Abstract
Chronic kidney disease of non-traditional origin (CKDnt) in Central America, also known as Mesoamerican Nephropathy (MeN), is of particular concern in agricultural populations. The member states of the Central American Integration System (SICA) determined in 2013 that there was an imperative need to address the situation in a comprehensive manner and defined policies for the intervention of the disease. A situation that currently worries health authorities is that cases are on the rise—without distinguishing or implementing effective actions to achieve a decrease in disease prevalence. The incidence of heat and strenuous activities on renal health is undeniable; however, labeling these variables as the only responsible causes for MeN has not catalyzed the implementation of health measures to lead to a preventive approach to solve the epidemic or to achieve a decrease in the number of new cases. This review addresses the role nephrotoxic metals present in the environment, mainly in soils and water, may have as part of a scenario of exposure to environmental toxins in which environmental, occupational, geographic and population variables interact. An integral approach was used to encompass the multicausality that is attributed to MeN and based on the multidisciplinary concept of the re-emerging discipline called medical geology.
1. Introduction
People affected by a type of nephropathy who do not present the risk factors or usual comorbidities for chronic kidney disease (CKD) have been reported in very specific areas of Mesoamerica (south of Mexico through Panama); comorbidities include diseases such as diabetes and uncontrolled hypertension, among others [1,2]. The official statistics show the existence of defined areas with similar characteristics in all countries of Mesoamerica; non-traditional kidney disease was originally known as MeN [3], which today has reached epidemic proportions, with a serious impact on Central American communities, and overburdens health systems [4]. In addition, atypical cases of CKD have been observed with similar characteristics in the north of Sri Lanka and Andhra Pradesh, India [5,6]. The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) in their book “Epidemia de Enfermedad Renal Crónica en comunidades agrícolas de Centroamérica” [7] summarized the situation as follows: “Over the last four decades, a growing number of young persons, in clusters of socially vulnerable, farming communities of different Central American countries, have shown a serious form of kidney failure of uncertain etiology, referred to as CKDnt” [3].
A study by Wesseling et al. (2015) found that the mortality increase from CKD in Costa Rica occurs mainly in the province of Guanacaste and was already present four decades ago among men, that is, since the 1970s (this coincides with the beginning of the statistical collection of data by the Health Ministry of Costa Rica) [8]. The prevalence of the disease is higher in dry, hot areas of low elevation, with extensive agricultural production, especially sugar cane; such cases are consistent with an occupational component [8,9]. At present, however, these statements have been questioned by some authors in recent research [10,11].
Similarly, recent investigations have identified that this disease is not limited to affecting or appearing in agricultural communities’ workers [12], as noted by Cerón et al. (2021) [13], who report MeN in children and women who are not related to agricultural activities or submitted to thermal stress conditions or repetitive dehydration. Other authors have reported that MeN can have multifactorial etiology [11,14,15]. Even today, the scientific community has not reached a solid consensus on the causal factors on the development of this disease [14,15].
1.1. Known Etiology of MeN
The first investigations into MeN’s etiology propose an extensive list of possible triggering factors, among which are occupational, toxic, genetic and metabolic factors [9]. Social and population determinants associated with those affected and areas of high prevalence have also been identified [2]. After over two decades of thorough research on MeN, to date there is no strong evidence allowing for a “single” etiological consensus [16]; nonetheless, the information generated over the last years on possible causes of MeN has narrowed the initial list, and recent information supports the hypothesis that the disease is related to direct nephrotoxic agents among which are included toxins such as heavy metals or metalloids: arsenic, cadmium, mercury, lead and vanadium which may be present in environmental matrices like air, water and soil; these may enter the human body where they find affinity with certain molecules and target organs, causing chronic effects affecting the kidney’s functionality [17,18]. The nephrotoxic effect of these metals may be potentiated by a triggering factor such as thermal stress and repetitive dehydration [19,20], which are favored by environmental conditions characteristic of high MeN prevalence areas and may result in a multi-causal disease. High environmental temperature, strenuous work, hydration deficiencies and lack of clear policies for the early management of the disease cause identification of the affected persons to be acknowledged belatedly by health authorities.
In general terms, medical geology is understood as the science dealing with the relationship between natural geological factors and their repercussion on people’s health [21]. The medical geology field of action is interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary, shared with diverse specialties such as medicine, geology, chemistry, meteorology, epidemiology, environmental biochemistry and toxicology, among others [22]. By analyzing MeN and focusing on medical geology, we can explore the potential relationships between nephrotoxic heavy metals and disease in a geological setting. This includes considering the origin, distribution, mobility and contact with human populations, as well as their effects and mechanism of action. The relationship between geological, environmental aspects and human health is complex and spurs multiple perspectives [23]; medical geology, however, offers tools enabling the comprehensive analysis of environmental toxins regarding the origin, mobility, exposure, contact with human beings and their toxicologic action mechanism [24], all of which may be related to a space defined as an “exposure scenario.” In this review, we emphasize the documentary analysis of low-dose heavy metals as toxic agents associated with MeN.
