Abstract
Resonance frequencies of a masonry bell tower were estimated by means of ambient noise measurements and compared with those computed by using fixed base, Winkler, and FE numerical, including subsoil. Given the geological complexity that characterizes the subsurface of the analyzed area, despite the presence of massive volcanic outcrops near the bell tower, we carried out a geophysical characterization of the subsoil by using active and passive seismic surveys. These surveys have identified a soft substrate underneath the construction; for this reason, the dynamic identification of the tower was performed, including the interaction with the soil. The resonance frequencies of the masonry bell tower computed by the models are very similar to those obtained using ambient noise. Results suggest that building resonance frequencies, estimated by ambient noise surveys, can be used because of their reliability especially when quick analyses are required at historical buildings located in seismically active areas needing plan actions to reduce their vulnerability. Moreover, such analyses, being performed on samplings acquired within the structure, allow for estimating its dynamic response, taking into account the effect of subsurface characteristics as well.
1. Introduction
One of the most relevant damage sources for architectural heritage are dynamic loads, such as those generated by earthquakes or vibrations caused by human activities. In particular, in the case of slender masonry buildings, such as bell towers, the evaluation of the dynamic response is a major issue, because of their intrinsic vulnerability to dynamic loads. The knowledge of the dynamic response is the starting point for seismic vulnerability evaluation, vibrational damage prevision, and preliminary effectiveness assessment of maintenance, restoration, and structural upgrade interventions.
Reliable information on the main mechanical and physical parameters of the structure is hard to acquire, particularly for historical and monumental constructions, in which only nondestructive tests can be carried out. Indeed, such buildings are characterized by a superposition of construction phases, whose details can hardly be detected even by accurate inspections. For instance, the mechanical characterization of traditional stone masonry is still an open problem, given the irregularity of the masonry geometry, its strong dependence on the methods adopted for guaranteeing the interconnections between the elements, etc.
Parameter identification by means of a nondestructive technique is a valuable way for calibrating the numerical models used for structural analysis. Among nondestructive methods, experimental dynamic identification of the structure is a helpful tool for obtaining comprehensive information about the mechanical response of historical construction.
Dynamic identification consists in determining modal parameters, i.e., modal frequencies, mode shapes, and modal damping, measuring the response of the structure to a measurable dynamic input (experimental modal analysis, EMA), or to an environmental excitation (operational modal analysis, OMA). In the latter case, velocities or accelerations on a structure subjected to small amplitude excitations are measured in predefined points. The technique is also known as output-only modal analysis because it is based on the dynamic response to unknown stochastic dynamic loads instead of artificial, controlled excitations. The major advantages of OMA techniques are their absolute nondestructiveness, low cost, and simple applicability, thanks to easy handling of the instrumentation. OMA technique can be coupled with procedures based on laser scanning and photogrammetry [1] or parametric scan-to-FEM approaches [2] in order to obtain accurate numerical models. As in most identification procedures, the main limits are the restricted amount of information that can usually be obtained, and the high uncertainty of data. Therefore, the experimentally obtained modal parameters are compared with those determined through numerical models, which are iteratively adjusted to match the measured quantities.
Many studies on dynamic identification of historical masonry towers have been carried out in the last decades [3,4], some of them related to either continuous monitoring [5,6] or the interaction of the structure with the vibrations induced by bell swinging [7,8].
A correct identification of the dynamic parameters of the structure requires, in any case, an accurate knowledge of the geometry of the mass and of the material properties, as well as of the boundary conditions of the analyzed structure. Often fixed boundary conditions are considered; however, for slender masonry towers, this hypothesis can lead to considerable errors. In fact, the effective degree of constraint given by the soil should be considered. For this purpose, one possibility is to include the structure–foundation–soil interaction in the numerical model. The knowledge of the subsoil stratigraphy, as well as the mechanical characterization of the layers, must be obtained through geological and geophysical surveys.
Many authors [9,10,11] proposed comparisons between a fixed base model of bell masonry towers and finite element models (FEM), accounting in a more or less accurate way for the subsoil. In this study, we follow a similar methodology using detailed experimental data for the subsoil and for the tower to validate the comparisons.
Here, a combined dynamic identification procedure, based on ambient noise and standard spectral ratio (SSR), is applied to build a refined FEM of a historical bell tower. Both the superstructure and the soil will be modelled, and the relevance of the combined model in the estimation of the dynamic characteristic of the structure will be discussed by means of a comparison with a fixed base model.
Subsoil can be characterized through both field surveys and geophysical approaches. In the first case, the availability of outcrops in the close proximity of the study area is a useful starting point to build up a geological model. Numerous studies involving numerical models or indirect/remote surveys rely on the preliminary field inspections, especially in the case of rock mass occurrence where the intact rock physical mechanical properties should be known [12,13,14]. On the other hand, the most used indirect techniques for characterizing the subsoil are active seismic surveys (seismic tomography and multichannel analysis of seismic waves, MASW), passive seismic surveys (HVSR) and geoelectrical surveys.
The HVSR method, thanks to its total noninvasiveness and speed of execution, represents one of the most widely used geophysical survey methodologies, especially in urban areas. By recording environmental noise in the three components of ground motion, it is indeed possible to define the resonance frequency and site effects [15]. This investigation technique has already been used in many scientific articles to characterize the subsoil of historical buildings [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
It is important to underline that the experimental data have been acquired in a single campaign, using the same experimental apparatus for both the dynamic identification of the structure and HVSR. The proposed technique, therefore, in addition to yielding reliable data, appears practical from an engineering point of view, thanks to its easiness of execution.
The proposed methodology was applied to the case study of the bell tower of the San Giuseppe church located in the city of Aci Castello (Sicily, Italy) (Figure 1a,b). Geomechanical and geophysical surveys were carried out to identify the mechanical and physical properties of the foundation soil. Modal parameters were obtained through ambient noise vibration data and compared with the results of numerical modal analyses of three different FEM models: fixed base structure, structure with Winkler-type foundation soil, and complete FE modeling of the structure and of the layered soil, as experimentally detected.
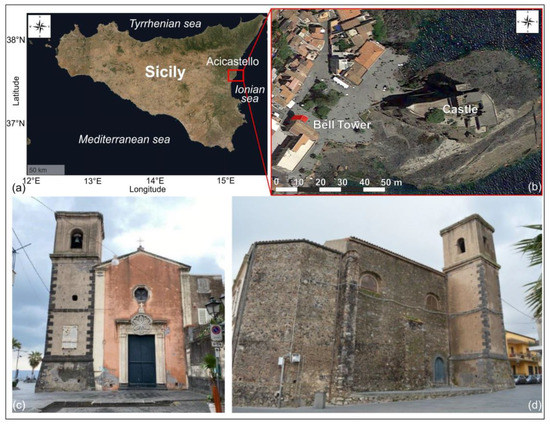

Figure 1.
(a) Location of Aci Castello municipality (Sicily), (b) position of San Giuseppe’s bell tower (highlighted in red), (c) west and (d) north views of the San Giuseppe church.
It will be shown that the fixed basis model can lead to significant errors, even in the presence of rocky sublayers, so that the influence of the soil cannot be neglected. However, the uncertainty related to the characterization of the soil requires supplementing the data obtained from dynamic analyses with further information.
The Case Study: Description of the Bell Tower
The study area is sited in the easternmost part of Aci Castello City (Figure 1a), which is located along the eastern flank of Mount Etna, one of the most relevant volcanoes in the world, today acknowledged as part of the UNESCO World Heritage List, thanks to its exceptional level of volcanic activity, which has been documented for over 2700 years [25]. In this paper, the bell tower of the San Giuseppe church is studied. The peculiarity of this location is the presence of a castle (Figure 1b) standing on a volcanic promontory overlooking the sea, whose origin probably dates back to the Roman period, and that has been rebuilt and restored several times during the history. The Normans built the present construction in the 12th century.
There are no certain data about the history of the San Giuseppe church (Figure 1b); it was probably built in 1748 on a site where, according to some scholars, another ancient church, which collapsed around 1547, previously existed. According to this opinion, the bell tower may belong to a previous constructive phase, with respect to the church, and could have been built before the 16th century [26]. This information is relevant for the characterization of the construction and appears to be confirmed by the architectural features of the tower, such as its bottom battered wall and the lava stone quoins [27]. The in-situ survey confirmed that the walls of the tower are disjointed from those of the church. For this reason, the tower will be considered as a separate structure, and any interaction with the church will be neglected, as a first approximation. This assumption is quite acceptable since only the determination of the modal frequencies of the tower is carried out in the present study. Any constraint conditions between the tower and the church should be evaluated in the case of structural analyses, such as nonlinear seismic analyses.
There are no data on the effects produced by the southeastern Sicilian 1693 earthquake, although it is likely that it was damaged because, as we will describe later in the text, it nearly destroyed Aci Castello.
San Giuseppe is a simple single-nave church, with a crypt of equal dimensions used as a burial place. The tower bell had a tapering pyramidal masonry spire on the top that was demolished in the early 20th century. Now, there is only a simple four-pitched roof with clay tiles on a wooden frame. In the belfry, two bells are hung without damping devices to the abutment of the arches.
Since its construction, the church has undergone several upgrades and preservation interventions, the most recent in 1970 and 1994. The last one was because the church was damaged by the earthquake in southeastern Sicily on 13 December 1990 [28]. Restoration has not transformed the building’s aspect and consisted in quoin and cornice consolidation, crack repair on walls with stone scales, and injection grouting, as well as improvement of the roof and of its drainage system.
The tower is 15.30 m high and has a rectangular plan with sides of 4.90 and 4.00 m at the base of the tapered wall and sides of 4.50 and 3.30 m at the top of the tapered wall (2.30 m). The 4.50 m dimension is reduced to 3.80 m from the base of the bell chamber. The main geometric features of the tower are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Geometric dimensions of the San Giuseppe tower.
The foundation, not inspected, probably merely consists of an extension of the perimeter walls below the ground floor, for a depth of approximately 1.50 m.
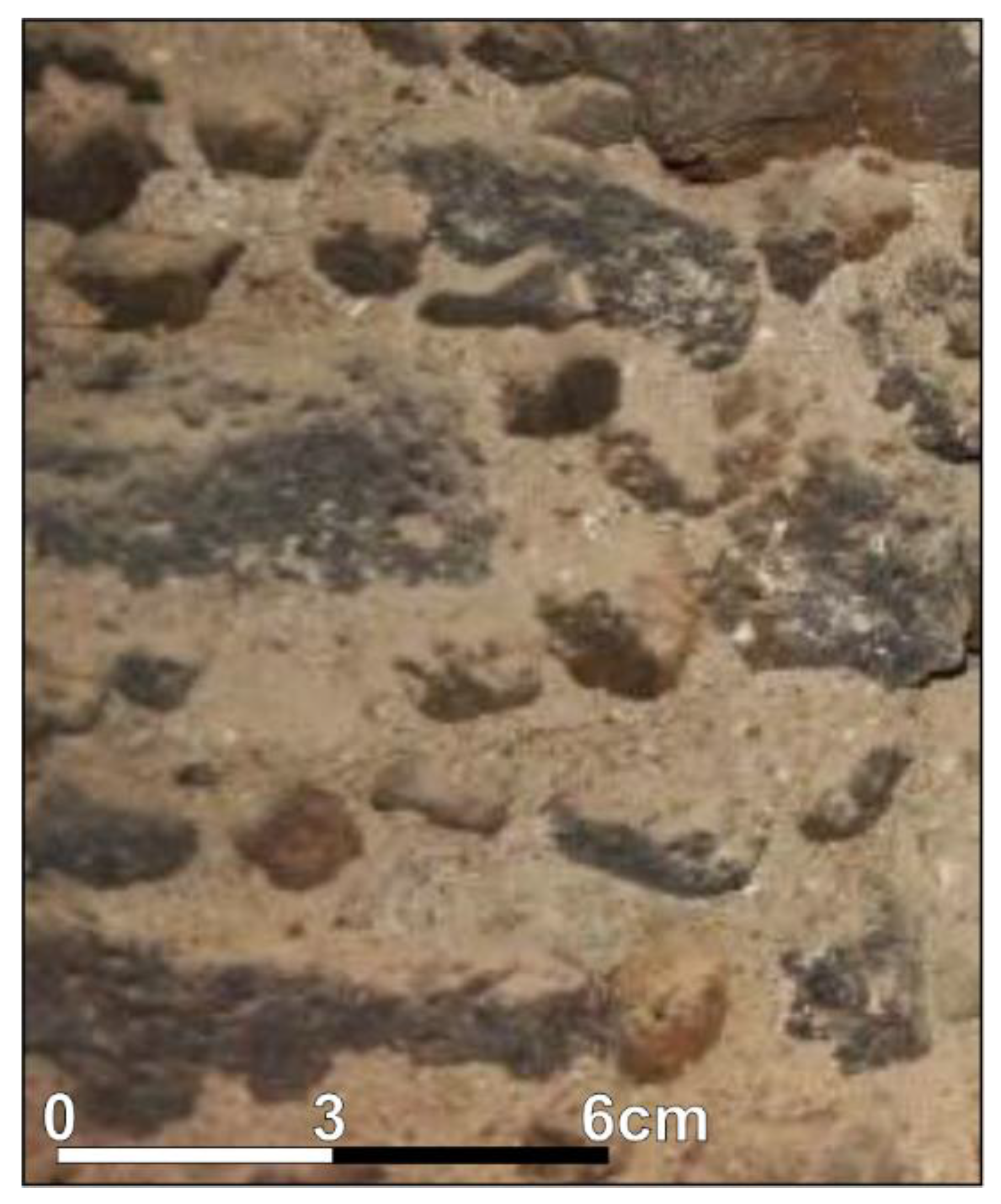
Direct inspection of the tower masonry revealed some similarities with the church one. It is mainly characterized by lava rubble with lime and gravel mortar and the addition of lava fragments and clay tiles to guarantee the horizontality of the successive layers (Figure 2). The walls have an average thickness between 0.65 and 0.70 m. A masonry stair, made up of brick steps, is placed within the tower, and it is supported by a rampant vault. A schematic plan of the tower is shown in Section 5.

