Hot Rolling Simulation System for Steel Based on Advanced Meshless Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Solution Method
2.1. Slice Model
2.2. Governing Equations
2.2.1. The Thermal Model
2.2.2. The Mechanical Model
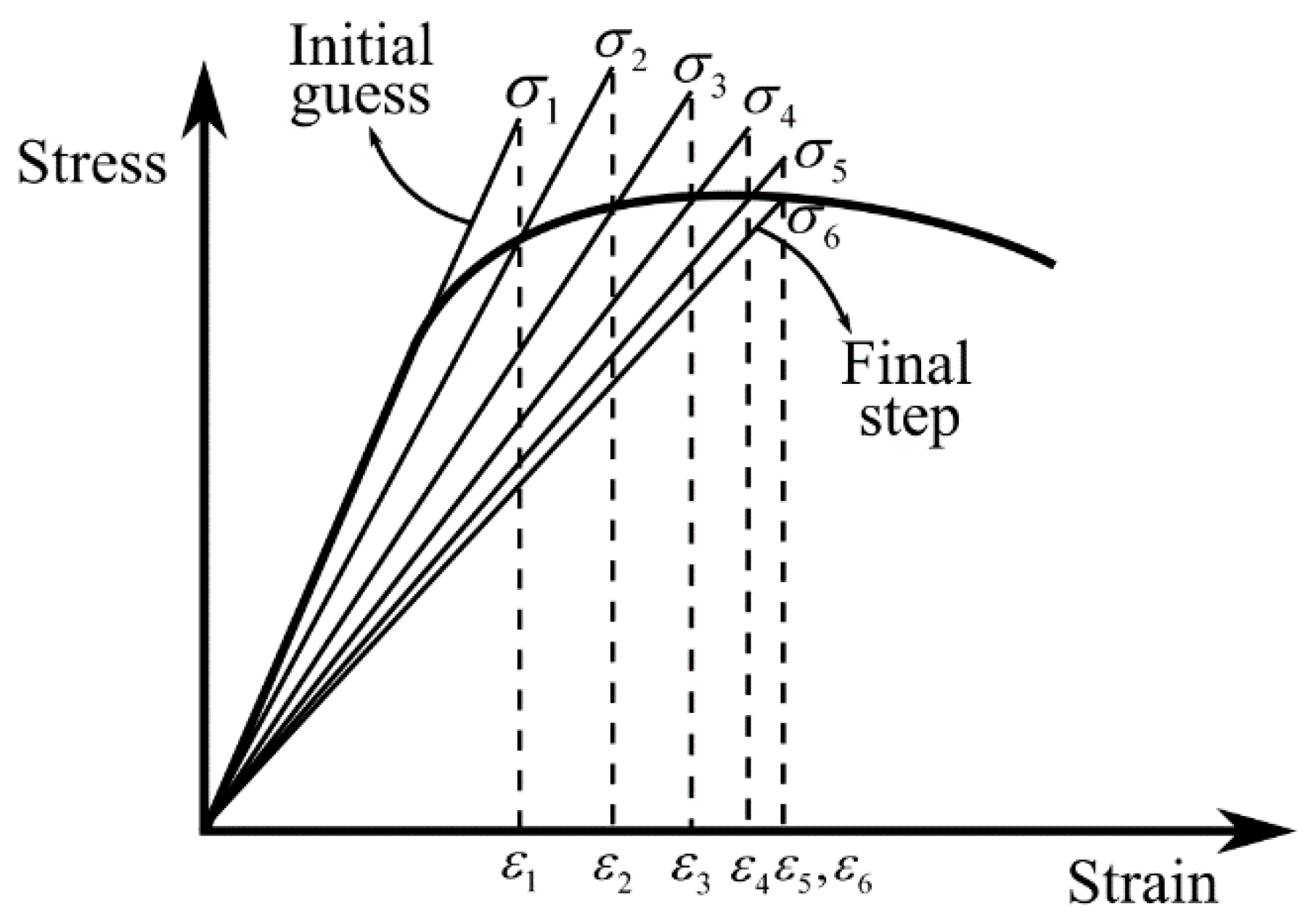
2.3. Thermomechanical Solution Procedure
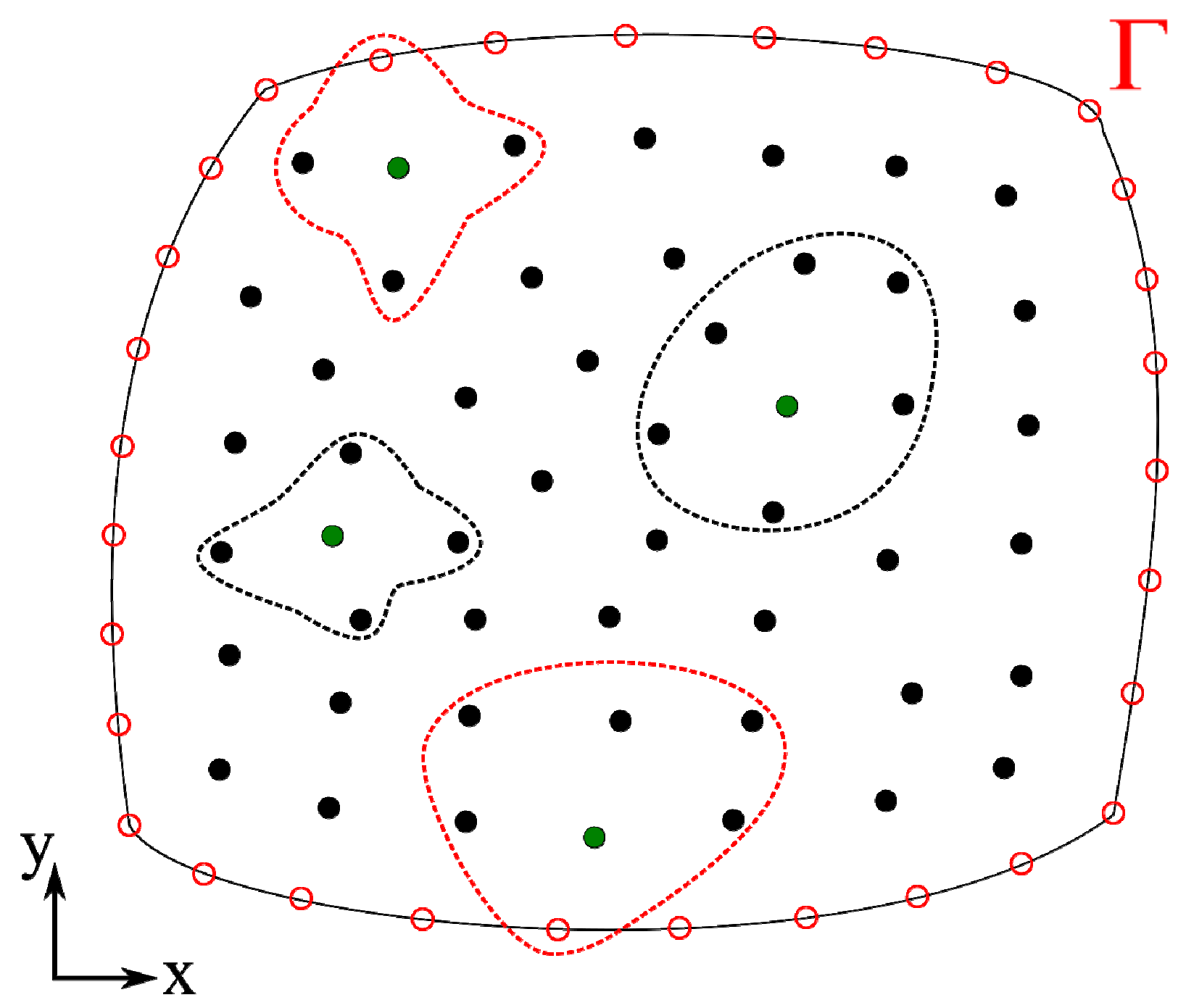
2.4. Collocation Node Distribution
3. Simulation Results
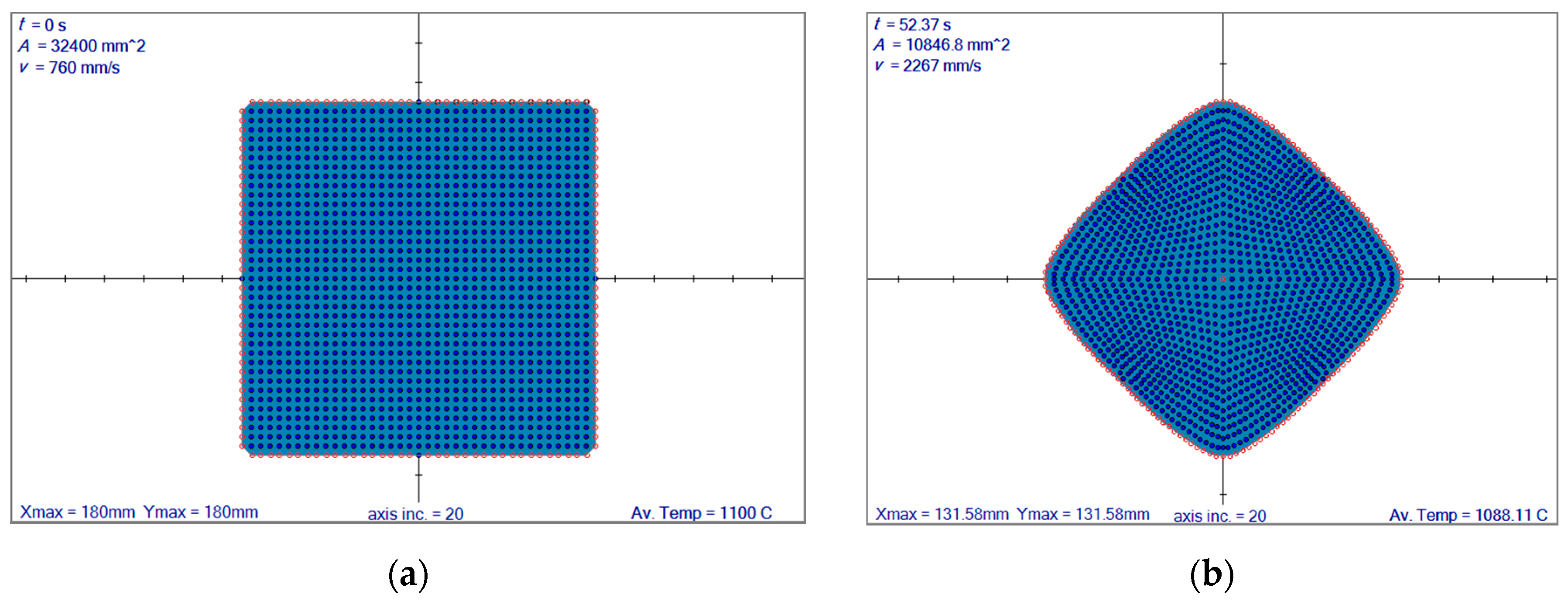
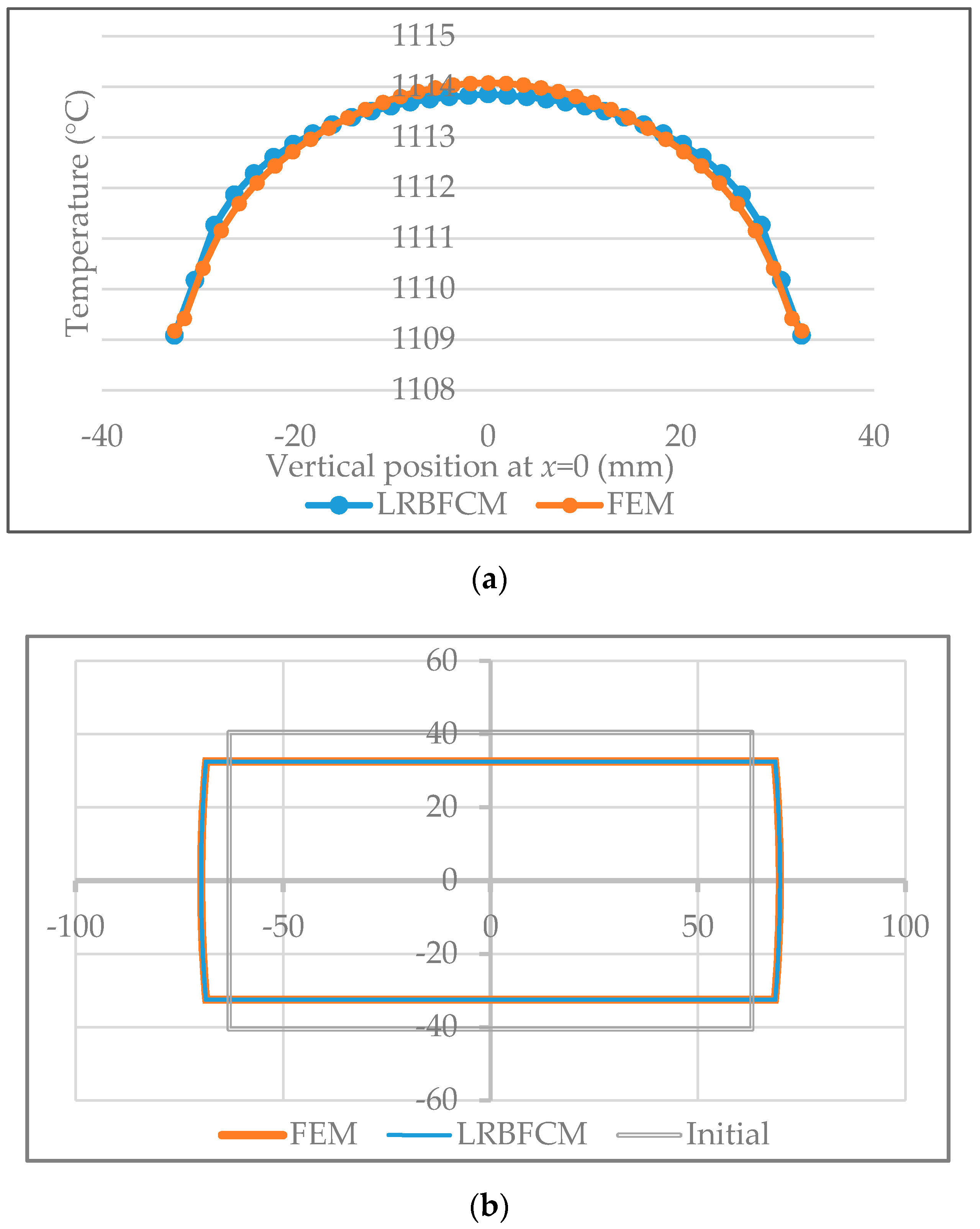
3.1. Comparison of the LRBFCM Solution with FEM in Terms of Deformation and Internal Heat Generation
3.2. Rolling Simulation Results 8 Flat Rolls
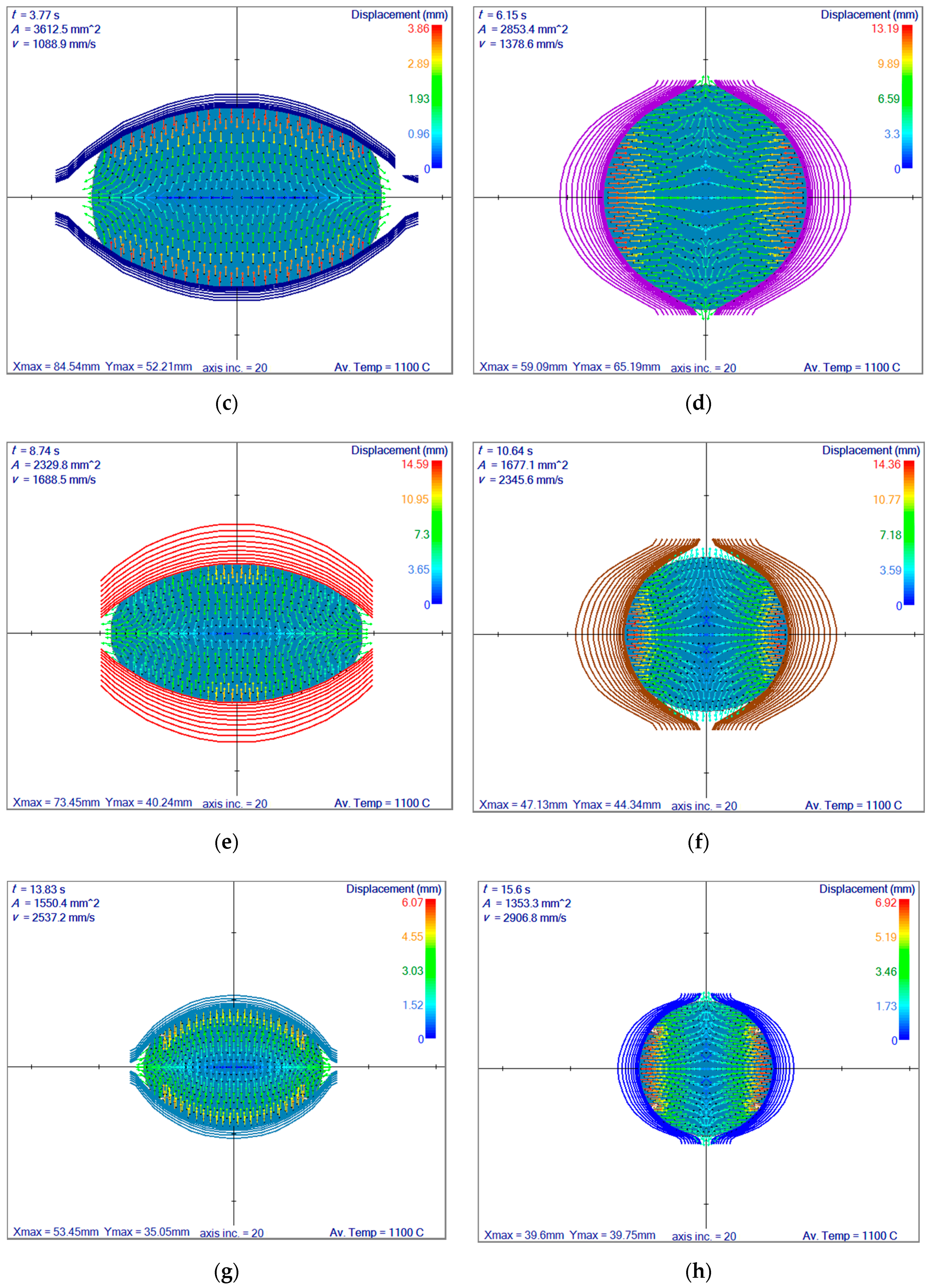
3.3. Rolling Simulation with 7 Oval Rolls
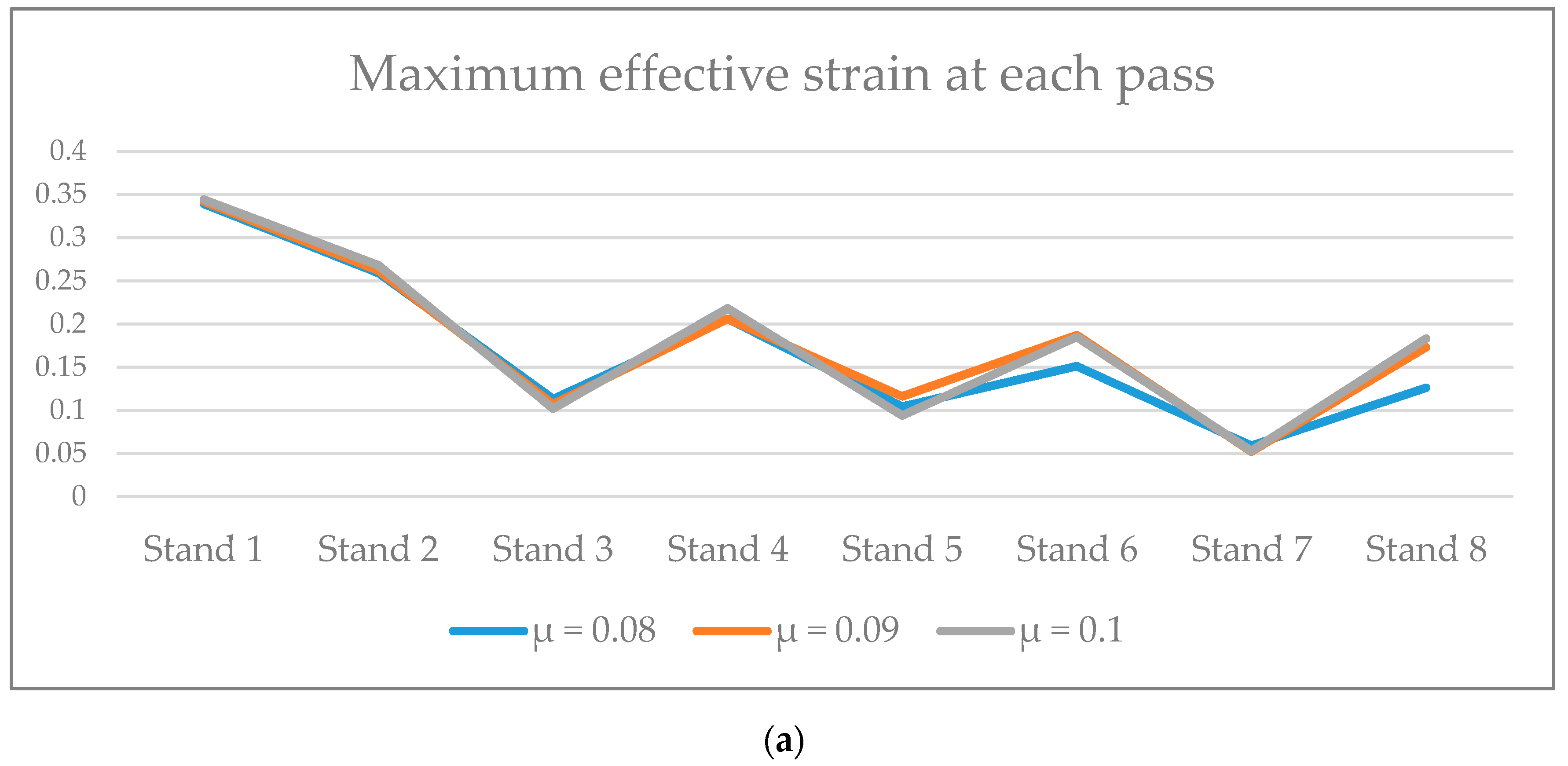
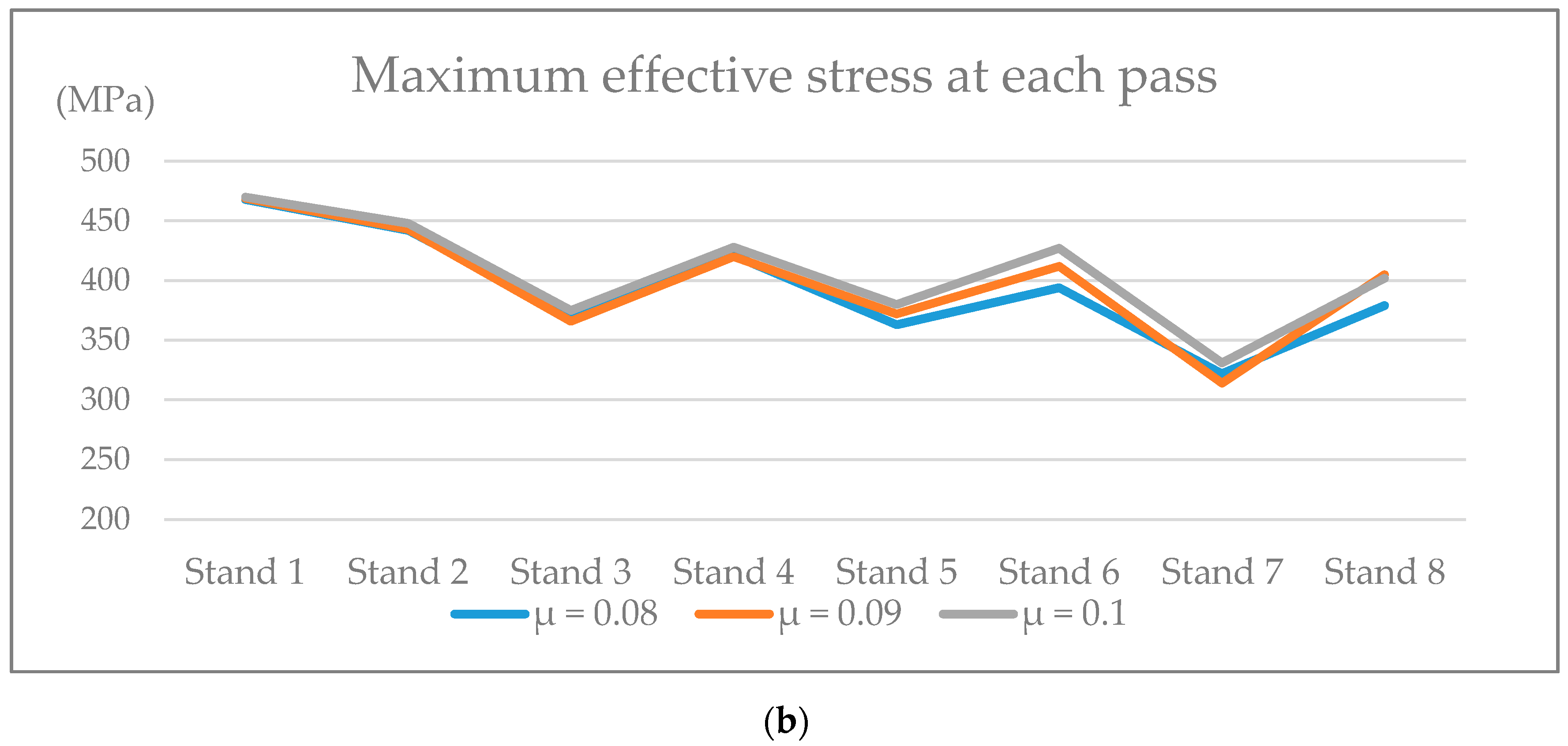
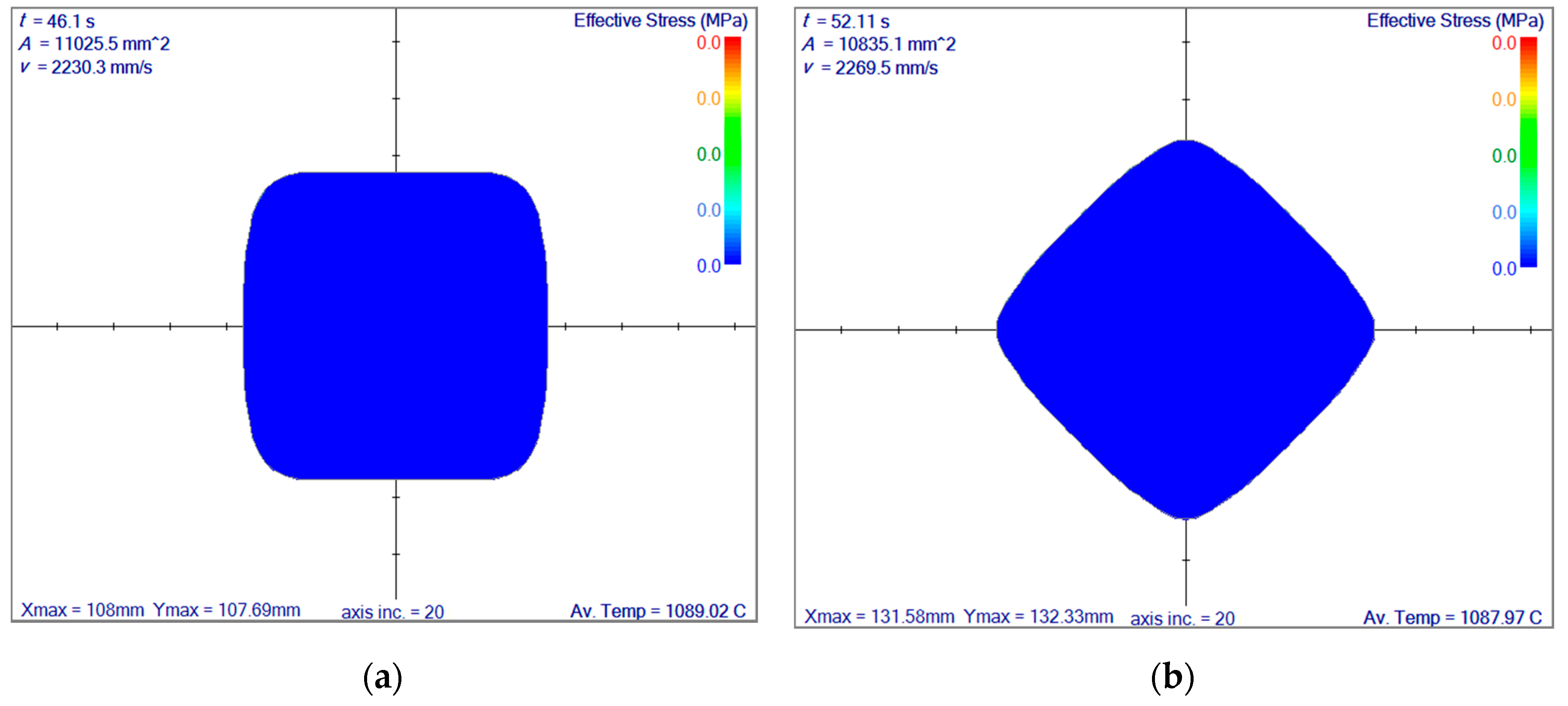
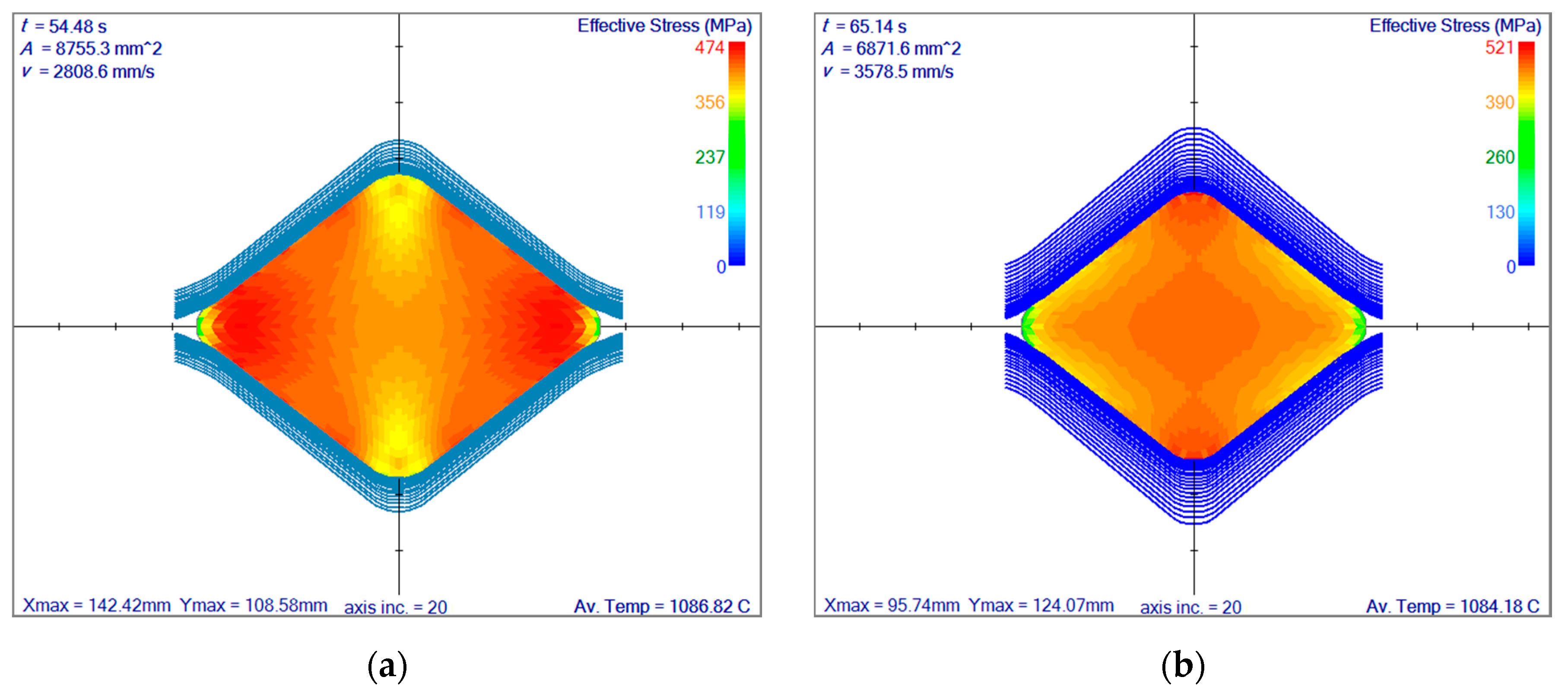
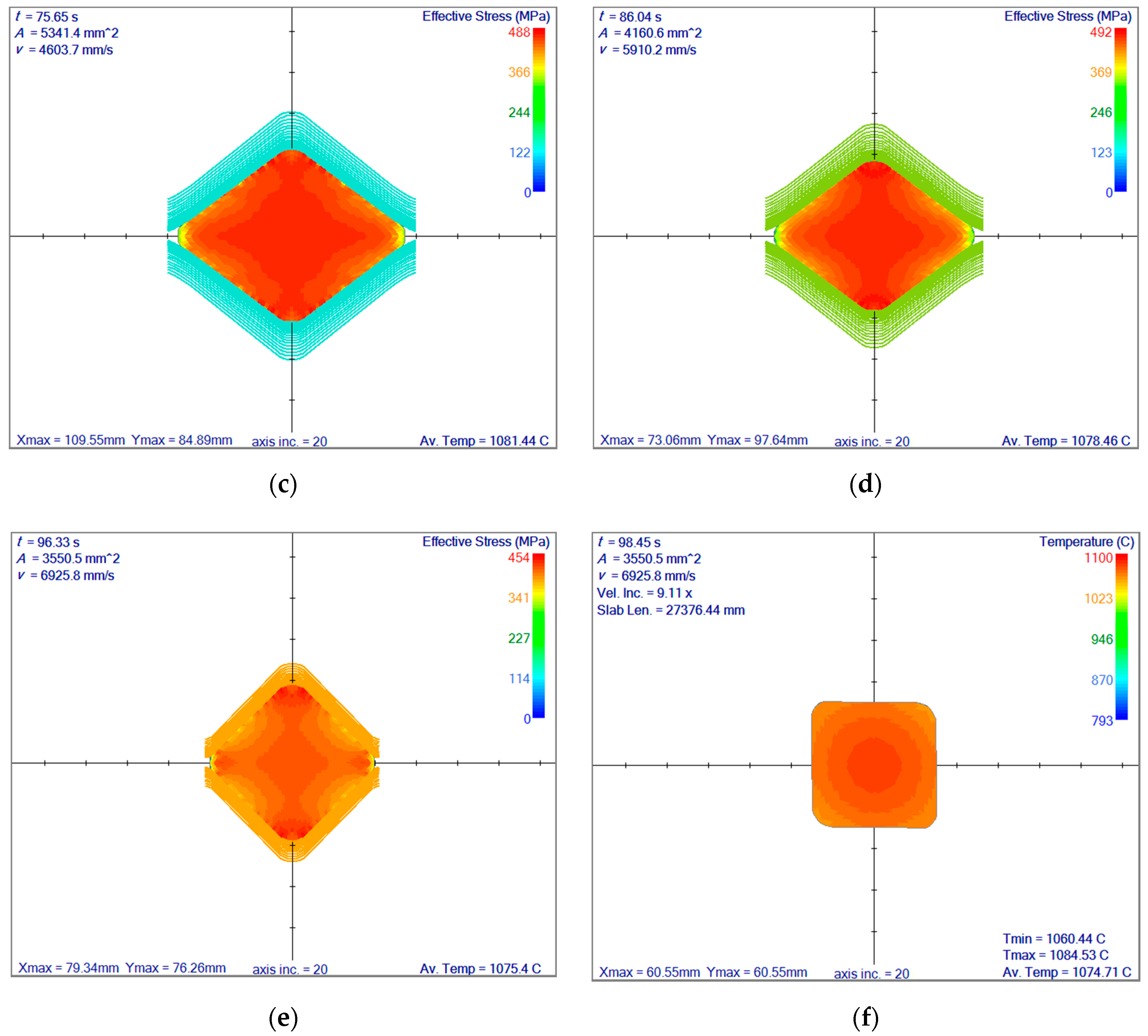
3.4. Rolling Simulation of Reversing Rolling Mill with 10 Passes
3.4.1. Selection of the Position in the Reversing Rolling
3.4.2. Reversing Rolling Mill Simulation–First Section
