Thermodynamic of Liquid Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen Thermal Plasma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamic Properties of Thermal Plasma
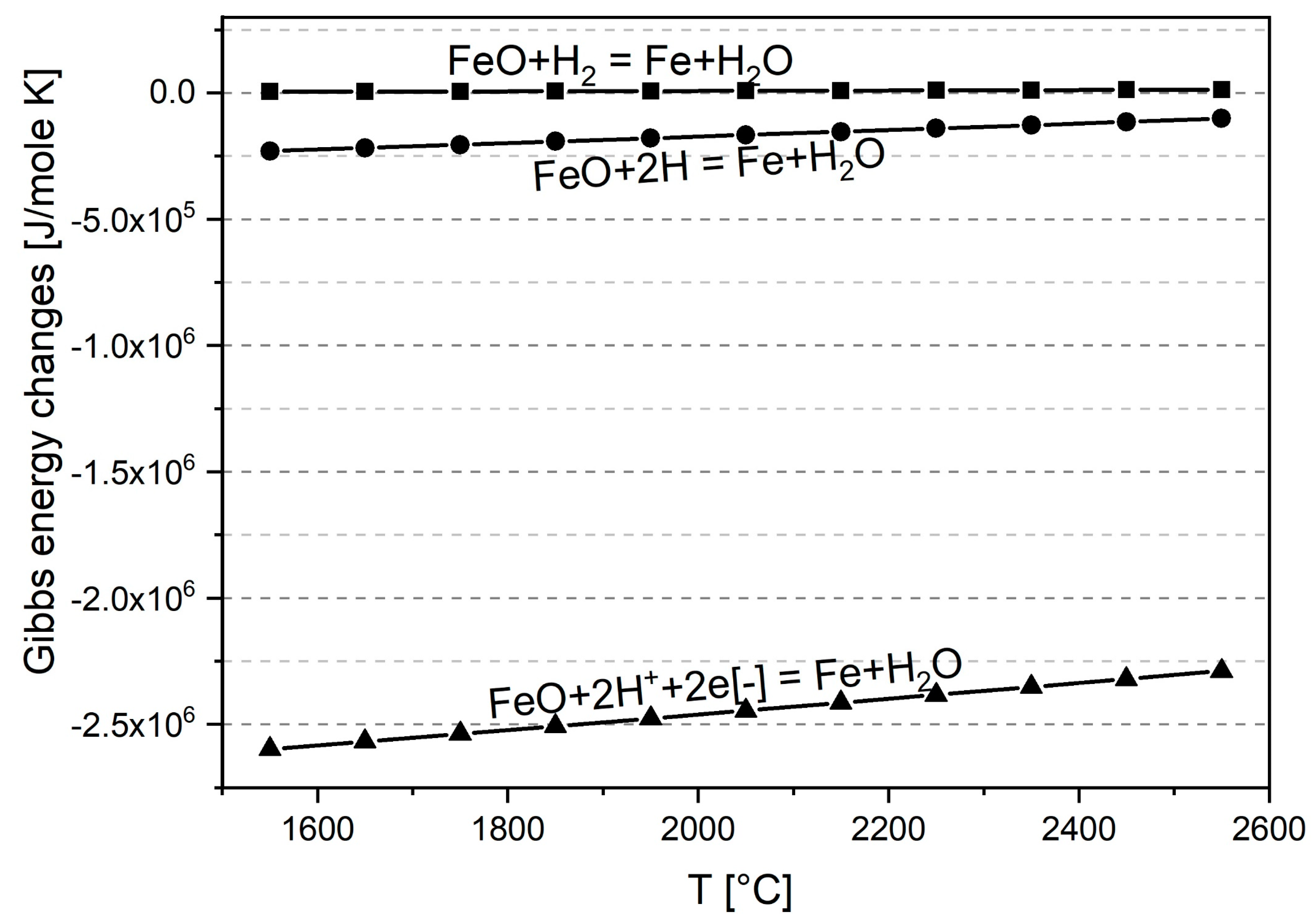
3. Effect of Charge Polarity on the Iron Ore Reduction Reactions
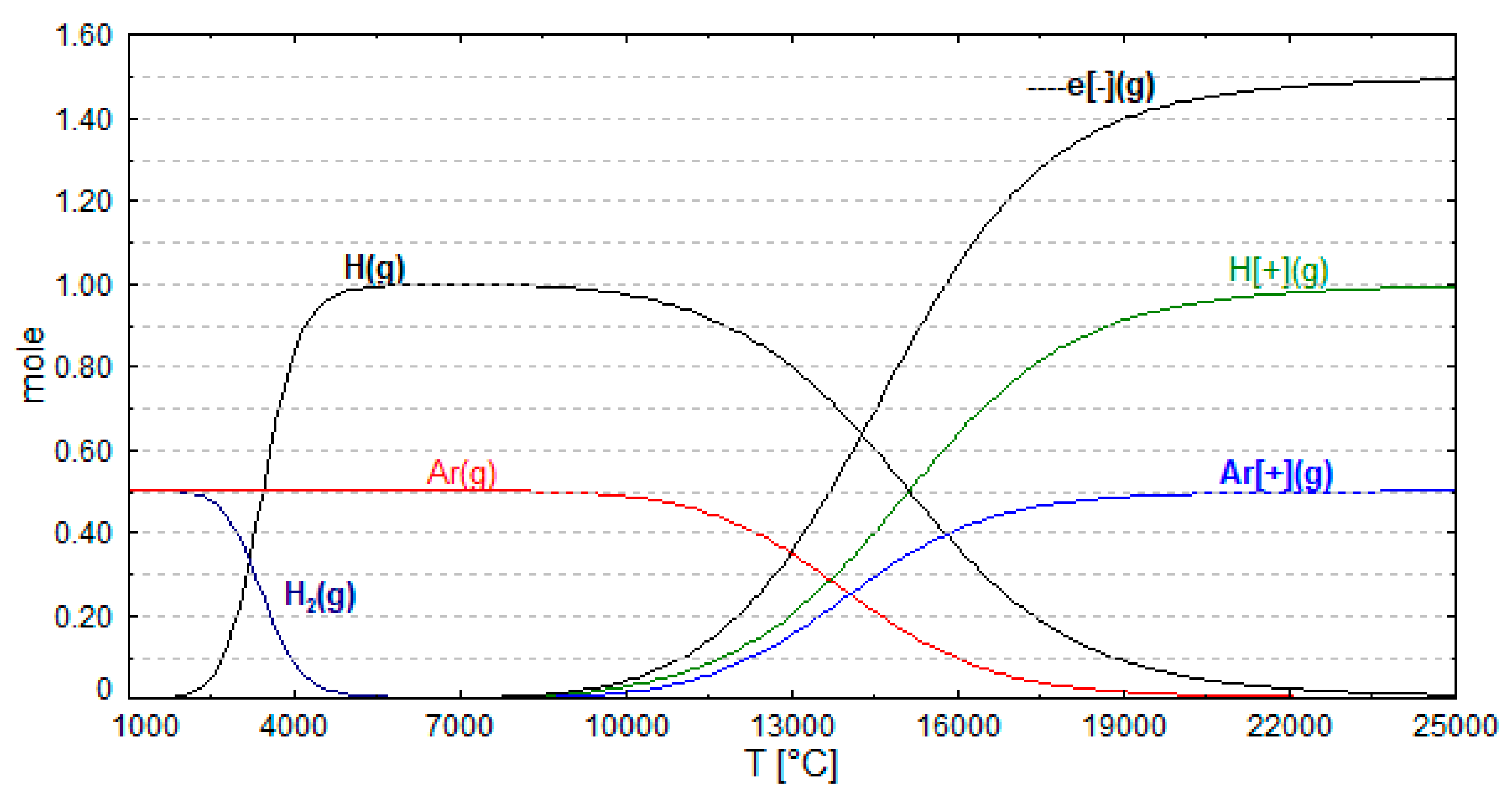
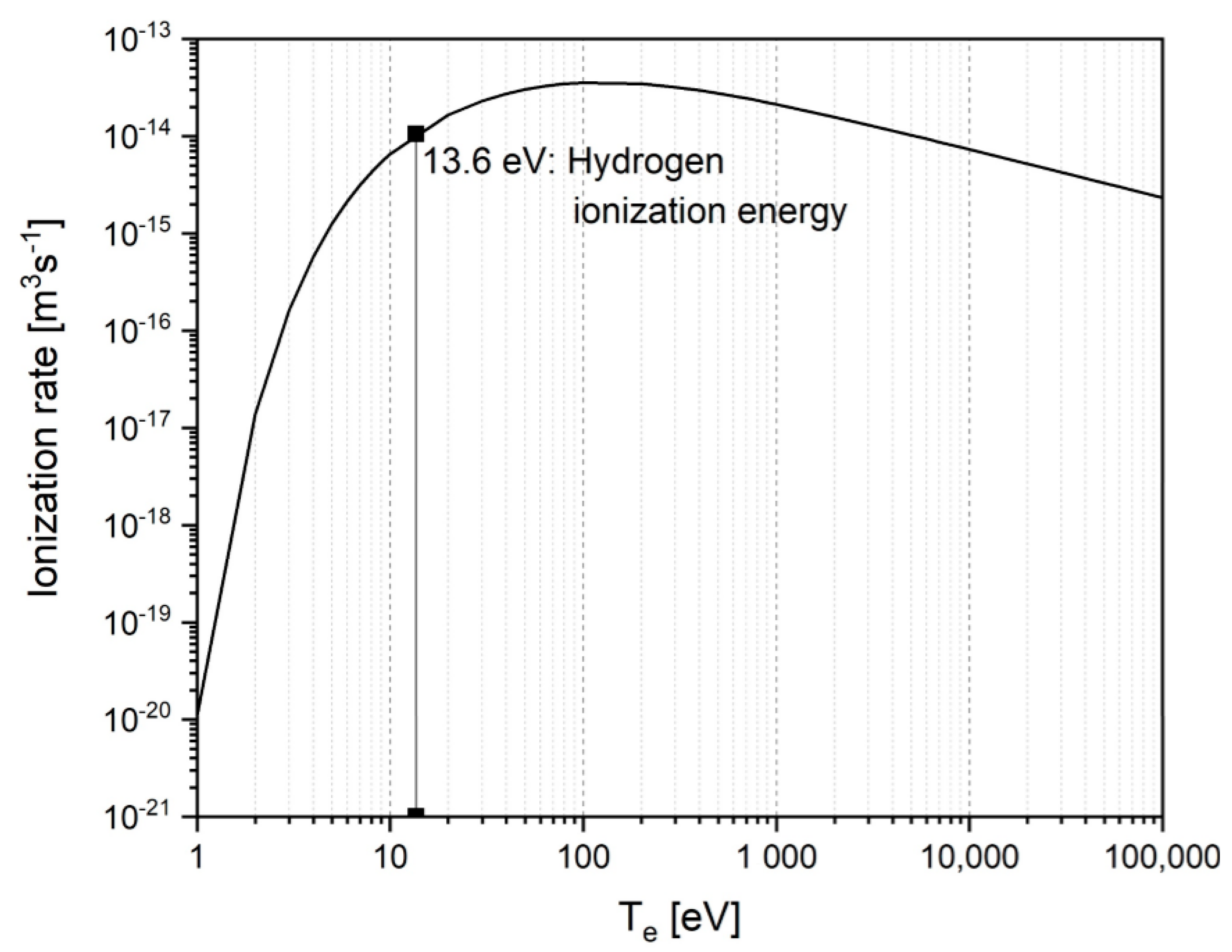
4. Ionization Degree of Hydrogen
5. Solubility of Hydrogen
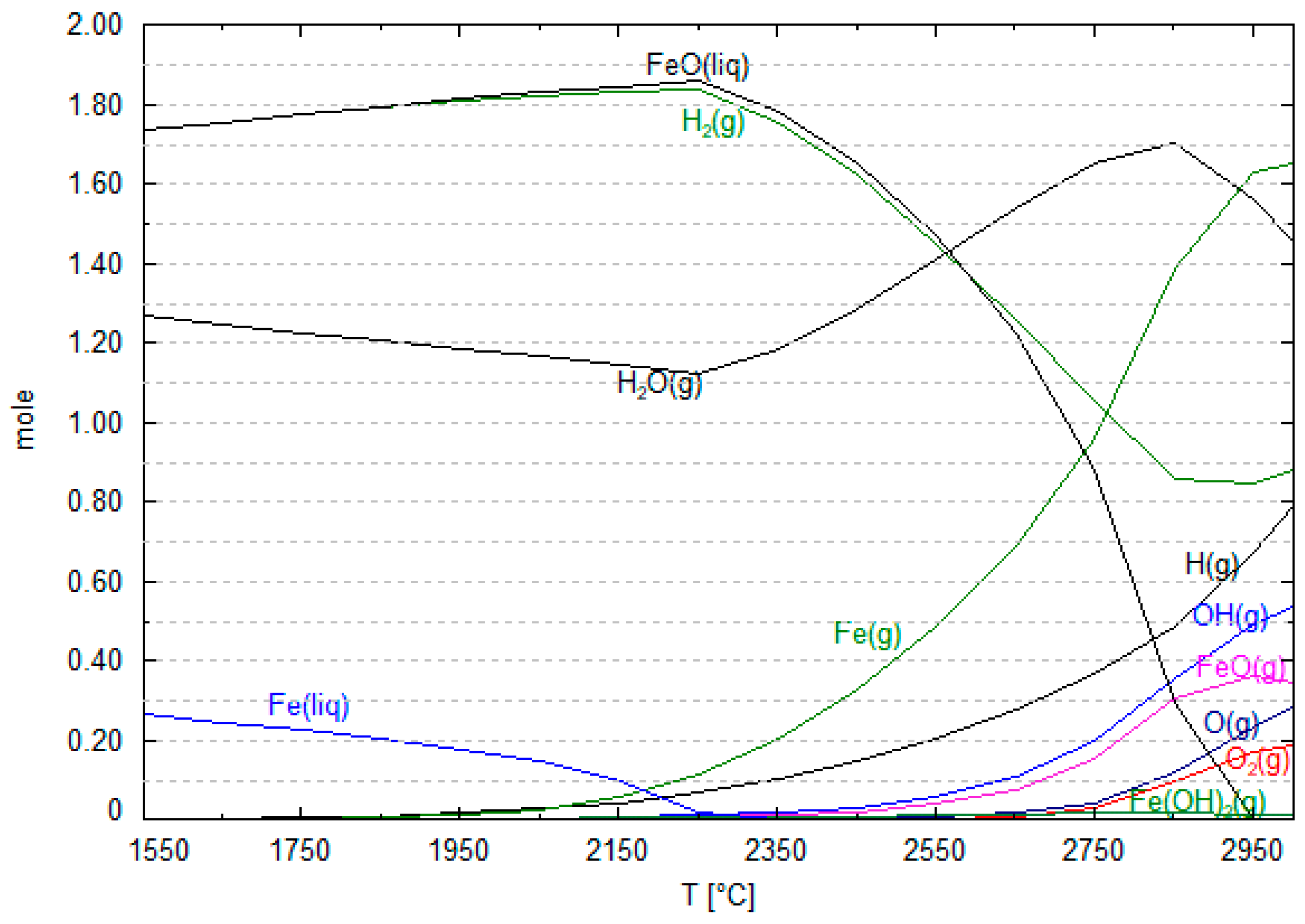
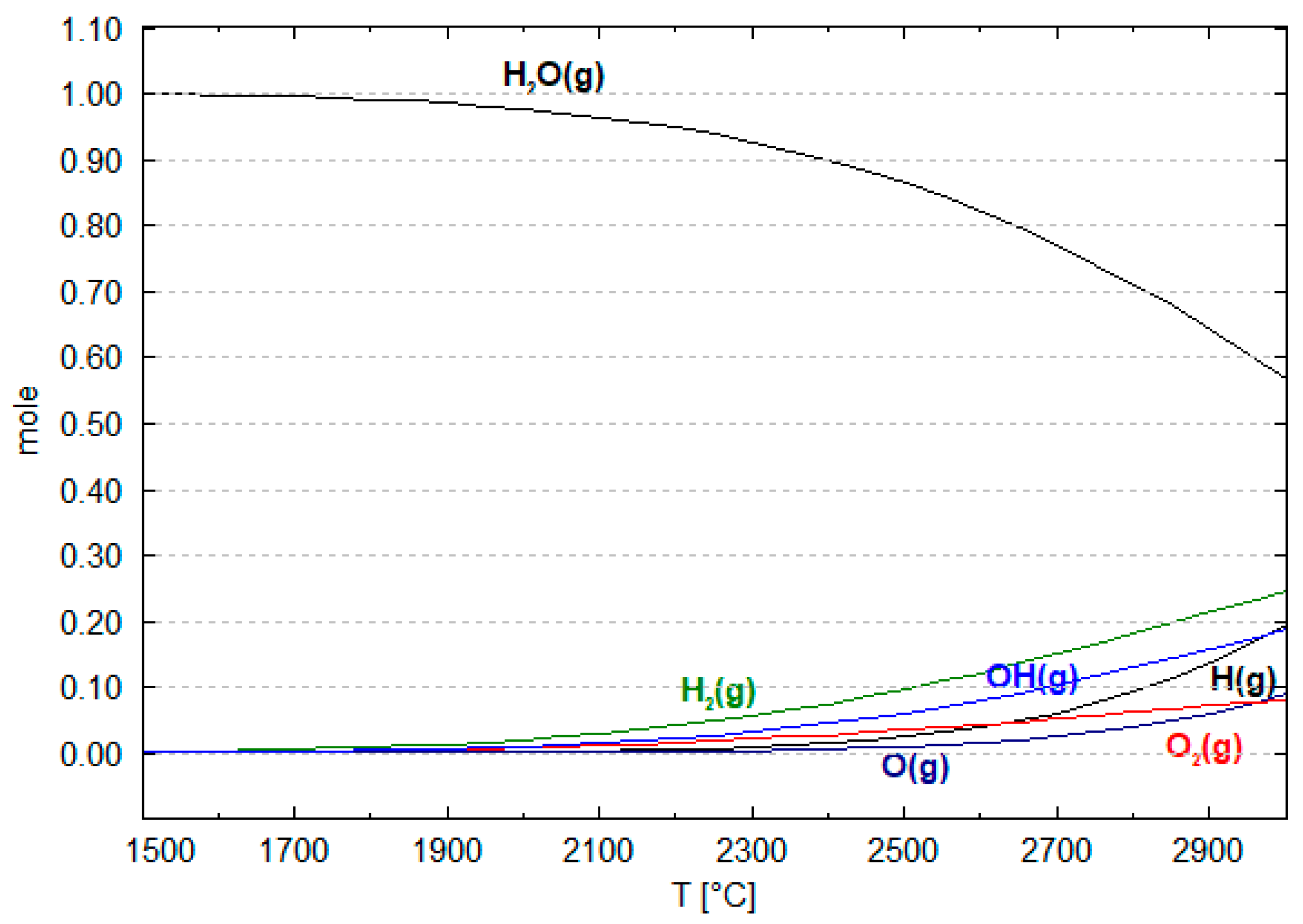
6. Mechanism of the Hematite Reduction Reaction in HPSR
7. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundak, M.; Lazic, L.; Crnko, J. CO2 Emissions in the Steel Industry; Croatian Metallurgical Society (CMS): Zagreb, Croatia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lisienko, V.G.; Chesnokov, Y.N.; Lapteva, A.V.; Noskov, V.Y. Types of greenhouse gas emissions in the production of cast iron and steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 150, 12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, K.; Bäck, E.; Krieger, W. Reduction of iron ore by a mixture of Ar-H2 with CO and CO2 under plasma application. In Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, Kyoto, Japan, 26–31 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschen, M.; Badr, K.; Pfeifer, H. Influence of direct reduced iron on the energy balance of the electric arc furnace in steel industry. Energy 2011, 36, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-W.; Li, C. The mechanism of reduction of iron oxide by hydrogen. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 400, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkdogan, E.T.; Vinters, J.V. Gaseous reduction of iron oxides: Part I. Reduction of hematite in hydrogen. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1971, 2, 3175–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q. Study on Kinetics of Iron Oxide Reduction by Hydrogen. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzani da Costa, A.; Wagner, D.; Patisson, F. Modelling a new, low CO2 emissions, hydrogen steelmaking process. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 46, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban-Ya, S.; Ighuchi, Y.; Nagasaka, T. Rate of reduction of liquid wustite with hydrogen. Tetsu-to-Hagane 1984, 70, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, H.L.; Clump, C.W. Reduction of iron ore with hydrogen in a direct current plasma jet. Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Des. Dev. 1970, 9, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, R.G.; Sandall, W.R.; Cheplick, P.G.; MacRae, D.R. Plasma reduction of iron oxide with hydrogen and natural gas at 100 kW and 1 MW. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1977, 4, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, S.; Iguchi, Y. Hydrogen reduction of liquid iron oxide fines in gas-conveyed systems. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, K. Smelting of Iron Oxides Using Hydrogen Based Plasmas. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bäck, E. Schmelzreduktion von Eisenoxiden Mit Argon-Wasserstoff-Plasma. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Plaul, J.F. Schmelzreduktion von hämatitischen Feinerzen im Wasserstoff-Argon-Plasma. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Robino, C.V. Representation of mixed reactive gases on free energy (Ellingharn-Richardson) diagrams. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1996, 27, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, M.I. Thermal plasma processing. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1991, 19, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, K.C.; Rajput, P.; Paramguru, R.K.; Bhoi, B.; Mishra, B.K. Reduction of oxide minerals by hydrogen plasma: An Overview. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2014, 34, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebler, H.; Plaul, J.F. Hydrogen plasma- smelting reduction- an option for steel making in the future. METABK 2004, 43, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, T.; Shibata, K.; Takeda, K. In-flight reduction of Fe2O3, Cr2O3, TiO2 and Al2O3 by Ar-H2 and Ar-CH4 plasma. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelles, J.P.; Heberlein, J.V.R.; Pfender, E. Non equilibrium Modeling of Arc Plasma Torches. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.E. A departure from local thermodynamic equilibrium within a freely burning arc and asymmetrical Thomson electron features. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1997, 30, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, M.I.; Fauchais, P.; Pfender, E. Thermal Plasmas. Fundamentals and Applications/Maher I. Boulos, Pierre Fauchais, and Emil