Effects of Fe3P Addition on Sintering Behaviors and Magnetic Properties of Fe-P Alloys Sintered at Low Temperatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Experimental Results
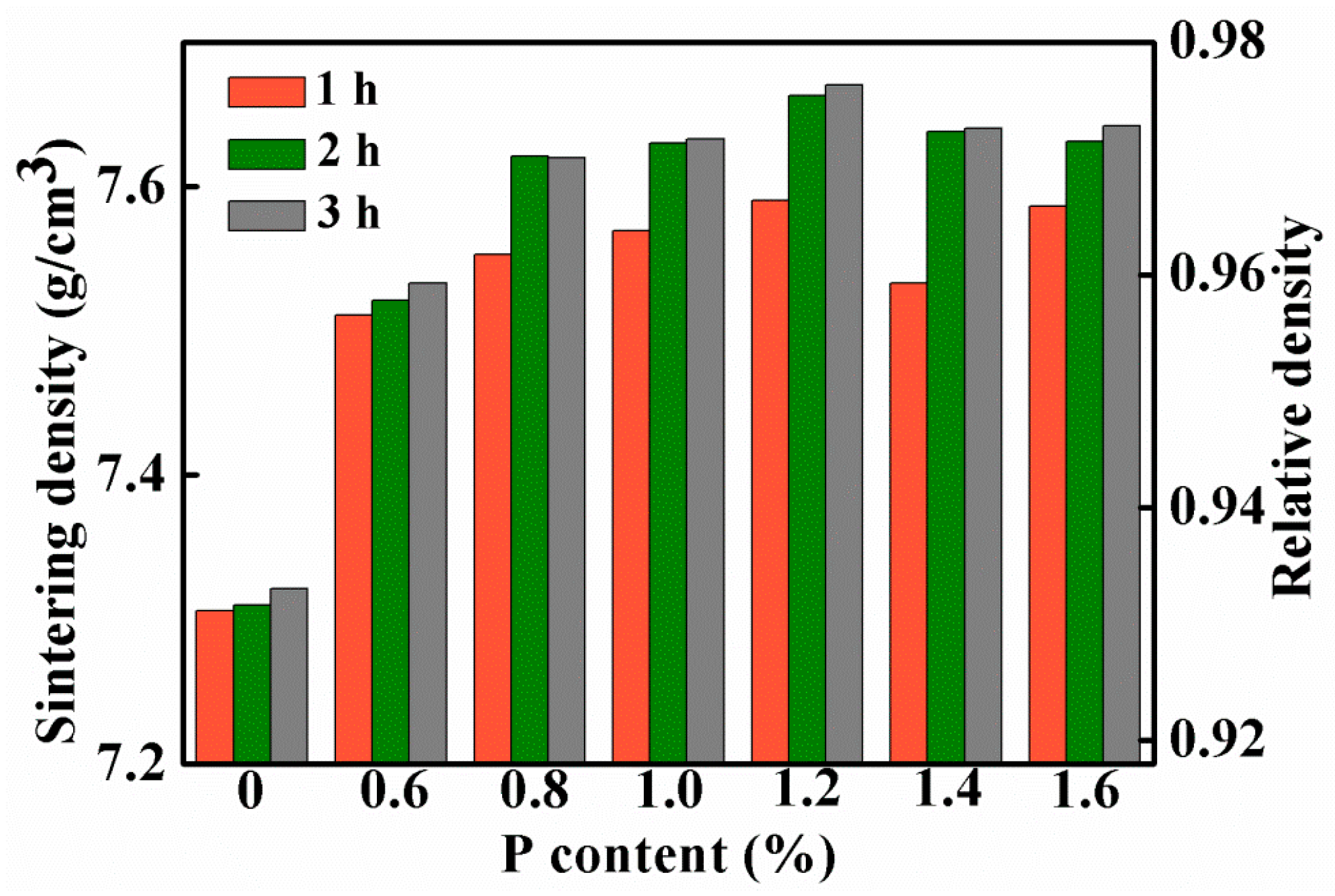
3.1. Effects of Sintering Parameters and P Contents on the Sintering Density
3.2. Thermal Analysis
3.3. Magnetic Properties
3.4. Microstructure Observation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chauhan, A.; Vaish, R. Magnetic material selection using multiple attribute decision making approach. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, S.K.; Prakash, U.; Misra, P.S.; Chandra, K. Development of P/M Fe-P soft magnetic materials. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Chandra, K.; Misra, P.S.; Sarma, B. Novel powder metallurgy technique for development of Fe-P-based soft magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Qu, X. Preparation of high performance sintered soft magnetic alloy by metal injection molding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuchamy, A.; Kumar, R.; Annamalai, A.R.; Agrawal, D.K.; Upadhyaya, A. An investigation on effect of heating mode and temperature on sintering of Fe-P alloys. Mater. Charact. 2016, 114, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, H. The magnetic and structural properties of the most important alloys of iron produced by mechanical alloying. Cheminform 2010, 41, 3374–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, H.; Janghorban, K. Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 189, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Beitollahi, A.; Eftekhariyekta, B.; Kanada, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Gopalan, R.; Herzer, G.; Hono, K. Microstructural and magnetic properties study of Fe-P rolled sheet alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 358–359, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, M.; Tian, L.; Zhang, L.; Khan, D.F.; Ding, X.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of Fe3P addition on magnetic properties and microstructure of injection molded iron. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 397, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveyra, J.M.; Illeková, E.; Coïsson, M.; Celegato, F.; Vinai, F.; Tiberto, P.; Moya, J.A.; Cremaschi, V.J. High performance of low cost soft magnetic materials. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2011, 34, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, E.; Pfeiffer, H. Influence of grain-size and impurities on magnrtic-properties of soft magnetic alloy 47.5 Percent Ni-Fe. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1974, 10, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D.C. Recent advances and future directions in magnetic materials. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5907–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.S.; Lin, S.T. Effect of phosphorous addition on the grain growth of Fe–50 wt.%Ni alloys. Scripta Mater. 2002, 47, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Mo, W.; Lv, Y.; Ye, S.; Gu, R.; Yu, P. The effect of trace amount of Ti and W on the powder metallurgy process of Cu. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 660, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.; Mehta, Y.; Chandra, K.; Mishra, P.S. Effect of carbon on mechanical properties of powder-processed Fe-0.35%P alloys. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2010, 33, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, S.S.; Jung, I.D.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.J. Development of powder injection molding process for sintered soft magnet with the addition of Fe-17 at.% P powder. Metal Powder Rep. 2017, 73, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrollahi, H.; Janghorban, K. Different annealing treatments for improvement of magnetic and electrical properties of soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 317, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kang, S.J.L. Theoretical analysis of liquid-phase sintering: Pore filling theory. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3191–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Qin, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. High magnetic performance of metal injection-molded pure iron using δ phase sintering. Mater. Lett. 2014, 121, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.S.; Lin, S.T. Effects of phosphorus addition on the magnetic properties of sintered Fe-50 wt.% Ni alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.F.; Deng, C.R.; Shi, Y.; Chow, Y.S.; Gang, T.B. Microstructure and soft magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe-Si powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 314, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, M.