A Hydrogeologic Framework for Understanding Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in a Watershed System in the Willamette Basin in Western Oregon, USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
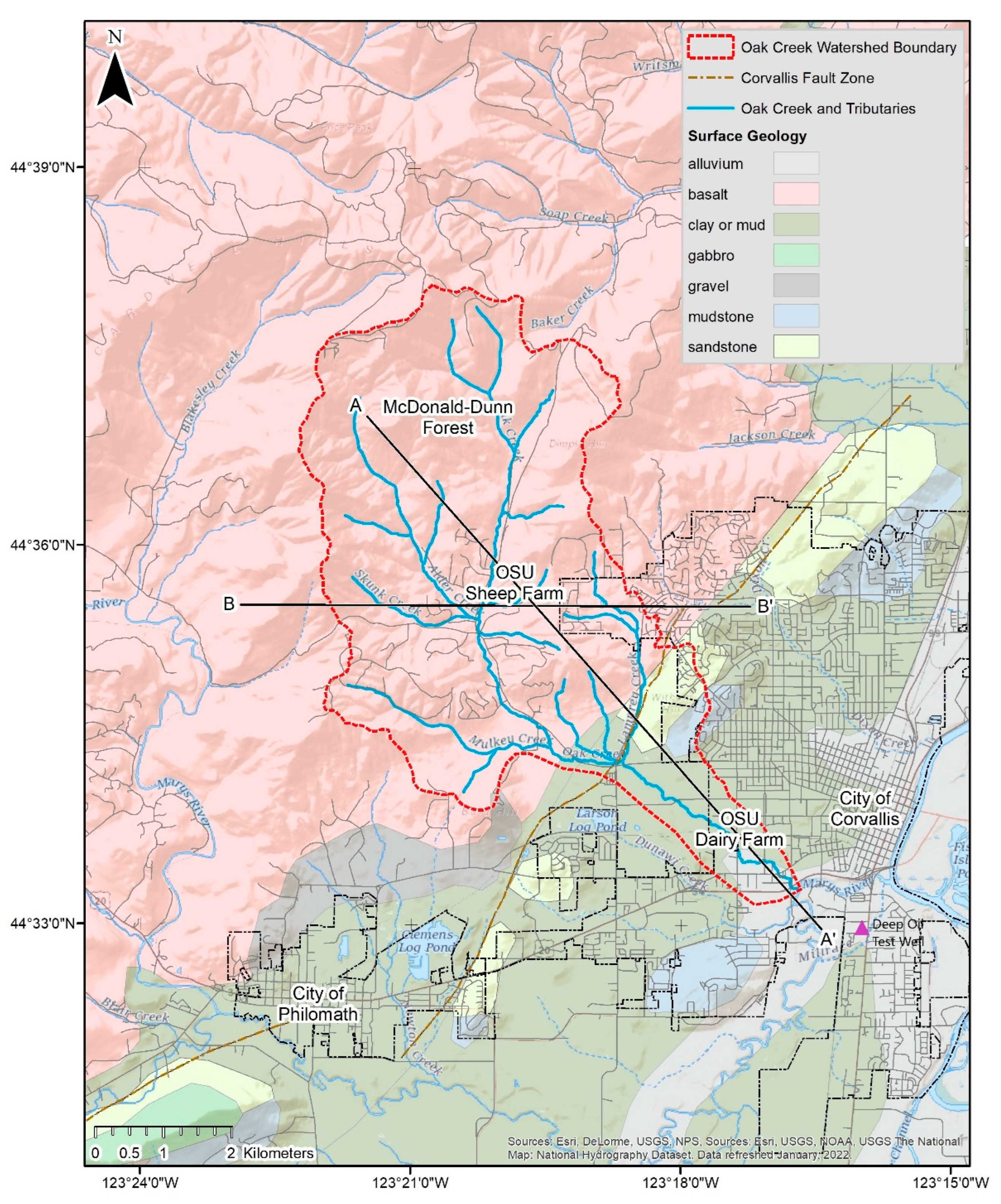
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Hydrogeologic Framework
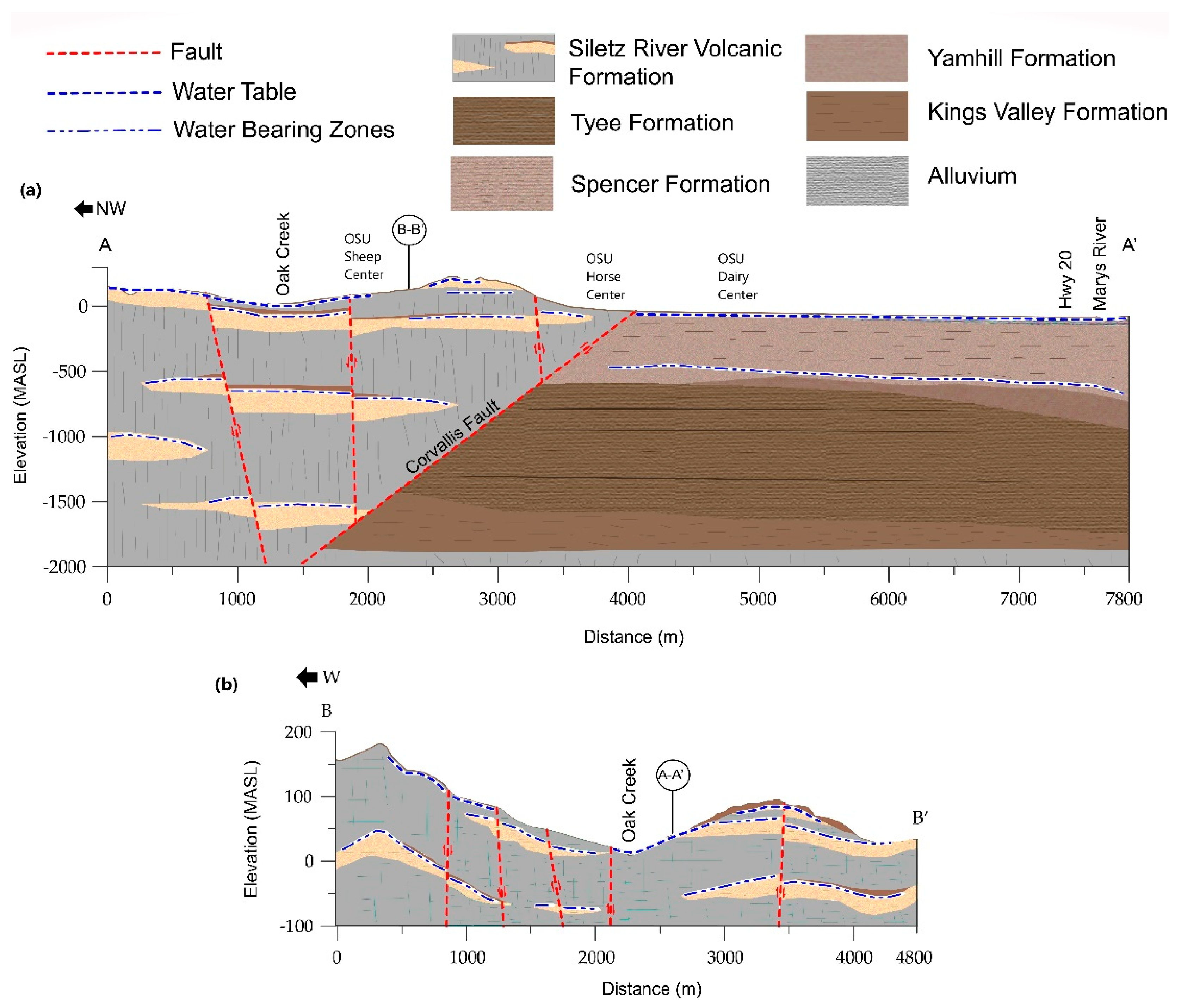
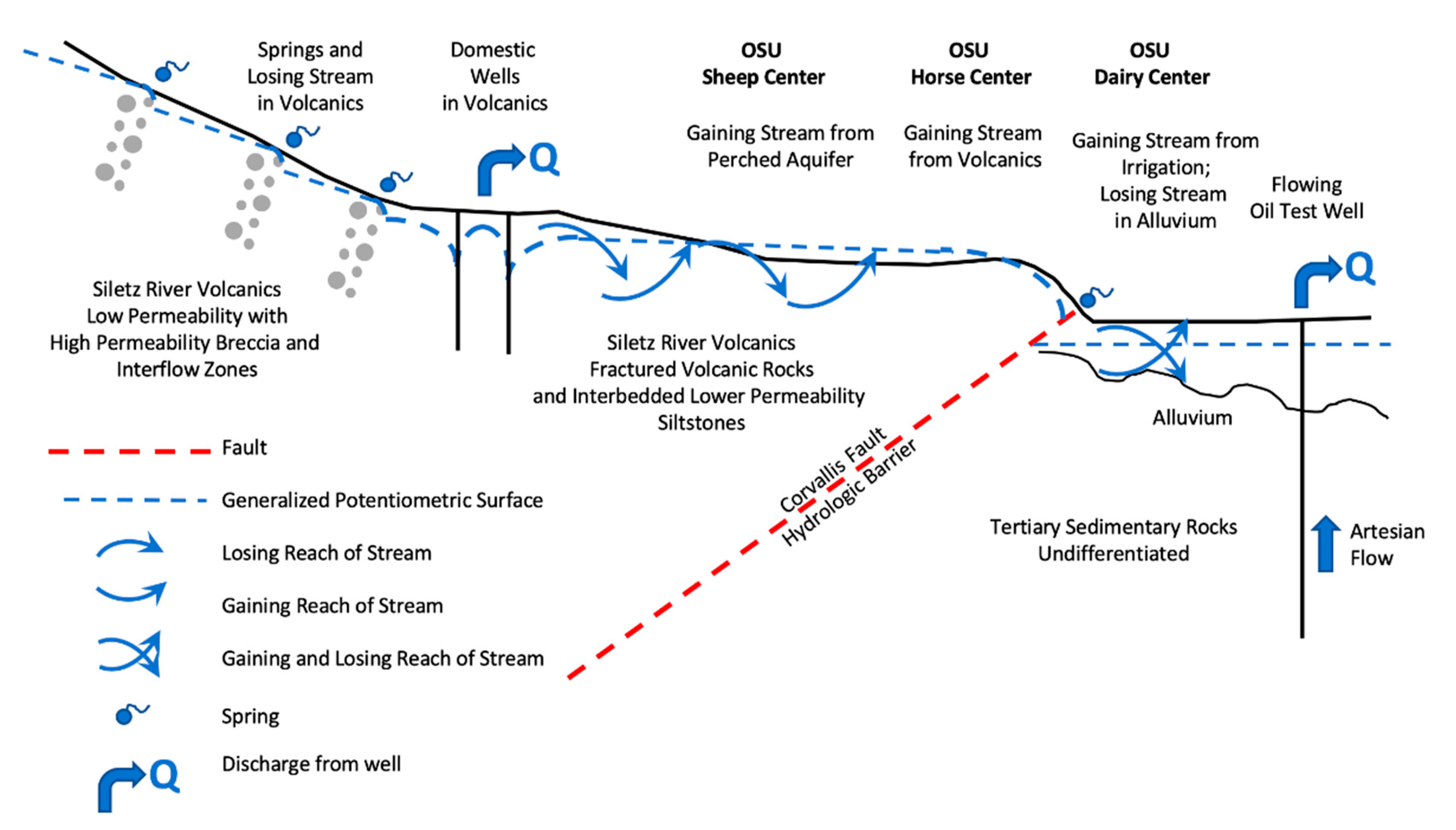
2.2.1. Site Geologic Conditions Map and Hydrogeologic Cross-Sections