Pfender. Vol.1; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.; Guo, S.; Xu, K. Reduction of metal oxide in nonequilibrium hydrogen plasma. China Nonferrous Metal 2004, 14, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Ito, M.; Ishikawa, H. Reduction and dephosphorization of molten iron oxide with hydrogen-argon plasma. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 1981, 1, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Kitahara, N.; Morinaka, I.; Sakuraya, K.; Ozawa, M.; Tanaka, M. Reduction of molten iron oxide and FeO bearing slags by H2-Ar plasma. ISIJ Int. 1984, 24, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhe, N.S.; Tak, A.K.; Bhoraskar, S.V.; Mathe, V.L.; Das, A.K. Transport properties of Ar-Al plasma at 1 atmosphere. In SOLID STATE PHYSICS: Proceedings of the 56th DAE Solid State Physics Symposium 2011, SRM University, Kattankulathur, Tamilnadu, India, 19–23 December 2011; AIP: Melville, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1025–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Lisal, M.; Smith, W.; Bures, M.; Vacek, V.; Navratil, J. REMC computer simulations of the thermodynamic properties of argon and air plasmas. Mol. Phys. 2002, 100, 2487–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, A. Plasma Physics. An Introduction to Laboratory, Space, and Fusion Plasmas/Alexander Piel; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Keidar, M.; Beilis, I. Plasma Engineering. Applications from Aerospace to Bio and Nanotechnology; Elsevier Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Janev, R.K.; Reiter, D.; Samm, U. Collision Processes