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, R.; Qu, X. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe–50%Ni alloy fabricated by powder injection molding. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 329, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Qu, X.; Khan, D.F. Magnetic properties of Fe–50%Ni alloy fabricated by metal injection molding. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Pavón, A.; Jiménez-Morales, A.; Rodriguez-Arbaizar, M.; Carreño-Morelli, E.; Torralba, J.M. Sintering optimisation of Fe-Si soft magnetic materials processed by metal injection moulding. Powder Metall. 2017, 60, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglo, G.I.; Ev, V.M.V.; Panasyuk, O.A. Effect of alloying impurities and conditions of heat treatment of iron-based powder materials and their magnetic properties. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1995, 33, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Chandra, K.; Misra, P.S. Design and development of powder processed Fe-P based alloys. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3198–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.S.; Oh, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.J. Microstructural and core loss behaviors of addictive Fe-17 at% P based on Fe-3.5 wt% Si alloys in powder injection molding. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, J.A.; Calero, J.A.; Dougan, M.J. Sintered soft magnetic materials. Properties and applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 254, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, C.; Yan, M. Enhanced magnetic properties of Fe soft magnetic composites by surface oxidation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 399, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daudt, N.F.; Santos, T.L.S.d.; Limberger, I.F.; Seeger, R.L.; Dorneles, L.S.; Binder, C.; Schaeffer, L. Highly porous Fe-2 wt%P alloy produced by plasma assisted debinding and sintering of injection-molded parts. Mater. Lett. 2018, 231, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebib, W.; Alleg, S.; Greneche, J.-M.; Sunol, J.J. Thermal stability of the nanocrystalline Fe-8P (wt.%) powder produced by ball milling. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2018, 193, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
