Utilization of a Porous Cu Interlayer for the Enhancement of Pb-Free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Joint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Material Selection
2.2. Joining Procedure and Soldering Process Set Up
2.3. Joint Strength Analysis
2.4. Microstructural Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Verification of Porosity Percentage
3.2. Effect of Porous Cu Interlayer Addition on Joint Strength
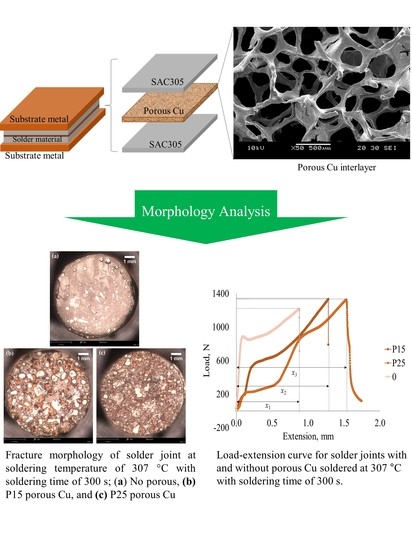
3.3. Effect of Porous Cu Interlayer Addition on Fracture Behaviour
3.3.1. Fractured Surface
3.3.2. Cross-Sectional Analysis
3.4. Interfacial Structure Analysis
3.5. Measurement of IMC Thickness
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The joint strength of the Pb-free SAC305 solder joint with the addition of porous Cu interlayer generally increased alongside with increasing soldering time and temperature.
- (2)
- The highest strength for the solder joint with P25 porous Cu addition was recorded at 51 MPa, at soldering time of 180 s and temperature of 307 °C, whereas the 54 MPa highest strength was achieved with P15 porous Cu addition at 300 s with 307 °C.
- (3)
- For solder joints without porous Cu, fracture occured along the interface of solder alloy and Cu substrate. In the case of solder joints soldered with P15 and P25 porous Cu interlayer, fractures occured at three regions, namely at the interface of solder and porous Cu interlayer, inside the porous Cu interlayer as well as inside the solder itself.
- (4)
- Microstructural analysis at the interfacial regions revealed the IMC phase at the SAC305/Cu substrate interface to have a scallop-liked configuration. With addition of porous Cu, both typical scallop-shaped as well as more uniform and continuous layers of IMC phases were observed. The typical scallop-liked configurations were more dominant for the solder joint with P15 porous Cu at the SAC305/P15 porous Cu interface, whereas the latter phase appeared to be more prominent for the solder joint with P25 porous Cu at the SAC305/P25 porous Cu interface.
- (5)
- The IMC layer at the interface of solder alloy and Cu substrate of all specimens was thicker than that at the interface of solder alloy and porous Cu. The IMC layers at these two regions also increased with soldering temperature. The uneven contact area at the interface of porous Cu and solder alloy resulted in the formation of a less pronounced IMC layer.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suganuma, K. The Current Status of Lead-Free Soldering. ESPEC Technol. Rep. 2002, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chidambaram, V.; Hattel, J.; Hald, J. High-temperature lead-free solder alternatives. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawah, D.A.; Said, S.B.M.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Che, F.X. High-Reliability Low-Ag-Content Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Joints for Electronics Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 2631–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.F.M.; Shnawah, D.A.; Badruddin, I.A.; Said, S.B.M.; Che, F.X.; Ariga, T. Microstructural stability of Sn-1Ag-0.5Cu-xAl (x = 1, 1.5, and 2 wt. %) solder alloys and the effects of high-temperature aging on their mechanical properties. Mater. Charact. 2013, 78, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuste, C.; Hodaj, F.; Petit, L. Solid state interaction between a Sn-Ag-Cu-In solder alloy and Cu substrate. Intermetallics 2013, 36, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.D.; Gao, Y.L.; Yang, B.; Xia, X.Z.; Zhai, Q.J.; Andersson, C.; Liu, J. Nanoparticles of the Lead-free Solder Alloy Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu with Large Melting Temperature Depression. J. Electron. Mater. 2008, 38, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayle, F.W.; Becka, G.; Badgett, J.; Whitten, G.; Pan, T.; Grusd, A.; Bauer, B.; Lathrop, R.; Slattery, J.; Anderson, I.; et al. High Temperature Lead-Free Solder for Microelectronics. JOM 2001, 53, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Gao, F.; Nishikawa, H.; Takemoto, T. Interaction behavior between the additives and Sn in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-based solder alloys and the relevant joint solderability. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 472, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, K.; Kim, S.; Kim, K. High-Temperature Lead-Free Solders: Properties and Possibilities. JOM 2009, 61, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellvarajoo, S.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Samsudin, Z. Effects of Fe2NiO4 nanoparticles addition into lead free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder pastes on microstructure and mechanical properties after reflow soldering process. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellvarajoo, S.; Abdullah, M.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Pb-free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder pastes added with NiO nanoparticles after reflow soldering process. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lee, N.-C.; Bachorik, P. An innovative composite solder preform for TLP bonding—Microstructure and properties of die attach joints. Electron. Packag. Technol. Conf. EPTC 2013 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadia, A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A. Effects of addition of copper particles of different size to Sn-3.5Ag solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 23, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degischer, H.P.; Kriszt, B. Handbook of Cellular Metals: Production, Processing, Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, T.; Tao, W.; Lu, T. Experimental study of air natural convection on metallic foam-sintered plate. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 38, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.F.; Zhang, H.W.; Li, Y.X. Heat transfer performance of lotus-type porous copper heat sink with liquid GaInSn coolant. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 80, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zheng, C.; Lou, H.; Sui, R. Bonding of silicon nitride ceramics using Fe-Ni/Cu/Ni/Cu/Fe-Ni interlayers. Mater. Lett. 2001, 47, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharinie, T.; Moshwan, R.; Yusof, F.; Hamdi, M.; Ariga, T. Vacuum brazing of sapphire with Inconel 600 using Cu/Ni porous composite interlayer for gas pressure sensor application. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamadon, N.H.; Miyashita, Y.; Yusof, F.; Hamdi, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Ariga, T. Formation behaviour of reaction layer in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder joint with addition of porous Cu interlayer. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 61, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-S.; Chung, C.-H.; Lee, M.-T.; Chiang, S.-B.; Wong, C.-C.; Wang, C.-C. An experimental study on the heat dissipation of LED lighting module using metal/carbon foam. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 48, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakpan, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Mutoh, Y.; Inoue, S.; Nagata, K.; Kodani, K. Creep-Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior of Pb-Containing and Pb-Free Solders at Room and Elevated Temperatures. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 2463–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewsey, D.J.; Zhao, Y.Y. Thermal conductivity of porous copper manufactured by the lost carbonate sintering process. Phys. Status Solidi 2008, 205, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, K.; Bock, J.; Jacobi, A.M. Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of Metal Foam Heat Exchangers. Available online: http://docs.lib.purdue.edu/iracc/1283 (accessed on 7 September 2016).
- Afendi, M.; wan Nordin, W.N.; Daud, R.; Tokuo, T. Strength and Fracture Characteristics of Shear Adhesive Dissimilar Joint. In Proceedings of the International Conference On Applications and Design in Mechnaical Engineering 2012, Penang, Malaysia, 27–28 February 2012.