in Low-Temperature Hydrogen Plasmas; Institut für Plasmaphysik, Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, EURATOM Association: Jülich, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Feinman, J. Plasma Technology in Metallurgical Processing; Iron and Steel Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Pfender, E. Thermal plasma technology: Where do we stand and where are we going? Plasma Chem Plasma Process 1999, 19, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, K.C.; Murphy, A.B. Hydrogen Plasma Processing of Iron Ore. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 1561–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeva, M.; Uhrlandt, D.; Murphy, A.B. A collisional-radiative model of iron vapour in a thermal arc plasma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 22LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, A.J.; Lieberman, M.A. Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, R. Spectral emission of fractional quantum energy levels of atomic hydrogen from a helium–hydrogen plasma and the implications for dark matter. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembovsky, V. How the polarity of a surface reacting with a low temperature plasma affects the thermodynamic variables in metallurgical reactions. Achta Phys. Slov. 1984, 34, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.E. The plasma–sheath boundary: Its history and Langmuir’s definition of the sheath edge. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 18, 14004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldston, R.J.; Rutherford, P.H. Introduction to Plasma Physics; Institute of Physics Pub.: Bristol, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri Seftejani, M.; Schenk, J. Kinetics of molten iron oxides reduction using hydrogen. La Metall. Ital. 2018, 7/8, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dembovský, V. Thermodynamics of dissolution and liberation of gases in the atomization of molten metals by plasma-induced expansion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1997, 64, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.H.; Chipman, J.; King, T.B.; Grant, N.J. Hydrogen in Steelmaking Slags. JOM 1956, 8, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-K.; Kim, S.-H. The solubility of water vapour in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO slag system. Steel Res. 2000, 71, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedeon, S.A.; Eagar, T.W. Thermochemical Analysis of Hydrogen Absorption in Welding: A new model that addresses the shortcomings of Sievert’s A new model that addresses the shortcoming of Sievert’s law for predicting hydrogen absorption is proposed. Weld. J. 1990, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Fruehan, R.J. The Making, Shaping, and Treating of Steel. [Vol. 2], Steelmaking and Refining Volume, 11th ed.; AISE Steel Foundation: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, I.-H. Thermodynamic Modeling of Gas Solubility in Molten Slags (II)—Water. ISIJ Int. 2006, 46, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandberg, J.; Sichen, D. Water vapor solubility in ladle-refining slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2006, 37, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoephasius, J.