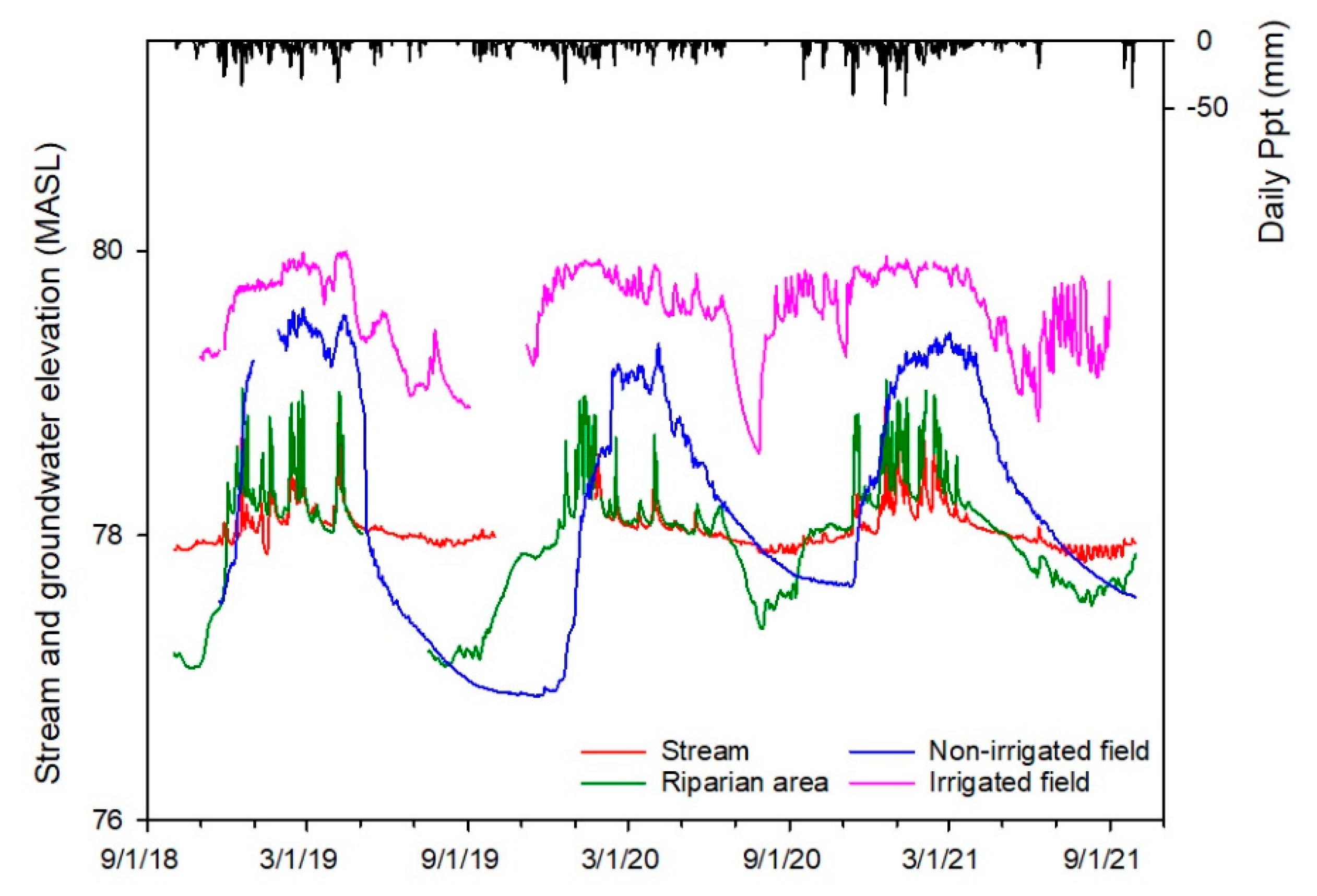
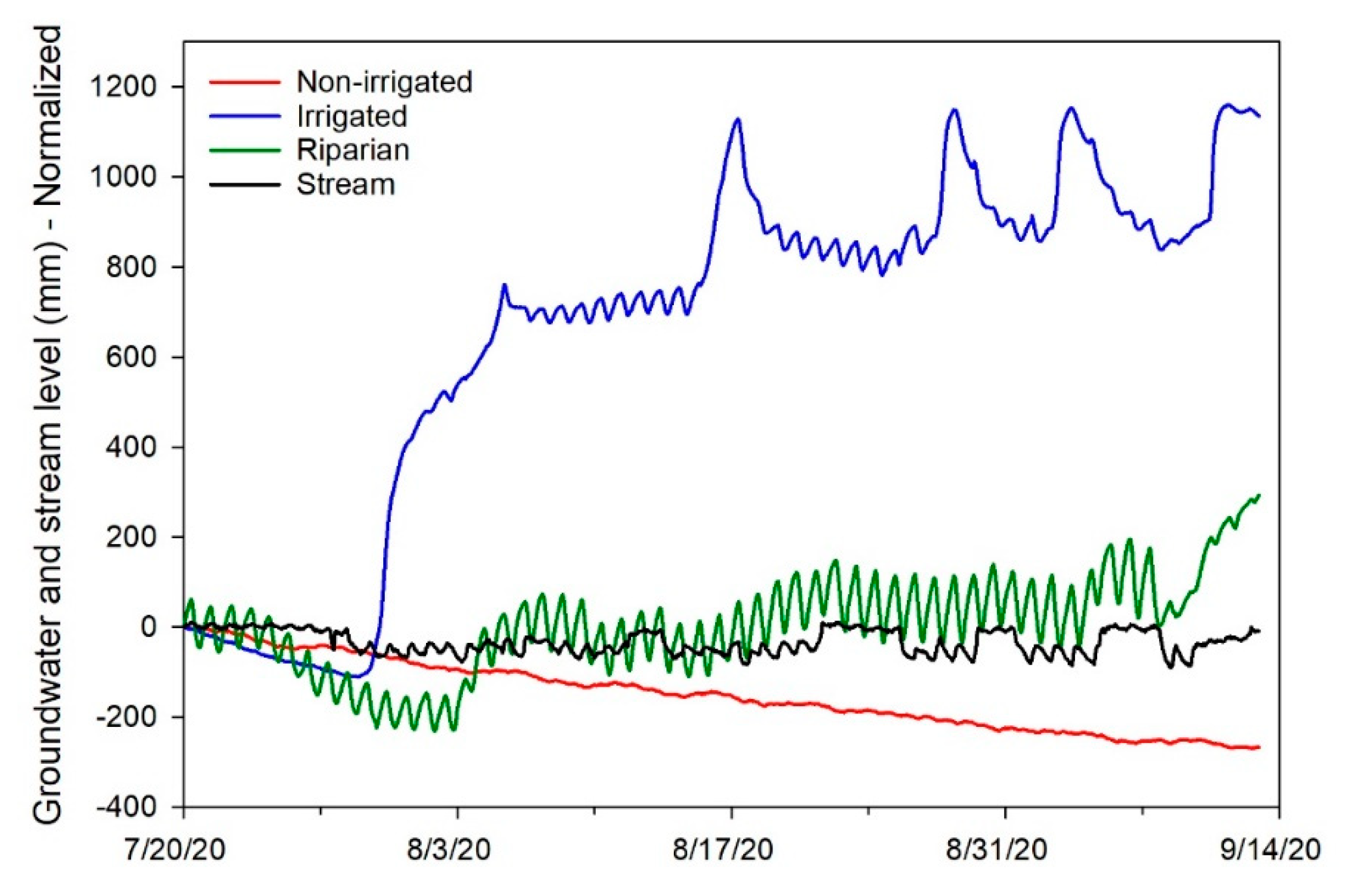
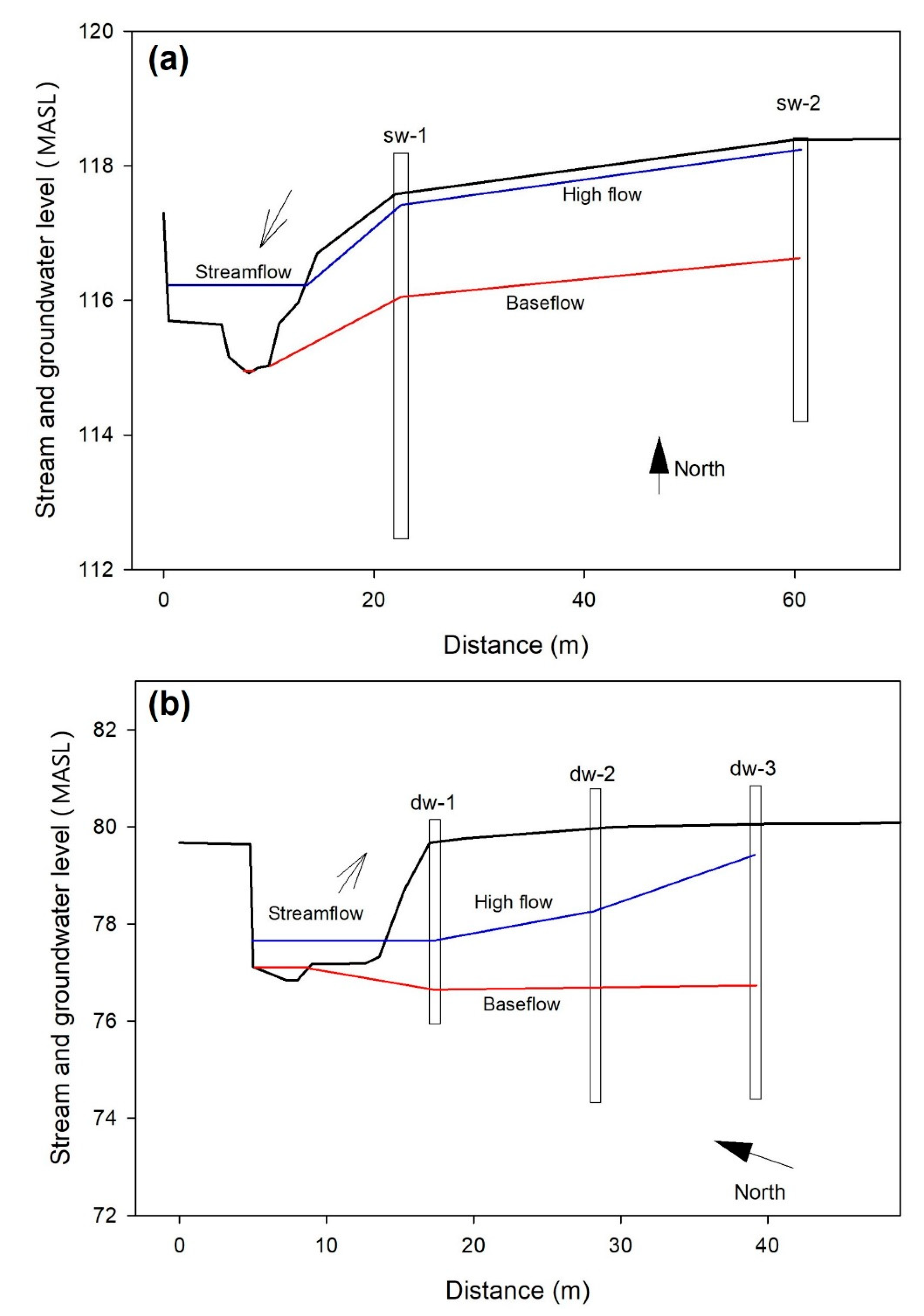
2.2.2. Stream-Aquifer Interactions
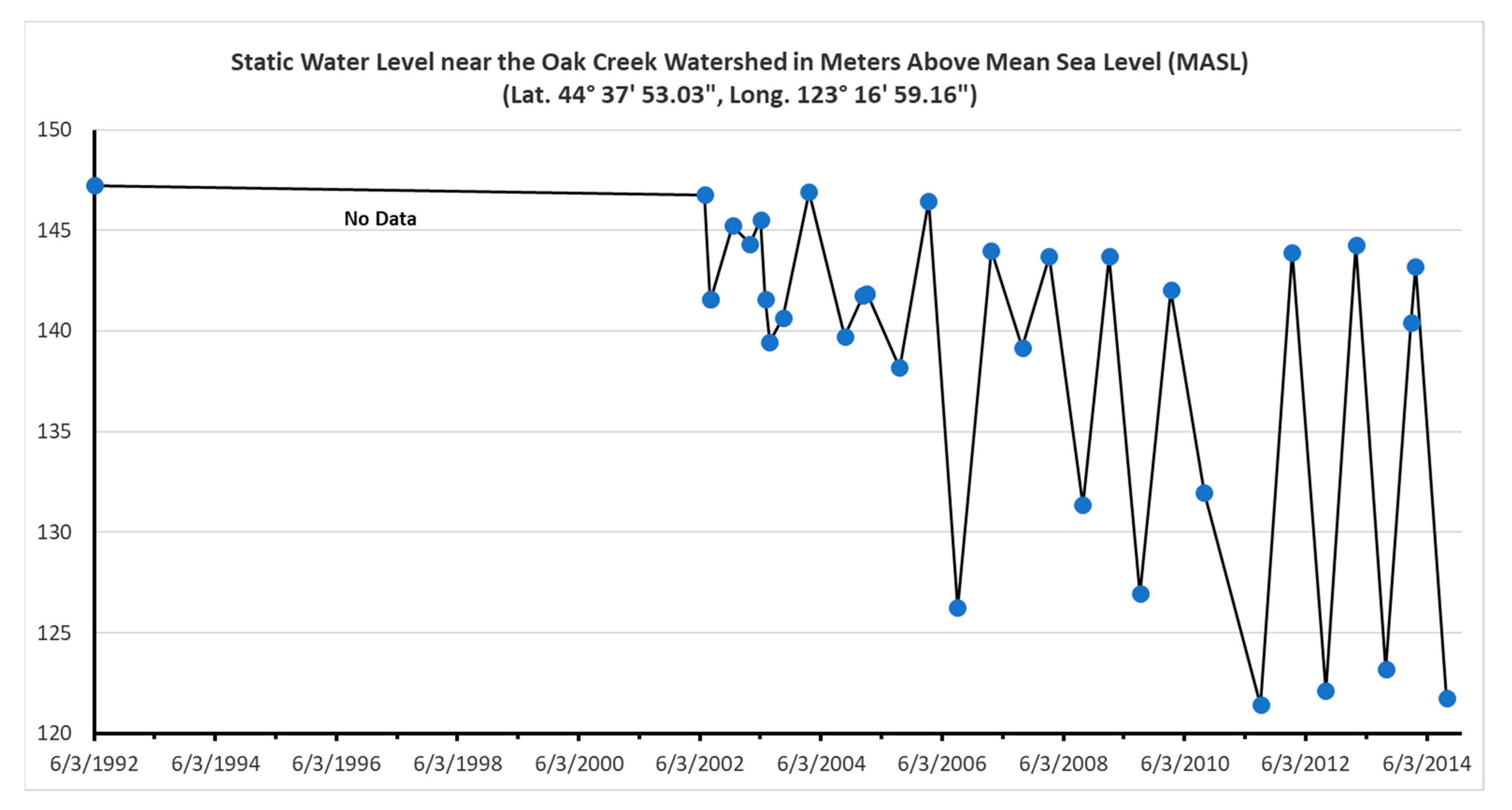
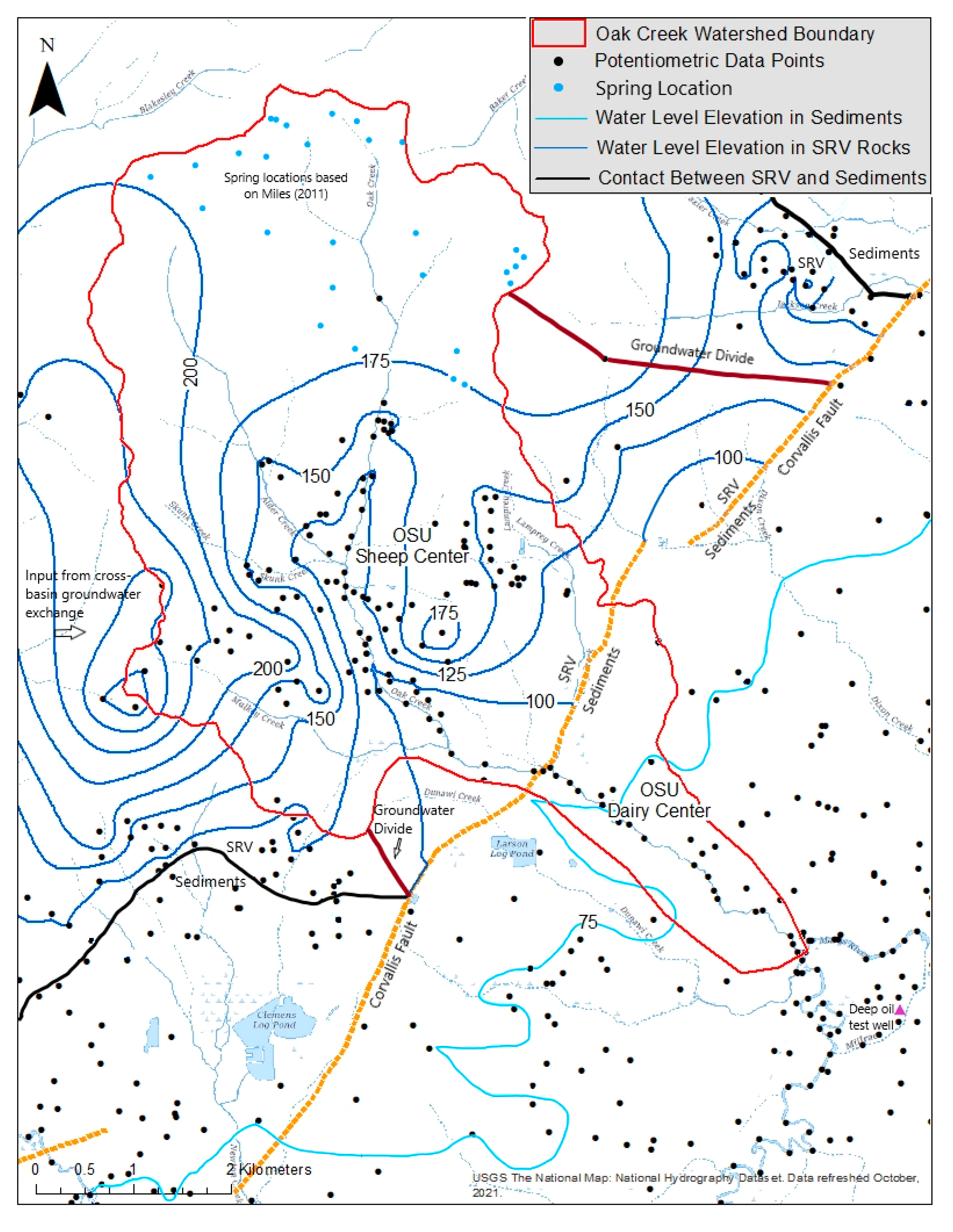
2.2.3. Potentiometric Surface Map
3. Results
3.1. Hydrogeologic Framework
3.1.1. Hydrogeologic Cross-Sections
3.1.2. Stream-Aquifer Relationships
3.1.3. Potentiometric Surface Map
3.1.4. Conceptual Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Interaction of Geology and Hydrology
4.2. Groundwater Compartmentalization
4.3. Land and Watershed Management Practices
4.4. Framework Adds to Role of Geology and Potential Groundwater Supplies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Barlow, P.M.; Leake, S.A. Streamflow Depletion by Wells: Understanding and Managing the Effects of Groundwater Pumping on Streamflow; Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012.
