Multiple Sulfur Isotope Records of the 3.22 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geologic Setting
3. Lithofacies and Sulfide Description of the Analyzed Rocks
4. Analytical Methods
4.1. Sulfur Isotope Analyses by SIMS
4.2. Sulfur Isotope Analyses by IR-MS
4.3. Electron Probe Micro Analyzer (EPMA) Analyses
5. Results
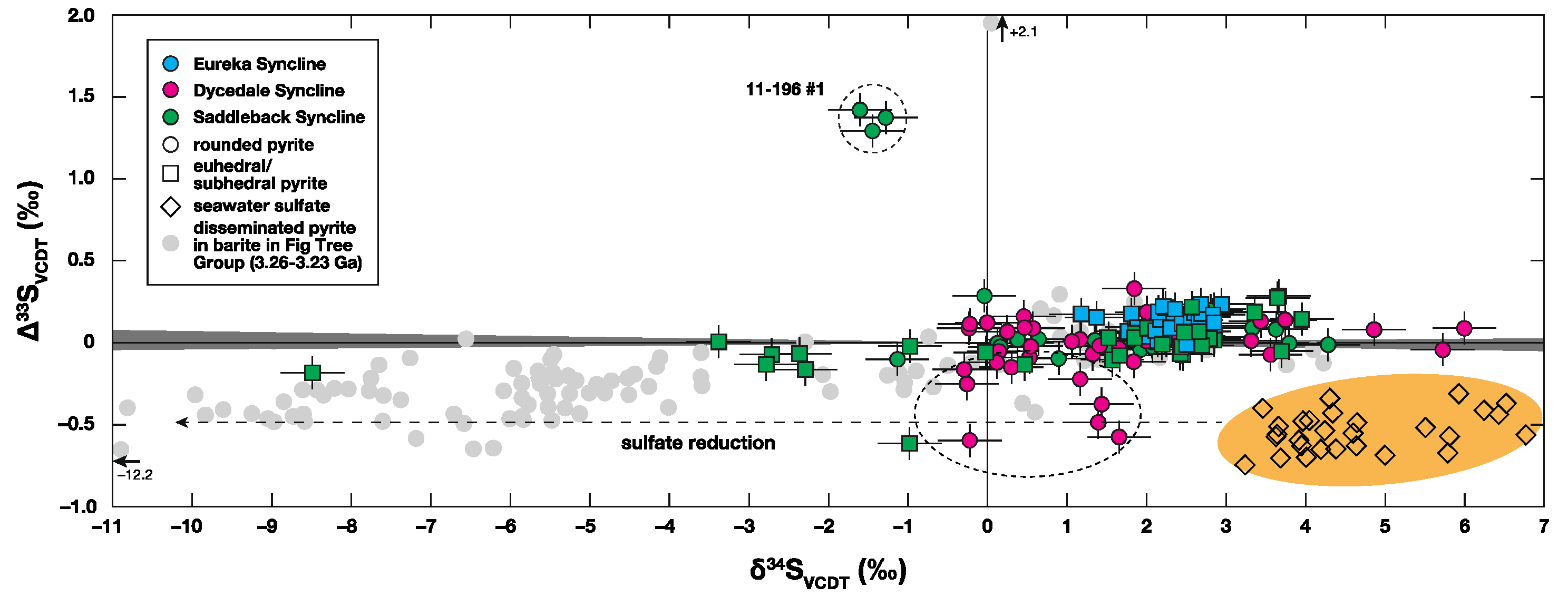
5.1. Sulfur Isotopic Variation through the Central BGB
5.2. Sulfur Isotopic Variation in a Chemostratigraphic Profile in the Saddleback Syncline
5.3. Sulfur Isotopic Variation within an Indivisual Pyrite Grain
5.3.1. Rounded Pyrite
5.3.2. Euhedral/Subhedral Pyrite
6. Discussion
6.1. Rounded Pyrite Origin
6.2. Euhedral/Subhedral Pyrite Origin
6.3. Metasomatic Fluid Circulation at 3.1–3.0 Ga in the Mesoarchean?
6.4. Sulfur Isotope Records of the Moodies Group in the Paleoarchean
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eriksson, K.A.; Simpson, E.L. Quantifying the oldest tidal record: The 3.2 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Geology 2000, 28, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, K.A.; Simpson, E.L.; Mueller, W. An unusual fluvial to tidal transition in the mesoarchean Moodies Group, South Africa: A response to high tidal range and active tectonics. Sediment. Geol. 2006, 190, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Eriksson, K.A.; Mueller, W.U. 3.2 Ga eolian deposits from the Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa: Implications for the origin of first-cycle quartz sandstones. Precambrian Res. 2012, 214–215, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.R.; Byerly, G.R.; Heubeck, C. Structural divisions and development of the west-central part of the Barberton Greenstone Belt. In Geologic Evolution of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa; Lowe, D.R., Byerly, G.R., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 37–82. [Google Scholar]
- Heubeck, C. The Moodies Group—A High-Resolution Archive of Archaean Surface Processes and Basin-Forming Mechanisms. In The Archaean Geology of the Kaapvaal Craton, Southern Africa; Kröner, A., Hofmann, A., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 133–169. [Google Scholar]
- Heubeck, C.; Engelhardt, J.; Byerly, G.R.; Zeh, A.; Sell, B.; Luber, T.; Lowe, D.R. Timing of deposition and deformation of the Moodies Group (Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa): Very-high-resolution of Archaean surface processes. Precambrian Res. 2013, 231, 236–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noffke, N.; Eriksson, K.A.; Hazen, R.M.; Edward, L.; Simpson, E.L. A new window into Early Archean life: Microbial mats in Earth’s oldest siliciclastic tidal deposits (3.2 Ga Moodies Group, South Africa). Geology 2006, 34, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubeck, C. An early ecosystem of Archean tidal microbial mats (Moodies Group, South Africa, ca. 3.2 Ga). Geology 2009, 37, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homann, M.; Heubeck, C.; Airo, A.; Tice, M.M. Morphological adaptations of 3.22 Ga-old tufted microbial mats to Archean coastal habitats (Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa). Precambrian Res. 2015, 266, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homann, M.; Sansjofre, P.; Van Zuilen, M.; Heubeck, C.; Gong, J.; Killingsworth, B.; Foster, I.S.; Airo, A.; Van Kranendonk, M.J.; Ader, M.; et al. Microbial life and biogeochemical cycling on land 3220 million years ago. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.T. Multiple sulfur isotopes and the evolution of Earth’s surface sulfur cycle. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 106, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, J.; Peters, M.; Johnston, D.T.; Strauss, H.; Masterson, A.; Wiechert, U.; Kaufman, A.J. Isotopic evidence for Mesoarchaean anoxia and changing atmospheric sulphur chemistry. Nature 2007, 449, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabhan, S.; Wiedenbeck, M.; Milke, R.; Heubeck, C. Biogenic overgrowth on detrital pyrite in ca. 3.2 Ga Archean paleosols. Geology 2016, 44, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, J.; Bao, H.; Thiemens, M. Atmospheric influence of Earth’s earliest sulfur cycle. Science 2000, 289, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farquhar, J.; Wing, B.A. Multiple sulfur isotopes and the evolution of the atmosphere. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 213, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Wing, B.; Johnston, D.; Farquhar, J.; Rumble, D. Mass-dependent fractionation of quadruple stable sulfur isotope system as a new tracer of sulfur biogeochemical cycles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2238–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFlamme, C.; Jamieson, J.W.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Thébaud, N.; Caruso, S.; Selvaraja, V. Investigating sulfur pathways through the lithosphere by tracing mass independent fractionation of sulfur to the Lady Bountiful orogenic gold deposit, Yilgarn Craton. Gondwana Res. 2018, 58, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, J.; Savarino, J.; Airieau, S.; Thiemens, M.H. Observation of wavelength-sensitive mass-independent sulfur isotope effects during S02 photolysis: Implications for the early atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 32829–32839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masterson, A.L.; Farquhar, J.; Wing, B.A. Sulfur mass-independent fractionation patterns in the broadband UV photolysis of sulfur dioxide: Pressure and third body effects. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 306, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Whitehill, A.R.; Lyons, J.R. Contribution of isotopologue self-shielding to sulfur mass-independent fractionation during sulfur dioxide photolysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 2444–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S. Photochemistry of sulfur dioxide and the origin of mass-independent isotope fractionation in Earth’s atmosphere. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Kaufman, A.J.; Farquhar, J.; Sumner, D.Y.; Beukes, N.J. Lithofacies control on multiple-sulfur isotope records and Neoarchean sulfur cycles. Precambrian Res. 2009, 169, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A. The geochemistry of sedimentary rocks from the Fig Tree Group, Barberton greenstone belt: Implications for tectonic, hydrothermal and surface processes during mid-Archaean times. Precambrian Res. 2005, 143, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubeck, C.; Lowe, D.R. Sedimentary petrography and provenance of the Archean Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt. In Geologic Evolution of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa; Lowe, D.R., Byerly, G.R., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 259–286. [Google Scholar]
- Anhaeusser, C.R.; Robb, L.J.; Viljoen, M.J. Provisional Geological Map of the Barberton Greenstone Belt and Surrounding Granitic Terrane, Eastern Transvaal and Swaziland (1:250000). 1981. Available online: https://www.worldcat.org/title/provisional-geological-map-of-the-barberton-greenstone-belt-and-surrounding-granitic-terrane-eastern-transvaal-and-swaziland/oclc/79698130 (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Heubeck, C.; Lowe, D.R. Late syndepositional deformation and detachment tectonics in the Barberton Greenstone-Belt, South-Africa. Tectonics 1994, 13, 1514–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.R. Accretionary history of the Archean Barberton Greenstone Belt (3.55–3.22 Ga), southern Africa. Geology 1994, 22, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubeck, C.; Bläsing, S.; Grund, M.; Drabon, N.; Homann, M.; Nabhan, S. Geological constraints on Archean (3.22 Ga) coastal-zone processes from the Dycedale Syncline, Barberton Greenstone Belt. