Sigma Phase: Nucleation and Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Duplex Stainless Steel and Superduplex Stainless Steel
2.2. Stereological Measures
2.3. Computational Thermodynamics
2.4. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction
3. Results and Discussion
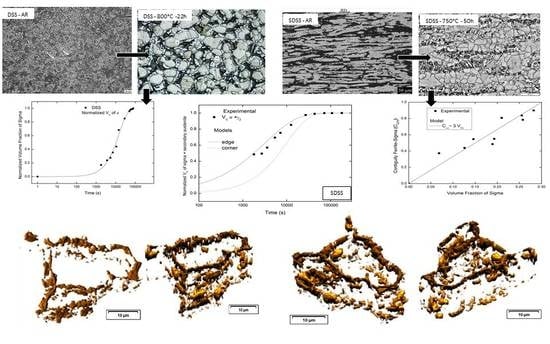
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
Duplex Stainless Steel Kinetics
3.2. Superduplex Stainless Steels
Contiguity, Interfacial Migration Rate, and Cahn Models
3.3. Computational Thermodynamics, Scanning Electron Microscopy, and Energy Dispersive Spectrometry
3.4. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction
4. Conclusions
- Classical JMAK equations can adjust the kinetics of sigma phase precipitation in DSS with equiaxial morphology of the austenite grains. Ferrite decomposition during aging generated depleted ferrite plus sigma, as found in superferritic stainless steels. Ferrite decomposition during aging in SDSS generated, as expected, sigma phase plus secondary austenite.
- For the first time, the microstructure of SDSS was studied, with the help of the contiguity ratio of ferrite/sigma. According to the contiguity ratio, the distribution of the nuclei of the sigma phase is random, and Cασ = 3 VVσ.
- Cahn’s equation for grain edge nucleation fitted well with the kinetics of precipitation of the sigma phase plus secondary austenite in SDSS.
- Computational thermodynamics indicated that the composition of the sigma phase aged at 800 °C for 108,000 s (30 h) was close to equilibrium.
- The 3D reconstruction, using the sample with the composition closest to equilibrium, verified that the sigma phase occupies the edges of the ferrite–austenite interfaces, and grows around the austenite. The sigma phase loses the interconnection at some points on the grain boundary. For the first time, there is experimental evidence of sigma phase nucleation at the ferrite–austenite edges. In other words, the grain edges are preferred sites for the nucleation of the sigma phase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Fonseca, G.; Barbosa, L.; Ferreira, E.; Xavier, C.; de Castro, J. Microstructural, Mechanical, and Electrochemical Analysis of Duplex and Superduplex Stainless Steels Welded with the Autogenous TIG Process Using Different Heat Input. Metals 2017, 7, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Fonseca, G.S.; de Oliveira, P.M.; Diniz, M.G.; Bubnoff, D.V.; Castro, J.A. De Sigma Phase in Superduplex Stainless Steel: Formation, Kinetics and Microstructural Path. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathirachinda, N.; Pettersson, R.; Pan, J. Depletion effects at phase boundaries in 2205 duplex stainless steel characterized with SKPFM and TEM/EDS. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escriba, D.M.; Materna-Morris, E.; Plaut, R.L.; Padilha, A.F. Chi-phase precipitation in a duplex stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnabosco, R. Kinetics of Sigma Phase Formation In a Duplex Stainless Steel 2. Experimental Procedure. Mater. Res. 2009, 12, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calliari, I.; Zanesco, M.; Ramous, E. Influence of isothermal aging on secondary phases precipitation and toughness of a duplex stainless steel SAF 2205. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 7643–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobranszky, J.; Szabo, P.J.; Berecz, T.; Hrotko, V.; Portko, M. Energy-dispersive spectroscopy and electron backscatter diffraction analysis of isothermally aged SAF 2507 type superduplex stainless steel. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2004, 59, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, D.M.E.; Junior, F.C.P.; Plaut, R.L.; Padilha, A.F. Comparative study on sigma phase precipitation of three types of stainless steels: Austenitic, superferritic and duplex. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, J.W.; Palmer, T.A.; Specht, E.D. Direct observations of sigma phase formation in duplex stainless steels using In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2007, 38, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badji, R.; Bouabdallah, M.; Bacroix, B.; Kahloun, C.; Belkessa, B.; Maza, H. Phase transformation and mechanical behavior in annealed 2205 duplex stainless steel welds. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Liu, F.; Ma, Y.Z.; Yang, G.C.; Zhou, Y.H. Modeling of σ-phase precipitation in a 2205 duplex stainless steel using an analytical soft impingement treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 4550–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilha, A.F.; Rios, P.R. Decomposition of Austenite in Austenitic Stainless Steels. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.A.; Mehl, R.F. Reaction Kinetics in Processes of Nucleation and Growth. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1939, 135, 416–441. [Google Scholar]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. I: General theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of Phase Change. II Transformation-Time Relations for Random Distribution of Nuclei. J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change. III. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. On the Statistical Theory of Metal Crystallization. Isvetiia Acad. Nauk. SSSR-Seriia Mat. 1937, 1, 335–359. [Google Scholar]
