1. Introduction
Owing to its uniqueness, characterized by the complex geological and morphological surface and subsurface features [
1], karst is an extremely challenging environment from a geotechnical engineering point of view. Many phenomena such as pervasive fracturing, extensive weathering, discontinuities, sinkholes, caverns, etc., add to the uncertainties commonly encountered when dealing with rock mass and these could eventually lead to the severe ground instability problems [
2]. Parise et al. [
3] give an extensive overview of the engineering problems in karst, with the conclusion that the design of engineering projects in karst environments requires specific approaches aimed at minimizing the detrimental effects of hazardous processes and environmental problems. Weary 2015 [
4] notes that, based on 15 years of karst related damage data, at least 300 million USD is annually spent on sinkhole collapse and subsidence issues in the United States alone. Considering that approximately 10% of the world’s surface [
5] is covered by karstic rock masses, the necessity for appropriate characterization techniques is strongly emphasized in order to mitigate karst-related issues and to preserve this extremely fragile environment [
6].
The traditional in situ geotechnical investigations of rock mass rely dominantly on destructive borehole drilling. If properly conducted, investigation boreholes can yield relatively unambiguous and credible evaluation of parameters necessary for the geotechnical design, but also require significant financial and time resources. Additionally, as the boreholes are usually drilled vertically, subvertical discontinuities parallel to the borehole axis often remain undetected, so there is a clear concern regarding uncertainty of a geotechnical model that rests solely on discrete and vertical investigation boreholes. Geophysical techniques, on the other hand, tend to give average rock mass properties on a large scale in a nondestructive manner, and as such they have a remarkably advantageous information-to-cost ratio [
7]. By allowing the geotechnical engineer to infer the large-scale properties between locations of drilling, geophysics can be considered as an optimal first-pass investigation technique for optimization of the drilling campaign. Because of the rapid technological development and simplifications of terrain procedures and interpretation, the application of geophysical surveys has intensified during recent decades, and today they are a non-negotiable part of rock mass investigation works. However, the obtained data are mostly ambiguous and will not imply a specific rock mass phenomenon. Because of the highly variable and unpredictable target characteristics, selection of the best-suited geophysical methods for karst investigation is usually not straightforward. Chalikakis et al. 2011 [
8] gave an extensive overview of the possibilities of using various geophysical techniques for karst exploration, including gravity, seismic, electrical, and electromagnetic techniques. Their application in karst is aimed at determining the limits and extent of a karst system [
9,
10], to identify near-surface highly fractured karst zones [
11,
12], to map the cavities and caverns [
13,
14], subsurface foundering [
15], sinkholes [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20], or discontinuities [
21], to map variable depth to bedrock [
22], etc.
This paper focuses on the potential of seismic surveys, through demonstration of several examples which highlight applicability and usefulness of seismic techniques for geotechnical engineering purposes. These examples contribute both to the advanced geophysical mapping of near-surface features, as well as to the credible derivation of rock mass parameters necessary for geotechnical design and quality control verifications. The work presented in the paper results from many years’ experience of utilizing seismic techniques for karst stratigraphic profiling and determination of rock mass properties, gained during construction and rehabilitation works of many geotechnical structures in Croatia, where more than 50% of the landmass is karst [
23].
