27% SiCn resulted in lower/no improvement in strength when compared to pure Mg and Mg-5Nb, Vf > 0.27% exhibited remarkable improvements in both yield and ultimate strengths. Such dependency on reinforcement Vf was reportedly due to the inherent properties of the matrix (here Mg-5Nb).
(v) The improvement in tensile as well as compressive properties for Vf > 0.27% was attributed to various mechanisms, such as grain boundary strengthening, dislocation strengthening, increase in dislocation density due to thermal mismatch and activation of non-basal slip systems.
(vi) The difference in tensile and compressive yield strengths (tensile-compressive yield asymmetry) was identified due to the extrusion process. The behavior was attributed to the strong texture dependency on properties in extruded Mg-based materials.
(vii) The inherent properties of the matrix and the reinforcements (both micron-scale Nb and nano-scale SiC) played a major role in defining the mechanical properties.
(viii) The distribution of the Nb and SiCn reinforcements significantly controlled the mechanical behavior of the Mg-5Nb-SiCn composites. The agglomerated Nb/SiCn particles acted as stress raisers and initiated void nucleation at the particle/matrix interface, resulting in debonding and composite fracture at low strains.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the funding support given by Qatar National Research Foundation under Grant No: NPRP 08-424-2-171 and WBS No: R265-000-346-597, for carrying out this project.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Emley, E.F. Principles of Magnesium Technology; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Avedesian, M.M.; Baker, H. ASM Specialty Handbook: Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kainer, K.U. Metal Matrix Composites: Custom Made Materials for Automotive and Aerospace Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, D.J. Particle reinforced aluminium and magnesium matrix composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 1994, 39, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.Z.; Liu, X.Y. Review of recent studies in magnesium matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 6153–6171. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.F.; Gupta, M. Development of ductile magnesium composite materials using titanium as reinforcement. J. Alloys Compounds 2002, 345, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.L.E.; Gupta, M. Enhancing thermal stability, modulus and ductility of magnesium using molybdenum as reinforcement. Advan. Eng. Mater. 2005, 7, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, M.; Jayaramanavar, P.; Vyas, V; Seenivasan, D.V.S.; Gupta, M. Effect of niobium particulate addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of pure magnesium. J. Alloys Compounds 2012, 513, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.F.; Gupta, M. Effect of different types of nano-size oxide particulates on microstructural and mechanical properties of elemental Mg. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieringa, H. Properties of magnesium alloys reinforced with nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes—A review. J Mater Sci. 2011, 46, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.S.; Wei, J.; Lee, L.C.; Gupta, M. Simultaneous enhancement in strength and ductility by reinforcing magnesium with carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 423, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.K.; Joshi, S.P.; Gupta, M. Hierarchical magnesium nano-composites for enhanced mechanical response. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6104–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.K.; Balasubramanian, K.; Gupta, M. Microwave synthesis and characterization of magnesium based composites containing nanosized SiC and hybrid (SiC+Al2O3) reinforcements. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2007, 129, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Hu, Z. Preparation and mechanical properties of nano-SiCp/Mg composites by ultrasonic dispersion. Advan. Mater. Res. 2010, 150–151, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Lai, M.O.; Saravanaranganathan, D. Synthesis, microstructure and properties characterization of disintegrated melt deposition Mg/SiC composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tszeng, T.C. The effects of particle clustering on the mechanical behavior of particle reinforced composites. Composites B 1998, 29B, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R. Reinforcement selection for MMCs based on Wetting information. In Proceedings of the International Conference on High Temperature Capillarity, Cracow, Poland, 29 June–2 July 1997.
- Ahmed, S.; Jones, F.R. Particulate agglomeration and the residual stress state on the modulus of filled resin Part I1: Moduli of untreated sand and glass bead filled composites. Composites 1990, 21, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Gupta, M. Effect of ball milling the hybrid reinforcements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-(Ti+n-Al2O3) composites. J. Alloys Compounds 2011, 509, 7229–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.F. Mg-Nb (magnesium-niobium) binary alloy phase diagrams. In ASM Alloy Phase Diagrams Center, II; Massalski, T.B., Ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990; Volume 3, p. 2526. [Google Scholar]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Gupta, M. Effect of Cr addition and carbon dioxide incorporation during processing on the microstructural and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksiazek, M.; Sobczak, N.; Mikulowski, B; Radziwill, W.; Surowiak, I. Wetting and bonding strength in Al/Al2O3 system. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 324, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Nai, S.M.L. Magnesium, Magnesium alloys and Magnesium Composites; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Purazrang, K.; Kainer, K.U.; Mordike, B.L. Fracture toughness behaviour of a magnesium alloy metal-matrix composite produced by the infiltration technique. Composites 1991, 22, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musson, N.J.; Yue, T.M. The effect of matrix composition on the mechanical properties of squeeze-cast aluminium alloy-Saffil metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 135, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, C.M. The effect of temperature on the tensile strength of short &alimna fiber/aluminium alloy metal matrix composites. Scr. Metall. 1989, 23, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Kailas, S.V.; Seshan, S.; Fleury, E. Properties of squeeze cast Mg-6Zn-3Cu alloy and its saffil alumina short fibre reinforced composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 3743–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliere, C.; Suery, M. Fabrication and properties of metal matrix composites based on SiC fibre reinforced aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1988, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, G.E. Mechanical Metallurgy; McGraw-Hill: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, V.H. Magnesium Nanocomposites: Current Status and Prospects for Army Applications. Report. Army Research Laboratory: Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG), MD, USA; September 2011, ARL-TR-5728.
- Reed-Hill, R.E. Role of deformation twinning in determining the mechanical properties of metals. In The Inhomogeneity of Plastic Deformation; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1973; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, M.R. Twinning and the ductility of magnesium alloys: Part I: “Tension” twins. Mate. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 464, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, S.R.; Mehrotra, P.; Lillo, T.M.; Stoica, G.M.; Liaw, P.K. Texture evolution of five wrought magnesium alloys during route A equal channel angular extrusion: Experiments and simulations. Acta. Mater. 2005, 53, 3135–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, M.; Levinson, A.; Harris, R.; Mishra, R.K.; Doherty, R.D.; Kalidindi, S.R. Deformation twinning in AZ31: Influence on strain hardening and texture evolution. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6230–6242. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Huang, J.C. The role of twinning and untwinning in yielding behavior in hot-extruded Mg-Al-Zn alloy. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanical Properties of Niobium and alloys versus temperature, Materials Data Sheet. Cabot Corporation Homepege, Boyertown, PA, USA. Available online: http://www.cabot-corp.com (accessed on 27 April 2012).
- Bauri, R.; Surappa, M.K. Processing and properties of Al-Li-SiCp composites. Sci. Technol. Advan. Mater. 2007, 8, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Kim, H.M.; Huh, D.; Suryanarayana, C.; Chun, B.S. Effect of clustering on the mechanical properties of SiC particulate-reinforced aluminum alloy 2024 metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 347, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, R.J.; Shi, N.; Feng, C.R.; Wang, L. Localized deformation of SiC-Al composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 131, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
