Thermal-Induced Phase Transformation Behavior of NiTiNb Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
3. Results
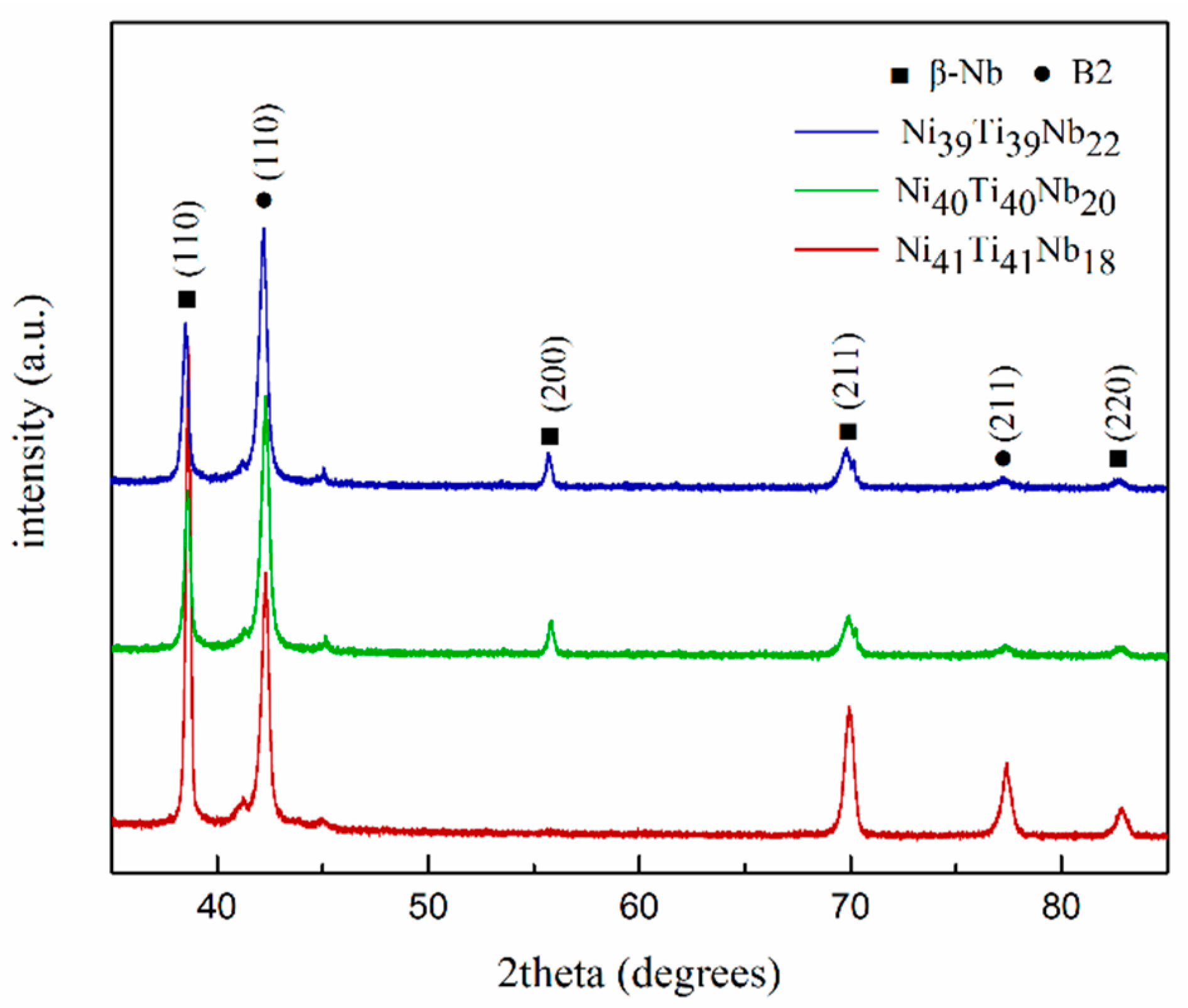
3.1. Microstructural and Analysis
3.2. Transformation Behavior
4. Discussion
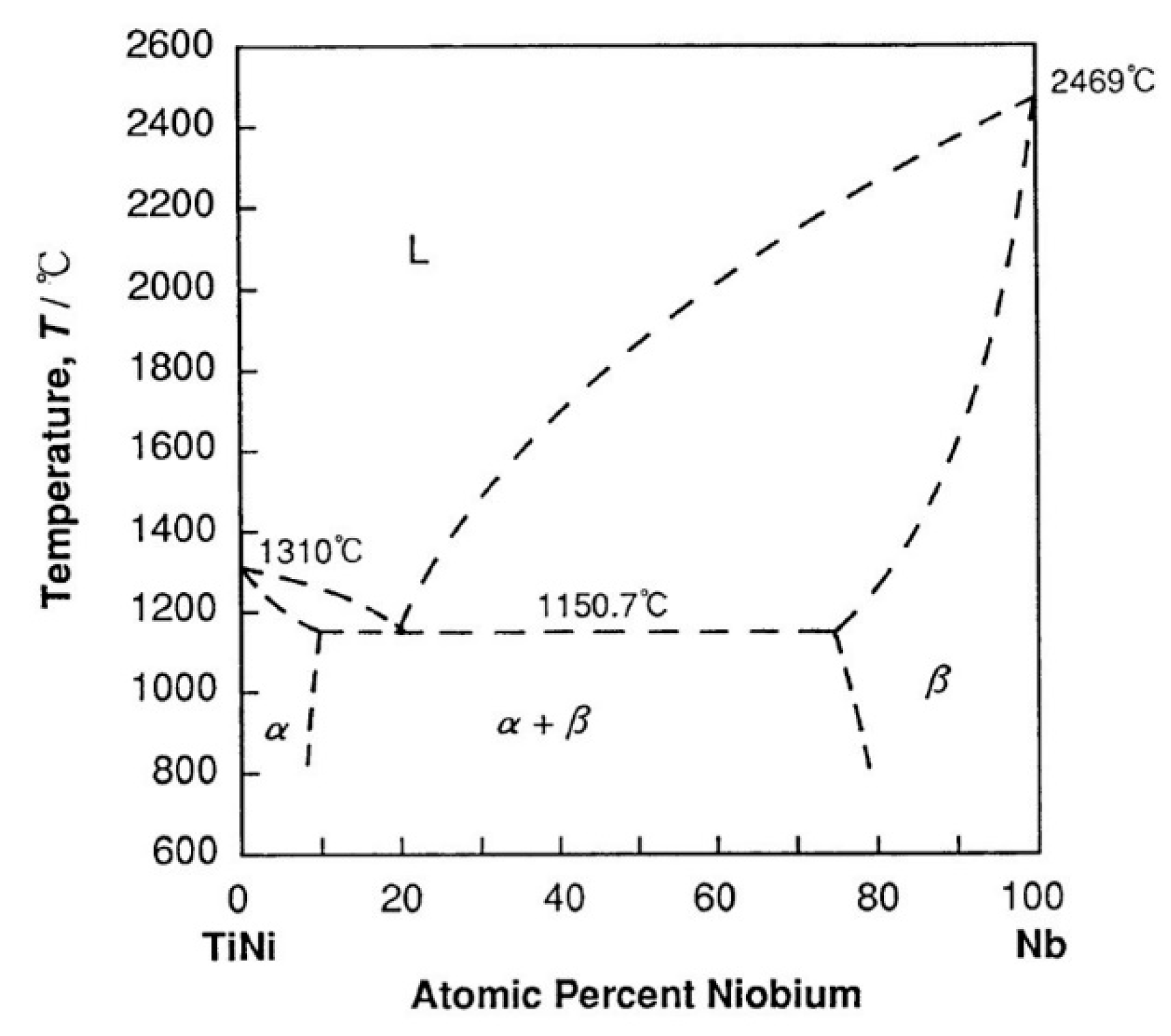
4.1. The Different Microstructure of the NiTiNb Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic Alloys
4.2. Two Peaks in DSC Curves
4.3. Martensite Transformation Temperature
5. Conclusions
- (1).
- The microstructure of NiTiNb hypoeutectic, eutectic, and hypereutectic alloys all involve the eutectic structure. The NiTiNb hypoeutectic alloys contain the primary NiTi phase and the NiTiNb hypereutectic contains the primary Nb-rich phase.
- (2).
- The phase transformation, martensite ↔ austenite, exhibited in three kinds of NiTiNb hypoeutectic, eutectic, and hypereutectic alloys in the case of heating and cooling. The Ni/Ti ratio difference between the primary NiTi matrix and NiTi in the eutectic structure affects the phase transformation behavior of Ni41Ti41Nb18 alloy so that the two peaks appear in DSC curves.
- (3).