1.2. Geographical Characteristics
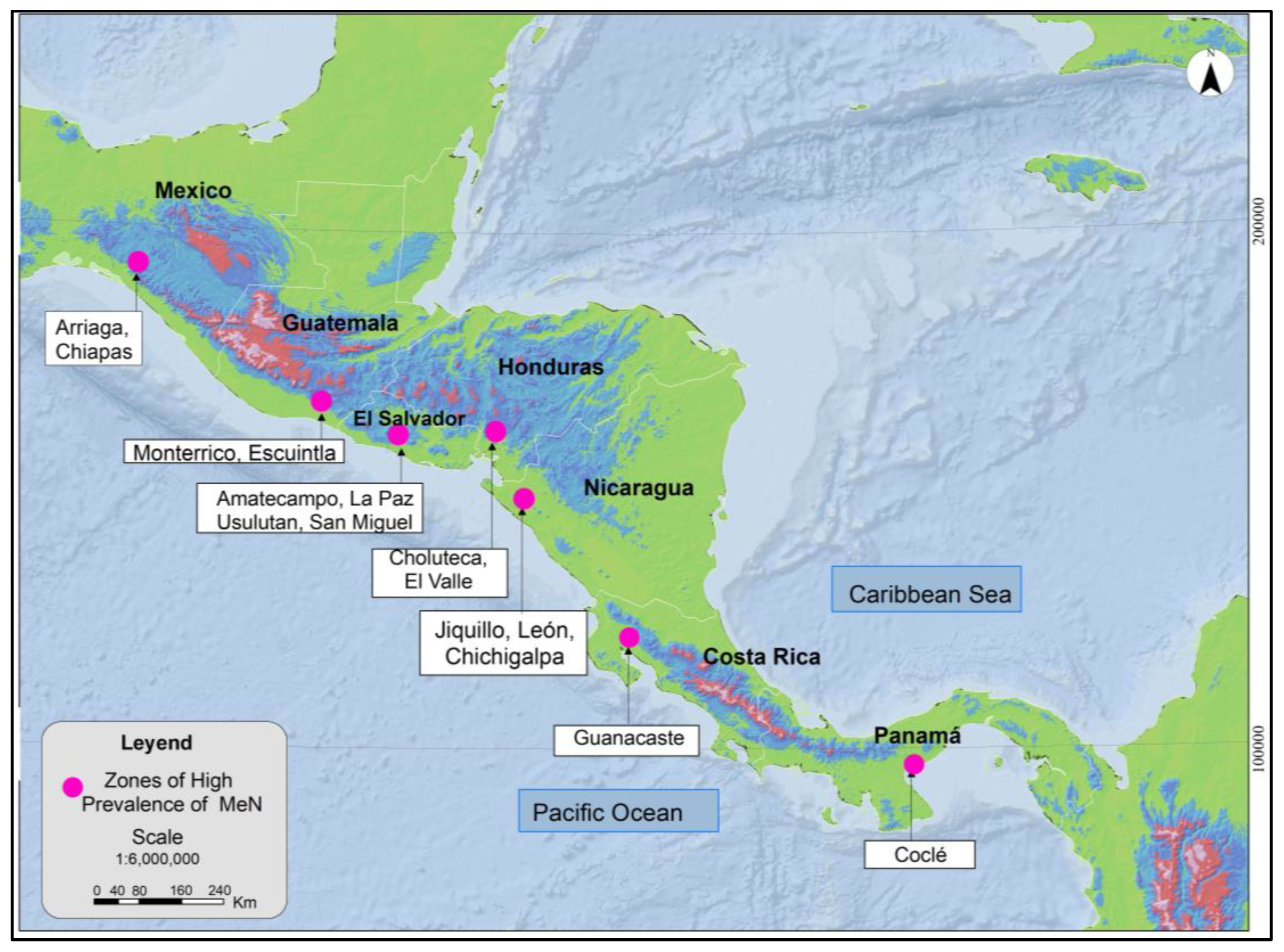
MeN occurs in a differentiated manner on the Pacific Coast of Mesoamerica, as noted in Figure 1. The areas identified have common characteristics, such as geographic location in low-elevation areas (≤500 masl) and towards the Pacific basin, presence of the disease with greater prevalence in communities with warm climates, and most of the affected work being in open space scenarios, mainly agricultural activities. The zones with greater incidence of MeN are found in very specific areas of low elevation above sea level, suggesting the relevance of a multidisciplinary approach, not underestimating the influence of environmental and geographical variables; therefore, it should be studied jointly by other disciplines such as atmospheric dynamics and environmental medicine.
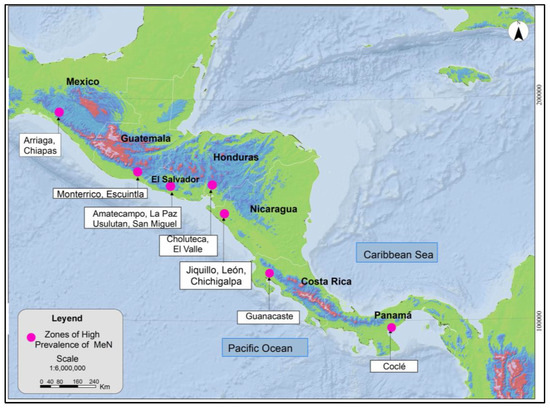
Figure 1.
Zones of high prevalence of MeN in Mesoamerica. Modified from (COMISCA, 2013 and Rotter & Trabanino, 2018) [25,26].
2. Characteristics of the Disease
Confirmation of MeN cases takes into account patients with kidney function outside of normal parameters (according to KDIGO categories) residing in Mesoamerica [6] and also presenting the following clinical profile: “Patient 10 to 60 years-old with GFRe (Based on CKD-EPI), of three months, (which may be retrospective, based on prospective or medical history since the first determination), GFR under 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 with functional or structural kidney damage (as is microalbuminuria or urinary sediment) in two determinations with at least three months between them; generally without the presence of a history of diagnostic of traditional chronic kidney disease (diabetes, arterial hypertension, lupus, hereditary nephropathy, autoimmune disease, obstructive uropathy, hypertensive cardiopathy, hypertensive chronic nephropathy, cardiopathy, congenital malformations, polycystic kidney disease, sickle-cell disease, vasculitis and myeloma), or the presence of acute kidney injury shown at the moment of diagnosis” [27].
MeN is considered, as well as other forms of CKD, as silent and asymptomatic in its first stages, only manifesting with typical symptoms in the advanced state of the disease, such as in stages G-4 and G-5 (as per KDIGO categories) [9]. However, it is common that in the early stages of the disease, patients report paroxysmal muscular weakness related to hypocalcemia events, associated with physical work or with hyponatremia, as well as aseptic dysuria, associated with possible urate crystals passing to the urine [6]. The main clinical characteristics of MeN are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main Clinical Characteristics of MeN.
The serum cystatin C has been well established as an early and accurate biomarker of CKD that is particularly helpful in patients for whom creatinine is an inadequate marker or for whom more cumbersome methods of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measurement are impractical [30].
To locate MeN in an exposure scenario, we begin by highlighting the situation in Central America. This narrow strip of land belongs to a zone called the Pacific Ring of Fire, which extends over 40,000 km (25,000 miles) and is horse-shoe shaped, with 452 volcanoes, which constitute around 75% of the active and inactive volcanoes worldwide [31]. This area likewise concentrates the population of the Pacific basin, representing one third of the total surface where over 70% of the agricultural activity of Central America is concentrated [32]. Since our subject of study is associated with agricultural areas related to the Pacific coast, the dynamic analysis to be established becomes relevant in these zones regarding toxic metals contained in these soils with volcanic activity, although with relatively low contents of heavy metals or within the permissible levels, which may enter the human body by inhalation or by ingestion, adequately called accidental geophagy [33]. Concentrations of heavy metals of volcanic origin have been isolated and quantified in soil and respirable dust from areas of high CKD prevalence in Costa Rica [34,35]. The winds in these areas, which often include wind farms, can reach high speeds [36].
