Characterisation of an Advanced Nickel Based Superalloy Post Cold Work by Swaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alloy Preparation
2.2. Metallography
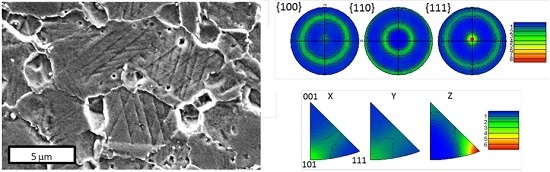
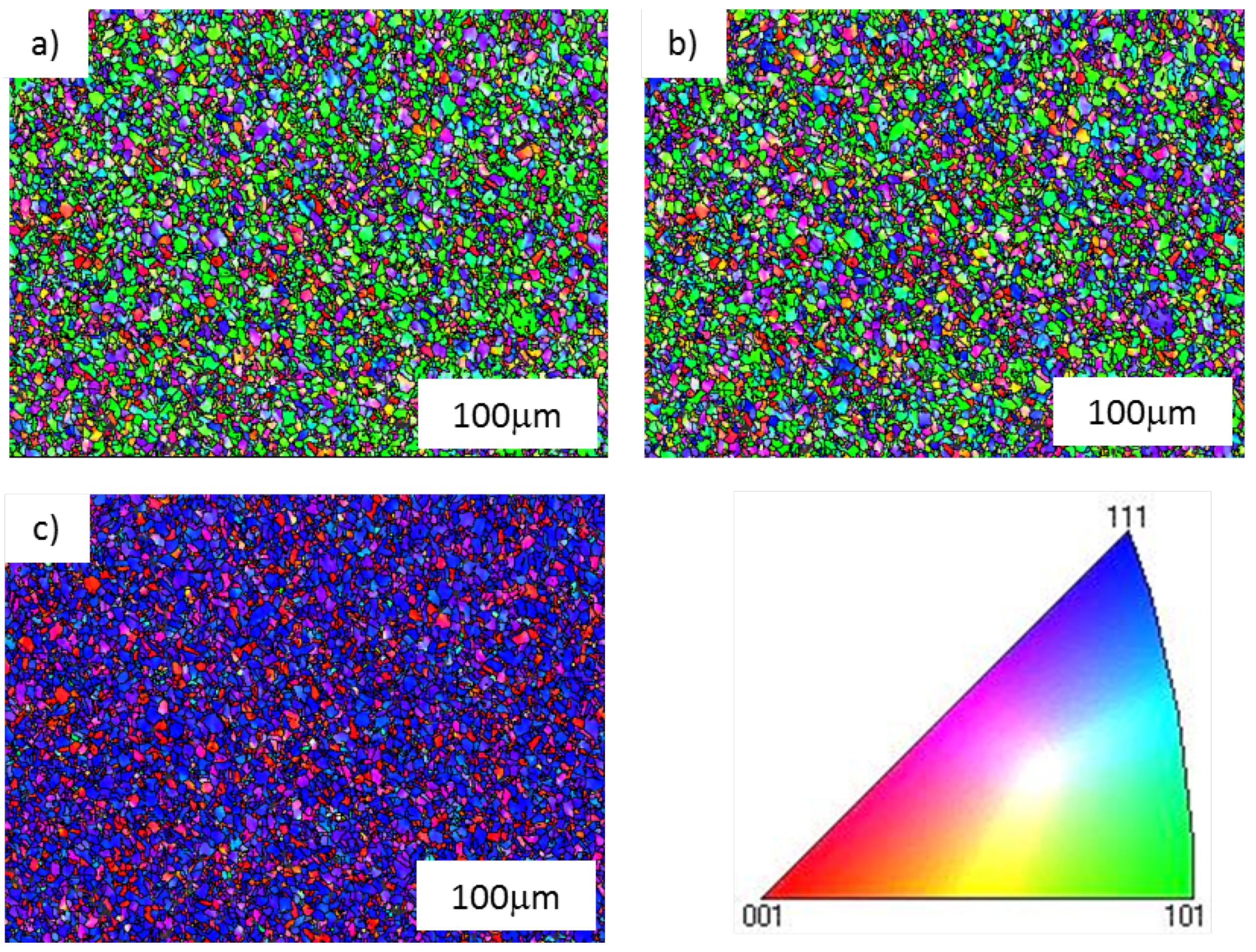
2.3. Micro-Texture Analysis
2.4. Residual Stress Measurements
3. Mechanical Properties
3.1. Micro-Hardness
3.2. Monotonic Tension
3.3. Fractography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