- Cahn, J.W. The kinetics of grain boundary nucleated reactions. Acta Metall. 1956, 4, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Preferential precipitation site of sigma phase in duplex stainless steel weld metal. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Abou-Ras, D.; Cizek, P.; Hodgson, P.D.; Rollett, A.D.; Beladi, H. Austenite-ferrite interface crystallography dependence of sigma phase precipitation using the five-parameter characterization approach. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Yang, J.R. Effects of solution treatment and continuous cooling on σ-phase precipitation in a 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 311, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Laleh, M.; Kosari, A.; Moayed, M.H.; Cizek, P.; Hodgson, P.D.; Beladi, H. The effect of phase transformation route on the intergranular corrosion susceptibility of 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 2019, 238, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, A.M.; Dehoff, R.T. Estimation of nucleation rate and growth rate from time dependence of global microstructural properties during phase transformations. Metall. Trans. A 1985, 16, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, R.A.; Rath, B.B. Modeling Recrystallization Kinetics in a Deformed Iron Single-Crystal. Metall. Trans. A-Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1989, 20, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, R.A.; Masumura, R.A. The microstructural path of grain-boundary-nucleated phase transformations. Acta Metall. Mater. 1992, 40, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, R.A.; Jensen, D.J. The Migration of High Angle Grain Boundaries during Recrystallization. Interface Sci. 1998, 104, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, R.A.; Juul Jensen, D. Microstructural path and temperature dependence of recrystallization in commercial aluminum. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, R.A. Microstructural descriptors and the effects of nuclei clustering on recrystallization path kinetics. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.L.M.; Assis, W.L.S.; Rios, P.R. Computer simulation of sequential transformations. Acta Mater. 2017, 126, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieurin, H.; Sandström, R. Sigma phase precipitation in duplex stainless steel 2205. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 444, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, M.V.; Spanos, G. Three-dimensional analysis of proeutectoid cementite precipitates. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, M.; Mangan, M.; Spanos, G.; Rosenberg, R. Three-dimensional analysis of microstructures. Mater. Charact. 2000, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.Y.; Spanos, G.; Rosenberg, R.O.; Kral, M.V. Three-dimensional observations of proeutectoid cementite precipitates at short isothermal transformation times. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Metals; Metals Handbook Committee. Metals Handbook.—Vol. 7: Atlas of Microstructures of Industrial Alloys; ASM: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Russ, J.C.; Dehoff, R. Classical Stereological Measures. In Practical Stereology; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 45–78. ISBN 0-306-46476-4. [Google Scholar]
- Talonen, J.; Aspegren, P.; Hänninen, H. Comparison of different methods for measuring strain induced α-martensite content in austenitic steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2004, 20, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, M.; Storz, O.; Glogowski, T. Effect of intermetallic precipitations on the properties of duplex stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2007, 58, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.W.; Hagel, W.G. Divergent pearlite in a manganese eutectoid steel. Acta Metall. 1963, 11, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillert, M.; Höglund, L.; Ågren, J. Escape of Carbon From Ferrite Plates in Austenite. Acta Metall. 1993, 41, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2205 | 0.023 | 0.320 | 1.85 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 22.50 | 5.30 | 2.90 | 0.166 | 0.030 |
| 2507 | 0.020 | 0.328 | 0.85 | 0.027 | 0.0009 | 24.89 | 6.82 | 3.72 | 0.278 | 0.156 |
| Elements | Fe | Cr | Mo | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermo-Calc | 53.7 | 34.5 | 8.3 | 3.0 |
| Experimental | 53.2 ± 1.0 | 30.2 ± 0.5 | 10.5 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 1.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca, G.S.d.; Mendes, P.S.N.; Silva, A.C.M. Sigma Phase: Nucleation and Growth. Metals 2019, 9, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010034
Fonseca GSd, Mendes PSN, Silva ACM. Sigma Phase: Nucleation and Growth. Metals. 2019; 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca, Gláucio Soares da, Priscila Sousa Nilo Mendes, and Ana Carolina Martins Silva. 2019. "Sigma Phase: Nucleation and Growth" Metals 9, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010034
APA StyleFonseca, G. S. d., Mendes, P. S. N., & Silva, A. C. M. (2019). Sigma Phase: Nucleation and Growth. Metals, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010034