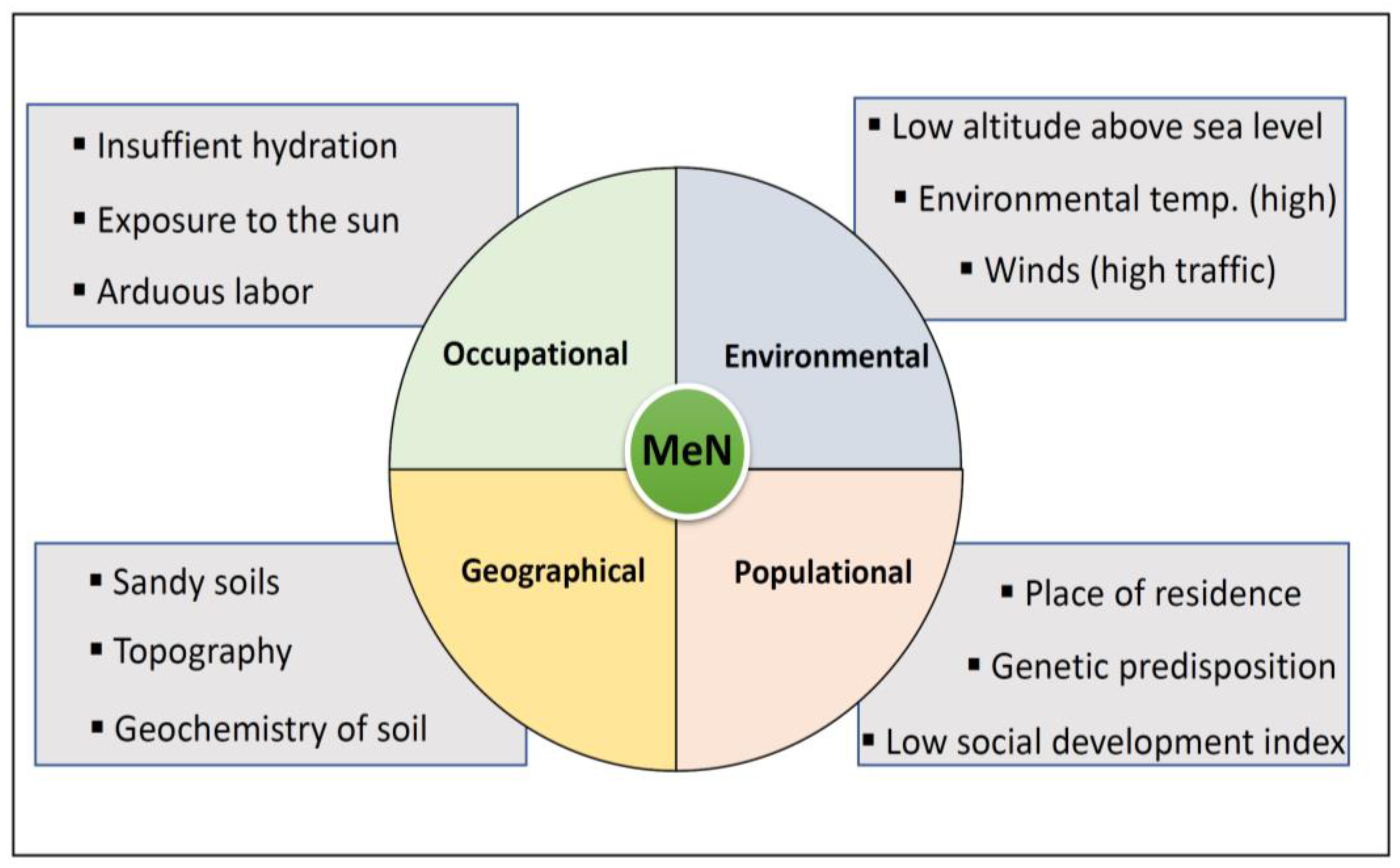
The origin of heavy metals in soils derives from the earth’s crust’s composition being expelled and exposed to the environment by natural processes like volcanic activity, erosion and weathering of the rocks [37]. Once they are released to the environment, they are persistent, and through biological processes they bioaccumulate and biomagnify. This same situation takes place at the human metabolism level, where, once toxins enter the body, their excretion is difficult with a tendency to bioaccumulation. In addition to being naturally present in soils, these metals may be part of some agrochemicals’ formula, be used in agriculture and follow the route of metals of natural origin until reaching human contact [38]. Risk factors for MeN which may influence the exposure scenario are summarized in Figure 2.
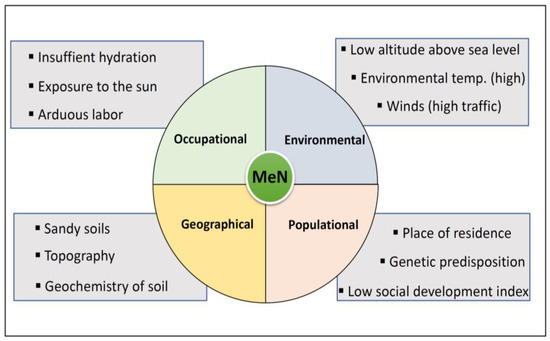
Figure 2.
Risk factors for MeN and associated exposure scenario.
Due to the volcanic nature of the region, the soils in this area are known to be rich in heavy metals such as arsenic, lead, cadmium, vanadium and mercury, which can have harmful effects on the kidneys [39,40]. These toxins can be exposed to the environment through natural or anthropogenic processes such as mining, agriculture or erosion.
The metals exposed in the soils can be mobilized by runoff of surface water or groundwater, contaminating the soil, aquifers and even water sources for human consumption on their way [37]. These toxins may be transported in water as an integral element of suspended solids or dissolved; toxins in water have the greatest toxic capacity [41].