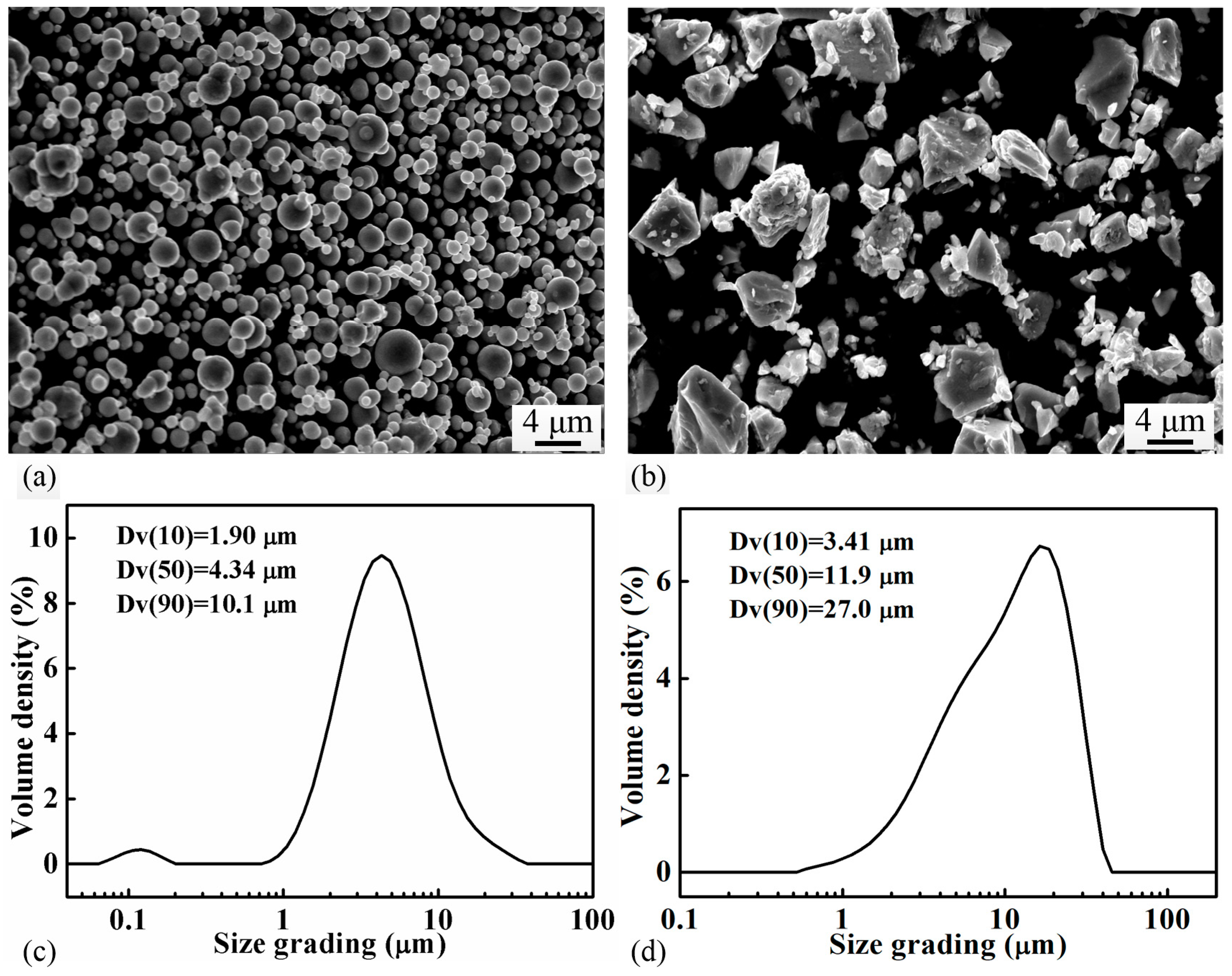





| P Content (wt.%) | 0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green density (g/cm3) | Soaking time 1 h | 5.72 | 5.71 | 5.71 | 5.72 | 5.71 | 5.72 | 5.72 |
| Soaking time 2 h | 5.72 | 5.72 | 5.72 | 5.72 | 5.71 | 5.72 | 5.72 | |
| Soaking time 3 h | 5.72 | 5.71 | 5.72 | 5.71 | 5.72 | 5.72 | 5.71 | |
| P Content (wt.%) | 0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering density (g/cm3) | Soaking time 1 h | 7.31 | 7.51 | 7.53 | 7.57 | 7.59 | 7.53 | 7.59 |
| Soaking time 2 h | 7.31 | 7.52 | 7.62 | 7.63 | 7.66 | 7.64 | 7.63 | |
| Soaking time 3 h | 7.32 | 7.53 | 7.62 | 7.63 | 7.67 | 7.64 | 7.64 | |
| P Content (%) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| Coercive force (A/m) | 211 | 187 | 185 | 172 | 181 | 199 |
| B6000 (mT) | 543 | 599 | 694 | 768 | 730 | 740 |
| Grain size (μm) | 20 | 27 | 30 | 31 | 29 | 29 |
| Reaction | ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔS (kJ/mol K) | ΔG = ΔH − TΔS (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4/3 Fe(s) + O2(g) = 2/3 Fe2O3(s) | −549 | −0.183 | ΔG = 0.183 T − 549 |
| 4/5 P(s) + O2(g) = 2/5 P2O5(s) | −602 | −0.192 | ΔG = 0.192 T − 602 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; Ye, S.; Yu, P. Effects of Fe3P Addition on Sintering Behaviors and Magnetic Properties of Fe-P Alloys Sintered at Low Temperatures. Metals 2019, 9, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030321
Ma R, Yu K, Liu L, Jiang H, Ye S, Yu P. Effects of Fe3P Addition on Sintering Behaviors and Magnetic Properties of Fe-P Alloys Sintered at Low Temperatures. Metals. 2019; 9(3):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030321
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Rui, Kaiping Yu, Litao Liu, Heng Jiang, Shulong Ye, and Peng Yu. 2019. "Effects of Fe3P Addition on Sintering Behaviors and Magnetic Properties of Fe-P Alloys Sintered at Low Temperatures" Metals 9, no. 3: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030321
APA StyleMa, R., Yu, K., Liu, L., Jiang, H., Ye, S., & Yu, P. (2019). Effects of Fe3P Addition on Sintering Behaviors and Magnetic Properties of Fe-P Alloys Sintered at Low Temperatures. Metals, 9(3), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030321





