On the Grain Growth Kinetics of a Low Density Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Low Density Steel
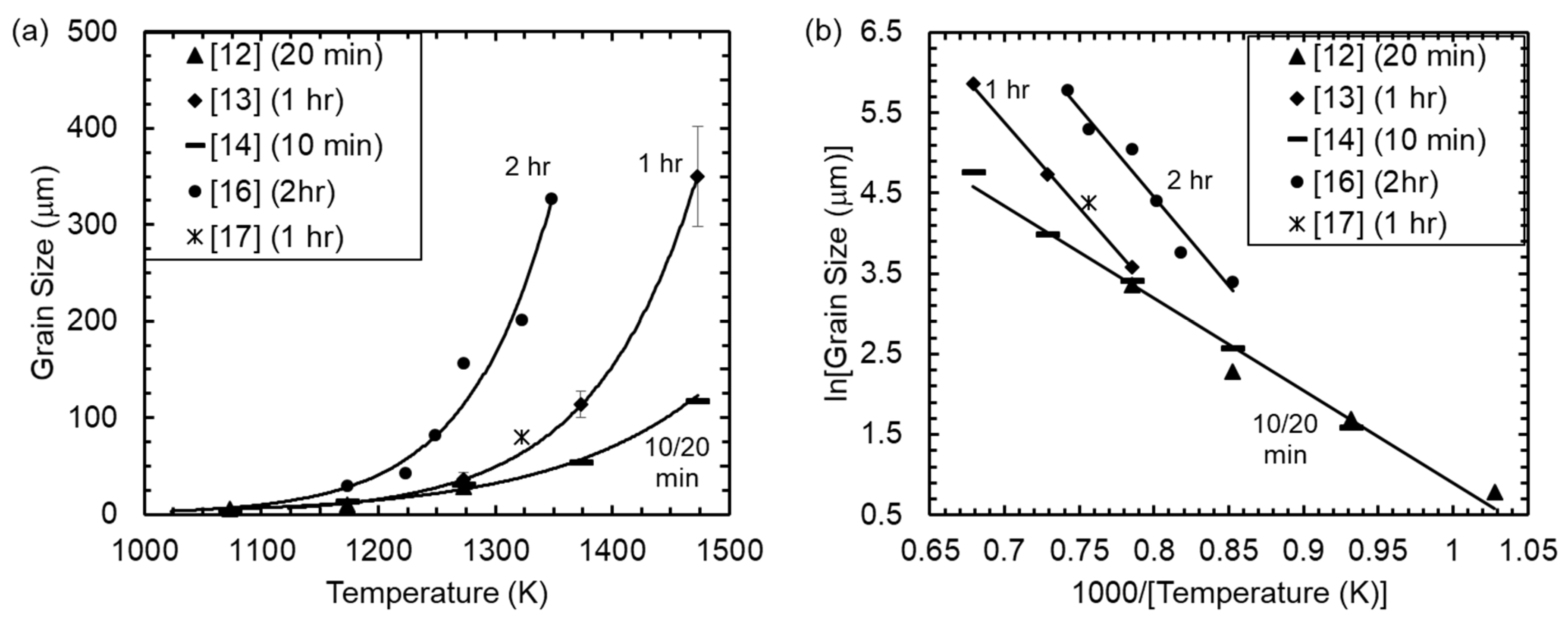
1.2. Grain Size and Grain Growth
1.3. Mechanical Behavior
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Grain Growth
4.2. Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Temperature | 0.5 h | 1 h | 2 h | 4 h | 15 h | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | K | D μm | 1/√D | Hardness HBW | D μm | 1/√D | Hardness HBW | D μm | 1/√D | Hardness HBW | D μm | 1/√D | Hardness HBW | D μm | 1/√D | Hardness HBW |
| 900 | 1173 | 32 ± 4 | 0.177 | 252 ± 3 | 29 ± 2 | 0.186 | 260 ± 3 | 30 ± 2 | 0.183 | 252 ± 4 | 34 ± 2 | 0.173 | 248 ± 3 | 35 ± 1 | 0.170 | 251 ± 4 |
| 950 | 1223 | 34 ± 2 | 0.171 | 251 ± 4 | 31 ± 4 | 0.174 | 244 ± 4 | 57 ± 8 | 0.132 | 236 ± 8 | 51 ± 3 | 0.140 | 240 ± 2 | 81 ± 6 | 0.112 | 244 ± 4 |
| 975 | 1248 | 47 ± 5 | 0.145 | 249 ± 2 | 45 ± 6 | 0.148 | 244 ± 2 | 82 ± 3 | 0.110 | 225 ± 4 | 75 ± 5 | 0.116 | 217 ± 5 | 68 ± 2 | 0.121 | 232 ± 5 |
| 1000 | 1273 | 74 ± 5 | 0.116 | 227 ± 1 | 86 ± 5 | 0.108 | 226 ± 3 | 156 ± 6 | 0.080 | 218 ± 8 | 101 ± 5 | 0.100 | 217 ± 3 | 73 ± 5 | 0.117 | 227 ± 4 |
| 1050 | 1323 | 116 ± 8 | 0.092 | 217 ± 5 | 160 ± 6 | 0.079 | 208 ± 3 | 201 ± 8 | 0.071 | 203 ± 5 | 250 ± 2 | 0.063 | 200 ± 4 | 161 ± 8 | 0.079 | 210 ± 5 |
| 1075 | 1348 | 240 ± 7 | 0.064 | 205 ± 4 | 252 ± 6 | 0.063 | 200 ± 2 | 327 ± 4 | 0.055 | 201 ± 7 | 370 ± 4 | 0.052 | 192 ± 4 | 475 ± 6 | 0.046 | 195 ± 5 |
References
- Frommeyer, G.; Brüx, U. Microstructures and mechanical properties of high-strength Fe–Mn–Al–C high-weight TRI-PLEX steels. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.; Alain, S.; Farral, M.; Tsuji, N.; Tanaka, Y. Austenitic steel for automotive application. Revue de Métallurgie 2006, 103, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, L.; Van Aken, D.C. High Manganese and Aluminum Steels for the Military and Transportation Industry. JOM 2014, 66, 1770–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, R.; Burnham, T.H. Special Steels, 2nd ed.; The Pitman Press: New York, NY, USA, 1933; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Sevillano, J.G. An alternative model for the strain hardening of FCC alloys that twin, validated for twinning-induced plasticity steel. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Zhang, X.F.; Qin, R.S. κ-carbide hardening in a low density high-Al high-Mn multiphase steel. Mater. Lett. 2015, 138, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, I.S.; Acselrad, O.; Shalkevich, A.; Chumakova, L.D.; Pereira, L.C. Heat Treatment and Thermal Stability of FeMnAlC alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 136, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazancova, E.; Ruziak, I.; Schindler, I. Influence of rolling condition and aging process on mechanical properties of high manganese steels. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2012, 12, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.M.; Qing, J.; Van Aken, D.C. Chemistry and properties of Medium-Mn Two-Stage TRIP steels. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2019, 49, 4615–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.M.; Van Aken, D.C. Nanocrystalline Advanced High Strength Steel Produced by Cold Rolling and Annealing. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Torabinejad, V.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Moemeni, S.; Imandoust, A. An investigation to the microstructural evolution of Fe-29Mn-5Al dual-phase twinning induced plasticity steel through annealing. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 5015–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Di, H.; Zhu, F. Influence of annealing temperature on mechanical properties and microstructure of a high manganese austenitic steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 217, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.D.; Huang, S.W.; Park, K.-T. Origin of Extended Tensile Ductility of a Fe-28Mn-10Al-1C Steel. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2009, 40A, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Lee, S.Y.; Han, J.; Hwang, B. Deformation behavior and tensile properties of an austenitic Fe-24Mn-4Cr-0.5C high manganese steel: Effect of grain size. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 742, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.M.; Van Aken, D.C. Dynamic Strain Aging Phenomena and Tensile Response of Medium-Mn TRIP Steel. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2018, 49, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, D.M.; Limmer, K.R. Effect of Solution Treatment on Grain Size and Toughness of Lightweight Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel. In Proceedings of the AIST2019, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, C.; Han, H.N.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Microstructure Evolution and Age-Hardening Behavior of a Micro-alloyed Austenitic Fe-30Mn-9Al-0.9C Light-Weight Steel. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2017, 48A, 4500–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.D.; Hwang, S.W.; Park, K.T. Factors influencing the tensile behavior of a Fe-28Mn-9Al-0.8C Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 508, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, M.; Langelier, B.; Purdy, G.R.; Zurob, H.S. Effect of Mn and C on Grain Growth in Mn Steels. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2019, 50A, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, N.I.; Park, M.S.; Van Aken, D.C.; Medvedeva, J.E. First Principles study of Mn, Al, and C distribution and their effect on stacking fault energy in fcc Fe. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 582, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarik, S.T.; Van Aken, D.C. Thermodynamic Driving Force of the γ → ε Transformation and Resulting Ms temperature in High-Mn Steels. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.M.; Baker, D.S.; Van Aken, D.C. On the Prediction of α-martensite Temperatures in Medium-Mn Steels. Metall. Meter. Trans. A 2017, 48, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, N.I.; Van Aken, D.C.; Medvedeva, J.E. Magnetism in bcc and fcc Fe with carbon and manganese. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2010, 22, 316002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E112-13 Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ASTM E18-17e1 Standard Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E 8/E 8M-08, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Hillert, M. On the Theory of Normal Gain Growth. Acta Met. 1965, 13, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, J.E.; Turnbull, D. Recrystallization and Grain Growth. Prog. Met. Phys. 1952, 3, 220–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, B.A.; Jones, A.R.; Ralph, B. Recrystallization of microduplex steels. Met. Sci. 1979, 13, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, B. Grain Boundaries in Engineering Materials. In Grain Boundary and Structure Kinetics, 1st ed.; ASM Intl.: Metal’s Park, OH, USA, 1979; pp. 181–208. [Google Scholar]
- Lücke, K.; Detert, K.A. Quantitative Theory of Grain-Boundary Motion and recrystallization in Metals in the presence of impurities. Acta Metall. 1957, 5, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, P.; Vandermeer, R.A. Mechanism of Boundary Migration in Recrystallization. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1962, 224, 917–928. [Google Scholar]
