Abstract
The coating of hollow alumino-silicate microspheres or cenospheres with thin layers of Cu by means of vibration-assisted magnetron sputtering yields a starting material with considerable potential for the production of new types of metal matrix syntactic foams as well as optimized variants of conventional materials of this kind. This study introduces the coating process and the production of macroscopic samples from the coated spheres via spark plasma sintering (SPS). The influence of processing parameters on the coating itself, and the syntactic foams are discussed in terms of the obtained density levels as a function of sintering temperature (which was varied between 850 and 1080 °C), time (0.5 to 4 min), and surface appearance before and after SPS treatment. Sintering temperatures of 900 °C and above were found to cause breaking-up of the homogeneous sputter coating into a net-like structure. This effect is attributed to wetting behavior of Cu on the alumino-silicate cenosphere shells. Cylindrical samples were subjected to conductivity measurements and mechanical tests, and the first performance characteristics are reported here. Compressive strengths for Cu-based materials in the density range of 0.90–1.50 g/cm3 were found to lie between 8.6 and 61.9 MPa, depending on sintering conditions and density. An approximate relationship between strength and density is suggested based on the well-known Gibson–Ashby law. Density-related strength of the new material is contrasted to similar findings for several types of established metal foams gathered from the literature. Besides discussing these first experimental results, this paper outlines the potential of coated microspheres as optimized filler particles in metal matrix syntactic foams, and suggests associated directions of future research.
1. Introduction
Metal-matrix syntactic foams (MMSF) using micro-scale filler particles for density reduction have recently been demonstrated to show attractive property profiles in combination with economic viability. The published literature encompasses melt- as well as powder-based processes and matrix materials ranging from magnesium to aluminum, titanium, zinc, iron, and steel, often in combination with either glass hollow spheres or cenospheres as additives. Cenospheres are a by-product of coal combustion and are available at low cost as so-called fly ash from coal-burning power plants. Effectively, they are a chemically inert [1] and temperature-resistant type of hollow ceramic micro beads which have successfully demonstrated their suitability for use as filler particle, even in conjunction with high temperature processes [2]. The present study looks at cenosphere adaptation by means of sputter coating in view of producing MMSF with optimized mechanical properties and reduced weight.
A comprehensive overview of MMSF methods and materials is offered by Gupta and Rohatgi [3]. Most processes investigated so far limit the effective range of porosities to an approximate maximum at around 50%. At the same time, several publications point at the fact that properties specifically under tensile load could benefit from improved interface strength between matrix and hollow particle, which is typically not achieved today [4,5]. The present study reverses the usual processing sequence by creating the interface between metal phase and hollow particles first and consolidating the resulting particles to form macroscopic bodies afterwards. The process employed for this purpose is vibration-assisted sputter coating of the hollow particles with metals. The expected benefits include increased interface strength, additional control over interface properties, and access to lower density materials through direct sintering of metal-coated spheres as done in the present study.
Sputter-coating of powders and even of hollow microspheres is not entirely new: Both Koppel et al. and Xiaozheng and Zhigang have reported electromagnetic absorption/shielding properties of Cu- [6] and Ni-coated [7] cenospheres in bulk condition [6] and embedded in a paraffin matrix [7]. Additional interest in this coating approach is based on the envisaged potential for performance optimization in conventional powder metallurgical syntactic foams through tailored interface definition. The main advantage of sputtering in this respect is its variability in terms of coating materials compared to conventional chemical powder coating methods, as well as the improved uniformity of the coating in terms of thickness and surface quality [8,9].
2. Materials and Methods
Cenospheres were acquired from Biotecha Latvia Ltd (Riga, Latvia). Their composition was chemically determined to be 53.8 ± 0.5 wt % SiO2, 40.7 ± 0.7 wt % Al2O3, 1.4 ± 0.2 wt % CaO, and 1.0 ± 0.2 wt % Fe2O3, plus smaller amounts (below 1 wt %) of MgO, Na2O, and K2O. Bulk density of the particles prior to coating was 0.39 ± 0.006 g/cm3 based on repeated Scott volumeter measurements according to ISO 3923-2-81.
Copper coating was conducted using an experimental magnetron sputtering setup at Sidrabe Ltd. (Riga, Latvia), in which the powder reservoir situated below the target was constantly agitated by a vibration source to ensure homogeneous coverage. The Cu sputter targets had a purity of 99.9%.
Consolidation of material samples for compression tests was done by spark plasma sintering (SPS) using KCE®-FCT HP D 10-GB equipment by FCT Systeme GmbH (Rauenstein, Germany). A graphite die of 21 mm diameter was filled with either 1 g (disc-shaped samples, nominal size of approximately 20 mm diameter and 2.5 mm thickness/height) or 5.5 g (cylindrical samples, nominal size approximately 20 mm diameter and 19 mm height) of Cu-coated cenospheres plus a graphite foil wrapping of 0.6 ± 0.2 mm thickness to prevent the sample from sticking to the die walls. Subsequently, the die was evacuated and the powder held at a constant pressure of 9.5 MPa throughout the process. Heating rates employed were 100 K/min for ramp-up and ~200 K/min during cooling. Sintering temperatures and times were varied in the ranges 850–1080 °C and 0.5–4.0 min, respectively. Sample core temperatures were acquired pyrometrically via a bore hole in the graphite punch. Prior to mechanical testing and density evaluation, the samples were machined in order to remove remainders of the graphite foil. This led to some variation in sample dimensions and weight which were naturally accounted for in the determination of both density and compression strength.
Imaging relied on a Zeiss EVO MA-15 scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) and Image Pro 7 image analysis tool by Media Cybernetics (version 7.0, Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD, USA, 2011).