Land topography, wind speed and wind direction have an important role in the transport and mobilization of nephrotoxic metals. This is particularly important if there are settlements located in the movement’s direction. Particulate material of natural or anthropogenic origin with heavy metals is easily transported over hundreds and thousands kilometers from their point of origin [37]. For example, in Central America, areas of high MeN prevalence have areas of high wind traffic associated with wind farms, which facilitates the movement of particles through the air region [42]. The annual entry of dust waves from the Sahara desert has been reported, known as “Sahara Dust”, causing an increase of particulate material in suspension levels (PM) [43,44]. The presence of cadmium, arsenic, vanadium and mercury has been reported in this dust [45]. A recent study quantified 204 ± 2 mg/kg of lead in a sample of this dust collected in Costa Rica in June of 2020 [35]. The presence of this environmental phenomenon represents an increased risk for people already exposed to adverse local conditions; such dust movement for the Central American area is favored by the displacement originating in the Intertropical Convergence Zone, determining air movement with certain characteristics of humidity and temperature [46].
3. Contact of Heavy Metals with Human Beings
Heavy metals are chemical elements with atomic mass >20 of metalloid or metallic nature [47] and considered toxic for human beings and the environment [48]. Likewise, nephrotoxic metals have the capacity of causing damage to kidney function. The most common of these metals in soils are cadmium, chromium, arsenic, mercury, lead, copper and zinc [47].
The oral and respiratory pathways represent the most important routes for entry of metals into human beings [49]; however, the oral pathway is most important because of its quick and efficient absorption in the mucous membrane, where toxins may pass to the bloodstream and from there to different body organs, including the kidneys [50].
Factors such as temperature and environmental humidity, the concentration of the toxin, the chemical species, mobilization route (water or air), the route of entry to the body and host susceptibility are variables influencing and determining the toxic contact effects on people [51]. This contact, even at very low concentrations or exposure levels, is considered a risk factor for causing functional or structural damages in organs such as the kidney [16]. Bioaccumulation of these heavy metals leads to a diversity of toxic effects in a variety of body tissues and organs. Metals such as arsenic, lead, cadmium and mercury are systemic poisons which, among their toxicologic characteristics and nephrotoxic capacities, can contribute to CKDnt [15,39,52].
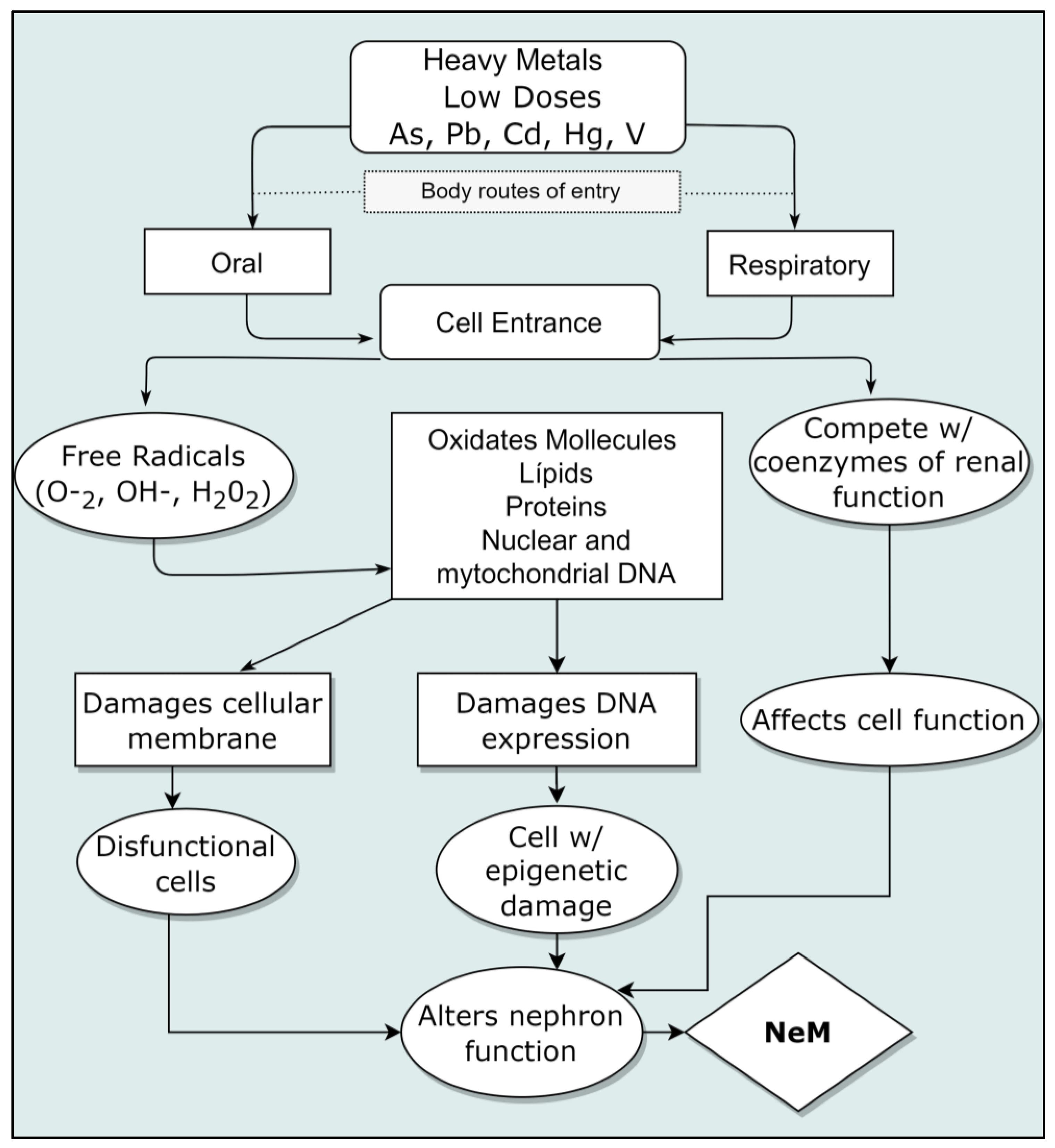
The described damages of nephrotoxic metals to cells include the generation of free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), intervening into nucleic acids by inactivating DNA repair; lipid peroxidation at cell membranes’ level and proteins’ level; inactivation of enzymes and conformational changes and neuronal damages as well. All this occurs even at low ingestion doses [53]. These metals can interrupt cellular events, including growth, proliferation, differentiation, repair processes of damages and apoptosis [17]. From the study of the action mechanisms, a weakening of antioxidant cellular defenses, enzymatic inactivation and oxidative stress are also revealed; some of them have selectivity to specific macromolecules’ bonds. Cadmium and arsenic, for example, cause genomic instability and defects in DNA repair [17]. Epigenome defects have been described after contact with arsenic at low doses (even close to the maximum permissible) and associated with pre and perinatal exposure [54]. A diagram of the interaction of cellular damages is shown in Figure 3. Damage to the kidneys produced by heavy metals is varied and described below.
