Study of the Surface Integrity and High Cycle Fatigue Performance of AISI 4340 Steel after Composite Surface Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
The Principle of Abrasive Water Jet Peening and Ultrasonic Surface Rolling
3. Results
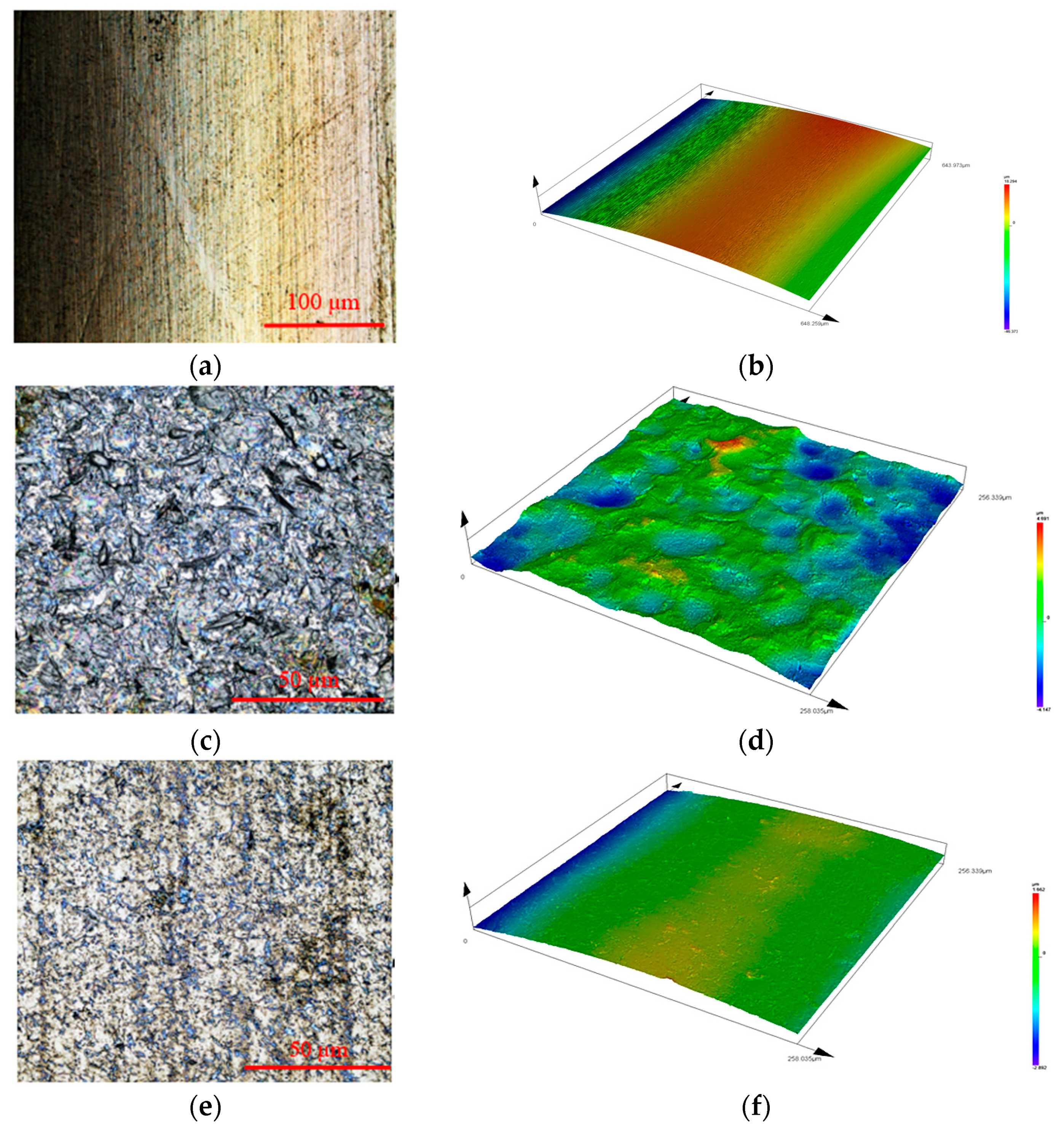