3.4.3. Rotation in between the First and Second Sections
3.4.4. Reversing Rolling Mill Simulation–Second Section
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
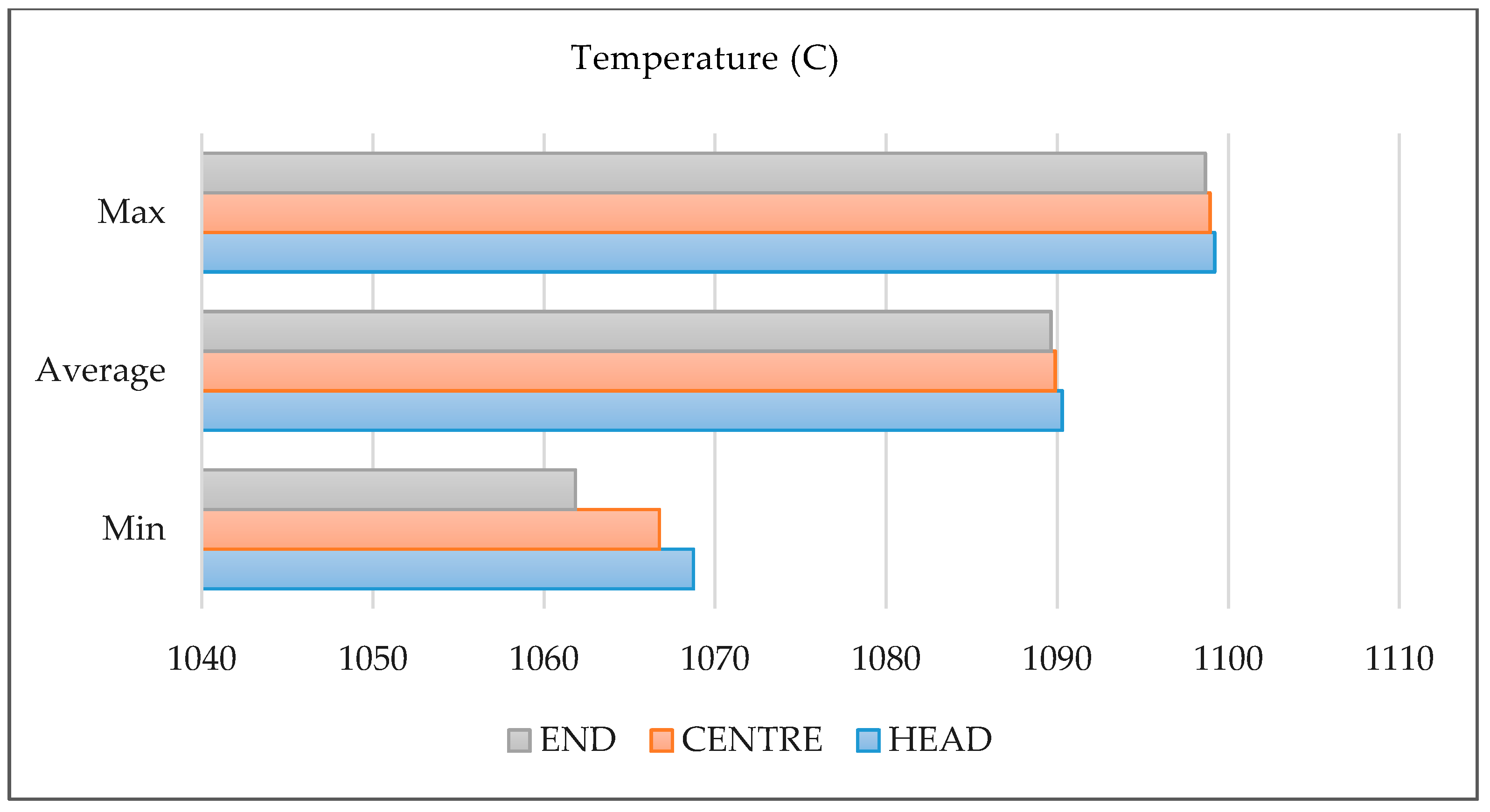
| Heat transfer coefficient to air | hair | 20 | W/m2·K |
| Heat transfer coefficient to roll | hroll | 10,000 | W/m2·K |
| Thermal conductivity of steel | λ | 29 | W/m2·K |
| Specific heat of steel | cp | 630 | J/kg·K |
| Initial rolling speed | ventry | 0.76 | m/s |
| Ambient temperature | Tair | 25 | °C |
| Roll surface temperature | Troll | 500 | °C |
| Initial slice temperature | Tinitial | 1100 | °C |
| Taylor-Quinney parameter | η | 0.9 | - |
| Time step | Δt | 10−4 | s |
| Coefficient of friction | μ | 0.1 | - |
| Material model | Mpa | ||
| Distance between rolling stands | - | 3 (for the first five rolling stands), 4.5 (after fifth rolling stand) | m |
| Exit distance of the billet in reversing rolling mill | - | 1 | m |
References