Figure 2.
Masonry of the bell tower: photo of the internal side.
2. The Study Area
2.1. Geological Setting
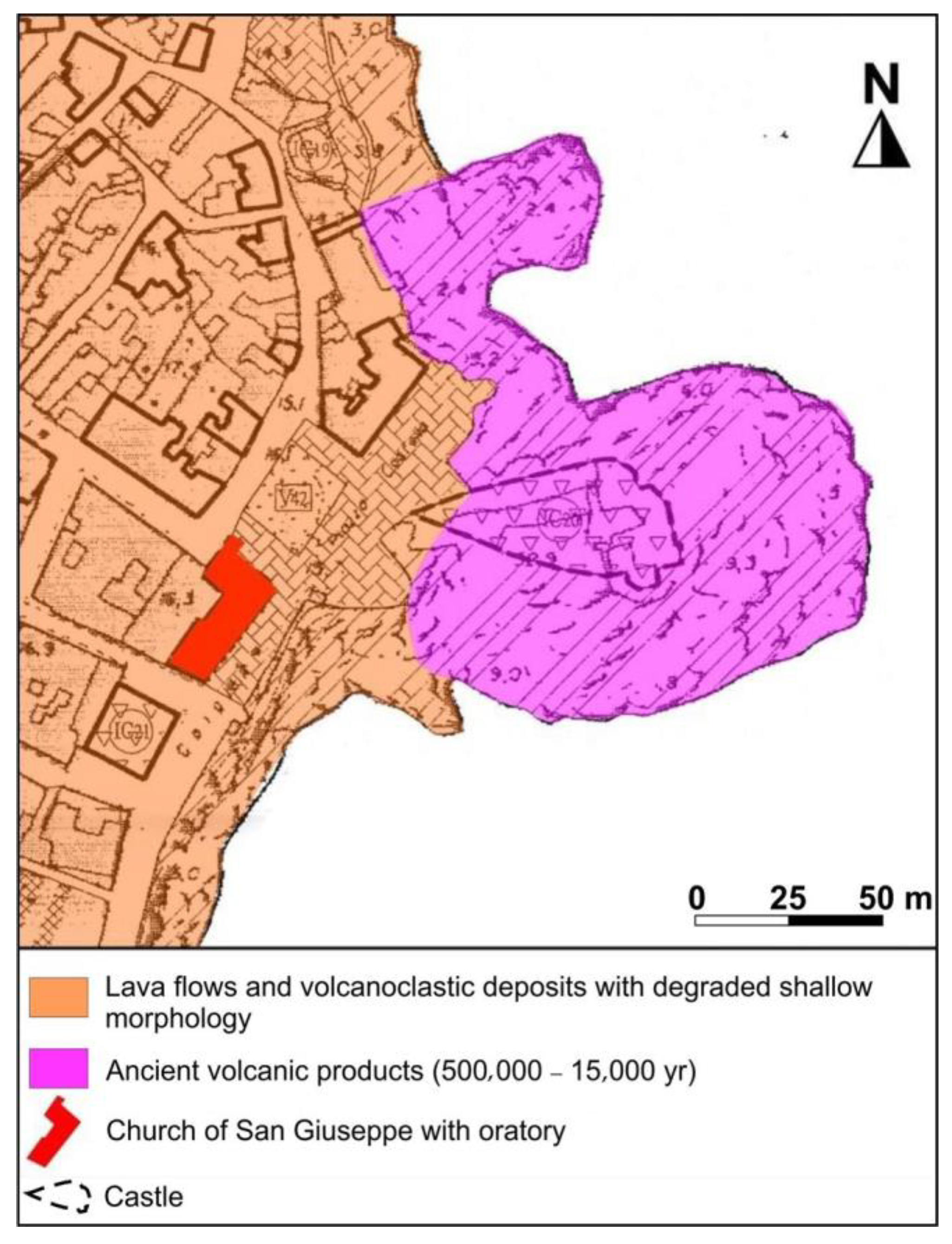
The study area is located at the easternmost part of Aci Castello City, in close proximity to the volcanic cliff holding up the village’s castle (Figure 3). From a geological point of view, such promontory represents a peculiarity, because it is among the few spots hosting volcanic outcrops related to the very first stages of Mount Etna formation (about 500,000 years ago), which mainly occurred in a submarine environment, and is formed by subvolcanic basaltic intrusions [29]. The basaltic cliff is surrounded by a prehistoric lava flow. Well-preserved outcrops of such lava flow occur along the coast, where a jointed volcanic rock mass, with a massive vesicular intact rock texture, can be observed. It belongs to the Pietracannone formation, which is representative of a volcanic succession with mineralogical composition ranging from basaltic to benmoreitic. Lavas are aphyric to highly porphyritic in texture, with phenocrysts of plagioclase, pyroxene, and olivine variable in quantity and size [30].
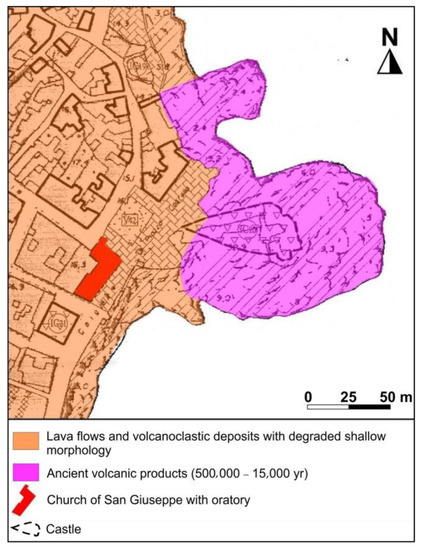
Figure 3.
Geological map of the study area (modified from [31]).
2.2. Seismic History and Seismic Hazard of Aci Castello
A detailed study of the main earthquakes, which affected Aci Castello, has been performed to reconstruct its seismic history. The analysis of the historical reports retrieved from the CFTMed catalogue [28] allowed for delineating the damage scenarios of the most relevant events. In particular, under the 1693 earthquake, only 8 of the 100 houses of the town did not collapse, although 6 of these were significantly damaged, while half of the San Mauro church collapsed [32]. Since the village was almost completely destroyed, it is likely that the San Giuseppe church was damaged as well, also considering that the 1908 and 1990 earthquakes caused damage to the church despite being much weaker than that of 1693. The 1693 earthquake caused 32 victims out of about 330 inhabitants [32]. The 20 February 1818 earthquake caused moderate damage [33,34], while the 1848 and 1990 [28,35] shocks caused slight damage (Table 2) in the city.

Table 2.
Observed intensity at Aci Castello. I0 is the epicentral intensity, Mw is the equivalent magnitude, Iobs is the observed MCS (Mercalli–Cancani–Sieberg) intensity according to Rovida et al. [36].
The castle was likely damaged in 1169 and in 1329. Destruction or damage was mainly caused by earthquakes occurring along the regional fault systems, whereas earthquakes located in the Etnean area were only slightly felt (Table 2).
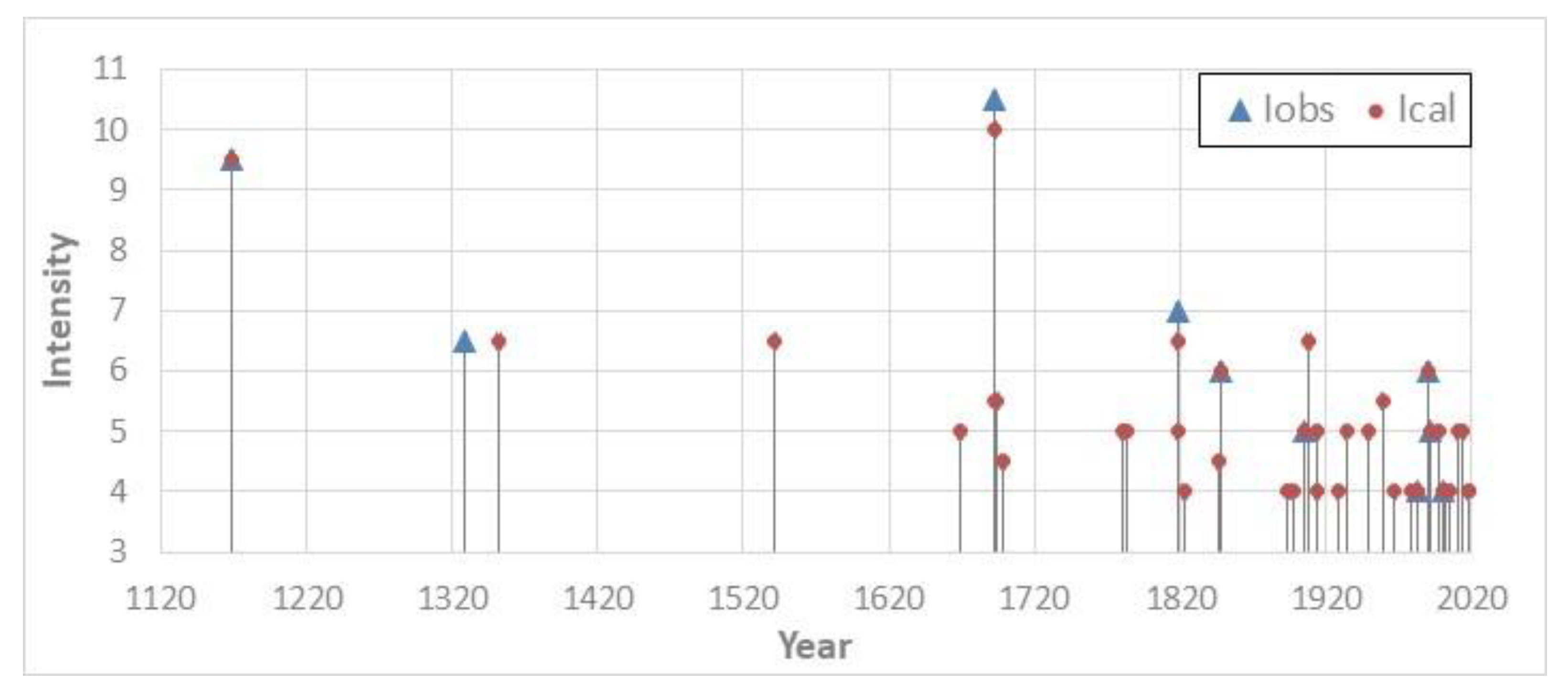
The seismic history is not complete due to the very few observed intensity values. Therefore, in order to evaluate the completeness of the site catalogue and to improve its reliability for hazard purposes, calculated site intensities Ical have been obtained using both the parametric Italian catalogue [36] and the cubic attenuation model proposed by Magri et al. [37]. This led us to include in our site catalogue further 30 earthquakes, without historical information, 6 of which with 5–6 ≤ Ical ≤ 6–7 (Figure 4). In the Database of the Italian Catalogue [36], there is no intensity observed for the 1908 earthquake, but from the computed intensity, we obtained Ical = 6–7 compatible with the observed damage at the bell tower.
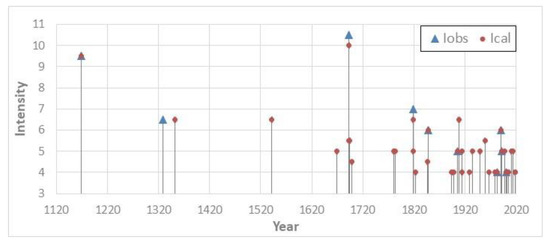
Figure 4.
Seismic history of Aci Castello (Sicily) in the last 1000 years from intensity IV. Iobs is observed intensity; Ical is calculated intensity.
3. Subsoil Characterization
3.1. Engineering Geological Properties of the Volcanic Bedrock
With the aim of collecting engineering geological data of the volcanic lavas constituting the bedrock of the study area, which outcrops in the close proximity of the church, laboratory tests on intact rock specimens and field rock mass surveys were performed. In the first case, 12 rock specimens underwent a physical-mechanical characterization. Due to the textural heterogeneity of volcanic rocks, mainly arising from the different vesicular grade [38], both massive and vesicular rock specimens were sampled. In the first case, rocks show a compact structure with no evidence of macroscopic voids, while the second variety is affected by vesicles, which can be referred to as frozen imprints of bubble of gas with variable size [39]. Literature experiences on the same rock type highlighted that the different rock structure plays a key role in the rock strength and deformability [40,41]. This aspect, which is certainly relevant at the intact rock scale, represents a technical issue in outcrops, where the transition between the two rock structures is not always well defined, and sometimes, the rock properties change within few decimeters [42].
