Prediction Model of Iron Ore Pellet Ambient Strength and Sensitivity Analysis on the Influence Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
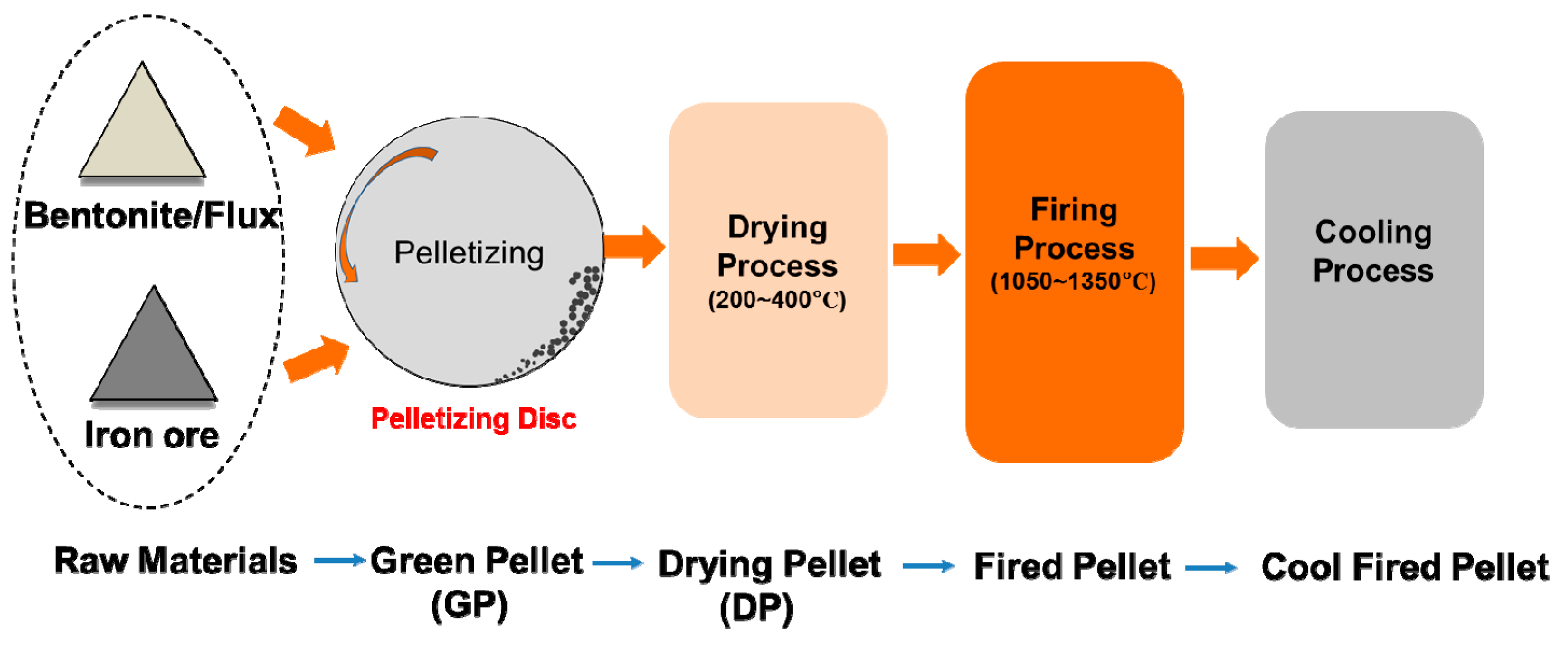
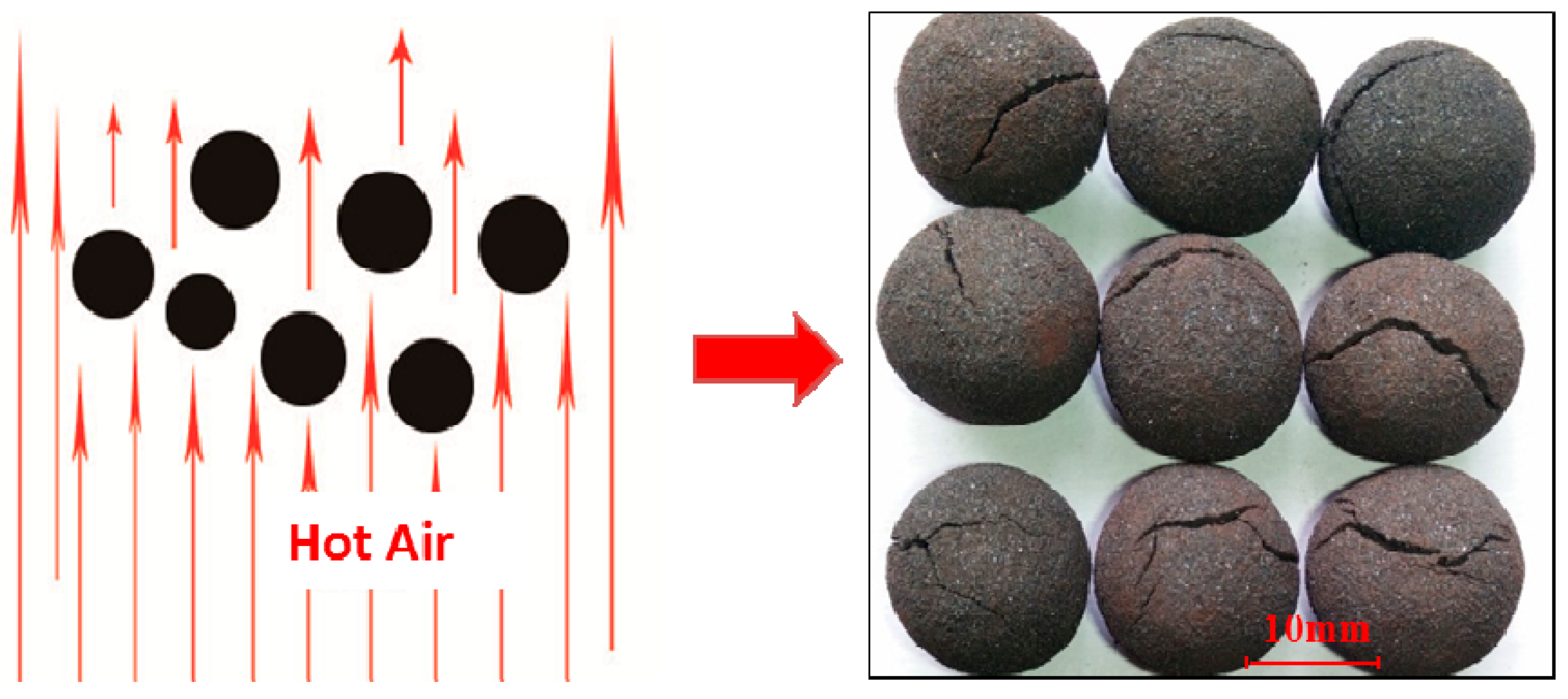
2.1. Pelletizing Process
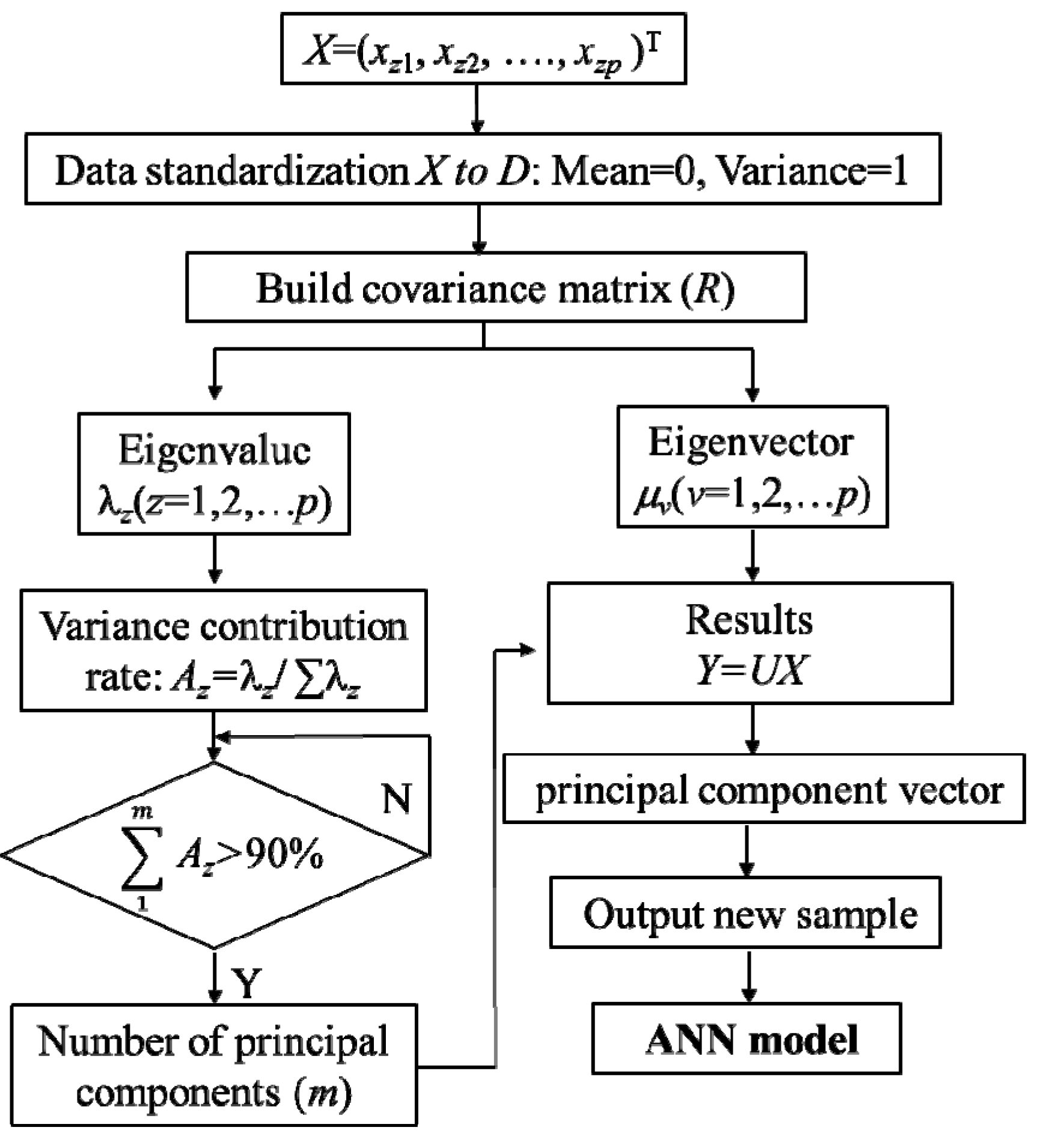
2.2. Principal Component Analysis
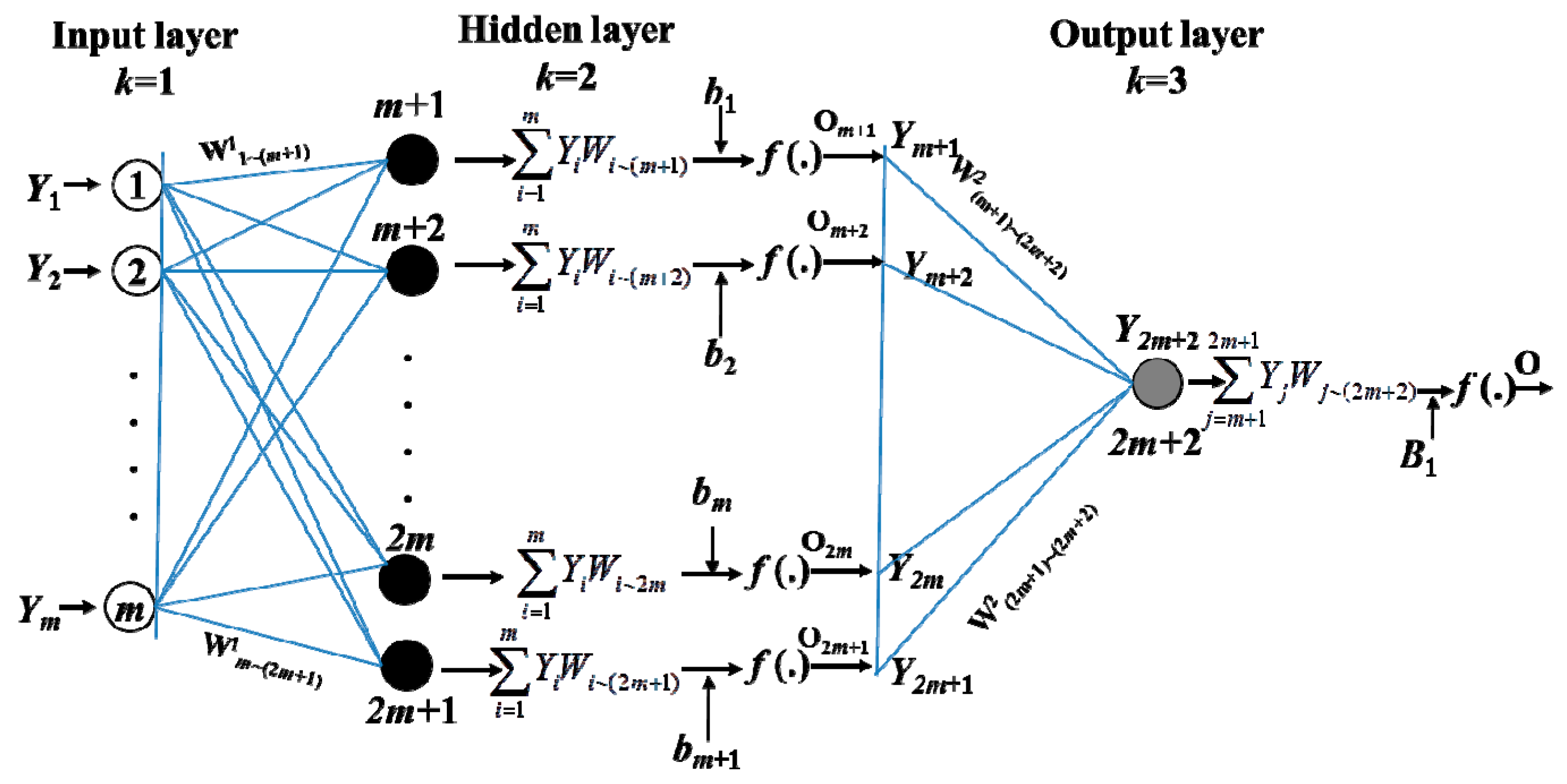
2.3. Artificial Neural Network
2.3.1. Information Forward Propagation of BP Network
2.3.2. Error Inverse Propagation of BP Network
2.3.3. Optimize the BP Network with GA
3. Results and Discussion
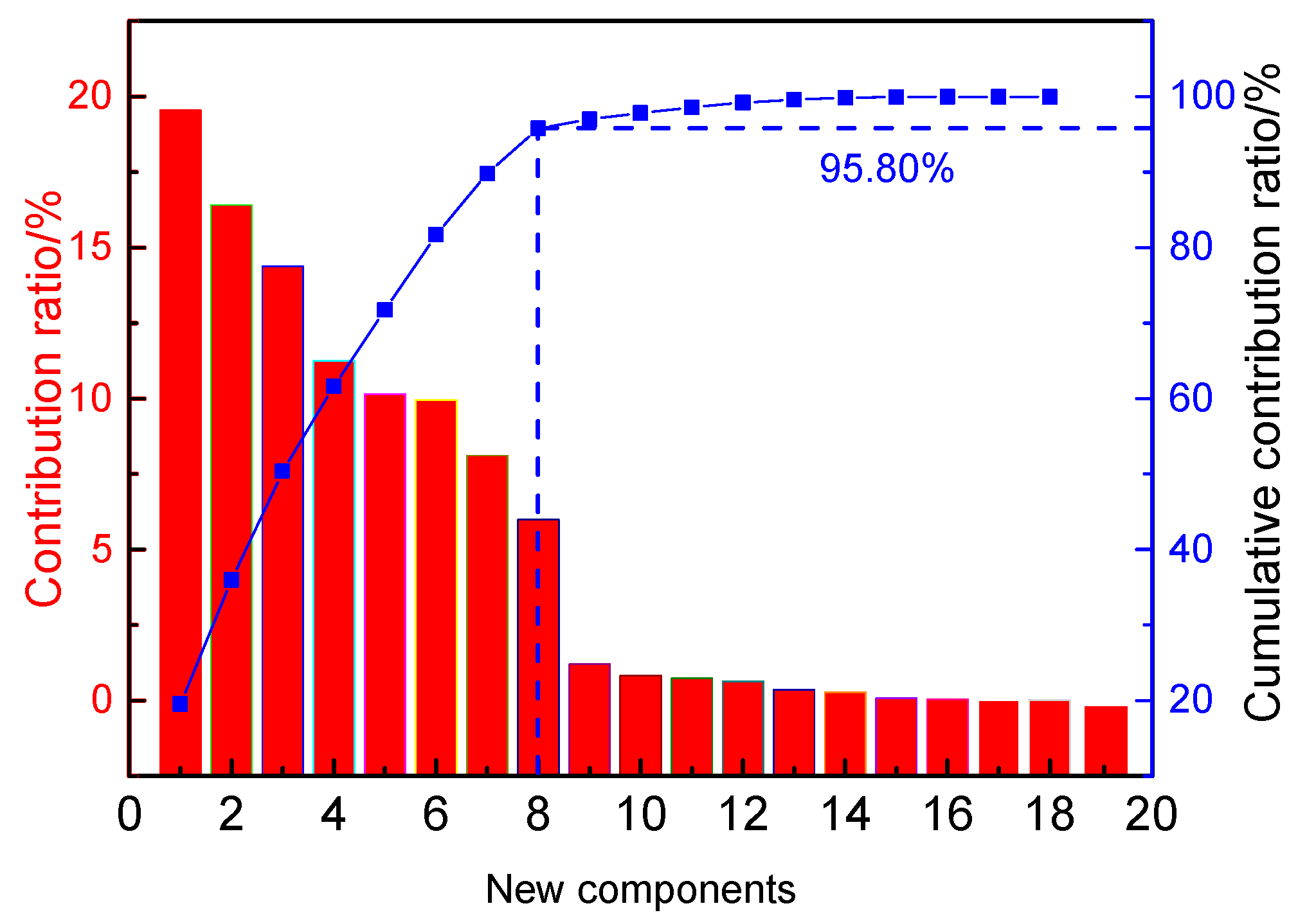
3.1. PCA
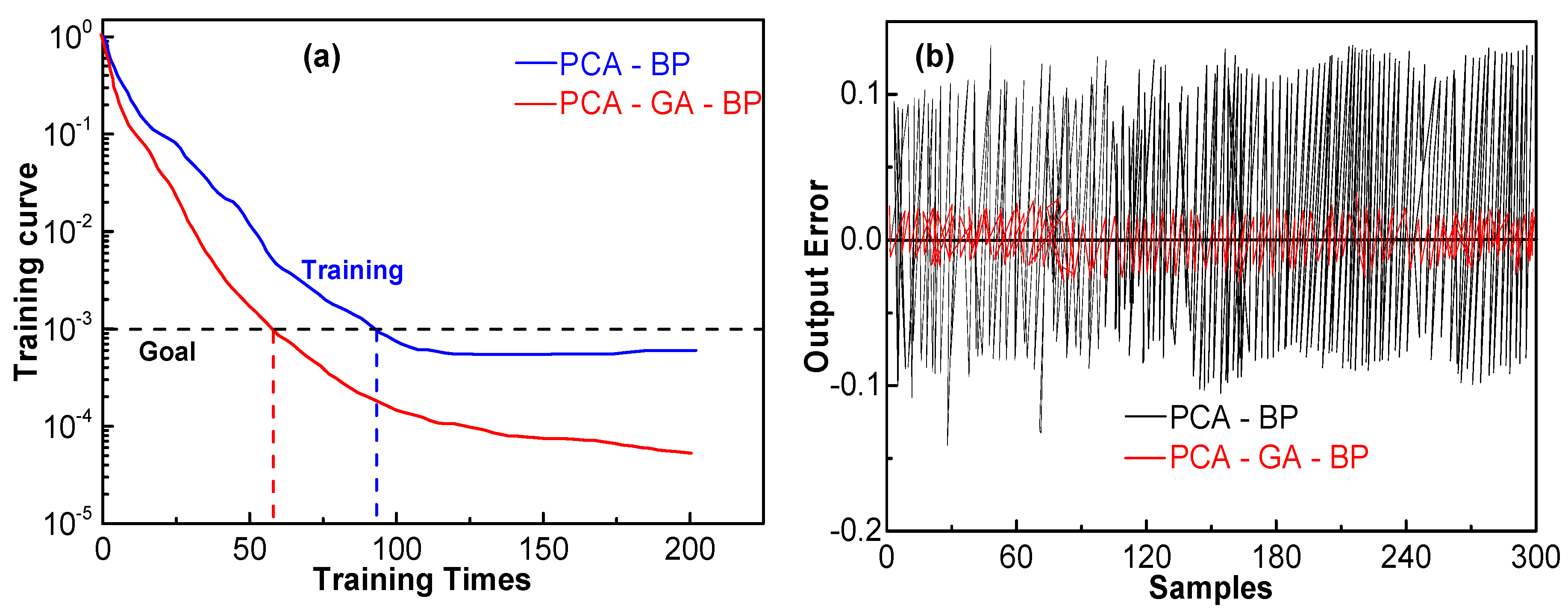
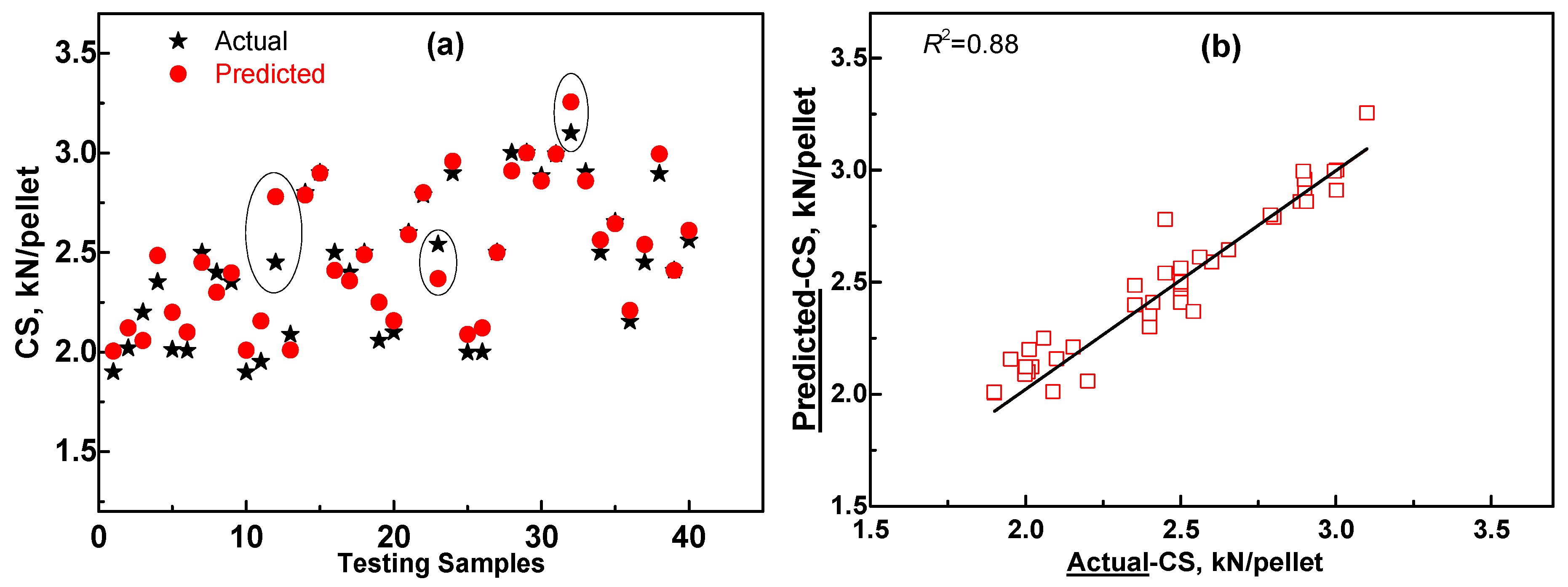
3.2. Training and Testing of the BP Network
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of the Influence Variables of CS
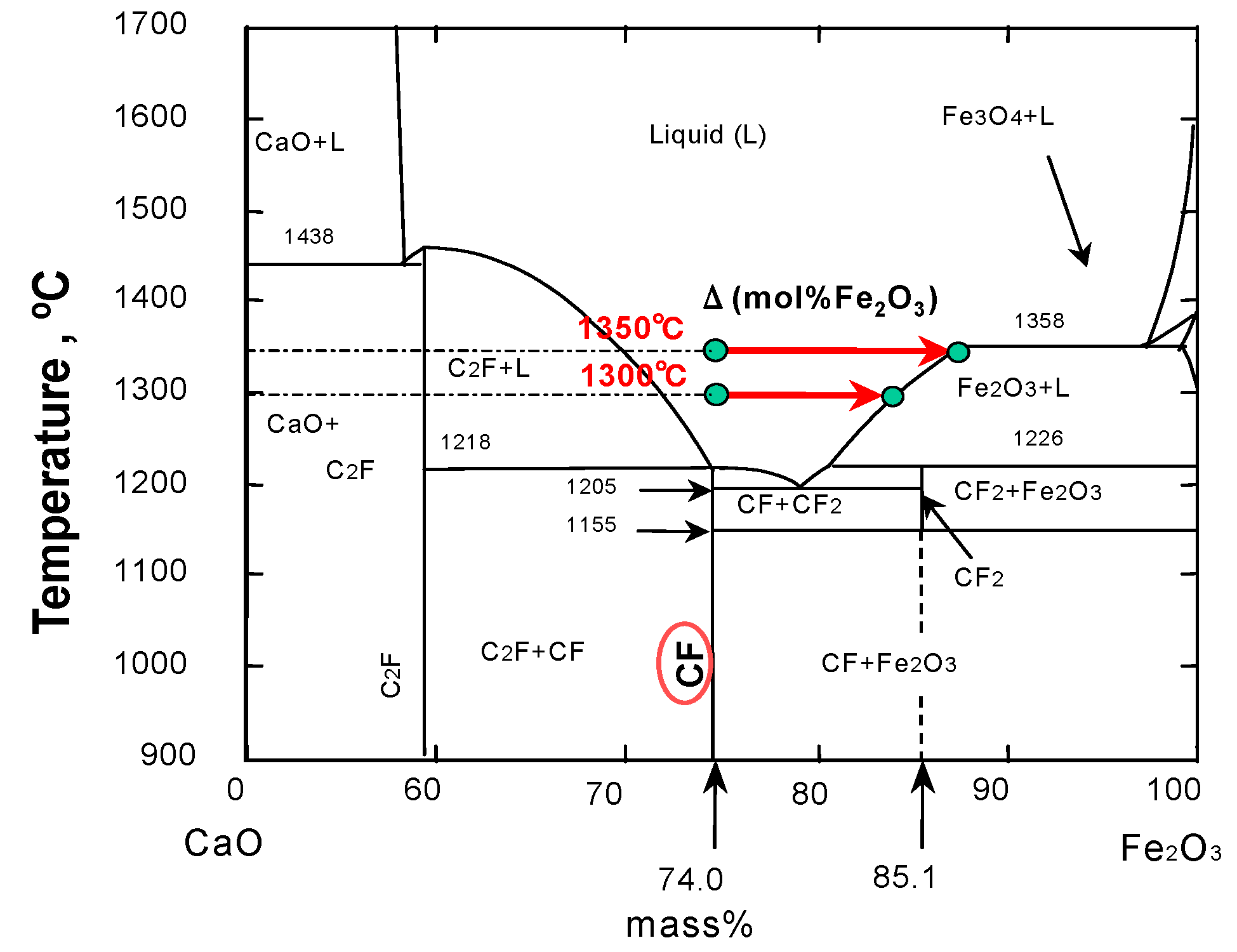
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, A.K. Principles of Blast Furnace Ironmaking; Cootha Publishing House: Brisbane, Australia, 1981; pp. 33–39. ISBN 10:0949917001. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.Y.; Zhu, D.Q. Basic Principles, Techniques and Equipment of the Iron Ore Oxidized Pellets; Central South University Press: Changsha, China, 2005; pp. 323–336. ISBN 9787811050516. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Shen, F.; Jiang, X.; Wei, G.; Zheng, H.Y. Gas-solid reduction kinetic model of MgO-fluxed pellets. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.; Karasev, A.; Jönsson, P.G. Evaluation of dust generation during mechanical wear of iron ore pellets. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Metallurgical Construction Association. Code for Design of Iron Pelletizing Engineering; China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 20–25. ISBN 1580177244. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, X.; Wei, G.; Zheng, H. Effect of magnesia on the compressive strength of pellets. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrnezhaad, S.K.; Ferdowsi, A.; Payab, H. Mathematical model for a straight grate iron ore pellet induration process of industrial scale. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.J. Modeling the development of strength in pellets. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 1986, 17, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.; Dorling, S.R. Artificial neural network (Multilayer Perceptron)—A review of applications in atmospheric sciences. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, C.; Wei, X. Design and selection of construction, parameters and training method of BP network. Comput. Eng. 2001, 92, 336–337. [Google Scholar]
- Markward, S.W.; Lu, Y.Z. Integrated Neural System for coating weight control of a hot Dip Galvanizing Lina. Iron Steel Eng. 1995, 72, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Portman, N.F.; Lindhoft, D. Application of neural networks in rolling mill automation. Iron Steel Eng. 1995, 72, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pomerleau, D.; Hodouin, D.; Poulin, É. A first principle simulator of an iron oxide pellet induration furnace–an application to optimal tuning. Can. Metall. Quart. 2013, 44, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yang, G.; Chen, X.; Gao, L.; Huang, X.; Li, X. Predictive models and operation guidance system for iron ore pellet induration in traveling grate-rotary kiln process. Comp. Chem. Eng. 2015, 79, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.J.; Song, B.C.; Park, Y.J.; Song, K. Classification of materials for explosives from prompt gamma spectra by using principal component analysis. Appl. Radiat. Isotopes. 