Cleaner Recycling of Spent Lead-Acid Battery Paste and Co-Treatment of Pyrite Cinder via a Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Method for Valuable Metal Recovery and Sulfur Conservation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Parameters
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
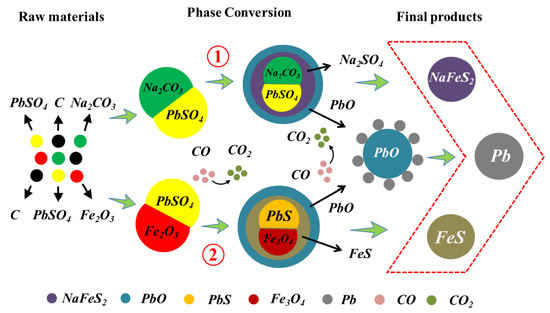
3.1. Phase Transformation Mechanisms
3.2. Batch Experiments of End of Life (EoL) Lead Paste
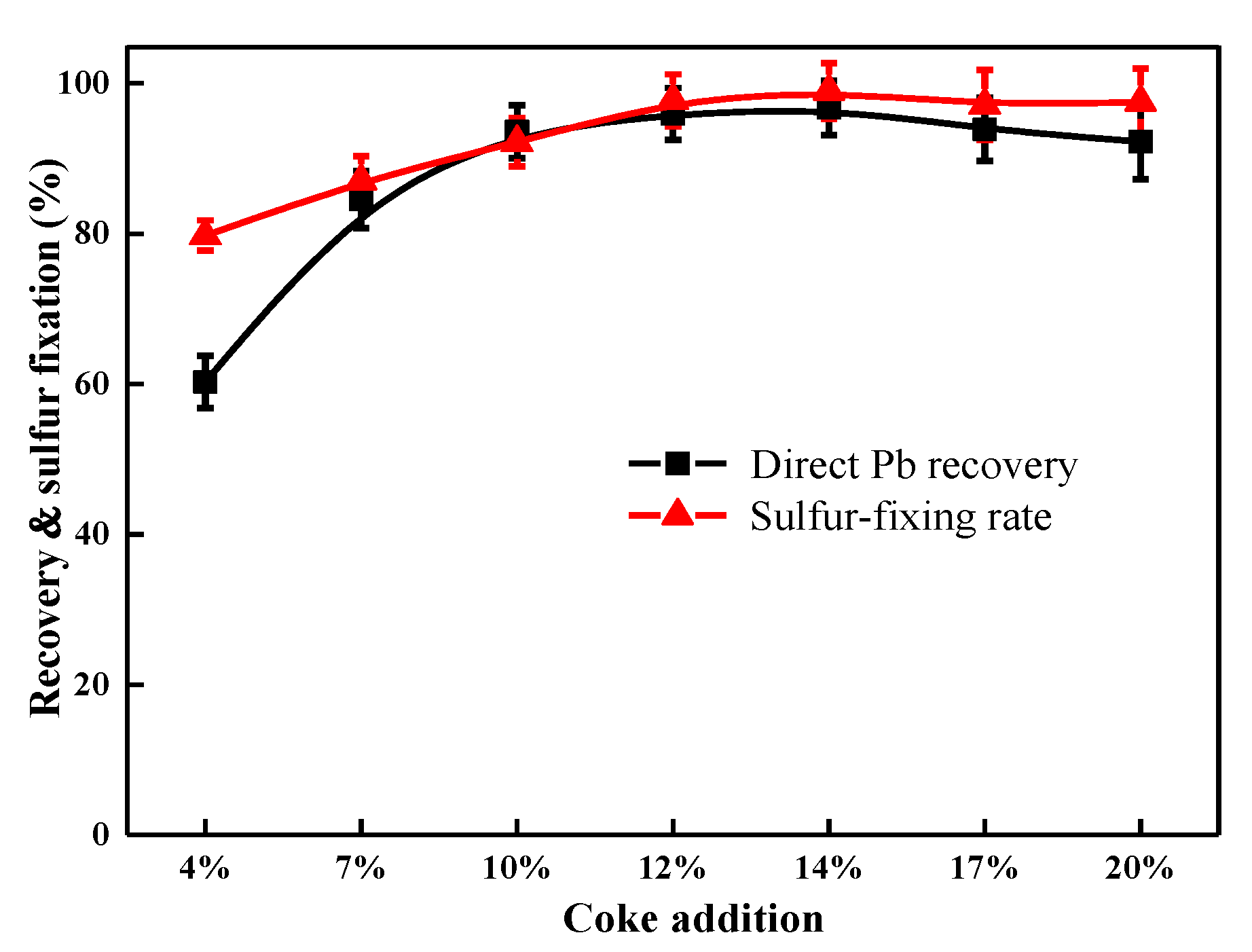
3.2.1. Influence of Coke Addition
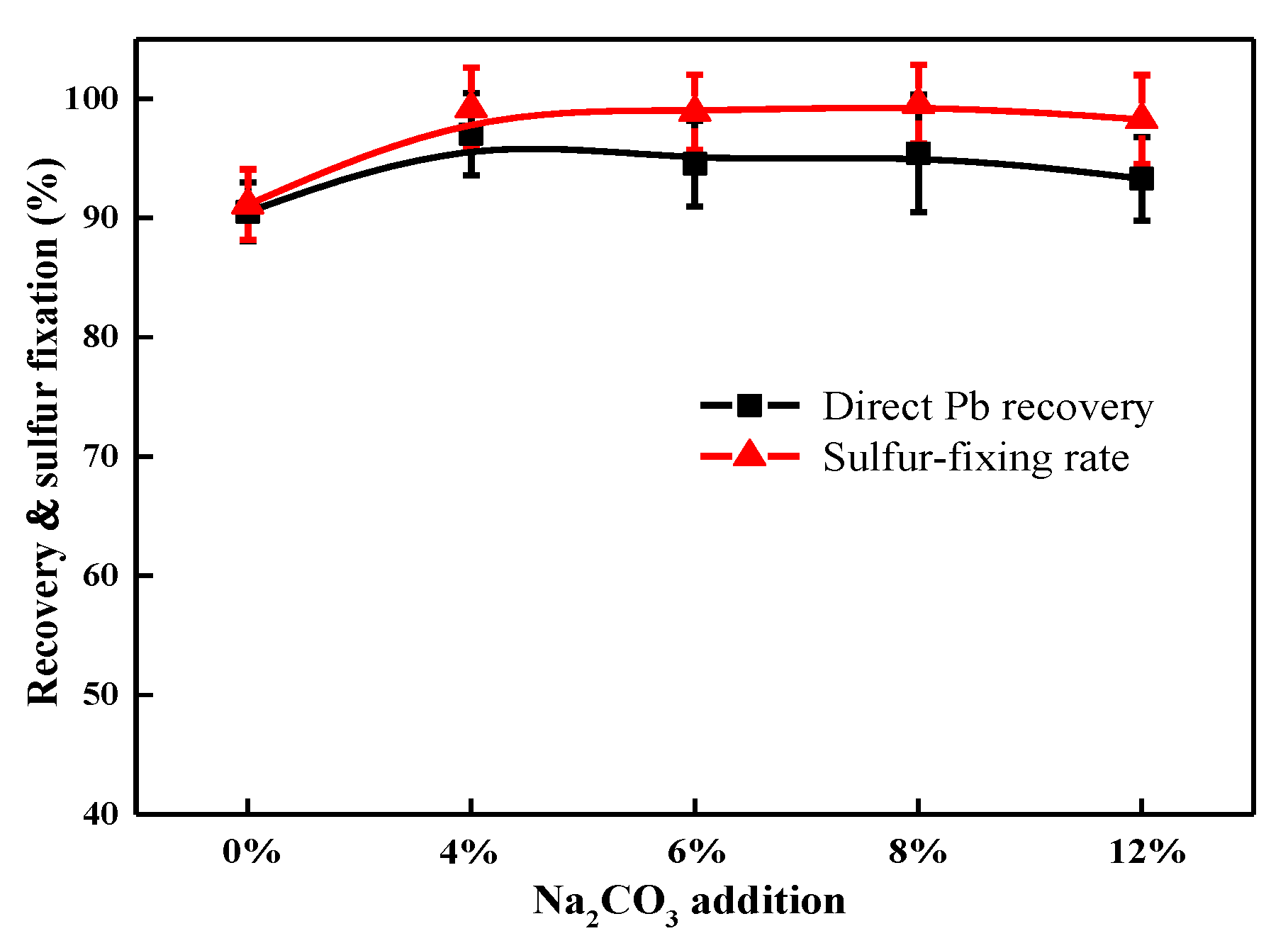
3.2.2. Influence of Na2CO3 Addition
3.2.3. Influence of Treatment Temperature
3.2.4. Influence of Treatment Time
3.3. Comprehensive Experiments and Characterization of Products
3.3.1. Comprehensive Experimental Results
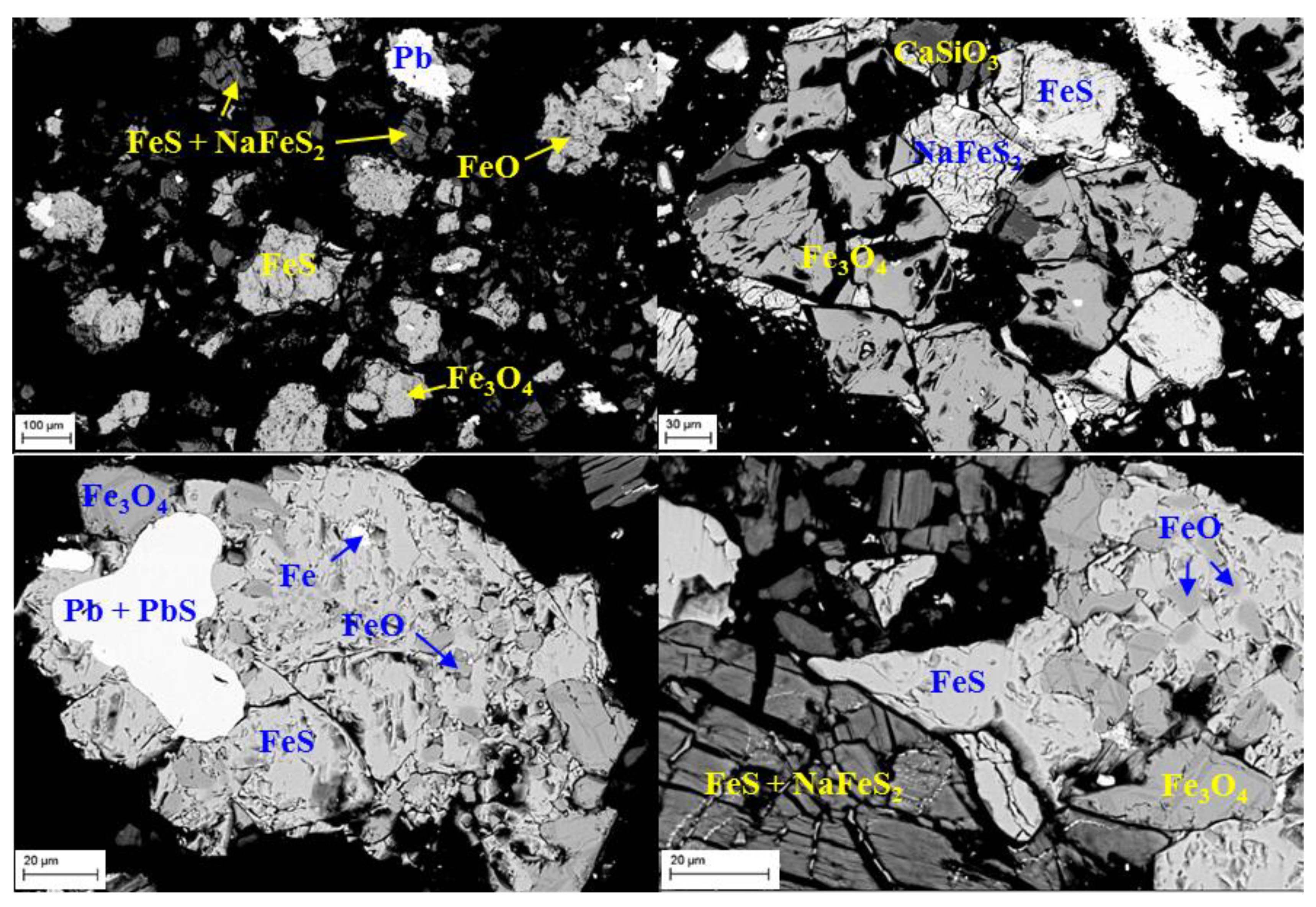
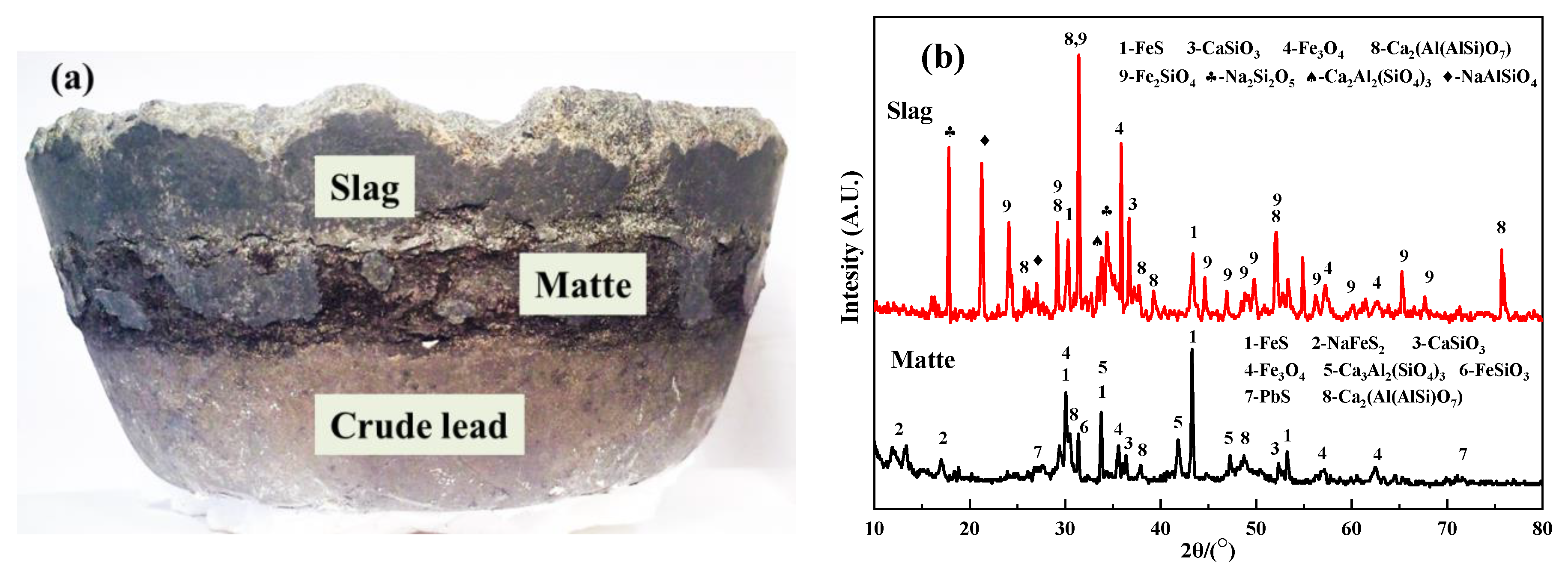
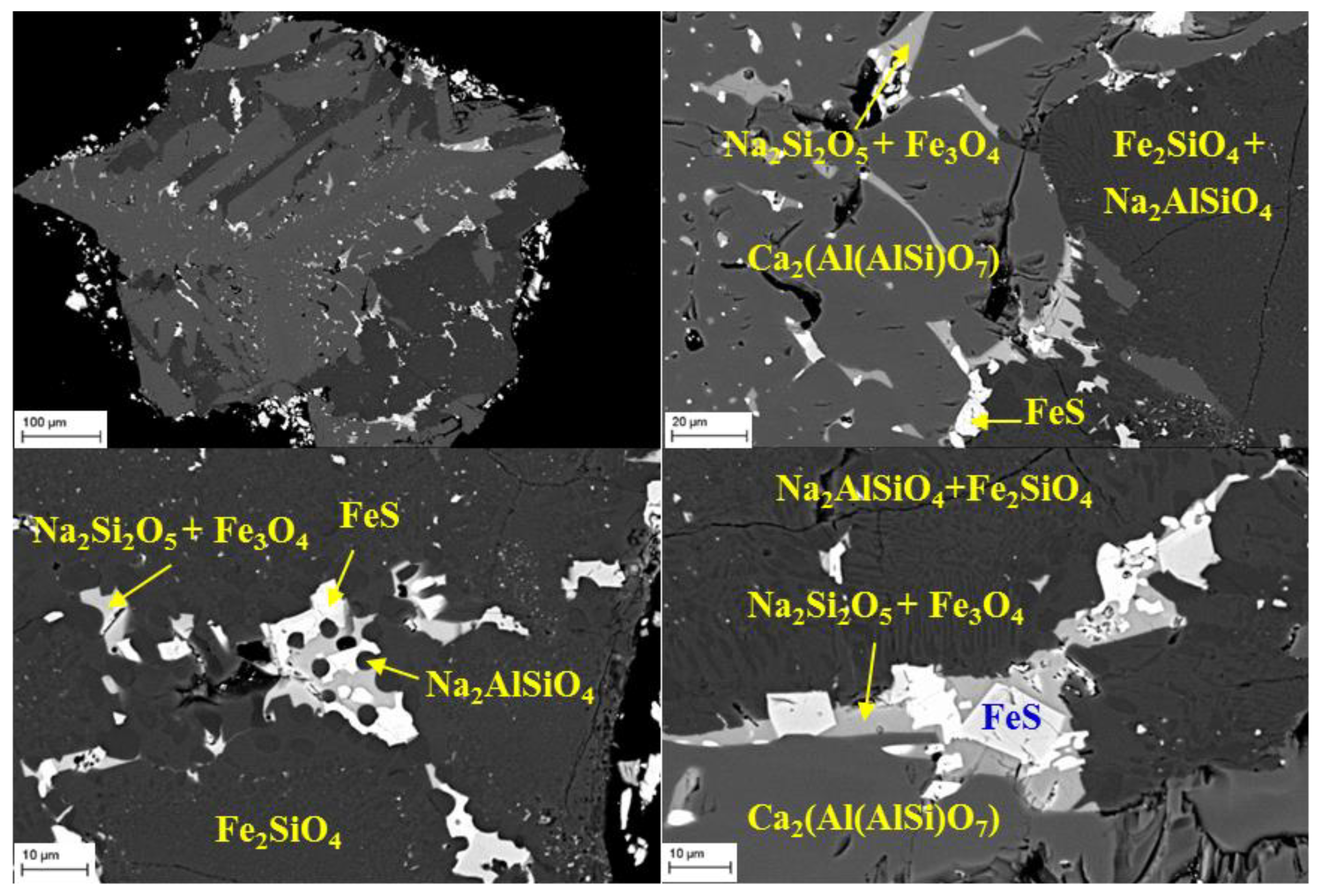
3.3.2. SEM-EDS Characterization of Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zuo, T. The lead-acid battery industry in China: outlook for production and recycling. Waste Manage. Res. 2015, 33, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; He, X.; Yang, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Kumar, R.V. Leaching of spent lead acid battery paste components by sodium citrate and acetic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q. The current status on the recycling of lead-acid batteries in China. Int. J. Electrochem Sci. 2013, 8, 6457–6466. [Google Scholar]
