Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.6CrFeCoNi and Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
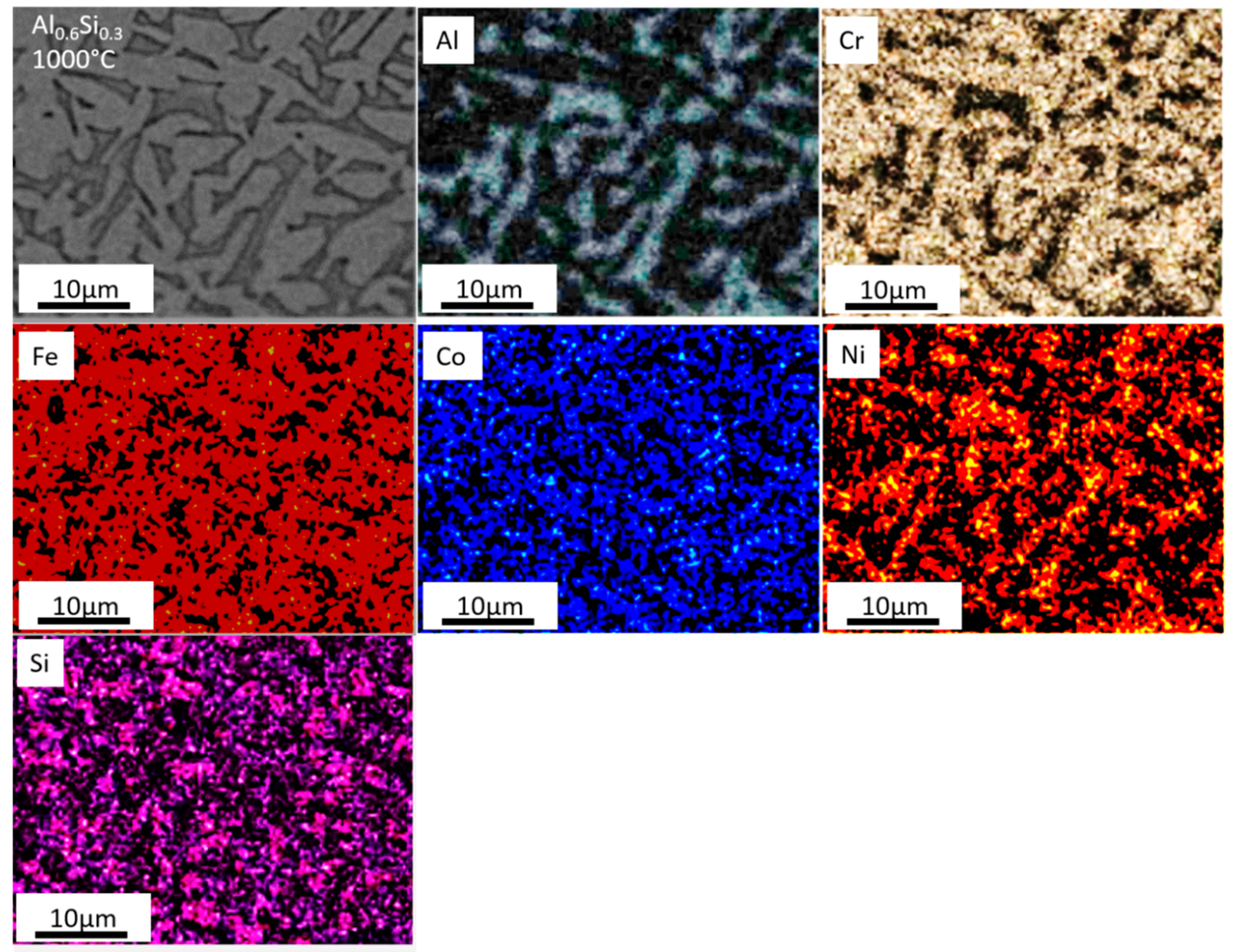
3.1. Phase Compositions and Microstructures
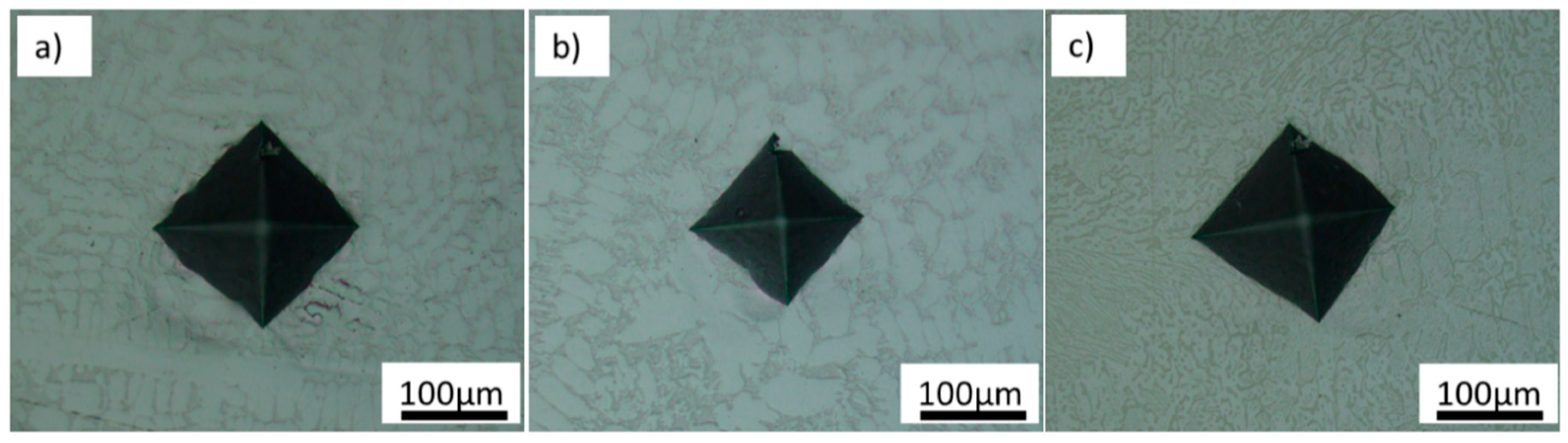