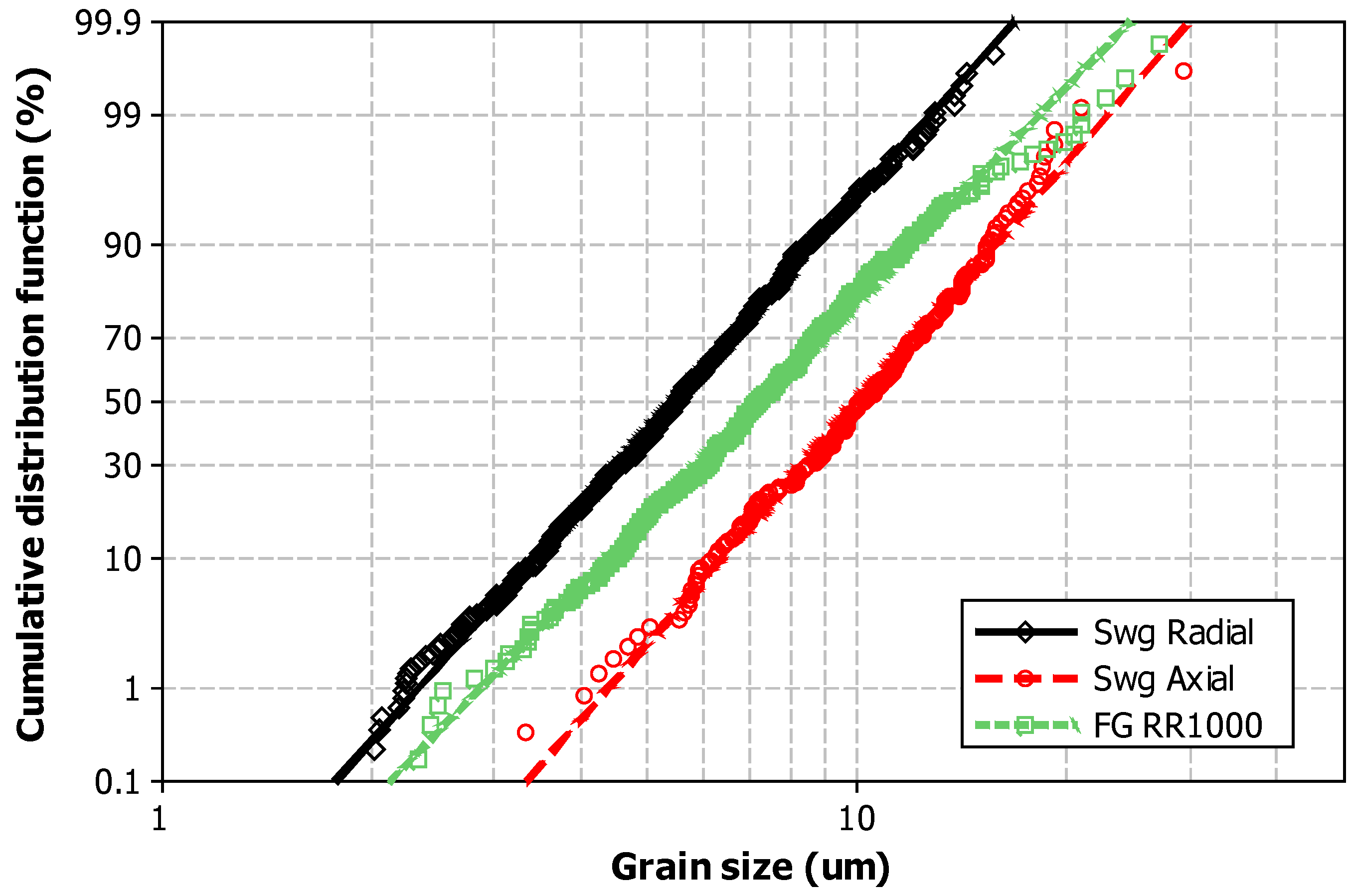
- The swaging process considerably deforms the microstructure of RR1000. The grain size was reduced from 7.8 μm to 5.7 μm in the radial direction, whilst increased and elongated in the axial direction (to a maximum grain Feret dimension of 8.9 μm).
- A relatively strong {111} fibre texture was induced parallel to the axial direction, along with a high level of intra-granular slip deformation.