2. Surface Geophysical Seismic Techniques
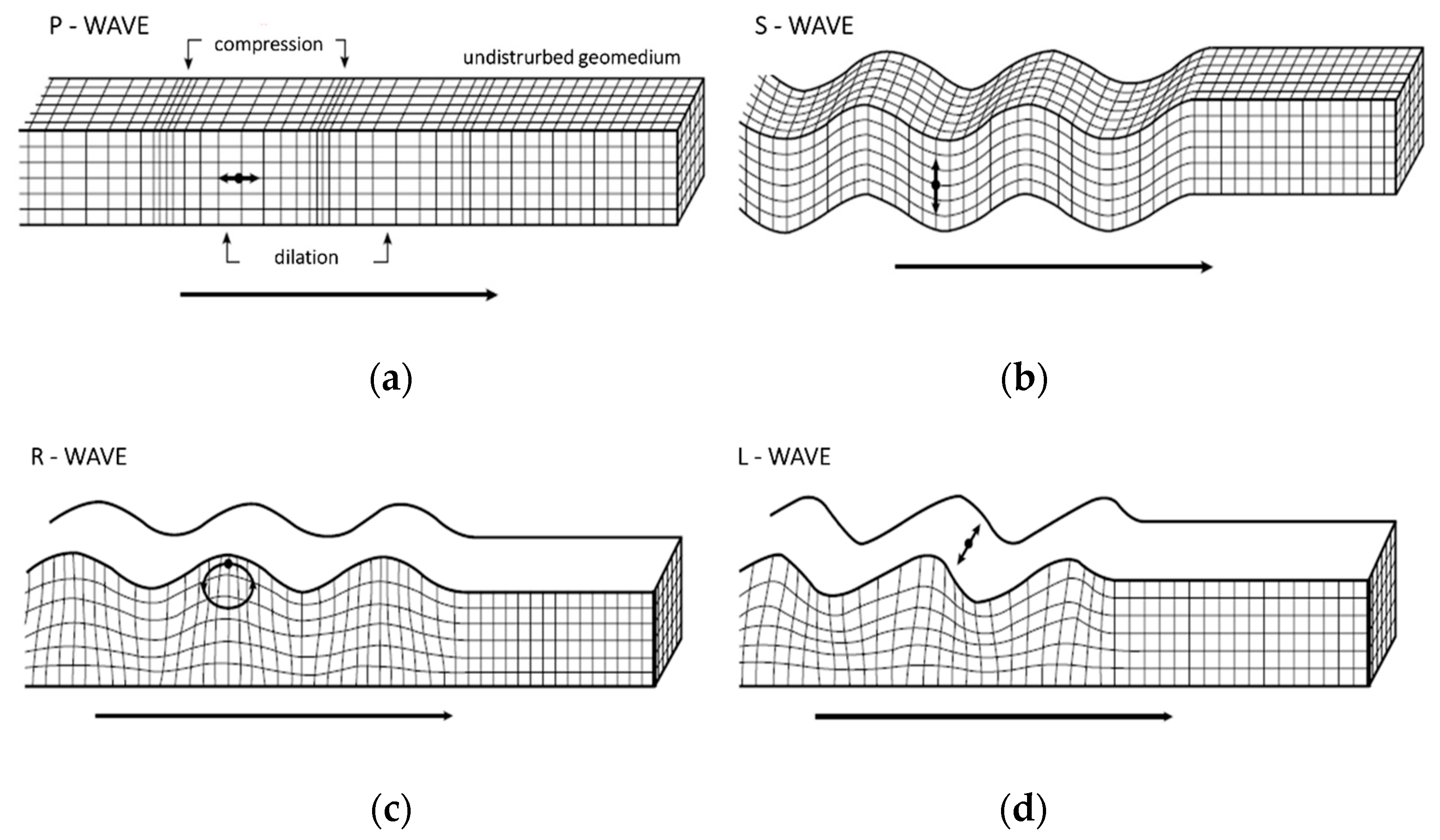
The seismic surveys are most commonly conducted from the terrain surface, emphasizing the nondestructive aspect of these investigations. The difference between the seismic techniques is reflected in the type of waves which are acquired and analyzed. As
Figure 1 shows, artificially generated seismic waves propagate from the surface through the rock mass as primary (P-), secondary (S-) and surface waves (Rayleigh, R-, and Love, L-, waves). Primary (longitudinal) waves oscillate along the direction of wave propagation, while secondary (shear) waves oscillate perpendicular to the propagation direction. Rayleigh waves have elliptical oscillations in the plane perpendicular to the surface during propagation, while Love waves, being the slowest ones, oscillate in the horizontal plane perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
2.1. P-wave Based Techniques
Techniques which analyze P-waves are most commonly used for engineering purposes and these include seismic refraction and seismic reflection techniques. Both refraction and reflection techniques yield a longitudinal velocity profile along the subsurface depth, which represents the physical-statistical structure of an image of longitudinal wave velocities in rock mass. The wave propagation velocities depend on the stiffness properties of the material through which they pass, after being generated by an impulse or controlled vibration at the karst terrain surface.