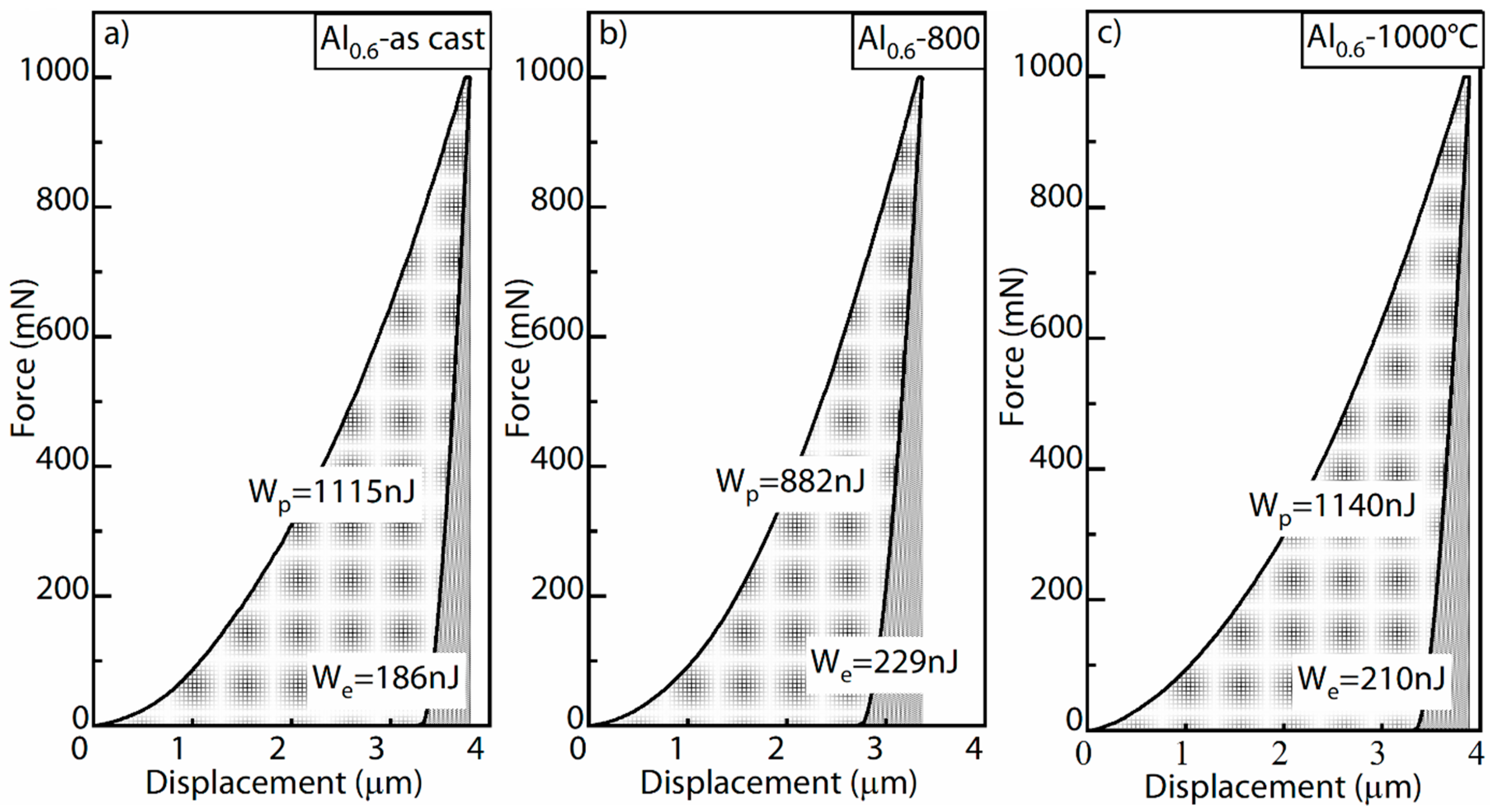
3.2. Young’s Modulus and Hardness
4. Conclusions
- (1)
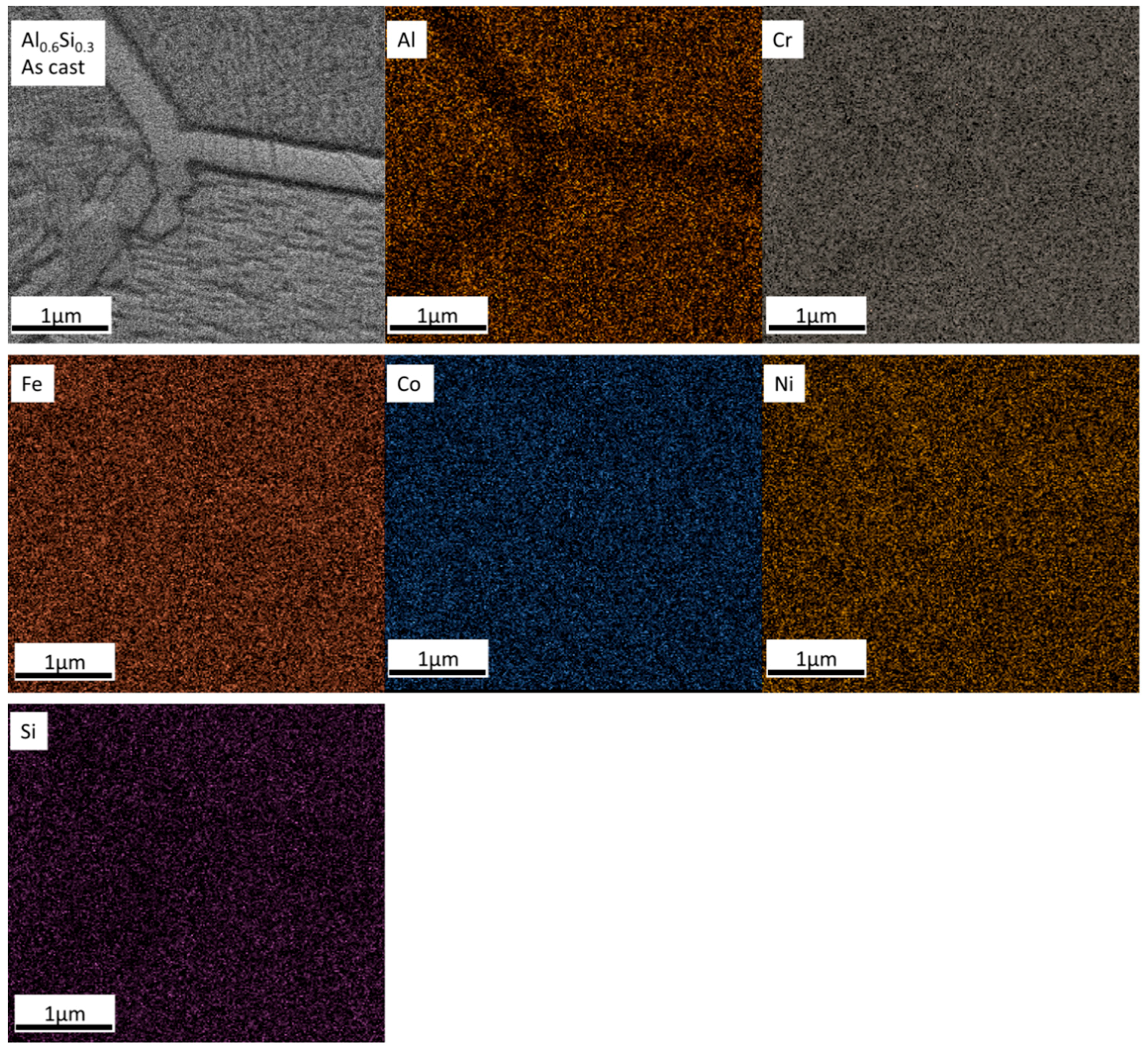
- In its as-cast state, the Al0.6CrFeCoNi alloy exhibited dual phases