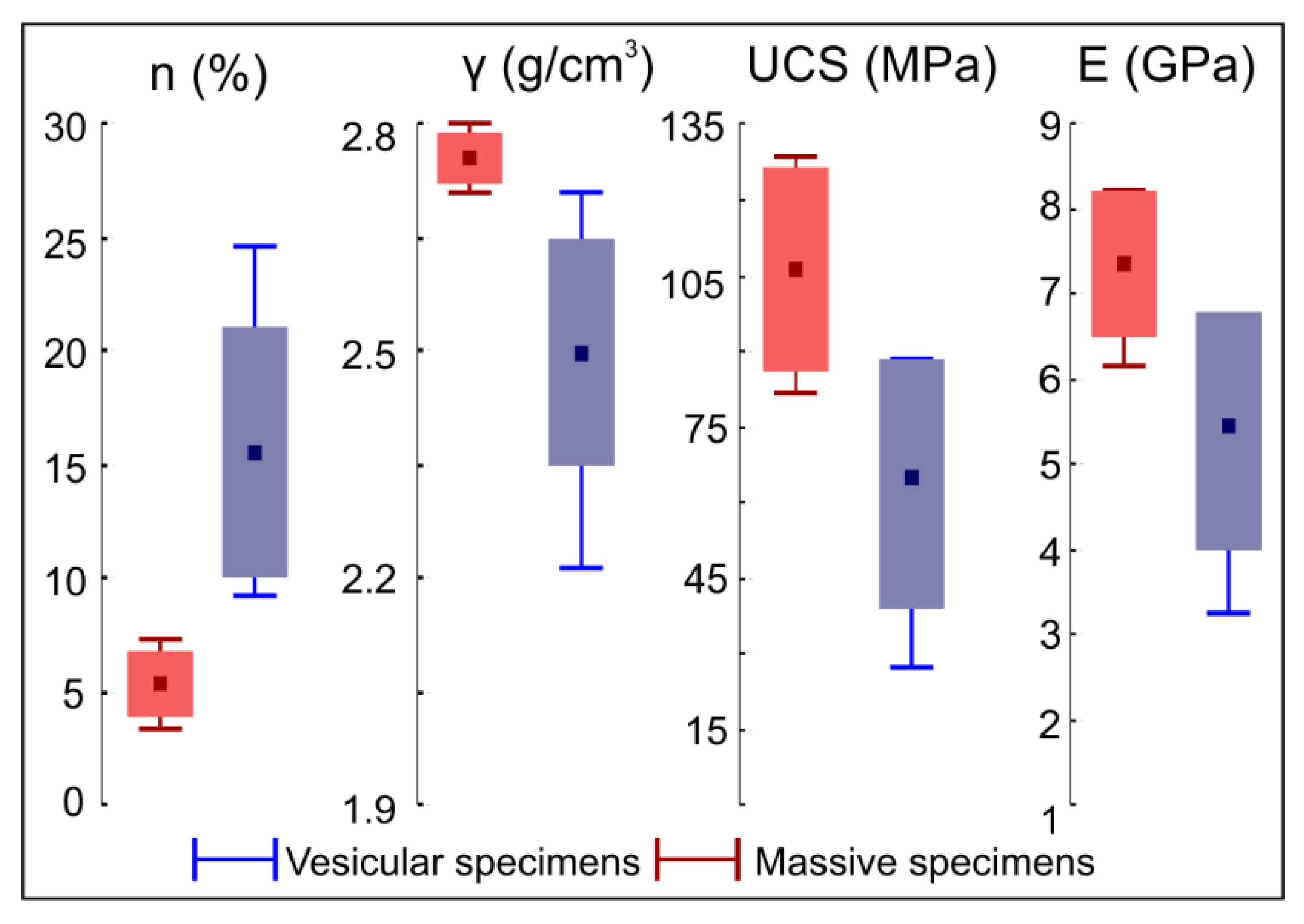
Collected specimens can be grouped into two categories according to the macroscopic presence of voids: massive and vesicular. In the first case, no or relatively few voids occur in the rock texture at the hand scale. Such rocks are characterized by an average of 2.8 g/cm3 bulk density and a total porosity ranging from 3.8% to 7.5%. On the other hand, vesicular specimens show a bulk density ranging between 2.3 and 2.7 g/cm3 and a total porosity from 9.4% to 24.9%. According to the classification proposed by Anon [43], such rocks can be classified as low to high porous rocks (Figure 5).
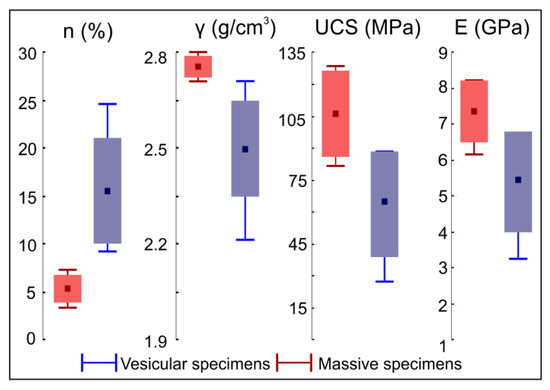
Figure 5.
Statistics of the main measured rock physical-mechanical parameters. Boxes indicate standard deviation, whiskers indicate maximum and minimum, and square is for the mean value. Key: n—total porosity, γ—bulk density, UCS—uniaxial compressive strength, E—Young’s modulus.
Mechanical uniaxial compression tests returned uniaxial compression strength (UCS) values between 80.6 and 128.2 MPa for massive specimens and between 28.1 and 86.3 MPa for vesicular ones. Lower UCS values are related to the more porous rocks, which show also lower elastic modulus, index of a slightly higher deformability attitude under stress. Young’s modulus values, indeed, are between 3.2 and 8.2 GPa (Figure 5). According to Singh and Ghose [44], resulting UCS values are characteristic of a medium to strong rock and of a strong to very strong rock for vesicular and massive specimens, respectively.
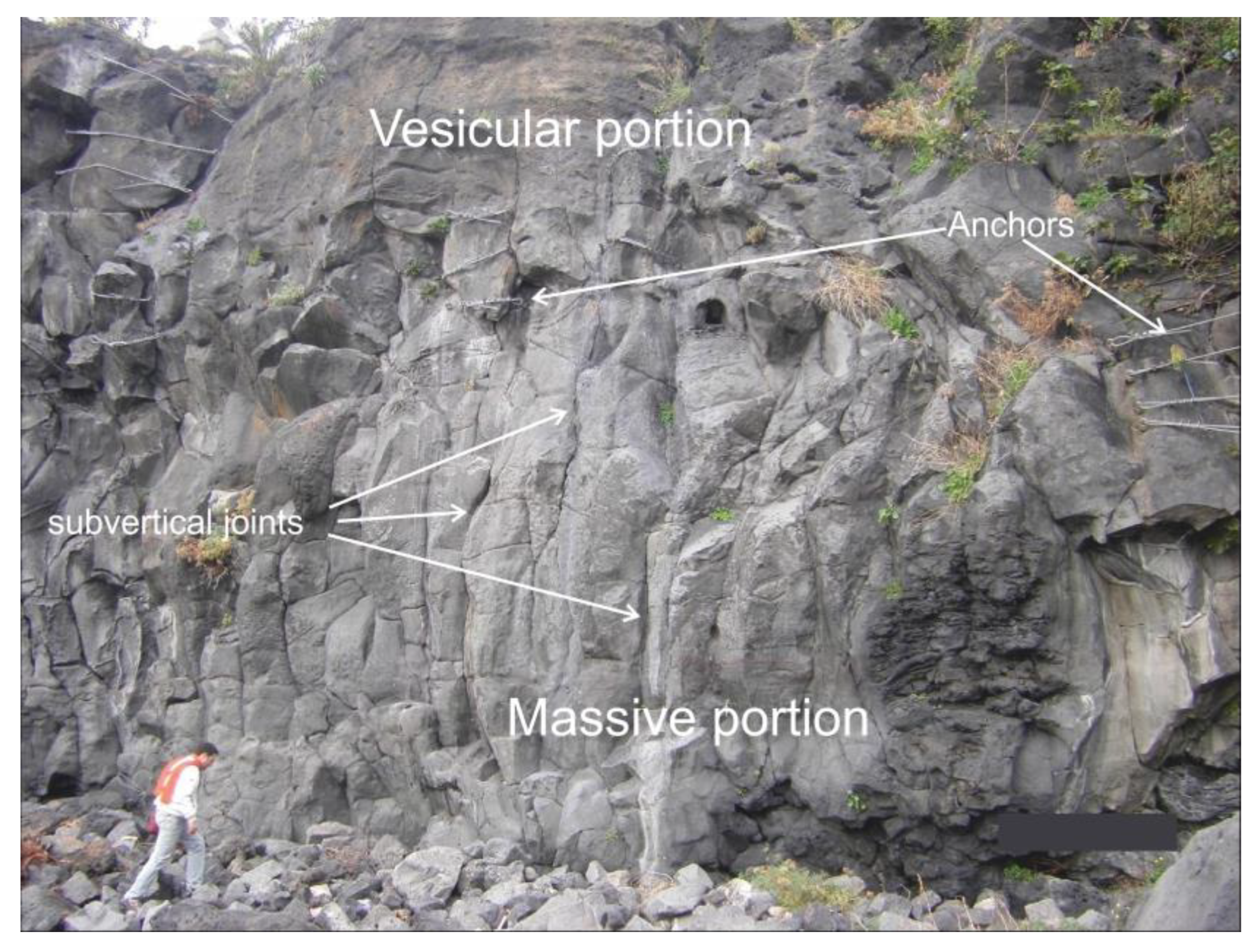
Rock mass characterization was carried out through a geomechanical survey at a 15 m high volcanic rock mass showing a massive basaltic succession, affected by a certain degree of fracturing, located a few tens of meters southeastwards away from the studied church. The rock mass has a columnar aspect, typical of massive volcanic flow succession, and shows a different degree of vesiculation, with a vesicular texture at its higher portion and a massive rock structure at its lower portion (Figure 6). Block shape is mainly prismatic, with an average size greater than 1 dm, and there are widespread anchors to secure local instability features. The rock mass survey was carried out according to the objective sampling criterion proposed by ISRM [45] by evaluating all the discontinuities intersecting a scanline. Based on surveyed data, four main discontinuity sets were recognized, with a general subvertical attitude, except for a subhorizontal set, and an average normal set spacing ranging from 35 to 57 cm. Joints show a different aperture grade, ranging between 0 and 10 mm, a slight weathering and no filling material.
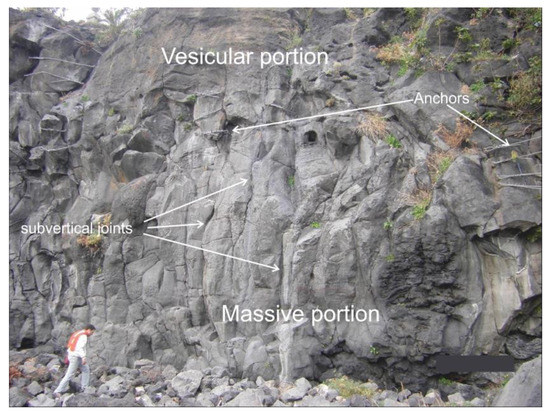
Figure 6.
Rock wall surveyed for geomechanical purposes.
Field and laboratory data were integrated for the application of the generalized Hoek and Brown failure criterion to achieve the main rock mass strength parameters. These were calculated for both the vesicular and massive rock mass portions by using the respective precautionary UCS values. Rock mass structure was assumed as “very blocky”, namely, formed by four discontinuity sets, and good discontinuity features were assumed, for a final representative Geological Strength Index (GSI) value of 50, according to the chart proposed by Marinos and Hoek [46]. In particular, the rock mass modulus of deformation E was calculated by Equations (1) and (2), used for massive (UCS > 100 MPa) and vesicular (UCS < 100 MPa) portions, respectively. The resulting values are 5.8 and 3.4 GPa, highlighting that the presence of vesicles within the intact rock is a feature slightly enhancing the rock mass deformation:
where D is a 0.7 assumed factor related to the degree of disturbance of the rock mass caused by blast damage and stress relaxation, which can range from 0 (undisturbed in situ rock mass) to 1 (very disturbed rock mass).
3.2. Geophysical Characterization of the Subsoil
For the site geophysical characterization, 27 ambient noise samplings were performed, mostly located along two orthogonal profiles, as shown in Figure 7a. Moreover, two active seismic surveys, a multichannel analysis of seismic waves (MASW) and a seismic refraction tomography, were carried out (Figure 8a). MASW is a noninvasive active seismic method that allows the definition of the 1D velocity profile of shear waves (Vs), based on the measurement of surface waves made at different receivers placed on the soil surface. The prevalent contribution to the surface waves is given by Rayleigh waves, which are transmitted with a velocity correlated to the stiffness of the soil portion affected by the wave propagation [47].