- Huggins, R.A. Lead-Acid Batteries; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 237–250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; Yang, S.; Klemettinen, L.; Rämä, M.; Wan, X.; Jokilaakso, A. A New Pyrometallurgical Recycling Technique for Lead Battery Paste without SO2 Generation—A Thermodynamic and Experimental Investigation. Extraction 2018 2018, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, L.; He, J.; Tang, M. One-Step Extraction of Lead from Spent Lead-Acid Battery Paste via Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Smelting: Thermodynamic Analysis. In 8th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Qiu, K. Recycling of waste lead storage battery by vacuum methods. Waste Manage. 2011, 31, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kuijp, T.J.; Huang, L.; Cherry, C.R. Health hazards of China’s lead-acid battery industry: A review of its market drivers, production processes, and health impacts. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Hou, P.; Liang, S.; Qu, S.; Xu, M.; Zuo, T. Environmental impact and economic assessment of secondary lead production: Comparison of main spent lead-acid battery recycling processes in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Cao, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Zheng, W.; Cao, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. Spent lead-acid battery recycling in China–A review and sustainable analyses on mass flow of lead. Waste Manage. 2017, 64, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qiu, K. Removing antimony from waste lead storage batteries alloy by vacuum displacement reaction technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 347, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qiu, K. Recovery of lead from lead paste in spent lead acid battery by hydrometallurgical desulfurization and vacuum thermal reduction. Waste Manage. 2015, 40, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreusch, M.A.; Ponte, M.J.J.S.; Ponte, H.A.; Kaminari, N.M.S.; Marino, C.E.B.; Mymrin, V. Technological improvements in automotive battery recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2007, 52, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassin, A.; Piantone, P.; Burnol, A.; Bodénan, F.; Chateau, L.; Lerouge, C.; Crouzet, C.; Guyonnet, D.; Bailly, L. Reactivity of waste generated during lead recycling: An integrated study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queneau, P.B.; Leiby, R.; Robinson, R. Recycling lead and zinc in the United States. World of Metallurgy-ERZMETALL 2015, 68, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.F.; Jiang, L.H.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, C.F.; Li, G.; Hwang, J.Y. Thermodynamics Analysis and Industrial Trials of Bottom-Blowing Smelting for Processing Lead Sulfate-Containing Materials. In 6th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Fan, E.; Xue, Q.; Bian, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Toward sustainable and systematic recycling of spent rechargeable batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7239–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Deep, A.; Szulejko, J.E.; Vellingiri, K.; Kumar, S.; Kwon, E.E.; Yun, S.T. Recovery of nanomaterials from battery and electronic wastes: A new paradigm of environmental waste management. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2018, 82, 3694–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Hou, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. An Emission-Free Vacuum Chlorinating Process for Simultaneous Sulfur Fixation and Lead Recovery from Spent Lead-Acid Batteries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2235–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Guo, X.; Marinova, D.; Fan, J. Industrial SO2 pollution and agricultural losses in China: evidence from heavy air polluters. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, C.; Adapala, S.; Meikap, B. Removal of hazardous gaseous pollutants from industrial flue gases by a novel multi-stage fluidized bed desulfurizer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Liang, S.; Hu, J. A critical review on secondary lead recycling technology and its prospect. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2016, 61, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zheng, Y. Utilization of low-grade pyrite cinder for synthesis of microwave heating ceramics and their microwave deicing performance in dense-graded asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, I.; Deveci, H.; Yazıcı, E.; Türk, T.; Süngün, Y. Potential use of pyrite cinders as raw material in cement production: Results of industrial scale trial operations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Tang, C.; Tang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; He, J. Reductive smelting of spent lead-acid battery colloid sludge in molten salt of sodium at low temperature. Chin. Nonferr. Metall. 2014, 43, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Tang, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. One-step extraction of antimony from low-grade stibnite in Sodium Carbonate–Sodium Chloride binary molten salt. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 93, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B. CMPR-a powder diffraction toolkit. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2005, 38, 1040–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roine, A. Outotec HSC Chemistry. Available online: www.hsc-chemistry.com (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Taskinen, P.; He, J.; Liao, F.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jokilaakso, A. Novel recycling process for lead-acid battery paste without SO2 generation-Reaction mechanism and industrial pilot campaign. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 217, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Taskinen, P.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jokilaakso, A. Spent Lead-Acid Battery Recycling via Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Smelting and Its Reaction Mechanism in the PbSO4-Fe3O4-Na2CO3-C System. JOM 2019, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Materials | Pb | S | Fe | SiO2 | CaO | Na | Mg | Al | Ba | Sb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead paste | 72.90 | 5.77 | 0.02 | 5.48 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.09 |
