Tsunami Damage Detection with Remote Sensing: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tsunami Physics and Acquisition of Tsunami Features with Remote Sensing
3. Tsunami Damage Interpretation in Remote Sensing
3.1. Extracting Tsunami Inundation Zone
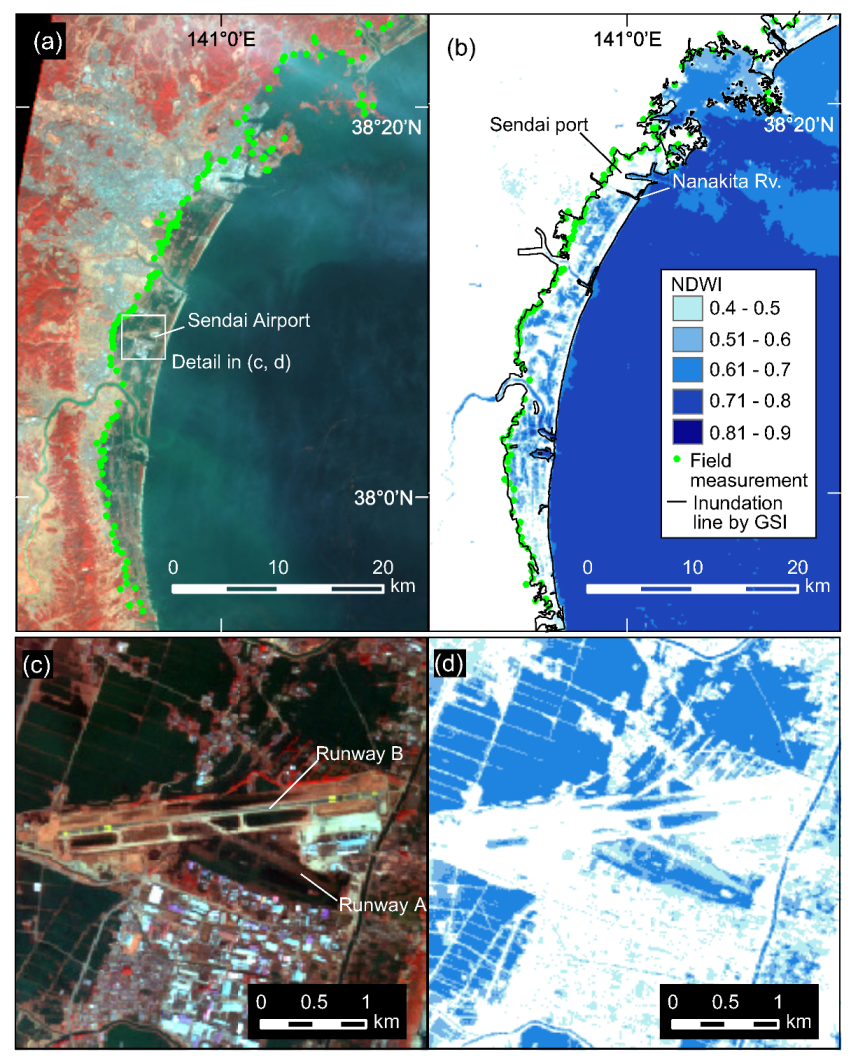
3.1.1. Using Optical Images
3.1.2. Using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Data
3.2. Interpretation of Tsunami-Induced Building Damage
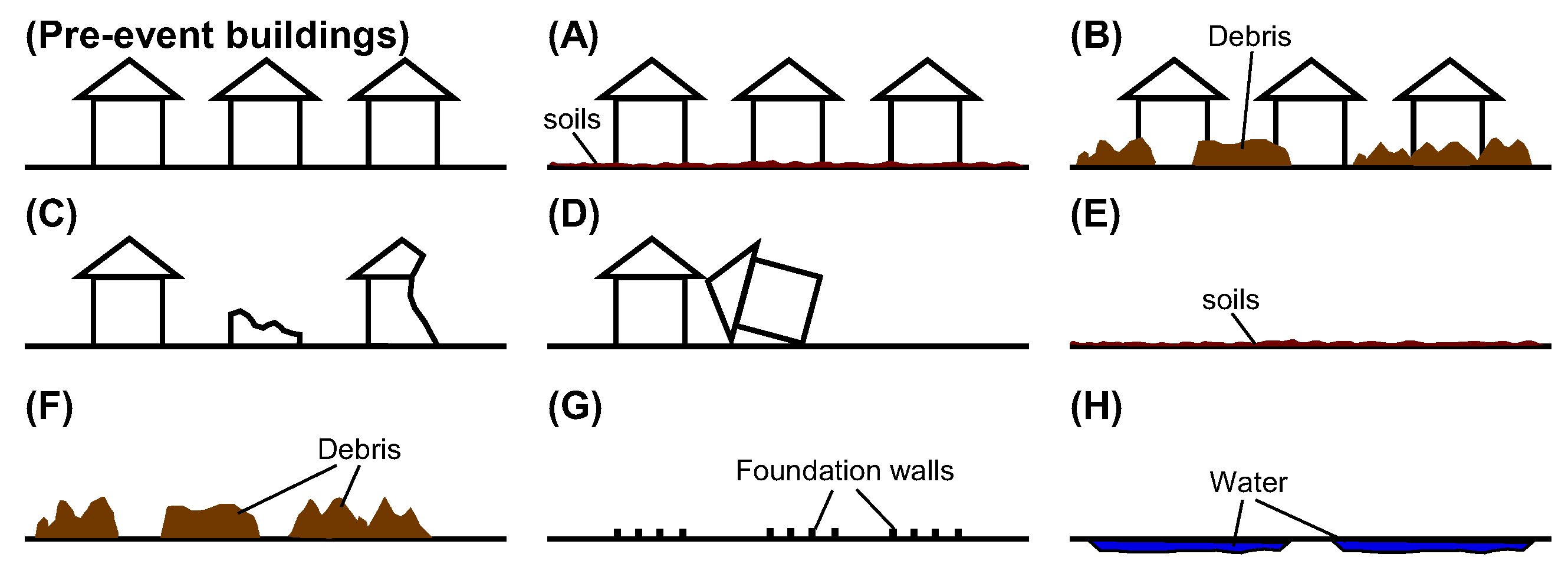
3.2.1. Using Optical Images
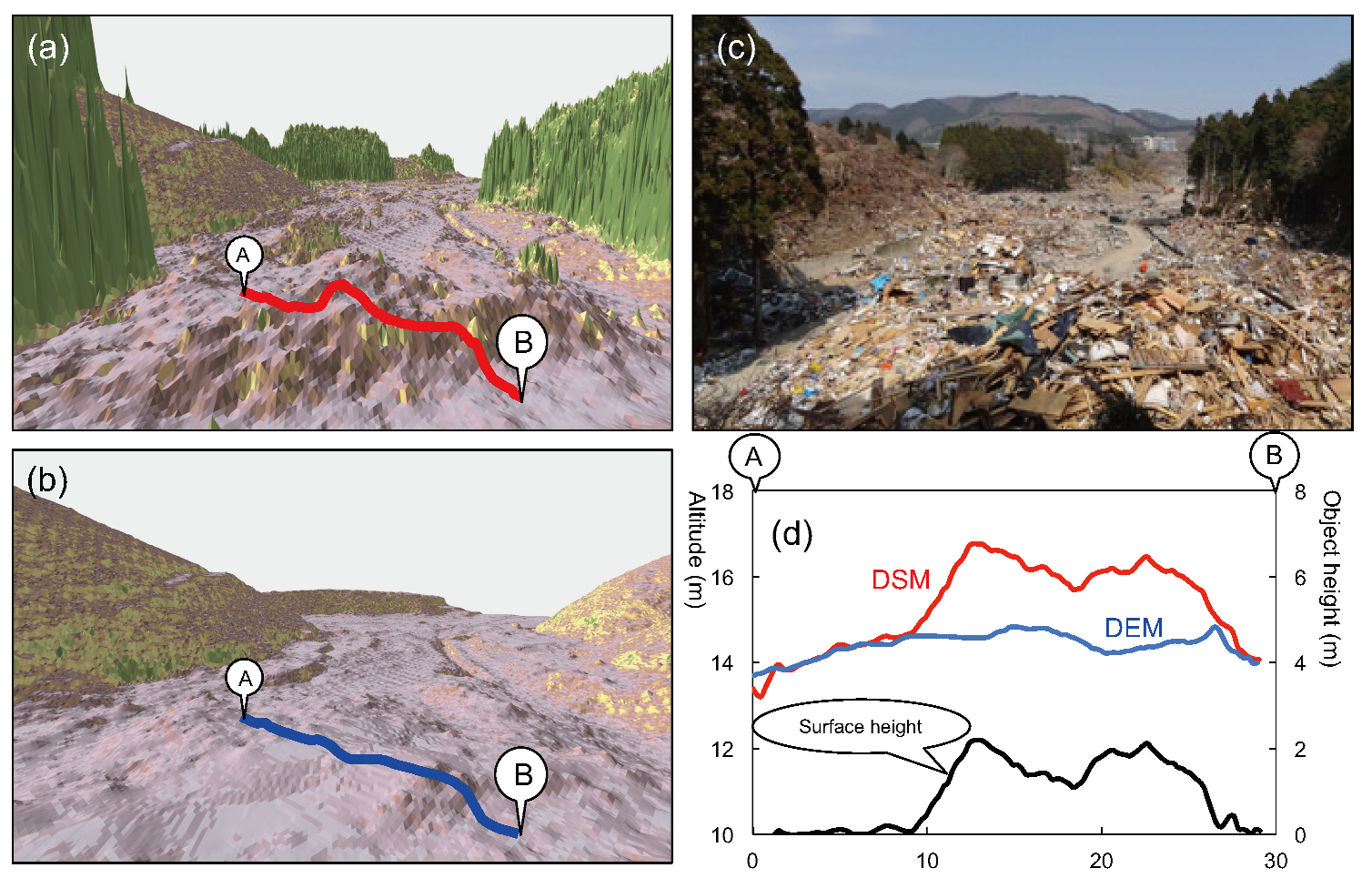
3.2.2. Using LiDAR data
3.2.3. Using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Data
3.3. From Change Detection to Machine Learning Algorithms
4. Application of Machine Learning to Tsunami Damage Detection
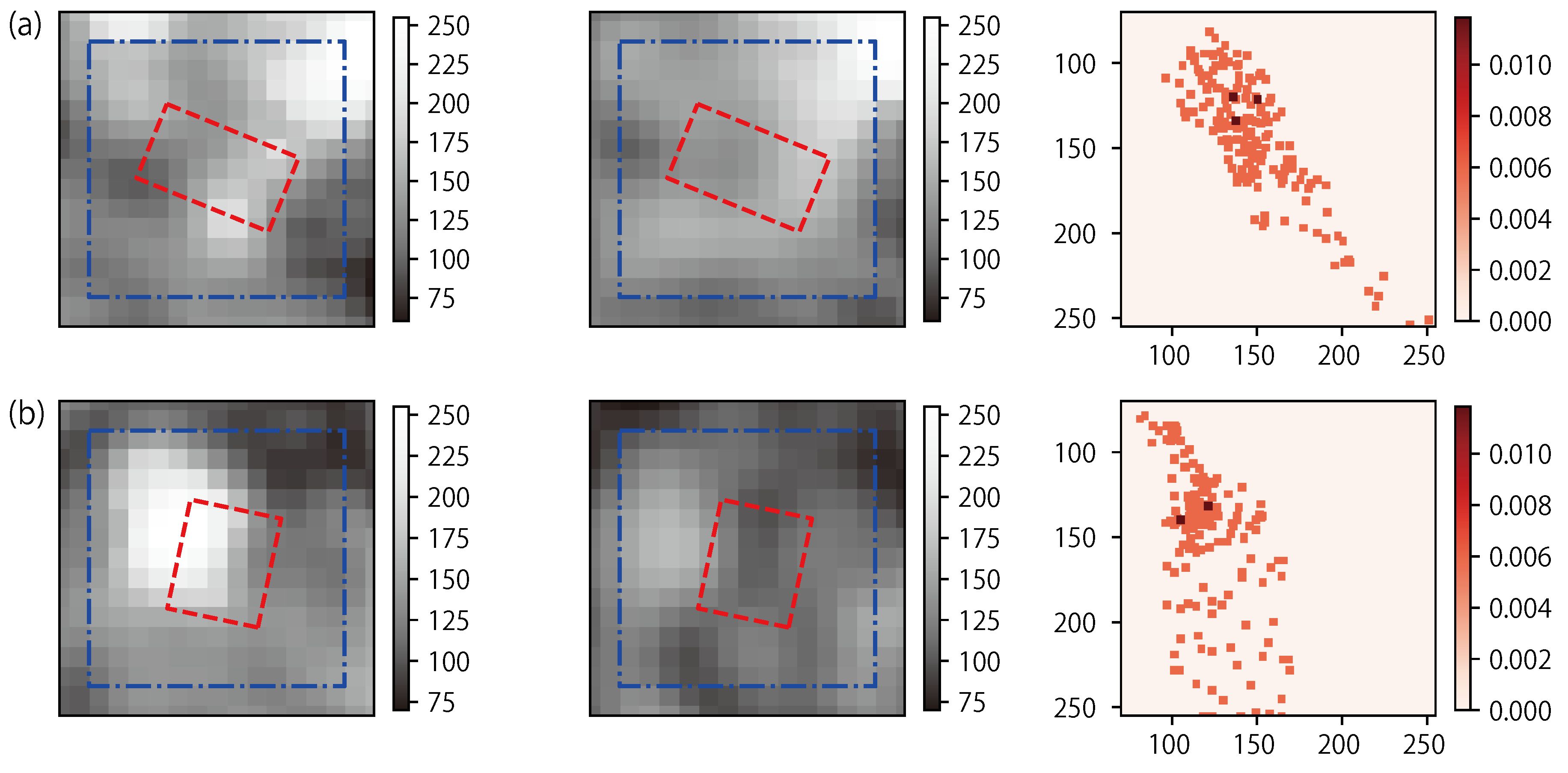
4.1. Unsupervised Machine Learning
4.1.1. Thresholding
4.1.2. K-Means Clustering
4.1.3. Expectation-Maximization (EM) Algorithm
4.1.4. Imagery, Hazard, and Fragility Function (IHF) Method
4.2. Supervised Machine Learning
4.2.1. Support Vector Machine
4.2.2. Decision Trees and Random Forest Classifiers
5. Application of Deep Learning to Tsunami Damage Detection
5.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
5.2. Deep Learning Methods for Damage Detection—Case Studies from the 2011 Tohoku tsunami
6. Future Perspective of Deep Learning for Detecting Tsunami Damage
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guha-Sapir, D.; Below, R.; Hoyois, P.H. EM-DAT: International Disaster Database. 2015. Available online: https://www.emdat.be (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED); The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). Tsunami Disaster Risk 2016: Past Impacts and Projections. 6p. 2016. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/50825_credtsunami08.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Koshimura, S. Tsunami. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences, 3rd ed.; Cochran, J.K., Bokuniewicz, J.H., Yager, L.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Alonso, A.; Utanda, A.; Palacios, M. Earth Observation Actionable Information Supporting Disaster Risk Reduction Efforts in a Sustainable Development Framework. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Huyck, C.; Greene, M.; Gill, S.P.; Bevington, J.; Svekla, W.; Desroches, R.; Eguchi, R.T. Crowdsourcing for Rapid Damage Assessment: The Global Earth Observation Catastrophe Assessment Network (GEO-CAN). Earthq. Spectra 2011, 27, S179–S198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M. Tsunami Observation by Ocean Bottom Pressure Gauge. In Tsunami: Progress in Prediction, Disaster Prevention and Warning; Advances in Natural and Technological Hazards Research, 4; Tsuchiya, Y., Shuto, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 287–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, J. The 26 December 2004 tsunami measured by satellite altimetry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2897–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y. Extracting the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami signals from sea surface height data observed by satellite altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 113, C01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshimura, S.; Oie, T.; Yanagisawa, H.; Imamura, F. Developing fragility functions for tsunami damage estimation using numerical model and post-tsunami data from Banda Aceh, Indonesia. Coast. Eng. J. 2009, 51, 243–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshimura, S.; Hayashi, S.; Gokon, H. The impact of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake tsunami disaster and implications to the reconstruction. Soils Found. 