- Lenard, J.G.; Pietrzyk, M.; Ceser, L. Mathematical and Physical Simulation of the Properties of Hot Rolled Products, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, W.L. Cold Rolling of Steel; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, W.L. Hot Rolling of Steel; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, R.B. The calculation of the roll force and torques in hot rolling mills. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1954, 168, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusatowski, Z. Hot rolling: A study of drought, spread and elongation. Iron Steel 1955, 28, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, R.H. Stress analysis of heated complex shapes. J. Am. Rocket Soc. 1962, 32, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcel, P.V.; King, L.P. Elastic-plastic analysis of two-dimensional stress systems by the finite element method. IJMS 1967, 9, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Osakada, K.; Oda, T. Simulation of plane-strain rolling by the rigid plastic finite element method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1982, 24, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacki, M.; Kedzierski, Z.; Kusiak, H.; Madej, M.; Pietrzyk, M. Simulation of metal flow, heat transfer and structure evolution during hot rolling in square-oval-square series. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1992, 34, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuma, T.; Yamada, K. Progress of Finite Element Simulation for Rolling Processes. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Numerical Methods in Industrial Forming Process, Toyohashi, Japan, 18–20 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Belytschko, T.; Lu, Y.Y.; Gu, L. Element-free Galerkin methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods. Eng. 1994, 37, 229–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onate, E.; Idelsohn, S.; Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. A finite point method in computational mechanics. Int. J. Numer. Methods. Eng. 1996, 39, 3839–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atluri, S.N.; Zhu, T. A new meshless local Petrov-Galerkin approach in computational mechanics. Comput. Mech. 