| PbSO4 | PbO | PbO2 | Pb | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 54.68 | 8.49 | 22.05 | 8.53 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Pyrite cinder | Pb | S | Fe | SiO2 | CaO | Na | MgO | Al2O3 | Cu | Ag* |
| 0.02 | 1.31 | 58.23 | 9.68 | 1.02 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 2.08 | 0.05 | 324 | |
| Coke | Industrial analysis (%) | Chemical composition of the ash (%) | ||||||||
| Fixed Carbon | Volatile | Ash | Fetotal | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | |||
| 84.05 | 1.13 | 13.94 | 15.96 | 30.96 | 18.18 | 4.05 | 1.45 | |||
| No. | Product | Chemical Compositions (wt.%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Fe | S | Na | Sb | Ag * | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | ||
| 1 | Crude lead | 98.87 | 0.26 | 0.04 | - | 0.075 | 136 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 98.02 | 0.38 | 0.07 | - | 0.089 | 115 | - | - | - | |
| Average | 98.45 | 0.32 | 0.06 | - | 0.082 | 126 | - | - | - | |
| 1 | Ferrous matte | 2.37 | 53.25 | 22.54 | 9.56 | - | - | - | - | |
| 2 | 2.73 | 52.66 | 24.39 | 9.68 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Average | 2.55 | 53.09 | 23.47 | 9.62 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 1 | Slag | 0.39 | 22.96 | 3.24 | 9.79 | - | 31.22 | 18.86 | 6.83 | |
| 2 | 0.59 | 24.31 | 3.19 | 9.88 | - | 30.72 | 18.50 | 6.14 | ||