Refraction technique analyses primary waves that return to the surface after refraction at the boundaries of layers exhibiting different velocities, by utilizing a simple Snell’s optics law. Several methods were developed to interpret the measurement results with the most commonly used the generalized reciprocal method (GRM) [
25], the delta-t-V method [
26], or diving wave tomography [
27]. Refraction techniques can provide insight into the near-surface karst heterogeneities, but an issue may arise if a near-surface fast layer hides the subsurface phenomena. Seismic reflection measures the propagation times of the waves reflected at the layer boundaries. The technique is particularly suitable for visualization of the structure of the subsurface at greater depths, i.e., the slopes of boundary planes, as well as for the identification of fault zones. The aim of the measurement is to obtain the reflection from the same point in the subsurface as many times as possible, in order to amplify the reflected signal and attenuate the noise by summing the waveforms. Static and dynamic correction must be performed before summing the waveforms. Several methods are used for interpretation, including the optimum offset method [
28], common depth point [
29], and high resolution seismic (HRS) method [
30]. As Chalikakis et al. 2011 [
8] note, structural information could be extracted from reflections in seismic data since these help to determine vertical and subvertical boundaries such as faults, while horizontal limits can be expected if there is a velocity contrast at the top or the bottom of the karst medium. In karstic terrains, the main issue arises due to uneven reflectors yielding weak wave reflections.
2.2. S-wave Based Techniques
The S-waves techniques used for engineering purposes are spectral analysis of surface waves (SASW) and its enhanced version of multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW). The investigation procedure includes positioning of geophones at predefined intervals and measuring of wave velocities arrival times, generated by a vertical mechanical impulse on the terrain surface. S-wave base techniques rely on the dispersive characteristics of Rayleigh’s R-waves and on the law that R-waves of different wavelengths or frequencies propagate to different depths. In the interpretation phase a Fourier analysis is carried out, whereby the signal is transformed from the time into the frequency domain [
31]. The propagation velocities for each wavelength, also called the phase velocities, primarily depend on the S-wave velocities, and very little on the P-wave velocities and the Poisson’s ratio (
ν). This means that the velocity of the surface R-wave is a good indicator of the velocity of the S-wave. It is normally assumed that the phase velocity is 92% of the speed of the S-waves [
32] and that this ratio varies in small ranges between 88% and 95% for the whole spectrum of the Poisson’s ratio 0–0.5 [
33].
The SASW technique uses a wave generator and only two geophones to create a 1D profile of S-wave velocities with depth, while the MASW equipment encompasses a generator and a series of geophones, yielding a 2D profile of S-wave velocities, along with more rapid data acquisition. SASW and MASW methods rely on the frequency spectrum of the energy generator, where application of a hammer as generator usually results in the lack of certain frequencies from the source spectrum, and thus with gaps in the velocity-depth profile. This disadvantage can be overcome by replacing the hammer with a vibrator generating controlled frequencies. This is the basis of the continuous surface wave system (CSWS), see [
34].
Nondestructive geophysical techniques for measuring the S-wave velocities are useful for subsurface imaging, particularly for determining the elastic modulus of karstic rock masses at very small strains. Further, in geotechnical earthquake engineering, the S-wave velocity is highlighted as one of the most important indicators for evaluating the soil type, as given in relevant design standard Eurocode 1998 [
35]. S-wave velocities provide information on
vs,30, the shear wave velocity in upper 30 m of soil/rock mass, from where a selection of appropriate amplification factors for seismic analysis can be made.
3. Mapping of Near-Surface Karstic Features
Karstified areas are known to be notoriously difficult ground for subsurface seismic imaging [
36] and many problems may arise during both the investigation and interpretation phase. These include set-up-related issues of effective source and receiver coupling to the ground, as well the karst-induced strong near-surface scattering effects, interfering with the signals of interest and aggravating the near-surface imagining procedures.
