Estimating the Influences of Prior Residual Stress on the Creep Rupture Mechanism for P92 Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation and Creep Test
2.2. Creep Damage and Crack Growth Model
2.3. FE Analysis Model
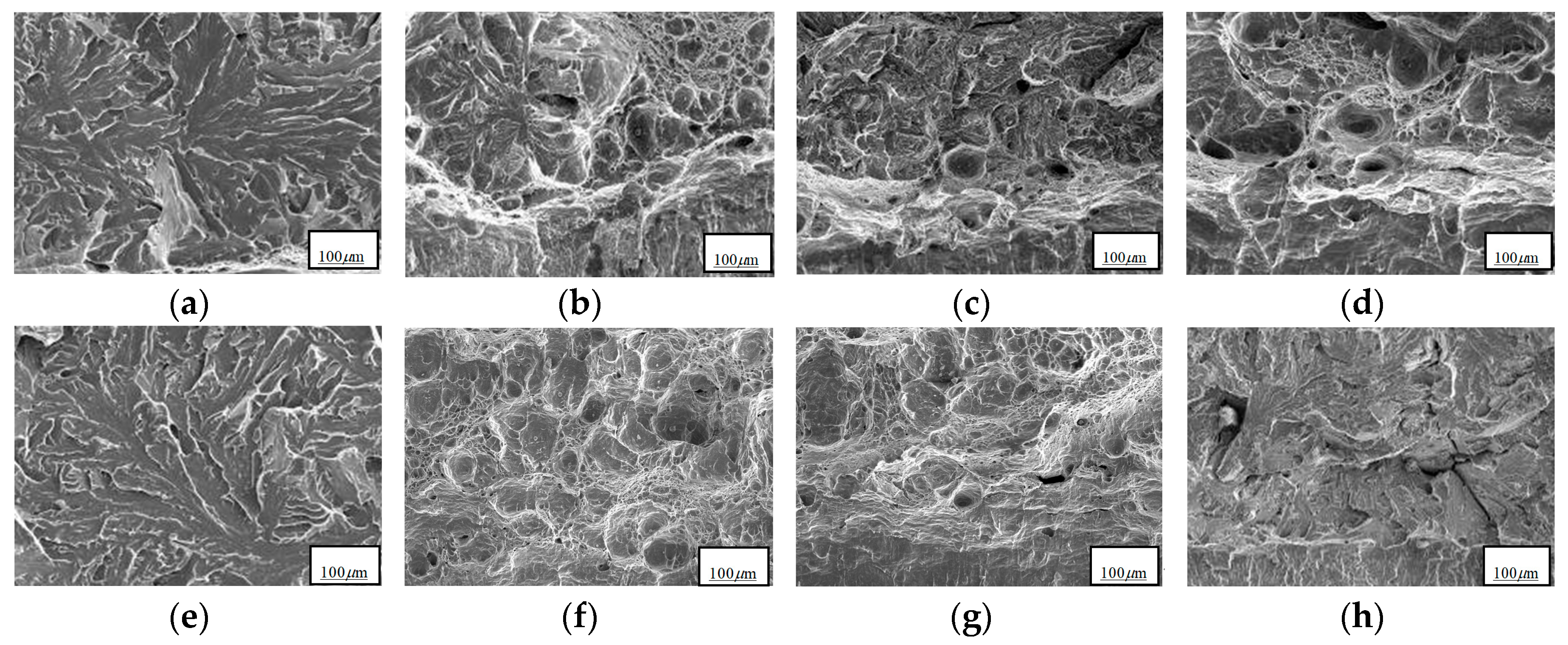
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skelton, R.P. Deformation, diffusion and ductility during creep—continuous void nucleation and creep-fatigue damage. Mater. High Temp. 2017, 34, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerkari, P.; Salonen, J.; Holmstrom, S.; Laukkanen, A.; Rantala, J.; Nikkarila, R. Creep damage and long term life modelling of an X20 steam line component. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 35, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodamorad, S.H.; Fatmehsari, D.H.; Rezaie, H.R.; Sadeghipour, A. Analysis of ethylene cracking furnace tubes. Eng. Fail. Anal.. 2012, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Suh, J.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Huh, J.Y.; Jung, W.S. Microstructural evolution and creep-rupture life estimation of high-Cr martensitic heat-resistant steels. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, D.; Chang, L.; Hui, X. Enhanced mechanical properties induced by refined heat treatment for 9Cr–0.5Mo–1.8W martensitic heat resistant steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Výrostkova, A.; Homolova, V.; Svoboda, M. Creep deformation and failure of E911/E911 and P92/P92 similar weld-joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Tabuchi, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Hongo, H.; Tanabe, T. Creep damage evaluation of 9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb steel welded joints showing type IV fracture. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2006, 83, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Wang, G.Z.; Tan, J.P.; Xuan, F.Z.; Tu, S.T. Effects of residual stress on creep damage and crack initiation in notched CT specimens of a Cr–Mo–V steel. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 97, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Xiu, J. Effect of residual stress on creep crack growth behavior in ASME P92 steel. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 110, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, H.; Sakurai, T. A trigger of Type IV damage and a new heat treatment procedure to suppress it. Microstructural investigations of long-term ex-service Cr-Mo steel pipe elbows. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2005, 82, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Sawada, K.; Kushima, H.; Kubo, K. Effect of stress on the creep deformation of ASME Grade P92/T92 steels. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 99, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.; Bradbury, A.; Aldrich-Smith, G.; Clyne, T.W. A procedure for extracting primary and secondary creep parameters from nanoindentation data. Mech. Mater. 2013, 65, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, R.; Yokobori, A.T.; Sato, K.; Tabuchi, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Yatomi, M. Creep crack initiation and growth behavior in weldments of high Cr steels. Strength Fract. Complexity 2014, 8, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, T.H.; Saber, M.; Sun, W. Testing and modelling of creep crack growth in compact tension specimens from a P91 weld at 650 °C. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2010, 77, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basirat, M.; Shrestha, T.; Potirniche, G.P.; Charit, I.; Rink, K. A study of the creep behavior of modified 9Cr–1Mo steel using continuum-damage modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2012, 37, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.P.; Cortellino, F.; Sun, W.; Hyde, T.H.; Shingledecker, J. Small punch creep testing: review on modelling and data interpretation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 1328–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.H.; Truman, C.E.; Smith, D.J. Using local out-of-plane compression (LOPC) to study the effects of residual stress on apparent fracture toughness. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 1516–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.R.; Liu, Z.D.; Cheng, S.C.; Yang, G.; Xie, J.X. Influences of strain rate and deformation temperature on flow stress and critical dynamic recrystallization of heat resistant steel T122. Acta Metall. Sinica 2007, 43, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.S.; Wang, Z.R.; Wang, Y. Numerical Investigations on Residual Stress in Laser Penetration Welding Process of Ultrafine-Grained Steel. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8609325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.D.; Faria, E.A.; Prado, A.G. Thermodynamic studies of the interaction at the solid/liquid interface between metal ions and cellulose modified with ethylenediamine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkaldy, J.S.; Vanugopalan, D. Prediction of microstructure and hardenability in low alloy steels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Phase Transformation in Ferrous Alloys, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 4–6 October 1983; Marder, A.R., Goldstein, J.I., Eds.; TMS-AIME: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1984; pp. 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.B.