consisting of a BCC and a FCC phase. The Al0.6CrFeCoNi alloy exhibited a single BCC phase due to the Si-alloying effect. Si-alloying increased the hardness of the Al0.6CrFeCoNi alloy for all the samples.
- (2)
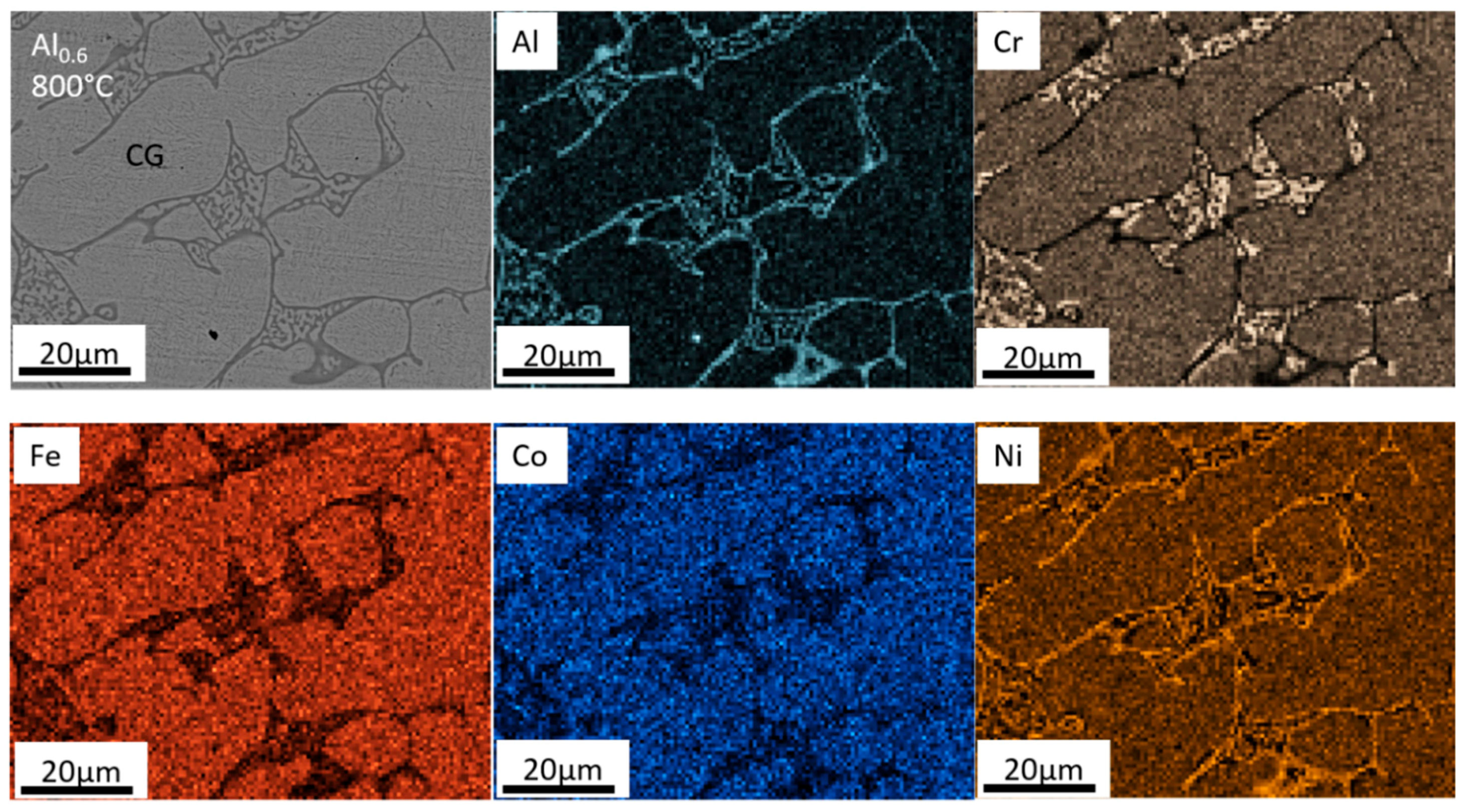