For geotechnical applications, the maximum investigation depth of interest will be specified by the nature of the project. Even though seismic methods can be useful when investigating near-surface depths, some limitations may arise if deeper subsurface karst features need to be mapped. For the seismic refraction technique, the investigation depth is limited to one fifth to one third of the length of the geophone spread. Additionally, the employed seismic source must match the desired depth of penetration. For most refraction surveys, the optimal energy source is a sledgehammer weighing approximately up to 8 kg, which can yield an investigation depth of about 15–20 m, depending on geology, surface conditions, etc. Therefore, the profile length and the source energy limit the depth penetration of the seismic refraction method. Mapping of deeper karst features would require very long profiles, which may be an unreasonable requirement, especially when conducting investigations in a limited surface area. Larger energy sources can be used for deeper mapping, such as accelerated weight drop, which is not portable and requires vehicle access to the shot points, or small explosives, whose application can pose a problem in the urban areas. On the other hand, S-wave-based techniques generally deal with surface waves in the lower frequencies (e.g., 1–30 Hz) when compared to high-resolution reflection or refraction surveys where seismic signals consist of wavelets with frequencies higher than 50 Hz. Therefore, S-wave-based techniques use a much shallower depth range of investigation. In recent decades, demand for increased investigation depth of S-wave-based techniques is continuously growing. Since it is practically impossible, or highly uneconomical, to employ active-source energy that yields larger investigation depths, passive-source based methods such as the microtremor survey method, can be used for this purpose. This method utilizes passive surface waves generated from natural (e.g., tidal motion) or anthropogenic (e.g., traffic) sources, usually of a low-frequency (1–30 Hz), thus providing a wide range of penetration depths.
This paper demonstrates several examples of usefulness of P-wave seismic surveys in detecting a series of karst phenomena along the transportation infrastructure, where the subsurface seismic mapping facilitated the evaluation of failure cause, as well the selection of the appropriate remediation technique. Further, given the interpretation issues of traditional mapping procedures in overlooking karstic features, several advanced mapping procedures are demonstrated. Despite the obvious usefulness of seismic surveys in these tasks, detailed understanding of both geometry and geophysical properties of the karstified near-surface area, as well the impact of karst structures on seismic-wave propagation, are critical to mitigate mapping issues.
3.1. Identification of Sinkhole and Suffusion Features
Many karst features are linked with the engineering activities and directly influence existing infrastructure, especially linear transportation infrastructure constructed in karst. Parise et al. [
37] stress that geophysical techniques may be successfully used to contribute to the mitigation of karst-related risks, and many studies attempt to adequately map hidden caverns and voids, because of the likely hazardous impact they may have on infrastructure. As Pazzi et al. [
38] note, caverns and voids, filled either with air, water or collapsed material, will yield some variations in the ground physical properties, thus providing fairly distinct geophysical contrast. Gutiérrez et al. [
2] further note that these features should therefore be investigated by applying multiple geophysical techniques, but the geophysical recognition of their presence has to adapt to the local geological conditions, as noted by Margiotta et al. [
18]. Some limitations of using the seismic P-wave-based techniques for mapping of these anomalies are given by Sheehan et al. [
39], who note that the presence of sharp high-contrast velocity boundaries can limit the seismic wave penetration depth since these will cause most of the energy to be reflected back to the surface, while energy that passes is refracted to shallow angles, limiting the penetration depth within the area below the transition. However, owing to the fact that, in normal circumstances, there will be a change in velocity below the void, with slight increase of velocity with depth in sedimentary karstic rock, seismic waves will eventually return to the surface, allowing for void mapping.
One example of a karstic anomaly that threatened the serviceability and safety of a highway network is demonstrated by Bacic et al. [
40]. A sinkhole of approximately 3 m in depth and of 10 m
2 aperture area, appeared between two lanes of a national highway in Croatia, immediately alerting the infrastructure managers to detect its origin and extent so that appropriate remediation measures be taken. Detailed geological mapping,
Figure 2, indicated that the reason the sinkhole occurrence lies in so-called ‘reverse’ karstification, where the rock mass dissolves from the bottom layers to the top layers, eventually causing the collapse sinkhole, i.e., surface material collapse, into the void at greater depth.