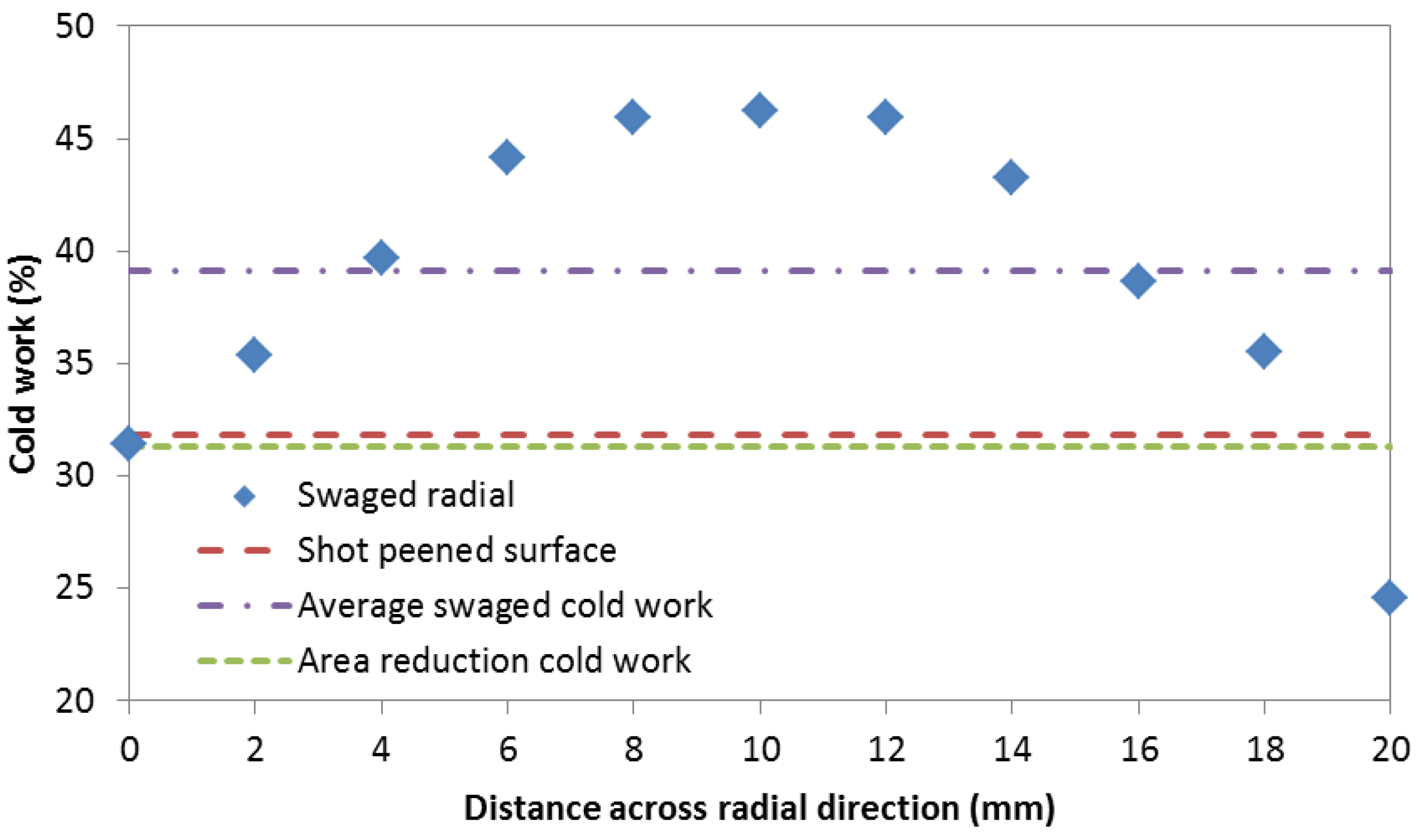
- The cold work imparted to the swaged RR1000 varied between 25.6% (at the surface) and 46.2% (in the centre). Micro-hardness correlated well with the degree of cold work. The levels of residual stress throughout the bulk of the swaged material were considerably lower to those typical of shot peened surfaces.