- With the same solution treatment, the specimens of Ni40Ti40Nb20 contain the lowest Ms. As the solution temperature increases, in NiTiNb alloys with the same chemical components, the Ms has a tendency to decrease.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biesiekierski, A.; Wang, J.; Gepreel, M.A.; Wen, C. A new look at biomedical Ti-based shape memory alloys. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, E.T.F.; Friend, C.M.; Allen, D.M.; Hora, J.; Webster, J.R. A technical and economic appraisal of shape memory alloys for aerospace applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Ma, N.; Li, H.N. Applications of shape memory alloys in civil structures. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Jani, J.; Leary, M.; Subic, A.; Gibson, M.A. A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 1078–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Rong, L.J.; Yan, D.S.; Li, Y.Y. TiNiNb wide hysteresis shape memory alloy with low niobium content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 371, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.C.; Zheng, Y.F.; Tong, Y.X.; Chen, F.; Tian, B.; Li, L.; Gunderov, D.V.; Valiev, R.Z. Transformation hysteresis and shape memory effect of an ultrafine-grained TiNiNb shape memory alloy. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, M.; Liao, G.; Guo, S.; Zhao, X. Martensitic transformation involved mechanical behaviors and wide hysteresis of NiTiNb shape memory alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Yan, D.S.; Rong, L.J.; Li, Y.Y. Effect of Niobium Content on Shape Memory Characteristics of (Ni47Ti44)100−xNbx Alloys. AIP Conf. Proc. 2004, 711, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.C.; Duerig, T.W.; Justi, S.; Melton, K.N.; Proft, J.L.; Yu, W.; Wayman, C.M. The study of niobium-rich precipitates in a NiTiNb shape memory alloy. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1990, 24, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.; Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K.; Nishida, N. Effects of Nb Addition on the Microstructure of Ti-Ni Alloys. Mater. Trans. 1992, 33, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Y.; Lu, S.Q.; Li, G.F.; Liu, J.W.; Peng, P. Nb solution influencing on phase transformation temperature of Ni47Ti44Nb9 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 609, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C. Influence of Addition of Nb on Phase Transformation, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Equiatomic NiTi SMA. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 4341–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H. Wide hysteresis NiTi(Nb) shape memory alloys with low Nb content (4.5at.%). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewerse, C.; Brinson, L.C.; Dunand, D.C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast quasibinary NiTi– Nb eutectic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 627, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareci, D.; Chelariu, R.; Cailean, A.; Sutiman, D. Electrochemical characterization of Ni47.7Ti37.8Nb14.5 shape memory alloy in artificial saliva. Mater. Corros. 2012, 63, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.W.; Wang, J.B.; Mi, X.J.; Miao, W.D.; Yuan, Z.S.; Zhou, J. Effects of Ni/Ti Ratio and Heat-Treatment on Transformation Temperature, Mechanical Properties and Shape Recovery Strain of Ni-Ti-Nb Alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 535–537, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Pourbabak, S.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Schryvers, D. Electron microscopy study of Nb-rich nanoprecipitates in Ni–Ti–Nb and their influence on the martensitic transformation. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Frenzel, J.; Martinez, G.T.; Van Rompaey, S.; Bakulin, A.; Kulkova, S.; Van Aert, S.; Schryvers, D. Site occupation of Nb atoms in ternary Ni–Ti–Nb shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 74, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Solution Treatment | Ni/Ti ratio of Primary NiTi Matrix | Ni/Ti Ratio of NiTi in Eutectic Structure | The Difference of Two Ni/Ti Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 750 °C × 1.5 h | 1.406 | 1.095 | 0.311 |
| 850 °C × 1.5 h | 1.399 | 1.113 | 0.286 |
| 950 °C × 1.5 h | 1.160 | 1.071 | 0.089 |
| Solution Treatment | Ni40Ti40Nb20 | Ni39Ti39Nb22 |
|---|---|---|
| 750 °C × 1.5 h | 1.143 | 1.117 |
| 850 °C × 1.5 h | 1.125 | 1.109 |
| 950 °C × 1.5 h | 1.097 | 1.088 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, H.; Ma, G.; Fan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Yi, Y. Thermal-Induced Phase Transformation Behavior of NiTiNb Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic Alloys. Metals 2019, 9, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020214
Yin H, Ma G, Fan Q, Wang Y, Huang S, Yi Y. Thermal-Induced Phase Transformation Behavior of NiTiNb Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic Alloys. Metals. 2019; 9(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Huilin, Guohua Ma, Qichao Fan, Yingying Wang, Shuke Huang, and Yong Yi. 2019. "Thermal-Induced Phase Transformation Behavior of NiTiNb Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic Alloys" Metals 9, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020214
APA StyleYin, H., Ma, G., Fan, Q., Wang, Y., Huang, S., & Yi, Y. (2019). Thermal-Induced Phase Transformation Behavior of NiTiNb Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic Alloys. Metals, 9(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020214





