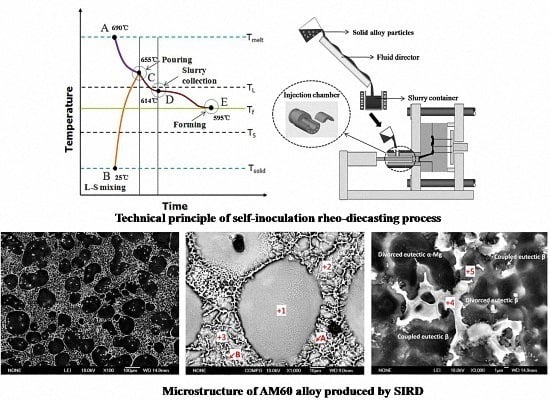
Rheo-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AM60 Alloy Produced by Self-Inoculation Rheo-Diecasting Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Slurry Preparation Procedure
2.2. Rheo-Diecasting Procedure
2.3. Microstructure Analysis and Tensile Testing
3. Results and Discussion
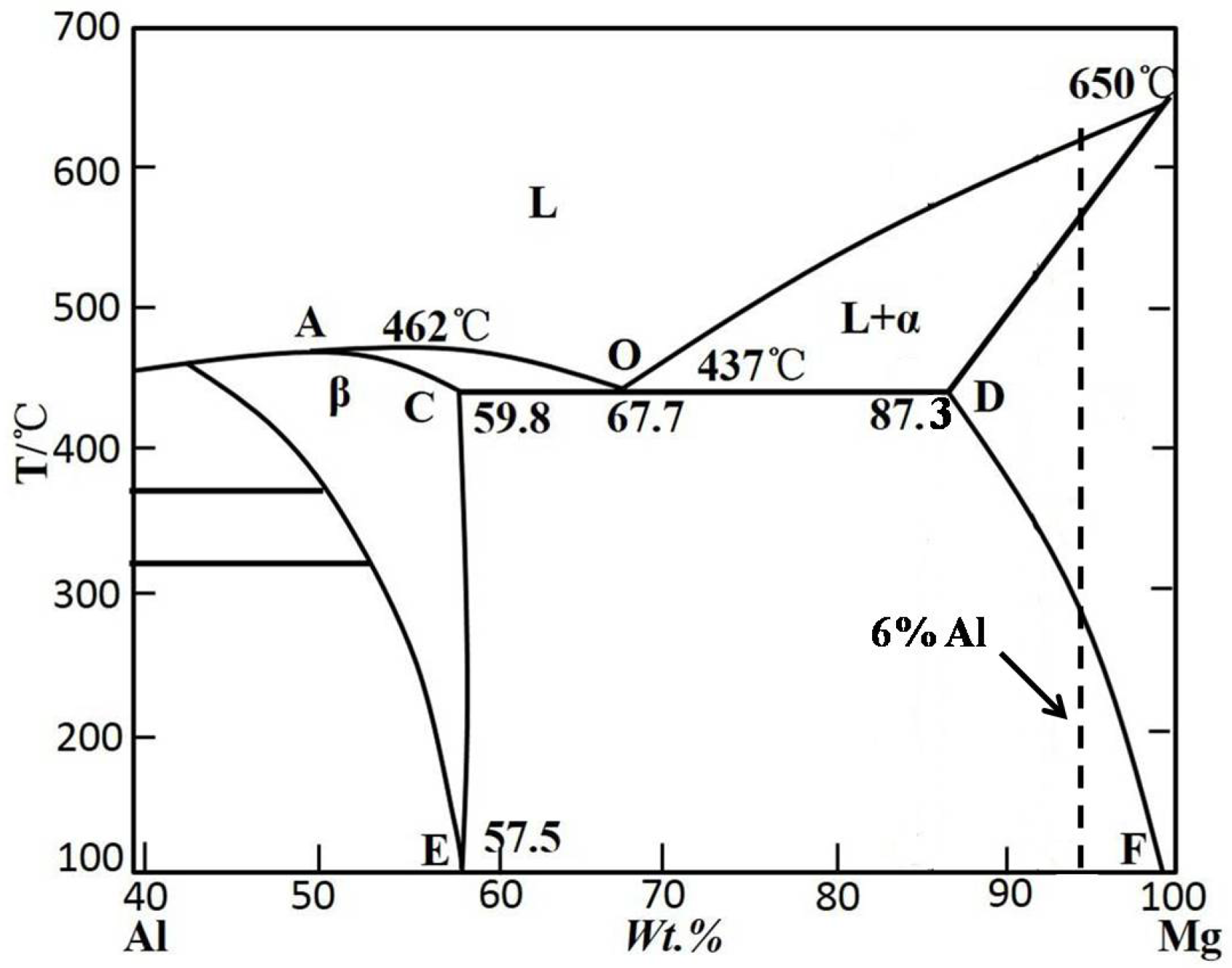
3.1. Preparation of Semisolid AM60 Alloy by Self-Inoculation Process
3.2. Microstructural Characteristics and Solidification of AM60 Slurry in SIRD Process
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Rheo-Diecasting AM60 Alloy
4. Conclusions
- (1).
- The slurry of AM60 alloy contains refined and irregular α-Mg particles produced with the self-inoculation pouring method, which evolves to a globular and coarse texture when continuously keeping the slurry in semisolid state at 595 °C;
- (2).
- The microstructure of the SIRD AM60 sample was dominated by fine primary α-Mg globules and less tiny dendrites in liquid matrix while the sample from conventional liquid die casting presents as porous dendrites;
- (3).