2012, 54, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, S.; Koshimura, S. The 2011 Tohoku Tsunami Flow Velocity Estimation by the Aerial Video Analysis and Numerical Modeling. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; 736p. [Google Scholar]
- Marghany, M. Advanced Remote Sensing Technology for Tsunami Modelling and Forecasting; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; 316p. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, O.M.; Aina, Y.A. Satellite Remote Sensing as a Tool in Disaster Management and Sustainable Development: Towards a Synergistic Approach. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 120, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adriano, B.; Gokon, H.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S.; Liu, W.; Matsuoka, M. Extraction of damaged areas due to the 2013 Haiyan typhoon using ASTER data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Herrera, M.T.; Navarrete-Pacheco, J.A. Satellite Data for a Rapid Assessment of Tsunami Inundation Areas after the 2011 Tohoku Tsunami. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 170, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Shan, J. A comprehensive review of earthquake-induced building damage detection with remote sensing techniques. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 84, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppasri, A.; Koshimura, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Gokon, H.; Kamthonkiat, D. Remote Sensing: Application of remote sensing for tsunami disaster. In Remote Sensing of Planet Earth; Chemin, Y., Ed.; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germay, 2012; pp. 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E. Development of Building Height Data in Peru from High-Resolution SAR Imagery. J. Disaster Res. 2014, 9, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Development of building height data from high-resolution SAR imagery and building footprint. In Safety, Reliability, Risk and Life-Cycle Performance of Structures and Infrastructures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 5493–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Miura, H.; Midorikawa, S.; Estrada, M. Extraction of Urban Information for Seismic Hazard and Risk Assessment in Lima, Peru Using Satellite Imagery. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sato, M. Tsunami Damage Investigation of Built-Up Areas Using Multitemporal Spaceborne Full Polarimetric SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S. Mapping of Building Damage of the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake Tsunami in Miyagi Prefecture. Coast. Eng. J. 2012, 54, 1250006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchi, K.; Yamazaki, F. Characteristics of Tsunami-Affected Areas in Moderate-Resolution Satellite Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, E.; Bricker, J.D.; Kure, S.; Adriano, B.; Yi, C.J.; Suppasri, A.; Koshimura, S. Field survey report and satellite image interpretation of the 2013 Super Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 5, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copernicus, Emergency