Convective Instability in Intraplate Oceanic Mantle Caused by Amphibolite-Derived Garnet-Pyroxenites—A Xenolith Perspective (Hyblean Plateau, Sicily)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background Information
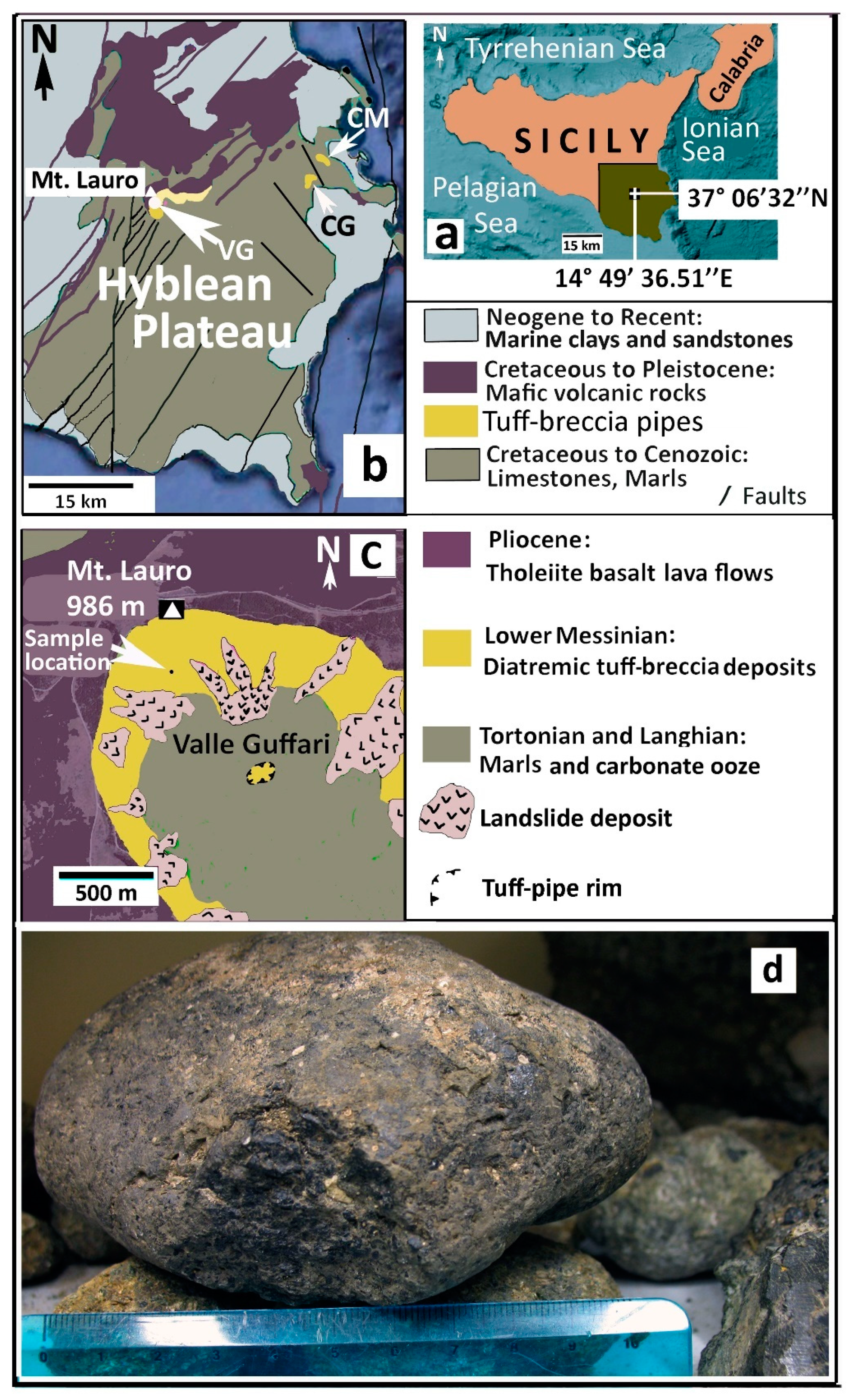
2.1. Geological Setting of the Hyblean Area
2.2. The Hyblean Volcanic Rocks
2.3. Hyblean Diatremes and Their Xenoliths
3. Materials and Methods
Analytical Methods
4. Results
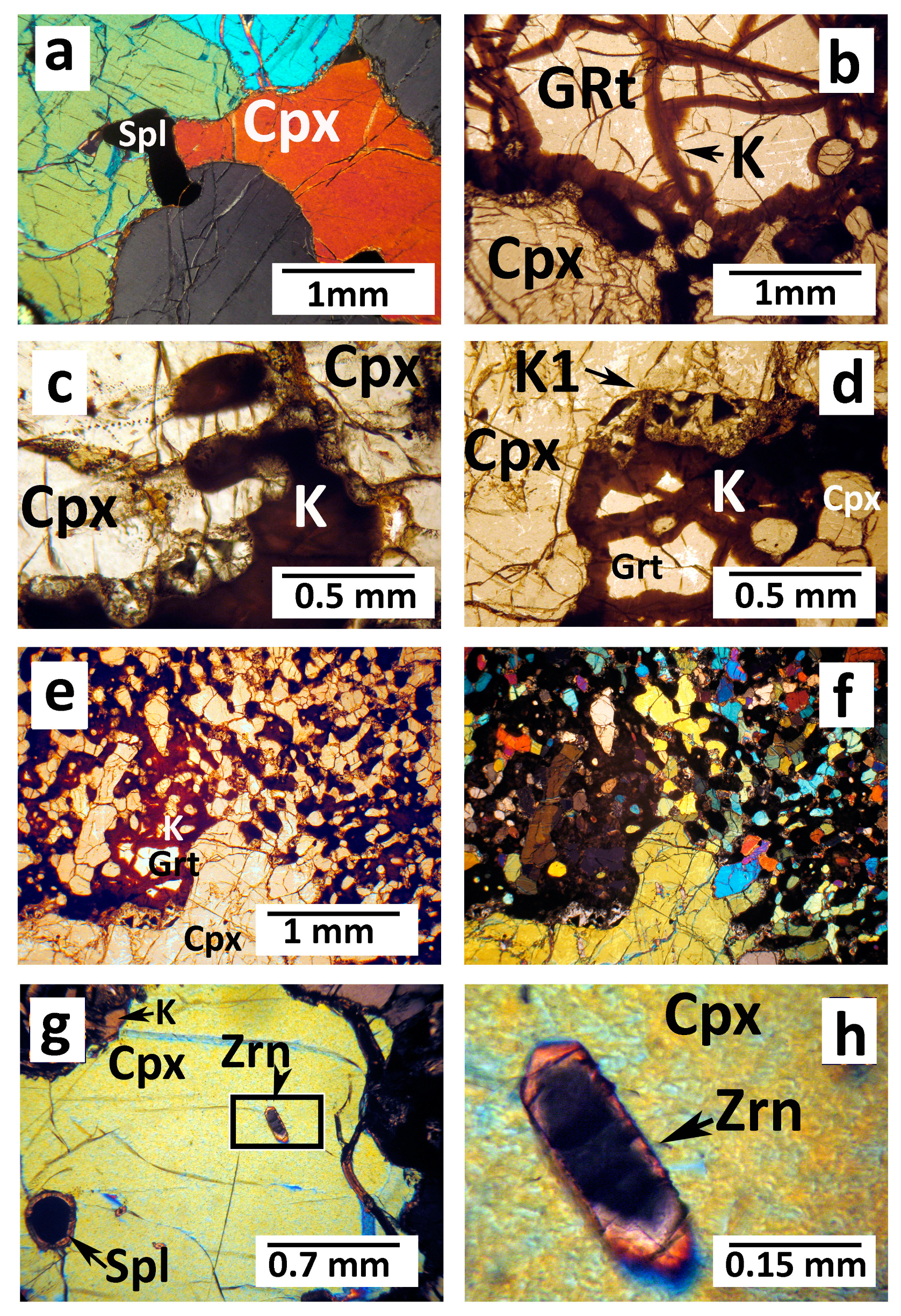
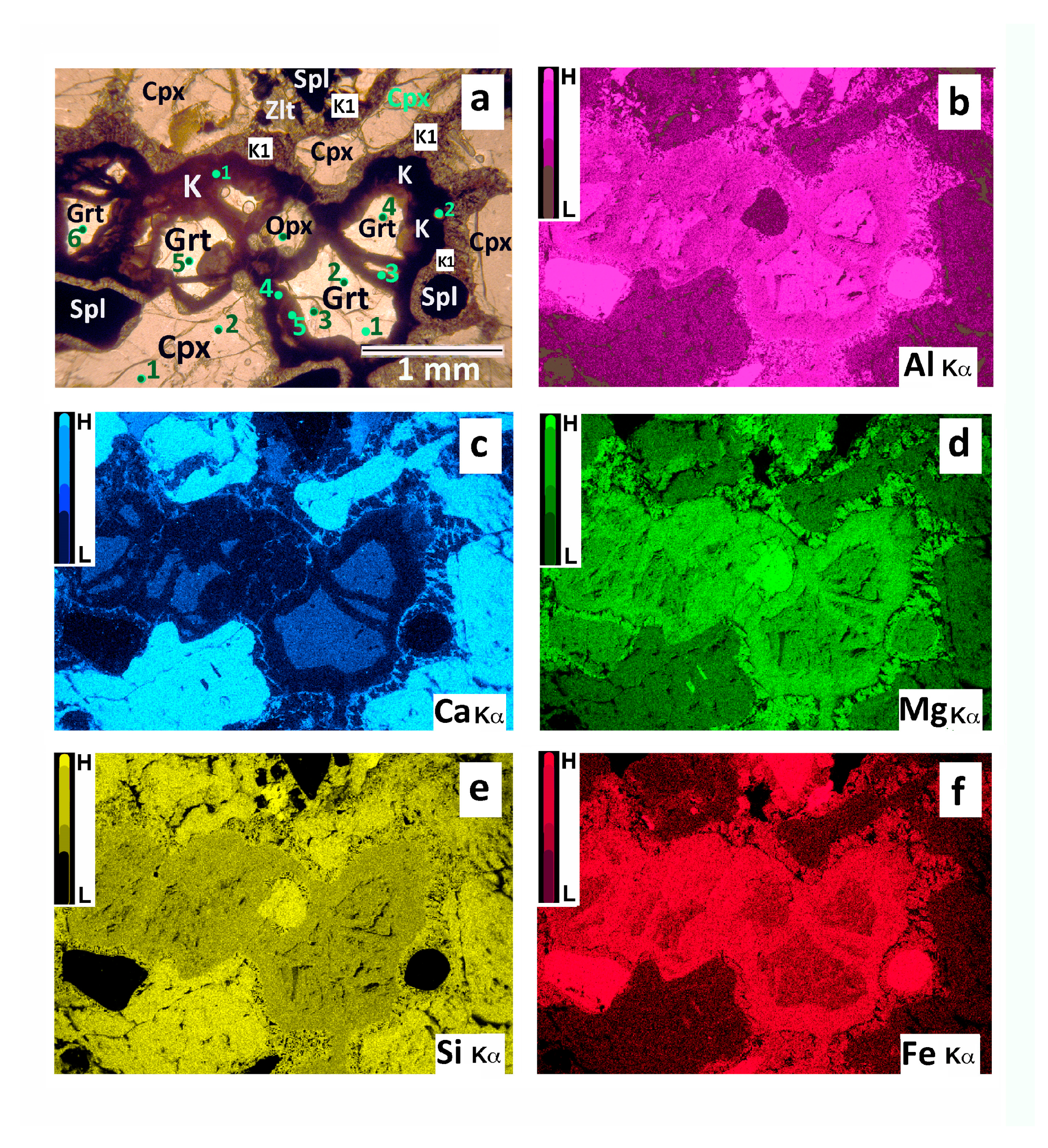
4.1. Optical and SEM Petrography
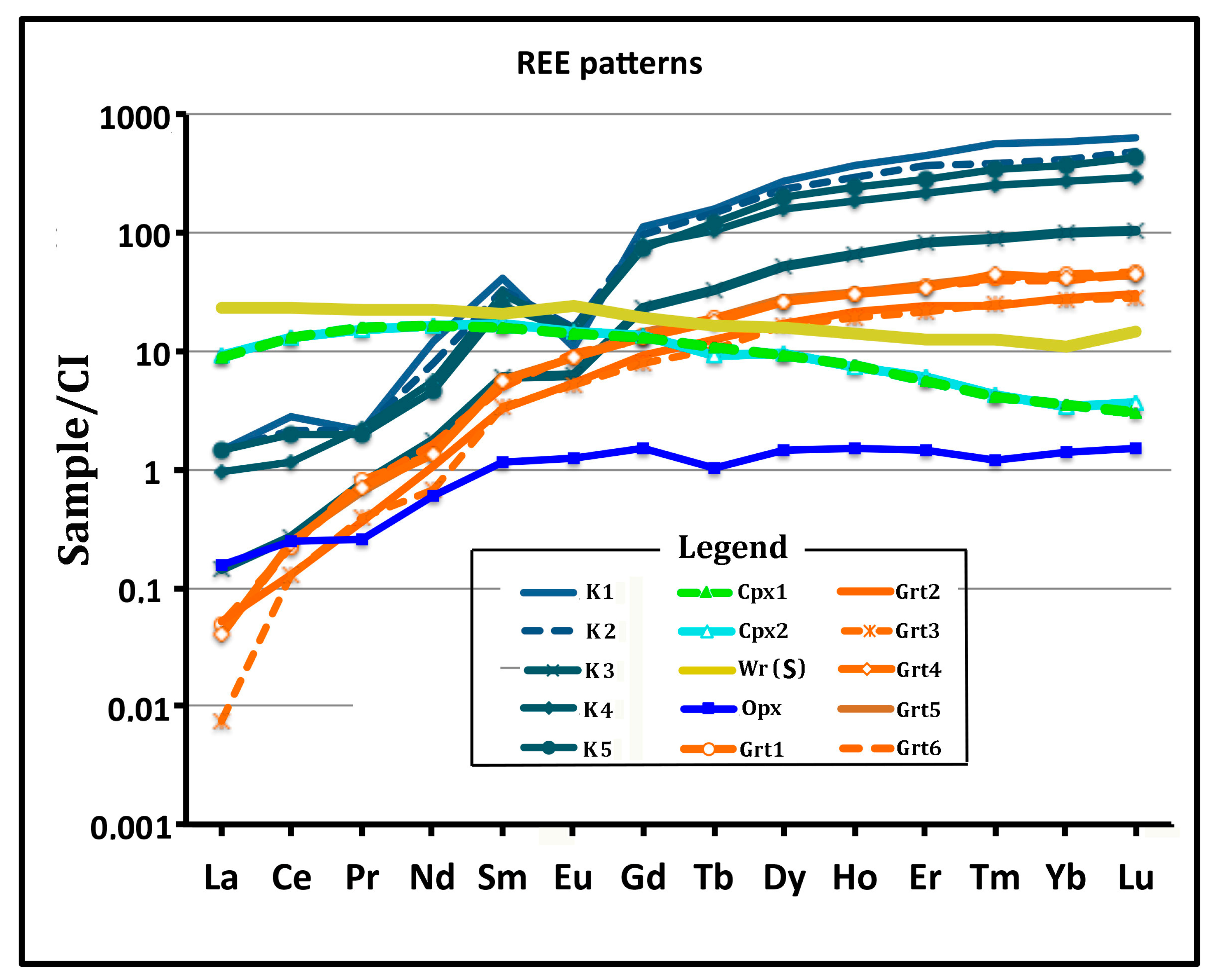
4.2. Chemistry of Minerals and Bulk Kelyphite
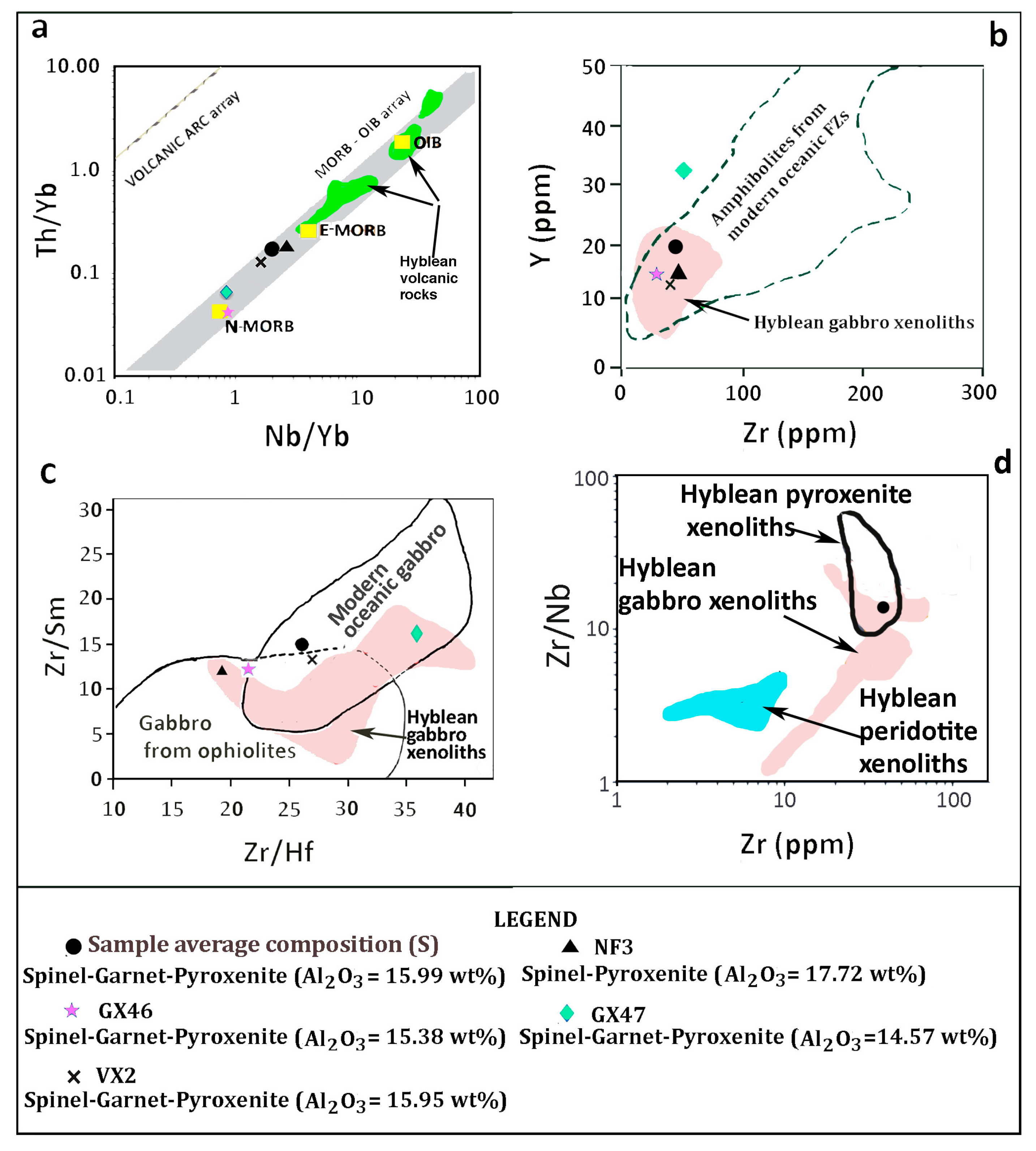
4.3. Whole Rock Chemistry
5. Discussion
5.1. Assessing the Petrologic History of the Sample—Stage I, from Troctolitic Gabbro to Amphibolite
5.2. Assessing the Petrologic History of the Sample—Stage II, from Amphibolite to Garnet–Pyroxenite
5.3. Assessing the Petrologic History of the Sample—Stage III, Kelyphite Replaces Garnet
5.4. Further Discussion
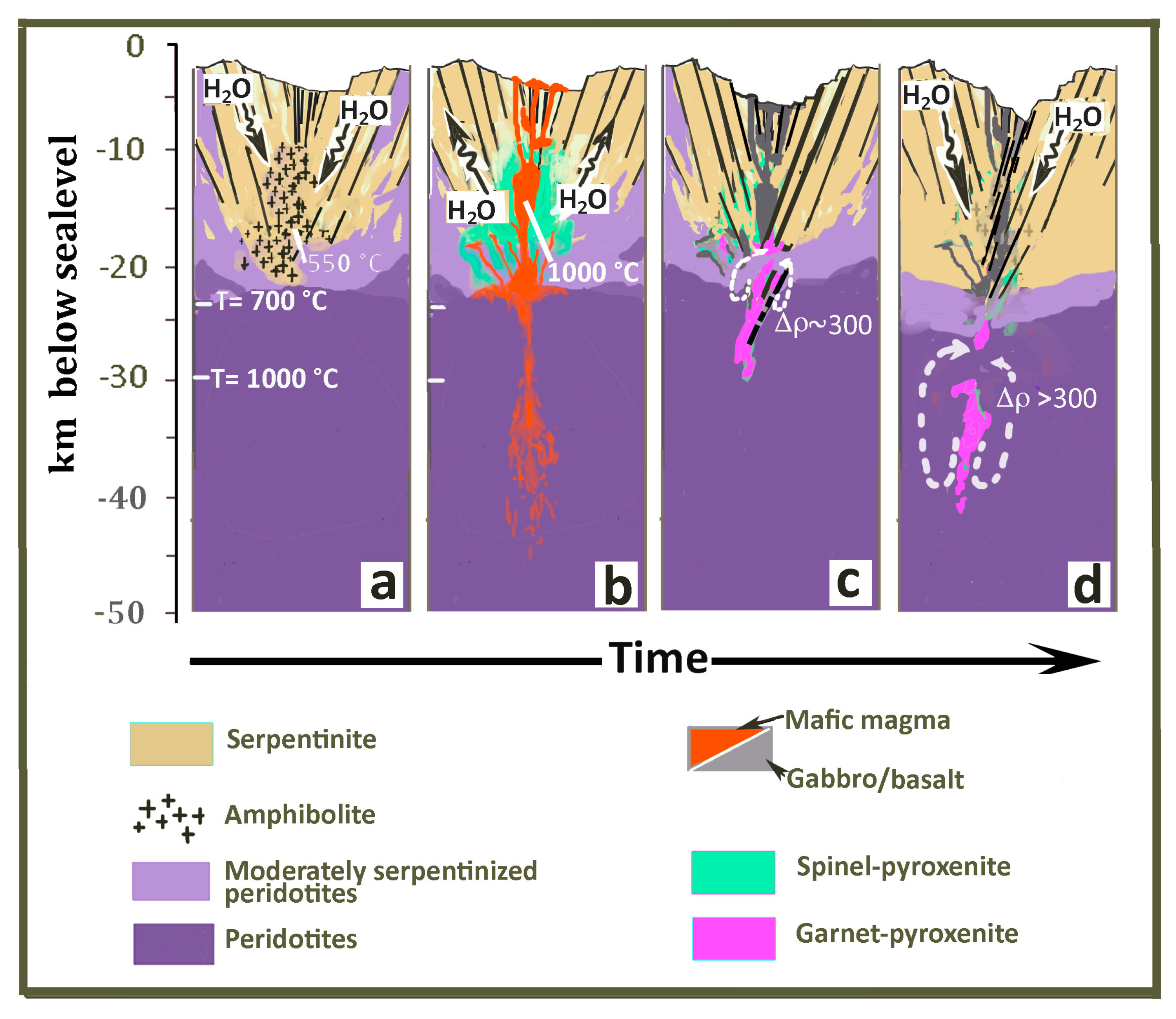
6. General Implications: Gravity Instability Development and the “Autochthonous-Recycled” Nature of Intraplate Garnet–Pyroxenites
6.1. Convective Instability in the Oceanic Lithosphere—The Garnet-Pyroxenite Perspective
6.2. The Garnet Geochemical Signature in Oceanic Basalts—The "Recycled-Autochthonous Pyroxenite" Hypothesis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Downes, H. Origin and significance of spinel and garnet pyroxenites in the shal-low lithospheric mantle: Ultramafic massifs in orogenic belts in Western Europe and NW Africa. Lithos 2007, 99, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-C.; Presnall, D.C. Liquidus Phase Relations in the System CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 at 2 0 GPa: Applications to Basalt Fractionation, Eclogites and Igneous Sapphirine. J. Petrol. 2000, 41, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Féménias, O.; Coussaert, N.; Demaiffe, D. Magmatic garnet-bearing mafic xenoliths (Puy Beaunit, French Massif Central): P–T path from crystallization to exhumation. Eur. J. Mineral. 2005, 17, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshav, S.; Sen, G.; Presnall, D.C. Garnet-Bearing xenoliths from Salt Lake Crater, Ohau, Hawaii: High-Pressure Fractionational Crystallization in the Oceanic mantle. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 1681–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzberg, C. Pyroxene geothermometry and geobarometry: Experimental and thermodynamic evaluation of some subsolidus phase relations involving clinopyroxene in the system CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Caby, R.; Liégeois, J.-P.C.; Mercier, J.-C.C.; Demaiffe, D. Dehydration, melting and related garnet growth in the deep root of the Amalaoulaou Neoproterozoic magmatic arc (Gourma, NE Mali). Geol. Mag. 2008, 146, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, J.M.D.; Pearson, D.G.; Macpherson, C.G.; Lowry, D.; Carracedo, J.-C. Pyroxenite-Rich mantle formed by recycled oceanic lithosphere: Oxygen–Osmium isotope evidence from Canary Island lavas. Geology 2009, 37, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, G. Eclogites and their geodynamic interpretation: A. history. J. Geodyn. 2001, 32, 165–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morten, L.; Obata, M. Possible high-temperature origin of pyroxenite lenses within garnet peridotite, northern Italy. Bull. Mineral. 1983, 106, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, D.; Cipriani, A.; Bonatti, E. Thermal effects of pyroxenites on mantle melting below mid-ocean ridges. Nat. Geosci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, C.; Ceuleneer, G.; Python, M.; Freydier, R.J.; Warren, R.J.; Dick, J.B. Pyroxenites from the Southwest Indian Ridge, 9–16°E: Cumulates from Incremental Melt Fractions Produced at the Top of a Cold Melting Regime. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Carbone, S.; Grasso, M.; Invernizzi, G.; Lentini, F.; Longaretti, G.; Merlini, S.; Mostardini, F. Sicilia orientale: Profilo geologico Nebrodi-Iblei. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1987, 38, 429–458. [Google Scholar]