A seismic refraction survey was conducted to determine the size and dispersion of the cavernous system on this highway section. Using a design set-up of 60 geophones at 2 m separation, an investigation depth of 27 m was achieved, where the delta-t-V tomography was used for seismic refraction inversion. A resulting refraction profile is shown in
Figure 3a, where an area of reduced P-wave velocities is clearly visible between the 30
th and 45
th meter in length and from the sixth to the 14
th meter in depth. This is attributed to a reversely formed cavern which caused collapse of surface material,
Figure 3b. Additionally, another area of lower P-wave velocity is visible at the beginning of a profile, which could cause similar problems in future.
Even though exact cavern dimensions are very difficult to obtain, seismic refraction provided a credible estimation of the approximate size of a cavern, being the 160 m3, providing the valuable information for the subsequent remediation works.
Shortly after, during the rainy period of winter, a significant terrain subsidence of unknown genesis and morphology appeared on same Rijeka-Zagreb highway section, just 40 km beyond the location of a sinkhole [
41]. The subsided area of 13 m
2 was located next to the western part of the highway security fence, in the vicinity of a highway tunnel (see
Figure 4) at the end of the drainage system of the tunnel cut slopes. Based on investigation works, which consisted of geological and geophysical investigations, it was concluded that the main reason for the formation of the opening was suffusion, accelerated by the concentrated water flow arriving from the poorly maintained drainage system. The suffosion can be described as
‘undermining through removal of sediment by mechanical and corrosional action of underground water’, as noted by Field [
42].
Seismic refraction profiling, shown
Figure 5a, was conducted along several profiles longitudinal and perpendicular to the highway axis. Below the distinctive pockets of low-velocity materials, the rapid increase of velocities with depth is observed. As the terrain is formed of disintegrated clastic formations of clay, silt and sand mixture, overlying upper fractured karstic dolomite, water run-off caused the mechanical transport of unconsolidated finer surface material into the weathered rock mass, and eventually led to a significant suffusion subsidence of the terrain,
Figure 5b.
3.2. Overlapping the P-Wave Images: A Hybrid Technique
Even though the seismic refraction and reflection are verified as a useful tool in mapping procedures, both techniques have their advantages and flaws. While the refraction methods are reliable in the identification of weathering zones of lower velocities at near-surface depths, reflection offers an advantage at larger depths in identification of faults and fissure systems. To exploit the advantages of each technique, Frei et al. [
43] developed a hybrid seismic technique, based on overlapping independently acquired results from seismic refraction and reflection, allowing for enhanced overall insight into the investigated karstic features.
An example of hybrid image derivation for an investigated karstic location is given in
Figure 6. As an integral part of investigation works conducted for the purpose of foundation design of the Peljesac bridge abutment in Croatia [
44], seismic surveying was conducted along two profiles of 60 m and 80 m in length.
The obtained refraction and reflection profiles were superimposed during the interpretation phase. The hybrid interpretation of the 60 m profile, having the SW–NE orientation, indicated the position of a fault from reflection data, while the refracted data provided information on the lower velocities in the near surface area. A zone with chaotic dispersion of reflected waves is characterized as a tectonic zone with an emphasized fault, while the low velocity near the surface is indicative of a mass of debris and loose material. The 80 m-long profile has the NW–SE orientation and is positioned along the identified fault of SW–NE profile, recognized from acquisition data as a zone of noncompacted material.
3.3. Advanced Identification of Karst Discontinuities: SQi Index
Despite being useful for the imaging of prominent faults, using the reflection technique, or larger voids and weathering zone, using the refraction technique, seismic surveys do not provide information on the density, distribution and orientation of discontinuities as exemplary products of karstification process. Because of this, and the fact that vertical boreholes fail to detect subvertical discontinuities, several seismic studies were conducted, such as [
45], to identify discontinuities with a higher level of confidence. The overall conclusion of these studies is that the refraction method provides a rough determination of directions of discontinuities. However, erroneous conclusions could be drawn if one tries to identify the discontinuities’ frequency, without any prior knowledge on the geometry of rock mass discontinuities from geological mapping works. At the same time, geometrical characterization of discontinuities remains an imperative for rock engineers, since these significantly influence the rock mass behavior during the construction and usage of geotechnical structures in the karst.