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2016, 119, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agangi, A.; Hofmann, A.; Eickmann, B.; Marin-Carbonne, J.; Reddy, S.M. An atmospheric source of S in Mesoarchaean structurally-controlled gold mineralisation of the Barberton Greenstone Belt. Precambrian Res. 2016, 285, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeh, A.; Gerdes, A.; Barton, J.M., Jr. Archean accretion and crustal evolution of the Kalahari Craton–the zircon age and Hf isotope record of granitic rocks from Barberton/Swaziland to the Francistown Arc. J. Petrol. 2009, 50, 933–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agangi, A.; Hofmann, A.; Eickmann, B.; Marin-Carbonne, J. Mesoarchaean Gold Mineralisation in the Barberton Greenstone Belt: A Review. In The Archaean Geology of the Kaapvaal Craton, Southern Africa; Kröner, A., Hofmann, A., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Anhaeusser, C.R. The geology of the Sheba Hills area of the Barberton Mountain Land, South Africa: With particular reference to the Eureka Syncline. Trans. Geol. Soc. S. Afr. 1976, 79, 253–280. [Google Scholar]
- Nabhan, S.; Luber, T.; Scheffler, F.; Heubeck, C. Climatic and geochemical implications of Archean pedogenic gypsum in the Moodies Group (∼3.2 Ga), Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 2016, 275, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamper, A.; Heubeck, C.; Demske, D.; Hoehse, M. Composition and microfacies of Archean microbial mats (Moodies Group, ca. 3.22 Ga, South Africa). SEPM Spec. Pub. 2011, 101, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, I.; Heubeck, C. Microbial-mat-associated tephra of the Archean Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt (BGB), South Africa: Resemblance to potential biostructures and ecological implications. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, M.J. Multiple Sulfur Isotope Determination by SIMS: Evaluation of Reference Sulfides for ∆33S with Observations and a Case Study on the Determination of ∆36S. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2013, 37, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Carbonne, J.; Rollion-Bard, C.; Bekker, A.; Rouxel, O.; Agangi, A.; Cavalazzi, B.; Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C.; Hofmann, A.; McKeegan, K.D. Coupled Fe and S isotope variations in pyrite nodules from Archean shale. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 392, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, É.; Philippot, P.; Rollion-Bard, C.; Cartigny, P.; Assayag, N.; Marin-Carbonne, J.; Mohan, M.R.; Sarma, D.S. Primary sulfur isotope signatures preserved in high-grade Archean barite deposits of the Sargur Group, Dharwar Craton, India. Precambrian Res. 2017, 295, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Raiswell, R.; Westrich, J.T.; Reaves, C.M.; Berner, R.A. The use of chromium reduction in the analysis of reduced inorganic sulfur in sediments and shale. Chem. Geol. 1986, 54, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröger, J.; Franke, J.; Hamer, K.; Schulz, H.D. Quantitative recovery of elemental sulfur and improved selectivity in a chromium-reducible sulfur distillation. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2009, 33, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, Y.; Aoyama, S.; Endo, Y.; Matsu’ura, F.; Foriel, J. Rapid quadruple sulfur isotope analysis at the sub-micromole level by a flash heating with CoF3. Chem. Geol. 2015, 419, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Rumble, D., III; Lowe, D.R. The five stable isotope compositions of Fig Tree barites: Implications on sulfur cycle in ca. 3.2 Ga oceans. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 4868–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerdink, D.L.; Mason, P.R.D.; Farquhar, J.; Reimer, T. Multiple sulfur isotopes in Paleoarchean barites identify an important role for microbial sulfate reduction in the early marine environment. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 331–332, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerdink, D.L.; Mason, P.R.D.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Reimer, T. High-resolution quadruple sulfur isotope analyses of 3.2 Ga pyrite from the Barberton Greenstone Belt in South Africa reveal distinct environmental controls on sulfide isotopic arrays. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Eigenbrode, J.L.; Pavlov, A.A.; Kharecha, P.; Rumble, D.; Kasting, J.F.; Freeman, K.H. New insights into Archean sulfur cycle from mass-independent sulfur isotope records from the Hamersley Basin, Australia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 213, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Ono, S.; Rumble, D.; Maruyama, S. Quadruple sulfur isotope analysis of ca. 3.5 Ga Dresser Formation: New evidence for microbial sulfate reduction in the early Archean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5675–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Farquhar, J.; Masterson, A.; Kaufman, A.J.; Buick, R. Evaluating the role of microbial sulfate reduction in the early Archean using quadruple isotope systematics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 279, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habicht, K.S.; Gade, M.; Thamdrup, B.; Berg, P.; Canfield, D.E. Calibration of Sulfate Levels in the Archean Ocean. Science 2002, 298, 2372–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machel, H.G. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings—Old and new insights. Sediment. Geol. 2001, 140, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Goldhaber, M.B. Sulfur and carbon isotopes. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 517–612. [Google Scholar]
- Machel, H.G.; Krouse, H.R.; Sassen, R. Products and distinguishing criteria of bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction. Appl. Geochem. 1995, 10, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosch, E.G.; McLoughlin, N. Paleoarchean sulfur cycle and biogeochemical surface conditions on the early Earth, Barberton, South Africa. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 377–378, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, P.; Van Zuilen, M.; Lepot, K.; Thomazo, C.; Farquhar, J.; Van Kranendonk, M.J. Early Archaean microorganisms preferred elemental sulfur, not sulfate. Science 2007, 317, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraja, V.; Caruso, S.; Fiorentini, M.L.; LaFlamme, C.K.; Bui, T.H. Atmospheric sulfur in the orogenic gold deposits of the Archean Yilgarn Craton, Australia. Geology 2017, 45, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyai, M.R.; Dirks, P.H.G.M.; Charlesworth, E.G. Archaean gold mineralisation during post-orogenic extension in the New Consort gold mine, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2011, 114, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montinaro, A.; Strauss, H.; Mason, P.R.D.; Roerdink, D.; Muünker, C.; Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Arndt, N.T.; Farquhar, J.; Beukes, N.J.; Gutzmer, J.; et al. Paleoarchean sulfur cycling: Multiple sulfur isotope constraints from the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 2015, 267, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Global Sedimentary Sulfur Isotope Database (GSSID). Available online: http://www.cet.edu.au/research-projects/special-projects/gssid-global-sedimentary-sulfur-isotope-database (accessed on 22 March 2020).
