Numerical Simulation of Solidification Behavior and Solute Transport in Slab Continuous Casting with S-EMS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Electromagnetic Field
2.2. Fluid Flow and Mass Transfer
2.3. Heat Transfer Model
2.4. Solute Transport Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Validation
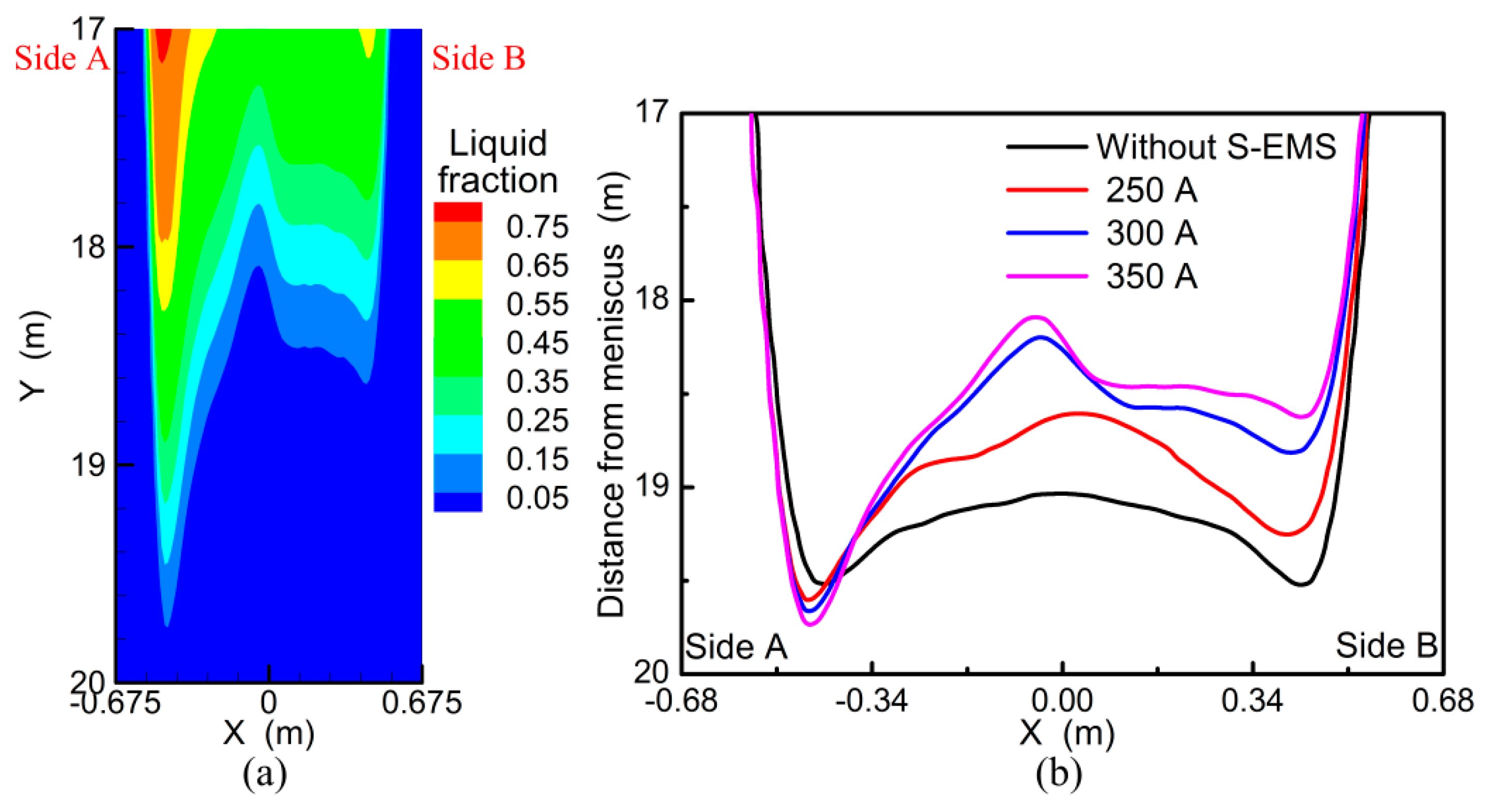
3.2. Transport Behavior without S-EMS
3.3. Linear Stirring in the Same Direction
3.4. Linear Stirring in the Opposite Direction
3.5. Effect of the Rotational Stirring Mode
4. Conclusions
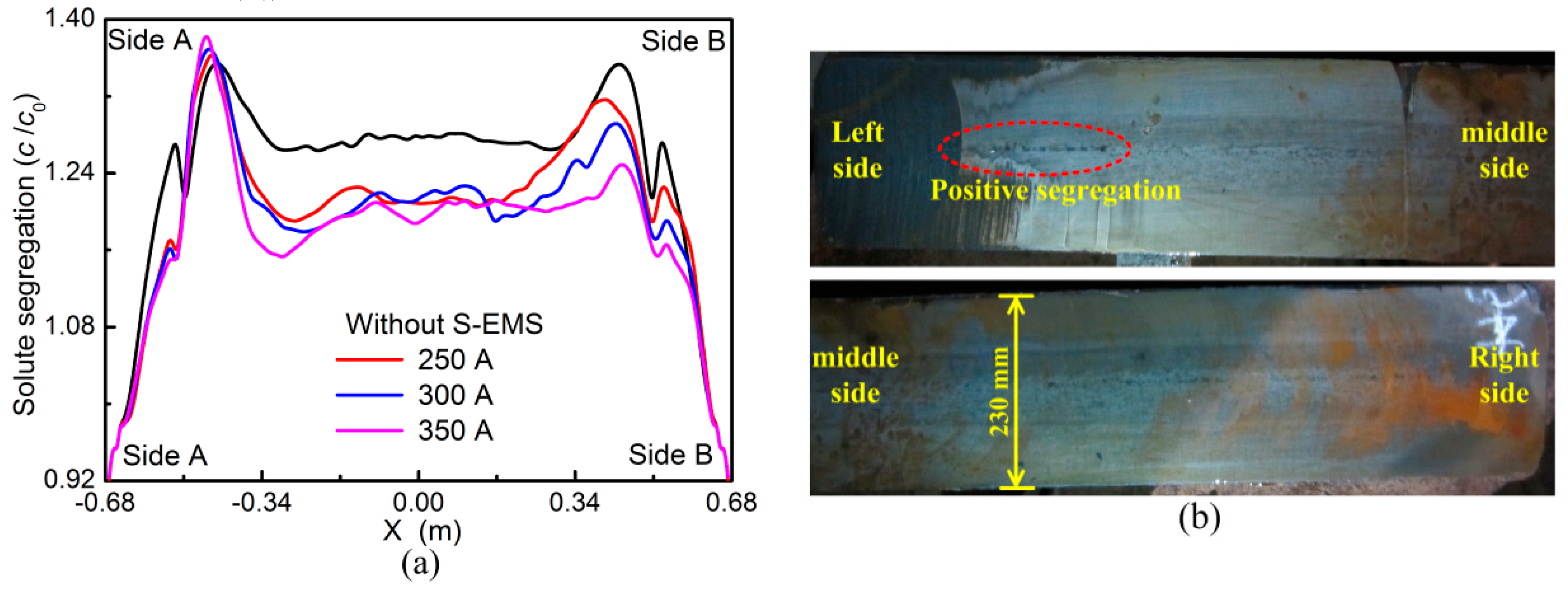
- Because liquid steel from SEN injects to strand narrow face directly, the solidification end near the 1/4 width of slab is postponed and solute element is enriched.
- With the linear stirring in the same direction applied, liquid flows from side B to side A and penetrates deep down along the solidification front. The solidification end near side A moves backward and solute segregation is deteriorated, which becomes more serious with higher current intensity.
- As the linear stirring in opposite direction is used, the solidification end near the side A moves forward, while that near the side B moves backward. Moreover, it is obtained that the centerline segregation near the side B is reduced, but that near the side A is deteriorated.