- Giampiccolo, E.; Brancato, A.; Manuella, F.C.; Carbone, S.; Gresta, S.; Scribano, V. New evidence for the serpentinization of the Palaeozoic basement of southeastern Sicily from joint 3-D seismic velocity and attenuation tomography. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 211, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, C.; Scarfì, L.; Palano, M.; Patanè, D. Foreland segmentation along an active convergent margin: New constraints in southeastern Sicily (Italy) from seismic and geodetic observations. Tectonophysics 2014, 630, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vai, G.B. Development of the palaeogeography of Pangaea from Late Carboniferous to Early Permian. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 196, 125–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribano, V. The ultramafic and mafic nodule suite in a tuff-breccia pipe from Cozzo Molino (Hyblean Plateau, SE Sicily). Rend. Soc. Ital. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 42, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Scribano, V.; Sapienza, G.T.; Braga, R.; Morten, L. Gabbroic xenoliths in tuff-breccia pipes from the Hyblean Plateau: Insights into the nature and composition of the lower crust underneath Southeastern Sicily, Italy. Mineral. Petrol. 2006, 86, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natland, J.H.; Dick, H.J.B. Formation of the lower ocean crust and the crystallization of gabbroic cumulates at a very slowly spreading ridge. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2001, 110, 191–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribano, V.; Ioppolo, S.; Censi, P. Chlorite/smectite-alkali feldspar metasomatic xenoliths from Hyblean Miocenic diatremes (Sicily, Italy): Evidence for early interaction between hydrothermal brines and ultramafic/mafic rocks at crustal levels. Ofioliti 2006, 31, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Manuella, F.C.; Scribano, V.; Carbone, S.; Brancato, A. The Hyblean xenolith suite (Sicily): An unexpected legacy of the Ionian–Tethys realm. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 1317–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuella, F.C.; Scribano, V.; Carbone, S.; Brancato, A. Reply to “Comment on Manuella et al ‘The Hyblean xenolith suite (Sicily): An unexpected legacy of the Ionian–Tethys realm’ by Beccaluva et al 2015”. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longaretti, G.; Rocchi, S. II magmatismo dell’avampaese ibleo (Sicilia orientale) tra il Trias e il Quaternario: Dati stratigrafici e petrologici del sottosuolo. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1990, 45, 911–925. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, S.; Grasso, M.; Lentini, F. Considerazioni sull’evoluzione geodinamica della Sicilia Sud-Orientale dal Cretaceo al Quaternario. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1982, 24, 362–386. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Tonarini, S.; D’Orazio, M.; Armenti, P.; Innocenti, F.; Scribano, V. Geochemical features of Eastern Sicily lithosphere as probed by Hyblean xenoliths and lavas. Eur. J. Mineral. 1996, 8, 1153–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmincke, H.-U.; Behncke, B.; Grasso, M.; Raffi, S. Evolution of the northwestern Iblean Mountains, Sicily: Uplift, Plicocene/Pleistocene sea-level changes, paleoenvironment and volcanism. Geol. Rundsch. 1997, 86, 637–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccaluva, L.; Siena, F.; Coltorti, M.; Di Grande, A.; Giudice, A.L.; Macciotta, G.; Tassinari, R.; Vaccaro, C. Nephelinitic to tholeiitic magma generation in a transtensional tectonic setting: An integrated model for the Iblean volcanism, Sicily. J. Petrol. 1998, 39, 1547–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trua, T.; Esperança, S.; Mazzuoli, R. The evolution of the lithospheric mantle along the N. African Plate: Geochemical and isotopical evidence from the tholeiitic and alkaline volcanic rocks of the Hyblean Plateau, Italy. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1998, 131, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; Bell, K.; Vaccaro, C. Mantle sources of the Cenozoic Iblean volcanism (SE Sicily, Italy): Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic constraints. Mineral. Petrol. 1999, 67, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, A.; Martelli, M.; Paonita, A.; Scribano, V.; Arienzo, I. A combined study of noble gases trace elements and Sr–Nd isotopes for alkaline and tholeiitic lava from the Hyblean Plateau (Italy). Lithos 2018, 314, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Lentini, F. Caratteri deposizionali delle vulcaniti del Miocene superiore negli Iblei (Sicilia Sud-Orientale). Geol. Rom. 1981, 20, 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Suiting, I.; Schmincke, H.-U. Internal vs. external forcing in shallow marine diatreme formation: A case study from the Iblean Mountains (SE-Sicily Central Mediterranean). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 186, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scribano, V. Deep-Seated xenoliths in alkaline volcanic rocks from the Hyblean Plateau (Sicily). Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1987, 38, 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza, G.; Scribano, V. Distribution and representative whole-rock chemistry of deep-seated xenoliths from the Iblean Plateau, southeastern Sicily, Italy. Period. Mineral. 2000, 69, 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Scribano, V.; Carbone, S.; Manuella, F.C. Diatreme eruption probably related to explosive interaction of rising magma with serpentinite diapirs in the shallow crust (Carlentini Formation, Hyblean area, Sicily): A xenolith perspective. Epitome 2007, 2, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Manuella, F.C.; Carbone, S.; Ferlito, C.; Hovland, M. Magma–Serpentinite interaction as the origin of diatremes: A case study from the Hyblean Plateau (southeastern Sicily). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 105, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, A.; Scribano, V.; Paonita, A. A Volcanological Paradox in a Thin-Section: Large Explosive Eruptions of High-Mg Magmas Explained Through a Vein of Silicate Glass in a Serpentinized Peridotite Xenolith (Hyblean Area, Sicily). Geosciences 2019, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scribano, V. Origin of websterite nodules from some alkaline volcanic rocks of Hyblean Plateau (South Eastern Sicily). Period. Mineral. 1987, 56, 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wilshire, E.; Shervais, J.W. Al-Augite and Cr-Diopside Ultramafic Xenoliths in Basaltic Rocks from Western United States. Phys. Chem. Earth 1975, 9, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P.; Vannucci, R. An ion microprobe study of clinopyroxenes in websteritic and megacryst:ic xenoliths from Hyblean Plateau (SE Sicily, Italy): Constraints on HFSE/REE/Sr frac-tionation at mantle depth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 124, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punturo, R.; Scribano, V. Dati geochimici e petrografici su xenoliti di clinopirossenite a grana ultragrossa e e websteriti nelle vulcanoclastiti mioceniche dell’alta Valle Guffari (Monti Iblei, Sicilia). Miner. Petrogr. Acta 1997, 40, 95–116. (in Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Nimis, P. Clinopyroxene geobarometry of pyroxenitic xenoliths from Hyblean Plateau (SE Sicily, Italy). Eur. J. Mineral. 1998, 10, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, P.; Mazzoleni, P.; Punturo, R.; Scribano, V. Gamet-Spinel-Pyroxenite xenoliths from Iblean Plateau (South-eastern Sicily, Italy). Mineral. Petrol. 1999, 66, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakov, S.K.; Sapienza, G.; Scribano, V. Application of a recent garnet-clinopyroxene geobarometer to mantle-pyroxenite xenoliths from Hyblean Plateau, south-eastern Sicily, Italy. GeoActa 2001, 1, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, G.; Yoshikawa, M.; Sapienza, G.T. Comparative study of ultramafic xe-noliths and associated lavas from South-Eastern Sicily: Nature of the lithospheric mantle and insights on magma genesis. Mineral. Petrol. 2010, 98, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, A.; Martelli, M.; Paonita, A.; Rizzo, A.; Brusca, L.; Scribano, V. New evidences of mantle heterogeneity beneath the Hyblean Plateau (southeast Sicily, Italy) as inferred from noble gases and geochemistry of ultramafic xenoliths. Lithos 2012, 132, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Fabries, J.; Ferguson, A.K.; Ginzburg, I.V.; Ross, M.; Seifert, F.A.; Aoki, K.; Gottardi, G. Nomenclature of Pyroxenes. Min. Petr. 1988, 39, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papike, J.J.; Cameron, K.; Baldwin, K. Amphiboles and pyroxenes: Characterization of other than quadrilateral components and estimates of ferric iron from microprobe data. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. 1974, 6, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Palme, H.; O’Neill, H.S.C. Cosmochemical estimates of Mantle Composition. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turrekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2004; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonough, W.F.; Sun, S.S. The Composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesov, B.A.; Geiger, C.A. Raman spectra of silicate garnets. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1998, 25, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingsheng, P.; Mao, H.K.; Dien, L.; Mao, E.C.T. Raman Spectroscopy of Garnet-group Mineras. Chin. J. Geochem. 1994, 13, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, D.; Andò, S.; Vignola, P.; Moltifiori, G.; Marino, I.-G.; Lottici, P.-P.; Diella, V. Micro-Raman spectroscopy as a routine tool for garnet analysis. Spectrochim. Acta 2009, A73, 484–491. [Google Scholar]