Compression tests were performed on an Instron 8801 universal testing machine (Instron, Norwood, MA, USA) at room temperature and a constant quasi-static test speed of 0.01 mm/s on three samples per material variant.
Apparent density and porosity of sintered MMSF were evaluated according to Archimedes’ principle (results are averaged over five samples per set of sintering conditions). Immersion in 2-prophanol (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, grade 99.5%) was employed to prevent Cu corrosion. The relative density of 2-prophanol at 22 °C (0.7834 g/cm3) was taken into account in the calculation. Samples were encapsulated during immersion to avoid infiltration of the open porosity present between coated microspheres.
3. Results
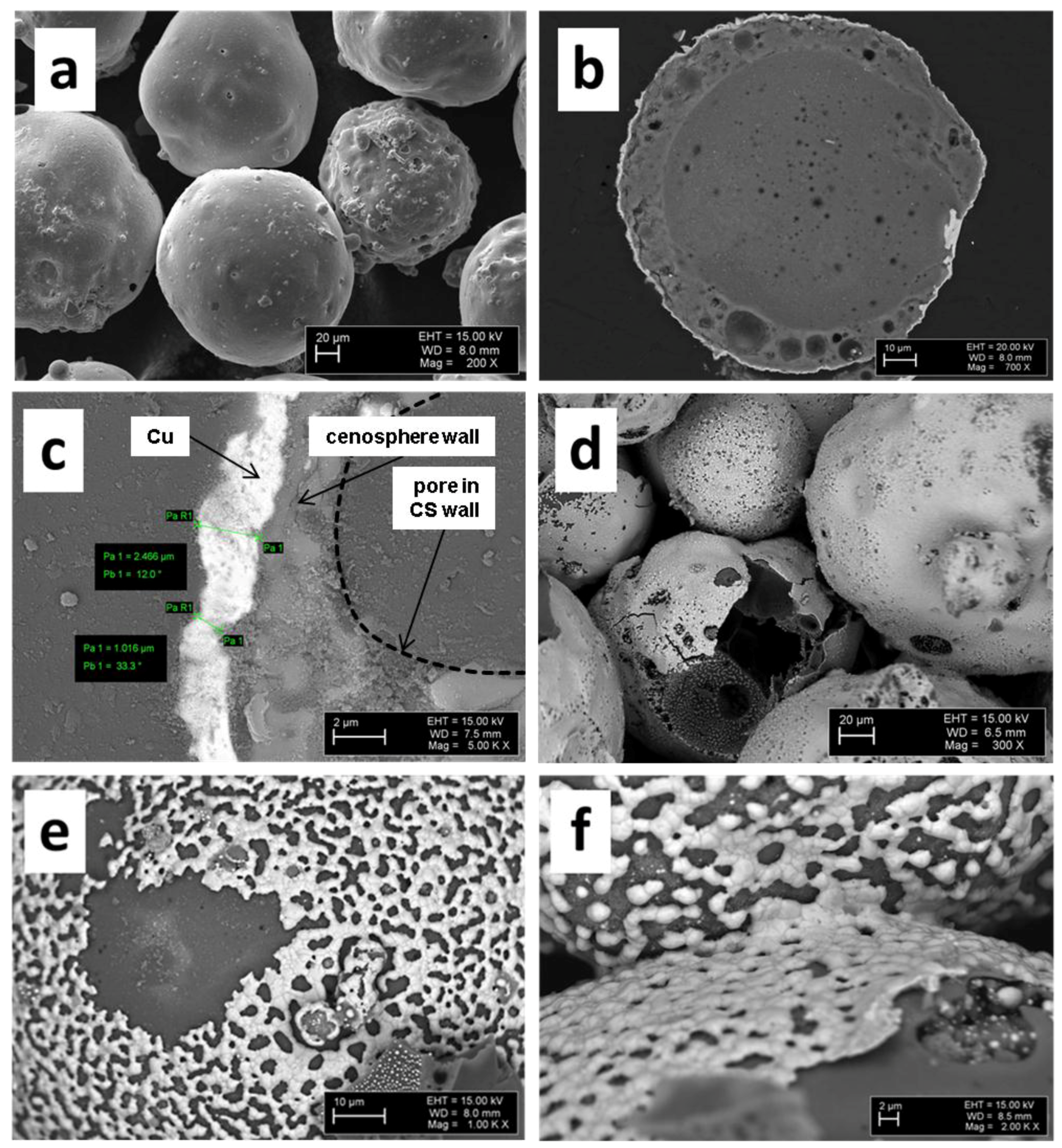
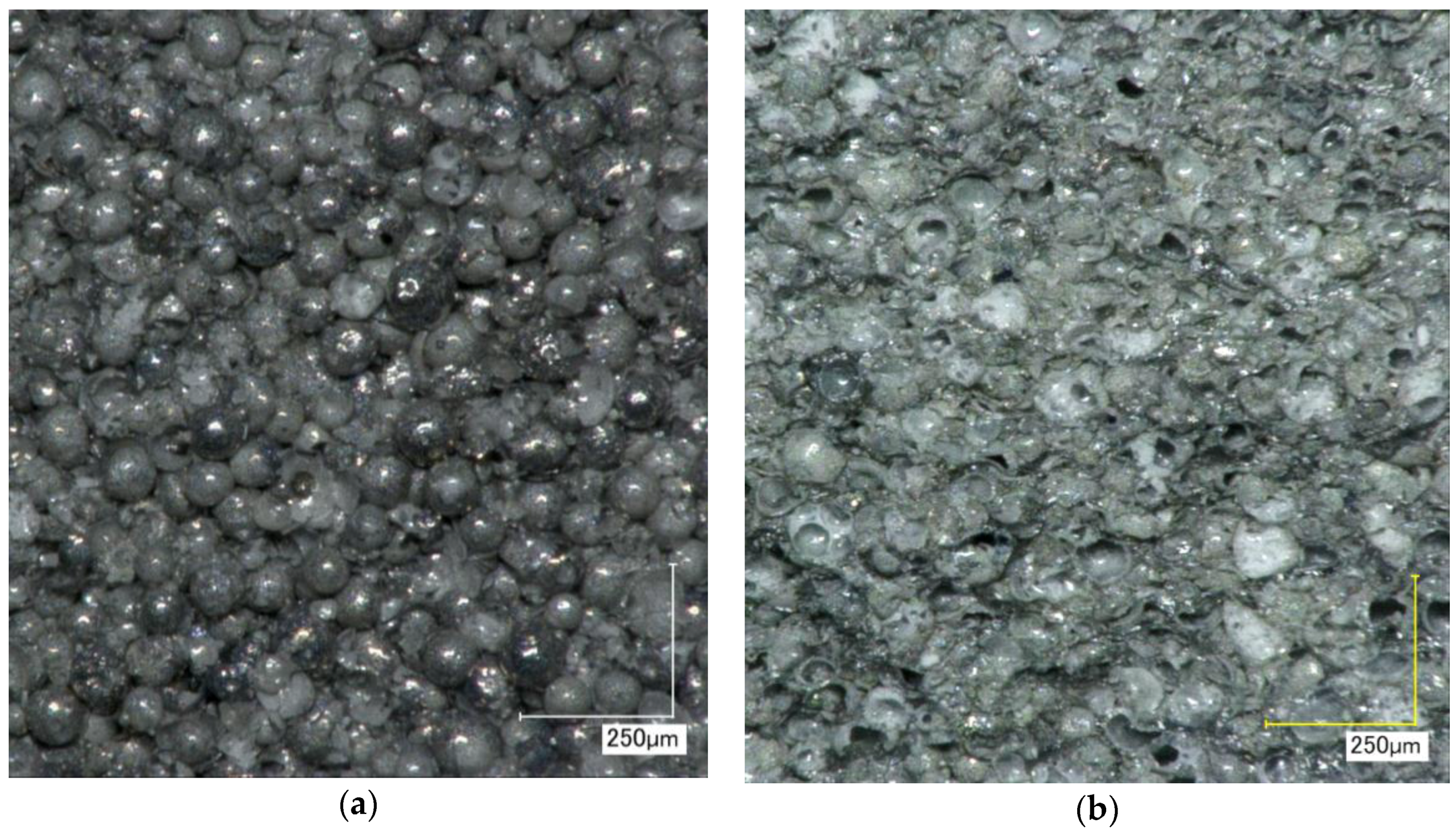
Vibration-assisted sputter coating led to homogeneous and continuous metal layers in a thickness range of approximately 0.4–2.5 µm, as depicted in Figure 1.
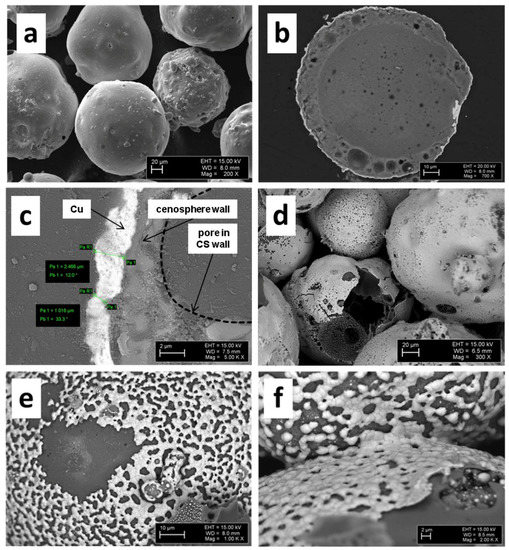
Figure 1.
Various views of copper-coated cenospheres (Cu@CS materials, disc-shaped samples) before (a–c) and after sintering (d–f): (a) outward appearance; (b) cross section; (c) detail showing coating thickness; (d) sintered at 800 °C; (e) sintered at 900 °C; and (f) detail view showing inter-particle connection after sintering at 900 °C.
Due to the coating process, powder bulk density increased from an initial 0.39 ± 0.006 g/cm3 to 0.51 ± 0.004 g/cm3. Assuming that the basic shape and flow characteristics remained unchanged, this increase must be related to the increase in particle density caused by the Cu layer. As can be seen in Figure 1d–f, the sintering process strongly affects the coating morphology. The net-like texture observed for temperatures of 900 °C and above is associated with inferior wetting between liquid Cu and the alumino-silicate cenospheres, which causes loss of the full metal coverage originally obtained during sputtering. Occurrence of this effect below the melting point of pure copper (1094 °C) may suggest some reaction between coating and substrate during sintering, and an associated formation of lower-melting phases. This interpretation is supported by a number of studies investigating the wetting of