| Average | 0.49 | 23.64 | 3.22 | 9.84 | - | 30.97 | 18.68 | 6.49 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Taskinen, P.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; Jokilaakso, A. Cleaner Recycling of Spent Lead-Acid Battery Paste and Co-Treatment of Pyrite Cinder via a Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Method for Valuable Metal Recovery and Sulfur Conservation. Metals 2019, 9, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080911
Li Y, Yang S, Taskinen P, Chen Y, Tang C, Jokilaakso A. Cleaner Recycling of Spent Lead-Acid Battery Paste and Co-Treatment of Pyrite Cinder via a Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Method for Valuable Metal Recovery and Sulfur Conservation. Metals. 2019; 9(8):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080911
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yun, Shenghai Yang, Pekka Taskinen, Yongming Chen, Chaobo Tang, and Ari Jokilaakso. 2019. "Cleaner Recycling of Spent Lead-Acid Battery Paste and Co-Treatment of Pyrite Cinder via a Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Method for Valuable Metal Recovery and Sulfur Conservation" Metals 9, no. 8: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080911
APA StyleLi, Y., Yang, S., Taskinen, P., Chen, Y., Tang, C., & Jokilaakso, A. (2019). Cleaner Recycling of Spent Lead-Acid Battery Paste and Co-Treatment of Pyrite Cinder via a Reductive Sulfur-Fixing Method for Valuable Metal Recovery and Sulfur Conservation. Metals, 9(8), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9080911