Titanium Powder Sintering in a Graphite Furnace and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Parts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Compaction and Sintering
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Testing
3. Results
3.1. Sintering Densification
3.2. Microstructural Observation
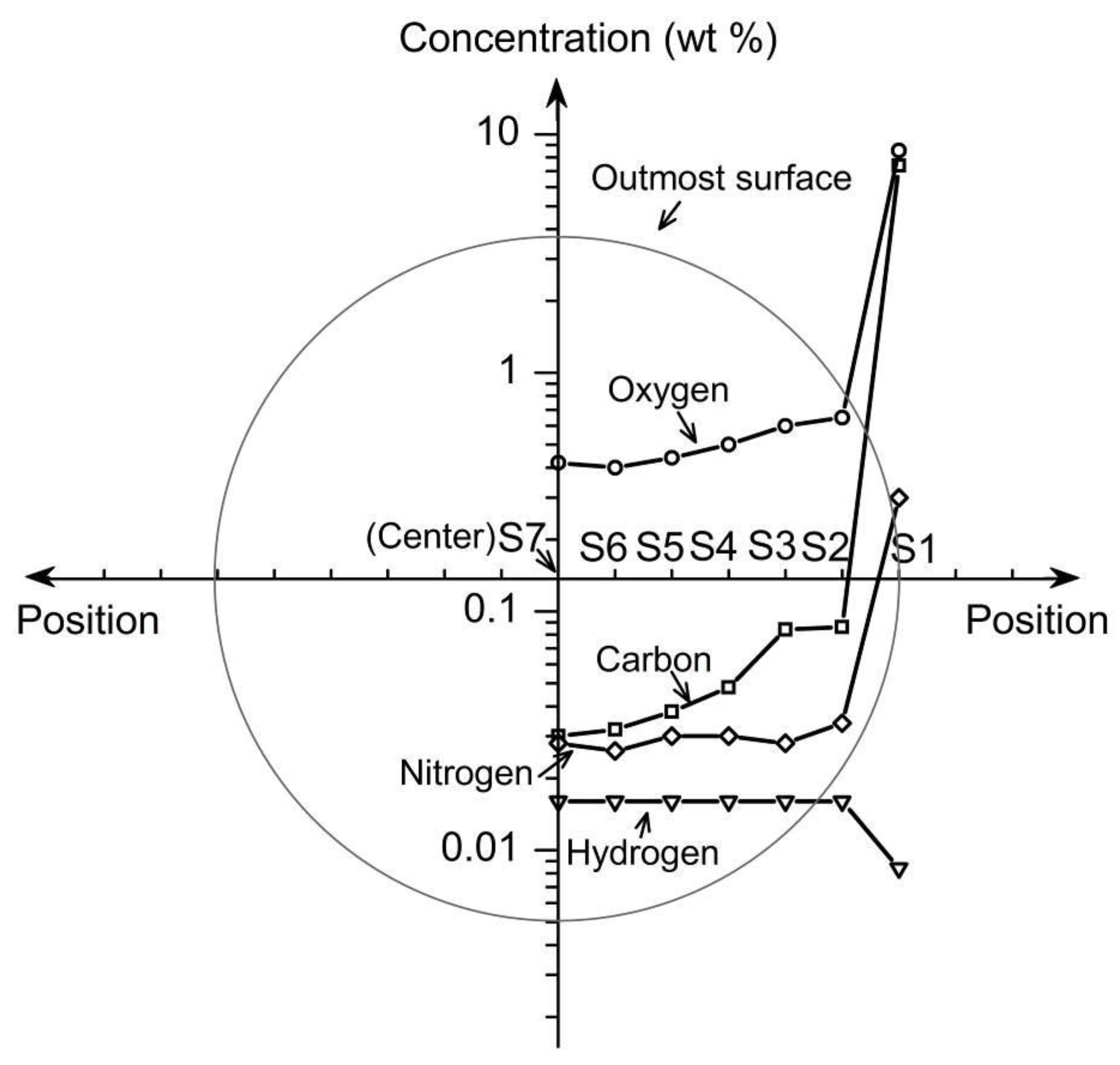
3.3. Close-Up Observation of Surface Contaminants
3.4. Phase Characterization of the Surface and the Interior
3.5. Mechanical Properties and Fractography
4. Discussion
4.1. Densification
4.2. The Formation of Contaminated Surface Layer and the Effect of Interstitials on Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donachie, J.M.J. Titanium—A Technical Guide, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Froes, F.H. Titanium—Physical Metallurgy, Processing, and Applications; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.-C.; Attar, H. Selective Laser Melting of Titanium Alloys and Titanium Matrix Composites for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkowitz, S.; Rowell, D. Superior Fatigue Properties for Blended Elemental P/M Ti-6Al-4V. JOM 1986, 38, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, V.A.R.; Galvani, E.T.; Petroni, S.L.G.; Paula, M.S.M.; Lemos, T.G. Production of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy for surgical implants by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5844–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, P. Dynamet Technology Approved by Boeing as Qualified Supplier for Powder Metallurgy Titanium Alloy Products. Available online: http://www.pm-review.com/dynamet-technology-approved-by-boeing-as-qualified-supplier-for-powder-metallurgy-titanium-alloy-products/ (accessed on 22 January 2017).