2009, 67, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ma, J.H.; Wu, Y.P. Application of artificial neural network in prediction of abrasion of rubber composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S. A competitive genetic algorithm for resource-constrained project scheduling. Nav. Res. Log. 2015, 45, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kadi, H.; Al-Assaf, Y. Prediction of the fatigue life of unidirectional glass fiber/epoxy composite lamina using different neural network paradigms. Compos. Struct. 2002, 55, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.; Arulshri, K.P.; Padmanaban, K.P.; Sasikumar, K.S.K. Design and optimization of machining fixture layout using ANN and DOE. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 65, 1573–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.J.; Holder, M.T.; Dries, L.A.; Zwickl, D.J.; Lewis, P.O.; Hillis, D.M. Genetic algorithms and parallel processing in maximum-likelihood phylogeny inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J. Crystal rule of Fe2O3 in oxidized pellet. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2007, 38, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Gao, Q.; Wei, G.; Jiang, X.; Shen, Y. Densification process of MgO bearing pellets. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhüttenleute, V.D.; Allibert, M. Slag Atlas, 2nd ed.; Verlag Stahleisen GmbH: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1995; p. 128. ISBN 3514004579. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, M.; Hoshi, M.; Kawaguchi, T. Improve of sinter softening property and reducibility by controlling chemical compositions. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wei, G.; Jiang, X.; Shen, F. Effect of calcinated magnesite on burst temperature of green pellet. J. Northeastern Univ. Nat. Sci. 2013, 34, 542–544. [Google Scholar]




| Input Variables | Average/Year | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Particle size of ore, −74 μm/% | 76.88 | 5.3 |
| Bentonite, % | 1.22 | 0.1 | |
| Green Pellet | Moisture of green pellet, % | 8.0 | 0.36 |
| CS of green pellet, N/pellet | 15 | 2.0 | |
| Dropping strength, Times/pellet | 6 | 0.6 | |
| Pellet diameter, mm | 13 | 1.0 | |
| Porosity of green pellet, % | 30 | 1.9 | |
| Chemical Composition | FeO, % | 0.7 | 0.02 |
| MgO, % | 0.6 | 0.03 | |
| CaO, % | 0.5 | 0.01 | |
| Al2O3, % | 1.5 | 0.04 | |
| Basicity (CaO/SiO2), Dimensionless | 0.09 | 0.001 | |
| Drying Process | Burst temperature, C | 450 | 20.0 |
| CS of drying pellet, N/pellet | 80 | 5.0 | |