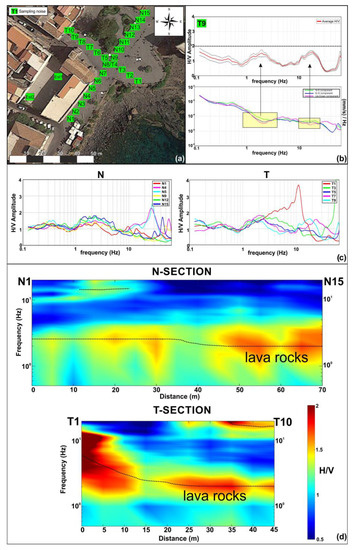
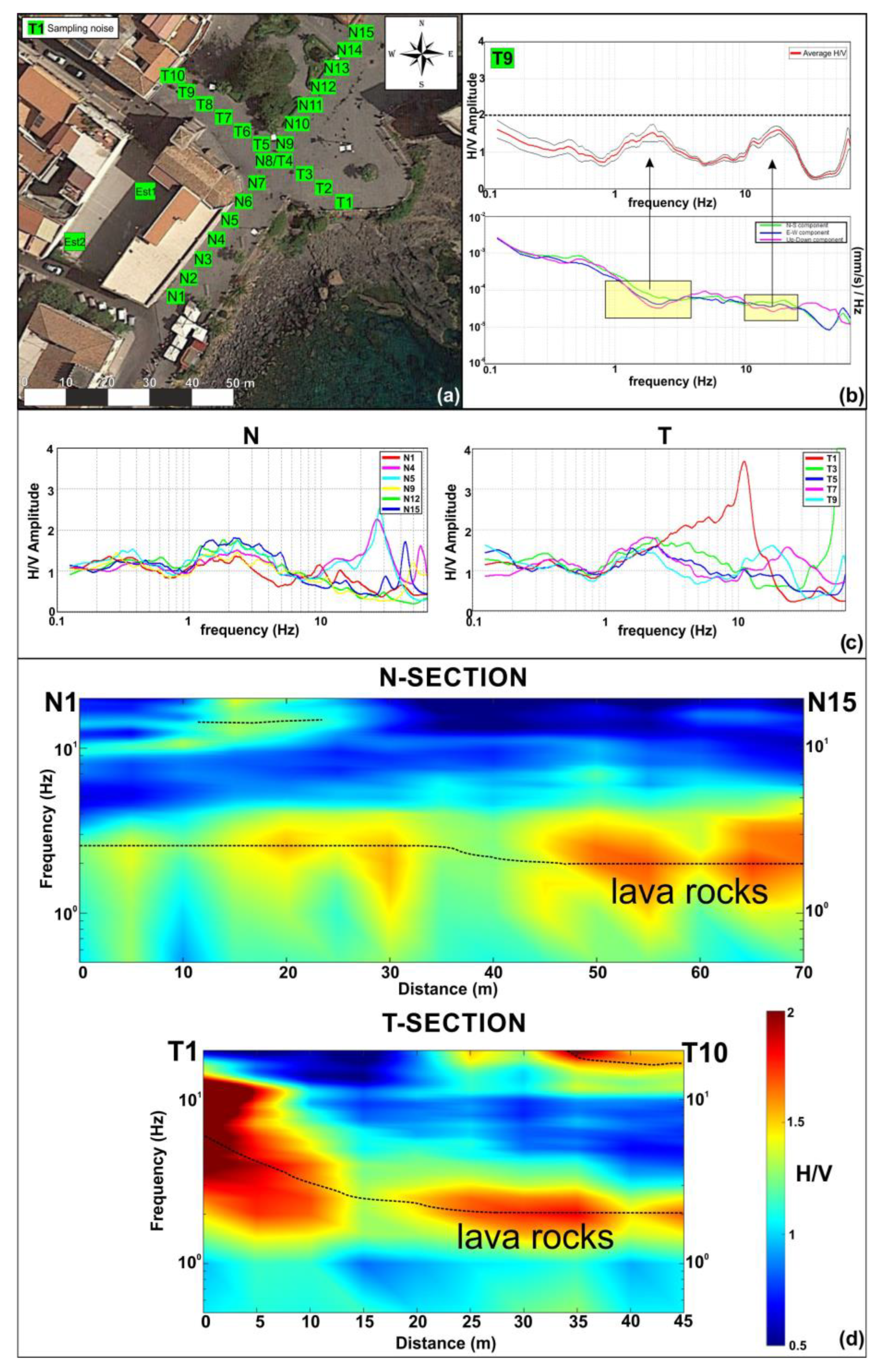
Figure 7.
(a) Position of the ambient noise samplings; (b) example of H/V spectrum performed in T9 position and graph of spectral amplitude components, the yellow areas indicating the typical “eye-shape” linked to stratigraphical transitions; (c) examples of H/V spectra related to ambient noise samplings performed along the two alignments; (d) 2D diagrams obtained along the two alignments (a), showing the distribution of the H/V amplitude values as a function of distance (x-axis) and frequency (y-axis, range 0.1–20 Hz).
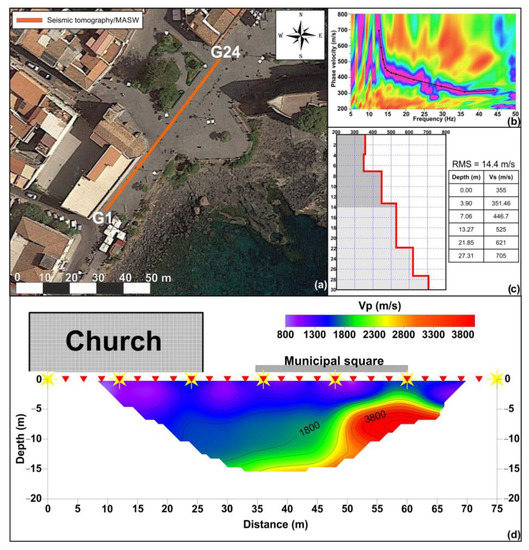
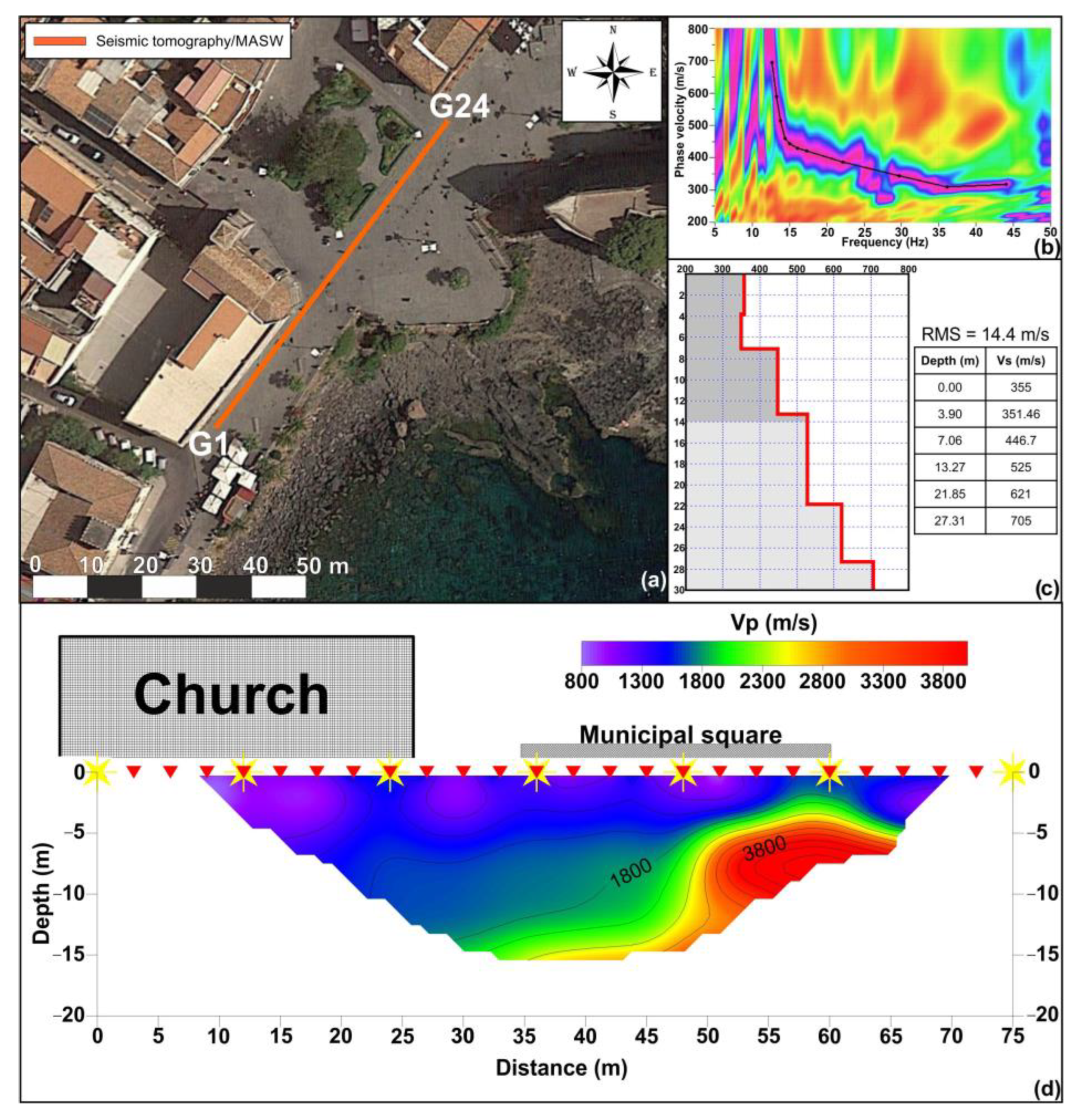
Figure 8.
(a) Location of the seismic tomography and MASW surveys; (b) dispersion curve obtained from processing of MASW survey; (c) velocity model obtained from MASW surveys; (d) 2D seismic tomography section.
Seismic tomography is an active seismic survey that allows for obtaining a seismostratigraphic reconstruction of the subsoil. It is based on the relationship between the speed of seismic waves and the physical-mechanical properties of the lithotypes, so it is possible to obtain information on the dynamic characteristics of the subsoil by analyzing the speed of propagation of elastic waves [48].
The HVSR [15,49] is a passive seismic technique based on the recording of ambient noise [50]. The ground motion recording in the three space components allows for evaluating the site response and, especially, the resonance frequency calculating the spectral ratio between the average of horizontal components and the vertical one.
3.2.1. HVSR Surveys
In the studied area, the passive seismic single station surveys were carried out, using six three-component electrodynamic velocimeters (Micromed Geophysics TROMINO®) with high sensitivity (±1.5 mm/s). The instruments measure the ambient seismic noise and transmit it to a digital acquisition system with a 23-bit minimum resolution. Design features allow a relative accuracy greater than 10−4 on the spectral components above 0.1 Hz.
Two samplings were performed in the courtyard next to the church; the other ambient noise measurements were carried out to the east and north of the San Giuseppe church, along two alignments with regular interdistance (5 m) (Figure 7a). The first, oriented SW–NE, consists of 15 ambient noise samplings (N1–N15), while the second, oriented SE–NW, is made up of 10 acquisition points (T1–T10) and crosses the first alignment at N8.
The velocimeters were arranged with the N–S component oriented parallel to the north direction. At each measuring points, ambient noise was recorded for 20 min with a sampling frequency of 128 Hz. Ambient noise samplings were processed using the HVSR technique, in the frequency range 0–64 Hz, dividing the recordings in time windows of 20 s length. During the processing, a smoothing of 10% with a triangular window function to all time windows was applied. Finally, the average of the H/V spectral ratios, obtained by each window, was calculated to obtain the average H/V spectrum for the measurement sites.
The obtained H/V spectra were analyzed together with the relative single components Fourier spectra to distinguish peaks connected with stratigraphic changes from those linked to anthropic noise [51,52]. In fact, when an impedance contrast is present in the subsoil, the Fourier spectra of single components show the characteristic “eye-shape”, formed between horizontal and vertical components [53]. On the contrary, when the three components move upwards at the same time, the related H/V peak is caused by anthropic noise.
It can also be observed that the vertical component spectrum exceeds the horizontal component spectra in certain ranges of the graph. Consequently, when the H/V spectrum is characterized by H/V amplitude values lower than 1, the presence of a velocity inversion in the subsoil can be hypothesized [53].
All the obtained H/V spectra show H/V amplitude values lower than 1 at high frequencies, probably caused by the presence of the paving instead of the natural ground.
Even if no significant spectral peaks (H/V amplitude > 2) [54] are observable in the obtained H/V spectra, it is possible to note a “broad-band” low amplitude peak in the frequency range of 1–5 Hz (Figure 7b).
Furthermore, the H/V spectra related to some measurement points (Est1, Est2, N4, N5, T7–T9) show at higher frequencies, between 10 and 30 Hz, an additional peak, characterized even in this case by low amplitude values (H/V amplitude < 2) (Figure 7b,c).
The surveying setting, with ambient noise measurements carried out at regular intervals along two profiles, allowed the combination of the H/V spectra obtained by each alignment (Figure 7d), using a MATLAB routine. Two 2D diagrams were obtained showing the distribution of the H/V amplitude values as a function of distance (x-axis) and frequency (y-axis) in the range of 0.1–20 Hz (Figure 7d). The obtained pseudo-sections provide useful information on the subsoil geometry. In the N-section, it is possible to identify a broadband frequency area characterized by H/V amplitude values close to 2, observable around the same frequency values throughout the entire alignment. It is therefore possible to identify an evident surface that can be associated with an impedance contrast, probably connected with the transition to underlying lavas. Another less evident impedance contrast is observable between 10 and 25 m from the beginning of the section, at higher frequency, probably associated, as shown later, with the transition between overlying fill material and underlying layers.
Even in the T-section, an impedance contrast ascribable to the transition to lavas can be recognized (Figure 7c), although in this profile, the surface does not occur at the same frequency values throughout the entire section. In the southeast portion, the impedance contrast is localized at higher frequency values. This seems to be in agreement with the massive lava flow cropping out nearby. Moving towards northwest, the detected surface is located at the same frequency values observed in the N-section. Toward the end of the section, between 30 and 45 m, it is possible to note a further impedance contrast at higher frequency, attributable to the transition “fill material/underlying layers”.
3.2.2. Seismic Tomography
In the investigated area, a seismic tomography was carried out using a digital multichannel array, consisting of 24 vertical geophones, with a natural frequency of 4.5 Hz and an 8 kg hammer used as energization source. The receivers were arranged along a SW–NE-oriented alignment, spaced 3 m apart for an array total length of 72 m. The distance of external shot points was 5 m, while additional 5 shots at regular interdistance were performed along the array. The signal related to each shot was recorded for 3 s, with a sample rate of 1 kHz (Figure 8a).
The seismic signals were processed using a tomographic method based on the evaluation of the seismic wave’s travel times between source points and geophones. A theoretical model is preliminarily considered; then the experimental travel time is compared with theoretical travel time, and using an iterative process, the starting model is varied to reduce the misfit between observed and calculated travel times.