- Salters, V.J.M.; Shimizu, N. World-Wide occurrence of HFSE-depleted mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, T.; Lin, E.H.; Xu, J.-A. Raman spectroscopic characteristics of Mg-Fe-Ca pyroxenes. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, V.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Bersani, D.; Lottici, P.-P. Raman fingerprint of chromate, aluminate andferrite spinels. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, D.; Aliatis, I.; Tribaudino, M.; Mantovani, L.; Benisek, A.; Carpenter, M.A.; Gatta, G.D.; Lottici, P.-P. Plagioclase composition by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T. Chapter 6—Raman Spectroscopy of Clay Minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2017, 8, 150–199. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, R.H. Texture development in cumulate rocks. In Layered Intrusions; Cawthorn, R.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1996; pp. 77–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lambart, S.; Laporte, D.; Schiano, P. Markers of the pyroxenite contribution in the major-element compositions of oceanic basalts: Review of the experimental constraints. Lithos 2013, 160, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, P.D.; Downes, H.; Sharkov, E.V.; Vetrin, V.R.; Ionov, D.A.; Carswell, D.A.; Beard, A. Petrology and geochemistry of xenoliths from the Northern Baltic shield: Evidence for partial melting and metasomatism in the lower crust beneath an Archean terrane. Lithos 1995, 36, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, A.; Dalton, C.A.; Langmuir, C.H.; Su, Y.; Schilling, J.-G. The mean composition of ocean ridge basalts. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, Z.; Yakymchuk, C.; Ren, K.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Xia, B. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Basalts from the South Mid-Atlantic Ridge (18.0°–20.6°S): Evidence of a Heterogeneous Mantle Source. Minerals 2019, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearce, J.A. Geochemical fingerprint of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos 2008, 100, 14–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith Nagihara, S.; Casey, J.F. Whole-Rock geochemistry of amphibolites and metagabbros from the West Iberia Margin, Leg 173. Proc. Ocean. Drill. Prog. Sci. Results 2001, 173, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Grimes, C.B.; John, B.E.; Kelemen, P.B.; Mazdab, F.K.; Wooden, J.L.; Cheadle, M.J.; Hanghøj, K.; Schwartz, J.J. Trace element chemistry of zircons from oceanic crust: A method for distinguishing detrital zircon provenance. Geology 2007, 35, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, T.; Pidgeonm, R.T.; Van Bronswijkc, W.; Kurtza, R. Transport of uranium, thorium and lead in metamict zircon under low-temperature hydrothermal conditions. Chem. Geol. 2002, 191, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bea, F.; Bortnikov, N.; Montero, P.; Zinger, T.; Sharkov, E.; Silantyev, S.; Skolotnev, S.; Trukhalev, A.; Francisco Molina-Palma, J. Zircon xenocryst evidence for crustal recycling at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Lithos, 2020; 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, A.; Aranovich, L. Zircon solubility in silicate melts: New experiments and probability of zircon crystallization in deeply evolved basic melts. Chem. Geol. 2019, 510, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaka, T.; Meyer, R.; Wintsch, R.P.; Wathen, B. Hydrothermal spinel, corundum and diaspore in lower oceanic crustal troctolites from the Hess Deep Rift. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 171, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanfilippo, A.; Dick, H.J.B.; Ohara, Y.; Tiepolo, M. New insights on the origin of troctolites from the breakaway area of the Godzilla Megamullion (Parece Vela back-arc basin): The role of melt-mantle interaction on the composition of the lower crust. Isl. Arc 2016, 25, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leake, B.E.; Woolley, A.R.; Arps, C.E.S.; Birch, W.D.; Gilbert, M.C.; Grice, J.D.; Hawthorne, F.; Kato, A.; Kisch, H.J.; Krivovichev, V.G.; et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles: Report of the Subcommittee on Amphi-boles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Dragovic, B.; Baxter, E.F.; Caddick, M.J. Pulsed dehydration and garnet growth during subduction revealed by zoned garnet geochronology and thermodynamic modeling, Sifnos, Greece. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 413, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, A.J.; Gardner, J.E.; Housh, T.B. Repeated recharge, assimilation and hybridization in magmas erupted from El Chichón as recorded by plagioclase and amphibole phenocrysts. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. 2008, 175, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, S.H.; Larsen, J.; Cooms, M.; Dunn, A.; Hayden, L. Amphibole reaction rims as a record of pre-eruptive magmatic heating: An experimental approach. Earth. Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 426, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutherford, M.; Devine, J. Magmatic conditions and magma ascent as indicated by hornblende phase equilibria and reactions in the 1995–2002 Soufrière Hills magma. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 1433–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baxter, E.F.; Caddick, M.J. Garnet growth as a proxy for progressive subduction zone dehydration. Geology 1993, 41, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plümper, O.; Piazolo, S.; Austrheim, H. Olivine Pseudomorphs after Serpentinized Orthopyroxene Record Transient Oceanic Lithospheric Mantle Dehydration (Leka Ophiolite Complex, Norway). J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 1943–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silantyev, S.A. Origin Conditions of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Plutonic Complex at 13°–17° N. Petrology 1998, 6, 351–387. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.C.; Rutherford, M.J. Experimental calibration of the aluminum-in-hornblende geobarometer with application to Long Valley caldera (California) volcanic rocks. Geology 1989, 17, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.B.; Wyllie, P.J. Garnet growth during amphibolite anatexis—Implications of a garnetiferous restite. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, A.; Ferry, J.M. Highly aluminous hornblende from low-pressure metacarbonates and a preliminary thermodynamic model for the Al content of calcic amphibole. Am. Mineral. 1991, 76, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.; Féménias, O.; Mercier, J.-C.C. Ocean-Floor hydrothermal metamorphism in the Limousin ophiolites (western French Massif Central): Evidence of a rare preserved Variscan oceanic marker. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2005, 23, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.C.; Manning, C.E. Solubility of corundum in the system Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–NaCl at 800 °C and 10 kbar. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S.; Williams-Jones, A.E. The role of hydrothermal processes in concentrating high-field strenght elements in the Strange Lake peralkaline complex, northeastern Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Kinny, P.D.; Wyborn, D. Chemistry of hydrothermal zircon: Investigating timing and nature of water-rock interaction. Water Rock Interact. 1998, 9, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Aarnes, I.; Svensen, H.; Connolly, J.A.D.; Podladchikov, Y.Y. How contact metamorphism can trigger global climate changes: Modeling gas generation around igneous sills in sedimentary basins. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 7179–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leeman, V.P.; Annen, C.; Dufek, J. Snaker River Plain—Yellowstone silicic volcanism: Implications for magma genesis and magma fluxes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2008, 304, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeev, R.R.; Holtz, F.; Koepke, J.; Parat, F. Experimental calibration of the effect of H2O on plagioclase crystallization in basaltic melt. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmincke, H.-U. Volcanism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, C.S.J.; Klügel, A. The pressure and temperature conditions and timing of glass formation in mantle-derived xenoliths from Baarley, West Eifel, Germany: The case for amphibole breakdown, lava infiltration and mineral–melt reaction. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 74, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapienza, G.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Morten, L. Petrology and Sr–Nd–Hf isotope geochemistry of gabbro xenoliths from the Hyblean Plateau: A MARID reservoir beneath SE Sicily? Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 157, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, A.; Scribano, V. Specific gravity measures on deep-seated nodules from Sicily. Rend. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1990, 13, 97–98. [Google Scholar]