| Bed depth, mm | 540 | 10.0 | |
| Firing Process | Firing temperature, C | 1250 | 15.0 |
| Firing time, min | 30 | 2.0 | |
| Gas consumption, m3/t | 50 | 3.5 | |
| Charging rate, ton/h | 600 | 15.0 | |
| New Components | λ | Contribution Rate (%) | Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.12 | 19.548 | 19.55 |
| 2 | 1.78 | 16.413 | 35.96 |
| 3 | 1.56 | 14.385 | 50.35 |
| 4 | 1.22 | 11.249 | 61.60 |
| 5 | 1.1 | 10.143 | 71.74 |
| 6 | 1.08 | 9.959 | 81.70 |
| 7 | 0.88 | 8.114 | 89.81 |
| 8 | 0.65 | 5.994 | 95.80 |
| 9 | 0.13 | 1.199 | 97.00 |
| 10 | 0.09 | 0.830 | 97.83 |
| 11 | 0.08 | 0.738 | 98.57 |
| 12 | 0.07 | 0.645 | 99.22 |
| 13 | 0.04 | 0.369 | 99.59 |
| 14 | 0.03 | 0.277 | 99.86 |
| 15 | 0.008 | 0.074 | 99.94 |
| 16 | 0.005 | 0.046 | 99.97 |
| 17 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 99.98 |
| 18 | 0.0009 | 0.007 | 99.99 |
| 19 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | 100.00 |
| Initial Variables: | Score Coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA1 | PCA2 | PCA3 | PCA4 | PCA5 | PCA6 | PCA7 | PCA8 | |
| Particle size | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.654 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bentonite | 0.536 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Moisture | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.859 | ~ |
