Quaternary Coastal Landscape Evolution and Sea-Level Rise: An Example from South-East Sicily
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
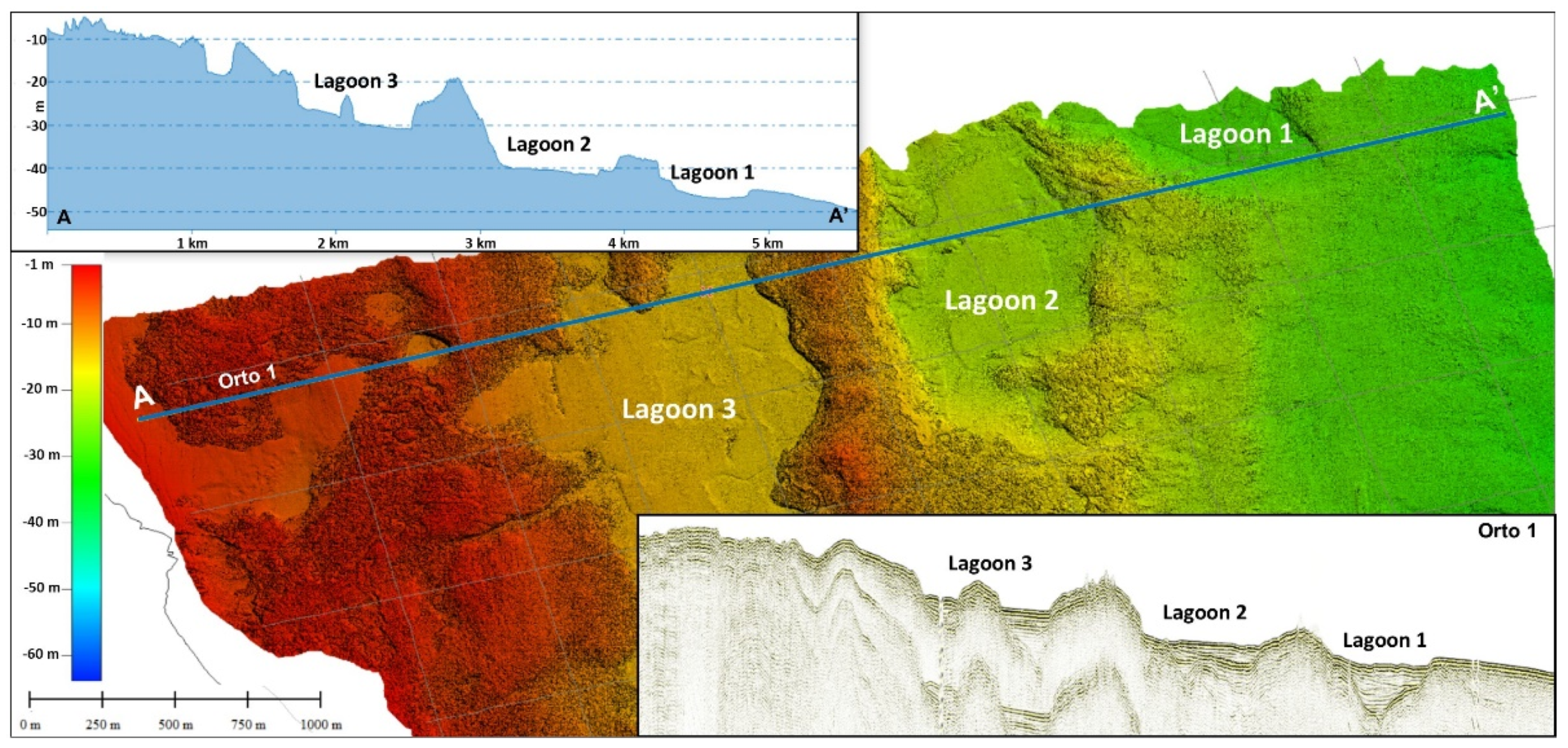
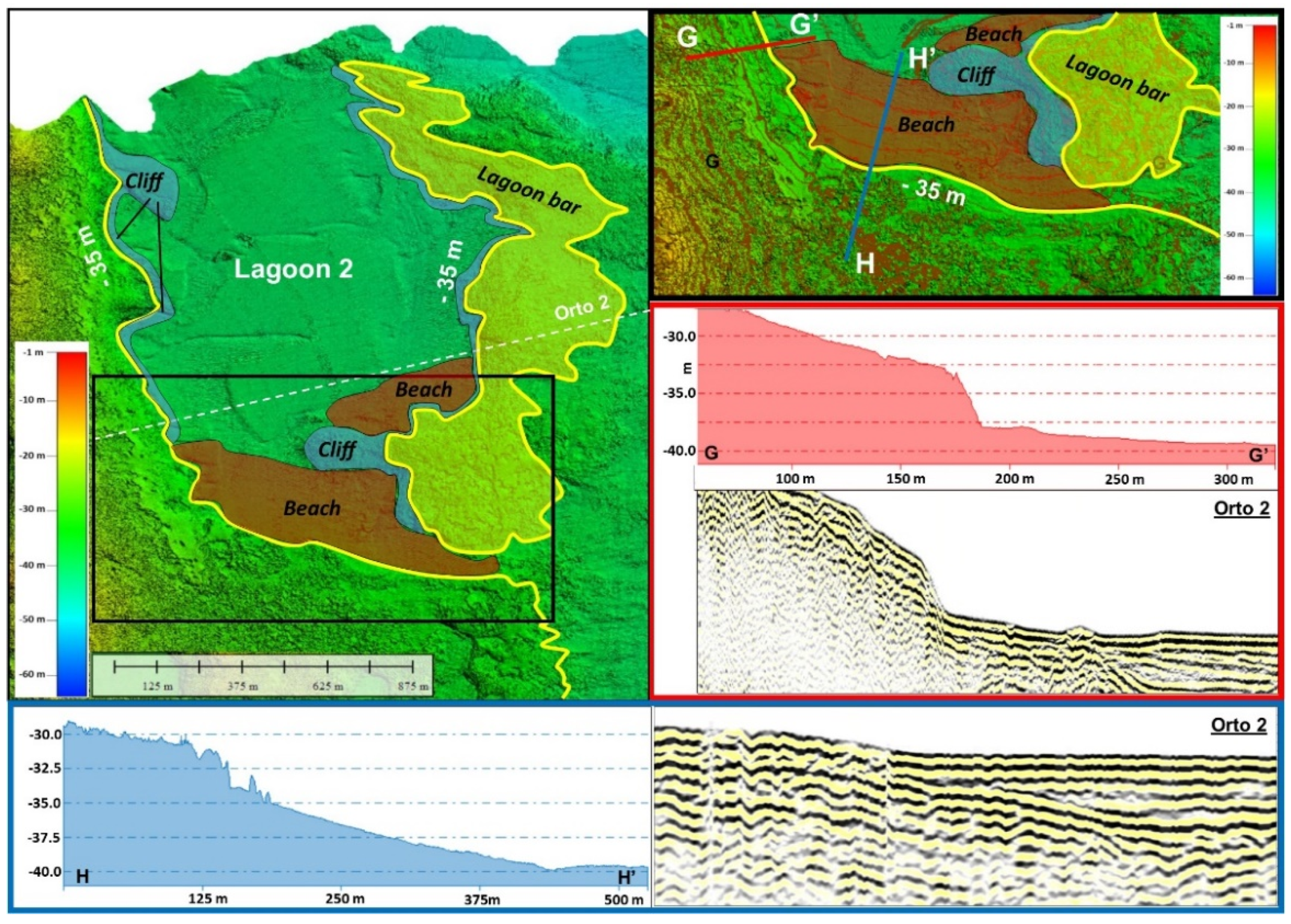
4.1. Northern Sector
4.2. Southern Sector
5. Discussion
5.1. Northern Sector: Barrier–Lagoon Systems
5.2. Southern Sector: Starved Area
5.3. Karst and Present Day Geomorphological Features
6. Conclusions
- Through the integrated interpretation of bathymetric (Multibeam data) and seismic-stratigraphic data (Sparker seismic profiles), we have provided a reconstruction of the depositional history of the offshore sector of the Marzamemi village, during the last sea-level rise. The main result of our analysis is that the rate of sediment supply—connected with the differential development of the hydrographic networks in the northern and southern area—and the paleo-topography control the geomorphological variability of transgressive depositional environments between the northern and southern sectors;
- The northern sector is characterized by the development of three barrier–lagoon systems whose position marks the main steps of the last sea level rise. The lagoons are bounded seaward by two ridges with different genetic meanings: the first, seawards, is exclusively associated with the depositional evolution of a typical barrier system; the second, landwards, represents a structural high connected mainly to the paleo-topography of the area.
- The southern sector is characterized by the incisions corresponding to paleo-rivers, whose path is strongly conditioned by the paleo-topography inheritance.