- Tensile testing generally showed increased ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield strength over non-swaged RR1000, but also resulted in reduced ductility. There was a considerable debit in ductility between room temperature and 500 °C before ductility then recovered at higher temperatures, thought to be through a dynamic strain ageing process.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, A.; Kim, S.-B.; Shackleton, J.; Bruno, G.; Preuss, M.; Withers, P.J. Relaxation of residual stress in shot peened Udimet 720Li under high temperature isothermal fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 2005, 27, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, D. Effects of plastic straining on residual stresses induced by shot-peening. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Shot Peening (ICSP3), Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, September 1987; Wohlfahrt, H., Kopp, R., Vöhringer, O., Eds.; DGM Informationsgesellschaft Verlag: Oberursel, Germany, 1987; pp. 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, N.; Watanabe, Y.; Kato, Y. Effect of shot peening on fatigue strength of carbon steel at elevated temperature. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Shot Peening Pre-Prints, Oxford, UK, 13–17 September 1993; pp. 134–139.
- Mitchell, R.J.; Hardy, M.C.; Preuss, M.; Tin, S. Development of γ′ Morphology in P/M Rotor Disc Alloys During Het Treatment; Green, K.A., Pollack, T.M., Harada, H., Howson, T.E., Reed, R.C., Shira, J.J., Watson, S., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Withers, P.J.; Axinte, D.; Preuss, M.; Andrews, P. Residual stresses in face finish turning of high strength nickel-based superalloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4896–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dai, S.; Chen, F.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Influence of cold rolling and ageing treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-30Nb-5Ta-6Zr alloy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 27, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayati, A.; Najafizadeh, A.; Kermanpur, A.; Forouzan, F. The effect of cold rolling regime on microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 304L stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewary, N.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Bera, S.; Chakrabarti, D.; Chatterjee, S. Influence of cold rolling on microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of low carbon high Mn TWIP steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Cao, W.; Dong, H. Effects of cold rolling reduction on retained austenite fraction and mechanical properties of high-Si TRIP steel. Int. J. Iron Steel Res. 2013, 20, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeya, R.; Nagarjuna, S.; Sarma, D.S. Effect of prior cold work on age hardening of Cu-3Ti-1Cr alloy. Mater. Charact. 2006, 57, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulstaar, M.A.; El-Danaf, E.A.; Waluyo, N.S.; Wagner, L. Severe plastic deformation of commercial purity aluminium by rotary swaging: Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlu, N.; Caliskan, N.K.; Bor, S. Effect of swaging on microstructure and tensile properties of W-Ni-Fe alloys. Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 2014, 42, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, A.; Rao, B.P.C.; Mahadevan, S.; Parameswaran, P.; Jayakumar, T.; Raj, B. Nondestructive assessment of tensile properties of cold worked AISI type 304 stainless steel using nonlinear ultrasonic technique. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.G.; Lee, S.B. The tensile and low-cycle fatigue behavior of cold worked 316L stainless steel: Influence of dynamic strain aging. Int. J. Fatigue 2004, 26, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.G.; Lee, S.B. Mechanism of dynamic strain aging and characterization of its effect on the low-cycle fatigue behaviour in type 316L stainless steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 340, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, G.E. Mechanical Metallurgy. In Materials Science and Metallurgy; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ševčík, A. High temperature strength analysis of low carbon steels in the as-cast state. Metalurgija 2005, 44, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
















| RR1000 | Co | Cr | Mo | Ti | Al | Ta | Hf | Zr | C | B | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | 18.5 | 15 | 5 | 3.6 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 0.027 | 0.015 | Balance |
| Sample | No. of Grains Measured | Average Grain Size (μm) | Feret Diameter (μm) | ASTM Class | Feret Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre Swage | 191 | 8 | 8 | 11.1 | 1.03 |
| Post Swage radial | 240 | 6 | 6 | 12.0 | 1.07 |
| Post Swage axial | 200 | 9 | 11 | 10.7 | 1.19 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bache, M.R.; O’Hanlon, J.; Withers, P.J.; Child, D.J.; Hardy, M.C. Characterisation of an Advanced Nickel Based Superalloy Post Cold Work by Swaging. Metals 2016, 6, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030054
Bache MR, O’Hanlon J, Withers PJ, Child DJ, Hardy MC. Characterisation of an Advanced Nickel Based Superalloy Post Cold Work by Swaging. Metals. 2016; 6(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleBache, Martin R., James O’Hanlon, Philip J. Withers, Daniel J. Child, and Mark C. Hardy. 2016. "Characterisation of an Advanced Nickel Based Superalloy Post Cold Work by Swaging" Metals 6, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030054
APA StyleBache, M. R., O’Hanlon, J., Withers, P. J., Child, D. J., & Hardy, M. C. (2016). Characterisation of an Advanced Nickel Based Superalloy Post Cold Work by Swaging. Metals, 6(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030054