- Solidification of the remaining liquid in the die cavity in SIRD occurred in three stages, α-Mg nucleation and growth on primary α-Mg phase which had formed during slurry preparation, α-Mg nucleated independently in liquid, and finally formation of skeleton devoiced eutectic. This solidification is substantially in a non-equilibrium state and resulted in Al segregation in the eutectic mixture;
- (4).
- The SIRD process provides products with increased tensile strength and elongation compared to liquid die casting due to the reduced degree of porosity and hot tearing.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curle, U.A.; Moller, H.; Wilkins, J.D. Shape rheocasting of high purity aluminium. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janudom, S.; Wannasin, J.; Basem, J.; Wisutmethangoon, S. Characterization of flow behavior of semisolid slurries containing low solid fractions in high-pressure die casting. Acta. Mater. 2013, 61, 6267–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Kang, Y.L.; Qi, M.F.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhu, G.M. R-HPDC Process with Forced Convection Mixing Device for Automotive Part of A380 Aluminum Alloy. Materials 2014, 7, 3084–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Qian, M.; Ji, S.; Fan, Z. The effects of rheo-diecasting on the integrity and mechanical properties of Mg–6Al–1Zn. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, D.H. Semisolid metal processing. Int. Mater. Rev. 1994, 39, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, M.; Cai, J. AlSi9Mg aluminum alloy semisolid slurry preparation by intermediate frequency electromagnetic oscillation process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 215, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z. Development of the rheo-diecasting process for magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 413, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.F.; Kang, Y.L.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, G.M.; Liao, W.N. Comparison of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ91D Alloy Formed by Rheomolding and High-Pressure Die Casting. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 3826–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorstad, J.L.; Thieman, M.; Kamm, R. Fundamental Requirements for Slurry Generation in the Sub-Liquidus Casting Process and the Economics of SLC Processing. In Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Semi-Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites, Limassol, Cyprus, 21–23 September 2004.
- Martinez, R.A. Formation and Processing of Rheocast Microstructure. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Boston, MA, USA, September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.S.; Lv, S.L.; An, P.; Nakae, H. Microstructure and property of rheocasting aluminum-alloy made with indirect ultrasonic vibration process. Mater. Lett. 2012, 73, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canyook, R.; Wannasin, J.; Wisuthmethangkul, S.; Flemings, M.C. Characterization of the microstructure evolution of a semisolid metal slurry during the early stages. Acta. Mater. 2012, 60, 3501–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D. Novel processing methods and mechanisms to control the cast microstructure in Al based alloys—390 and wrought alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester, MA, USA, May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Findon, M.M. Semi-solid slurry formation via liquid metal mixing. Master’s Thesis, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester, MA, USA, July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H. Binary Alloys Phase Diagram; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, B.; Li, Y.D.; Ma, Y.; Chen, T.J.; Hao, Y. Preparation of non-dendritic microstructure of AM60 alloy for rheo-forming using self-inoculation method. Int. J. Cast. Metal. Res. 2012, 25, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.M.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.J. Effects of Solid-Liquid Mixing on Microstructure of Semi-Solid A356 Aluminum Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 2014, 45, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.G.; Cao, F.R.; Chen, L.Q.; Li, J.P.; Wang, C. Dynamical solidification behaviors and microstructural evolution during vibrating wavelike sloping plate process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 2592–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.C. Coarsening in solidification processing. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, S.; Salvo, L.; Suery, M.; Dahle, A.K.; Boller, E. Coarsening mechanisms in a dendritic Al–10% Cu alloy. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Atkinson, H.V. Microstructural coarsening of 7005 aluminum alloy semisolid billets with high solid fraction. Mater. Charact. 2014, 90, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Roberts, K.; Fan, Z. Isothermal coarsening of fine and spherical particles in semisolid slurry of Mg–9Al–1Zn alloy under low shear. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhen, Z.; Fan, Z. Effects of rheo-die casting process on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AM50 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2005, 21, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, Z.T.; Li, T.J.; Cockcroft, S. Research on microstructures of sub-rapidly solidified AZ61 magnesium alloy. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wessen, M.; Granath, O. Effect of injection velocity on porosity formation in rheocast Al component using rheometal process. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 2010, 23, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Position | Mg | Al | Mn | Zn | O | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94.73/93.98 | 1.81/1.62 | 0.34/0.155 | 0.4/0.15 | 2.7/4.11 | 100 |
| 2 | 94.6/94.2 | 1.9/1.7 | 0.52/0.23 | 0.56/0.21 | 2.42/3.66 | 100 |
| 3 | 91.59/90.09 | 2.83/2.51 | 0.39/0.17 | 0.46/0.17 | 4.72/7.06 | 100 |
| 4 | 60.37/60.24 | 31.1/27.96 | 0.26/0.11 | 0.76/0.28 | 7.52/11.4 | 100 |
| 5 | 83.85/82.76 | 11.02/9.8 | 0.24/0.1 | -/- | 4.89/7.33 | 100 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, B.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Hu, G.; Tang, C. Rheo-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AM60 Alloy Produced by Self-Inoculation Rheo-Diecasting Process. Metals 2016, 6, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030069
Xing B, Li Y, Feng J, Hu G, Tang C. Rheo-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AM60 Alloy Produced by Self-Inoculation Rheo-Diecasting Process. Metals. 2016; 6(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Bo, Yuandong Li, Junyan Feng, Guangshan Hu, and Chengli Tang. 2016. "Rheo-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AM60 Alloy Produced by Self-Inoculation Rheo-Diecasting Process" Metals 6, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030069
APA StyleXing, B., Li, Y., Feng, J., Hu, G., & Tang, C. (2016). Rheo-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AM60 Alloy Produced by Self-Inoculation Rheo-Diecasting Process. Metals, 6(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6030069