3.1. Specimen Surface Microstructure
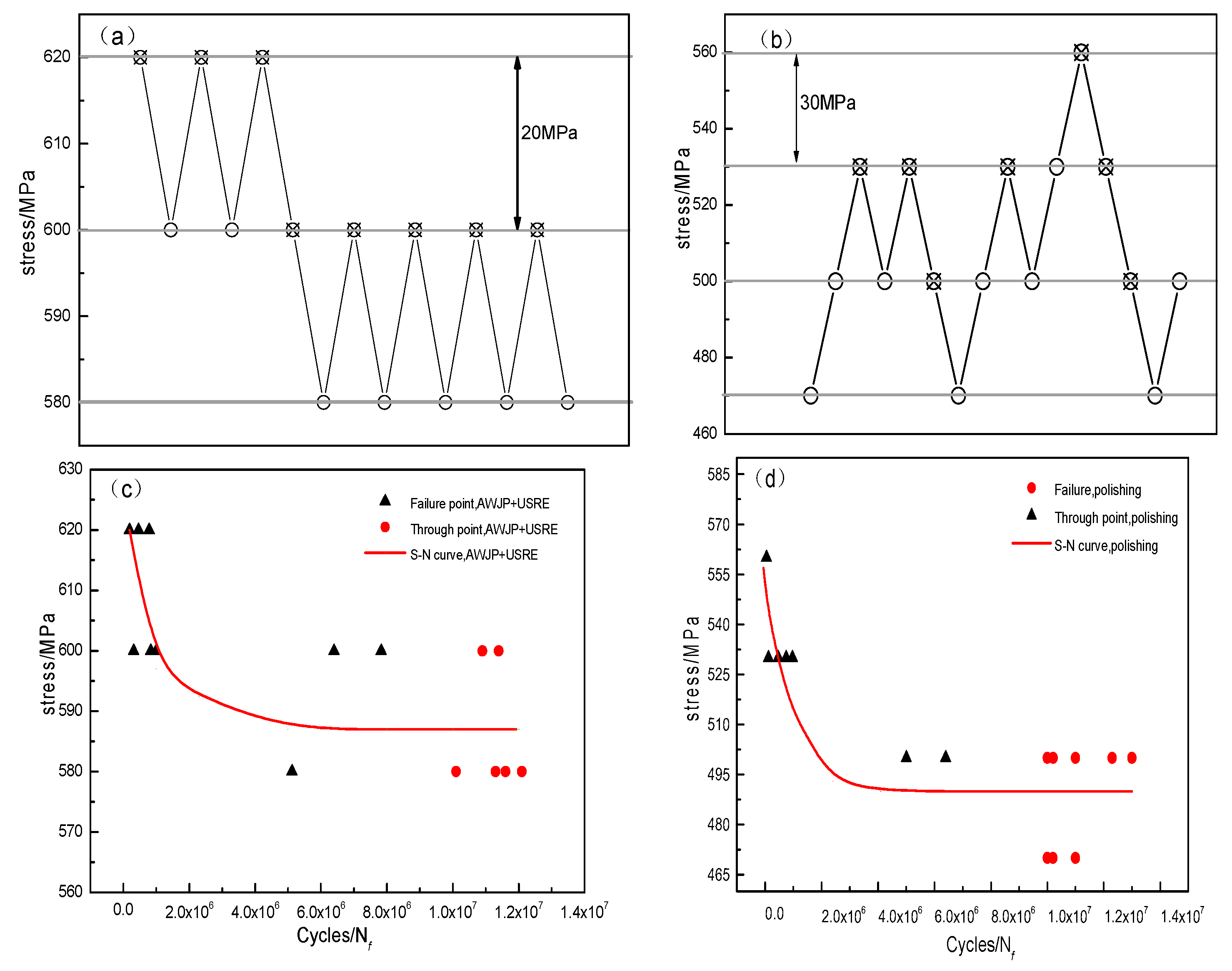
3.2. Fatigue Limit Curve and S-N Curve
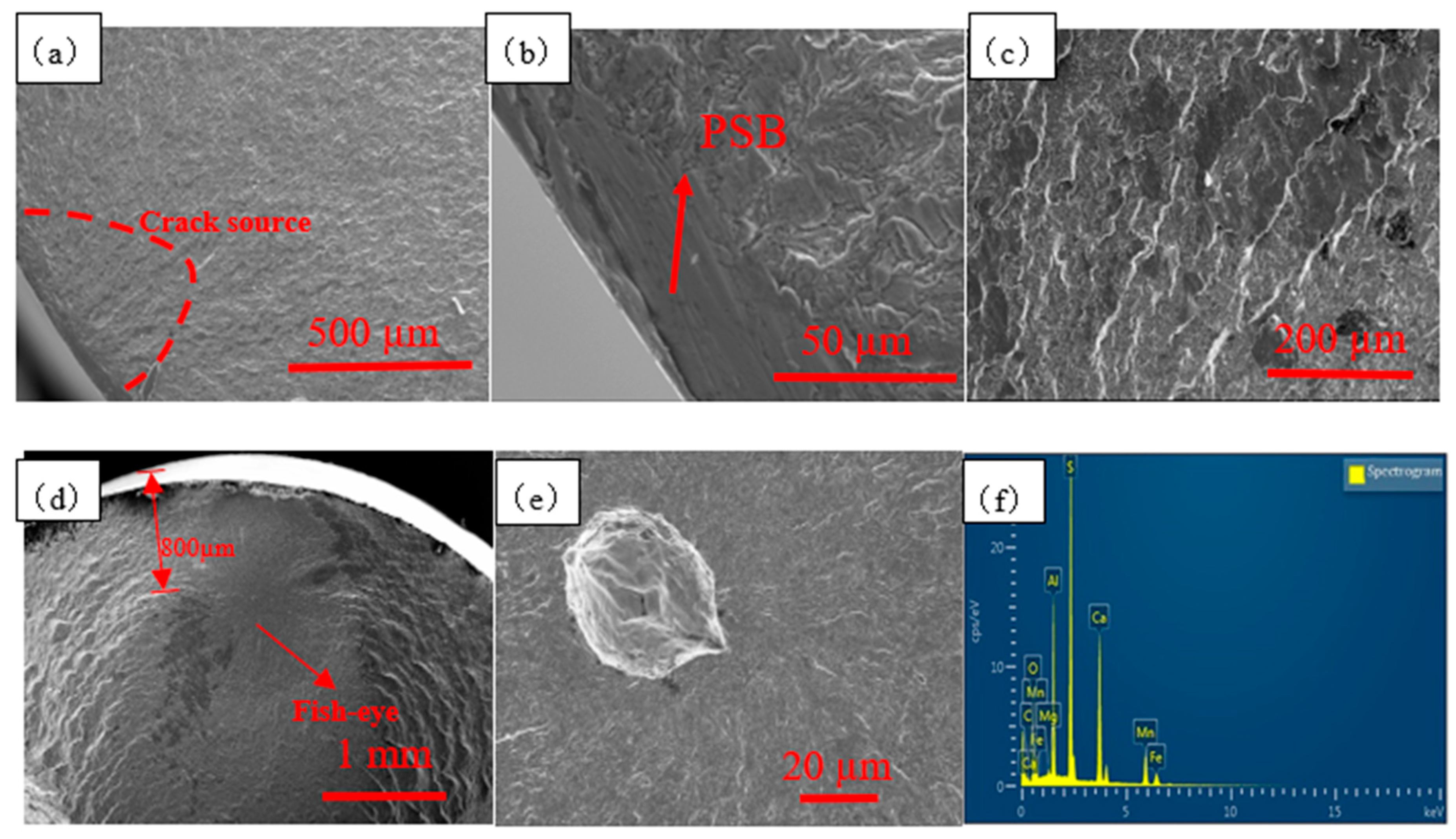
3.3. Fatigue Fracture
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Roughness on Fatigue Life
