Earthquake, Fire, and Water: Destruction Sequence Identified in an 8th Century Early Islamic Harbor Warehouse in Caesarea, Israel
Abstract
1. Introduction
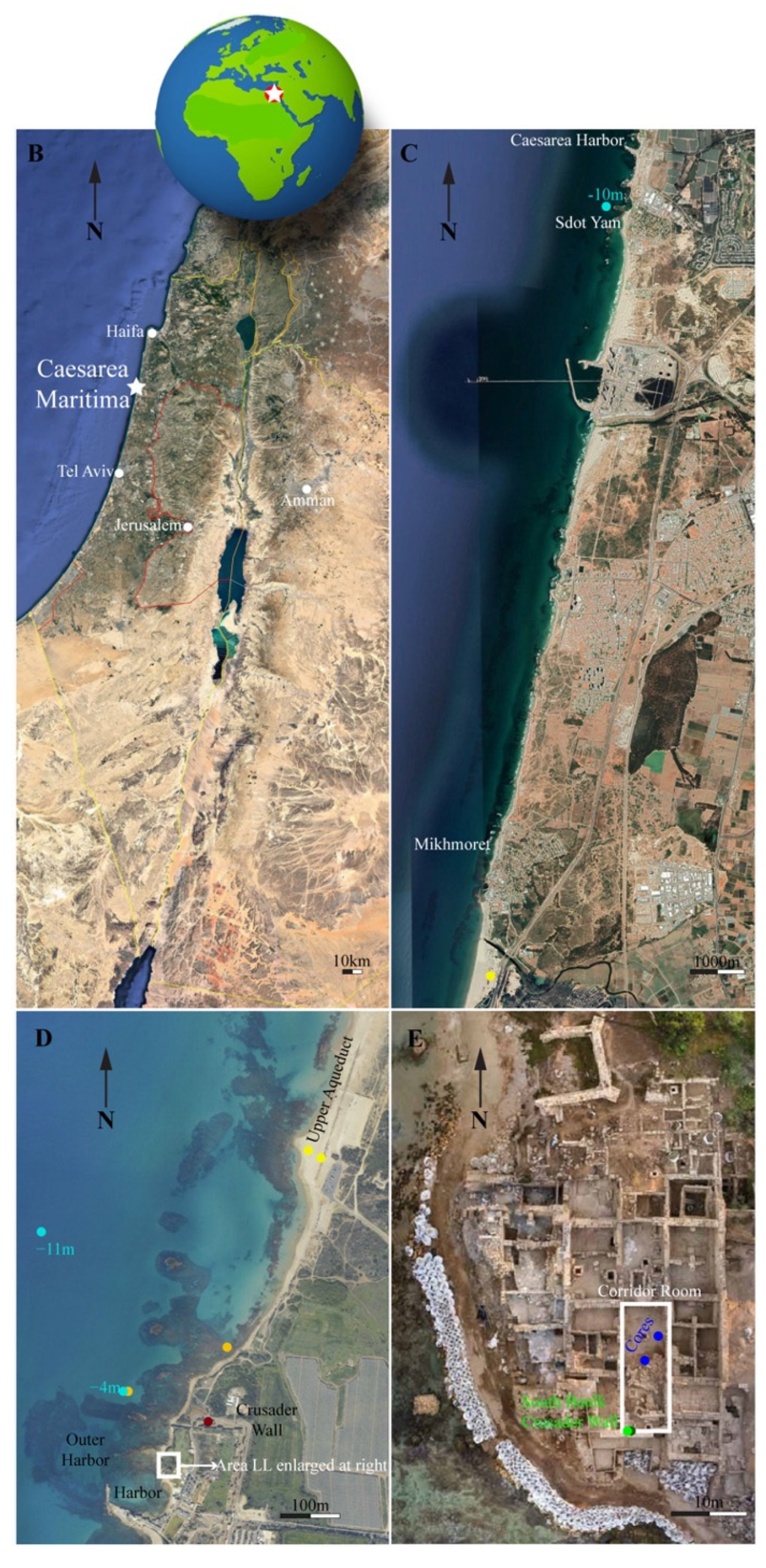
2016. Area LL Excavation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fieldwork
2.1.1. Coring and Excavation Collections
2.1.2. Core Description
2.1.3. Reference Sample Collection
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Granulometry
2.2.2. Total Organic Carbon
2.2.3. Foraminiferal Analysis
2.2.4. Portable-Optically Stimulated Luminescence (P-OSL)
3. Results
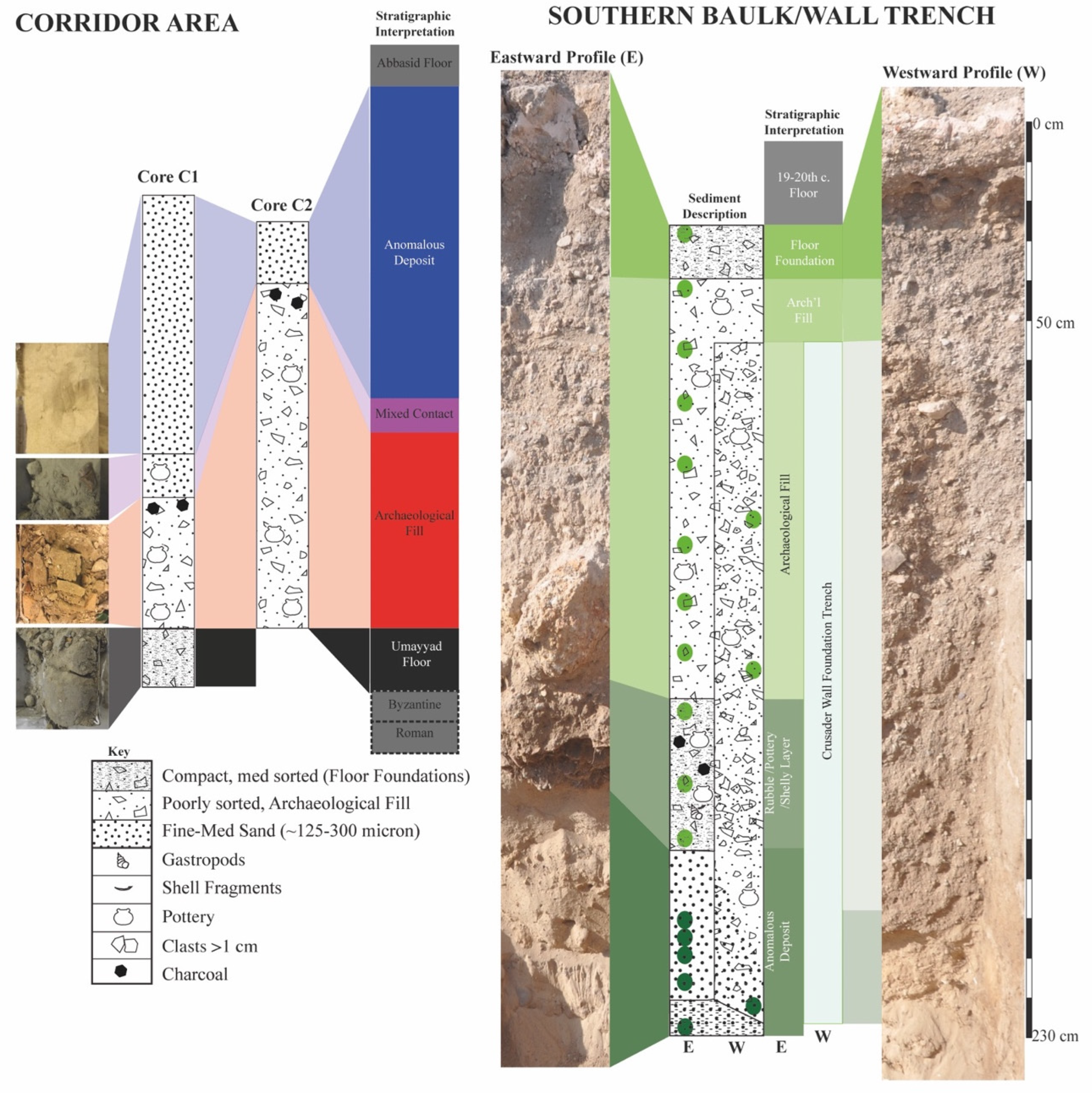
3.1. Core C1
3.1.1. Description of LL Cores
3.1.2. Grain Size Distribution
3.1.3. Total Organic and Inorganic Carbon Content
3.1.4. Foraminiferal Analysis
3.1.5. Portable OSL
3.2. LL Southern Baulk
3.2.1. Grain Size Distribution
3.2.2. Foraminiferal Abundance and Taphonomic Analysis
3.3. Reference Samples
3.3.1. Grain Size Distribution
3.3.2. Total and Inorganic Carbon
3.3.3. Foraminiferal Analysis
3.4. Dating
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Anomalous Samples to Reference Set
4.2. Foraminifera Taphonomy as Tsunami Marker
4.3. Probable Origin of the Anomalous Deposit
4.4. Chronological Association with the Earthquake of 749 CE
4.5. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Events
4.6. Lack of Other Identified Onshore Deposits
4.7. Tsunami Sediment Source
4.8. Summary of Events, Presuming Tsunami Interpretation
4.9. Tsunami in Caesarea Maritima and Social Context: The Umayyad-Abbasid Shift of Power
5. Significance
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bony, G.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C.; Kaniewski, D.; Perinçek, D. A High-Energy Deposit in the Byzantine Harbour of Yenikapi, Istanbul (Turkey). Quat. Int. 2012, 266, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.J.; Van Der Plicht, J.; MacGillivray, J.A. The Minoan Santorini Eruption and Tsunami Deposits in Palaikastro (CRETE): Dating by Geology, Archaeology, 14C, and Egyptian Chronology. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, H.; Goodman-Tchernov, B. Tsunamis and the Port of Caesarea Maritima over the Longue Durée: A Geoarchaeological Perspective. J. Rom. Archaeol. 2010, 23, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, H.; Goodman-Tchernov, B.; Sharvit, J. Archaeological Evidence for the Tsunami of January 18, A.D. 749: A Chapter in the History of Early Islamic Qâysariyah (Caesarea Maritima). J. Rom. Archaeol. 