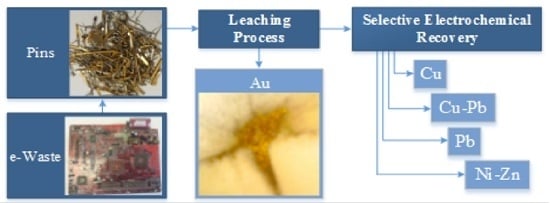
Urban Mining and Electrochemistry: Cyclic Voltammetry Study of Acidic Solutions from Electronic Wastes (Printed Circuit Boards) for Recovery of Cu, Zn, and Ni
Abstract
Share and Cite
Reyes‐Valderrama, M.I.; Salinas‐Rodríguez, E.; Montiel‐Hernández, J.F.; Rivera‐Landero, I.; Cerecedo‐Sáenz, E.; Hernándezvila, J.; Arenas‐Flores, A. Urban Mining and Electrochemistry: Cyclic Voltammetry Study of Acidic Solutions from Electronic Wastes (Printed Circuit Boards) for Recovery of Cu, Zn, and Ni. Metals 2017, 7, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020055
Reyes‐Valderrama MI, Salinas‐Rodríguez E, Montiel‐Hernández JF, Rivera‐Landero I, Cerecedo‐Sáenz E, Hernándezvila J, Arenas‐Flores A. Urban Mining and Electrochemistry: Cyclic Voltammetry Study of Acidic Solutions from Electronic Wastes (Printed Circuit Boards) for Recovery of Cu, Zn, and Ni. Metals. 2017; 7(2):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes‐Valderrama, Ma. Isabel, Eleazar Salinas‐Rodríguez, J. Fabian Montiel‐Hernández, Isauro Rivera‐Landero, Eduardo Cerecedo‐Sáenz, Juan Hernándezvila, and Alberto Arenas‐Flores. 2017. "Urban Mining and Electrochemistry: Cyclic Voltammetry Study of Acidic Solutions from Electronic Wastes (Printed Circuit Boards) for Recovery of Cu, Zn, and Ni" Metals 7, no. 2: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020055
APA StyleReyes‐Valderrama, M. I., Salinas‐Rodríguez, E., Montiel‐Hernández, J. F., Rivera‐Landero, I., Cerecedo‐Sáenz, E., Hernándezvila, J., & Arenas‐Flores, A. (2017). Urban Mining and Electrochemistry: Cyclic Voltammetry Study of Acidic Solutions from Electronic Wastes (Printed Circuit Boards) for Recovery of Cu, Zn, and Ni. Metals, 7(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020055