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground Water and Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between Groundwater and Surface Water: The State of the Science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, P.; Ochoa, C.G.; Jarvis, W.T.; Deboodt, T. A Hydrogeologic Framework for Understanding Local Groundwater Flow Dynamics in the Southeast Deschutes Basin, Oregon, USA. Geosciences 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyfried, M.S.; Schwinning, S.; Walvoord, M.A.; Pockman, W.T.; Newman, B.D.; Jackson, R.B.; Phillips, F.M. Ecohydrological Control of Deep Drainage in Arid and Semiarid Regions. Ecology 2005, 86, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, N.; Ochoa, C.G. The Seasonal Water Balance of Western-Juniper-Dominated and Big-Sagebrush-Dominated Watersheds. Hydrology 2021, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Faunt, C.C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.C.; Alley, W.M.; McGuire, V.L.; McMahon, P.B. Groundwater Depletion and Sustainability of Irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochoa, C.G.; Fernald, A.G.; Guldan, S.J.; Tidwell, V.C.; Shukla, M.K. Shallow Aquifer Recharge from Irrigation in a Semiarid Agricultural Valley in New Mexico. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbert, H. Effect Of Subsurface Geology On The Water Quality Of Springs At The Raystown Field Station. J. Ecol. Res. 2002, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Menichino, G.T.; Hester, E.T. Hydraulic and Thermal Effects of In-Stream Structure-Induced Hyporheic Exchange across a Range of Hydraulic Conductivities. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 4643–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K. Effects of Watershed Topography, Soils, Land Use, and Climate on Baseflow Hydrology in Humid Regions: A Review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2011, 35, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calver, A. Riverbed Permeabilities: Information from Pooled Data. Groundwater 2001, 39, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, T.C.; Harvey, J.W.; Frank, O.L.; Alley, W.M. Ground Water and Surface Water: A Single Resource; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1998.
- Barthel, R.; Banzhaf, S. Groundwater and Surface Water Interaction at the Regional-Scale—A Review with Focus on Regional Integrated Models. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Yao, J.; Tan, Z. Assessing Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions in a Complex River-Floodplain Wetland-Isolated Lake System. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickolas, L.B.; Segura, C.; Brooks, J.R. The Influence of Lithology on Surface Water Sources. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 1913–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, C.; Caruso, P.; Ray, G.; Deboodt, T.; Jarvis, W.; Guldan, S. Ecohydrologic Connections in Semiarid Watershed Systems of Central Oregon USA. Water 2018, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savoca, M.; Welch, W.; Johnson, K.; Lane, R.C.; Clothier, B.; Fasser, E. Hydrologic Framework, Groundwater Movement, and Water Budget in the Chambers-Clover Creek Watershed and Vicinity, Pierce County, Washington; USGS: Washinton, DC, USA, 2010.
- Welch, W.; Johnson, K.; Savoca, M.; Lane, R.C.; Fasser, E.; Gendaszek, A. Hydrogeologic Framework, Groundwater Movement, and Water Budget in the Puyallup River Watershed and Vicinity, Pierce and King Counties, Washington; U.S. Geological Survey: Washinton, DC, USA, 2015.
- Goldfinger, C. Evolution of the Corvallis Fault and Implications for the Oregon Coast Range. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, E.I.; Bakker, M. Groundwater Flow through Anisotropic Fault Zones in Multiaquifer Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, J.; Evans, J.; Forster, B.C. Fault Zone Architecture and Permeability Structure. Geology 1996, 24, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.; Stuyfzand, P.; Grischek, T.; Lluria, M.; Pyne, D.; Jain, R.; Bear, J.; Schwarz, J.; Weiping, W.; Escalante, E.; et al. Sixty Years of Global Progress in Managed Aquifer Recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 27, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woody, J.L. A Preliminary Assessment of Hydrogeologic Suitability for Aquifer Storage AndRecovery (ASR) in Oregon. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Embleton, D.G. Use of Exempt Wells As Natural Underground Storage and Recovery Systems. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2012, 148, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.; Jarvis, T.; Tullos, D. Domestic Well Aquifer Storage and Recovery Using Seasonal Springs. Water Resour. IMPACT 2017, 19, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tuthill, D.R., Jr.; Carlson, R.D. Incentivized Managed Aquifer Recharge Basin Scale Implementation Provides Water for Private Users, Groundwater Districts, Municipalities and Others. Water Rep. 2018, 176, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, K.; Runyon, J.; Fernald, S.; Gallagher, A.; Johnson, R.; Snyder, K.; Eden, S.; Zybach, R. Marys River Watershed: Preliminary Assessment; Marys River Watershed Council: Philomath, OR, USA, 1999; p. 146. [Google Scholar]
- Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon, USA—Climate Summary. Available online: https://wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?or1862 (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Miles, E.S. A GIS study of Benton County, Oregon, Groundwater: Spatial Distributions of Selected Hydrogeologic Parameters. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Benton County Staff. Benton County TMDL Water Quality Implementation Plan; Benton County Soil and Water Conservation District: Benton County, OR, USA, 2008.
- Frank, F.J. Ground Water in the Corvallis-Albany Area, Central Willamette Valley, Oregon; U.S. Geological Survey: Washinton, DC, USA, 1974; p. 55.