- With the rotational stirring mode applied, liquid steel is driven to move around in the cross section and solid shell grows uniformly. As the current intensity increases, liquid steel solidifies simultaneously in the later stage and the centerline segregation is reduced.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, K.; Basu, B. Mathematical modeling of macrosegregation of iron carbon binary alloy: role of double diffusive convection. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1995, 26, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayata, K.; Mori, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Matsuda, H. Low superheat teeming with electromagnetic stirring. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, W.; Luo, S.; Ji, C.; Zhu, M. Numerical simulation of slab centerline segregation with mechanical reduction during continuous casting process. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2018, 122, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, M.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, H. Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a round bloom mold with in-mold rotary electromagnetic stirring. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43, 1657–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, E.G.; He, J. Numerical simulation of linear electromagnetic stirring in secondary cooling region of slab caster. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2003, 10, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, Z. Mathematical modelling of billet casting with secondary cooling zone electromagnetic stirrer. Ironmaking Steelmaking 2013, 40, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.Z.; Chen, D.F.; Wang, H.D.; Long, M.J. Numerical analysis of coupled turbulent flow and macroscopic solidification in a round bloom continuous casting mold with electromagnetic stirring. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Jha, P.K. Influence of electromagnetic stirrer position on fluid flow and solidification in continuous casting mold. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 48, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.B.; Zhang, J.Q. Study on the macrosegregation behavior for the bloom continuous casting: Model development and validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2014, 45, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.B.; Zhu, M.Y. Solidification structure and macrosegregation of billet continuous casting process with dual electromagnetic stirrings in mold and final stage of solidification: A numerical study. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.; Terrail, Y.; Durand, F.; Fautrelle, Y. Channel segregation during solidification and the effects of an alternating traveling magnetic field. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, M.R.; Rogers, G.D. Structural effects and band segregation formation during the electromagnetic stirring of strand-cast steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1984, 15, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayata, K.; Mori, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Wakasugi, I. Improvement of macrosegregation in continuously cast bloom and billet by electromagnetic stirring. ISIJ Int. 1984, 24, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.S.; Chang, Y.W. Macrosegregation behavior in continuously cast high carbon steel blooms and billets at the final stage of solidification in combination stirring. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Deng, A.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, E. Numerical simulation of flow and solidification in continuous casting process with mold electromagnetic stirring. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Q.; Zhu, M.Y. Influence of electromagnetic stirring on transport phenomena in round billet continuous casting mould and macrostructure of high carbon steel billet. Ironmaking Steelmaking 2012, 39, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhu, M. Flow and solidification in billet continuous casting machine with dual electromagnetic stirrings of mold and the final solidification. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, G.M.; El-Kaddah, N. An improved model for the flow in an electromagnetically stirred melt during solidification. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.; Pritchard, W.H. The problem of rupture of the billet in the continuous casting of steel. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1954, 178, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, T.; Matsuno, J.; Murata, K.; Ooi, H.; Kodama, M. Secondary cooling pattern for the prevention of surface cracks of continuous casting slab. Tetsu-to-Hagané 1976, 62, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Qian, L.; Yin, Y.B. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of macrosegregation in continuously cast billets. Metals 2017, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

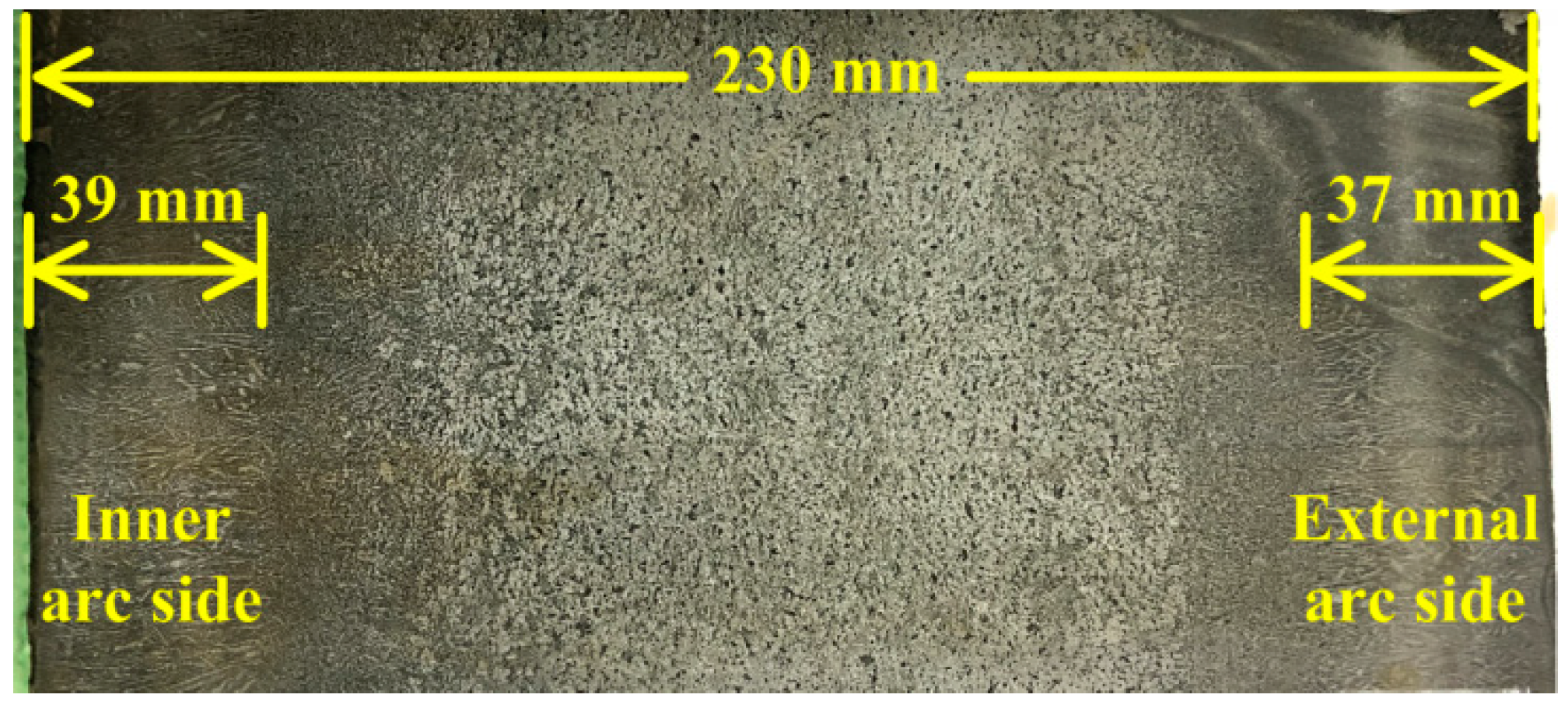









| Item | Value (unit) |
|---|---|
| Slab dimensions | 230 × 1350 (mm) |
| Steel density (ρ) | 7000 (kg·m−3) |
| Liquid viscosity (μl) | 0.006 (kg·m−1·s−1) |
| Thermal conductivity (k) | 30 (W·m−1·K−1) |
| Specific heat (Cp) | 690 (J·kg−1·K−1) |
| Latent heat (L) | 27,5000 (J·kg−1) |
| Casting speed (vc) | 0.9 (m·min−1) |
| Casting temperature (T0) | 1798 (K) |
| Solute content (c0) | 0.25 (%) |
| Partition coefficient (kp) | 0.34 |
| Liquid and solid diffusion coefficient (Dl and Ds) | 2 × 10−9 (m2·s−1) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, D.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, L. Numerical Simulation of Solidification Behavior and Solute Transport in Slab Continuous Casting with S-EMS. Metals 2019, 9, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040452
Jiang D, Zhu M, Zhang L. Numerical Simulation of Solidification Behavior and Solute Transport in Slab Continuous Casting with S-EMS. Metals. 2019; 9(4):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040452
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Dongbin, Miaoyong Zhu, and Lifeng Zhang. 2019. "Numerical Simulation of Solidification Behavior and Solute Transport in Slab Continuous Casting with S-EMS" Metals 9, no. 4: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040452
APA StyleJiang, D., Zhu, M., & Zhang, L. (2019). Numerical Simulation of Solidification Behavior and Solute Transport in Slab Continuous Casting with S-EMS. Metals, 9(4), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040452