- Qian, M. Cold compaction and sintering of titanium and its alloys for near-net-shape or preform fabrication. Int. J. Powder Metall. 2010, 46, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bolzoni, L.; Esteban, P.G.; Ruiz-Navas, E.M.; Gordo, E. Mechanical behaviour of pressed and sintered titanium alloys obtained from prealloyed and blended elemental powders. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 14, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujita, T.; Ogawa, A.; Ouchi, C.; Tajima, H. Microstructure and properties of titanium alloy produced in the newly developed blended elemental powder metallurgy process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 213, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Luo, S.D.; Bettles, C.J.; Schaffer, G.B.; Qian, M. The effect of Si additions on the sintering and sintered microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-3Ni alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7381–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Luo, S.D.; Schaffer, G.B.; Qian, M. The Sintering, Sintered Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Fe-Si Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4896–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Gabbitas, B.; Matthews, S.; Zhang, D. The development of porous titanium products using slip casting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, W. Malleable Alloys of Titanium. Z. Metall. 1937, 29, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, M.; Schaffer, G.B.; Bettles, C.J. Sintering of Titanium and its Alloys, in Sintering of Advanced Materials: Fundamentals and Processes; Fang, Z.Z., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 324–355. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.S.; Wartman, F.S.; Hayes, E.T. Ductile Titanium—Its Fabrication and Physical Properties. Trans. Am. Inst. Mining Met. Eng. 1946, 166, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Limberg, W.; Ebel, T.; Pyczak, F.; Schimansky, F.P. Influence of the sintering atmosphere on the tensile properties of MIM-processed Ti 45Al 5Nb 0.2B 0.2C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 552, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensburger, D.S.; Pugin, V.S.; Fedorchenko, I.M. Properties of electrolytic and reduced titanium powders and sinterability of porous compacts from such powders. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1968, 7, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, D.F.; German, R.M. Proceedings of PM 2004 Powder Metallurgy World Congress; European Powder Metallurgy Association: Vienna, Austria, 2004; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kanto Yakin Kogyo Co. Available online: http://www.k-y-k.co.jp/en/product01.html (accessed on 22 January 2017).
- Metal Powder Reports. Furnace Masters Difficult Metals. Met. Powder Rep. 2004, 59, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Cao, P.; Jones, M.I. Effect of Contaminants on Sintering of Ti and Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Powders in an Argon-Back-Filled Graphite Furnace. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 520, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Z.; Jones, M.I. Investigation of chloride impurities in hydrogenated–dehydrogenated Kroll processed titanium powders. Powder Metall. 2013, 56, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M. Sintering Theory and Practice; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hausner, H.H.; Smith, G.D.; Antes, H.W. Modern Development in Powder Metallurgy, Volume 13: Ferrous and Nonferrrous Materials; Metal Powder Industries Federation: Prinston, NJ, USA, 1981; pp. 537–549. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, L.P.; Baril, E. Effect of Oxygen Concentration and Distribution on the Compression Properties on Titanium Foams. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrad, H. Effect of interstitial solutes on the strength and ductility of titanium. Prog. Mater Sci. 1981, 26, 123–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, K.; Kohno, T.; Kondo, T.; Horata, A. Tensile Behavior of Sintered Titanium by MIM Process. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 1995, 42, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, H. The rate controlling mechanism during yielding and flow of α-titanium at temperatures below 0.4 TM. Acta Metall. 1966, 14, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Conrad, H. Effects of interstitial content and grain size on the strength of titanium at low temperatures. Acta Metall. 1973, 21, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, Z.Z.; Sun, P. A critical review of mechanical properties of powder metallurgy titanium. Int. J. Powder Metall. 2010, 46, 45–57. [Google Scholar]











| Slices | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintered density (%) | 95.7 ± 0.1 | 95.6 ± 0.3 | 95.9 ± 1.0 | 95.3 ± 0.1 | 95.8 ± 0.2 |
| Specimen | Green Density (600 MPa CIP, %) | Sintered Density (%) | Densification (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder | 87.0 | 95.8. | 69.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Cao, P.; Jones, M.I. Titanium Powder Sintering in a Graphite Furnace and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Parts. Metals 2017, 7, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020067
Yu C, Cao P, Jones MI. Titanium Powder Sintering in a Graphite Furnace and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Parts. Metals. 2017; 7(2):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Changzhou, Peng Cao, and Mark Ian Jones. 2017. "Titanium Powder Sintering in a Graphite Furnace and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Parts" Metals 7, no. 2: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020067
APA StyleYu, C., Cao, P., & Jones, M. I. (2017). Titanium Powder Sintering in a Graphite Furnace and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Parts. Metals, 7(2), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020067