4.2. Residual Stress Impact on Fatigue Performance
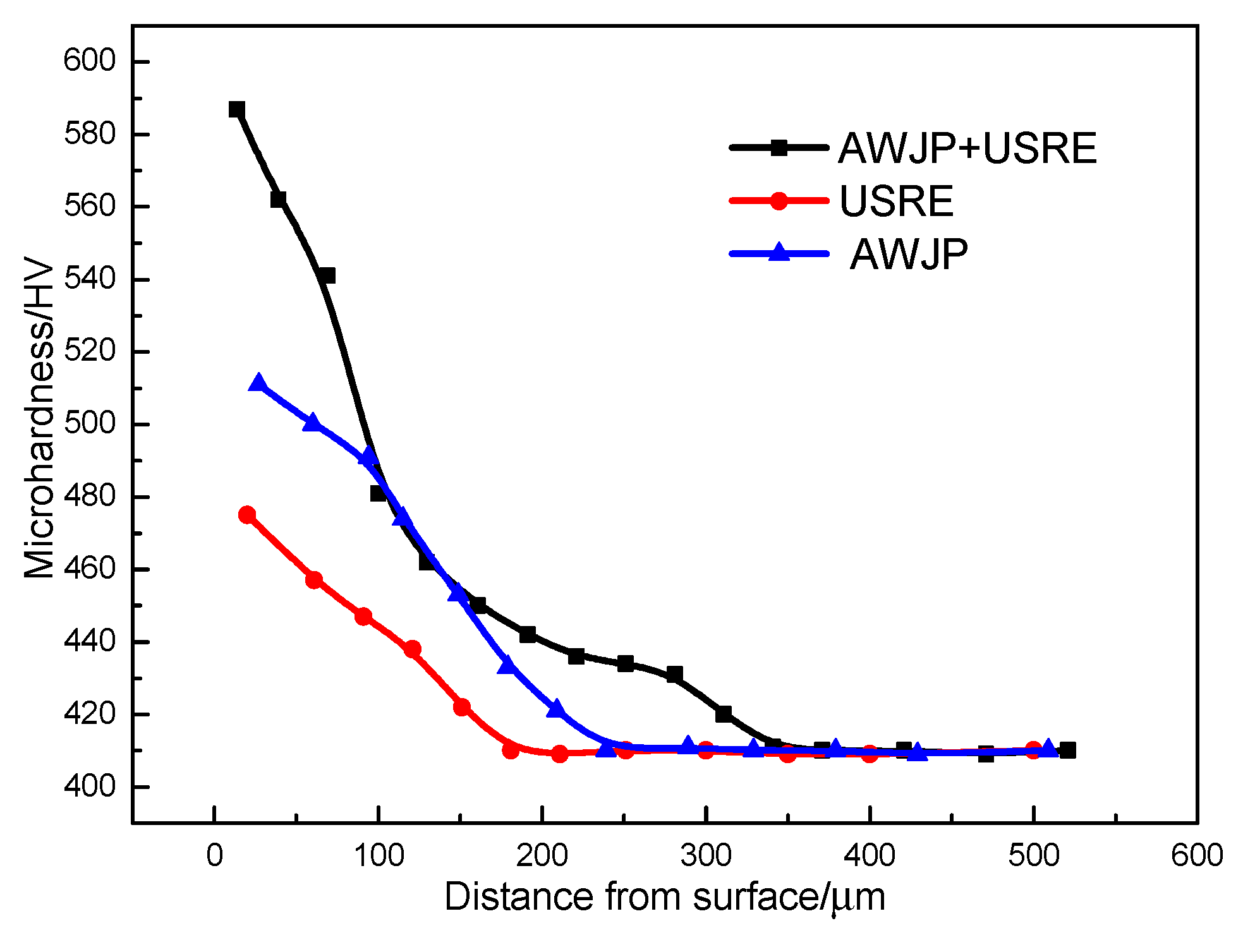
4.3. Influence of Deformation Layer Structure on Fatigue Performance
5. Conclusions
- In the surface state, the modified composite plastic deformation layer reaches 310 µm from the surface. The composite modification at a depth of 90 µm is comparable to a single modified layer at a depth of 220 µm; the material Ra is reduced from 1.57 µm to 0.06 µm through after AWJP. A crystalline layer appears 40 µm away from the surface. The particle size reached 70 nm.