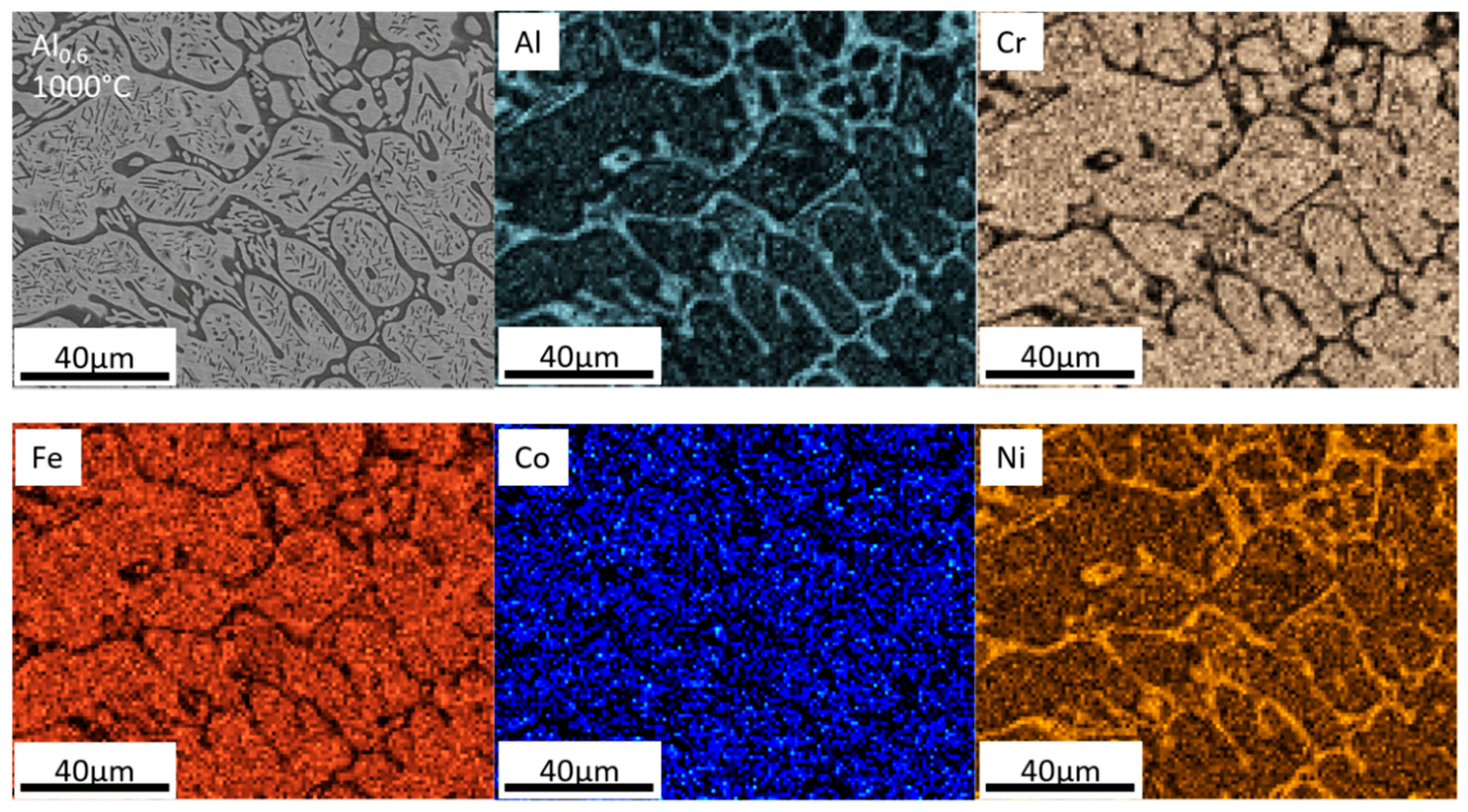
- For the Al0.6CrFeCoNi alloy, the heat treatment at T = 800 °C and T = 1000 °C caused a phase transformation from a FCC-type to a BCC-type phase and coarsened the microstructure. A BCC-type needle-like precipitate started to emerge in the microstructure at T = 800 °C and became larger at T = 1000 °C. The σ-CrFe phase precipitated from the matrix at T = 800 °C and disappeared at T = 1000 °C.