-C.; Reitz, J.; Friedrich, B. ESR Refining Potential for Titanium Alloys using a CaF2-based Active Slag. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2007, 9, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Park, J.G.; Lee, C.-H.; Sohn, I. Hydrogen Dissolution in the TiO2–SiO2–FeO and TiO2–SiO2–MnO Based Welding-Type Fluxes. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, L.E. Solubility of Water in Molten Glass; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlster, M.; Reichel, H.-H. Die Wasserstofflöslichkeit von Schlacken des Systems CaO-FeO-SiO2. Arch. Eisenhüttenwes. 1969, 40, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.B.; Tanaka, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Tashiro, S.; Lowke, J.J. CFD modeling of arc welding: The importance of the arc plasma. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on CFD in the Mineral and Process Industries, Melbourne, Australia, 9–11 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasaka, T.; Ban-ya, S. Rate of reduction of liquid iron oxide. Tetsu-to-Hagane 1992, 78, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, T.; Hino, M.; Ban-ya, S. Interfacial kinetics of hydrogen with liquid slag containing iron oxide. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2000, 31, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, S.; Bilgen, E. An overall assessment of hydrogen production by solar water thermolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1989, 14, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
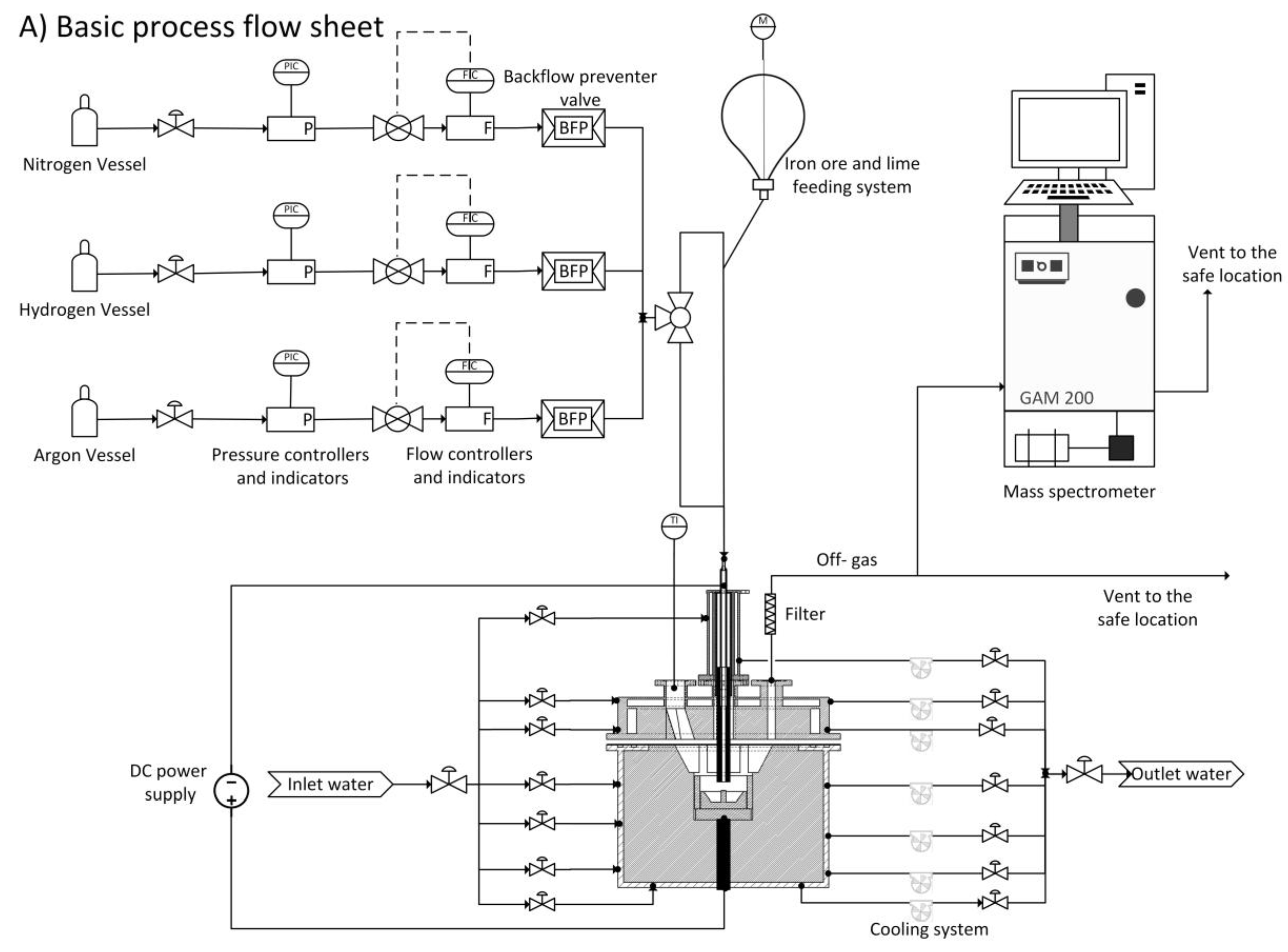
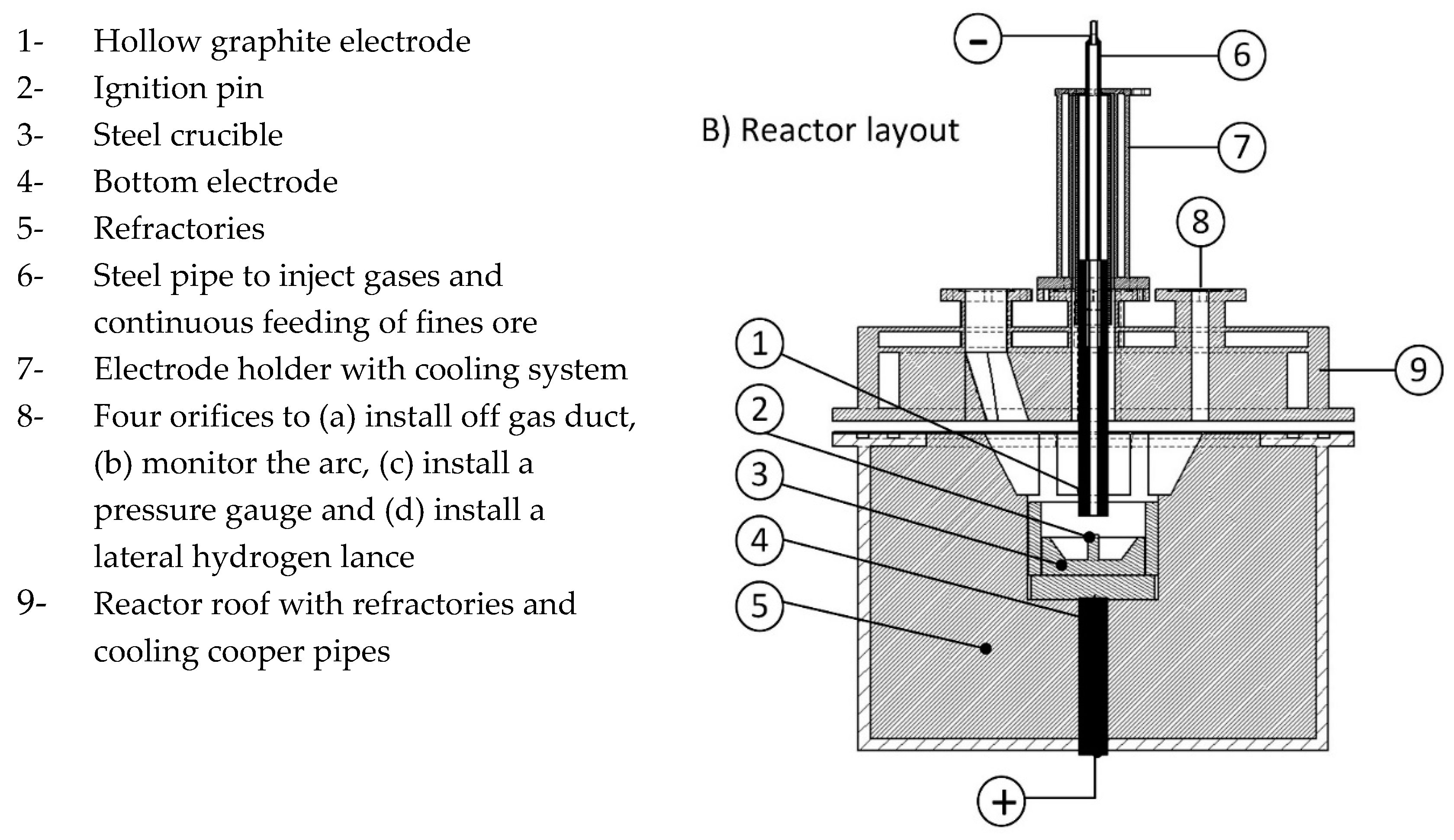


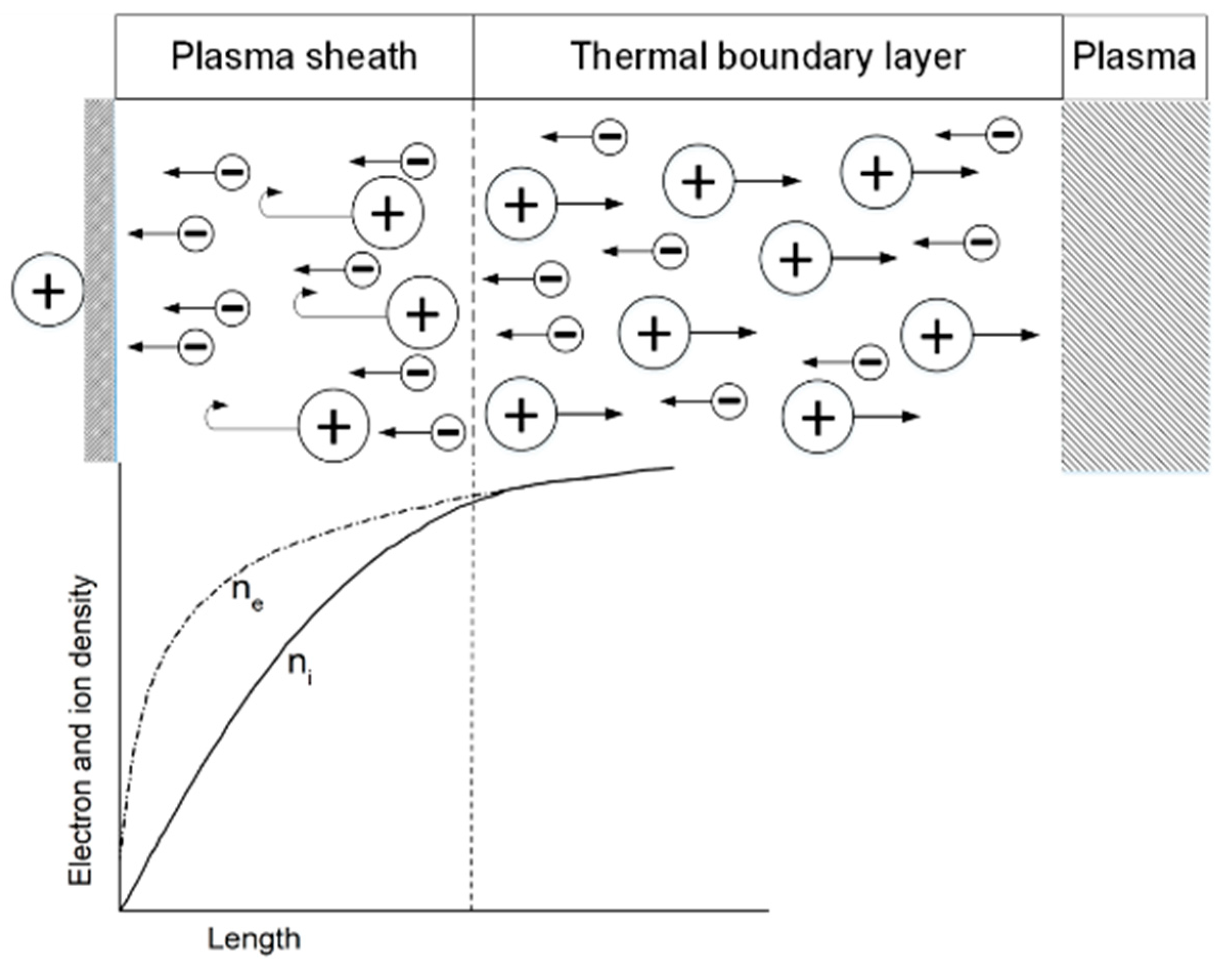
| Collisional ionization | |
| Collisional ionization | |
| Collisional excitation | |
| Photoionization | |
| Three-body recombination | |
| Two-body recombination | |
| Wall recombination |
| Result of | Unit | H2O | H2 | O2 | H | O | OH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baykara et al. [56] | mol % | 91.14 | 4.27 | 1.55 | 0.53 | 0.19 | 2.33 |
| Present work | mol % | 92.0 | 4.3 | 1.6 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 2.33 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naseri Seftejani, M.; Schenk, J. Thermodynamic of Liquid Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen Thermal Plasma. Metals 2018, 8, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121051
Naseri Seftejani M, Schenk J. Thermodynamic of Liquid Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen Thermal Plasma. Metals. 2018; 8(12):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121051
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaseri Seftejani, Masab, and Johannes Schenk. 2018. "Thermodynamic of Liquid Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen Thermal Plasma" Metals 8, no. 12: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121051
APA StyleNaseri Seftejani, M., & Schenk, J. (2018). Thermodynamic of Liquid Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen Thermal Plasma. Metals, 8(12), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121051