A step forward in identification of discontinuity systems was made by Gazdek et al. [
46], through the development of a model that relies on measured P-wave velocities. By extracting the data from the traditional refraction profile, the authors introduced the seismic quality index (SQi), which serves as a comparative indicator of the discontinuity state of rock mass. It provides more precise discontinuity zonation and increases significance of discontinuities in terms of the existing classification of carbonate rock mass in karst regions. SQi is defined by the quantification of seismic energy transient, as a measure of mechanical disturbance energy transmission, where for every seismic velocity field an indicator of seismic quality of geomedia can be defined.
Figure 7 shows the original geophysical-geological interpretation of the seismic refraction profile, derived for the purpose of foundation design of a shopping mall in Rijeka, a city located in a typical karst environment.
Positions of the investigation boreholes are superimposed with the refraction image, with highlighted values of the rock quality designation (RQD) index. Additionally, possible locations and the presence of discontinuities, mapped by the visual mapping of the surface terrain, are indicated. However, the actual positions of discontinuities can only be speculated and attributed to the abrupt bending of the P-wave velocities contours. To minimize speculation as much as possible and to enhance the discontinuity mapping, a refraction image is reconstructed to provide information on SQi, see
Figure 8. The numerical value of the SQi is standardized by the maximum velocity in the refraction profile, attributed to the zone of fresh rock mass as basic refractor. A division of the SQi value in 20 groups is shown, where Gazdek et al. [
46] stress that the chosen group number depends on geological complexity of the observed refraction profile. In this case, as the range of measured P-wave velocities is from 250 to 4500 m/s, a change in the SQi by 1 indicates a velocity changes by 225 m/s, hence change increment in the index by 5%. The black dots that interrupt the continuity of seismic quality index (SQi) values are noticeable and these can be interpreted as subvertical discontinuities.
The benefits of introducing the SQi as an auxiliary method of the quality state for any rock mass categorization system are evident, as the demonstrated procedure allows precise zonation of discontinuities in karstic carbonate rock masses. It should be noted that the SQi mostly relates to the state of surface and subsurface zones, up to a depth of 50 m, where most of the geotechnical structures are located.
4. Seismic Survey as Quality Control Tool: Evaluation of Soil Improvement Degree
In addition to utilizing seismic surveys for the mapping of the near-surface karst phenomena, benefits for geotechnicians manifest also in the possibility of obtaining physical-mechanical properties of karstic rock mass by utilizing the propagation of elastic waves. The emphasis in investigation works for the purpose of geotechnical design, has largely shifted from identification of rock mass strength to rock mass stiffness characterization. The reason for this lies in the fact that the construction sites in urban environments are usually very narrow, and the excavation of tunnels, foundation pits, etc., cause displacements of rock masses, significantly influencing the nearby structures. Unlike the traditional civil engineering materials, such as concrete or steel, rock mass exhibits reduction of stiffness properties with the strain increase; see
Figure 9.
By utilizing the measured S-wave velocities, geophysical techniques provide a good estimation of very small strain shear stiffness, by using the equation:
where
G0 is small strain shear modulus [Pa],
ρ is rock mass density [kg/m
3], while
vs is measured shear wave velocity [m/s]. From here, a very small strain Young modulus can be obtained:
where
is Poisson’s ratio [-].
The usability of geophysically determined small strain stiffness can be verified on the examples of evaluating the soil improvement degree after implementation of one of the improvement techniques. A karstic terrain is often characterized by the soil deposits overlying the weathered sedimentary rock mass, where these deposits regularly have the unsatisfactory stiffness and strength characteristics to overtake the loads imposed from the above structure. For the purpose of construction on these soils, several soil improvement techniques could be employed, such as grouting or vibro-based methods, where the selection of appropriate techniques depends on the several factors such as soil type, loading condition, local contractor tradition etc. When implementing soil improvement, much attention is given to quality control in achieving the desired level of improvements. The quality control campaign usually consists of sampling and estimating stiffness and strength from laboratory tests, by monitoring the in situ improvement parameters using the standard penetration test SPT [
47] or static penetration test CPT [
48], or by conducting on-site large-scale loading tests to evaluate the overall behavior of improved soil. However, these tests cannot be used reliably in determining the degree of increase of the average stiffness characteristics of improved soil.