- Punturo, R.; Kern, H.; Scribano, V.; Atzori, P. Petrophysical and petrological characteristics of deep-seated xenoliths from Hyblean Plateau, south-eastern Sicily, Italy: Suggestions for a lithospheric model. Mineral. Petrogr. Acta 2000, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, N.I. Elasticity of ultrabasic rocks. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 5921–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Christensen, N.I. Seismic velocities of lower crustal and upper mantle rocks from the slow spreading Mid-Atlantic Ridge, south of the Kane Transform zone (MARK). Proc. Ocean. Drill. Program. Part B Sci. Results 1997, 153, 437–454. [Google Scholar]
- Jull, M.; Kelemen, P.B. On the conditions for low Experimental calibration of the aluminum-in-hornblende geobarometer with application to Long Valley caldera (California) volcanic rocks and crustal convective instability. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid 2001, 106, 6423–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, H.P.; Richards, M.A.; Baumgardner, J.R. A sensitivity study of three-dimensional spherical mantle convection at 108 Rayleigh number: Effects of depth-dependent viscosity, heating mode and endothermic phase change. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 11991–12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseman, G.A.; Molnar, P. Gravitational (Rayleigh-Taylor) instability of a layer with non-linear viscosity and convective thinning of continental lithosphere. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 128, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rayleigh, L. Investigation of the character of an incompressible heavy fluid of variable density. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. J. 1997, 1, 170–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The instability of liquid surfaces when accelerated in a direction perpendicular to their planes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Set. 1950, 201, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Brueckner, H.K. Sinking intrusion model for the emplacement of garnet-bearing peridotites into continent collision orogens. Geology 1998, 26, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mével, C. Serpentinization of abyssal peridotites at mid-ocean ridges. C. R. Geosci. 2003, 335, 825–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, J.E.; Edmond, H.N. Ultraslow-Spreading ridges rapid paradigm changes. Oceanography 2007, 20, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannat, M.; Sauter, D.; Lavier, L.; Bickert, M.; Momoh, E.; Leroy, S. On spreading modes and magma supply at slow and ultraslow mid-ocean ridges. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 519, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Singh, S.C. Seismic evidence of a two-layer lithospheric deformation in the Indian Ocean. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirth, G.; Kohlstedt, D.L. Water in the oceanic upper mantle; implications for rheology, melt extraction and the evolution of the lithosphere. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 144, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, P. Recent Studies of Serpentinite Occurrences in the Oceans: Mantle-Ocean Interactions in the Plate Tectonic Cycle. Geochemistry 2002, 62, 257–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, N.I. The Abundance of Serpentinites in the Oceanic Crust. J. Geol. 1972, 80, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramberg, H. Model Experimentation of the Effect of Gravity on Tectonic Processes. Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 1967, 14, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoff, B.; Wojtal, F. Displacement control of geological structures. J. Struct. Geol. 1999, 21, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobkovsky, L.I.; Ismail-Zadeh, A.T.; Krasovsky, S.S.; Kuprienko, P.Y.; Cloetingh, S. Gravity anomalies and possible formation mechanism of the Dnieper–Donets Basin. Tectonophysics 1996, 268, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wong, T.-F. Network modeling of the evolution of permeability and dilatancy in compact rock. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 2963–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, M.R. The solid-state flow of polymineralic rocks. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 8647–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.G. Plate tectonic emplacement of Upper mantle peridotites along continental edges. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, T.J.G. Serpentinization faults and their role on the tectonics of slow-spreading ridges. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 11616–11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail-Zadeh, A.T.; Panza, G.F.; Naimark, B.M. Stress in the Descending Relic Slab beneath Vrancea Region, Romania. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2000, 157, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.; Bonjer, K.