Short Term Effects of Livestock Manures on Soil Structure Stability, Runoff and Soil Erosion in Semi-Arid Soils under Simulated Rainfall
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
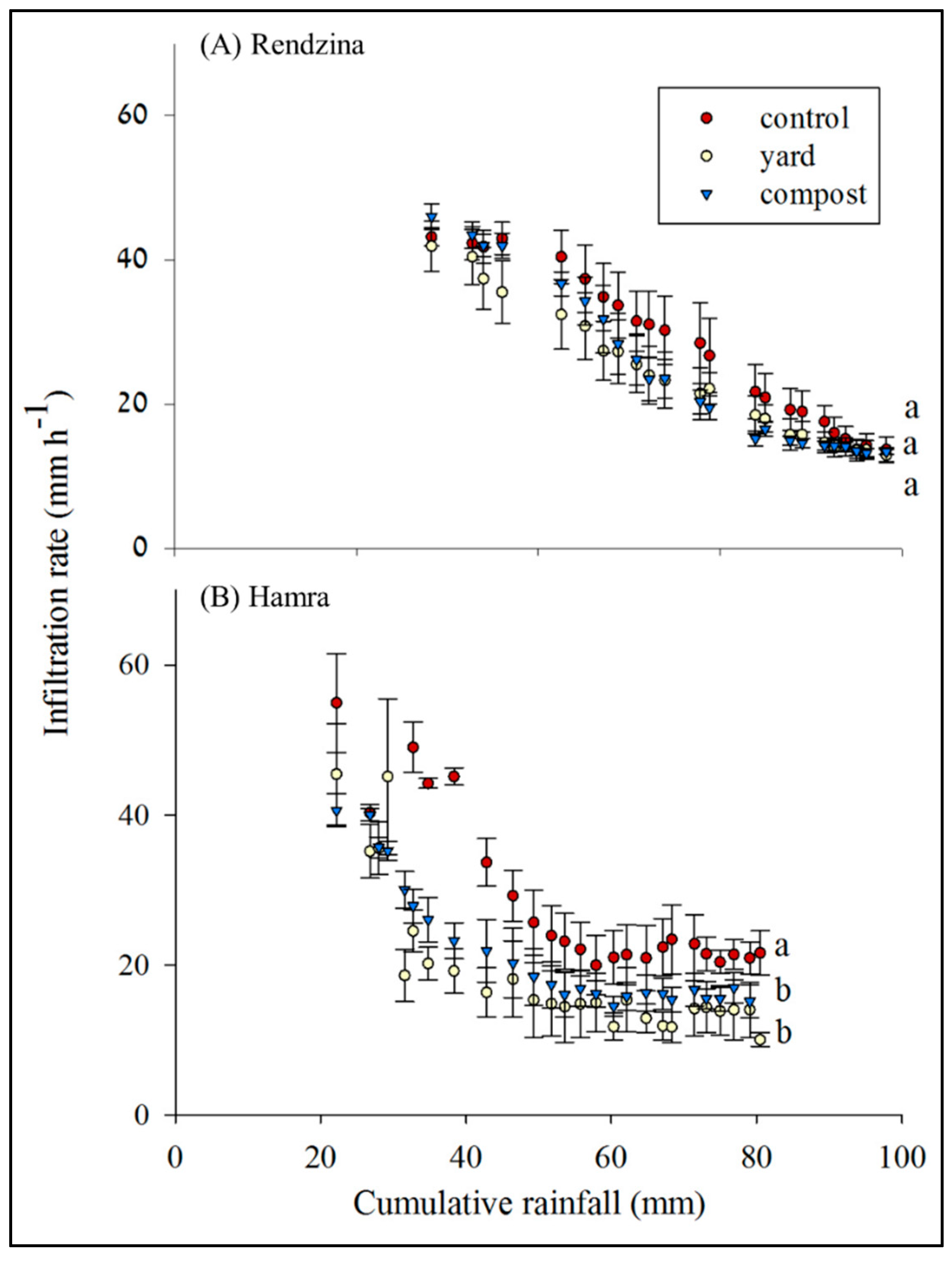
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; ISBN 9780123485250. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, R.; Domzzał, H.; Słowińska-Jurkiewicz, A.; van Ouwerkerk, C. Soil compaction processes and their effects on the structure of arable soils and the environment. Soil Tillage Res. 1995, 35, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirzaker, R.J.; Passioura, J.B.; Wilms, Y. Soil structure and plant growth: Impact of bulk density and biopores. Plant Soil 1996, 185, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passioura, J.B. Soil structure and plant growth. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.N.; Tanveer, M.; Shahzad, B.; Yang, G.; Fahad, S.; Ali, S.; Bukhari, M.A.; Tung, S.A.; Hafeez, A.; Souliyanonh, B. Soil compaction effects on soil health and cropproductivity: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10056–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.H.; Skidmore, E.L. Soil Structure as Influenced by Simulated Tillage. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, G.J.; Shainberg, I. Sodic Soils. Encycl. Soils Environ. 2004, 4, 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hur, M.; Yolcu, G.; Uysal, H.; Lado, M.; Paz, A. Soil structure changes: Aggregate size and soil texture effects on hydraulic conductivity under different saline and sodic conditions. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2009, 47, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.J.; Shainberg, I. Mineral soil surface crusts and wind and water erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2004, 29, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Banin, A. Determination of organic matter content in arid-zone soils using a simple “loss-on-ignition” method. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1989, 20, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P.; Olsson, K.A. Sodicity and soil structure. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Soil mineralogy effects on seal formation, runoff and soil loss—A review. Appl. clay Sci. 2004, 24, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.J.; Mamedov, A.I.; Goldstein, D. Sodicity and water quality effects on slaking of aggregates from semi-arid soils 1. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M.; Shainberg, I. Soil wetting and texture effects on aggregate stability, seal formation, and erosion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agassi, M.; Bloem, D.; Ben-Hur, M. Effect of drop energy and soil and water chemistry on infiltration and erosion. Ater Resour 1994, 30, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakindiki, I.I.C.; Ben-Hur, M. DIVISION S-6—SOIL & WATER MANAGEMENT & CONSERVATION Soil Mineralogy and Texture Effects on Crust Micromorphology, Infiltration, and Erosion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, M.; Plaut, Z.; Ben-Hur, M. Water salinity and sodicity effects on soil structure and hydraulic properties. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, S.; Tabuchi, T.; Warkentin, B.P. Soil-Water Interactions. Mechanisms and Applications; Marcell Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Naidu, R. Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 1998, 51, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezketa, E.; Aragüés, R.; Gazol, R. Efficiency of sulfuric acid, mined gypsum, and two gypsum by-products in soil crusting prevention and sodic soil reclamation. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimoyiannis, D.G.; Tsadilas, C.D.; Valmis, S. Factors affecting aggregate instability of Greek agricultural soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, M.Y.; Richardson, E.V. Mechanics of Soil Erosion From Overland Flow Generated By Simulated Rainfall. Hydrol. Pap. Colo. State Univ. 1973, 63, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, S.; Katra, I.; Argaman, E.; Ben-Hur, M. Erodibility of waste (Loess) soils from construction sites under water and wind erosional forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, W.W. Physical properties and structure. In Soil Factors in Crop Production in a Semi-Arid Environmen; Russell, J.S., Greacen, E.L., Eds.; University of Queensland Press: Manchester, NH, USA, 1977; pp. 78–104. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 10th ed.; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, J.F.; Hornick, S.B. Agricultural use of organic amendments: A historical perspective. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 1992, 7, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Kwak, J.H.; Lim, S.S.; Park, H.J.; Chang, S.X.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.Y. Synthetic fertilizer and livestock manure differently affect δ15N in the agricultural landscape: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.; Dabert, P.; Barrington, S.; Burton, C. Livestock waste treatment systems for environmental quality, food safety, and sustainability. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5527–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thu, C.T.T.; Cuong, P.H.; Hang, L.T.; Van Chao, N.; Anh, L.X.; Trach, N.X.; Sommer, S.G. Manure management practices on biogas and non-biogas pig farms in developing countries-Using livestock farms in Vietnam as an example. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 27, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.D.; Hiltunen, E. Application of livestock waste compost to cultivate microalgae for bioproducts production: A feasible framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilea, R.C. Intensive livestock farming: Global trends, increased environmental concerns, and ethical solutions. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2009, 22, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Malik, A. Roles of organic soil amendments and soil organisms in the biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Antignani, V.; Capodilupo, M.; Scala, F. Identifying the characteristics of organic soil amendments that suppress soilborne plant diseases. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M.; Mentges, M.I.; Rodrigues, M.F.; Cavalli, J.P.; Awe, G.O.; Mentges, L.R. Compressibility and elasticity of subtropical no-till soils varying in granulometry organic matter, bulk density and moisture. Catena 2018, 165, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, L.; Schjønning, P.; Elmholt, S.; Munkholm, L.J. The effects of organic matter application and intensive tillage and traffic on soil structure formation and stability. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 136, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.; Frankenberger, W.T.; Stolzy, L.H. The Influence of Organic Matter on Soil Aggregation and Water Infiltration. JPA 1989, 2, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Gonzalez, J.L. Influence of organic amendments on soil structure and soil loss under simulated rain. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.T.; D’Angelo, E.M.; Williams, M.A. Improving soil structure by promoting fungal abundance with organic soil amendments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 75, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Piqueres, A.; Edel-Hermann, V.; Alabouvette, C.; Steinberg, C. Response of soil microbial communities to compost amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bertoldi, M.; Vallini, G.; Pera, A. The Biology of Composting: A Review. Waste Manag. Res. 1983, 1, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, G.; Pera, A.; Giovannetti, M.; Poggio, G.; Bertoldi, M. Variations of soil structure and microbial population in a compost amended soil. Plant Soil 1988, 106, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li-Xian, Y.; Guo-Liang, L.; Shi-Hua, T.; Gavin, S.; Zhao-Huan, H. Salinity of animal manure and potential risk of secondary soil salinization through successive manure application. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Chang, C. Does long-term heavy cattle manure application increase salinity of a clay loam soil in semi-arid southern Alberta? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderGheynst, J.S.; Pettygrove, S.; Dooley, T.M.; Arnold, K.A. Estimating electrical conductivity of compost extracts at different extraction ratios. Compost Sci. Util. 2004, 3, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Sommer, S.G.; Chadwick, D.; Qing, C.; Guoxue, L.; Michel, F.C. Current Approaches and Future Trends in Compost Quality Criteria for Agronomic, Environmental, and Human Health Benefits. Adv. Agron. 2017, 144, 143–233. [Google Scholar]