Cu and Cu alloys on ceramic substrates, mainly focusing on alumina. The fact that no studies specifically addressing the combination of Cu and alumino-silicate as the cenosphere shell materials were found is alleviated by Chidambaram et al.’s observation that wetting in liquid metal–ceramic systems tends to be determined by the liquid metal’s contact to the interface formed between the two partners, rather than the direct contact between liquid metal and ceramic [10]. An example in this respect has been reported by Espie et al., who showed that contact angles between a copper alloy on the one hand and alumina, mullite, and silicate ceramics on the other hand are almost identical [11]. Interface formation itself has been studied in detail by Kelber et al. [12], who conclude that interface-forming reactions between Cu and alumina specifically are limited to less than a full monolayer under the conditions of measurement, with metallic copper being observed at higher levels of coverage. Cu-alumina wetting is described as poor or even non-wetting under these circumstances, and the observed variation in literature values is explained based on variations in surface conditions that were not accounted for. Hydroxylation is mentioned in this context, which has been found to significantly lower the contact angle [12]. Chidambaram et al. and Meier et al. further stress the role of oxygen for improving wetting between Cu and alumina [11,13]. As contact angle value, the former report 34.4° at 1300 °C for a copper alloy containing 3 wt % of oxygen [11], while Eustathopoulos suggest between 120° and 130° both for pure copper in contact with Al2O3 and SiO2 [14]. In the present case, the oxygen content of the Cu layer may be assumed to fall below the previously mentioned 3 wt %, which was achieved by oxide addition. The contact angle can thus be expected to approach the higher 120°–130° boundary rather than the lower one. In contrast, the full coverage achieved in the solid state through sputter coating would correspond to perfect wetting, and thus a contact angle approaching 0°. Given that the true contact angle value for this combination of materials is likely to be much higher, the disruption of the continuous surface layer during melting is not surprising.