2014, 27, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, N.; Master, D.; Goodman-Tchernov, B. Possible Tsunami Inundation Identified amongst 4–5th Century BCE Archaeological Deposits at Tel Ashkelon, Israel. Mar. Geol. 2018, 396, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Tchernov, B.N.; Dey, H.W.; Reinhardt, E.G.; McCoy, F.; Mart, Y. Tsunami Waves Generated by the Santorini Eruption Reached Eastern Mediterranean Shores. Geology 2009, 37, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoglu, V.; Sterba, J.H.; Katz, T.; Cayır, U.; Gundogan, U.; Tyuleneva, N.; Tugcu, I.; Bichler, M.; Erkanal, H.; Goodman-Tchernov, B.N. Volcanic Ash, Victims, and Tsunami Debris from the Late Bronze Age Thera Eruption Discovered at C¸es¸me-Ba Glararası (Turkey). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114213118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, E.G.; Goodman, B.N.; Boyce, J.I.; Lopez, G.; Van Hengstum, P.; Rink, W.J.; Mart, Y.; Raban, A. The Tsunami of 13 December A.D. 115 and the Destruction of Herod the Great’s Harbor at Caesarea Maritima, Israel. Geology 2006, 34, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadgen, B.G.; Goff, J.R. Tsunamis in the New Zealand Archaeological Record. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 200, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.R.; McFadgen, B.G. Catastrophic Seismic-Related Events and Their Impact on Prehistoric Human Occupation, Coastal New Zealand. Antiquity 2001, 75, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vött, A.; Hadler, H.; Willershäuser, T.; Ntageretzis, K.; Brückner, H.; Warnecke, H.; Grootes, P.M.; Lang, F.; Nelle, O.; Sakellariou, D. Ancient Harbours Used as Tsunami Sediment Traps-the Case Study of Krane (Cefalonia Island, Greece). BYZAS 2014, 19, 743–771. [Google Scholar]
- Ünlü, S.; Alpar, B.; Altınok, Y.; Ozer, N.; Unlu, S.; Altinok, Y. Rapid Coastal Changes and Tsunami Impacts at the Patara Harbour (Turkey). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Land-Sea Interaction in the Coastal Zone, Byblos, Lebanon, 6–8 November 2012; pp. 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Ubeid, K.F. Tsunami Event Identified in a Sedimentary Record of the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Stud. Quat. 2021, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, V.; Oppo, D.; Moore, A.L.; Gusman, A.R.; Mtelela, C.; Iacopini, D.; Taviani, M.; Mjema, E.; Mulaya, E.; Che, M.; et al. A 1000-Yr-Old Tsunami in the Indian Ocean Points to Greater Risk for East Africa. Geology 2020, 48, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Tchernov, B.N. Archaeological Dating of Tsunami and Storm Deposits. Geol. Rec. Tsunamis Other Extreme Waves 2020, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, G.; Grützner, C.; Reicherter, K.; Preusser, F. Geo-Archaeological Evidence for a Holocene Extreme Flooding Event within the Arabian Sea (Ras Al Hadd, Oman). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 113, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtienberg, G.; Yasur-Landau, A.; Norris, R.D.; Lazar, M.; Rittenour, T.M.; Tamberino, A.; Gadol, O.; Cantu, K.; Arkin-Shalev, E.; Ward, S.N. A Neolithic Mega-Tsunami Event in the Eastern Mediterranean: Prehistoric Settlement Vulnerability along the Carmel Coast, Israel. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtienberg, G.; Gadol, O.; Levy, T.E.; Norris, R.D.; Rittenour, T.M.; Yasur-Landau, A.; Tamberino, A.; Lazar, M. Changing environments and human interaction during the Pleistocene–Early Holocene from the shallow coastal area of Dor, Israel. Quat. Res. 2022, 105, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtienberg, G.; Cantu, K.; Mischke, S.; Sivan, D.; Norris, R.D.; Rittenour, T.M.; Edelman-Furstenberg, Y.; Yasur-Landau, A.; Sisma-Ventura, G.; Levy, T.E. Holocene sea-level rise and coastal aquifer interactions: Triggering mechanisms for environmental change and impacts on human settlement patterns at Dor, Israel. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 294, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuciński, W. The Post-Depositional Changes of the Onshore 2004 Tsunami Deposits on the Andaman Sea Coast of Thailand. Nat. Hazards 2012, 60, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettier, R.; Schlunegger, F.; Schneider, H.; Rieke-Zapp, D.; Schwab, M. Relationships between Landscape Morphology, Climate and Surface Erosion in Northern Peru at 5°S Latitude. Int. J. Earth-Sci. 2009, 98, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, S.L.; Kench, P.S. Sedimentology and Preservation Potential of Carbonate Sand Sheets Deposited by the December 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami: South Baa Atoll, Maldives. Sedimentology 2008, 55, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Imamura, F.; Keerthi, N.; Kunthasap, P.; Matsui, T.; Minoura, K.; Ruangrassamee, A.; Sugawara, D.; Supharatid, S. Distribution and Significance of the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami Deposits. Initial Results from Thailand and Sri Lanka. In Tsunamiites–Features and Implications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Spiske, M.; Piepenbreier, J.; Benavente, C.; Bahlburg, H. Preservation Potential of Tsunami Deposits on Arid Siliciclastic Coasts. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 126, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, S.V.; Reinhardt, E.G.; Boyce, J.I.; Pilarczyk, J.E.; Jupp, B.P. Particle-Size Distribution of Inferred Tsunami Deposits in Sur Lagoon, Sultanate of Oman. Mar. Geol. 2009, 257, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.R.; Lane, E.; Arnold, J. The Tsunami Geomorphology of Coastal Dunes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, D.; Shimamoto, T.; Hirose, T.; Gunatilake, J.; Wickramasooriya, A.; DeLile, J.; Young, S.; Rathnayake, C.; Ranasooriya, J.; Murayama, M. Thickness and Grain-Size Distribution of the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami Deposits in Periya Kalapuwa Lagoon, Eastern Sri Lanka. Sediment. Geol. 2010, 230, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, B.F.; ten Brink, U.S.; Buckley, M.; Halley, R.S.; Jaffe, B.E.; López-Venegas, A.M.; Reinhardt, E.G.; Tuttle, M.P.; Watt, S.; Wei, Y. Geomorphic and Stratigraphic Evidence for an Unusual Tsunami or Storm a Few Centuries Ago at Anegada, British Virgin Islands. Nat. Hazards 2012, 63, 51–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, B.F.; Moore, A. A Tsunami About 1000 Years Ago in Puget Sound. Science 1992, 258, 1614–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Sawai, Y.; Ikehara, K.; Nakashima, R.; Hara, J.; Kanai, Y. Shallow-Marine Deposits Associated with the 2011 Tohoku-Oki Tsunami in Sendai Bay, Japan. J. Quat. Sci. 2015, 30, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela, M.; Costa, P.J.M.; Fatela, F.; Drago, T.; Hoska, N.; Andrade, C.; Freitas, M.C. The AD 1755 Tsunami Deposits Onshore and Offshore of Algarve (South Portugal): Sediment Transport Interpretations Based on the Study of Foraminifera Assemblages. Quat. Int. 2016, 408, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bergh, G.D.; Boer, W.; De Haas, H.; Van Weering, T.C.E.; Van Wijhe, R. Shallow Marine Tsunami Deposits in Teluk Banten (NW Java, Indonesia), Generated by the 1883 Krakatau Eruption. Mar. Geol. 2003, 197, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, F.; Alt-Epping, U.; Lebreiro, S.; Voelker, A.; Schneider, R. Sedimentological Record of Tsunamis on Shallow-Shelf Areas: The Case of the 1969 AD and 1755 AD Tsunamis on the Portuguese Shelf off Lisbon. Mar. Geol. 2008, 249, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Fournier, J.; Poizot, E.; Etienne, S.; Morin, J.; Lavigne, F.; Wassmer, P. Boulder and Fine Sediment Transport and Deposition by the 2004 Tsunami in Lhok Nga (Western Banda Aceh, Sumatra, Indonesia): A Coupled Offshore–Onshore Model. Mar. Geol. 2010, 268, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedile, A.; De