The SoilSpy Rosina and SeisOpt® 2D software were used for data processing. The SoilSpy Rosina software allows the picking of the first arrivals of the compression waves at the receivers, with times in mseconds. The SeisOpt® 2D software allows the search of a subsurface model showing the Vp distribution, characterized by the minimum misfit compared with the experimental data and geologically compatible with the studied area.
The SeisOpt® 2D software is based on the generalized simulated optimization method (GSAO) [55]; this inversion algorithm allows a nonlinear procedure of inversion of arrival times of seismic waves recorded. The advantage of this technique is related to the absolute independence from the initial velocity model.
The seismic tomography allowed for investigating the subsoil to a maximum depth of about 16 m. The final 2D (Figure 8d) seismostratigraphic model shows the presence of an area, between 50 and 65 m from the beginning of the alignment, characterized by high longitudinal wave velocity values (Vp > 2000 m/s). This portion of the subsurface, considering the high velocity values and the geometric shape, can be associated with the presence of the ancient lava flow, according to the geological setting of the studied area. The other areas of the section are characterized by velocity values compatible with the presence of material with poorer physical and mechanical characteristics (Figure 8d).
3.2.3. MASW Surveys
The MASW survey (Figure 8a), oriented SW–NE, was performed using a digital multichannel array, composed of 24 vertical geophones with a natural frequency of 4.5 Hz. The energization system consisted of an 8 kg hammer and an iron base perfectly coupled to the flooring. The receivers were 3 m spaced, for a total alignment length of 72 m. Five shots were performed, at 6 m from the first and the last geophones, to increase the energy content and improve the signal-to-noise ratio (stacking technique). The signal related to each shot was recorded for 3 s, with a sample rate of 512 Hz.
The experimental dispersion curve was obtained using the Geopsy processing software [56], computing the f–k spectrum on the signal obtained by stacking the five recorded shots. The dispersion curve was picked on the maxima of the spectrum absolute value (Figure 8b). An inversion process implemented on a Dinver routine (Geopsy software) was used to obtain the 1D shear wave velocity profile. The RMS associated with the model is 14.4 m/s.
The Vs-depth profile (Figure 8c) shows Vs values of about 350 m/s within the depth interval of 0–4 m; below this layer, velocities gradually increase with depth, reaching, at the maximum investigated depth, Vs values of about 700 m/s. The first layer, characterized by low velocity values, is attributable to the presence of loose material; the gradual increase in velocity values with depth is in agreement with the presence of an ancient fractured lava flow. This represents the volcanic bedrock, whose outcrops were surveyed in the close proximity of the church.
3.3. Results Arising from Field Surveys
In order to model the foundation soil of the bell tower, data obtained from both geomechanical and geophysical surveys were used to generate a simplified profile of the subsoil.
The shear wave velocities were derived from the MASW survey. The MASW survey provides a velocity profile representing the average of the S-wave velocity distribution below the array. In consideration of this, having performed the seismic tomography survey along the same alignment, we derived a 1D Vp profile, comparable with that obtained by MASW, averaging the Vp values obtained from the tomographic section within the thickness of the seismo-layers identified by the 1D vs. profile derived from MASW.
Although the outcrops available in close proximity to the building are represented by fractured volcanic rock masses, with good geomechanical strength properties (see Section 4), HV spectra highlight the presence of impedance contrasts. In particular, the HV spectra, related to the acquisitions performed near the specific spot of the building, show an impedance contrast at high frequencies (around 15 Hz), likely related to loose material laying on the volcanic succession. This loose material layer, 2 to 6 m thick, is characterized by quite low seismic velocity, as highlighted by the results of active seismic surveys. This may be read either as material employed to fill the voids arising by the presence of metric to decametric caves, whose evidence is still visible along the NW coast scarp where caves are still used as boat recovery by local people, or as a layer consisting of debris originated from the ruin of the previous church, as observed in the close Catania old town [57].
Based on such consideration, the subsoil below the bell tower was modeled as loose material laying on the massive volcanic rock mass, whose shallow underground evidence is suggested by geophysical surveys (Figure 8).
The subsoil was subdivided for simplicity in six layers, whose wave velocities were determined from the experimental measurements. Using the well-known expressions for the wave speeds:
and the relations between shear and oedometric moduli and Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio, the results reported in Table 3 have been obtained.

Table 3.
Soil mechanical parameters obtained from geognostic surveys and derived from theoretical correlations.
Resulting elastic modulus values are lower than those obtained by the geomechanical analysis carried out on the volcanic outcrop, especially for the shallowest subsoil layers. Indeed, as shown by the geophysical surveys, the subsoil near the site of the church presents top layers of loose material, probably filling material employed for levelling the area, even likely after the collapse of the old church. Much greater values are found for the basaltic-type layer occurring near the castle and in depth, where the P-wave velocity values reach 3800 m/s (Figure 8d).
4. Dynamic Identification of the Bell Tower
In order to determine experimentally modal parameters of the bell tower, an operational modal analysis with the technique of standard spectral ratio (SSR) was carried out. Triaxial electrodynamic velocimeters (Micromed Geophysics TROMINO®), the same used for the geophysical survey, were employed.
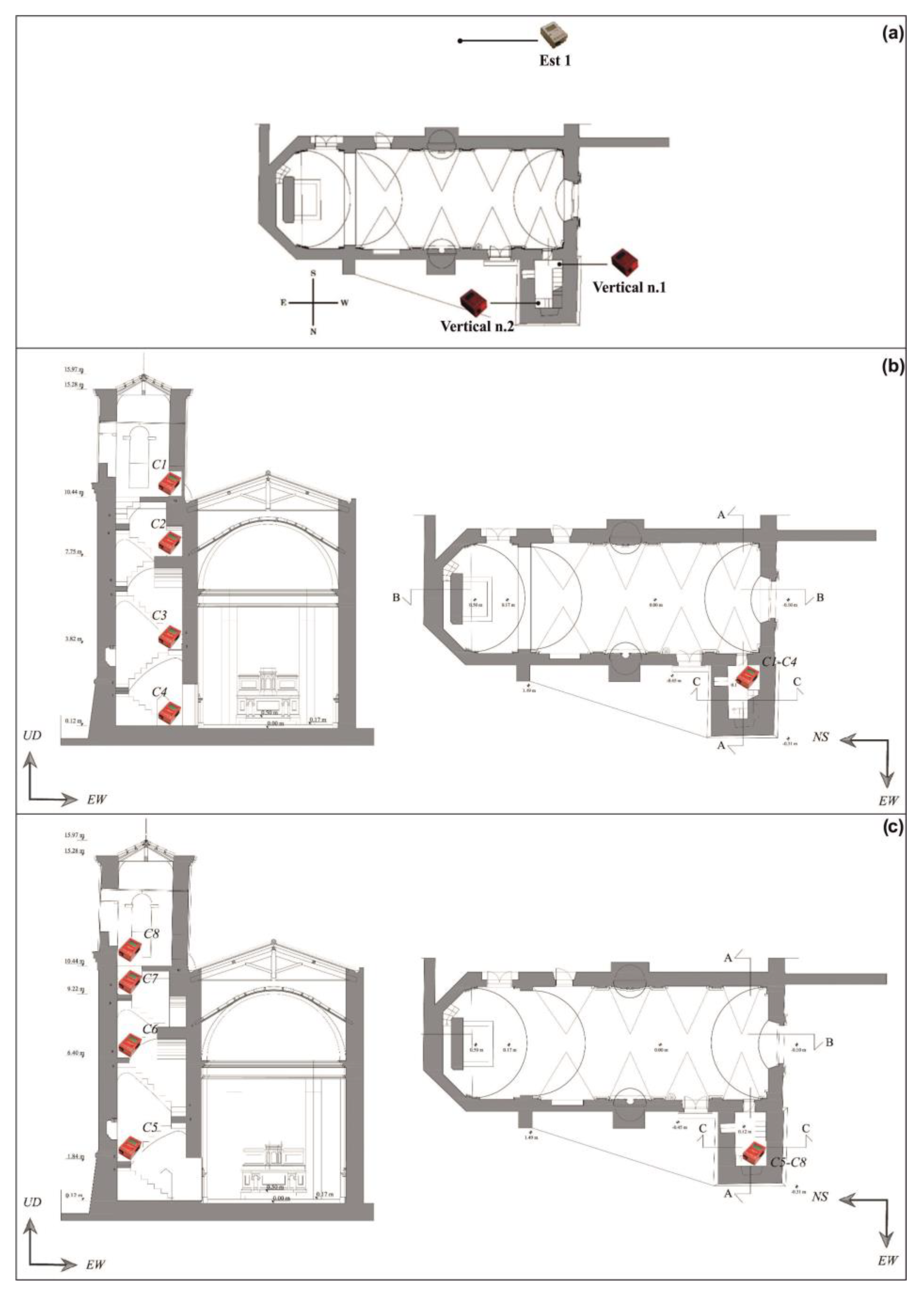
The tower was instrumented with four sensors, and a fifth one was positioned outside the tower, as indicated in Figure 9a, in order to measure the free field signal. Two series of measurements were executed, placing the instruments on the tower along two different verticals (Figure 9b,c). The measurement heights are reported in Table 4.
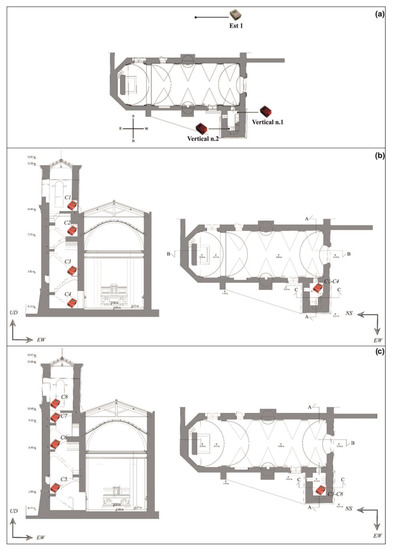
Figure 9.
(a) Velocimeters’ position in plan of the bell tower of San Giuseppe (Aci Castello, Sicily); (b) velocimeters’ position in section of the bell tower of San Giuseppe (Aci Castello, Sicily). Vertical n. 1 (see Table 4); (c) velocimeters’ position in section of the bell tower of San Giuseppe (Aci Castello, Sicily). Vertical n. 2 (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Height at which the sensors were placed in the tower.
Each measurement lasted 30 min, divided in windows of 32 s. The sampling frequency was set to 128 Hz. Therefore, each window contained 4096 = 212 sampling points, giving rise to a spectral resolution Δf = 0.0312 Hz.
For each channel, the fast Fourier transform (FFT) of each window was determined, employing a Henning triangular filter, obtaining a spectrogram of the signal. Windows where noise differed from the average trend were eliminated.