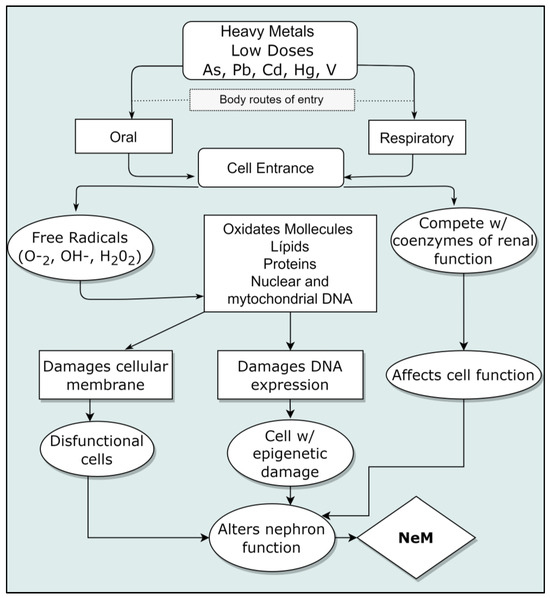
Figure 3.
Mechanism of kidney cellular damage caused by nephrotoxic metals. Modified from (Azeh Engwa et al., 2019) [53].
3.1. Arsenic
The toxicity of arsenic depends not only of the concentration but also its chemical species [55]. This metalloid can exist organically and inorganically and is considered one of the most toxic elements; it is found associated with the soil, and its inorganic form is more toxic than its organic form [56]. The inorganic form (iAs) predominates in natural environments, such as soil and groundwater [57]; this increases the risk of producing toxic effects, particularly at low doses for chronic exposure. A large percentage of absorbed arsenic is filtrated in the kidneys. Therefore, this organ becomes an important site for the bioaccumulation of this metal [58]. Arsenic may cause serious health problems; among them, some are noteworthy for their severity and carcinogenic processes in diverse organs, including bladder and kidney cancer [59]. One of the ways arsenic causes injury is through the inhibition of mitochondrial enzymes leading to a deterioration of cellular respiration [60]. It has been shown in toxicological studies with animal models that arsenic induces a continuous inflammatory response in liver and kidney [61].
3.2. Lead
Lead is found naturally in matrices such as water, soil and air both in organic and inorganic form [62]. Lead compounds have affinity for diverse soft and hard organs including the kidneys [63]. The toxic dose determines the effects, which are usually limited and reversible. However, chronic intoxications sustained for long periods with accumulative processes because of prolonged exposure can finish as a serious condition due to the development of renal fibrosis, resulting in an irreversible renal disease [62]. This metal mainly affects the proximal tubules [64]. Within the toxicity mechanisms induced by lead, oxygen reactive species generation has been noted (ROS), which is key in structural disruption and the chromosomic sequence; it can also interrupt transcription processes by replacing zinc in regulatory proteins [53].
3.3. Cadmium
The use of this metal in agricultural supplies may expose water for human consumption and soils to toxic levels [58,65]. There is evidence showing the presence of unexpected damage on people’s health due to minimum levels of cadmium exposure within the allowed values [66]. In humans, this metal can produce kidney disease at relatively low concentrations considered chronic, low dose intoxication [41].
3.4. Mercury
Mercury, like other heavy metals, is found naturally on the earth’s crust. It generally enters the environment through rock weathering by natural processes and eventually contaminates aquifers and soils, coming into contact with human beings [67]. Humans are rarely exposed to high concentrations of mercury and acute effects are rare, except for those caused by industrial accidents [68]. Kidneys and the brain are the main target organs for mercury; in the kidney, mercury may be stored, producing renal damage [69].
3.5. Vanadium
Vanadium, like other heavy metals, is widely distributed in the environment [70] and occurs naturally in variable concentrations in matrices such as soil and water [71]. When of natural origin, it is mainly a product of volcanic activity and soil erosion [72]. In vitro studies have shown that vanadium acts as a phosphate analog and, as such, interferes with various ATPasas, phosphatases and phosphate transfer enzymes; at high concentrations, it has been shown that vanadium inhibits Na + K + ATPasa, Ca2 + ATPasa, H + K + ATPasa, K + ATPasa, Ca + MgATPasa, dyneinATPasa, actomyosinATPasa, alkaline and acid phosphatases, glucose-6-phosphatase, ribonuclease, phosphodiesterase and phosphotyrosilphosphatase [73].
3.6. Silica
Exposure to silica concentrations has been related to an increased risk of developing chronic kidney disease [74,75]. Noticeable in zones of high MeN prevalence are the vast extensions of agricultural areas, especially sugar cane. In some countries of the area, including Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua and El Salvador, prior to cutting sugar cane, the plantations of sugar cane are burned, causing air movement with small particles known as “fly-ashes”. These fly-ashes are parts of the cane’s foliage that have silica residues, which are considered to increase the risk of developing kidney disease [76]. The ash is usually transported by the wind over long distances, arriving at communities and homes and even being ingested by people as they fall on water or foodstuffs. The occupational risks of the sugar cane industry are high throughout the cultivation cycle; however, they increase during harvesting due to the high intensity of work and the arrival of many temporary workers prompted by internal and international migrations, as is the case of Nicaraguan workers migrating to Costa Rica (the sugar cane plantations in the north zone) [77]. A reduction in the renal function of sugarcane cutters during the harvesting stage has been documented, as well as differences related to the type of work [78]. One of the major problems in agricultural workers is the thermal stress to which they are exposed and which is associated with insufficient hydration [79].
4. Chronic Effect of Nephrotoxic Metals at Low Doses
It is known that acute and chronic intoxication produced by heavy metals has the capacity to produce renal damage. The seriousness of the damage and the type of injury largely depend on the toxic species and the metal’s toxicokinetics [18].
