Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Consolidated by Different Sintering Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
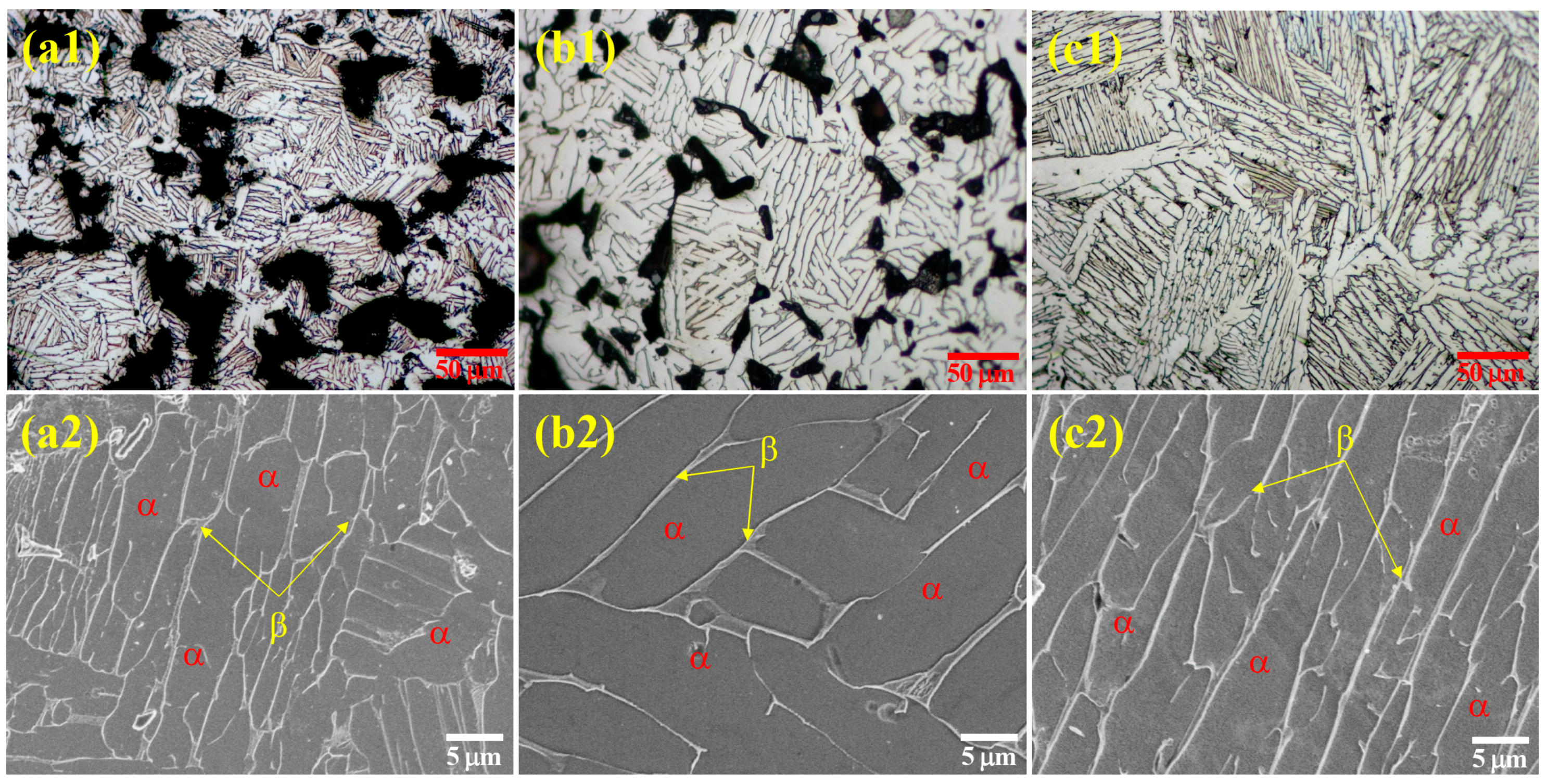
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Compositions
3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norgate, T.E.; Wellwood, G. The potential applications for titanium metal powder and their life cycle impacts. JOM 2006, 58, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, F.H.; Friedrich, H.; Kiese, J.; Bergoint, D. Titanium in the family automobile: The cost challenge. JOM 2004, 56, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.; Tamirisakandala, S.; Miracle, D.B.; Ramamurty, U. Microstructural effects on the mechanical behavior of B-modified Ti–6Al–4V alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4983–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Sen, I.; Gopinath, K.; Ramamurty, U. Influence of minor addition of boron on tensile and fatigue properties of wrought Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 540, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Williams, J.C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 844–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.Q.; Chen, F.; Cai, Y.X.; Jian, Y.N. Influence of particle size on property of Ti-6Al-4V alloy prepared by high-velocity compaction. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Nash, G.L.; Nash, P. Effect of density and pore morphology on fatigue properties of sintered Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 55, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.P.; Haase, C.; Lapovok, R.; Estrin, Y. Improving sinterability of Ti-6Al-4V from blended elemental powders through equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, Y.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Arias, S.; Echeverry, M.; Robledo, S.; Amigo, V.; Pavón, J.J. Processing, characterization and biological testing of porous titanium obtained by space–holder technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6565–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, J.S.; Chen, H.B. High-strength Ti-6Al-4V with ultrafine-grained structure fabricated by high energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 585, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, R.P.; Bai, C.G.; Lei, J.F.; Yang, R. Effect of hot isostatic pressing conditions and cooling rate on microstructure and properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy from atomized powder. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E.; Esquivel, E.V.; Quinones, S.A.; Gaytan, S.M.; Martinez, E.Y.; Medina, F.; Hernandez, D.H.; Martinez, E.; Martinezl, J.L.; Stafford, S.W.; et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of electron beam-rapid manufactured Ti-6Al-4V biomedical prototypes compared to wrought Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Attar, H.; Calin, M.; Eckert, J. Review on manufacture by selective laser melting and properties of titanium based materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Technol. 2016, 31, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Hao, Y. Additive manufacturing of Titanium alloys by electron beam melting: A review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M. Sintering Theory and Practice; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Bayat, H.; Rastgo, M.; Zadeh, M.M.; Vereecken, H. Particle size distribution models, their characteristics and fitting capability. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 872–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Tousi, S.S.; Yazdani-Rad, R.; Manafi, S.A. Effect of volume fraction and particle size of alumina reinforcement on compaction and densification behavior of Al-Al2O3 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Nash, P. Sintering mechanisms of Armstrong prealloyed Ti-6Al-4V powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 607, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Villa, J.L.; Lemus-Ruiz, J.; Bouvard, D.; Jiménez, O.; Vergara-Hernández, H.J.; Olmos, L. Sintering study of Ti6Al4V powders with different particle sizes and their mechanical properties. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2018, 25, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccino, R.; Morret, F.; Fellerin, F.; Guichard, D.; Raisson, G. High performance and high complexity net shape parts for gas turbines: the ISOPREC® powder metallurgy process. Mater. Des. 2000, 21, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashl, S.J.; Hebeisen, J.C.; Hjorth, C.G. Producing large P/M near-net shapes using hot isostatic pressing. JOM 1999, 7, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, F.H.; Mashl, S.J.; Hebeisen, J.C.; Moxson, V.S.; Duz, V.A. The technologies of titanium powder metallurgy. JOM 2004, 56, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, H.V.; Davies, S. Fundamental aspects of hot isostatic pressing: An overview. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 2981–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delo, D.P.; Piehler, H.R. Early stage consolidation mechanisms during hot isostatic pressing of Ti-6Al-4V powder compacts. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mei, J.; Wain, N.; Wu, X. Effect of hot-isostatic-pressing parameters on the microstructure and properties of powder Ti-6Al-4V hot-isostatically-pressed samples. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, P.V.; Luan, N.V.; Phuong, D.D.; Minh, P.N.; Weibel, A.; Mesguich, D.; Laurent, C. Microstructure, microhardness and thermal expansion of CNT/Al composites prepared by flake powder metallurgy. Composites Part A 2018, 105, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashby, M.F. The properties of foams and lattices. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Ser. A 2006, 364, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Nava, E.; Smith, C.J.; Derguti, F.; Tammas-Williams, S.; Léonard, F.; Withers, P.J.; Todd, I.; Goodalla, R. The effect of density and feature size on mechanical properties of isostructural metallic foams produced by additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASM Handbook Committee, American Society for Metals. Properties and Selection: Stainless Steels, Tool Materials and Special-Purpose Metals, 9th ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1980; p. 388. [Google Scholar]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dinh Phuong, D.; Van Duong, L.; Van Luan, N.; Ngoc Anh, N.; Van Trinh, P. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Consolidated by Different Sintering Techniques. Metals 2019, 9, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9101033
Dinh Phuong D, Van Duong L, Van Luan N, Ngoc Anh N, Van Trinh P. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Consolidated by Different Sintering Techniques. Metals. 2019; 9(10):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9101033
Chicago/Turabian StyleDinh Phuong, Doan, Luong Van Duong, Nguyen Van Luan, Nguyen Ngoc Anh, and Pham Van Trinh. 2019. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Consolidated by Different Sintering Techniques" Metals 9, no. 10: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9101033
APA StyleDinh Phuong, D., Van Duong, L., Van Luan, N., Ngoc Anh, N., & Van Trinh, P. (2019). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Consolidated by Different Sintering Techniques. Metals, 9(10), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9101033