Management Service. Available online: https://emergency.copernicus.eu/mapping/ems/what-copernicus (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- IWG-SEM, International Working Group on Satellite-Based Emergency Mapping. Available online: http://www.un-spider.org/network/iwg-sem (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Sentinel Asia. Available online: https://sentinel.tksc.jaxa.jp/sentinel2/topControl.jsp (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Vu, T.T.; Matsuoka, M.; Yamazaki, F. Dual-scale approach for detection of tsunami-affected areas using optical satellite images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, F.; Matsuoka, M. Remote Sensing Technologies in Post-disaster Damage Assessment. J. Earthq. Tsunami 2007, 1, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshimura, S.; Namegaya, Y.; Yanagisawa, H. Tsunami Fragility—A New Measure to Identify Tsunami Damage. J. Disaster Res. 2009, 4, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murao, O.; Hoshi, T.; Estrada, M.; Sugiyasu, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Yamazaki, F. Urban Recovery Process in Pisco After the 2007 Peru Earthquake. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, T.; Murao, O.; Yoshino, K.; Yamazaki, F.; Estrada, M. Post-Disaster Urban Recovery Monitoring in Pisco After the 2007 Peru Earthquake Using Satellite Image. J. Disaster Res. 2014, 9, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshimura, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Gokon, H.; Namegaya, Y. Searching Tsunami Affected Area by Integrating Numerical Modeling and Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3905–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S.; Imai, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Namegaya, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Developing fragility functions for the areas affected by the 2009 Samoa earthquake and tsunami. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamazaki, F.; Maruyama, Y.; Miura, H.; Matsuzaki, S.; Estrada, M. Development of Spatial Information Database of Building Damage and Tsunami Inundation Areas following the 2010 Chile Earthquake. In 2010 Chile Earthquake and Tsunami Technical Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, C.N.; Gokon, H.; Jimbo, M.; Koshimura, S.; Sato, M. Disaster debris estimation using high-resolution polarimetric stereo-SAR. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 120, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshimura, S.; Hayashi, S. Tsunami flow measurement using the video recorded during the 2011 Tohoku tsunami attack. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 6693–6696. [Google Scholar]
- Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S. Structural vulnerability in the affected area of the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake tsunami, inferred from the post-event aerial photos. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 6617–6620. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka, T.; Koshimura, S. Quantitative Analysis of Tsunami Debris by Object-Based Image Classification of the Aerial Photo and Satellite Image. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 (Coast. Eng.) 2012, 68, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F.; Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S. Extraction of Damaged Buildings due to the 2011 Tohoku, Japan Earthquake Tsunami. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 4038–4041. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka, T.; Koshimura, S. Three Dimensional Mapping of Tsunami Debris with Aerial Photos and LiDAR Data. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 (Coast. Eng.) 2013, 69, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Chen, S.-W.; Satake, M. Polarimetric SAR Analysis of Tsunami Damage Following the March 11, 2011 East Japan Earthquake. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 2861–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F.; Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S. Extraction of Tsunami-Flooded Areas and Damaged Buildings in the 2011 Tohoku-Oki Earthquake from TerraSAR-X Intensity Images. Earthq. Spectra 2013, 29, S183–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S. Estimation of tsunami-induced building damage using L-band synthetic aperture radar data. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 (Coast. Eng.) 2015, 71, I_1723–I_1728. [Google Scholar]
- Gokon, H.; Post, J.; Stein, E.; Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Mück, M.; Geiß, C.; Koshimura, S.; Matsuoka, M. A Method for Detecting Buildings Destroyed by the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunami Using Multitemporal TerraSAR-X Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, L.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Evaluation of tsunami fragility curves for building damage level allocation. Res. Rep. Tsunami Eng. 2017, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, Y.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. New Insights into Multiclass Damage Classification of Tsunami-Induced Building Damage from SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moya, L.; Marval Perez, L.; Mas, E.; Adriano, B.; Koshimura, S.; Yamazaki, F. Novel Unsupervised Classification of Collapsed Buildings Using Satellite Imagery, Hazard Scenarios and Fragility Functions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Towards Operational Satellite-Based Damage-Mapping Using U-Net Convolutional Network: A Case Study of 2011 Tohoku Earthquake-Tsunami. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moya, L.; Mas, E.; Adriano, B.; Koshimura, S.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W. An integrated method to extract collapsed buildings from satellite imagery, hazard distribution and fragility curves. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 31, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, L.; Zakeri, H.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. 3D gray level co-occurrence matrix and its application to identifying collapsed buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 149, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Piscini, A.; Cinti, F.R.; Amici, S.; Nappi, R.; DeMartini, P.M. The 2011 Tohoku (Japan) Tsunami Inundation and Liquefaction Investigated Through Optical, Thermal, and SAR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Sakurada, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Ito, R.; Hikosaka, S.; Nakamura, R. Damage detection from aerial images via convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Fifteenth IAPR International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Nagoya, Japan, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, B.; Xia, J.; Baier, G.; Yokoya, N.; Koshimura, S. Multi-Source Data Fusion Based on Ensemble Learning for Rapid Building Damage Mapping during the 2018 Sulawesi Earthquake and Tsunami in Palu, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moya, L.; Muhari, A.; Adriano, B.; Koshimura, S.; Mas, E.; Marval-Perez, L.R.; Yokoya, N. Detecting urban changes using phase correlation and ℓ1-based sparse model for early disaster response: A case study of the 2018 Sulawesi Indonesia earthquake-tsunami. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sen. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalized difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3015–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawak, S.D.; Luis, A.J. A Rapid Extraction of Water Body Features From Antarctic Coastal Oasis Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Lin, A. Distribution of inundation by the great tsunami of the 2011 Mw 9.0 earthquake off the Pacific coast of Tohoku (Japan), as revealed by ALOS imagery data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7073–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdoo, B.G.; Richardson, N.; Borrero, J. Inundation distances and run-up measurements from ASTER, QuickBird and SRTM data, Aceh coast, Indonesia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2961–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkura, M. Application of SAR data to monitoring earth surface changes and displacement. Adv. Space Res. 1998, 21, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokon, H. Estimation of Tsunami-Induced Damage Using Synthetic Aperture Radar. Ph.D. Thesis, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, S.; Giulio-Tonolo, F.; Lyons, J.; Kucera, J.; Jones, B.; Schneiderhan, T.; Guha-Sapir, D. Global trends in satellite-based emergency mapping. Science 2016, 353, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, G.; de Boissezon, H.; Hosford, S.; Pasco, X.; Montfort, B.; Ranera, F. The evolution of Earth Observation satellites in Europe and its impact on the performance of emergency response services. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 127, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.F.; Fritz, H.; Yoo, J. Hurricane disaster assessments with image-driven data mining in high-resolution satellite imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Thiel, M.; Schenk, A.; Roth, A.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Delineation of Urban footprints from TerraSAR-X data by analyzing speckle characteristics and intensity information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S. Object-Based Building Damage Assessment Methodology Using Only Post Event ALOS-2/PALSAR-2 Dual Polarimetric SAR Intensity Images. J. Disaster Res. 2017, 12, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Developing a building damage function using SAR images and post-event data after the Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 (Coast. Eng.) 2015, 71, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuoka, M.; Estrada, M. Development of Earthquake-Induced Building Damage Estimation Model Based on ALOS / PALSAR Observing the 2007 Peru Earthquake. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Japan International Cooperation Agency. The Sstudy on the Urgent Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Support Program for Aceh Province and Affected Areas in North Sumatra (Urgent Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Plan for Banda Aceh City) in the Republic of Indonesia: Final Report (1); Volume 2.