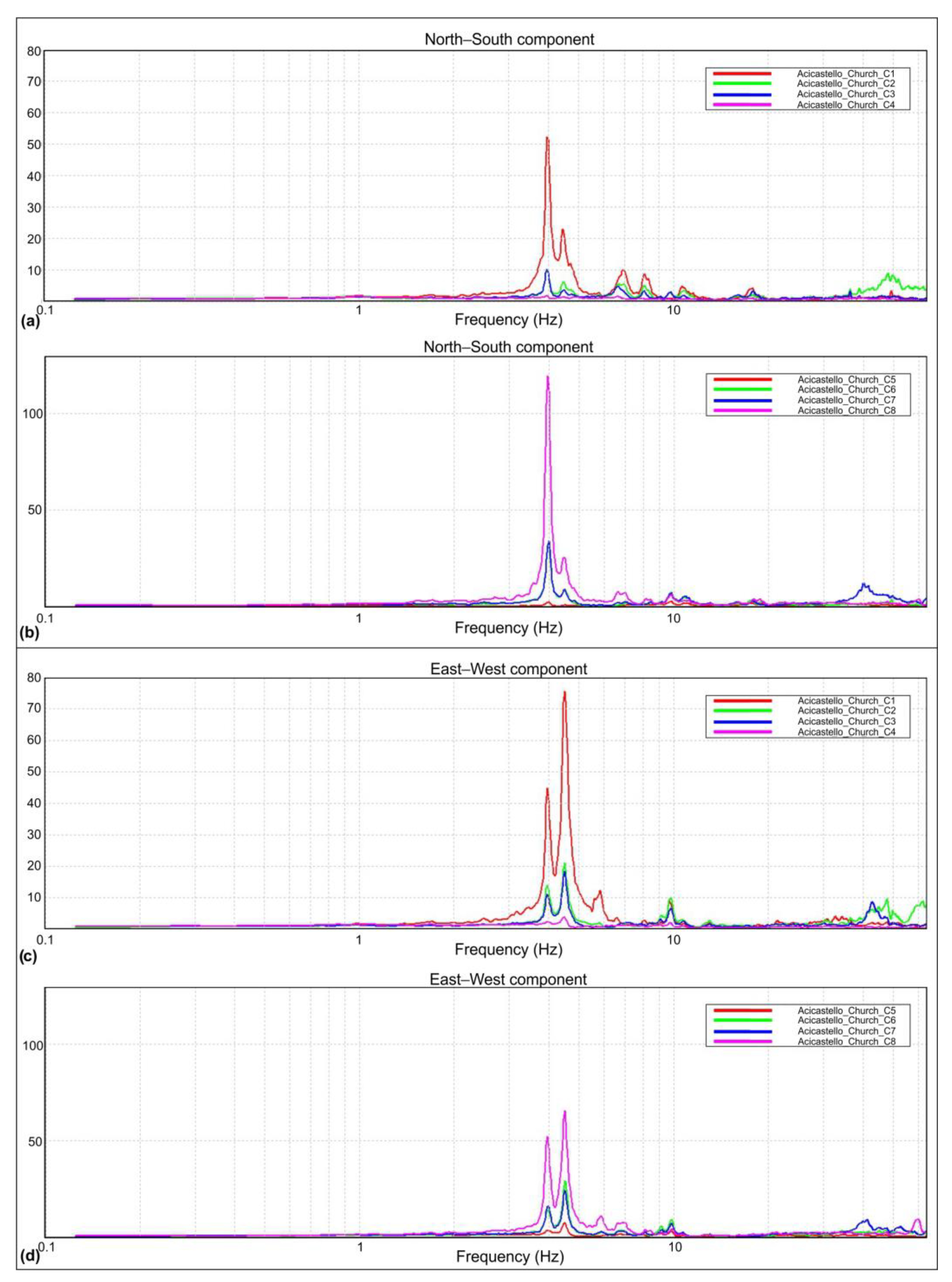
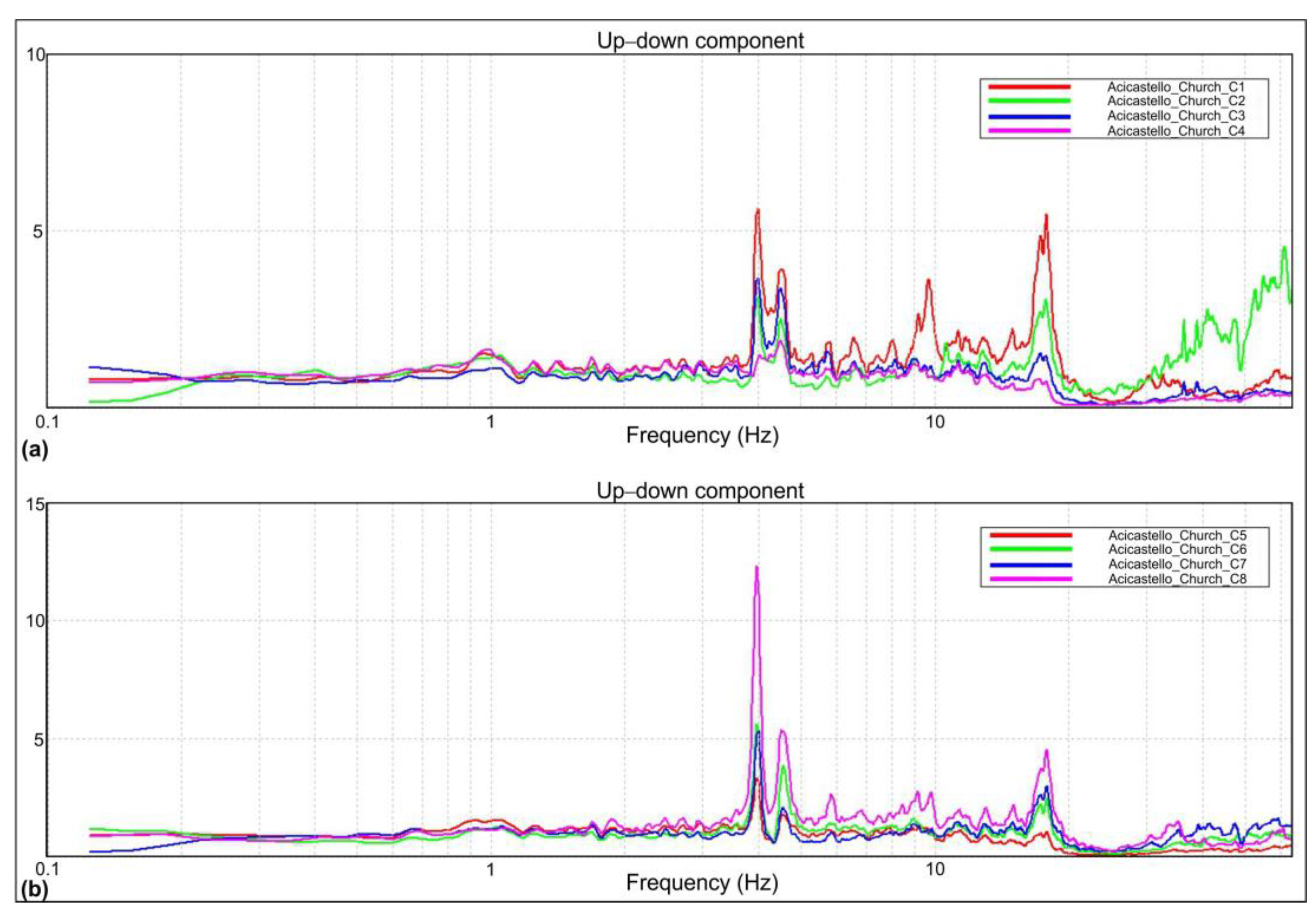
Successively, for each time window, the ratio between the FFT spectrogram of the signal and the spectrogram of the reference site was then performed. Finally, the average of all ratios was calculated in order to obtain the final spectral ratio. The average spectral ratios for the three directions obtained are represented in Figure 10a,b for the direction N–S (parallel to the church), Figure 10c,d for the E–W direction and Figure 11 for the vertical direction.
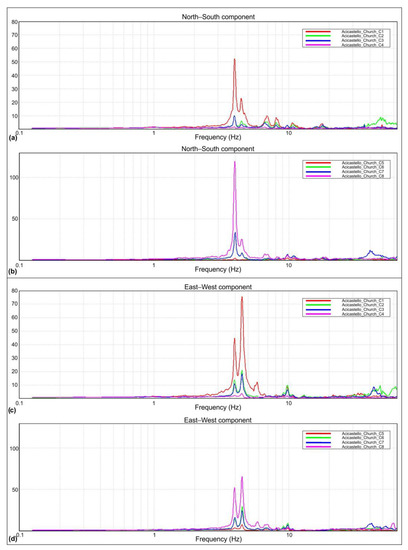
Figure 10.
Averaged spectral ratios for Vertical n. 1 (a) and Vertical n. 2 (b) in the N–S direction; averaged power spectra for Vertical n. 1 (c) and Vertical n. 2 (d) in the E–W direction.
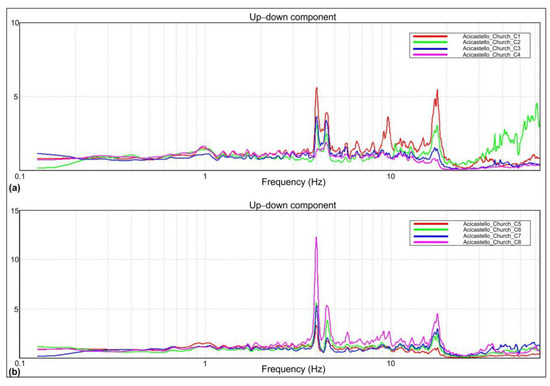
Figure 11.
Averaged spectral ratios for Vertical n. 1 (a) and Vertical n. 2 (b) (Z direction).
The tower’s modal vibration frequencies can be identified as those at which the maximum amplitude of the SSR curve in the specific direction occurs on both verticals. Further peaks in the same direction for both vertical 1 and vertical 2 represent higher modes in that direction.
This technique allows for detecting with sufficient confidence the frequencies of vibration of the structure, even though it does not allow the determination of the modes, given the lack of synchronization.
The measurements obtained in the three directions show a substantial agreement between the different sensors and for the three directions. The estimated frequencies are summarized in Table 5. From the consideration of the absolute power spectra of the signals, information about the modal shapes has been obtained. From the analysis of these modal forms, the association between the identified frequencies and the corresponding directions was deduced. However, this aspect is not discussed in this work.

Table 5.
Comparison between the main modal frequencies values obtained for San Giuseppe’s bell tower (Aci Castello, Sicily) and different soil models and experimental data.
5. Numerical Model
5.1. Modal Analysis of Fixed Base Tower
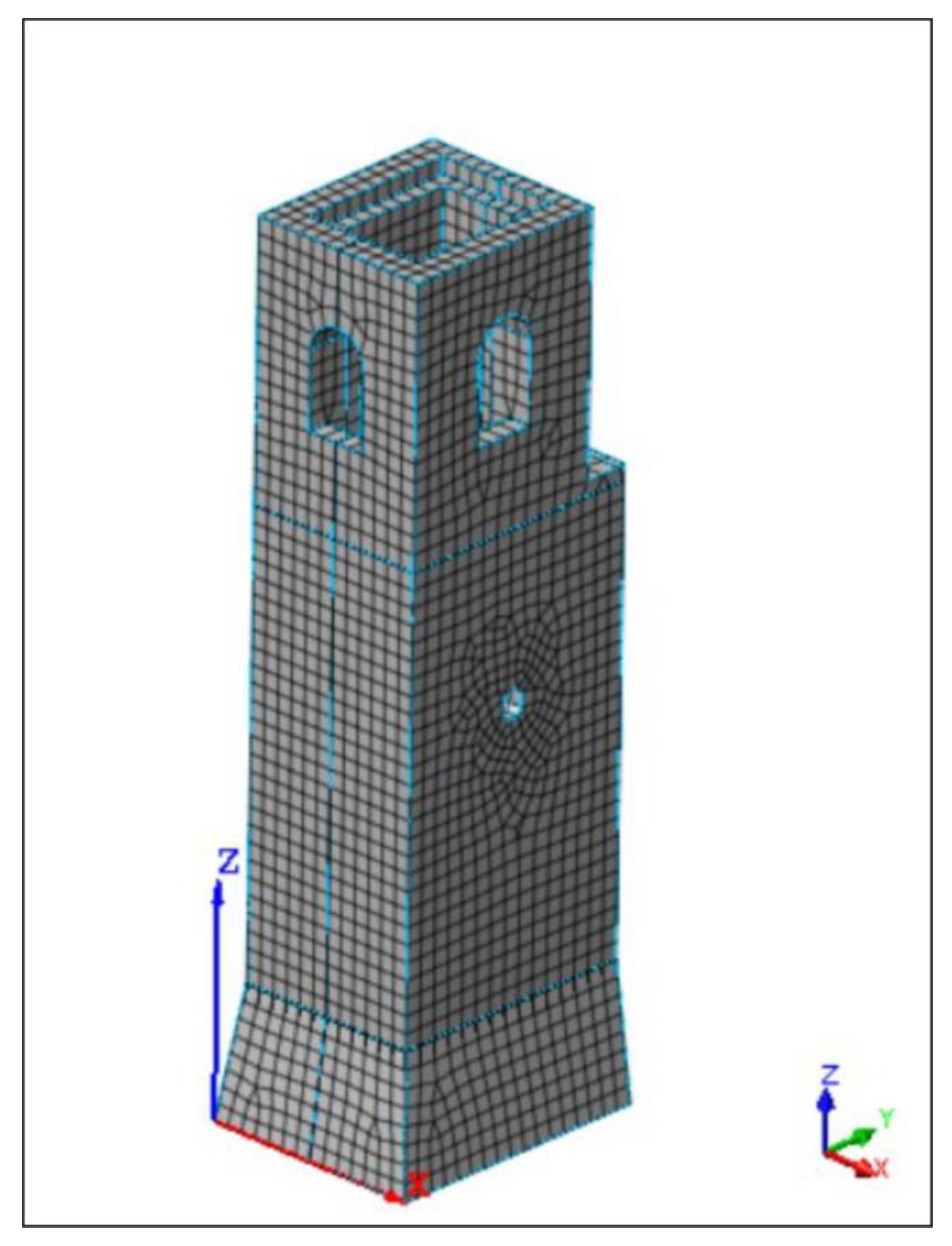
A 3D model of the tower was built in the Midas FEA software using a hybrid hexahedral and tetrahedral, 300 mm average dimension element mesh (Figure 12), according to the geometrical survey. The foundation of the tower was not modeled, and fixity constraint was applied at the base.
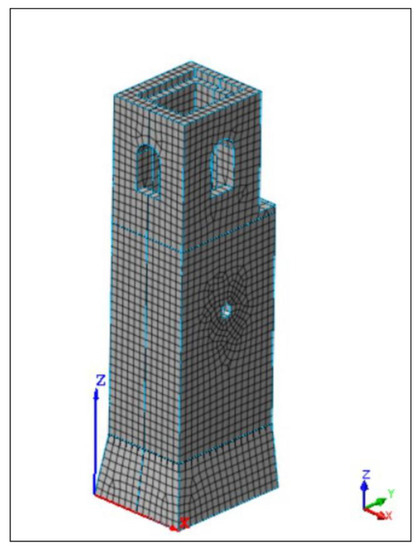
Figure 12.
Model of the tower in Midas FEA software. Hybrid hexahedral and tetrahedral, 300 mm average dimension element mesh.
The mechanical parameters assigned to the masonry, modelled as a linear elastic isotropic material, are shown in Table 6. The density and elastic stiffness were reasonably estimated on the basis of literature data [58], in the absence of experimental determination.

Table 6.
Mechanical parameters assigned to the masonry, modelled as a linear elastic isotropic material.