The average increase in stiffness of the improved soil can be successfully carried out using spectral analysis of surface waves (SASW). The overall procedure includes measurements of S-wave velocities along the predefined profiles on surface, prior to and following soil improvement. By using the Equations (1) and (2), small strain shear modulus, or Young’s modulus respectively, can be calculated. The ratio of small strain stiffness prior to and following improvement represents a degree of soil improvement, which is then used as a measure of success of the improvement works:
where
IR [-] stands for improvement ratio.
During the excavation of the northern tunnel pipe of the St. Kuzam tunnel in karst rock mass in Croatia, a collapse of encountered soil occurred [
49]. The collapse of material inside the tunnel pipe resulted in the extensive subsidence of the terrain surface above the tunnel, forming an irregular subsided shape shown on
Figure 10a. As an optimal soil remediation technique, which should provide continuation of excavation works, a jet-grouting technique was employed. Prior to the grouting, a surface depression was filled with granular material. In total, 95 jet-grouting columns were installed to enhance the physical-mechanical properties of soil, with the layout of installed columns shown on
Figure 10a
An improvement quality control campaign was established prior to the continuation of the excavation works, including borehole drilling and taking of column samples to provide information on the jet-grouting unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and stiffness. Considering the discrete nature of drilling and sampling quality control works, the SASW method was employed to provide information on the average degree of improvement. Four SASW profiles were positioned on the terrain surface, three of them being approximately perpendicular and one positioned parallel the tunnel axis. As it is reasonably assumed, the inclusion of grout at high pressures resulted in stiffer soil, yielding the higher measured shear wave velocities after the improvement, in comparison to the values before improvement,
Figure 10b. Calculated
IR for investigation profiles 1 to 4 was 4.41, 4.31, 4.66 and 5.03 respectively. After it was proven that the degree of improvement was adequate, further excavation of the tunnel pipes could continue.
Seismic surveys can be conducted as an integral part of the quality program, to evaluate the degree of soil improvement to satisfy the structure foundation limit states. On such example is given by Kovacevic et al. [
50] for the location of eight crude oil storage tanks in the Omisalj terminal, each being 79 m in diameter and having the capacity of 80,000 m
3. The subsurface investigation works pointed to the presence of fill material, underlain by weathered rock mass and compacted rock mass at larger depths. Since the backfill material includes mixture of fragmented limestone, concrete, asphalt and clay material, it was concluded that the location is not suitable for accommodating storage tank foundations without implementing appropriate improvement of backfill and weathered rock mass properties. The optimal improvement solution included consolidation grouting of a weathered karstic rock mass and high-pressure jet-grouting of a backfill material. Five SASW test fields were defined, and based on measured S-wave velocities, an
IR calculated using the Equation (3) was in range from 2.14 to 2.35. Since the improvement design requested the
IR of at least 2, it can be concluded that selected improvement technique satisfied the requested criteria.
5. Estimation of Karst Rock Mass Large Strain Stiffness
Straightforwardly obtained stiffness values from the measured velocities of seismic waves have engineering significance only if the small strain range is relevant, such as the cases of the above-demonstrated soil improvement quality control. However, the range of strains relevant for most of geotechnical engineering structures is much higher than the one corresponding to the small strain stiffness. To determine large strain stiffness, essential for rock mass analysis, designers traditionally rely on direct correlations with rock mass classifications where the information is obtained either by the visual surveying or by destructive testing procedures [
51].
Considering the practicality of obtaining the information on seismic wave velocities, many studies [
52,
53] have worked on establishment of a correlation between the velocities of P-waves and standard parameters from engineering classification. A significant progress in direct estimation of large strain stiffness of karst from velocity of seismic waves was given by Juric Kacunic et al. [
54]. Based on long-term experience in monitoring behavior of karstic rock mass during the construction and usage of geotechnical structures, it was observed that measured values of rock mass, as a rule, are much greater than the values gained from calculations, while the measured deformation and displacement trends significantly differ from those assumed by the design. Since these values and trends strongly depend on the rock mass stiffness, a direct correlation is established between the velocity of P-waves and large strain stiffness characteristics of fragmented rock mass:
where
Em is the stiffness in GPa,
GSI is geological strength index in % and
vp is the velocity of longitudinal waves in km/s.