—Main Report. 2005. Available online: http://open_jicareport.jica.go.jp/216/216/216_108_11802741.html (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Fernandez Galarreta, J.; Kerle, N.; Gerke, M. UAV-based urban structural damage assessment using object-based image analysis and semantic reasoning. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamazaki, F.; Kubo, K.; Tanabe, R.; Liu, W. Damage assessment and 3d modeling by UAV flights after the 2016 Kumamoto, Japan earthquake. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3182–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Nex, F.; Kerle, N.; Vosselman, G. Towards a more efficient detection of earthquake induced facade damages using oblique UAV imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2017, 42, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshimura, S.; Fukuoka, T. Remote Sensing Approach for Mapping and Monitoring Tsunami Debris. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 4829–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, L.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W.; Yamada, M. Detection of collapsed buildings from lidar data due to the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake in Japan. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. A Split-Based Approach to Unsupervised Change Detection in Large-Size Multitemporal Images: Application to Tsunami-Damage Assessment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.J. Change Detection of Remote Sensing Image Based on Multi-Band KL Transform. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 500, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokon, H.; Koshimura, S.; Megur, K. Verification of a method for estimating building damage in extensive tsunami affected areas using L-band SAR data. J. Disaster Res. 2017, 12, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jensen, J.R. A Machine-Learning Approach to Automated Knowledge-Base Building for Remote Sensing Image Analysis with GIS Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone, L.; Prieto, D.F. Automatic analysis of the difference image for unsupervised change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazi, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Melgani, F. An unsupervised approach based on the generalized Gaussian model to automatic change detection in multitemporal SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1997, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redner, R.A.; Walker, H.F. Mixture Densities, Maximum Likelihood and the Em Algorithm. SIAM Rev. 1984, 26, 195–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kim, D.J. Polarimetric SAR remote sensing of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake using ALOS/PALSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppasri, A.; Mas, E.; Charvet, I.; Gunasekera, R.; Imai, K.; Fukutani, Y.; Abe, Y.; Imamura, F. Building damage characteristics based on surveyed data and fragility curves of the 2011 Great East Japan tsunami. Nat. Hazards 2013, 66, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT). Results of the Survey on Disaster Caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake (First Report). 2011. Published on 4 August 2011. Available online: http://www.mlit.go.jp/report/press/city07_hh_000053.html (accessed on 22 April 2019).