- Roerdink, D.L.; Mason, P.R.D.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Brouwer, F.M. Reworking of atmospheric sulfur in a Paleoarchean hydrothermal system at Londozi, Barberton Greenstone Belt, Swaziland. Precambrian Res. 2016, 280, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philippot, P.; van Zuilen, M.; Rollion-Bard, C. Variations in atmospheric sulphur chemistry on early Earth linked to volcanic activity. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zuilen, M.A.; Philippot, P.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Lepland, A. Sulfur isotope mass-independent fractionation in impact deposits of the 3.2 billion-year-old Mapepe Formation, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 142, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacey, D.; Noffke, N.; Cliff, J.; Barley, M.E.; Farquhar, J. Micro-scale quadruple sulfur isotope analysis of pyrite from the∼3480 Ma Dresser Formation: New insights into sulfur cycling on the early Earth. Precambrian Res. 2015, 258, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, É.; Philippot, P.; Rollion-Bard, C.; Cartigny, P. Multiple sulfur-isotope signatures in Archean sulfates and their implications for the chemistry and dynamics of the early atmosphere. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7432–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aoyama, S.; Ueno, Y. Multiple sulfur isotope constraints on microbial sulfate reduction below an Archean seafloor hydrothermal system. Geobiology 2017, 16, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galić, A.; Mason, P.R.D.; Mogollón, J.M.; Wolthers, M.; Vroon, P.Z.; Whitehouse, M.J. Pyrite in a sulfate-poor Paleoarchean basin was derived predominantly from elemental sulfur: Evidence from 3.2 Ga sediments in the Barberton Greenstone Belt, Kaapvaal Craton. Chem. Geol. 2017, 449, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K.; Yamazaki, R.; Satish-Kumar, M.; Ueno, Y.; Hokada, T.; Toyoshima, T. Multiple sulfur isotope geochemistry of Dharwar Supergroup, Southern India: Late Archean record of changing atmospheric chemistry. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 464, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busigny, V.; Marin-Carbonne, J.; Muller, E.; Cartigny, P.; Rollion-Bard, C.; Assayag, N.; Philippot, P. Iron and sulfur isotope constraints on redox conditions associated with the 3.2 Ga barite deposits of the Mapepe Formation (Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 210, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, R.S.; Mandernack, K.W.; Shanks III, W.C. Laboratory chalcopyrite oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: Oxygen and sulfur isotope fractionation. Chem. Geol. 2010, 269, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saitoh, M.; Nabhan, S.; Thomazo, C.; Olivier, N.; Moyen, J.-F.; Ueno, Y.; Marin-Carbonne, J. Multiple Sulfur Isotope Records of the 3.22 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt. Geosciences 2020, 10, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040145
Saitoh M, Nabhan S, Thomazo C, Olivier N, Moyen J-F, Ueno Y, Marin-Carbonne J. Multiple Sulfur Isotope Records of the 3.22 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt. Geosciences. 2020; 10(4):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaitoh, Masafumi, Sami Nabhan, Christophe Thomazo, Nicolas Olivier, Jean-François Moyen, Yuichiro Ueno, and Johanna Marin-Carbonne. 2020. "Multiple Sulfur Isotope Records of the 3.22 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt" Geosciences 10, no. 4: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040145
APA StyleSaitoh, M., Nabhan, S., Thomazo, C., Olivier, N., Moyen, J.-F., Ueno, Y., & Marin-Carbonne, J. (2020). Multiple Sulfur Isotope Records of the 3.22 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt. Geosciences, 10(4), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040145