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D. Effect of ultrafast cooling on preventing abnormal microstructural banding at centerline of steel plate. J. Northeastern Univ. 2017, 38, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, J.; Tracey, D. Computational fracture mechanics. In Numerical and Computer Methods in Structural Mechanics; Fenves, S.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 585–623. [Google Scholar]
- Hayhurst, D.R.; Hayhurst, R.J.; Vakili-Tahami, F. Continuum damage mechanics predictions of creep damage initiation and growth in ferritic steel weldments in a medium bore branched pipe under constant pressure at 590 °C using a five-material weld model. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 461, 2303–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jing, H.Y.; Xu, L.Y.; An, J.C.; Xiao, G.C. Numerical investigation of factors affecting creep damage accumulation in ASME P92 steel welded joint. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, B.; Hao, L.; Lu, S.; Yue, C.; Fei, B. Experimental investigation of creep crack growth behavior in nickel base superally by constant displacement loading method at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 665, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Mehmanparast, A.; Davies, C.M.; Nikbin, K.M. Evaluation of fracture mechanics parameters for bimaterial compact tension specimens. Mater. Res. Innovations 2013, 17, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. Research on life assessment method considering constraint effect for P92 pipe with defects at elevated temperature. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yatomi, M.; O’Dowd, N.P.; Nikbin, K.M.; Webster, G.A. Theoretical and numerical modelling of creep crack growth in a carbon–manganese steel. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2006, 73, 1158–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Tu, S.T.; Gong, J.M. Application of Runge–Kutta–Merson algorithm for creep damage analysis. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2000, 77, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, C.J. The significance of bragg’s law in electron diffraction and microscopy, and bragg’s second law. Acta Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.D.; Matlock, D.K.; Dimelfi, R.J. A model for creep fracture based on the plastic growth of cavities at the tips of grain boundary wedge cracks. Acta Metall. 1977, 25, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhurst, D.R.; Lin, J.; Hayhurst, R.J. Failure in notched tension bars due to high-temperature creep: Interaction between nucleation controlled cavity growth and continuum cavity growth. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2008, 45, 2233–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, G.C.; Karlsson, P.W.; Pedersen, A. Partial discharges in ellipsoidal and spheroidal voids. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1989, 24, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.M.; Rice, J.R. Constrained creep cavitation of grain boundary facets. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
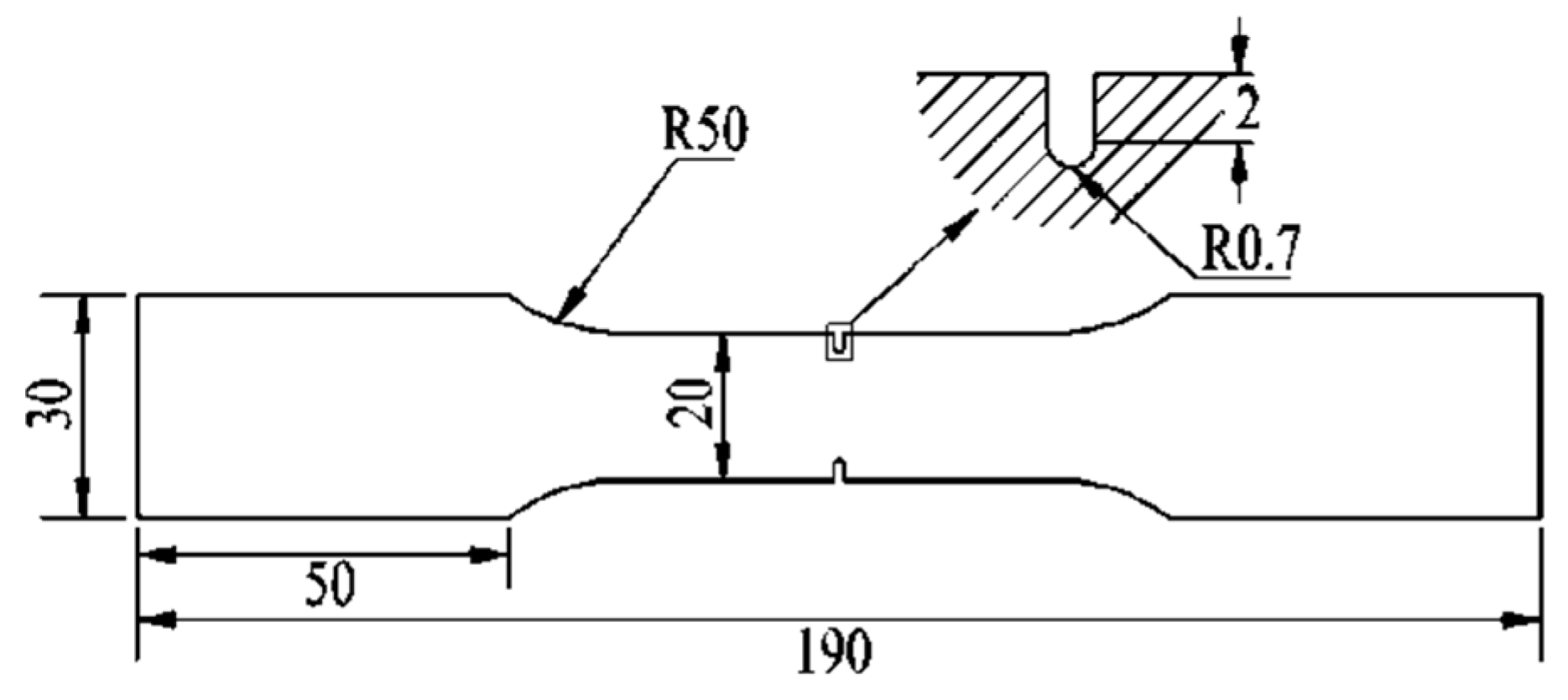
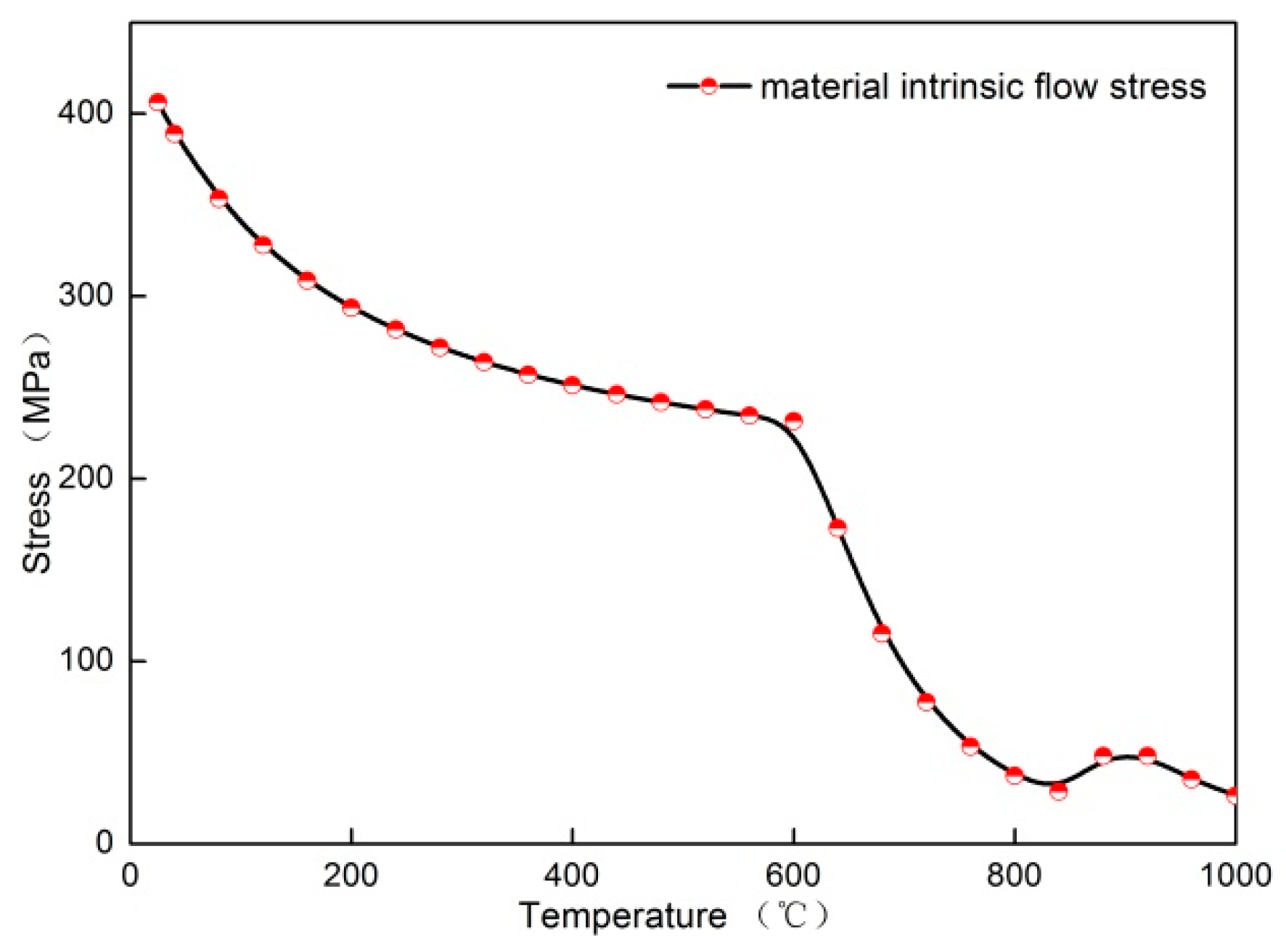




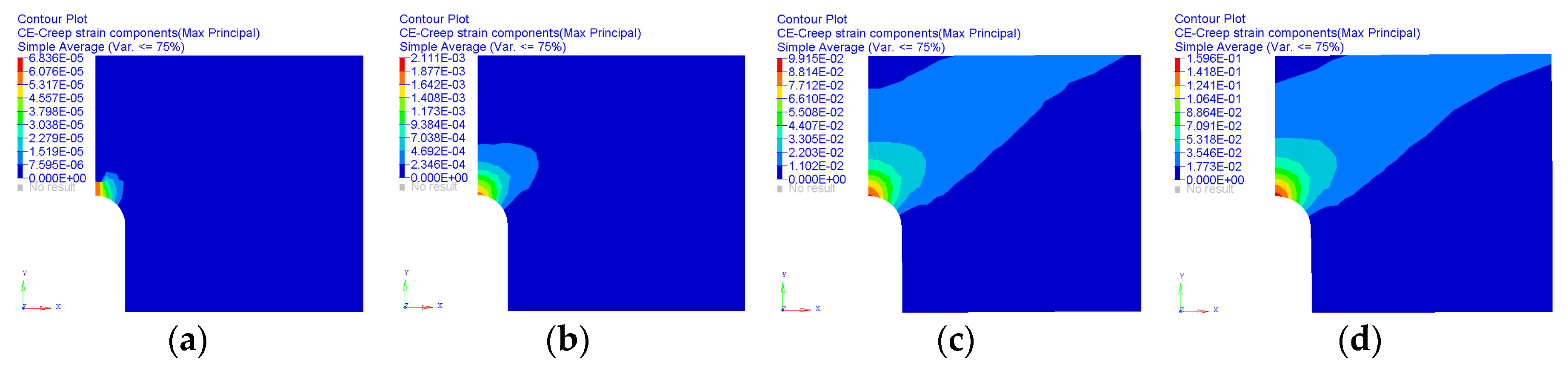

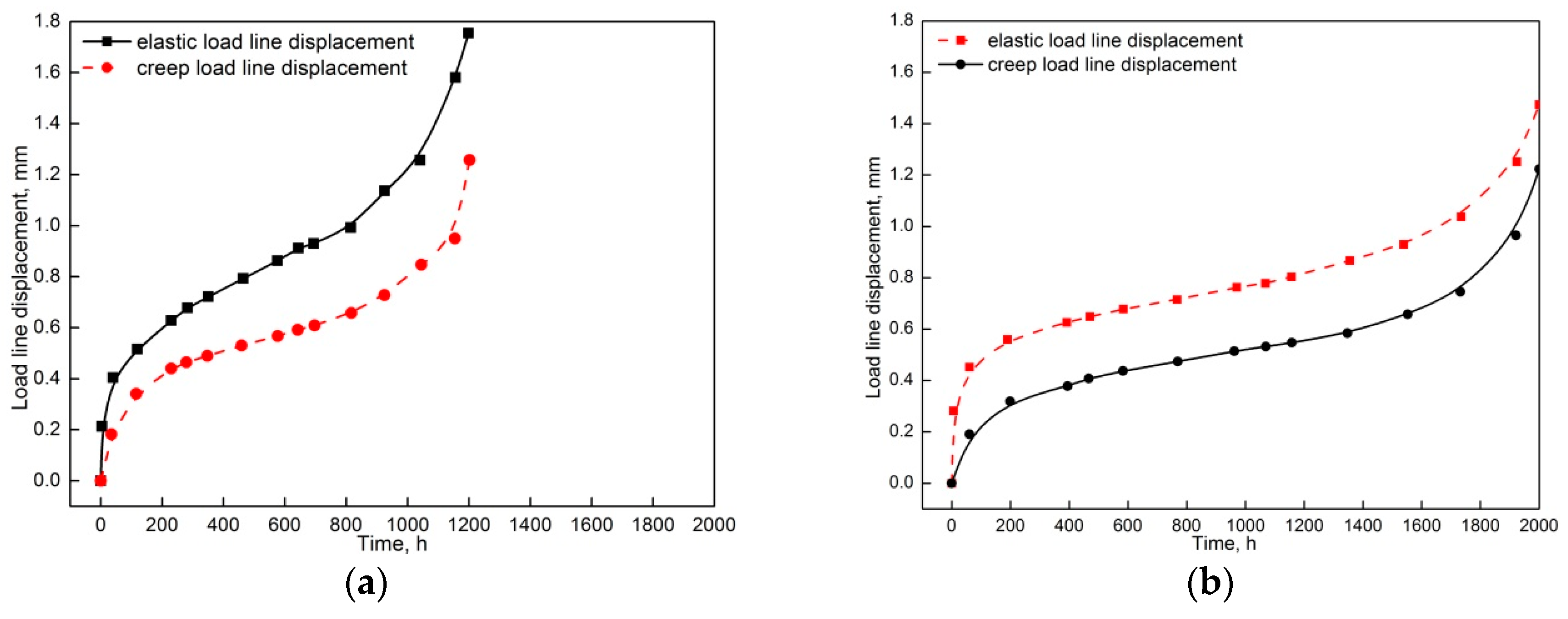

| Material | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Mo | S | P | Nb | V | Al | Ni | W | N | B | Bal. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P92 steel | 0.1 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 8.95 | 0.96 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.08 | 0.215 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 1.47 | 0.043 | 0.001 | Fe |