- Wieland, M.; Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F. Learning Change from Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Performance Evaluation of a Support Vector Machine to Detect Earthquake and Tsunami-Induced Changes. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F. Urban monitoring and change detection of central Tokyo using high-resolution X-band SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 2133–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees (Wadsworth Statistics/Probability); Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinlan, J.R. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1993; 312p. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; Kuncheva, L.I.; Alonso, C.J. Rotation Forest: A New Classifier Ensemble Method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainforth, T.; Wood, F. Canonical Correlation Forests. arXiv 2005, arXiv:1507.05444. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus, Emergency Management Service, EMSR317: Earthquake in Indonesia. 2018. Available online: https://emergency.copernicus.eu/mapping/list-of-components/EMSR317 (accessed on 2 April 2019).
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Gao, C.; Singh, S.; Koch, M.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. A framework of rapid regional tsunami damage recognition from post-event TerraSAR-X imagery using deep neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengio, Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2009, 2, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, A.; Michelini, A.; Jozinović, D. An investigation of rapid earthquake characterization using single-station waveforms and a convolutional neural network. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2019, 90, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, A.; Hashemi-Beni, L.; Thompson, G.; Kordjamshidi, P.; Langan, T.E. Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Flood Extent Mapping Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Data. Sensors 2019, 19, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Martinis, S.; Wieland, M. Urban flood mapping with an active self-learning convolutional neural network based on TerraSAR-X intensity and interferometric coherence. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, R.; Rishi, M.; Tiwari, A.; Dua, R. A Novel Deep Learning Framework Approach for Natural Calamities Detection. In Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 561–569. [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, G.; Trekin, A.; Potapov, G.; Ignatiev, V.; Burnaev, E. Satellite imagery analysis for operational damage assessment in emergency situations. In Proceedings of the 21th International Conference on Business Information Systems (BIS), Berlin, Germany, 18–20 July 2018; pp. 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, L.; Wang, J. The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation in Image Classification using Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.04621. [Google Scholar]