Despite the observed loss of film coherence, SPS sintering still leads to good particle interconnection, as is illustrated by Figure 1f. This finding is reinforced by measurements showing varying electrical conductivities between 2.05 × 104 and 3.6 × 104 S/m for all samples, thus suggesting the existence of a continuous metallic network within the bulk of the material, even in those cases in which the aforementioned net-like structure formed.
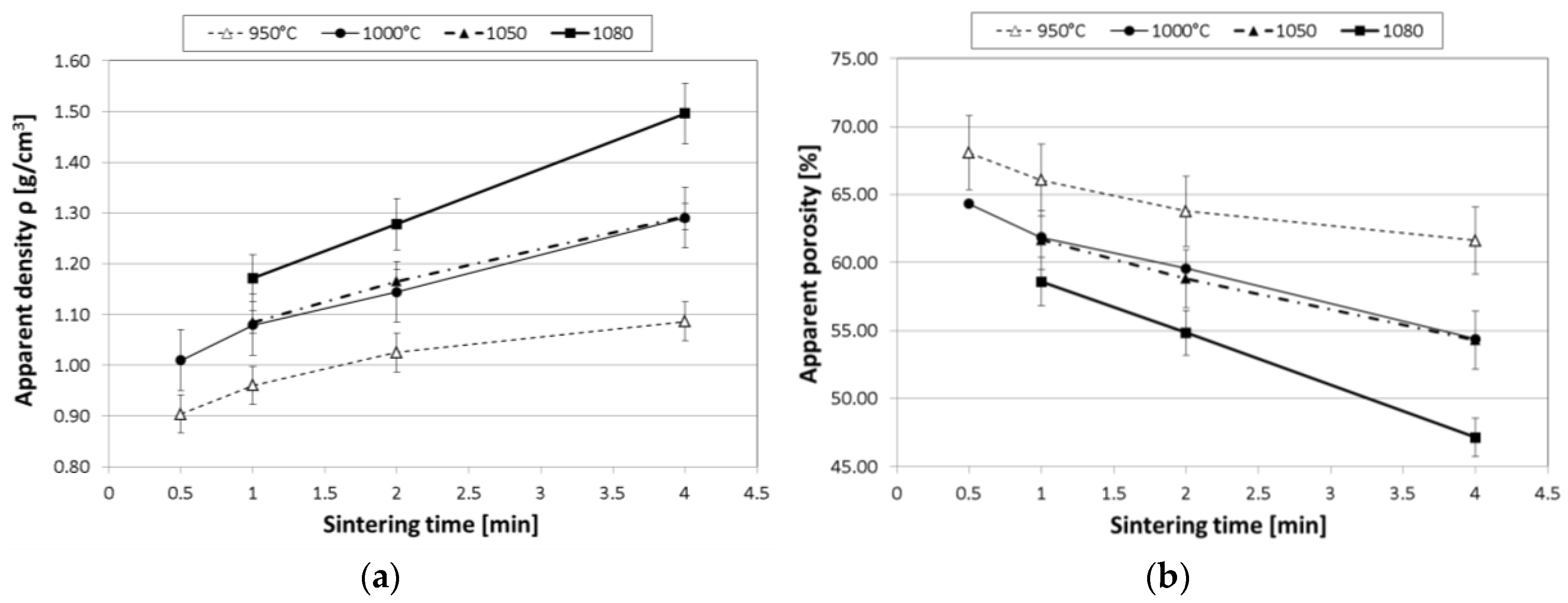
The dependence of density on the SPS sintering parameters is represented in Figure 2 and Table 1 for cylindrical samples. Initial tests on disc-shaped samples had shown no influence of sintering parameters on density at lower processing temperatures (850, 900 °C). For this reason, the temperature range studied was limited to 950 °C and above for the cylindrical samples subsequently subjected to mechanical evaluation. The upper temperature limit of 1080 °C was motivated by the melting temperature of pure copper.
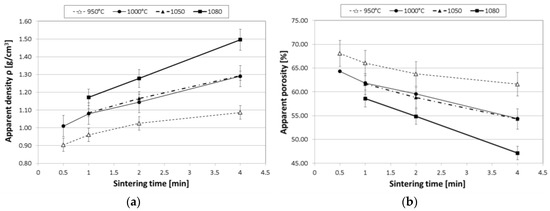
Figure 2.
Dependence of (a) density determined according to Archimedes’ principle; and (b) apparent porosity on spark plasma sintering (SPS) conditions for Cu@CS materials, measured on cylindrical samples.

Table 1.
Density and compressive strength values for Cu-coated cenospheres (Cu@CS) as measured on cylindrical samples.