- Day, P.R. Physical basis of particle size analysis by the hydrometer method. Soil Sci. 1950, 70, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, L.E. Organic Carbon. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Norman, A.G., Ed.; ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1367–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, L.E.; Moodie, C.D. Carbonate. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Norman, A.G., Ed.; ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1379–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, H.D. Cation Exchange Capacity-Ammonium Acetate Method. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties 2; Norman, A., Ed.; ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; p. 545. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, J.; Goldberg, D.; Seginer, I. A Rainfall Simulator with a Rotating Disk. Trans. ASAE 1967, 10, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrol, V.; Ben-Hur, M.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; Keizer, J.J.; Martins, M.A.S.; Tenaw, H.; Tchehansky, L.; Graber, E.R. Biochar effects on soil water infiltration and erosion under seal formation conditions: Rainfall simulation experiment. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agassi, M.; Shainberg, I.; Morin, J. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration and Soil Sodicity on Infiltration Rate and Crust Formation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) Test. In Encyclopedia of Research Design; SAGE Publications Inc: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Larney, F.J.; Olson, A.F.; Miller, J.J.; Tovell, B.C. Sels hydrosolubles, cuivre, zinc et solides dans l’eau de ruissellement des meules de fumier de bovin composté. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 94, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U.; Ireson, A.; van der Kamp, G.; Davies, S.R.; Wheater, H.S. Impacts of climate variability on wetland salinization in the North American prairies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppus, R.; Imeson, A.C. Extreme events controlling erosion and sediment transport in a semi-arid sub-Andean valley. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2002, 27, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Mena, M.; Albaladejo, J.; Castillo, V.M. Factors influencing surface runoff generation in a Mediterranean semi-arid environment: Chicamo watershed, SE Spain. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soil Type | Texture | Organic Matter (OM) | CaCO3 | Exchange Sodium Potential (ESP) | Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | Soil Water Extract (1:4.5) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | [%] | [meq/100 g] | Electrical Conductivity (EC) | pH | Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) | |||
| [%] | [ds m−1] | [--] | ||||||||
| Sandy soil (Hamra) | 6.7 | 0 | 93.3 | 0.2 (0.0) | 0.6 (0.0) | 0.6 (0.3) | 4.2 (0.1) | 0.1(0.0) | 6.7 (0.0) | 0.3 (0.0) |
| clayey soil (Rendzina) | 51.3 | 24.3 | 24.4 | 4.7 (0.1) | 41 (0.4) | 0.5 (0.1) | 51.2 (1.0) | 0.2 (0.0) | 6.9 (0.0) | 0.5 (0.0) |
| Manure Type | General Content | Manure Water Extract (1:10) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Matter | OM | C/N | N | P | K | pH | EC | Cl− | Na+ | SAR | |
| [%] | [--] | [%] | [--] | [dS m−1] | [meq L−1] | [--] | |||||
| compost | 74.6 | 62.1 | 14.7 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 2 | 7.2 | 11.3 | 48.5 | 47.5 | 19.6 |
| Resting area (yard manure) | 52.9 | 68 | 15.4 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 2 | 7.2 | 10.9 | 50.5 | 45 | 22.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goldberg, N.; Nachshon, U.; Argaman, E.; Ben-Hur, M. Short Term Effects of Livestock Manures on Soil Structure Stability, Runoff and Soil Erosion in Semi-Arid Soils under Simulated Rainfall. Geosciences 2020, 10, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060213
Goldberg N, Nachshon U, Argaman E, Ben-Hur M. Short Term Effects of Livestock Manures on Soil Structure Stability, Runoff and Soil Erosion in Semi-Arid Soils under Simulated Rainfall. Geosciences. 2020; 10(6):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060213
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoldberg, Nurit, Uri Nachshon, Eli Argaman, and Meni Ben-Hur. 2020. "Short Term Effects of Livestock Manures on Soil Structure Stability, Runoff and Soil Erosion in Semi-Arid Soils under Simulated Rainfall" Geosciences 10, no. 6: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060213
APA StyleGoldberg, N., Nachshon, U., Argaman, E., & Ben-Hur, M. (2020). Short Term Effects of Livestock Manures on Soil Structure Stability, Runoff and Soil Erosion in Semi-Arid Soils under Simulated Rainfall. Geosciences, 10(6), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060213