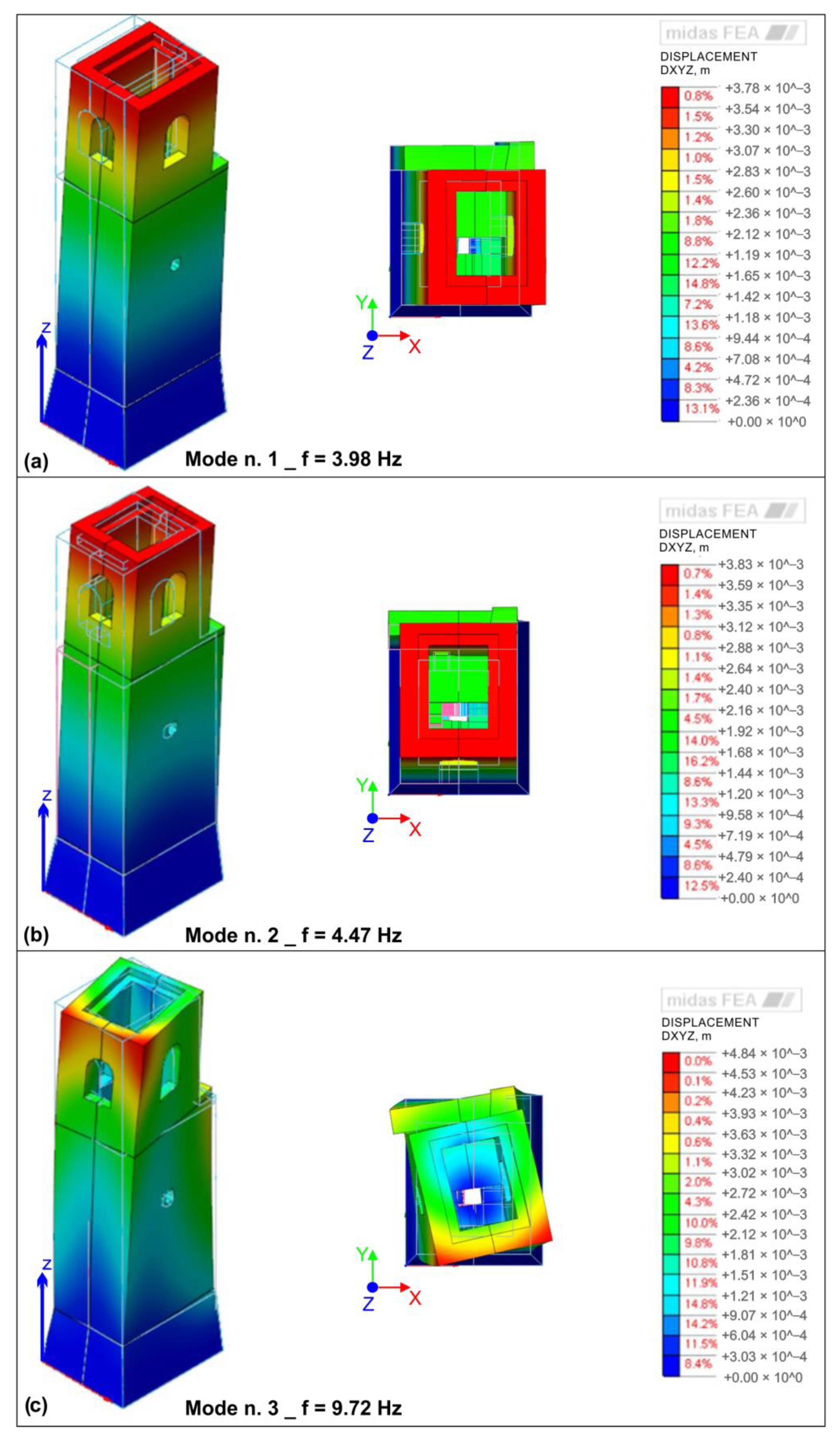
Figure 13 shows the mode shapes of San Giuseppe’s bell tower identified through numerical analysis on Midas FEA. The first three vibrational modes have been identified. The first and the second modes are bending modes, respectively, on the Y-axis (i.e., east–west axis) and X-axis (i.e., north–south axis) direction; the third mode is a torsional mode around the Z-axis (Vertical axis). Associated frequency values are close to the experimental ones (Table 5).
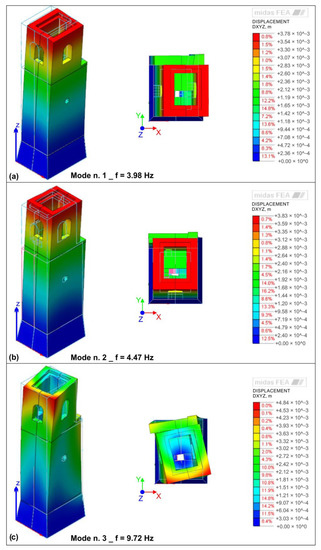
Figure 13.
Perspective and plan views of the mode shapes of San Giuseppe’s bell tower (Aci Castello, Sicily) identified from numerical analysis on Midas FEA. (a) Mode n. 1, bending around Y-axis (i.e., north–south axis); (b) mode n. 2, bending around X-axis (i.e., east–west axis); (c): mode n. 3, torsional around Z-axis (vertical axis).
It must be remarked that the numerical model is oversimplified for several reasons. First, it considers the masonry isotropic, while shear and axial stiffness greatly depend on the type of masonry and on its layout. Second, the tower probably was built in different epochs, so that the masonry layout is not homogeneous throughout the tower height. However, the geometry of the construction was detected with reasonable accuracy. Finally, no interaction with the body of the church was considered in the FEM model. This hypothesis, which is certainly inadequate in the case of FEM models intended for structural analyses, such as nonlinear seismic analyses, can be accepted for the purpose of a preliminary estimate of the natural frequencies of the tower. Fully refined structural models should include the church, the unilateral contact between the tower and the church in the absence of connection, or bimodule nonlinear springs in the case of weak wall-to-wall connection. Moreover, nonlinear constitutive models should be taken into account for both the tower masonry and the soil.
5.2. Numerical Model Accounting for the Subsoil
A full 3D model of the tower including the layered soil was implemented in order to assess the influence of the soil interaction on the dynamic properties of the tower. In addition, a simplified model of the tower rests on a Winkler-type foundation, whose parameters were calibrated according to the results of the experimental tests performed on the foundation soil. The latter model is very appealing from an engineering point of view due to its simplicity.
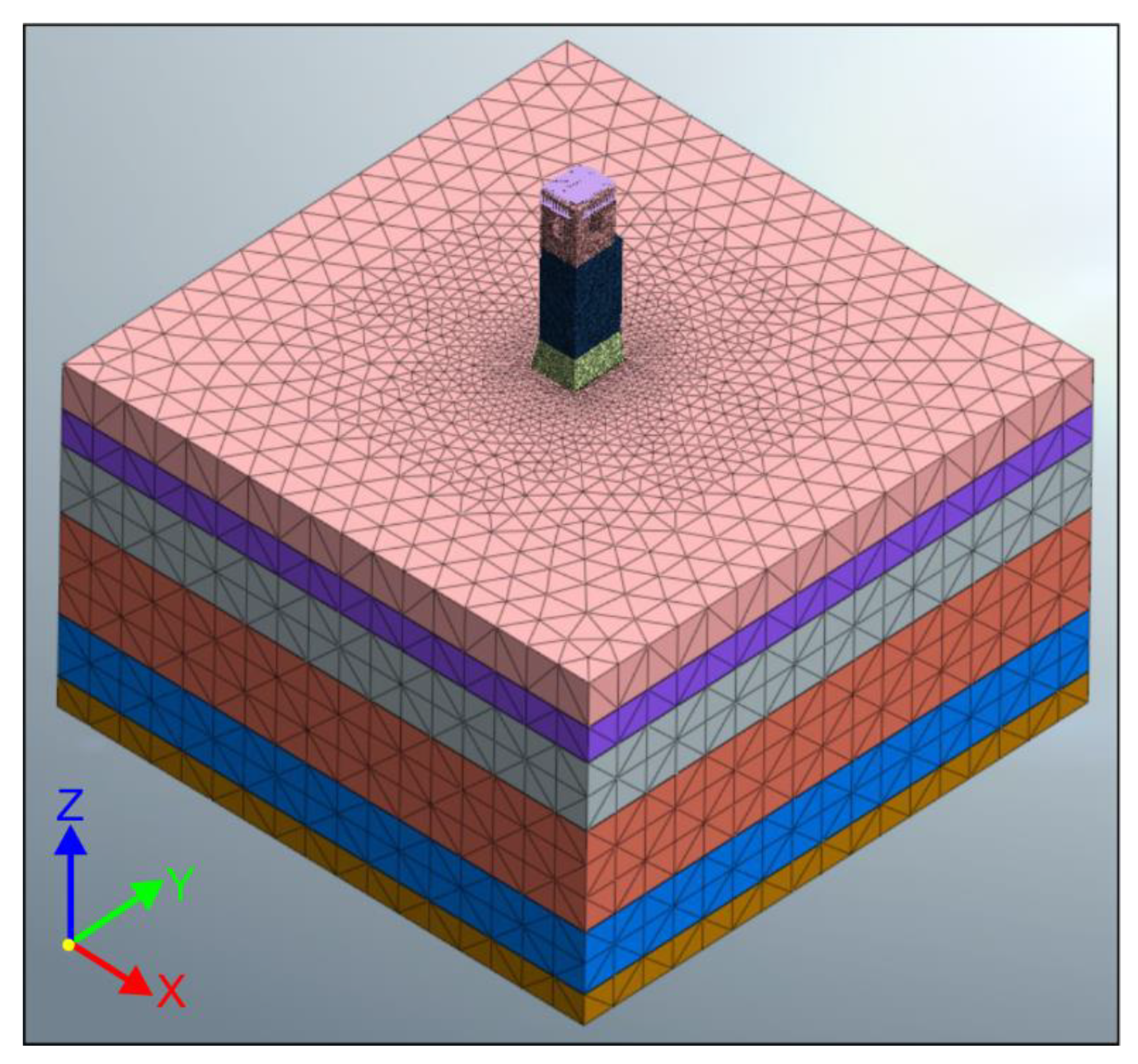
A volume of soil 50 × 50 m and 30 m deep was discretized, divided in six horizontal layers whose physical and mechanical properties determined from the geophysical survey are listed in Table 3, as schematically shown in Figure 14. The bedrock was assumed at a depth of 30 m, where the fixity constraint was assigned, whereas unidirectional boundary conditions orthogonal to the lateral sides of the soil volume were assigned. The planar dimension of the volume is such that, at the edge, the vertical deformations in the soil due to the tower’s self-weight are almost completely elapsed. A linear elastic isotropic model was adopted for the soil.
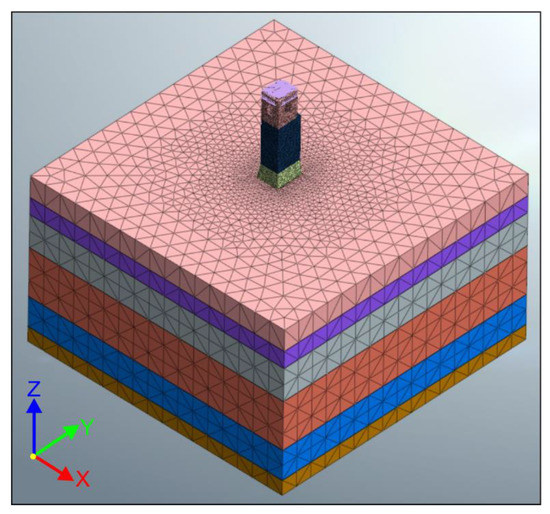
Figure 14.
FE model of the soil as uniform-depth horizontal layers.
The simplified approach according to Winkler’s method [59] considers the ground as a distributed bilateral constraint schematized with a bed of springs reacting only along their own axis and for which mutually independent elastic-linear behavior is assumed. Tangential stresses at the soil–foundation interface are also assumed to be zero. The assumption of mutually independent springs implies that a force applied at one point in the ground produces failure only at the loaded point.
Springs are endowed with stiffness k. It is not an intrinsic property of the soil but generally depends on the shape and size of the foundation, the distribution of the acting loads, the stratigraphy, and composition of the foundation soil and is given by
where Eed is the oedometric modulus and H is the thickness of the compressible soil layer. For a strip foundation, can be assumed, where B is the width of the foundation.
In the present study, the Winkler constant was approximately estimated as
where the dynamic modulus was derived from the wave velocities of the upper layers, as reported in Table 3, and an average strip footing width B of 1.55 m was considered.
The results of the modal analyses are reported in Table 5, where are also added the results of the fixed base model and the frequencies experimentally evaluated.
The stiffest configuration, with fixity at the bottom of the tower, gives the highest values. The Winkler model and FEM model gave almost the same values of X and Y frequencies. The Z frequency is approached by the model considering the interaction with the soil (Table 5).
The soil modeling introduces the lowering of all the three frequencies, as expected, due to the presence of the softer layers. However, the matching with the experimental results becomes worse, especially in the X and Y cases.
The factors that can determine these differences are many. The estimation of the mechanical parameters of the masonry, first of all, affects the solution, despite the accuracy of the discretized geometry. A model updating procedure should be applied to the full model [60], introducing a more realistic distinction of the materials along the height of the building and adequately tuning the material parameters. However, in the aim of the present paper, these first-step results allow us to highlight that a correct description of the stratigraphy is important, even in the presence of rocky sites, as the presence of soft surface layers due to leveling works of the foundation plane is frequent.
6. Concluding Remarks
Resonance frequencies of a masonry bell tower were obtained by means of vibration measurements using ambient noise, a technique widely employed, thanks to its simplicity of use. A dynamic identification of the tower was performed by means of an FE numerical model. It was shown that the inclusion in the model of the interaction with the soil cannot be disregarded in the case studied in this work, since a soft substrate was present underneath the construction. In fact, although a volcanic rock mass, with good geomechanical properties, crops out a few meters away from the church, its evidence in the tower subsoil was found, by geophysical analysis, below a thick loose material layer. The presence of such soft soil is likely due to a man-made filling, probably with debris of pre-existing buildings. Therefore, the subsoil was characterized by means of geophysical tests (MASW, HVSR) for an area close to the construction site. As demonstrated by the use of simplified models, only the most superficial layers affect in this case the dynamic response. In fact, in the Winkler model, the thickness H of the compressible soil layer was approximated to 1.5 B; i.e., it is approximately 7.50 m. Furthermore, the results of the Winkler model and the full 3D model of the tower including the layered soil are fully comparable. Differences are still present between the numerical and the experimental results that are due to the simplifications introduced in modelling the masonry.
