An Experimental Investigation on Dike Stabilization against Floods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
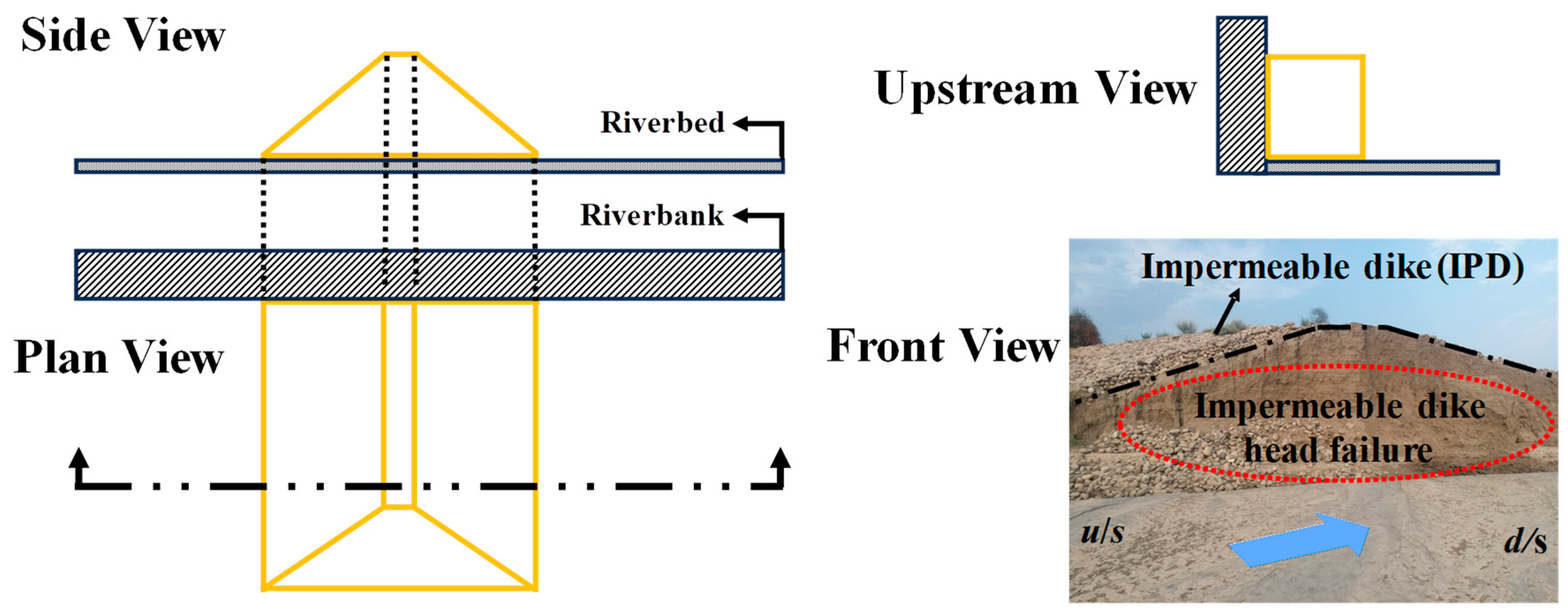
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.1.1. Channel Characteristics
2.1.2. Flow Conditions
2.1.3. Properties of Soil
2.2. Dike Model and Pile Shape Designs
2.3. Analysis and Scour Measurement
2.3.1. Scour Distribution
2.3.2. Variation in Scour Depth over Time around an Impermeable Dike
3. Results
3.1. Flow Structures
3.2. Scour Characteristics
3.2.1. Scour Maps of Impermeable and Combined Dikes
3.2.2. Maximum Scouring near the Dike Model
3.2.3. Scour Depth at Dike–Wall Junctions
3.2.4. Scour Hole Dimensions
4. Discussion
4.1. Basic Flow Behavior
4.2. Scouring Process
5. Conclusions
- In CD-ST15 case, streamlined tapered (ST) provides the best results in terms of scour hole lengths (, , ), scour depth reduction at the nose (48%), u/s dike–wall junction (45%), and d/s dike–wall junction (65%). The decreased scour depth and length in the CD-ST15’s front suggest that the streamlined tapered design redirects the flow towards the downstream side, reducing scour at that location. When it comes to deposition on the d/s side, delta vane (CD-DV5) provides the most deposition (4.3 cm) when compared to other shapes.