- In the southern sector, the relatively scarce sediment supply rate did not heal the morphology of the paleo-rivers. Conversely, in the northern sector, the considerable sediment supply rate has buried most of the paleo-rivers, as confirmed by the available seismic profiles.
- Karst processes have a significant impact on the development of transgressive bodies and on the features of the calcarenite seabed, similar to those observed in the onshore portions of the Marzamemi hinterland (Vendicari Reserve).
- The different depositional setting between the northern and southern sectors also controls the distribution of organisms, with a greater concentration of Posidonia Oceanica meadows in the southern sector, where the rocky substrate outcrops more extensively.
- The shallow incisions within the barrier–lagoon systems and the development of bedforms, reveal the present-day deep current activity whose circulation depends on the distribution of the transgressive bodies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Storms, J.E.A.; Weltje, G.J.; Terra, G.J.; Cattaneo, A.; Trincardi, F. Coastal dynamics under conditions of rapid sea-level rise: Late Pleistocene to Early Holocene evolution of barrier–lagoon systems on the northern Adriatic shelf (Italy). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swift, D.J.P. Coastal erosion and transgressive stratigraphy. J. Geol. 1968, 76, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belknap, D.F.; Kraft, J.C. Preservation potential of transgressive coastal lithosomes on the U.S. Atlantic shelf. Mar. Geol. 1981, 32, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummedal, D.; Swift, D.J.P. Transgressive stratigraphy at sequence-bounding unconformities: Some principles derived from Holocene and Cretaceous examples. In Sea Level Fluctuation and Coastal Evolution; Nummedal, D., Pilkey, O.H., Howard, J.D., Eds.; Special Publication; SEPM: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1987; pp. 241–260. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, D.J.P.; Phillips, S.; Thorne, J.A. Sedimentation on Continental Margins, IV: Lithofacies and depositional systems. In Shelf Sand and Sand-Stone Bodies: Geometry, Facies, and Sequence Stratigraphy; Swift, D.J.P., Ed.; Special Publication, International Association for Sediment; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; Volume 14, pp. 89–152. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, A.; Steel, R.J. Transgressive deposits: A review of their variability. Earth Sci. Rev. 2003, 62, 187–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Barrier Island. In Encyclopedia of Estuaries. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Kennish, M.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kjerfve, B. Coastal lagoons. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Kjerfve, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.; Dalrymple, R.; Zaitlin, B.A. Classification of clastic coastal depositional environments. Sediment. Geol. 1992, 80, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.J.; List, J.H.; Williams, S.J.; Stolper, D. Complexities in barrier island response to sea level rise: Insights from numerical model experiments, North Carolina Outer Banks. J. Geoph. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, F03004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruggieri, R.; De Waele, J. Lower-to Middle Pleistocene flank margin caves at Custonaci (Trapani, NW Sicily) and their relation with past sea levels. Acta Carsologica 2014, 43, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canora, F.; Fidelibus, D.; Spilotro, G. Coastal and inland karst morphologies driven by sea level stands: A GIS based method for their evaluation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, M.M. Karst Landforms; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; p. 362. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, J.N. Karst Geomorphology, 2nd ed.; Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 1985; p. 293. [Google Scholar]
- James, N.P.; Choquette, P.W. Paleokarst; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.N. Groundwater processes in karst terranes. In Groundwater Geomorphology: The Role of Subsurface Water in Earth Surface Processes and Landforms; Higgins, C.G., Coates, D.R., Eds.; Spec. Paper 252; The Geological Society of America, Inc.: Boulder, CO, USA, 1990; pp. 177–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; p. 562. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia, F.J.; Geremia, F.; Privitera, S.; Amore, C. The probable karst origin and evolution of the Vendicari coastal lake system (SE Sicily, Italy)/Verjetni Kraski Izvor In Razvoj Obalnega Jeserskega Sistema Vendicari (Jv Sicilija, Italija). Acta Carsologica 2014, 43, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Gams, I. The polje: The problem of its definition. Z. Geomorph. 1978, 22, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Julian, M.; Nicod, J. Les karsts des Alpes du Sud et de Provence. Z. Geomorph. 