Considering the high probability that an earthquake of moderate magnitude will occur and that events of intensity 7 MCS have badly damaged the tower bell in the past, these findings can be useful clues for further numerical modelling, and finalize additional engineering investigations aimed at reducing the seismic vulnerability of the analyzed building.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.I., M.C. and L.C.; methodology, S.I., M.C., S.G. and M.S.B.; software, D.L.R. and M.G.; validation, D.L.R., S.G. and G.M.; formal analysis, S.G., G.M., M.G. and D.L.R.; investigations—engineering geological rock characterization, G.P. and S.M.; geophysical surveys, S.I., S.G. and G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, all authors; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, S.G., G.M., M.G. and D.L.R.; supervision, S.I., L.C. and M.C.; funding acquisition, G.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the project “CH2V—Cultural Heritage Hazard and Vulnerability” (University of Catania, Linea 2-PIACERI, funds granted to Giovanna Pappalardo).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sánchez-Aparicio, L.J.; Riveiro, B.; González-Aguilera, D.; Ramos, L.F. The combination of geomatic approaches and operational modal analysis to improve calibration of finite element models: A case of study in Saint Torcato Church (Guimarães, Portugal). Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, M.F.; Hajjat, A.E.; Masciotta, M.G.; Oliveira, D.V.; Lourenço, P.B. A Parametric Scan-to-FEM Framework for the Digital Twin Generation of Historic Masonry Structures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, C.; Saisi, A. Ambient vibration testing of historic masonry towers for structural identification and damage assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, M.; Trevisani, D.; Cecchi, A. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Historical Bell Tower. Int. J. Archit. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Saisi, A.; Gentile, C.; Guidobaldi, M. Post-earthquake continuous dynamic monitoring of the Gabbia Tower in Mantua, Italy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabboi, A.; Gentile, C.; Saisi, A. From continuous vibration monitoring to FEM-based damage assessment: Application on a stone-masonry tower. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivorra, S.; Pallarés, F.J. Dynamic investigations on a masonry bell tower. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivorra, S.; Pallarés, F.J.; Adam, J.M. Masonry bell towers: Dynamic considerations. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Struct. Build. 2011, 164, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Feyzabadi, M.; Kioumarsi, M. Model updating of a masonry tower based on operational modal analysis: The role of soil-structure interaction. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, G.; D’Ayala, D.; Betti, M.; Bartoli, G. Analytical and numerical seismic assessment of heritage masonry towers. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 969–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, S.; Camata, G.; Candigliota, E.; Spacone, E.; Valente, C. Identificazione strutturale di una torre in muratura per la messa a punto del modello numerico. In Proceedings of the XIII Convegno ANIDIS L’Ingegneria Sismica in Italia ANIDIS, Bologna, Italy, 28 June–2 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gigli, G.; Morelli, S.; Fornera, S.; Casagli, N. Terrestrial laser scanner and geomechanical surveys for the rapid evaluation of rock fall susceptibility scenarios. Landslides 2014, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, S.; Caliò, D.; Pappalardo, G. UAV-based photogrammetry and Infrared Thermography ap-plied to rock mass survey for geomechanical purposes. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Mineo, S.; Imposa, S.; Grassi, S.; Leotta, A.; La Rosa, F.; Salerno, D. A quick combined approach for the characterization of a cliff during a post-rockfall emergency. Landslides 2020, 17, 1063–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y. A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface. Railway Technical Research Institute. Q. Rep. 1989, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Moisidi, M.; Vallianatos, F.; Makris, J.; Soupios, P.; Nikolintaga, M.I. HVSR and electrical tomography for seismic response estimation: An example from a cultural heritage site in Greece. In ESC General Assembly Papers, SCF-0; European Seismological Commission: Potsdam, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Castellaro, S.; Imposa, S.; Barone, F.; Chiavetta, F.; Gresta, S.; Mulargia, F. Georadar and passive seismic survey in the Roman Amphitheatre of Catania (Sicily). J. Cult. Herit. 2008, 9, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imposa, S.; Barone, F.; Bella, D.; Cristaldi, M.; Gresta, S. A procedure to estimate the seismic hazard in an urban area: An application to Acireale (Eastern Sicily). Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imposa, S.; Lombardo, G.; Panzera, F.; Grassi, S. Ambient vibrations measurements and 1D site response modelling as a tool for soil and building properties investigation. Geosciences 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babacan, A.E.; Akın, Ö. The investigation of soil–structure resonance of historical buildings using seismic refraction and ambient vibrations HVSR measurements: A case study from Trabzon in Turkey. Acta Geophys. 2018, 66, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Imposa, S.; Patti, G.; Boso, D.; Lombardo, G.; Panzera, F. Geophysical surveys for the dynamic characterization of a cultural heritage building and its subsoil: The S. Michele Arcangelo Church (Acireale, eastern Sicily). J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 36, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Patti, G.; Tiralongo, P.; Imposa, S.; Aprile, D. Applied geophysics to support the cultural heritage safeguard: A quick and non-invasive method to evaluate the dynamic response of a great historical interest building. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 189, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Barbano, M.S.; Pirrotta, C.; Morreale, G.; Imposa, S. Seismic Soil–Structure Interaction of Three Historical Buildings at the University of Catania (Sicily, Italy). Heritage 2022, 5, 3562–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imposa, G.; Grassi, S.; Barontini, A.; Morreale, G.; Russo, S.; Lourenço, P.B.; Imposa, S. Extended Tromograph Surveys for a Full Experimental Characterisation of the San Giorgio Cathedral in Ragusa (Italy). Sensors 2023, 23, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappalardo, G.; Mineo, S.; Carbone, S.; Monaco, C.; Catalano, D.; Signorello, G. Preliminary recognition of geohazards at the natural reserve “Lachea Islet and Cyclop Rocks” (Southern Italy). Sustainability 2021, 13, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E. Aci Castello. Antiqua Civitas Castri Aci; ITA: Editoriale Agorà: Montevideo, Uruguay, 2020; p. 431. ISBN 978–88–89930-47-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mondello, A. Torri Campanarie Degli Edifici Ecclesiastici Tradizionali Allo Specchio Tra Conoscenza e Sicurezza. Tecnologia e Forma Negli Areali a Rischio Nella Sicilia Orientale e Della Castilla y Leòn. Ph.D. Thesis, Evaluation and Mitigation of Urban and Territorial Risks Course, University of Catania, Catania, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guidoboni, E.; Ferrari, G.; Mariotti, D.; Comastri, A.; Tarabusi, G.; Sgattoni, G.; Valensise, G. CFTI5Med, Catalogo dei Forti Terremoti in Italia (461 a.C.-1997) e Nell’area Mediterranea (760 a.C.-1500); Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV): Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, R.A.; Cristofolini, R. Subaqueous volcanism in the Etnean area: Evidence for hydromagmatic activity and regional uplift inferred from the Castle Rock of Acicastello. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2000, 95, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, S.; Coltelli, M.; Groppelli, G.; Lentini, F. Geological map of Etna volcano, 1: 50,000 scale. Ital. J. Geosci. 2011, 130, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, C.; De Guidi, G.; Ferlito, C. The morphotectonic map of Mt. Etna. Ital. J. Geosci. 2010, 129, 408–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGS (Archivio General de Simancas). Correspondencia de Virreyes y Ministros con S.M. Relazione delle Città e luoghi Devastati in Sicilia, a Causa dei Terremoti del 9 e 11 Gennaio; Numero Antico Dei Vivi, Numero dei Morti Nelle Rovine e Rendite che Pagavano ogni anno. Secretarías Provinciales, Sicilia, legajo 1222 (1693), Palermo maggio 1693. Available online: http://www.cftilab.it/file_repository/pdf_T/003011-665148_T.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- ASC (Archivio di Stato di Catania). 1818. Quadro de’ danni sofferti nel distretto di Catania pe’ tremuoti de 20 e 28 febbraro 1818, Tavola necrologica causata da’ tremuoti, s.d. Intendenza borbonica, b.4209 categoria XXI (Miscellanea).
- ASC (Archivio di Stato di Catania). 1818-19. Tavola riassuntiva dei danni cagionati dal terremoto del 20 febbraio 1818 nel Comune di Aci Castello, s.d. Intendenza borbonica, b.4210 categoria XXI (Miscellanea).
- De Rubeis, V.; Gasparini, C.; Maramai, A.; Anzidei, A. Il terremoto siciliano del 13 dicembre 1990. In Proceedings of the Contributi allo Studio del Terremoto della Sicilia Orientale del 13 Dicembre 1990; Boschi, E., Basili, A., Eds.; ING Pubblicazione: Rome, Italy, 1993; Volume 537, pp. 9–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rovida, A.N.; Locati, M.; Camassi, R.D.; Lolli, B.; Gasperini, P. Catalogo Parametrico dei Terremoti Italiani (CPTI15), Versione 4.0; Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV): Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, L.; Mucciarelli, M.; Albarello, D. Estimates of site seismicity rates using ill-definition macrosismic data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1994, 143, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Mineo, S.; Marchese, G. Effects of cubical specimen sizing on uniaxial compressive strength of Etna volcanic rocks (Italy). Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2013, 2, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.S.J.; Pinkerton, H. Effect of degassing on rheology of basaltic lavas. Nature 1978, 276, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harthi, A.; Al-Amri, R.; Shehata, W. The porosity and engineering properties of vesicular basalt in Saudi Arabia. Eng. Geol. 1999, 54, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Mineo, S. Investigation on the mechanical attitude of basaltic rocks from Mount Etna through InfraRed Thermography and laboratory tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Punturo, R.; Mineo, S.; Contrafatto, L. The role of porosity on the engineering geological properties of 1669 lavas from Mount Etna. Eng. Geol. 2017, 221, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon, O.H. Classification of rocks and soils for engineering geological mapping. Part 1: Rock and soil materials. Bull. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol. 1979, 19, 364–437. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.N.; Ghose, A.K. Engineered Rock Structures in Mining and Civil Construction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISRM. The complete ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 1974–2006. In Suggested Methods Prepared by the Commission on Testing Methods; Ulusay, R., Hudson, J.A., Eds.; Suggested Methods Prepared by the Commission on Testing Methods; International Society for Rock Mechanics: Ankara, Turkey, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Marinos, P.; Hoek, E. GSI: A Geological Friendly Tool for Rock Mass Strength Estimation. In Proceedings of the GeoEng 2000 at the International Conference on Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, Melbourne, Australia, 19–24 November 2000; pp. 1422–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.B.; Miller, R.D.; Xia, J. Multichannel analysis of surface waves. Geophysics 2000, 64, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imposa, S.; De Guidi, G.; Grassi, S.; Scudero, S.; Barreca, G.; Patti, G.; Boso, D. Applying geophysical techniques to investigate a segment of a creeping fault in the urban area of San Gregorio di Catania, southern flank of Mt. Etna (Sicily—Italy). J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogoshi, M.; Igarashi, T. On the propagation characteristics of the microtremors. J. Seismol. Soc. Jpn. 1970, 23, 264–280. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, H.; Suto, K. The Microtremor Survey Method; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Imposa, S.; Motta, E.; Capilleri, P.; Imposa, G. HVSR and MASW seismic survey for characterizing the local seismic response: A case study in Catania area (Italy). In Proceedings of the 1st IMEKO TC4 International Workshop on Metrology for Geotechnics, MetroGeotechnics 97–102, Benevento, Italy, 17–18 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, S.; Spoldi, E.; Ippolito, I.; Imposa, G.; Bretini, A. Detection of 2009 L’Aquila’s Earthquake Effects on Collemaggio Church through Experimental Surveys. J. Archit. Eng. 2022, 28, 05021017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellaro, S.; Mulargia, F. The effect of velocity inversions on H/V. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2009, 166, 567–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SESAME European Project. Guidelines for the Implementation of the H/V Spectral Ratio Technique on Ambient Vibrations. Measurements, Processing and Interpretation. WP12. Deliverable D23.12. 2005. Available online: https://www.earth-prints.org/bitstream/2122/8423/1/Del-D23-HV_User_Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Pullammanappallil, S.K.; Louie, J.N. A generalized simulated-annealing optimization for inversion of first-arrival times. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathelet, M.; Chatelain, J.-L.; Cornou, C.; Di Giulio, G.; Guillier, B.; Ohrnberger, M.; Savvaidis, A. Geopsy: A User-Friendly Open-Source Tool Set for Ambient Vibration Processing. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 1878–1889. Available online: http://www.geopsy.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Monaco, C.; Catalano, S.; De Guidi, G.; Gresta, S.; Langer, H.; Tortorici, L. The geological map of the urban area of Catania (Eastern Sicily): Morphotectonic and seismotectonic implications. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2000, 55, 425–438. [Google Scholar]
- Liberatore, D.; Gambarotta, L.; Beolchini, G.C.; Binda, L.; Magenes, G.; Cocina, S.; Giudice, L.; Scuderi, S. Tipologie edilizie in muratura del Comune di Catania. In Progetto Catania: Indagine Sulla Risposta Sismica di due Edifici in Muratura; Monografie: Liberatore, Catania, Italy, 2000; pp. 3–22. ISBN 8890044934. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, E. Die Lehre von der Elasticitaet Und Festigkeit; Kessinger Publishing: Whitefish, MT, USA, 1867; ISBN 978-1166781811. [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis, A.; Lourenço, P.B.; Sica, S.; Pecce, M.R. Influence of the ground on the structural identification of a bell-tower by ambient vibration testing. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 155, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).