- Hall, J. Hydrogeologic Framework and Surface Water-Groundwater Temperature Relations of the Oak Creek Watershed, Western Oregon, USA. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Snavely, P.D., Jr. Tertiary Geologic Framework, Neotectonics, and Petroleum Potential of the Oregon-Washington Continental Margin. In Geology and Resource Potential of the Continental Margin of Western North America and Adjacent Ocean Basins—Beaufort Sea to Baja California; Circum-Pacific Council for Energy and Mineral Resources. Earth Science Series; Scholl, D.W., Grantz, A., Vedder, J.G., Eds.; Springer: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; pp. 305–335. [Google Scholar]
- Snavely, P.D.; Wagner, H.C. Geophysical Data Collected on the Southern Washington Continental Shelf along Line 12, USGS R/V S.P. Lee Cruise 3-76; Open-File Report 82-424; US Geological Survey: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1982.
- Couch, R.W.; Braman, D.E.; Newton, V.C. Geology of the Continental Margin near Florence, Oregon; Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries Oil and Gas Inv.: Portland, OR, USA, 1980; Volume 6, pp. 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dehlinger, P.; Couch, R.W.; Gemperle, M. Continental and Oceanic Structure from the Oregon Coast Westward across the Juan de Fuca Ridge. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1968, 5, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keach, R.W.I.; Oliver, J.E.; Brown, L.D.; Kaufman, S. Cenozoic Active Margin and Shallow Shale Cascades Structure: COCORP Results from Western Oregon. (Consortium for Continental Reflection Profiling). Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1989, 101, 1520–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snavely, P.D.; Wagner, H.C.; MacLeod, N.S. Rhythmic-Bedded Eugeosynclinal Deposits of the Tyee Formation, Oregon Coast Range. Bull. Kans. Geol. Surv. 1966, 169, 461–480. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.A.; Johnson, A.I. Summary of Hydrologic and Physical Properties of Rock and Soil Materials, as Analyzed by the Hydrologic Laboratory of the U.S. Geological Survey, 1948–1960; Water Supply Paper; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washinton, DC, USA, 1967.
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W.; Geological Survey (USA). Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-471-50744-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yeats, R.; Graven, E.P.; Werner, K.S.; Goldfinger, C.; Popowski, T. Tectonics of the Willamette Valley, Oregon; U.S. Geological Survey: Washinton, DC, USA, 1996.
- Harpham, K. Taming the Tumalo: A Damned Dam Repurposed for Recharge. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K. Land Use Impacts on Water Quality in Oak Creek Watershed. Bachelor’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, B. ASR: Aquifer Storage Rescues a Small Water Supply District. Water Resour. IMPACT 2017, 19, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Niem, A.R.; MacLeod, N.S.; Parke, D.S.; Huggins, D.; Fortier, J.D.; Meyer, H.J.; Seeling, A.; Niem, W.A. Onshore-Offshore Geologic Cross Section, Northern Oregon Coast Range to Continental Slope; DOGAMI Special Paper 26; State of Oregon, Dept. of Geology and Mineral Industries: Portland, OR, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose, P.S.; Meckel, T.A. Maturing Global CO2 Storage Resources on Offshore Continental Margins to Achieve 2DS Emissions Reductions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaree, D.E. Nitrate Derived From Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems (NOWTS): A Study of Public Perceptions, Politics, and Perpetual Permitting in the Western US. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.D.; Carpenter, A.T. USDA Source Water Protection Funding: Successes and Opportunities. J. AWWA 2020, 112, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugato, C.J. City of Philomath, Water System Master Plan; Westech Engineering, Inc.: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]

| Formation Name | Generalized Lithology | Permeability Architecture | Hydrologic Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alluvium | Sand, gravel, cobbles thin, 10 m thick | Porous media. | Prolific yield for irrigation near Willamette River. |
| Spencer/Tyee/Yamhill, undifferentiated | Shale, siltstone, interbedded sandstone, up to 3000 m thick | Microfractures in siltstones and shale, porous media in sandstones. | Low yield for domestic wells. Some saline water and artesian flow in deep sandstones. |
| Siletz River Volcanics | Basalts with interbedded claystone and sandstone, up to 1000 m thick | Fractures, conduit flow in interflows. Stratigraphic and structural groundwater compartments common. | Moderate yield for domestic and municipal wells. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochoa, C.G.; Jarvis, W.T.; Hall, J. A Hydrogeologic Framework for Understanding Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in a Watershed System in the Willamette Basin in Western Oregon, USA. Geosciences 2022, 12, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030109
Ochoa CG, Jarvis WT, Hall J. A Hydrogeologic Framework for Understanding Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in a Watershed System in the Willamette Basin in Western Oregon, USA. Geosciences. 2022; 12(3):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030109
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchoa, Carlos G., William Todd Jarvis, and Jesse Hall. 2022. "A Hydrogeologic Framework for Understanding Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in a Watershed System in the Willamette Basin in Western Oregon, USA" Geosciences 12, no. 3: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030109
APA StyleOchoa, C. G., Jarvis, W. T., & Hall, J. (2022). A Hydrogeologic Framework for Understanding Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in a Watershed System in the Willamette Basin in Western Oregon, USA. Geosciences, 12(3), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030109