IDm designates the deformation index for rock mass (in the range 0–1).
An example of the usefulness of proposed large strain stiffness model is given for the case of the Kantrida swimming hall in Rijeka in Croatia. During its construction and usage, intensive measurements of horizontal and vertical deformations of rock mass were carried out using a vertical inclinometer and sliding deformeter. These measurements have shown significant difference in both values and trends when compared to those assumed by the foundation pit design.
By utilizing the finite difference method, numerical analyses were performed to calculate the horizontal and vertical displacements at various depths. As an input for numerical analysis, four different constitutive models were applied, with differences in defining the large strain stiffness. Model 1, proposed by Serafim and Pereira [
55], Model 2, proposed by Hoek, Carranza-Torres and Corkum [
56], and Model 3, proposed by Hoek and Diederichs [
57], rely on the estimation of rock mass large strain stiffness from the rock mass classification values, estimated values of rock mass disturbance and measured values of uniaxial compressive strength. Model 4 given by Equation (4) however, also utilizes velocities of P-wave obtained from seismic refraction measurements, obtained at the location for the purpose of a design, see
Figure 11.
The results of the numerical analysis are given in
Figure 12 and are compared with the field measurements. It is clear that the Model 4 shows a smaller deviation from the measured values than what is the case for Models 1 to 3.
Model 4 has a distinctly nonlinear change in large strain stiffness with depth, and, therefore, the nonlinear trend of calculated displacements. This is due to the fact that the stiffness value depends on the square of the velocity of propagation of longitudinal waves along the depth. Therefore, consideration of the P-wave velocities of as one of the indicators of stiffness at large strains, significantly contributes to a more realistic assessment of the behavior of geotechnical structures in karst.
6. Conclusions
Long-term experience of utilizing seismic techniques for karst stratographic profiling and determination of rock mass properties, gained during construction and rehabilitation works of geotechnical structures in Croatia, resulted in a series of practical examples, some of which are presented in this paper. Even though the application of seismic surveys became a non-negotiable requirement for investigations of notoriously complex karst environment, geotechnical engineers are often not sufficiently familiar with the possibilities that these surveys provide. Advanced seismic mapping of near-surface features can provide valuable information, often overlooked by the traditional image interpretation procedures. This includes a hybrid technique, which implies superimposition of independently acquired results from seismic refraction and reflection, allowing for enhanced overall insight into the investigated karstic features both at near-surface and larger depths. Further, to overcome the obvious flaw of vertical boreholes which fail to detect subvertical discontinuities, this paper demonstrates the efforts in more precise discontinuity zonation of karstic terrain, by introducing the seismic quality index (SQi) as a comparative indicator of the discontinuity state of rock mass extracted from the seismic refraction image. As an auxiliary method of the quality state for any rock mass categorization system, SQi is mostly related to the state of surface and subsurface zones, up to a depth of 50 m, where most of the geotechnical structures are located. In addition to being utilized for advanced mapping of karst subsurface, seismic methods are a reliable tool in estimating karstic rock mass parameters, which are of huge importance for the design and quality control of geotechnical works. Small strain stiffness values can be obtained by S-wave based techniques. These surveys are proven as reliable tools in assessing the average increase in stiffness of the improved soil, which often overlays the weathered sedimentary rock mass that originally does not have satisfactory stiffness and strength characteristics to support the loads imposed from the above structure. In addition, seismic survey results are used for the estimation of large strain stiffness, more relevant for a design of geotechnical structures in karst. Consideration of the P-wave velocities as one of the indicators of stiffness at large strains, significantly contributes to a more realistic assessment of the behavior of geotechnical structures in karst, when compared to the traditional assessments relying solely on rock mass classifications. The highlighted practical examples, given in this paper, offer a step forward from the traditional interpretation of seismic surveys, making them a valuable tool in geotechnical engineering investigation works, design and quality control campaign.