- Dastur, Y.N.; Leslie, W.C. Mechanism of Work Hardening in Hadfield manganese Steel. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khzouz, E. Grain Growth Kinetics in Steel, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Major Qualifying Project. Available online: https://web.wpi.edu/Pubs/E-project/Available/E-project-042211-104204/unrestricted/MQP_-_Grain_Growth_Kinetics_in_Steels.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-K. Prediction of austenite grain growth during austenitization of low alloy steels. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, B.P.; Tangri, K. Grain Growth behaviour of type 316L stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 149, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnock, W.; Nutting, J. The Effect of Carbon and Nickel upon the Stacking-Fault Energy of Iron. Met. Sci. J. 1967, 1, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraiuolo, A.; Smithm, A.; Sevillano, J.G.; De las Cuevas, F.; Pratolongo, G.; Gouveia, H.; Mendes, M.; Karjalainen, P. Metallurgical design of high strength austenitic Fe-C-Mn steels with excellent formability. Metal. Des. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Annealing Temperature | R2 Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 1173 K (900 °C) | 0.194 × 102 | 0.588 |
| 1223 K (950 °C) | 0.350 × 103 | 0.898 |
| 1248 K (975 °C) | 1.95 × 103 | 0.975 |
| 1273 K (1000 °C) | 5.63 × 103 | 0.957 |
| 1323 K (1050 °C) | 8.01 × 103 | 0.973 |
| 1348 K (1075 °C) | 10.9 × 103 | 0.922 |
| Condition | Hardness (HBW) | Grain Size (μm) | Modulus (GPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Total Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1173 K | 245 ± 7 | 30 ± 2 | 155 ± 3 | 555 ± 7 | 957 ± 7 | 63 ± 1 |
| 1223 K | 236 ± 9 | 57 ± 8 | 154 ± 3 | 505 ± 1 | 919 ± 4 | 72 ± 2 |
| 1273 K | 224 ± 3 | 156 ± 6 | 152 ± 5 | 440 ± 2 | 851 ± 13 | 83 ± 4 |
| 1323 K | 201 ± 2 | 201 ± 8 | 155 ± 6 | 410 ± 6 | 811 ± 4 | 86 ± 7 |
| Alloy | Element in wt.% | Q (kJ/mol) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Mn | Mo | Ni | Al | Si | ||
| 1045 [34] | 0.48 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.08 | - | 0.215 | 253 |
| 4140 [34] | 0.38 | 1.03 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 0.16 | - | 0.23 | 175 |
| 4340 [34] | 0.42 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.23 | 1.07 | - | 0.24 | 213 |
| 8620 [34] | 0.21 | 0.56 | 0.81 | 0.15 | 0.45 | - | 0.24 | 288 |
| 9310 [34] | 0.12 | 1.3 | 0.61 | 0.14 | 3.49 | - | 0.24 | 273 |
| 52100 [34] | 0.98 | 1.57 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.10 | - | 0.2 | 353 |
| 316L [36] | 0.03 | 17.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 12.0 | - | 0.75 | 317 |
| This Study | 1.00 | 0.12 | 30.8 | 0.5 | 0.10 | 9.2 | 0.7 | 467 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Field, D.M.; Limmer, K.R.; Hornbuckle, B.C. On the Grain Growth Kinetics of a Low Density Steel. Metals 2019, 9, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090997
Field DM, Limmer KR, Hornbuckle BC. On the Grain Growth Kinetics of a Low Density Steel. Metals. 2019; 9(9):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090997
Chicago/Turabian StyleField, Daniel M., Krista R. Limmer, and Billy C. Hornbuckle. 2019. "On the Grain Growth Kinetics of a Low Density Steel" Metals 9, no. 9: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090997
APA StyleField, D. M., Limmer, K. R., & Hornbuckle, B. C. (2019). On the Grain Growth Kinetics of a Low Density Steel. Metals, 9(9), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090997