| Parameter | β | N (um) | D (m2/s) | ΔT (°C) | q | σ0.2 (MPa) | n | ε0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0.3054 | 20 | 2.09 × 10−12 | 123.1 | 3 | 440 | 0.129 | 1 |
| Residual Stress Level | Pre-Compression Load (KN) | Loading Speed (mm/min) | Compressing Magnitude (%) | Stretching Magnitude (%) | Maximum Residual Stress Value (MPa) | Material Intrinsic Flow Stress Value (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High level | 42.8 | 0.16 | 3.82 | 2.15 | 182 | 145 |
| Low level | 20.6 | 0.12 | 1.78 | 1.03 | 97 | 145 |
| Material Parameter | A (MPa/h) | B (MPa−1) | C | H (MPa) | H* | Kc (MPa−3/h) | E (GPa) | v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 2.21618 × 10−9 | 3.473 × 10−3 | 9.85 × 10−2 | 2.43 × 106 | 0.5929 | 9.227 × 10−4 | 125 | 0.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Liang, G.; Zhao, J. Estimating the Influences of Prior Residual Stress on the Creep Rupture Mechanism for P92 Steel. Metals 2019, 9, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060639
Liu D, Li Y, Xie X, Liang G, Zhao J. Estimating the Influences of Prior Residual Stress on the Creep Rupture Mechanism for P92 Steel. Metals. 2019; 9(6):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dezheng, Yan Li, Xiangdong Xie, Guijie Liang, and Jing Zhao. 2019. "Estimating the Influences of Prior Residual Stress on the Creep Rupture Mechanism for P92 Steel" Metals 9, no. 6: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060639
APA StyleLiu, D., Li, Y., Xie, X., Liang, G., & Zhao, J. (2019). Estimating the Influences of Prior Residual Stress on the Creep Rupture Mechanism for P92 Steel. Metals, 9(6), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060639





