Roasting Pretreatment Combined with Ultrasonic Enhanced Leaching Lead from Electrolytic Manganese Anode Mud
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Instrument
2.3. Calculation of Lead Leaching Rate
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Roasting Pretreatment Experienment
3.2. Characterization of Roasted Electrolytic Manganese Anode Mud
3.3. Effects of Ammonium Acetate Concentration
3.4. Effects of Liquid to Solid Ratio
3.5. Effect of Temperature
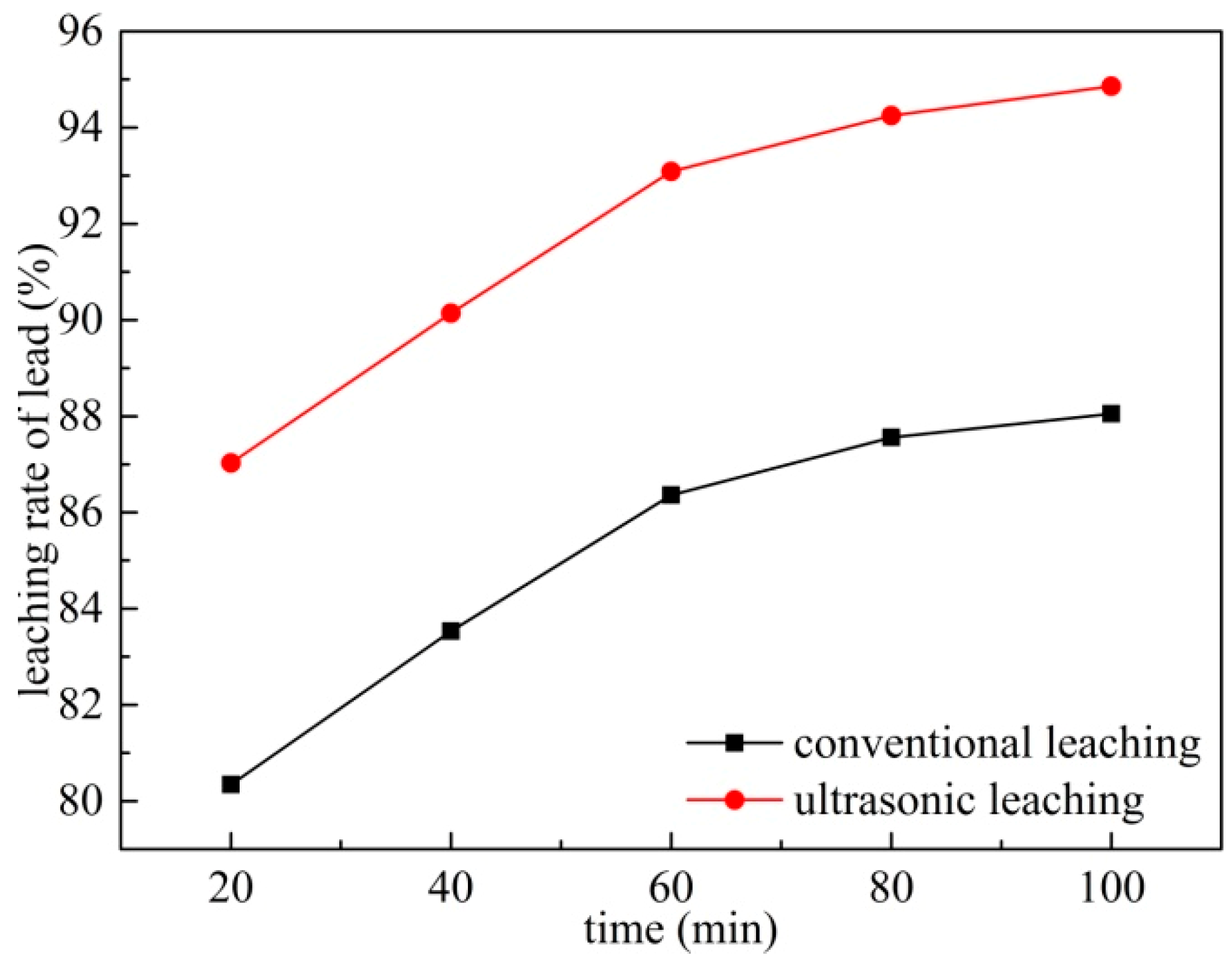
3.6. Effects of Leaching Time
3.7. Effect of Rotating Speed
3.8. Effect of Ultrasonic Power
3.9. Characterization of Leaching Residue
3.10. Kinetic Analysis of the Leaching Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, N.; Dan, Z.; Wang, F. Electrolytic manganese metal industry experience based China’s new model for cleaner production promotion. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Lee, J.W. Concurrent production of carbon monoxide and manganese (II) oxide through the reaction of carbon dioxide with manganese. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhou, C.; Dan, Z. Preparation and characteristics of steam-autoclaved bricks produced from electrolytic manganese solid waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, J.B.; Williams, R.P.; Pandolfo, A.G. Microporosity of heat-treated manganese dioxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 165, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.G.; He, Z.C. Investigation on process mineralogy of manganese anode slime and impurity removal. Min. Metall. 2005, 4, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, C.Y.; Li, D.H.; Liu, Z.H. Activation and purification of electrolytic-manganese anode slime and its application. Battery Bimon. 2011, 41, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.G.; Tang, C.B.; Chen, Y. One-step extraction of antimony from low-grade stibnite in Sodium Carbonate-Sodium Chloride binary molten salt. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 93, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C.A. Hydrometallurgy of precious metals recovery. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 30, 127–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, C.X.; Li, F.; Yang, M.H.; Zhang, H. Rapid Synthesis of hierarchically structured multifunctional Metal-Organic zeolites with enhanced volatile organic compounds adsorption capacity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15385–15394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, N.; Meux, E.; Lecuire, J.M. Hydrometallurgical extraction of zinc from zinc ferrites. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 70, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, X. Recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries by ultrasonic-assisted leaching process. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravotto, G.; Gaudino, E.C.; Cintas, P. On the mechanochemical activation by ultrasound. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7521–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.L.; Zhang, X.F.; Tang, S.Z. Ultrasound-assisted HCl-NaCl leaching of lead-rich and antimony-rich oxidizing slag. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 27, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Li, L.; Wu, Z. Ultrasonic-Assisted Acid Leaching of Indium from Blast Furnace Sludge. Metal. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şayan, E.; Bayramoğlu, M. Statistical modeling and optimization of ultrasound-assisted sulfuric acid leaching of TiO2, from red mud. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 71, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Brunelli, K.; Dabalà, M. Ultrasound effects on zinc recovery from EAF dust by sulfuric acid leaching. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2015, 22, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, J.; Tan, Q. Green Process of Metal Recycling Coprocessing Waste Printed Circuit Boards and Spent Tin Stripping Solution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3524–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, J.H.; Peng, Y. Supporting Information: Effects of MnO2 Crystal Structure and Surface Property on the NH3-SCR Reaction at Low Temperature. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2012, 28, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.S.; Narayana, K.L.; Swamy, K.M. Influence of ultrasound in ammoniacal leaching of a copper oxide ore. Metal. Mater. Trans. B 1997, 8, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X. Crystal structure preparation and discharge performancefor manganese dioxides and related manganese oxides (I). Battery Bimon. 2004, 34, 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, D. Thermodynamic Analysis of Common Regularities for Gold Chlorination Leaching Systems. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2006, 30, 703–706. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y.; Li, S.W.; Peng, J.H. Ultrasound Augmented leaching of nickel sulfate in sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide media. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 40, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamani, S.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I. Ultrasonic-energy enhance the ionic liquid-based dual microextraction to preconcentrate the lead in ground and stored rain water samples as compared to conventional shaking method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Peng, J. Comparison of ultrasonic-assisted and regular leaching of germanium from by-product of zinc metallurgy. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, O.M.; Mahir, I.; Mahmut, B. Leaching of silver from solid waste using ultrasound assisted thiourea method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2005, 12, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Akçay, M.; Elik, A.; Savaşcı, Ş. Effect of ultrasonication on extraction rate and on recovery of strontium from river sediment using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Analyst 1989, 114, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, E.D.; Zhang, L.B. A comparison of ultrasound-augmented and conventional leaching of silver from sintering dust using acidic thiourea. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelo, J.L.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. Ultrasonic extraction followed by sonolysis-ozonolysis as a sample pretreatment method for determination of reactive arsenic toward sodium tetrahydroborate by flow injection-hydride generation AAS. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3732–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Ger, M.D.; Chen, S.I. Study on Thermal Decomposition of Pentolites by modified vacuum stability apparatus and differential scanning calorimetry. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 1992, 17, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, J. Pressure leaching of high silica Pb–Zn oxide ore in sulfuric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Rivera-Landero, I. Leaching of silver contained in mining tailings, using sodium thiosulfate: A kinetic study. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.S.; Li, X.H.; Chen, M.A. Kinetics comparison of oxidizing acid leading and conventional acid leading of indium sulfide. Met. Mine 2014, 43, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tang, M.T. Dissolution kinetics of low grade complex copper ore in ammonia-ammonium chloride solution. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Hao, L.I.; Sun, Y.W. Leaching kinetics of zinc silicate in ammonium chloride solution. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, C.F.; Heal, G.R. Solid-liquid diffusion controlled rate equations. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 340, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Yin, Z.L.; Hu, H.P. kinetics of zinc silicate (hemimorphite) in ammoniacal solution. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Yang, T.Z.; Zhang, D.C. Leaching of low grade zinc oxide ores in NH4Cl-NH3, solutions with nitrilotriacetic acid as complexing agents. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Horckmans, L.; Spooren, J. Selective leaching of Pb, Cu, Ni and Zn from secondary lead smelting residues. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, I.A.; Varga, T.; Egedy, A. Kinetic models based on analysis of the dissolution of copper, zinc and brass from WEEE in a sodium persulfate environment. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2015, 83, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Element | Pb | Mn | S | O | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt. %) | 6.06 | 57.58 | 3.91 | 28.04 | 1.58 | 1.06 |
| Temperature (K) | Correlation Coefficients (R2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 − (1 − x)1/3 | 1 − 2/3x − (1 − x) 2/3 | 1/3ln(1 − x) − 1 + (1 − x)−1/3 | |
| 298 | 0.99539 | 0.99231 | 0.98747 |
| 303 | 0.98677 | 0.99563 | 0.99915 |
| 308 | 0.99245 | 0.98687 | 0.97883 |
| 313 | 0.99640 | 0.99918 | 0.99737 |
| Temperature (K) | Correlation Coefficients (R2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 − (1 − x)1/3 | 1 − 2/3x − (1 − x) 2/3 | 1/3ln(1 − x)− 1 + (1 − x)−1/3 | |
| 298 | 0.99506 | 0.99070 | 0.97861 |
| 303 | 0.98465 | 0.98949 | 0.99749 |
| 308 | 0.97710 | 0.98913 | 0.97639 |
| 313 | 0.98989 | 0.99888 | 0.98912 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Long, H. Roasting Pretreatment Combined with Ultrasonic Enhanced Leaching Lead from Electrolytic Manganese Anode Mud. Metals 2019, 9, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050601
Xie H, Li S, Zhang L, Wang Y, Long H. Roasting Pretreatment Combined with Ultrasonic Enhanced Leaching Lead from Electrolytic Manganese Anode Mud. Metals. 2019; 9(5):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050601
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Huimin, Shiwei Li, Libo Zhang, Yongmi Wang, and Hailin Long. 2019. "Roasting Pretreatment Combined with Ultrasonic Enhanced Leaching Lead from Electrolytic Manganese Anode Mud" Metals 9, no. 5: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050601
APA StyleXie, H., Li, S., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., & Long, H. (2019). Roasting Pretreatment Combined with Ultrasonic Enhanced Leaching Lead from Electrolytic Manganese Anode Mud. Metals, 9(5), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050601