1998, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lee, J.D.; Eskandarian, A. Meshless Methods in Solid Mechanics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cueto, E.; Chinesta, F. Meshless methods to the simulation of material forming. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2013, 8, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoglu, U.; Šarler, B. Simulation of hot shape rolling of steel in continuous rolling mill by local radial basis function collocation method. Comp. Model. Eng. 2015, 109, 447–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoglu, U.; Šarler, B. Rolling simulation system for non-symmetric groove types. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 15, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertnik, R.; Mramor, K.; Šarler, B. Solution of three-dimensional temperature and turbulent velocity field in continuously cast steel billets with electromagnetic stirring by a meshless method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2019, 104, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrič, B.; Šarler, B. Local radial basis function collocation method for linear thermoelasticity in two dimensions. Int. J. Numer. Method H. 2015, 25, 1488–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenard, J.G. Primer on Flat Rolling, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hanoglu, U.; Šarler, B. Thermo-mechanical analysis of hot shape rolling of steel by a meshless method. Procedia Eng. 2011, 10, 3173–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoglu, U.; Šarler, B. Multi-pass hot rolling simulation using a meshless method. Comput. Struct. 2018, 194, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Han, D.J. Plasticity for Structural Engineers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Vertnik, R.; Šarler, B. Meshfree local radial basis function collocation method for diffusion problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 2006, 51, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Oh, S.; Altan, T. Metal Forming and Finite Element Method; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.J.F.; Soni, B.K.; Weatherill, N.P. Handbook of Grid Generation; CRC: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- DEFORM 2D, Scientific forming technologies corporation, Version 10.1. 