Table 1 shows a good match between density values based on weighing and measurement of samples on the one hand and density determination via Archimedes’ principle on the other, with the latter consistently leading to slightly higher results, while showing no deviation in terms of the general tendencies observed. The latter can be summarized as follows: in the temperature range studied, both increasing the sintering temperature at constant time and increasing sintering time at constant temperature will lead to an increase in density. When considering the time range from 1 to 4 min common to all temperature levels, the former approach leads to changes from 13.1% (950 °C) to 19.5% (1000 °C), 19.2% (1050 °C), and 27.6% (1080 °C). This leads to the assumption that sintering at 1000 °C already provides sufficient mobility to reach useful densities, while the added step observed at 1080 °C may be due to the copper coating changing from solid to liquid state. This transition would induce greater particle mobility and a greater likelihood of Cu surface layer interpenetration, as well as particle fracture events under the influence of the consolidation pressure. Superposition of these effects plus possible rearrangement of particles during sintering explains the difference between the coated powder’s bulk density and sample densities. This interpretation, however, would imply that the network structures seen in Figure 1 must have formed in the solid state—always provided that the temperature reading at the basis of this assumption represents a homogeneous condition within the sample at all stages of the process, which is at least questionable in SPS sintering.
The corresponding perspective for density change at constant times and rising temperature levels shows increases of 22.1% (1 min), 24.7% (2 min), and 37.8% (4 min), respectively. Figure 2 represents these findings graphically, adding as further information the apparent porosity of the materials. This measure includes both the remaining open porosity between the microspheres—which typically show point-to-point extended to small area contact—and the internal porosity of the original cenospheres. It is calculated based on the measured sample density as well as the particle density of the coated cenospheres, which in turn depends on the initial density of the cenospheres, the density of the coating material, and the thickness of the coating.
4. Discussion
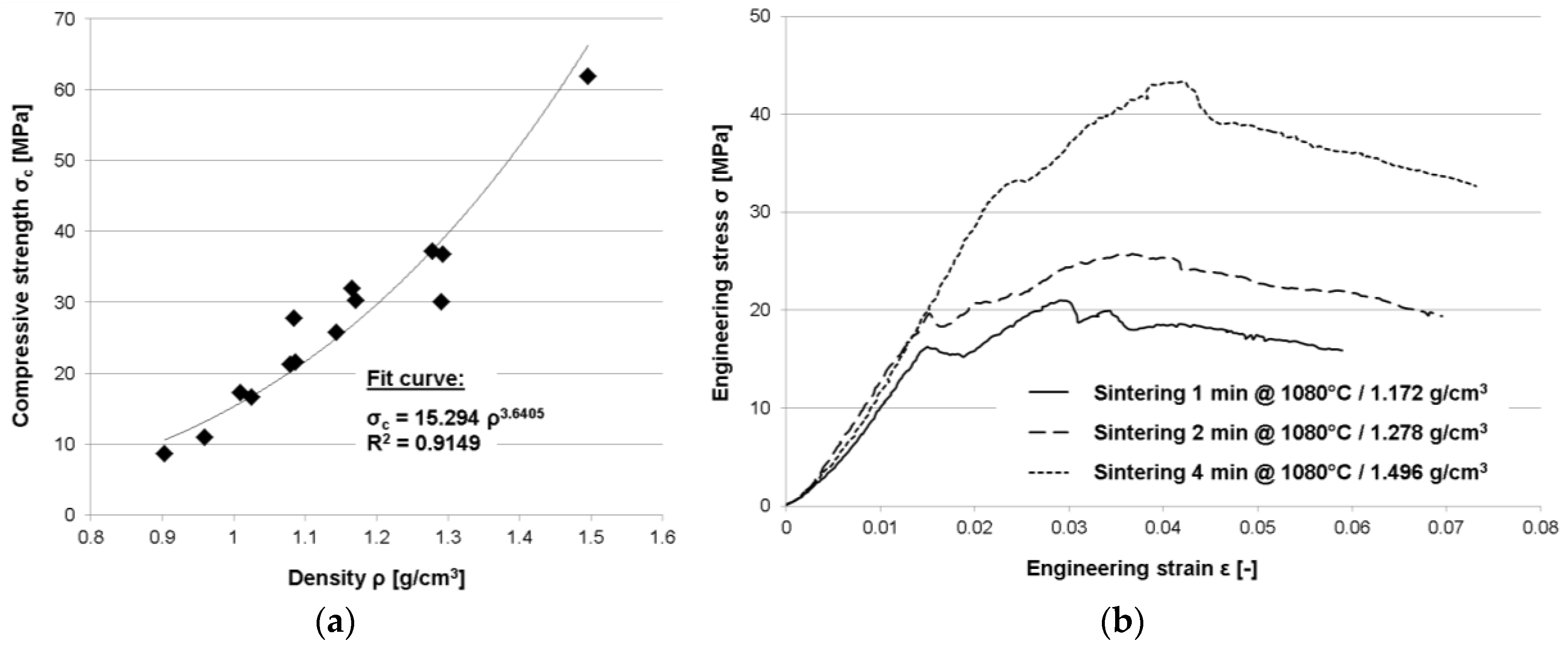
Besides density levels, Table 1 above reports the compressive strength values for the sintered specimens. Strength values correspond to the peak stress observed in stress–strain curves as depicted in Figure 3b. The data shown here is also depicted graphically in Figure 3a, where the relation between density and strength is evaluated. Though the density range covered is comparatively narrow, the data supports the increase of stress levels with density typical of many kinds of foams.
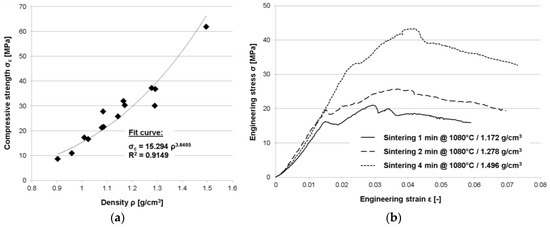
Figure 3.