- (3)
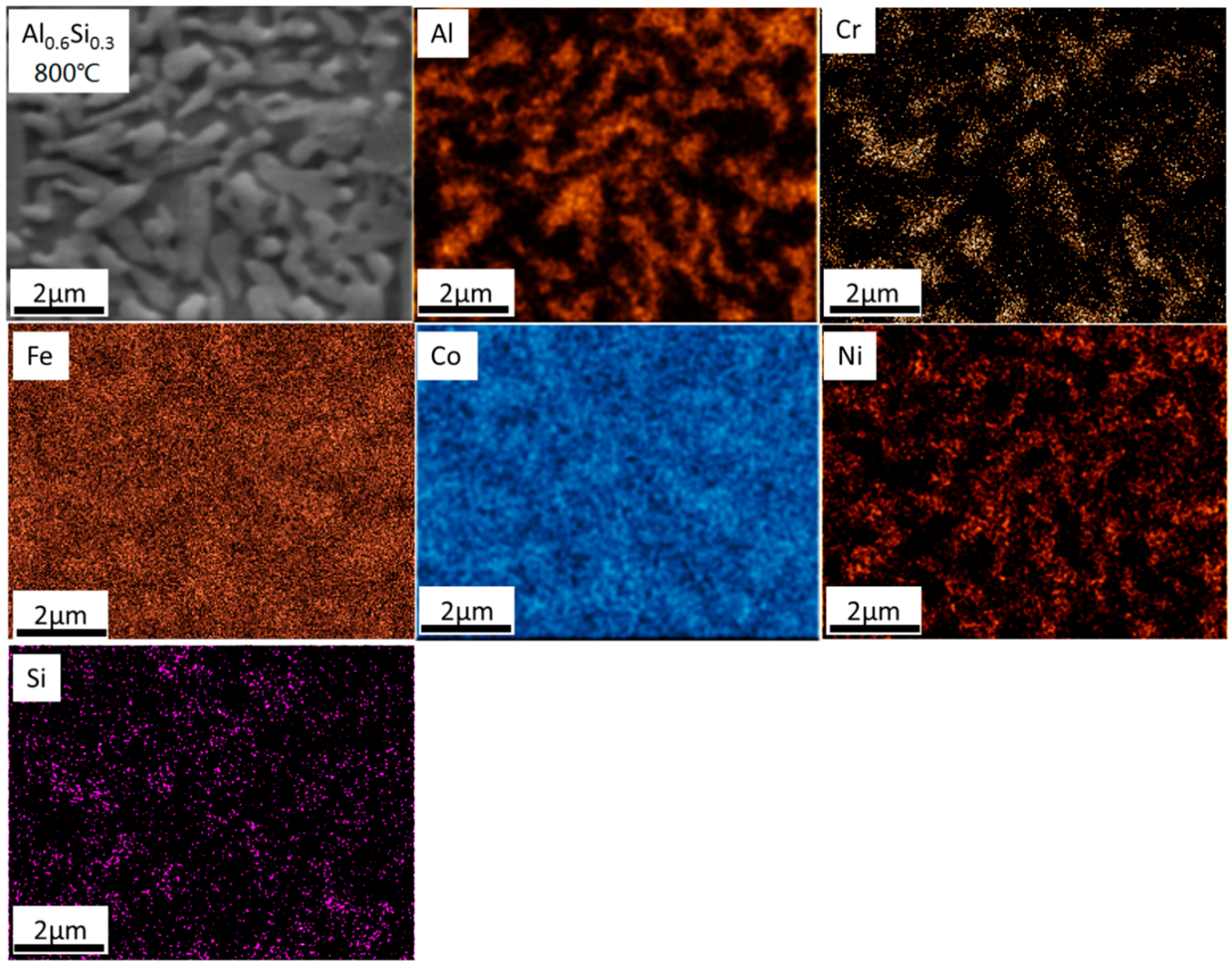
- For the Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 alloy, the FCC phase and the Cr15Co9Si6 phase precipitated at T = 800 °C. At T = 1000 °C, the phase composition was similar to that observed at T = 800 °C, while the microstructure was coarser and the elemental distribution was more non-uniform.