2009. Available online: http://www.deform.com (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Hanoglu, U. Simulation of Hot Shape Rolling of Steel by a Meshless Method. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nova Gorica, Nova Gorica, Slovenia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačič, M.; Šarler, B. Genetic programming prediction of the natural gas consumption in a steel plant. Energy 2014, 66, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačič, M.; Stopar, K.; Vertnik, R.; Šarler, B. Comprehensive electric arc furnace electric energy consumption modeling: A pilot study. Energies 2019, 12, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


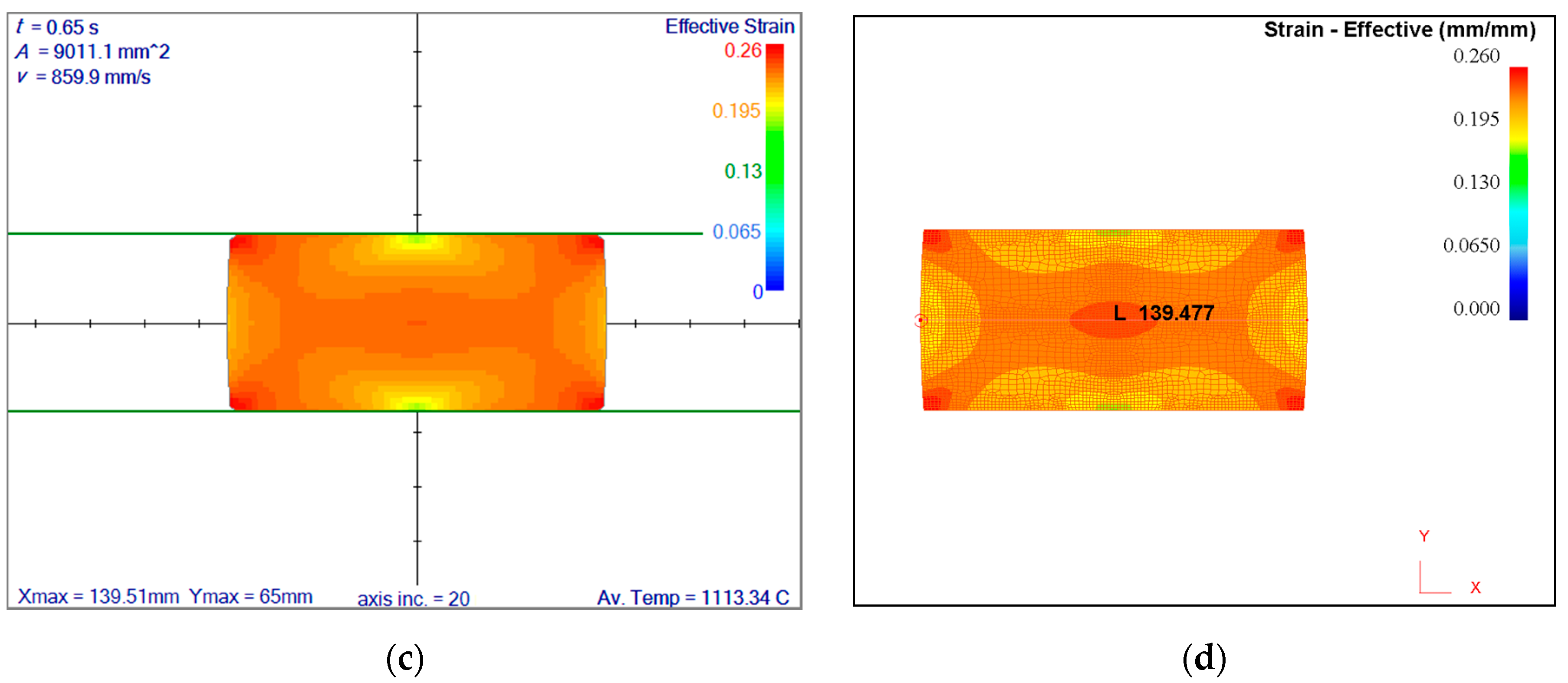


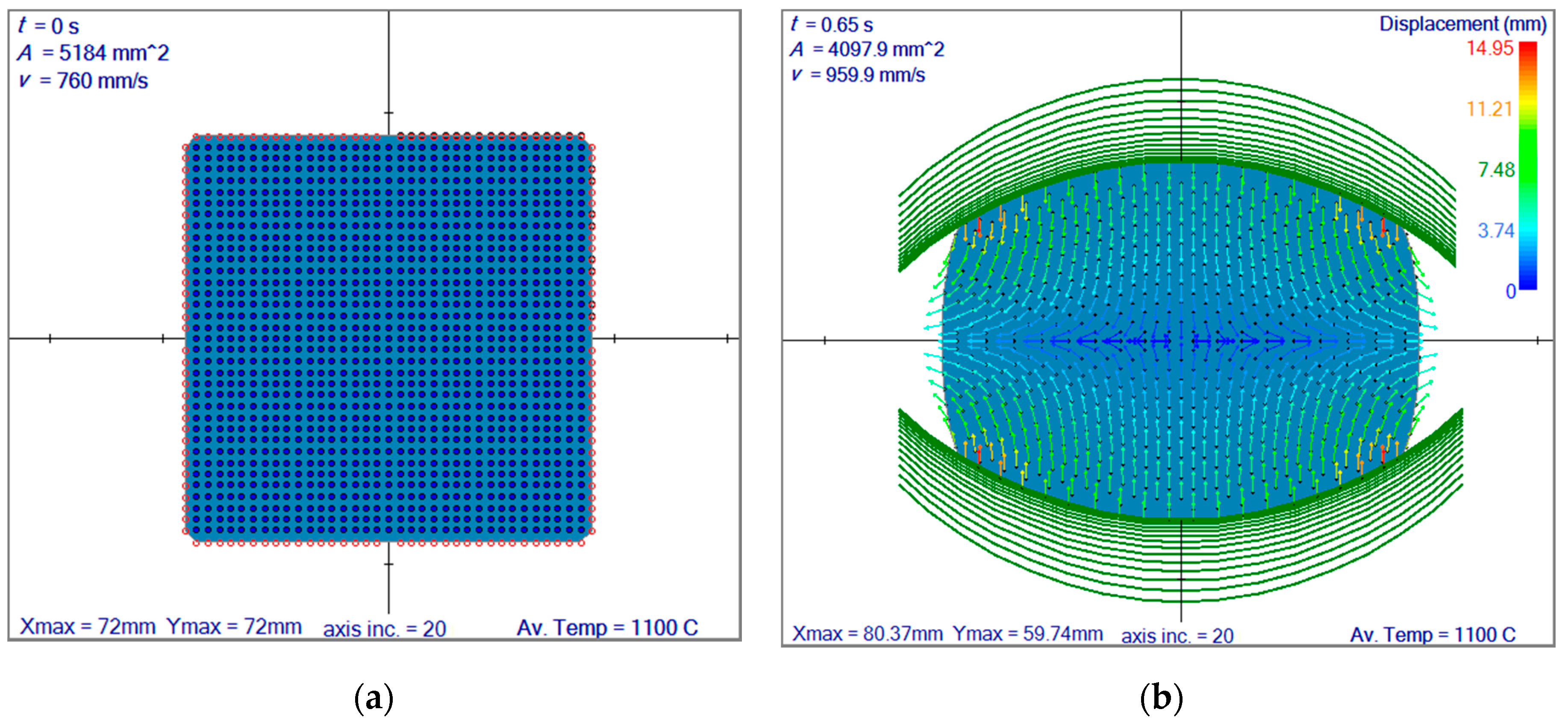

| Head | Centre | End |
|---|---|---|
| Initial slice | Initial Slice | Initial Slice |
 | 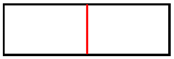 |  |
| First roll | First roll | First roll |
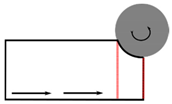 |  | 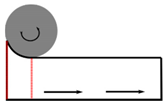 |
| Second roll | Second roll | Second roll |
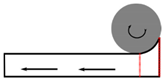 | 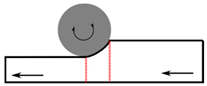 | 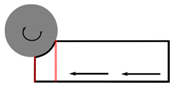 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanoglu, U.; Šarler, B. Hot Rolling Simulation System for Steel Based on Advanced Meshless Solution. Metals 2019, 9, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070788
Hanoglu U, Šarler B. Hot Rolling Simulation System for Steel Based on Advanced Meshless Solution. Metals. 2019; 9(7):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070788
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanoglu, Umut, and Božidar Šarler. 2019. "Hot Rolling Simulation System for Steel Based on Advanced Meshless Solution" Metals 9, no. 7: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070788
APA StyleHanoglu, U., & Šarler, B. (2019). Hot Rolling Simulation System for Steel Based on Advanced Meshless Solution. Metals, 9(7), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070788