Mechanical performance of Cu@CS materials: (a) Compressive strength data plotted vs. (geometry-based, see Table 1) density values; (b) Examples of typical engineering stress–strain curves for different density levels, underlining the limited failure strain observed.
The general relationship between density and strength observed for the samples tested across sintering conditions is plotted in Figure 3a, which also contains a curve fit covering the relevant density range from approximately 0.90 to 1.50 g/cm3. Once again, density values determined via Archimedes’ principle have been selected as the basis of this evaluation. Considering the limited amount of data available so far, the chosen power law leads to an acceptable fit quality. However, further studies on this material will have to scrutinize this relationship both with respect to its type and actual parameter values, since it is usually associated with conventional two-phase foams rather than three phase syntactic materials [15]. Its value in the present case lies in the possibility of estimating properties at density levels not explicitly tested, and in a limited extrapolation option. Not surprisingly, coated and sintered cenospheres exhibit predominantly brittle failure as well as sample fragmentation, which together counteract the formation of a prolonged plateau region. The exemplary stress–strain curves representing different density levels in Figure 3b illustrate this general observation. Irrespective of the density and sintering conditions, none of the samples exceeds 7% of engineering strain at failure by any margin. The stress–strain curve itself has a stepped appearance, which is indicative of the observed fracture and partial disintegration of samples during compression. Apparently, the volume fraction of the (ductile) metallic phase present in the samples does not suffice to counterbalance the failure mechanism associated with the cenospheres and thus the ceramic phase.
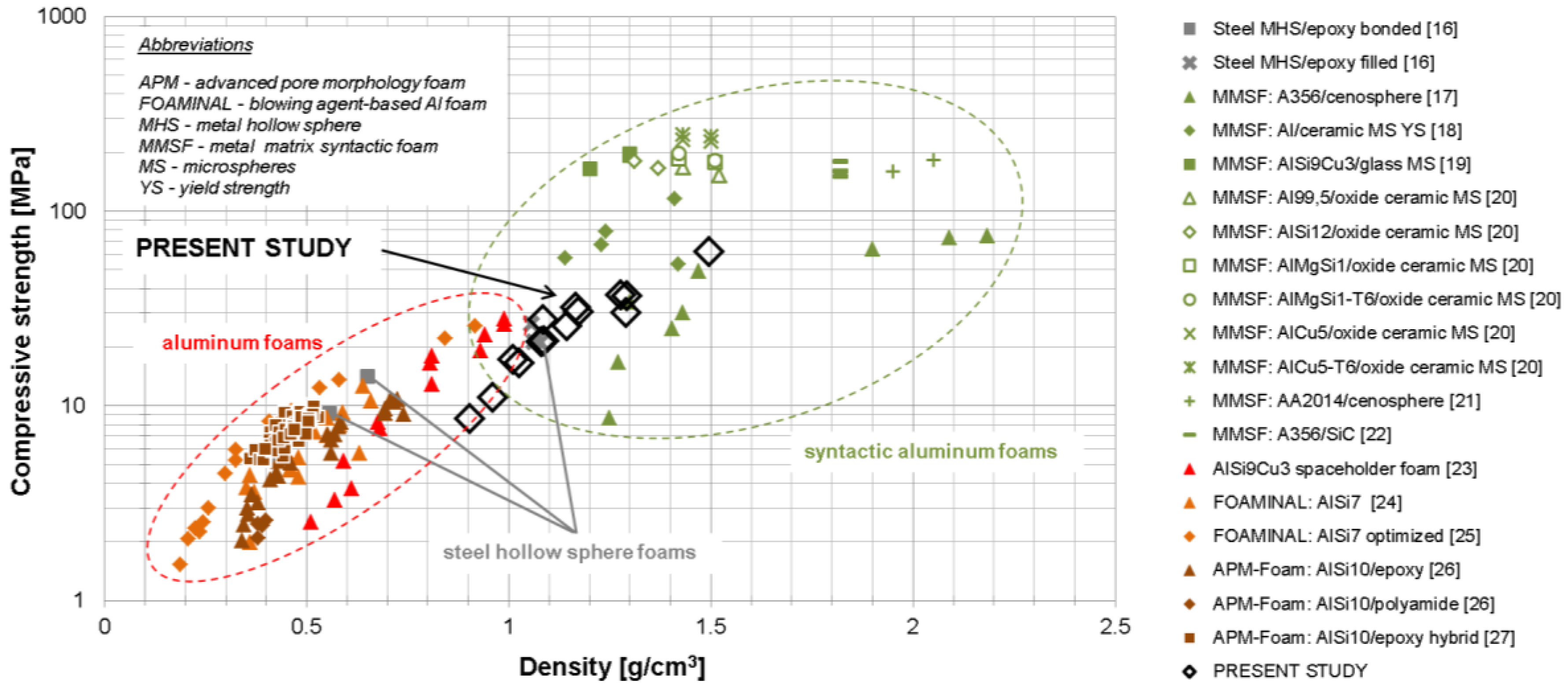
Comparison with other types of materials in terms of strength is difficult due to the specific character of the material, which takes an intermediate position between a true metal matrix syntactic foam and a ceramic foam, though leaning towards the latter. In addition, the mixed open- vs. closed cell character comes in. In terms of density-normalized strength values, however, the properties determined are similar to those known from several other types of foams in a matching density range. An example can be drawn from comprehensive comparisons of the latter, such as those by Weise et al. [4], which have partially been taken up, focusing on the lower density range, in Figure 4 below: note, however, that the comparison is semi-quantitative at best, since strength definitions vary among the data gathered from the literature.