| CS of green pellet | 0.639 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Dropping strength | 0.551 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pellet diameter | ~ | ~ | 0.589 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Porosity | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.789 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| FeO | ~ | −0.669 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MgO | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.898 | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| CaO | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.898 | ~ | ~ |
| Al2O3 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.458 |
| Basicity (CaO/SiO2) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 0.758 | ~ | ~ |
| Burst temperature | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | −0.856 | ~ |
| CS of drying pellet | 0.655 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bed depth | ~ | ~ | 0.985 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Firing temperature | ~ | 0.858 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Firing time | ~ | ~ | 0.854 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Gas consumption | ~ | 0.746 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Charging rate | ~ | ~ | −0.850 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, H.; Shen, F. Prediction Model of Iron Ore Pellet Ambient Strength and Sensitivity Analysis on the Influence Factors. Metals 2018, 8, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080593
Gao Q, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Zheng H, Shen F. Prediction Model of Iron Ore Pellet Ambient Strength and Sensitivity Analysis on the Influence Factors. Metals. 2018; 8(8):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080593
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Qiangjian, Yingyi Zhang, Xin Jiang, Haiyan Zheng, and Fengman Shen. 2018. "Prediction Model of Iron Ore Pellet Ambient Strength and Sensitivity Analysis on the Influence Factors" Metals 8, no. 8: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080593
APA StyleGao, Q., Zhang, Y., Jiang, X., Zheng, H., & Shen, F. (2018). Prediction Model of Iron Ore Pellet Ambient Strength and Sensitivity Analysis on the Influence Factors. Metals, 8(8), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080593