1989, 75, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia, F.J.; Gutiérrez, F.; Gutiérrez, M. The Jiloca karst polje-tectonic graben (Iberian Range, NE Spain). Geomorphology 2003, 52, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, C.; Madonia, G.; Parise, M.; Vattano, M. Karst of Sicily and its conservation. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2012, 74, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distefano, S.; Gamberi, F.; Baldassini, N.; Di Stefano, A. Quaternary Evolution of Coastal Plain in Response to Sea-Level Changes: Example from South-East Sicily (Southern Italy). Water 2021, 13, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burollet, P.F.; Mugniot, G.M.; Sweeney, P. The geology of the Pelagian Block: The margins and basins of Southern Tunisia and Tripolitania. In The Ocean Basins and Margins; Nairn, A., Kanes, W., Stelhi, F.G., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lentini, F.; Carbone, S.; Catalano, S. Main structural domains of the central mediterranean region and their Neogene tectonic evolution. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 1994, 36, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, S.; Romagnoli, G.; Tortorici, G. Kinematics and dynamics of the Late Quaternary rift-flank deformation in the Hyblean Plateau (SE Sicily). Tectonophysics 2010, 486, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, F.; Carbone, S. Geologia della Sicilia-Geology of Sicily. Mem. Descr. Carta Geol. Ital. 2014, 95, 31–98. [Google Scholar]
- Argnani, A.J. The Gela nappe: Evidence of accretionary mélange in the Maghrebian foredeep of Sicily. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1989, 38, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, F.; Carbone, S.; Grasso, M.; Invernizzi, G.; Lentini, F.; Longaretti, G.; Merlini, S.; Mostardini, F. Sicilia orientale: Profilo geologico Nebrodi—Iblei. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1989, 38, 429–458. [Google Scholar]
- Finetti, I.R.; Lentini, F.; Carbone, S.; Del Ben, A.; Di Stefano, A.; Guarnieri, P.; Pipan, M.; Prizzon, A. Crustal tectonostratigraphy and geodynamics of the Southern Apennines from CROP and other integrating seismic and geological data. In CROP Project: Deep Seismic Exploration of the Central Mediterranean and Italy; Finetti, I.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 225–261. [Google Scholar]
- Distefano, S.; Gamberi, F.; Di Stefano, A. Stratigraphic and structural reconstruction of an offshore sector of the Hyblean Foreland ramp (southern Italy). Ital. J. Geosci. 2019, 138, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisetti, F.; Vezzani, L. The structural features of the Hyblean Plateau and the Mount Judica area (South-Eastern Sicily): A microtectonic contribution to the deformational history of the Calabrian Arc. Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1980, 99, 55–102. [Google Scholar]
- Grasso, M.; Lentini, F. Sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the eastern Hyblean Plateau (Southeast Sicily) during Late Cretaceous to Quaternary time. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1982, 39, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedley, H.M.; Cugno, G.; Grasso, M. Gravity slide and resedimentation processes in a Miocene carbonate ramp, Hyblean Plateau, southeastern Sicily. Sediment. Geol. 1992, 79, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, G.; Catalano, S.; Pavano, F.; Tortorici, G. Geological map of the Tellaro River Valley (Hyblean Foreland, southeastern Sicily, Italy). J. Maps 2015, 11, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carveni, P.; Romano, R.; Capodicasa, A.; Tricomi, S. Geologia dell’area vulcanica di Capo Passero (Sicilia sud-orientale). Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1991, 47, 431–447. [Google Scholar]
- Groppelli, G.; Pasquarè, F.A. Nuovi contributi alla ricostruzione della stratigrafia vulcanica dell’area di Capo Passero, Siciliasud-orientale, nel quadro del vulcanismo del Cretacico superiore nel Plateau Ibleo. Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2004, 123, 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- La Rosa, N. Note esplicative della carta Geologica d’Italia. Foglio 652 “Capo Passero” alla scala 1:50,000. Serv. Geol. Ital. 1974, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Colacicchi, R. Geologia del territorio di Pachino. Geol. Roman. 1963, 2, 343–404. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, S.; Lentini, F.; Pistorio, A. Il geosito “Calcari a rudiste e coralli del Cretacico superiore di Capo Passero-Pachino” (Monti Iblei, Sicilia SE). Geol. Ambiente 2016, 3, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gennari, R.; Iaccarino, S.M.; Di Stefano, A.; Sturiale, G.; Cipollari, P.; Manzi, V.; Roveri, M.; Cosentino, D. The Messinian- Zanclean boundary in the Northern Apennine. Stratigraphy 2008, 5, 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- De Visser, J.P.; Ebbing, J.H.J.; Gudjonsson, L.; Hilgen, F.J.; Jorissen, F.J.; Verhallen, P.J.J.M.; Zevenboom, D. The origin of rhythmic bedding in the Pliocene Trubi Formation of Sicily, southern Italy. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1989, 69, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riforgiato, F.; Foresi, L.M.; Di Stefano, A.; Aldinucci, M.; Pelosi, N.; Mazzei, R.; Salvatorini, G.; Sandrelli, F. The Miocene/Pliocene boundary in the Mediterranean area: New insights from a high-resolution micropaleontological and cyclostratigraphic study (Cava Serredi section, Central Italy). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2011, 305, 310–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taviani, M.; Angeletti, L.; Campiani, E.; Ceregato, A.; Foglini, F.; Maselli, V.; Trincardi, F. Drowned karst landscape offshore the Apulian margin (southern Adriatic Sea, Italy). J. Cave Karst Stud. 2012, 74, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distefano, S.; Gamberi, F.; Baldassini, N.; Di Stefano, A. Neogene stratigraphic evolution of a tectonically controlled continental shelf: The example of the Lampedusa Island. Ital. J. Geosci. 2019, 138, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rende, S.F.; Bosman, A.; Di Mento, R.; Bruno, F.; Lagudi, A.; Irving, A.D.; Cellini, E. Ultra-High-Resolution Mapping of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile Meadows through Acoustic, Optical Data and Object-based Image Classification. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercilla, G.; Díaz, J.I.; Alonso, B.; Farran, M. Late Pleistocene-Holocene sedimentary evolution of the northern Catalonia continental shelf (northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Cont. Shelf Res. 1995, 15, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercilla, G.; Alonso, B.; Baraza, J. Sedimentary evolution of the northwestern Alboran Sea during the Quaternary. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1992, 12, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farràn, M.; Maldonado, A. The Ebro continental shelf: Quaternary seismic stratigraphy and growth patterns. Mar. Geol. 1990, 95, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzì, L.; Anfuso, G.; Manno, G.; Distefano, S.; Urso, S.; Chiarella, D.; Di Stefano, A. Shoreline evolution and environmental changes at the NW area of the Gulf of Gela (Sicily, Italy). Land 2021, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, C.H. Sea level rise effects on shoreline position. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1985, 111, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, D.M.; Fenster, M.S.; Britt, A.A.; Buynevich, I.V. Coastal impacts due to sea-level rise. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2008, 36, 601–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- List, J.H.; Sallenger, A.H.; Hansen, M.E.; Jaffe, B.E. Accelerated relative sea-level rise and rapid coastal erosion: Testing a causal relationship for the Louisiana barrier islands. Mar. Geol. 1997, 140, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M. Geomorphology of the Canale di Pirro karst polje (Apulia, southern Italy). Z. Geomorph. Suppl. 2006, 147, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia, F.J.; Gutiérrez, F.; Gutiérrez, M. Origin and evolution of Gallocanta polje. Z. Geomorph. 2002, 46, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Chiantore, M.; Montefalcone, M.; Parravicini, V.; Rovere, A. Mediterranean Sea biodiversity between the legacy from the past and a future of change. In Life in the Mediterranean Sea: A Look at Habitat Changes; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Chapter 1; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Milliman, J.D.; Gao, S.; Cheng, P. Holocene development of the Yellow River’s subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. 2004, 209, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.W.; Chivoiu, B.; Enwright, N.M. Sea-Level Rise Modeling Handbook: Resource Guide for Coastal Land Managers, Engineers, and Scientists; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Lafayette, LA, USA, 2015.














Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Distefano, S.; Gamberi, F.; Borzì, L.; Di Stefano, A. Quaternary Coastal Landscape Evolution and Sea-Level Rise: An Example from South-East Sicily. Geosciences 2021, 11, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11120506
Distefano S, Gamberi F, Borzì L, Di Stefano A. Quaternary Coastal Landscape Evolution and Sea-Level Rise: An Example from South-East Sicily. Geosciences. 2021; 11(12):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11120506
Chicago/Turabian StyleDistefano, Salvatore, Fabiano Gamberi, Laura Borzì, and Agata Di Stefano. 2021. "Quaternary Coastal Landscape Evolution and Sea-Level Rise: An Example from South-East Sicily" Geosciences 11, no. 12: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11120506
APA StyleDistefano, S., Gamberi, F., Borzì, L., & Di Stefano, A. (2021). Quaternary Coastal Landscape Evolution and Sea-Level Rise: An Example from South-East Sicily. Geosciences, 11(12), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11120506