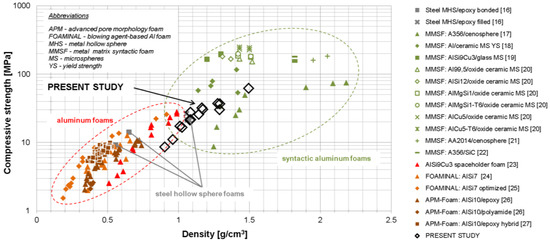
Figure 4.
Comparing the mechanics of Cu@CS materials with other types of foams: Absolute compressive strength values of similar density materials are contrasted. Note that exact strength definitions may differ slightly between material variants. An explanation of abbreviations used in the diagram is provided in the upper left corner. The representation as such follows Weise et al. [4]. The data shown were collated from references [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
Considering the comparison offered in Figure 4 in more detail, and specifically the current positioning of syntactic foams based on metal-coated cenospheres, the following tendencies are apparent when it comes to structural applications:
- Increasing the thickness of the coating while maintaining the coating materials will lead to increased density and strength, but based on the unfavorable strength vs. density ratio of pure copper, most likely also to a reduction or at least stagnation of density-related specific strength.
- Replacement of Cu as coating material with either steel or aluminum alloys should increase specific strength, in the latter case ultimately exceeding the levels of conventional aluminum foams and approaching those of aluminum matrix syntactic foams.
- While the aforementioned increase of specific strength may be reached at reduced absolute density in the case of aluminum, it will be achieved at identical or slightly increased density in the case of steel. Nevertheless, based on the added open porosity, this would still position the respective material at the lowest-density end of steel matrix foams realized so far.
5. Conclusions
The present investigation shows that the sputter coating of cenospheres creating thin metal layers on their surfaces is feasible and yields materials which can be consolidated directly by sintering to form performant materials with density-related compressive properties similar to those of other types of metal, ceramic, and hybrid foams, despite the fact that process optimization is still pending. Future studies will investigate the mechanical performance of this new type of material in more detail, looking at the influence of coating thickness on mechanical performance and failure mechanisms. Beyond direct consolidation of coated microspheres, their use as filler in conventional powder metallurgically produced metal matrix syntactic foams needs to be scrutinized. For this purpose, the production of steel coated microspheres will be investigated (a first sample of this type of material is depicted in Figure 5), and beyond cenospheres, the processing of high strength glass microspheres will be studied. The latter are an established filler for steel MMSF up to sintering temperatures of 1000 °C [28,29], but do not withstand the 1200 °C typical for 316 L matrices [4,30]. Benefits expected from the sputter coating of the glass spheres include the assumption that the full enclosure of the glass sphere will prevent the formation of satellite glass phases via inter-particle capillaries observed otherwise [4].
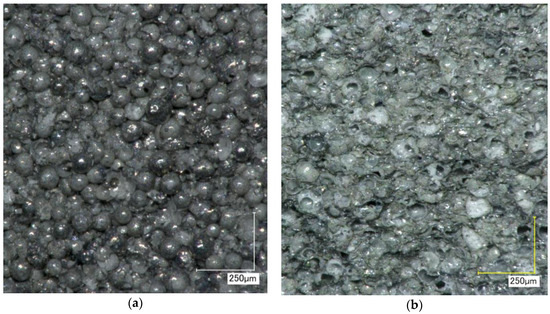
Figure 5.
Early images of steel@CS materials: (a) Outer surface of sample sintered 4 min at 1100 °C; (b) Fracture surface of corresponding sample.
Besides this suggested switch in coating materials, it will definitely be worth evaluating Cu-coated microspheres as filler in aluminum and aluminum alloy matrices in view of the expected reaction with the matrix, starting from the formation of a Cu-enriched diffusion layer around the microspheres and up to the emergence of a transient liquid phase during sintering based on low melting eutectics in the respective systems. Besides this specific point, the fact that aluminum matrix syntactic foams are often produced from sintered filler particle preforms by pressure assisted melt infiltration [19] deserves special attention. This latter procedure will necessarily lead to a 3–3 type interpenetrating (metal and ceramic) phase composite, whereas a preform made of metal-coated filler particles could lead to a 0–3 type composite in which the brittle ceramic phase is discontinuous. Especially in terms of ductility, this configuration may be expected to bear beneficial effects.
In the case of both the suggested steel and aluminum matrix syntactic foams, determination of mechanical properties will be an important part of evaluating their application potential. In general, properties are expected to improve with interface characteristics. With respect to processing the base materials, another notable side effect for powder-based Al matrix MMSF is the fact that Cu coating may effectively eliminate the particle density gap between Al powders on the one hand and cenospheres or glass microspheres on the other, and could thus counteract the risk of demixing and/or segregation effects during powder handling. This is of interest both for conventional powder metallurgical processes and powder-based additive manufacturing methods, and could thus widen the scope of processing options as well as manufacturable geometries for this type of material. Finally, the technique has several interesting implications for polymer matrix syntactic foams, as it can provide lightweight conductive fillers positively affecting properties like electromagnetic shielding capacity. As has been mentioned in the introduction, the effect as such has already been considered, but there is still a lot of room for performance optimization [6,7].
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support by Kaspars Ozols of Institute of Technical Physics, Faculty of Material Science and Applied Chemistry, Technical Riga Technical University, Riga, Latvia, who performed electro conductivity studies on samples from the present test series.