- Maximum flow concentration was observed in the impermeable dike’s detention and reflux zones, while maximum scour depth was observed between these two zones due to highly concentrated flow at the dike nose. Concentrated flow faded as permeability increased from 5 piles to 15 piles, resulting in scour depth reduction at all three critical locations (dike’s nose, u/s, and d/s dike–wall junction). However, the increase in permeability deposition was reduced to the maximum value (3.3 cm) for CD-ST15.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, K. Environmental Hazards: Assessing Risk and Reducing Disaster; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Buijs, J.; Boelens, L.; Bormann, H.; Restemeyer, B.; Terpstra, T.; van der Voorn, T. Adaptive planning for flood resilient areas: Dealing with complexity in decision-making about multilayered flood risk management. In Proceedings of the 16th Meeting: Adaptive Planning for Spatial Transformation, Groningen, The Netherlands, 23–25 May 2018; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi, Y.; Tanaka, N. Effectiveness of a compound defense system of sea embankment and coastal forest against a tsunami. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 151, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Amjath-Babu, T.S.; Kächele, H.; Müller, K. Non-structural flood risk mitigation under developing country conditions: An analysis on the determinants of willingness to pay for flood insurance in rural Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2119–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.C.; Arthur, R.; Spruce, M.; Williams, H.T. Social sensing of flood impacts in India: A case study of Kerala 2018. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 74, 102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, A.R.; Donato, K. Extreme weather and migration: Evidence from Bangladesh. Popul. Environ. 2019, 41, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthur, A. Preserving the Environment Due to the Flash Floods in Vellar River at Tv Puthur, Virudhachalam Taluk, Tamil Nadu: A Case Study. Int. J. Struct. Civil Eng. Res. 2013, 2, 2319–6009. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Pasha, G.A.; Ghani, U.; Ullah, M.K.; Ahmed, A. Flow dynamics around permeable spur dike in a rectangular channel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 4999–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.; Qiao, D.; Yan, J.; Ning, D.; Pasha, G.A.; Iqbal, S. Flow characteristics around permeable spur dike with different staggered pores at varying angles. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 5219–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, T.; Herget, J. Controls on local scour and deposition induced by obstacles in fluvial environments. Catena 2012, 91, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Valyrakis, M.; Qi, M.; Sharma, A.; Lodhi, A.S. Experimental assessment and prediction of temporal scour depth around a spur dike. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ddv Kuhnle, R.; Alonso, C. Flow near a model spur dike with a fixed scoured bed. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2013, 28, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeli, P.; Boudaghpour, S.; Rostami, M.; Mirzaee, M. Experimental investigation of permeability and length of a series of spur dikes effects on the control of bank erosion in the meandering channel. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Mizutani, H. Bed morphology and grain size characteristics around a spur dyke. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2012, 27, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Sharma, P.K. Estimation of maximum scour depth near a spur dike. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 43, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nakagawa, H. Characteristics of local flow and bed deformation at impermeable and permeable spur dykes. Annu. J. Hydraul. Eng. JSCE 2009, 53, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.P.; Jiang, J.C. Experiments and numerical simulations on transport of dissolved pollutants around spur dike. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 341–353. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, S. Experiments and numerical simulations of dike erosion due to a wave impact. Water 2015, 7, 5831–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Kawaike, K.; Baba, Y. Experiment and simulation of turbulent flow in local scour around a spur dyke. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2009, 24, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. Pier scour in clear water for sediment mixtures. J. Hydraul. Res. 2012, 50, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yeo, H.; Kim, S.; Ji, U. Permeability effects of single groin on flow characteristics. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Pasha, G.A.; Ghani, U.; Ahmed, A.; Farooq, R.; Haider, R. Investigation of Flow Dynamics Around a Combination of Different Head Shapes of Spur Dikes. Teh. Vjesn. 2022, 29, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Nayyer, S.; Farzin, S.; Karami, H.; Rostami, M. A numerical and experimental investigation of the effects of combination of spur dikes in series on a flow field. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami-Yarahmadi, M.; Pagliara, S.; Yabarehpour, E.; Najafi, N. Study of Scour and Flow Patterns around Triangular-Shaped Spur Dikes. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A. Design of Spur-Type Streambank Stabilization Structures; (No. FHWA/RD-84/101; SCR-371-83-039); Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center: McLean, VA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Alauddin, M.; Tashiro, T.; Tsujimoto, T. Design of groynes modified with both alignment and permeability for lowland river problems. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. A2 (Appl. Mech. (AM)) 2011, 67, I_645–I_652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat, S.H.; Tominaga, A. Influence of pile group density on minimizing local scour of a double spur dike group. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 Hydraulic Eng. 2014, 70, I_85–I_90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, A.; Sadat, S.H. Combination of permeable and impermeable spur dikes to reduce local scour and to create diverse river bed. River Sediment. 2016, 101, 450–456. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzeldin, R.M. Numerical and experimental investigation for the effect of permeability of spur dikes on local scour. J. Hydroinformatics 2019, 21, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Pervin, R.; Hasan, M.Z. Effect of Various Groins in a Series on Channel Bed Morphology: An Experimental Investigation. Stavební Obz. -Civ. Eng. J. 2022, 31, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Tanaka, N. Experimental Study on Flow Characteristics and Energy Reduction around a Hybrid Dike. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 21, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, V. Scale effects in physical hydraulic engineering models. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Tanaka, N.; Reheman, N. Experimental study on reduction of scouring and tsunami energy through a defense system consisting a seaward embankment followed by vertically double layered vegetation. Ocean Eng. 2021, 234, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.M.; Testik, F.Y. Onshore scour characteristics around submerged vertical and semicircular breakwaters. Coast Eng. 2009, 56, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeres-Ferradosa, T.; Chambel, J.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.V.C.; Giannini, G.; Haerens, P. Scour Protections for Offshore Foundations of Marine Energy Harvesting Technologies: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ghumman, A.R. Experimental investigation of flood energy dissipation by single and Hybrid Defense System. Water 2019, 11, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, G.A.; Tanaka, N. Undular hydraulic jump formation and energy loss in a flow through emergent vegetation of varying thickness and density. Ocean Eng. 2017, 141, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, M.; Schendel, A.; Hildebrandt, A.; Schlurmann, T. Scour development around a jacket structure in combined waves and current conditions compared to monopile foundations. Coast. Eng. 2019, 152, 103515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Meftah, M.; Mossa, M. Scour holes downstream of bed sills in low-gradient channels. J. Hydraul. Res. 2006, 44, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, Y.M. Mechanics of local scour around submarine pipelines. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1990, 116, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsian, M.; Vaghefi, M. Experimental study on scour and flow field in a scour hole around a T-shape spur dike in a 90° Bend. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2009, 24, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevis, W.; García-Villalba, M.; Niño, Y. Experimental and large eddy simulation study of the flow developed by a sequence of lateral obstacles. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2014, 14, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safie, O.; Tominaga, A. Effects of pile density and arrangement on flow characteristics and sediment deposition around a pile-group dike. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. A2 (Appl. Mech. (AM)) 2019, 75, I_487–I_498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, M.T.; Stephen, M.F.; Dean, R.G.; Mulcahy, S. Permeable wood groins: Case study on their impact on the coastal system. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 33, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, A.M.; Dougherty, E. Bridge pier geometry effects on local scour potential: A comparative study. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 234, 109326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothyari, U.C.; Ranga Raju, K.G. Scour around spur dikes and bridge abutments. J. Hydraul. Res. 2001, 39, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, M.; Ghodsian, M.; Neyshabouri, S.A. Scour and flow field around a spur dike in a 90° Bend. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A.; Saeed, H.N. Local scour depth at the nose of permeable and impermeable spur dykes. Univ. Khartoum Eng. J. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Altinakar, M. Effects of a Permeable Hydraulic Flashboard Spur Dike on Scour and Deposition; World Environmental and Water Resources Congress: Henderson, NV, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, H.; Basser, H.; Ardeshir, A.; Hosseini, S.H. Verification of numerical study of scour around spur dikes using experimental data. Water Environ. J. 2012, 28, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.; Qiao, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Ning, D. Role of grouped piles on flow characteristics around impermeable spur dike. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 20, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Sharma, P.K. Scour around impermeable spur dikes: A review. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 24, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, H.; Ardeshir, A.; Saneie, M.; Salamatian, S.A. Prediction of time variation of scour depth around spur dikes using neural networks. J. Hydro. 2011, 14, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safie, O.; Tominaga, A. Flow characteristics around pile-group groynes with different arrangements of piles. In Proceedings of the River Flow 2020: Proceedings of the 10th Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics, Delft, The Netherlands, 7–10 July 2020; pp. 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florsheim, J.L.; Mount, J.F.; Chin, A. Bank Erosion as a Desirable Attribute of Rivers. BioScience 2008, 58, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, S.H.; Tominaga, A. Optimal distance between pile-group and spur-dike to reduce local scour. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 Hydraulic Eng. 2015, 71, I_187–I_192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, N.; Tanaka, N.; Rahman, M.A. Role of tree crown height for effective mitigation capability of inland coastal forest considering the flow structures and scour phenomena. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 238, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomers, A.; Aguilar Lopez, J.P.; Warmink, J.J.; Hulscher, S.J. Modelling effects of an asphalt road at a dike crest on dike cover erosion onset during wave overtopping. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmans, G.J.C.M.; Verheij, H.J. (Eds.) Scour Manual: Current-Related Erosion; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hakim, M.; Yarahmadi, M.B.; Kashefipour, S.M. Use of spur dikes with different permeability levels for protecting bridge abutment against local scour under unsteady flow conditions. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 49, 1842–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.S.; Hasan, M.M.; Tanaka, N. Analysis of flow around impermeable groynes on one side of symmetrical compound channel: An experimental study. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 56–66. [Google Scholar]









| Sr. No | Authors | Modifications within Dike | Extra Circular Pile Dike | Pile Modifications | Scouring Behavior | Scour Measurements at Dike Nose + Upstream and Downstream of Dike Wall Junctions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alauddin, M., Tashiro, T., & Tsujimoto, T. [26] | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| 2 | Zhang, H., Nakagawa, H., Ogura, M., & Mizutani, H. [16] | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| 3 | Sadat, S. H., & Tominaga, A. [27] | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| 4 | Sadat, S. H., & Tominaga, A. [28] | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| 5 | Ezzeldin, R. M. [29] | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| 6 | Iqbal, S., Pasha, G. A., Ghani, U., Ullah, M. K., & Ahmed, A. [8] | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| 7 | Mohammed, A., Pervin, R., & Hasan, M. Z. [30] | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| 8 | Haider, R., Qiao, D., Yan, J., Ning, D., Pasha, G. A., & Iqbal, S. [9] | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 9 | Iqbal, S., & Tanaka, N. [31] | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| 10 | Present study | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cases Name | Impermeable Dike Length (cm) | Permeable Dike Length (cm) | Dike Height (cm) | Froude Number, Fr | Number of Piles | Pile Density 1/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPD | 17.5 | 0 | 19 | 0.59 | ||
| CD-APF5 | 14.5 | 3 | 19 | 0.59 | 5 | 0.1 |
| CD-C5 | 14.5 | 3 | 19 | 0.59 | 5 | 0.1 |
| CD-DV5 | 14.5 | 3 | 19 | 0.59 | 5 | 0.1 |
| CD-ST5 | 14.5 | 3 | 19 | 0.59 | 5 | 0.1 |
| CD-APF10 | 11.5 | 6 | 19 | 0.59 | 10 | 0.12 |
| CD-C10 | 11.5 | 6 | 19 | 0.59 | 10 | 0.12 |
| CD-DV10 | 11.5 | 6 | 19 | 0.59 | 10 | 0.12 |
| CD-ST10 | 11.5 | 6 | 19 | 0.59 | 10 | 0.12 |
| CD-APF15 | 8.5 | 9 | 19 | 0.59 | 15 | 0.125 |
| CD-C15 | 8.5 | 9 | 19 | 0.59 | 15 | 0.125 |
| CD-DV15 | 8.5 | 9 | 19 | 0.59 | 15 | 0.125 |
| CD-ST15 | 8.5 | 9 | 19 | 0.59 | 15 | 0.125 |
| Cases Name | Dike Nose (%) | u/s Junction (%) | d/s Junction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD-APF5 | 23 | 21 | 19 |
| CD-C5 | 21 | 21 | 17 |
| CD-DV5 | 10 | 8 | 46 |
| CD-ST5 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| CD-APF10 | 26 | 27 | 32 |
| CD-C10 | 20 | 20 | 35 |
| CD-DV10 | 15 | 14 | 52 |
| CD-ST10 | 25 | 27 | 64 |
| CD-APF15 | 32 | 35 | 42 |
| CD-C15 | 37 | 38 | 40 |
| CD-DV15 | 26 | 26 | 55 |
| CD-ST15 | 43 | 45 | 65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, S.; Tanaka, N. An Experimental Investigation on Dike Stabilization against Floods. Geosciences 2023, 13, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13100307
Iqbal S, Tanaka N. An Experimental Investigation on Dike Stabilization against Floods. Geosciences. 2023; 13(10):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13100307
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Sohail, and Norio Tanaka. 2023. "An Experimental Investigation on Dike Stabilization against Floods" Geosciences 13, no. 10: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13100307
APA StyleIqbal, S., & Tanaka, N. (2023). An Experimental Investigation on Dike Stabilization against Floods. Geosciences, 13(10), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13100307