Low concentrations of metals such as lead, mercury and cadmium cause a renal disfunction known as de Fanconi syndrome, characterized by an increase of protein levels, glucose and amino acids in urine, as well as a glomerular filtration rate reduction for a defect on the proximal tubular function [18]. For example, health effects related to arsenic in human beings are associated with the process of biotransformation, even at the lowest doses allowed in water (10 µg/L); this occurs because of the action of metabolites resulting in molecular damage induction accumulating over time. The effects derived from these alterations include genomic instability associated with oxidative damage, alteration of gene expression (including coding and non-coding RNA), localized epigenetic reprogramming and histone post-transduction modifications [54]. These alterations directly affect the molecular pathways involved in the beginning and progression of many conditions which could take decades after the exposure. It is important to mention that arsenic metabolites generated during their biotransformation can also cross the placental barrier resulting in fetal exposure to this toxin at similar levels as the mother’s level. As such, the more immediate effects to the molecular damage induced by arsenic can be observed as adverse effects on fetal development and pregnancy [54].
5. Conclusions
The geographic location of the areas with high incidence of MeN in Central America has a cause which is not easily explained. Within the regions with high and low prevalence of MeN, there are similar environmental, geographic and occupational characteristics. This means that some workers in warm and low altitude areas with extensive agriculture are not affected by MeN even though they have the same burden of physical exertion and high environmental temperature.
The nephrotoxic properties of arsenic, lead, mercury, cadmium, vanadium and silica, as well as the additive effect among them, have been widely documented and have been related to cases of chronic kidney disease of non-traditional causes; however, the analysis of these toxicants in relation to MeN has not been exhaustive, provoking a search for a direct relationship between toxicants and the presence of the disease.
We propose an analysis that considers: (a) analysis of the toxicants in soil and water: including concentration, chemical species, levels of exposure and route of entry into the organism; (b) environmental and geographical factors, such as ambient temperature, relative humidity, meters above sea level and atmospheric movement of particles in a defined geographical area; and (c) patient-related factors, such as family genetics, nutrition and general health status. An integral analysis of these variables under the same exposure scenario will allow us to evaluate the contribution of all these factors and to explain why cases occur in a certain geographical area and not in others with similar characteristics.
Controlling MeN has many pending tasks, and one of the important aggravating factors is that the lesions to the kidney are irreversible. In some patients in early stage 1 or 2 and with appropriate intervention, patients can maintain their renal function and have a good prognosis for life; unfortunately, the later the diagnosis, the lower the life expectancy for those affected. Most of the time the diagnosis is made at stage 4 or 5 when renal viability is compromised and progression to advanced CKD is imminent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.V.-R., V.M.-C. and M.G.S., writing—original draft preparation B.V.-R., writing—review and editing B.V.-R., V.M.-C. and M.G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Javier Estrada Zeledón, Nephrology Service of the Enrique Baltodano Briceño Hospital, Costa Rica, for reviewing this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Courville, K.; Bustamante, N.; Hurtado, B.; Pecchio, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Núñez-Samudio, V.; Landires, I. Chronic Kidney Disease of Nontraditional Causes in Central Panama. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez Polo, V.; Garcia-Trabanino, R.; Rodriguez, G.; Madero, M. Mesoamerican Nephropathy (MeN): What We Know so Far. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2020, 13, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Epidemia de Enfermedad Renal Crónica En Comunidades Agrícolas de Centroamérica. Definición de Caso, Bases Metodológicas y Enfoque Para Vigilancia de Salud Pública. 2017. Available online: http://iris.paho.org (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Pan American Health Organization Resolution CD52/8. Chronic Kidney Disease in Farming Communities de Centroamérica. 2013. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/bitstream/handle/10665.2/4401/CD52_8esp.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Correa-Rotter, R.; Wesseling, C.; Johnson, R.J. CKD of Unknown Origin in Central America: The Case for a Mesoamerican Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, C.; Crowe, J.; Hogstedt, C.; Jakobsson, K.; Lucas, R.; Wegman, D.H. Resolving the Enigma of the Mesoamerican Nephropathy: A Research Workshop Summary. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, W.E.; Ordunez, P. Epidemia de Enfermedad Renal Crónica en Comunidades Agrícolas de Centroamérica. Definición de Casos, Base Metodológica Y Enfoques Para la Vigilancia de Salud Pública; OPS: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wesseling, C.; van Wendel de Joode, B.; Crowe, J.; Rittner, R.; Sanati, N.A.; Hogstedt, C.; Jakobsson, K. Mesoamerican Nephropathy: Geographical Distribution and Time Trends of Chronic Kidney Disease Mortality between 1970 and 2012 in Costa Rica. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 72, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Trabanino, R.; Cerdas, M.; Madero, M.; Jakobsson, K.; Barnoya, J.; Crowe, J.; Jarquín, E.; Guzmán-Quilo, C.; Correa-Rotter, R. Nefropatía mesoamericana: Revisión breve basada en el segundo taller del Consorcio para el estudio de la Epidemia de Nefropatía en Centroamérica y México (CENCAM). Nefrol. Latinoam. 2017, 14, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbán, P.A. Pesticides and heat stress in the global epidemic of chronic kidney disease from nontraditional causes. Archives of Occupational Risk Prevention. Occup. Risk Prev. Arch. 2018, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Nast, C.C.; Jayasumana, C.; Schreurs, G.; Roels, F.; Herath, C.; Kojc, N.; Samaee, V.; Rodrigo, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; et al. Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities Is a Toxin-Induced Proximal Tubular Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisher, L.K.; Butler-Dawson, J.; Dally, M.; Jaramillo, D.; Newman, L.S. Enfermedad renal crónica de causa desconocida: Investigaciones en Guatemala y oportunidades para su prevención. Cienc. Tecnol. Salud 2020, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón, A.; Ramay, B.M.; Méndez-Alburez, L.P.; Lou-Meda, R. Factors Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease of Non-Traditional Causes among Children in Guatemala. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2021, 45, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, C.