Author Contributions
Andrei Shishkin and Irina Hussainova conceived and designed the experiments; Andrei Shishkin, Maria Drozdova and Viktor Kozlov performed the experiments; Andrei Shishkin, Irina Hussainova and Dirk Lehmhus analyzed the data; Andrei Shishkin, Maria Drozdova and Irina Hussainova contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Andrei Shishkin and Dirk Lehmhus wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shishkin, A.; Mironovs, V.; Lapkovskis, V.; Treijs, J.; Korjakins, A. Ferromagnetic Sorbents for Collection and Utilization of Oil Products. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 604, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, A.; Mironovs, V.; Zemchenkov, V.; Antonov, M. Hybrid syntactic foams of metal—Fly ash cenosphere—Clay. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 674, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Rohatgi, P.K. Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams: Processing, Microstructure, Properties and Applications; DEStech Publications Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Weise, J.; Lehmhus, D.; Baumeister, J.; Kun, R.; Bayoumi, M.; Busse, M. Production and properties of 316 L stainless steel cellular materials and syntactic foams. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni, L.; Scapin, M.; Lehmhus, D.; Baumeister, J.; Busse, M.; Avalle, M.; Weise, J. High Strain Rate Tensile and Compressive Testing and Performance of Mesoporous Invar (FeNi36) Matrix Syntactic Foams Produced by Feedstock Extrusion. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, T.; Shishkin, A.; Hussainova, I.; Haldre, H.; Tint, P. Electromagnetic shielding properties of ceramic spheres coated with paramagnetic metal. Agron. Res. 2016, 14, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Shen, Z. The electromagnetic shielding of Ni films deposited on cenosphere particles by magnetron sputtering method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-F.; Li, D.-H.; Shen, X.-Q.; Liu, W. Preparation and magnetic properties of nano-Ni coated cenosphere composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3753–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-F.; Shen, X.-Q.; Liu, W. Synthesis and characterization of Co/cenosphere core–shell structure composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, P.R.; Meier, A.; Edwards, G.R. The nature of interfacial phenomena at copper-titanium/alumina and copper-oxygen/alumina interfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 206, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espie, L.; Drevet, B.; Eustathopolous, N. Experimental study of the influence of interfacial energies and reactivity on wetting in metal/oxide systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1994, 25, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelber, J.A.; Niu, C.; Shepherd, K.; Jennison, D.R.; Bogicevic, A. Copper wetting of α-Al2O3(0001): Theory and experiment. Surf. Sci. 2000, 446, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, A.; Baldwin, M.D.; Chidambaram, P.R.; Edwards, G.R. The effect of large oxygen additions on the wettability and work of adhesion of copper-oxygen alloys on polycrystalline alumina. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 196, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustathopoulos, N.; Nicholas, M.G.; Drevet, B. Wettability at High Temperatures; Pergamon Materials Series; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1999; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vesenjak, M.; Fiedler, T.; Ren, Z.; Öchsener, A. Behaviour of syntactic and partial hollow sphere structures under dynamic loading. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, P.K.; Kim, J.K.; Gupta, N.; Alaraj, S.; Daoud, A. Compressive characteristics of A356/fly ash cenosphere composites synthesized by pressure infiltration technique. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.F.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhao, Y.Y. Al matrix syntactic foam fabricated with bimodal ceramic microspheres. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2732–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, J.; Yezerska, O.; Busse, M.; Haesche, M.; Zanetti-Bueckmann, V.; Schmitt, M. Production and properties of micro-porous glass bubble zinc and aluminium composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2007, 38, 901–906. [Google Scholar]
- Orbulov, I.N.; Ginsztler, J. Compressive characteristics of metal matrix syntactic foams. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass Goel, M.; Peroni, M.; Solomos, G.; Mondal, D.P.; Matsagar, V.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Larcher, M.; Marburg, S. Dynamic compression behavior of cenosphere aluminum alloy syntactic foam. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, D.D.; Strbik, O.M., III; Hammond, V.H.; Gupta, N.; Cho, K. Development of high performance lightweight aluminum alloy/SiC hollow sphere syntactic foams and compressive characterization at quasi-static and high strain rates. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 550, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, K.; Berg, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Busse, M. Multifunktionale Aluminiumschwämme durch Schmelzinfiltration von Platzhaltern. Aluminium 2006, 82, 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Avalle, M.; Lehmhus, D.; Peroni, L.; Pleteit, H.; Schmiechen, M.; Belingardi, G.; Busse, M. AlSi7 metallic foams—Aspects of material modelling for crash analysis. Int. J. Crashworth. 2009, 14, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmhus, D.; Busse, M. Mechanical performance of structurally optimized AlSi7 aluminum foams—An experimental study. Mater. Werkst. 2014, 45, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmhus, D.; Baumeister, J.; Stutz, L.; Schneider, E.; Stöbener, K.; Avalle, M.; Peroni, L.; Peroni, M. Mechanical characterization of particulate aluminum foams—Strain-rate, density and matrix alloy vs. adhesive effects. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 12, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, J.; Baumeister, J.; Hohe, J.; Böhme, W.; Beckmann, C. Epoxy Aluminum Hybrid Foam—An Innovative Sandwich Core Material with Improved Energy Absorption Characteristics. In Proceeding of the 10th International Conference on Sandwich Structures, Nantes, France, 27–29 August 2012.
- Peroni, L.; Scapin, M.; Avalle, M.; Weise, J.; Lehmhus, D.; Baumeister, J.; Busse, M. Syntactic Iron Foams–On Deformation Mechanisms and Strain-Rate Dependence of Compressive Properties. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2012, 14, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, D.D.; Shunmugasamy, V.S.; Gupta, N.; Lehmhus, D.; Weise, J.; Baumeister, J. Quasi-static and high strain rates compressive response of iron and Invar matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni, L.; Scapin, M.; Fichera, C.; Lehmhus, D.; Weise, J.; Baumeister, J.; Avalle, M. Investigation of the mechanical behaviour of AISI 316L stainless steel syntactic foams at different strain-rates. Compos. Part B 2014, 66, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).