- (4)
- The precipitation of the σ-CrFe phase in the Al0.6CrFeCoNi alloy after heat treatment at T = 800 °C caused an increase in the alloy hardness and a decrease in toughness. The hardness and the percentage of plastic work during the indentation test were comparable for the as-cast sample and heat-treated sample at T = 1000 °C.
- (5)
- The phase transformation from BCC to FCC in the Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 alloy decreased the hardness and increased the toughness at T = 800 °C. As the microstructure got coarser, the hardness decreased and the toughness increased further at T = 1000 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.C.; Tao, T.; Warnken, N. Alloys-by-design: Application to nickel-based single crystal superalloys. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 5898–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.-C.; Sato, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Harada, H. On the creep and phase stability of advanced Ni-base single crystal superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 490, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Wanderka, N.; Murty, B.S.; Glatzel, U.; Banhart, J. Decomposition in multi-component AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.C.; Yang, K.C.; Yeh, J.W.; Kuo, C.M. Developing an advanced Si-bearing DS Ni-base superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 585, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.M.; Fu, H.M.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, A.M.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.Q. Microstructure and compressive properties of multiprincipal component AlCoCrFeNiCx alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3476–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzinié, J.P.; Dirras, G.; Perrière, L.; Chauveau, T.; Leroy, E.; Champion, Y.; Guillot, I. Microstructure of a near-equimolar refractory high-entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2014, 126, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. Effect of molybdenum on the pitting resistance of Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mox alloys in chloride solutions. Corrosion 2011, 67, 085002-1–085002-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, M.-H.; Tsai, M.-H.; Wang, W.-R.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-Y.; Li, C.-E.; Huang, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-F.; Yeh, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J. Structural and thermodynamic factors of suppressed interdiffusion kinetics in multi-component high-entropy materials. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Cao, T.; Xue, Y. Cooling rate-dependent microstructure and mechanical properties of Al x Si 0.2 CrFeCoNiCu 1−x high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Nie, Z.; Wang, F.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, T.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y. Reversible deformation-induced martensitic transformation in Al 0.6 CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy investigated by in situ synchrotron-based high-energy X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cheng, X.; Cai, H.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y. Influence of increasing Al concentration on phase, microstructure and mechanical behaviors of Ni1.5CoFeCu1−xAlxV0.5 high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-H.; Yang, C.-C.; Yeh, J.-W. Industrial development of high-entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2006, 31, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.A.; Tin, S.; Rae, C.M.F. A castability model based on elemental solid-liquid partitioning in advanced nickel-base single-crystal superalloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2761–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Alfano, J.P.; Martens, R.L.; Weaver, M.L. High-temperature oxidation behavior of Al-Co-Cr-Ni-(Fe or Si) multicomponent high-entropy alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Weaver, M.L. Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Yeh, A.-C. The evolution of microstructures and high temperature properties of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 653, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Tang, H.B.; Zhang, A.L. Microstructure and oxidation behavior of new refractory high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbel, M.; Lindner, T.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy coatings produced by HVOF. Coatings 2017, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbel, M.; Lindner, T.; Kohrt, C.; Lampke, T. Processing of AlCoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy by atmospheric plasma spraying. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 181, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, Z.; He, D.; Bobzin, K.; Zhao, L.; Öte, M.; Königstein, T. High temperature oxidation behavior of Al 0.6 CrFeCoNi and Al 0.6 CrFeCoNiSi 0.3 high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Brögelmann, T.; Kruppe, N.C.; Arghavani, M.; Mayer, J.; Weirich, T.E. Plastic deformation behavior of nanostructured CrN/AlN multilayer coatings deposited by hybrid dcMS/HPPMS. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 332, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-R.; Wang, W.-L.; Yeh, J.-W. Phases, microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 589, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uporov, S.; Bykov, V.; Pryanichnikov, S.; Shubin, A.; Uporova, N. Effect of synthesis route on structure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2017, 83, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-C.; Zhang, P.; Xue, Y.-F.; Wang, F.-C.; Wang, L.; Cao, T.-Q.; Tan, Z.; Cheng, B.-Y.; Wang, B.-P. Microstructure evolution of Al 0.6 CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy powder prepared by high pressure gas atomization. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhekne, P.; Swarnakar, A.K.; Chopkar, M.K. Analysis of Si addition on phase formation in AlCoCrCuFeNiSix high entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-R.; Wang, W.-L.; Wang, S.-C.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2012, 26, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xia, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, J.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. Precipitation behavior of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys under ion irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.-O.; Sundman, B. Thermodynamic properties of the Cr Fe system. Calphad 1987, 11, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Hedström, P.; Selleby, M.; Odqvist, J.; Thuvander, M.; Chen, Q. An improved thermodynamic modeling of the Fe–Cr system down to zero kelvin coupled with key experiments. Calphad 2011, 35, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-F.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, S.-K.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0≤x≤2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 488, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.H.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J.S.; Chang, H.; Xue, X.Y.; Zhou, L. Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, V.A.; Yakovlev, A.V.; Pluzhnikova, T.N. Laws of Changing the Structure and Properties of Metallic Glasses upon Annealing and Loca Mechanical Loading. Russ. Phys. J. 2012, 54, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | FCC (wt %) | BCC (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| Al0.6-as-cast | 100.0 | 59.1 |
| Al0.6-800 °C | 100.0 | 66.3 |
| Al0.6-1000 °C | 61.0 | 100.0 |
| Al0.6Si0.3-as-cast | - | 100.0 |
| Al0.6Si0.3-800 °C | 95.0 | 100.0 |
| Al0.6Si0.3-1000 °C | 59.8 | 100.0 |
| Sample | HV5 | HV0.1 | EIT/GPa | E/GPa | We/nJ | Wp/nJ | Wp/(We + Wp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al0.6-as-cast | 245 ± 21 | 269 ± 25 | 158 ± 10 | 174 ± 12 | 186 | 1115 | 85.7% |
| Al0.6-800 °C | 338 ± 30 | 363 ± 39 | 155 ± 11 | 170 ± 12 | 229 | 882 | 79.4% |
| Al0.6-1000 °C | 241 ± 17 | 265 ± 20 | 152 ± 8 | 167 ± 9 | 210 | 1140 | 84.4% |
| Sample | HV5 | HV0.1 | EIT/GPa | E/GPa | We/pJ | Wp/pJ | Wp/(We + Wp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al0.6Si0.3-as-cast | 616 ± 54 | 669 ± 47 | 176 ± 12 | 194 ± 14 | 260 | 640 | 71.1% |
| Al0.6Si0.3-800 °C | 558 ± 50 | 605 ± 39 | 166 ± 6 | 183 ± 7 | 255 | 711 | 73.6% |
| Al0.6Si0.3-1000 °C | 425 ± 39 | 459 ± 56 | 162 ± 6 | 178 ± 7 | 243 | 807 | 76.8% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Bobzin, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, L.; Öte, M.; Königstein, T.; Tan, Z.; He, D. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.6CrFeCoNi and Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110974
Chen L, Bobzin K, Zhou Z, Zhao L, Öte M, Königstein T, Tan Z, He D. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.6CrFeCoNi and Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 High-Entropy Alloys. Metals. 2018; 8(11):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110974
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lijia, Kirsten Bobzin, Zheng Zhou, Lidong Zhao, Mehmet Öte, Tim Königstein, Zhen Tan, and Dingyong He. 2018. "Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.6CrFeCoNi and Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 High-Entropy Alloys" Metals 8, no. 11: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110974
APA StyleChen, L., Bobzin, K., Zhou, Z., Zhao, L., Öte, M., Königstein, T., Tan, Z., & He, D. (2018). Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al0.6CrFeCoNi and Al0.6CrFeCoNiSi0.3 High-Entropy Alloys. Metals, 8(11), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110974