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C.S.; De Silva, P.H.C.; Siribaddana, S.; De Broe, M.E. Kidney Diseases in Agricultural Communities: A Case Against Heat-Stress Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasumana, C.; Orantes, C.; Herrera, R.; Almaguer, M.; Lopez, L.; Silva, L.C.; Ordunez, P.; Siribaddana, S.; Gunatilake, S.; De Broe, M.E. Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities: A Worldwide Epidemic with Social, Occupational and Environmental Determinants. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2016, 32, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseling, C.; Glaser, J.; Rodríguez-Guzmán, J.; Weiss, I.; Lucas, R.; Peraza, S.; da Silva, A.S.; Hansson, E.; Johnson, R.J.; Hogstedt, C.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease of Non-Traditional Origin in Mesoamerica: A Disease Primarily Driven by Occupational Heat Stress. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2020, 44, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, O.; Jacquillet, G.; Tauc, M.; Cougnon, M.; Poujeol, P. Effect of Heavy Metals on, and Handling by, the Kidney. Nephron. Physiol. 2005, 99, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.; Haby, M.M.; Illanes, E.; Sanchez-Viamonte, J.; Elias, V.; Reveiz, L. Risk Factors for Chronic Kidney Disease of Non-Traditional Causes: A Systematic Review. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2019, 43, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes-Navarro, C.M.; Herrera-Valdés, R.; Almaguer-López, M.; Brizuela-Díaz, E.G.; Alvarado-Ascencio, N.P.; Morales, E.J.F.; Bayarre-Vea, H.D.; Calero-Brizuela, D.J.; Vela-Parada, X.F.; Zelaya-Quezada, S.M. Enfermedad renal crónica en niños y adolescentes en las comunidades agrícolas de El Salvador: Estudio NefroSalva Pediátrico (2009–2011). MEDICC Rev. 2016, 18, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Centeno, J.A.; Forcada, E.G.; Búa, P.P. La Geología Médica: Una disciplina emergente. Rev. Salud Ambiente. 2016, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos Reyes, C.A.; Ríos Gutiéttez, M.P.; Joya Neira, S. The Importance of Minerals in Medical Geology: Impacts of the Environment on Health. Arch. Med. Manizales 2020, 21, 182–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F.P.; Sandoval, O.A.A.; Prieto, J. Geological Factors and Health Problems. J. Chem. Health Risks 2013, 3, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh, J.; Maity, J.P.; Mushtaq, S.; Vithanage, M.; Seneweera, S.; Schneider, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Khan, N.I.; Hamawand, I.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; et al. Medical Geology in the Framework of the Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COMISCA. Enfermedad Renal Cronica de las Comunidades Agricolas de Centroamerica. 2013. Available online: https://www.sica.int/documentos/10b-enfermedad-renal-cronica-de-las-comunidades-agricolas-de-centroamerica_1_79230.html (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Rotter, R.C.; Trabanino, R.G. Nefropatía mesoamericana: Una nueva enfermedad renal crónica de alta relevancia regional. Acta Médica Grupo Ángeles 2018, 16, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Salud; Dirección de Vigilancia de la Salud. Protocolo de Vigilancia de La Enfermedad Renal Crónica No Tradicional; Ministerio de Salud: San Jose, Costa Rica, 2019.
- Arici, M. Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinician’s Guide; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wijkström, J.; González-Quiroz, M.; Hernandez, M.; Trujillo, Z.; Hultenby, K.; Ring, A.; Söderberg, M.; Aragón, A.; Elinder, C.-G.; Wernerson, A. Renal Morphology, Clinical Findings, and Progression Rate in Mesoamerican Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.W.; Ciccia, E.A.; Devarajan, P. Cystatin C as a Biomarker of Chronic Kidney Disease: Latest Developments. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinga, B.D.R. Ring of Fire: An Encyclopedia of the Pacific Rim’s Earthquakes, Tsunamis, and Volcanoes; Bloomsbury Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- González, M.B. Las erupciones volcánicas y sus consecuencias en la Cuenca del Pacífico. PORTES Rev. Mex. Estud. Sobre Cuenca Pacífico 2018, 12, 165–177. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams, P.W. Geophagy and the Involuntary Ingestion of Soil. In Essentials of Medical Geology; Selinus, O., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Campos, V.; Ulloa, O.; Siebecker, M.; Zimmerman, A.J.; Weindorf, D.C.; Quirós, M.; Estrada, J.; Ulate, S. Establishing a Scenario of Exposure to Environmental Toxins Associated with Nephropathies in Agricultural Areas of Costa Rica Based on Geological Medicine. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2146203/v1 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Ulate, S. Cuantificación de Metales Pesados en Aire y Suelo y su Posible Relación con la Prevalencia de Nefropatía Mesoamericana en el Cantón de Cañas, Guanacaste, Costa Rica; Instituto Tecnológico de Costa Rica: Cartago, Costa Rica, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ulloa, O. Desarrollo de Un Modelo Sobre La Incidencia de Variables Ambientales y Geográficas En Las Tasas de Prevalencia de La Nefropatía Mesoamericana En Costa Rica. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto Tecnológico de Costa Rica, Cartago, Costa Rica, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Kapri, A.; Goel, R. Heavy Metal Pollution: Source, Impact, and Remedies. In Biomanagement of Metal-Contaminated Soils; Khan, M.S., Zaidi, A., Goel, R., Musarrat, J., Eds.; Environmental Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 20, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoytcheva, M. Pesticide in the Modern World: Effects of Pesticide Exposures, 1st ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, O. Insuficiencia Renal Por Metales Pesados. Efecto Nefrotóxico de Los Metales Pesados y Su Reabsorción/Eliminación Por El Riñón. 2010. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=57613001041 (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Sabath, E.; Robles, O. Medio ambiente y riñón: Nefrotoxicidad por metales pesados. Nefrología 2012, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruibe, J.; Ogwuegbu, M.; Egwurugwu, J. Heavy Metal Pollution and Human Biotoxic Effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 5, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, V.; Ulloa, O.; Siebecker, M.; Zimmerman, A.J.; Weindorf, D.C.; Quiroz, M.; Estrada, J. Establishing a Scenario of Exposure to Environmental Toxins Associated with Chronic Kid-Ney Disease in Agricultural Areas of Costa Rica Based on Medical Geology; Research Square: Durham, NC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Venero, S. Saharan Dust Effects on Human Health: A Challenge for Cuba’s Researchers. MEDICC Rev. 2016, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Tong, D.; Wu, G.; Dan, M.; Teng, B. A Systematic Review of Global Desert Dust and Associated Human Health Effects. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, I.; Derbyshire, E.; Carrillo, T.; Caballero, E.; Engelbrecht, J.P.; Romero, L.E.; Mayer, P.L.; Rodríguez de Castro, F.; Mangas, J. Saharan Dust and the Impact on Adult and Elderly Allergic Patients: The Effect of Threshold Values in the Northern Sector of Gran Canaria, Spain. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 27, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, M.E. Boletín Meteorológico Mensual; Instituto Meteorológico Nacional de Costa Rica: Aranjuez, Costa Rica, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Shentu, J.; Yang, X.; Baligar, V.C.; Zhang, T.; Stoffella, P.J. Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils: Sources, Indicators and Assessment. J. Environ. Indic. 2015, 9, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selinus, O. (Ed.) Essentials of Medical Geology: Revised Edition; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, M.; Repetto, G. Toxicología Fundamental, 4th ed.; Editorial Díaz de Santos: Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nava-Ruíz, C.; Méndez-Armenta, M. Efectos neurotóxicos de metales pesados (cadmio, plomo, arsénico y talio). Arch. Neurocienc. 2011, 16, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Johri, N.; Jacquillet, G.; Unwin, R. Heavy Metal Poisoning: The Effects of Cadmium on the Kidney. BioMetals 2010, 23, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeh Engwa, G.; Udoka Ferdinand, P.; Nweke Nwalo, F.; Unachukwu, N.M. Mechanism and Health Effects of Heavy Metal Toxicity in Humans. In Poisoning in the Modern World—New Tricks for an Old Dog; Karcioglu, O., Arslan, B., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.D.; Lam, W.L. Health Effects Associated with Pre- and Perinatal Exposure to Arsenic. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 664717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Shao, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Nephroprotective Effect of Astaxanthin against Trivalent Inorganic Arsenic-Induced Renal Injury in Wistar Rats. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, M.; Paranagama, P.; Amarasinghe, M.; Wijewardane, K.; Dahanayake, K.; Fonseka, S.; Rajakaruna, K.; Mahamithawa, A.; Samarasinghe, U.; Senanayake, V. Possible Link of Chronic Arsenic Toxicity with Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka. 2013. Available online: https://www.iiste.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Xu, M.; Niu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Feng, G.; Wang, H.; Li, S. Retracted: Proanthocyanidins Antagonize Arsenic-Induced Oxidative Damage and Promote Arsenic Methylation through Activation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8549035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.; Bridges, C. Chronic Kidney Disease and Exposure to Nephrotoxic Metals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-P.; Tsai, K.-S.; Chen, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-F.; Yang, R.-S.; Liu, S.-H. Arsenic Induces Apoptosis in Myoblasts through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Pathway. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Experientia Supplementum; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Yan, N.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Li, B. Arsenic Induces Continuous Inflammation and Regulates Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg Balance in Liver and Kidney In Vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 8414047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patočka, J.; Černý, K. Inorganic Lead Toxicology. Acta Medica 2003, 46, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead Toxicity: A Review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiekhani, M.; Ommati, M.M.; Azarpira, N.; Heidari, R.; Salarian, A.A. Glycine Supplementation Mitigates Lead-Induced Renal Injury in Mice. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenod, F. Nephrotoxicity and the Proximal Tubule. Nephron Physiol. 2003, 93, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L.; Åkesson, A. Current Status of Cadmium as an Environmental Health Problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Mercury. 1999. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/tp.asp?id=115&tid=24 (accessed on 28 May 2020).
- Nordberg, G.; Nordberg, G. Metales: Propiedades químicas y toxicidad productos químicos. Enciclopedia Salud Segur. Trab. 2017, 2, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-D.; Zheng, W. Human Exposure and Health Effects of Inorganic and Elemental Mercury. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2012, 45, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, N.; Sahin, M.; Gubbuk, I.H. Synthesized of Sporopollenin-Immobilized Schiff Bases and Their Vanadium(IV) Sorption Studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2012, 22, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortoul, T.I.; Rojas-Lemus, M.; Rodriguez-Lara, V.; Gonzalez-Villalva, A.; Ustarroz-Cano, M.; Cano-Gutierrez, G.; Gonzalez-Rendon, S.E.; Montaño, L.F.; Altamirano-Lozano, M. Overview of Environmental and Occupational Vanadium Exposure and Associated Health Outcomes: An Article Based on a Presentation at the 8th International Symposium on Vanadium Chemistry, Biological Chemistry, and Toxicology, Washington DC, August 15–18 2012. J. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 11, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Polidori, A.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Cassee, F.R.; Sioutas, C. Physicochemical and Toxicological Profiles of Particulate Matter in Los Angeles during the October 2007 Southern California Wildfires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, A.; Wiszniewska, B.; Szypulska-Koziarska, D.; Kaczmarek, P.; Romanowski, M.; Różański, J.; Słojewski, M.; Ciechanowski, K.; Marchelek-Myśliwiec, M.; Kalisińska, E. The Concentration of Vanadium in Pathologically Altered Human Kidneys. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 180, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramadan, M.A.; Abdelgwad, M.; Fouad, M.M. Predictive Value of Novel Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease among Workers Occupationally Exposed to Silica. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2021, 37, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vupputuri, S.; Parks, C.G.; Nylander-French, L.A.; Owen-Smith, A.; Hogan, S.L.; Sandler, D.P. Occupational Silica Exposure and Chronic Kidney Disease. Ren. Fail. 2012, 34, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.J.B.; Rincón, C.R.; Rodríguez, L.C. Inhalación de sílice y sus efectos en la salud. Pneuma 2012, 8, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Organización Iberoamericana de Seguridad Social. Informe de La Situación de Estrategia Iberoamerican de Seguridad y Salud En El Trabajo. 2015–2020, 2015. Available online: https://oiss.org/estrategia-iberoamericana/publicaciones (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Laws, R.L.; Brooks, D.R.; Amador, J.J.; Weiner, D.E.; Kaufman, J.S.; Ramírez-Rubio, O.; Riefkohl, A.; Scammell, M.K.; López-Pilarte, D.; Sánchez, J.M.; et al. Changes in Kidney Function among Nicaraguan Sugarcane Workers. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2015, 21, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, C.; Crowe, J.; Peraza, S.; Aragón, A.; Partanen, T. Trabajadores de la Caña de Azúcar; OISS: Houston, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).