- Composite modification can obtain a smooth gradient structure. the fatigue limit of the unmodified matrix is increased from 510 MPa to 595.9 MPa (an increase of 85.9 MPa), and the roughness, residual stress, and gradient are analysed herein. The effect of the structure on the fatigue properties of the material indicates that the gradient structure is the most important factor affecting the fatigue properties of the material. The surface and the fine grain on the surface can effectively prevent the initiation of fatigue crack in the fatigue process, and the large grain at the center can affect the propagation of fatigue crack in the fatigue process, so as to improve the fatigue performance of the material.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hensel, J.; Eslami, H.; Nitschke-Pagel, T.; Dilger, K. Fatigue strength enhancement of butt welds by means of shot peening and clean blasting. Metals 2019, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Shaw, L. Analysis of fatigue resistance improvements via surface severe plastic deformation. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Choi, N.S. Fatigue life analysis of shot-peened bearing steel. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, U.S.; Joshi, S.N.; Davim, J.P. Incorporation of material behavior in modeling of metal forming and machining processes: A review. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 655–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahmer, D.M.; Polvorosa, R.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Alonso-Pinillos, U.; Abate, G.; Riu, F. Alternatives for specimen manufacturing in tensile testing of steel plates. Exp. Tech. 2016, 40, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Hall, C.; Hooper, R.; Charrault, E.; Murphy, P.; Santos, V. Finite element analysis of surface integrity in deep ball-burnishing of a biodegradable AZ31B Mg alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Pereira, O.; González, H.; Urbikain, G.; Laye, J. Burnishing of FSW aluminum Al–Cu–Li components. Metals 2019, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierwa, A.; Markopoulos, A.P. Influence of ball-burnishing process on surface topography parameters and tribological properties of hardened steel. Machines 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzionk, S.; Scibiorski, B.; Przybylski, W. Surface texture analysis of hardened shafts after ceramic ball burnishing. Materials 2019, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, B.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Lu, M.; Zhang, J.; Liang, F. Effect of basketweave microstructure on very high cycle fatigue behavior of TC21 titanium alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.S.; Voorwald, H.J.C. An evaluation of shot peening residual stress and stress relaxation on the fatigue life of AISI 4340 steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, D.; Yao, C. Effect of turning and surface polishing treatments on surface integrity and fatigue performance of nickel-based alloy GH4169. Metals 2018, 8, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.W.; Smaga, M.; Beck, T. Surface morphology and its influence on cyclic deformation behavior of high-Mn TWIP steel. Metals 2018, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiani, E.; Zavatta, N. The Effect of laser peening without coating on the fatigue of a 6082-T6 aluminum alloy with a curved notch. Metals 2019, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieblich, M.; Barriuso, S.; Ibáñez, J.; Ruiz-de-Lara, L.; Díaz, M.; Ocaña, J.L.; Alberdi, A.; González-Carrasco, J.L. On the fatigue behavior of medical Ti6Al4V roughened by grit blasting and abrasiveless waterjet peening. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 63, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehnder, A.T.; Rosakis, A.J. Dynamic fracture initiation and propagation in 4340 steel under impact loading. Int. J. Fract. 1990, 43, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, J.; Liang, S.Y. Evaluation of an analytical model in the prediction of machining temperature of AISI 1045 steel and AISI 4340 steel. J. Manuf. Mater. Process 2018, 2, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Hu, H. Effect of shot peening on high cycle fatigue limit of FGH4097 P/M superalloys at room temperature. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.; Qing, G. Study of the Fatigue behavior and the mechanism of fatigue failure within ultra-high-cycle regimein 40 Cr steel and 50 axles steel (abstract of the Ph.D. dissertation). China Railway Sci. 2006, 27, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.H. Improved fatigue properties of ultrafine-grained copper under cyclic torsion loading. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5857–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppel, H.W. An overview: Fatigue behaviour of ultrafine-grained metals and alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Surface Characteristics and Fatigue Behavior of Gradient Nano-Structured Magnesium Alloy. Metals 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Lin, F. Fatigue behavior of a plain-woven glass fabric laminate under tension/torsion biaxial loading. J. Compos. Mater. 1995, 29, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Wang, Z.G. Dependence of intergranular fatigue cracking on the interactions of persistent slip bands with grain boundaries. Acta Mater. 2003, 29, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Swygenhoven, H.V.; Suresh, S. Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys. Acta Mater. 2003, 29, 5743–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, A.; Zeuner, A.T.; Zimmermann, M. Fatigue behavior of non-optimized laser-cut medical grade Ti-6Al-4V-ELI sheets and the effects of mechanical post-processing. Metals 2019, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A. Fatigue limit and crack growth in ultra-fine grain metals produced by severe plastic deformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W. Enhancing torsion fatigue behaviour of a martensitic stainless steel by generating gradient nanograined layer via surface mechanical grinding treatment. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P. Crack tip plasticity in plastically graded Ni–W electrodeposited nanocrystalline alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 41, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H. Revealing extraordinary intrinsic tensile plasticity in gradient nano-grained copper. Science 2011, 331, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y. Microstructures and dislocation configurations in nanostructured Cu processed by repetitive corrugation and straightening. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, A.; Terzano, M.; Brighenti, R.; Artoni, F.; Carpinteri, A. How Soft Polymers Cope with Cracks and Notches. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.E.; Plunkett, R. Stress concentration factors. Nav. Eng. J. 1955, 67, 697–708. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y. Influence of Shot Peening on Tension-Tension Fatigue Properties of TC18 Titanium Alloy. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 2004, 33, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Dalaei, K.; Karlsson, B. Influence of overloading on fatigue durability and stability of residual stresses in shot peened normalized steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7323–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M. Application of different fatigue strength criteria on shot peened notched parts. Part 2: Nominal and local stress approaches. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 289, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, I. Mechanical and thermal stability of mechanically induced near-surface nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 403, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalaei, K.; Karlsson, B.; Svensson, L.E. Stability of shot peening induced residual stresses and their influence on fatigue lifetime. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Element | C | Si | S | P | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.0019 | 0.0021 | 0.90 | 1.65 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.009 |
| Tensile Strength σb/MPa | Yield Strength σs/MPa | Elongation δ/% | Reduction of Area ψ/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1160 | 1098 | 18.7 | 54.6 |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Water flow pressure, MPa | 100 |
| Forward speed, mm/min | 10 |
| Speed, r/min | 30 |
| Target distance, mm | 10 |
| Nozzle angle | 90° |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Static pressure, N | 320 |
| Amplitude, um | 6 |
| Speed, r/min | 280 |
| Forward speed, mm/r | 0.08 |
| Rolling times | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, H.; Liang, Y. Study of the Surface Integrity and High Cycle Fatigue Performance of AISI 4340 Steel after Composite Surface Modification. Metals 2019, 9, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080856
Fu H, Liang Y. Study of the Surface Integrity and High Cycle Fatigue Performance of AISI 4340 Steel after Composite Surface Modification. Metals. 2019; 9(8):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080856
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Hai, and Yilong Liang. 2019. "Study of the Surface Integrity and High Cycle Fatigue Performance of AISI 4340 Steel after Composite Surface Modification" Metals 9, no. 8: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080856
APA StyleFu, H., & Liang, Y. (2019). Study of the Surface Integrity and High Cycle Fatigue Performance of AISI 4340 Steel after Composite Surface Modification. Metals, 9(8), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080856