- Seide, F.; Agarwal, A. CNTK: Microsoft’s open-source deep-learning toolkit. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 2135. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, N.; Takahashi, T.; Yasuda, T.; Yanagisawa, H. Survey of 2011 Tohoku earthquake tsunami inundation and run-up. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, M.; Soh, J.; Puca, A.; Manning, M.; Gollob, D. Microsoft azure and cloud computing. In Microsoft Azure; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Building Damage Assessment in the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal, Earthquake Using Only Post-Event Dual Polarization Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. Earthq. Spectra 2017, 33, S185–S195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Machine Learning Based Building Damage Mapping from the ALOS-2/PALSAR-2 SAR Imagery: Case Study of 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake. J. Disaster Res. 2017, 12, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Adriano, B.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Identifying Building Damage Patterns in the 2016 Meinong, Taiwan Earthquake Using Post-Event Dual-Polarimetric ALOS-2/PALSAR-2 Imagery. J. Disaster Res. 2018, 13, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
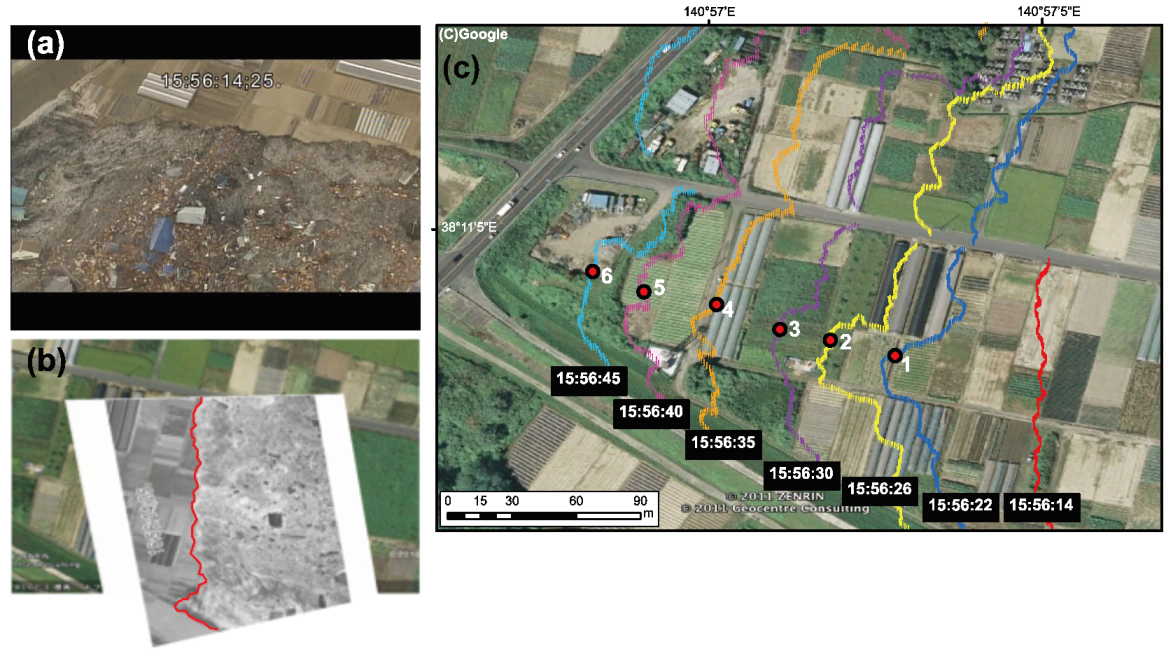











| Tsunami Features | Platforms | Sensors/Sensing Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Mid-ocean propagation | Satellites | Altimeter (Sea surface level) |
| Inland penetration | Aircrafts | Videos |
| Inundation zone | Satellites, Aircrafts | Optical sensors, SAR |
| Structural damage | Satellites, Aircrafts Drones | Optical sensors, SAR |
| Debris | Satellites, Aircrafts, Drones | Optical sensors, SAR, LiDAR |
| Search and rescue | Aircrafts, Drones | Optical sensors, Videos |
| Event | Reference |
|---|---|
| 2004 Indian Ocean | [9,24,29,30,31] |
| 2007 Pisco, Peru | [32,33] |
| 2009 American Samoa, US | [34,35] |
| 2010 Maule, Chile | [36] |
| 2011 Tohoku, Japan | [10,16,22,23,34,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] |
| 2018 Sulawesi, Indonesia | [55,56] |
| Input | Event | Degree of Automation | Metric | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radarsat-1 | 2004IO | automatic | OA | 0.95–0.99 | [78] |
| VNIR | 2011T | required visual inspection | NA | NA | [53] |
| ALOS-2 Polarimetric SAR | 2011T | automatic | g-mean | 0.27–0.90 | [86] |
| SAR, demand, fragility function | 2011T | automatic | F1 | 0.80–0.85 | [49] |
| TerraSAR-X, ALOS-2 | 2011T | required training data | F1 | 0.62–0.86 | [91] |
| TerraSAR-X | 2011T | required training data | F1 | 0.62–0.71 | [48] |
| TerraSAR-X | 2011T | required training data | F1 | 0.80–0.91 | [52] |
| TerraSAR-X | 2011T | required training data | OA | 0.67 | [45] |
| Planet, ALOS-2, Sentinel-1, 2 | 2018S | required training data | OA | 0.83–0.92 | [55] |
| Planet, Sentinel-2, urban footprint data | 2018S | required training data | OA | 0.85 ± 0.06 | [56] |
| Network Structure | Input Data | Accuracy | Damage Class | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet and VGG | Aerial Photo | 0.94–0.96 | WA, S | [54] |
| Wide residual networks [89] | TerraSAR-X (SAR) | 0.75 | WA, C, S | [102] |
| U-net | WorldView-2 (Optical) | 0.71 | WA, C, S | [50] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koshimura, S.; Moya, L.; Mas, E.; Bai, Y. Tsunami Damage Detection with Remote Sensing: A Review. Geosciences 2020, 10, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050177
Koshimura S, Moya L, Mas E, Bai Y. Tsunami Damage Detection with Remote Sensing: A Review. Geosciences. 2020; 10(5):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050177
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoshimura, Shunichi, Luis Moya, Erick Mas, and Yanbing Bai. 2020. "Tsunami Damage Detection with Remote Sensing: A Review" Geosciences 10, no. 5: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050177