-P.; Bock, G.; Cornea, I.; Radu, C.; Enescu, D.; Jianu, D.; Nourescu, A.; Merkler, G.; Moldoveanu, T.; et al. The Romanian Earthquake of March 4, 1977. II. Aftershocks and Migration of Seismic Activity. Tectonophysics 1979, 53, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccani, E. A new method of discriminating different types of post-Archean ophiolitic basalts and their tectonic significance using Th-Nb and Ce-Dy-Yb systematics. Geosci. Front. 2015, 6, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirschmann, M.M.; Stolper, E.M. A possible role for garnet pyroxenite in the origin of the garnet signature in MORB. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 124, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmann, M.M.; Kogiso, T.; Baker, M.B.; Stolper, E.M. Alkalic magmas generated by partial melting of garnet pyroxenite. Geology 2003, 31, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffione, M.; Thieulot, C.; van Hinsbergen, D.J.J.; Morris, A.; Plümper, O.; Spakman, W. Dynamics of intraoceanic subduction initiation: 1. Oceanic detachment fault inversion and the formation of supra-subduction zone ophiolites. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palin, R.M.; Santosh, M.; Cao, W.; Li, S.S.; Hernández-Uribe, D.; Parsons, A. Secular change and the onset of plate tectonics on Earth. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Calcic Pyroxene | Ca-Poor Pyroxene | ||||||
| wt% | Cpx a | Cpx b | Cpx c | Cpx d | Opx a | Opx b | OpxK1 |
| SiO2 | 49.52 | 49.51 | 48.48 | 49.40 | 51.23 | 52.86 | 49.71 |
| TiO2 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.59 | 1.75 | 0.54 | 0.09 | 0.00 |
| Al2O3 | 9.27 | 9.15 | 9.52 | 9.30 | 6.89 | 7.00 | 10.28 |
| FeO* | 7.78 | 7.75 | 7.81 | 7.55 | 12.53 | 12.71 | 12.95 |
| MnO | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.00 |
| MgO | 13.68 | 14.16 | 13.54 | 13.76 | 27.20 | 25.55 | 24.90 |
| CaO | 16.73 | 16.35 | 17.81 | 16.77 | 1.35 | 1.88 | 2.14 |
| Na2O | 1.45 | 1.51 | 1.41 | 1.50 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100.02 | 99.99 | 100.24 | 100.02 | 100.11 | 100.25 | 99.98 |
| Garnet | Kel(K) Plag | ||||||
| wt% | Grt a | Grt b | Grt c | Grt d | Grt e | RASTER | (K1) |
| SiO2 | 42.97 | 44.24 | 44.02 | 42.09 | 41.99 | 41.38 | 45.16 |
| TiO2 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.00 |
| Al2O3 | 20.48 | 19.77 | 20.94 | 22.78 | 23.50 | 18.01 | 34.01 |
| FeO | 12.79 | 12.52 | 11.28 | 12.04 | 12.05 | 16.16 | 1.55 |
| MnO | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.57 | 0.00 |
| MgO | 17.50 | 16.99 | 16.09 | 16.17 | 15.01 | 22.23 | 1.06 |
| CaO | 5.31 | 5.34 | 6.57 | 5.98 | 6.33 | 1.10 | 17.23 |
| Na2O K2O Total | 0.00 0.00 100.03 | 0.00 0.00 99.94 | 0.00 0.00 100.08 | 0.00 0.00 99.94 | 0.00 0.00 99.44 | 0.12 0.02 100.28 | 0.74 0.00 99.75 |
| Spinel | Whole Rock (S) | ||||||
| wt% | Spl a | Spl b | Spl c | S 1 | S 2 | S 3 | S[Av] |
| SiO2 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 40.64 | 41.71 | 42.35 | [41.54] |
| TiO2 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 0.33 | 1.53 | 1.48 | 1.48 | [1.50] |
| Al2O3 | 57.17 | 57.20 | 61.23 | 16.01 | 16.19 | 15.77 | [15.99] |
| FeO | 23.08 | 23.71 | 19.33 | 9.85 | 9.73 | 9.43 | [9.65] |
| MnO | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.13 | [0.12] |
| MgO | 17.68 | 18.03 | 18.13 | 15.12 | 14.35 | 13.48 | [14.45] |
| CaO | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12.59 | 13.15 | 12.31 | [12.70] |
| Na2O | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.06 | 1.06 | 1.10 | [1.07] |
| K2O | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | [0.05] |
| P2O5 Total | 0.00 99.44 | 0.00 100.00 | 0.00 99.32 | 0.06 96.96 | 0.09 97.89 | 0.13 96.29 | [0.10] |
| S | Grt1 | Grt2 | Grt3 | Kel1 | Kel2 | Kel3 | Cpx1 | Cpx2 | Opx1 | Opx2 | Spl1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppm | ||||||||||||
| Li | <10 | <1.5 | <1.5 | <1.5 | 30.88 | 20.04 | 4.05 | 2.31 | 2.46 | 3.66 | 4.28 | 5.44 |
| Be | <5 | <0.8 | <0.8 | <0.8 | 8.02 | 11.92 | 1.23 | <0.6 | 0.65 | <0.6 | <0.6 | 0.00 |
| B | nd | <1.14 | <1.06 | <1.15 | 68.03 | 33.20 | 8.09 | <0.72 | <0.80 | <1.63 | <1.66 | 0.00 |
| Sc | 35 | 105.36 | 104.55 | 105.07 | 1570.10 | 1229.39 | 245.62 | 34.95 | 35.26 | 35.77 | 35.56 | 1.06 |
| Ti | 9000 | 3401 | 3395 | 3285 | 4848 | 3484 | 7706 | 11726 | 12068 | 7813 | 8085 | 9313 |
| V | 353 | 139.68 | 138.80 | 136.86 | 2145.77 | 1402.37 | 360.36 | 393.16 | 400.70 | 448.88 | 461.18 | 1377 |
| Cr | 94.33 | 32.04 | 30.24 | 32.74 | 524.61 | 313.22 | 73.45 | 24.86 | 25.12 | 39.03 | 38.35 | 626 |
| Co | 85.27 | 76.58 | 77.75 | 78.95 | 1167.63 | 796.35 | 192.5 | 47.97 | 48.96 | 223.42 | 228.90 | 717 |
| Ni | 252 | 20.51 | 19.29 | 19.44 | 607.71 | 339.23 | 67.35 | 96.90 | 102.11 | 395.76 | 412.48 | 2080 |
