Influence of Thickness and Chemical Composition of Hot-Rolled Bands on the Final Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets Subjected to Two Different Decarburizing Atmospheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Carbon Concentration on Magnetic Properties
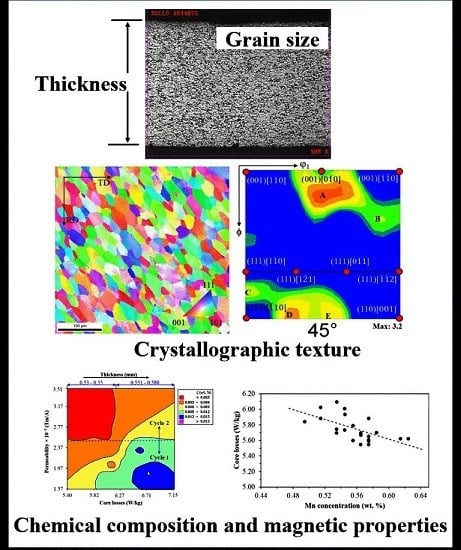
3.2. Influence of Steel Thickness on Core Losses
3.3. Effect of Ti, Sb and Mn Concentrations on Core Losses
3.4. Effect of Grain Size on Magnetic Properties
3.5. Effect of Decarburization Annealing on Crystallographic Texture
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Magnetic properties of the experimental steels are enhanced by the reduction of C, which is favored if dew point is increased from 21 to 25 °C, and gases ratio is changed from of 85% N2-15% H2 to 80% N2-20% H2.
- (2)
- Grain size is also dependent on decarburizing annealing conditions, it changes from ASTM 8 in the temper rolled condition to about 4 and 3 when applying Cycle 1 (21 °C, 85% N2-15% H2) and Cycle 2 (25 °C, 80% N2-20% H2), respectively.
- (3)
- Crystallographic texture of temper-rolled samples is characterized by the presence of components near to the ideal cube texture, and the absence of components belonging to γ-fiber texture. Cycle 1 promotes the development of components , and which belong to the so called θ-fiber texture, while Cycle 2 favors the development of orientations near to the ideal texture component, but in this case cube and rotated cube textures, were not developed.
- (4)
- Thinner thicknesses, higher concentrations of Sb and Mn, and lower C and Ti contents lead to lower core losses and higher permeability enhancing the magnetic behavior of the experimental GNO electrical steels. Therefore, the best magnetic properties were obtained when applying Cycle 2 independently of the crystallographic texture developed.
- (5)
- Additions of Mn and Sb increase the resistivity reducing the total core losses. Although Ti was expected to reduce core losses since it also increases the electrical resistivity, an opposite behavior was observed. Apparently, the strong affinity of Ti for carbon and nitrogen promotes the formation of stable carbonitrides which affect the wall domain motion during magnetization causing a detrimental effect on magnetic properties.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moses, A.J. Energy efficient electrical steels: magnetic performance prediction and optimization. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, J. Control of Surface Graded Transformation Textures in Steels for Magnetic Flux Carrying Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, O.; Schneider, J. Influence of deformation process on the improvement of non-oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 254, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, S.; Hectors, D.; Henrotte, F.; Hafner, M.; Herranz, M.; Hameyer, K.; Goes, P. Magnetic material optimization for hybrid vehicle PMSM drive. World Electr. Veh. J. 2009, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sidor, Y.; Kovac, F. Microstructural aspects of grain growth kinetics in non-oriented electrical steels. Mater. Charact. 2005, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacaltchuk, C.M.B.; Castello, G.A.; Ebrahimi, M. Effect of magnetic field applied during secondary annealing on texture and grain size of silicon steel. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.T.; Szpunar, J.A. Effect of initial grain size on texture evolution and magnetic properties in nonoriented electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckley, P. Electrical Steels for Rotating Machines, 1st ed.; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2002; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.K.; Huang, W.Y. Texture effect on magnetic properties by alloying specific elements in non-grain oriented silicon steels. ISJ Int. 2005, 45, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.H.; Schneider, J.; Long, L.H.; Sun, Y.; Gao, F.; Hu, L.H.; Yu, S.H.; Li, L.; Qiao, G.D.; Yu, L.Z.; et al. Fabrication of high permeability non-oriented electrical steels by increasing <001> recrystallization texture using compacted strip casting processes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 577–586. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, F.J.G.; Emura, M.; Teixeira, J.C.; de Campos, M.F. Effect of grain size, deformation, aging and anisotropy on hysteresis loss of electrical steels. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2000, 215, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Fukuda, B. Recent developments of non-oriented electrical steel sheets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1984, 5, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huňady, J.; Černík, M.; Hilinski, E.J.; Predmerský, M.; Magurova, A. Influence of chemistry and hot rolling conditions on high permeability non-grain oriented silicon steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, I.; Yashiki, H. Magnetic properties and recrystallization texture of phosphorus-added non-oriented electrical steel sheets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, J.; Salinas, A.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Deaquino, L. Effect of processing conditions on the final microstructure and magnetic properties in non-oriented electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 406, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.K. Texture effects on magnetic properties in high-alloyed non-oriented electrical steels. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2007, 49, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, E.; Salinas, A.; Deaquino, L.; Márquez, F. High temperature oxidation and its effects on microstructural changes of hot-rolled low carbon non-oriented electrical steels during air annealing. Oxid. Met. 2015, 83, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadam, R.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Farag, M.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Es-Saheb, M.H. Processing optimization and characterization of magnetic non-oriented electrical silicon steel. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 3242–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Darja, S.; Monika, J.; Jalklic, A.; Cop, A. Correlation of titanium content and core loss in non-oriented electrical steel sheets. Metalurgija 2010, 49, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, P. Effect of antimony on the structure, texture and magnetic properties of high efficiency non-oriented electrical steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 602, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.F.D.A.; Brandao, L.; Cunha, M.A.D. Influence of grain size and additions of Al and Mn on the magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steels with 3 wt % Si. Mater. Res. 2008, 11, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunday, J.; Cernik, M.; Hilinski, E.; Predmersky, M.; Magurova, A. Influence of chemistry and hot rolling conditions on high permeability non-grain oriented silicon steel. Metals 2005, 15, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Darja, P. Non-oriented electrical steel sheets. Mater. Technol. 2010, 44, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury, A. Low silicon non-grain-oriented electrical steel: Linking magnetic properties with metallurgical factors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 313, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Hsiao, I.-C.; Tsai, M.-C. Texture Improvement of 3% Si non-oriented electrical steel. China Steel Tech. Rep. 2015, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, K.M.; Alvarenga, E.D.A.; Buono, V.T.L. Decarburization kinetics during annealing of a semi-processed electrical steel. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darja, S.P.; Monika, J.; Hans, J.G.; Vasilij, P. Decarburization of non-oriented electrical steel sheets doped with selenium. Mater. Thehnol. 2001, 35, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, E.; Salinas, A. Effect of annealing prior to cold rolling on magnetic and mechanical properties of low carbon non-oriented electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, K.; Lindenmo, M. Precipitates in electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PremKumar, R.; Samajdar, I.; Viswanathan, N.N.; Singal, V.; Seshadri, V. Relative effect(s) of texture and grain size on magnetic properties in a low silicon non-grain oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 264, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, A.; Obata, Y.; Okamura, S. History and development of non-oriented electrical steel in Kawasaki steel. Kawasaki Steel Tech. Rep. 1998, 39, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- De Campos, M.; Yonamine, T.; Fukuhara, M.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Achete, C.A.; Missell, F.P. Effect of frequency on the iron losses of 0.5% and 1.5% Si nonoriented electrical steels. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 2812–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Ros-Yanez, T.; Vandenbossche, L.; Dupré, L.; Melkebeek, J.; Houbaert, Y. The effect of Si and Al concentration gradients on the mechanical and magnetic properties of electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 290, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steniner, D.; Jenko, M.; Jaklič, A.; Čop, A. The correlation between the content of titanium in steel and electromagnetic properties of oriented electrical steel. Metalurgija 2010, 49, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lotten, T.M.; Pragasen, P. Core losses in motor laminations exposed to high-frequency or nonsinusoidal excitation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Euraopean coal and steel community. Methods for Determining the Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Steel Sheet and Strip with 25 cm Epstein Frame; European Committee for Standardization: Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gasper, N.; Janko, K.; Ales, N.; Darja, S.P. Correlation between the excess losses and the relative permeability in fully finished non-oriented electrical steels. Mater. Tehnol. 2014, 48, 997–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, O.; Randle, V. Introduction to Texture Analysis: Macrotexture, Microtexture, and Orientation Mapping, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bunge, H.J. Texture Analysis in Materials Science: Mathematical Methods, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Castro Cerda, F.M.; Kestens, L.A.; Monsalve, A.; Petrov, R.H. The effect of ultrafast heating in cold-rolled low carbon steel: Recrystallization and texture evolution. Metals 2016, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, F.; Stoyka, V.; Petryshynets, I. Strain induced grain growth in non-oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.K. Magnetic anisotropies and textures in high-alloyed non-oriented electrical steels. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Honjou, N.; Minaga, T.; Yashiki, H. Effects of manganese and sulfur contents and slab reheating temperatures on the magnetic properties of non-oriented semi-processed electrical steel sheets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 234, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| C | Si | Al | S | Mn | P | Cu | Cr | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.035 | 0.4 | 0.33 | 0.0033 | 0.55 | 0.013 | 0.34 | 0.023 | 0.033 | 0.019 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calvillo, N.; Soria, M.D.J.; Salinas, A.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Reyes, I.A.; Carrillo, F.R. Influence of Thickness and Chemical Composition of Hot-Rolled Bands on the Final Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets Subjected to Two Different Decarburizing Atmospheres. Metals 2017, 7, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7060229
Calvillo N, Soria MDJ, Salinas A, Gutiérrez EJ, Reyes IA, Carrillo FR. Influence of Thickness and Chemical Composition of Hot-Rolled Bands on the Final Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets Subjected to Two Different Decarburizing Atmospheres. Metals. 2017; 7(6):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7060229
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalvillo, Nephtali, Ma. De Jesús Soria, Armando Salinas, Emmanuel J. Gutiérrez, Iván A. Reyes, and Francisco R. Carrillo. 2017. "Influence of Thickness and Chemical Composition of Hot-Rolled Bands on the Final Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets Subjected to Two Different Decarburizing Atmospheres" Metals 7, no. 6: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7060229
APA StyleCalvillo, N., Soria, M. D. J., Salinas, A., Gutiérrez, E. J., Reyes, I. A., & Carrillo, F. R. (2017). Influence of Thickness and Chemical Composition of Hot-Rolled Bands on the Final Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets Subjected to Two Different Decarburizing Atmospheres. Metals, 7(6), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7060229