- Kim, K.S.; Huh, S.H.; Suganuma, K. Effects of fourth alloying additive on microstructures and tensile properties of Sn-Ag-Cu alloy and joints with Cu. Microelectron. Reliab. 2003, 43, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, A.A.; Zhu, Y.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Joining ceramics to metals using metallic foam. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of Zn addition in Sn-rich alloys on interfacial reaction with Au foils. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daly, A.A.; Fawzy, A.; Mohamad, A.Z.; El-Taher, A.M. Microstructural evolution and tensile properties of Sn-5Sb solder alloy containing small amount of Ag and Cu. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 4574–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daly, A.A.; Hammad, A.E. Development of high strength Sn-0.7Cu solders with the addition of small amount of Ag and In. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 8554–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, P.J.; Kim, J.S. Are intermetallics in solder joints really brittle? Proc. Electron. Compon. Technol. Conf. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattner, U.R. Phase diagrams for lead-free solder alloys. JOM 2002, 54, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, H.; Nurulakmal, M.S.; Arezodar, A.F.; Abdullah, J. Effect of iron and indium on IMC formation and mechanical properties of lead-free solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 553, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cao, Y.; Joo, S.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Li, M. Cu6Sn5 precipitation during Sn-based solder/Cu joint solidification and its effects on the growth of interfacial intermetallic compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 582, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.; Das, D.; Osterman, M.; Pecht, M. Thermal cycling reliability of lead-free solders (SAC305 and Sn3.5Ag) for high-temperature applications. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2011, 11, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.T.; Tan, A.W.; Yusof, F. Influence of nanoparticle addition on the formation and growth of intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in Cu/Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu solder joint during different thermal conditions. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 033505. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.M.L.; Yu, D.Q.; Law, C.M.T.; Wang, L. Properties of lead-free solder alloys with rare earth element additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 44, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Solder Alloy | Cu | Ag | Bi | Fe | As | Ni | Pb | Sb | Sn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu | 0.516 | 3.083 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.022 | 0.015 | Bal. |
| Solder Alloy | Melting Temperature, °C | Tensile Strength, MPa | Young Modulus, MPa | Hardness, HV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu | 217 | 50.6 | 54 | 13.3 |
| Parameters | Setting Value |
|---|---|
| Soldering temperature, °C | 267, 287, 307 |
| Soldering time, s | 60, 180, 300 |
| Porous Cu | 0, P15, P25 |
| Point | Element (at. %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Sn | Phase | |
| A | 55.17 | 44.6 | Cu6Sn5 |
| B | 55.41 | 44.41 | Cu6Sn5 |
| C | 67.19 | 32.77 | Cu3Sn |
| D | 56.71 | 43.16 | Cu6Sn5 |
| E | 72.33 | 27.67 | Cu3Sn |
| F | 55.42 | 44.5 | Cu6Sn5 |
| G | 63.4 | 36.32 | Cu3Sn |
| H | 56.35 | 43.12 | Cu6Sn5 |
| I | 66.25 | 33.5 | Cu3Sn |
| Soldering Temperature, °C | IMC Thickness, µm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Porous | P15 | P25 | |||
| SAC/Cu | SAC/Porous | SAC/Cu | SAC/Porous | ||
| 267 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 4.6 | 3.9 |
| 287 | 5.0 | 4.8 | 4.1 | 5.5 | 4.4 |
| 307 | 6.4 | 6.5 | 4.9 | 6.8 | 4.5 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamadon, N.H.; Tan, A.W.; Yusof, F.; Ariga, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Hamdi, M. Utilization of a Porous Cu Interlayer for the Enhancement of Pb-Free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Joint. Metals 2016, 6, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6090220
Jamadon NH, Tan AW, Yusof F, Ariga T, Miyashita Y, Hamdi M. Utilization of a Porous Cu Interlayer for the Enhancement of Pb-Free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Joint. Metals. 2016; 6(9):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6090220
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamadon, Nashrah Hani, Ai Wen Tan, Farazila Yusof, Tadashi Ariga, Yukio Miyashita, and Mohd Hamdi. 2016. "Utilization of a Porous Cu Interlayer for the Enhancement of Pb-Free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Joint" Metals 6, no. 9: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6090220
APA StyleJamadon, N. H., Tan, A. W., Yusof, F., Ariga, T., Miyashita, Y., & Hamdi, M. (2016). Utilization of a Porous Cu Interlayer for the Enhancement of Pb-Free Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Joint. Metals, 6(9), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6090220