| Cu | 44.67 | 1.81 | 0.71 | 1.29 | 338.77 | 265.57 | 26.96 | 4.69 | 1.81 | 2.10 | 1.88 | 2.55 |
| Zn | 156 | 37.65 | 37.60 | 36.32 | 967.25 | 809.32 | 131.14 | 41.18 | 42.30 | 216.35 | 211.58 | 31.06 |
| Rb | 2.55 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 49.31 | 14.86 | 26.56 | 0.09 | 0.02 | <0.03 | <0.02 | 0.00 |
| Sr | 185.67 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 357.09 | 257.55 | 238.9 | 87.53 | 87.26 | 1.54 | 1.56 | 0.10 |
| Y | 19.67 | 72.83 | 73.72 | 71.10 | 829.99 | 643.10 | 148.03 | 15.53 | 15.01 | 3.19 | 3.22 | 0.00 |
| Zr | 44.10 | 45.92 | 43.93 | 42.41 | 564.90 | 455.80 | 104.09 | 40.50 | 39.76 | 10.48 | 11.30 | 0.16 |
| Nb | 3.67 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 2.22 | 0.63 | 0.063 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| Cs | 0.73 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 5.28 | 1.80 | 0.319 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.00 |
| Ba | 157.33 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 75.49 | 41.93 | 1908.09 | 0.60 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| La | 5.53 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.053 | 3.36 | 3.22 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| Ce | 14.30 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 2.70 | 2.02 | 0.253 | 12.60 | 12.66 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.00 |
| Pr | 2.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.104 | 2.12 | 2.16 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| Nd | 10.17 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.16 | 8.56 | 5.64 | 1.27 | 11.79 | 11.90 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.00 |
| Sm | 3.13 | 1.33 | 1.27 | 1.16 | 9.59 | 7.65 | 1.38 | 4.03 | 3.62 | <0.1 | 0.27 | 0.00 |
| Eu | 1.35 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 1.37 | 0.54 | 1.30 | 1.24 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.00 |
| Gd | 3.84 | 4.41 | 4.10 | 3.83 | 34.69 | 30.01 | 7.12 | 4.23 | 3.97 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.00 |
| Tb | 0.59 | 1.12 | 1.14 | 1.08 | 9.25 | 8.56 | 1.89 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| Dy | 3.96 | 10.63 | 10.04 | 10.08 | 103.42 | 89.62 | 20.29 | 3.61 | 3.56 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 0.00 |
| Ho | 0.76 | 2.72 | 2.64 | 2.69 | 31.61 | 25.19 | 5.55 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| Er | 2.05 | 9.08 | 9.03 | 8.71 | 114.58 | 91.85 | 20.53 | 1.48 | 1.39 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.00 |
| Tm | 0.31 | 1.55 | 1.47 | 1.45 | 19.91 | 13.60 | 3.21 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| Yb | 1.77 | 10.89 | 11.31 | 9.87 | 145.54 | 104.14 | 25.05 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.00 |
| Lu | 0.36 | 1.65 | 1.79 | 1.73 | 24.03 | 18.84 | 3.99 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| Hf | 1.67 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 11.17 | 6.78 | 1.87 | 1.53 | 1.51 | 0.31 | 0.48 | 0.12 |
| Ta | 0.00 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.11 | <0.07 | <0.006 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.03 | <0.02 | 0.00 |
| Pb | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 2.27 | 1.59 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.13 | <0.09 | <0.16 | 0.29 |
| Th | 0.33 | <0.02 | <0.01 | <0.02 | <0.20 | 0.44 | <0.016 | 0.06 | 0.04 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.00 |
| U | 0.13 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.03 | <0.25 | <0.23 | 0.021 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.03 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scribano, V.; Carbone, S. Convective Instability in Intraplate Oceanic Mantle Caused by Amphibolite-Derived Garnet-Pyroxenites—A Xenolith Perspective (Hyblean Plateau, Sicily). Geosciences 2020, 10, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090378
Scribano V, Carbone S. Convective Instability in Intraplate Oceanic Mantle Caused by Amphibolite-Derived Garnet-Pyroxenites—A Xenolith Perspective (Hyblean Plateau, Sicily). Geosciences. 2020; 10(9):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090378
Chicago/Turabian StyleScribano, Vittorio, and Serafina Carbone. 2020. "Convective Instability in Intraplate Oceanic Mantle Caused by Amphibolite-Derived Garnet-Pyroxenites—A Xenolith Perspective (Hyblean Plateau, Sicily)" Geosciences 10, no. 9: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090378
APA StyleScribano, V., & Carbone, S. (2020). Convective Instability in Intraplate Oceanic Mantle Caused by Amphibolite-Derived Garnet-Pyroxenites—A Xenolith Perspective (Hyblean Plateau, Sicily). Geosciences, 10(9), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090378