Martini, P.M.; Pantosti, D.; Bellucci, L.; Del Carlo, P.; Gasperini, L.; Pirrotta, C.; Polonia, A.; Boschi, E. Possible Tsunami Signatures from an Integrated Study in the Augusta Bay Offshore (Eastern Sicily-Italy). Mar. Geol. 2011, 281, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischke, S.; Schudack, U.; Bertrand, S.; Leroy, S.A.G. Ostracods from a Marmara Sea Lagoon (Turkey) as Tsunami Indicators. Quat. Int. 2012, 261, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Avşar, U. Sedimentary Geochemical Evidence of Historical Tsunamis in the Eastern Mediterranean from Ölüdeniz Lagoon, SW Turkey. J. Paleolimnol. 2019, 61, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cita, M.B.; Aloisi, G. Deep-Sea Tsunami Deposits Triggered by the Explosion of Santorini (3500 y BP), Eastern Mediterranean. Sediment. Geol. 2000, 135, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Tchernov, B.N.; Katz, T.; Shaked, Y.; Qupti, N.; Kanari, M.; Niemi, T.; Agnon, A. Offshore evidence for an undocumented tsunami event in the ‘low risk’ Gulf of Aqaba-Eilat, Northern Red Sea. PLoS ONE. 2016, 11, e0145802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyuleneva, N.; Braun, Y.; Katz, T.; Suchkov, I.; Goodman-Tchernov, B. A New Chalcolithic-Era Tsunami Event Identified in the Offshore Sedimentary Record of Jisr Al-Zarka (Israel). Mar. Geol. 2018, 396, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, J.E.; Dura, T.; Horton, B.P.; Engelhart, S.E.; Kemp, A.C.; Sawai, Y. Microfossils from coastal environments as indicators of paleo-earthquakes, tsunamis, and storms. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 413, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dura, T.; Hemphill-Haley, E.; Sawai, Y.; Horton, B.P. The application of diatoms to reconstruct the history of subduction zone earthquakes and tsunamis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 152, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, A.; Rockwell, T.; Ward, S.N.; Guidoboni, E.; Comastri, A. Tsunami Hazard Evaluation of the Eastern Mediterranean: Historical Analysis and Selected Modeling. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Tchernov, B.N.; Austin, J.A. Deterioration of Israel’s Caesarea Maritima’s Ancient Harbor Linked to Repeated Tsunami Events Identified in Geophysical Mapping of Offshore Stratigraphy. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 3, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holum, K.G. Caesarea Palaestinae, a Paradigmatic Transition? In Shaping the Middle East, Jews, Christians, and Muslims in an Age of Transition 400–800 C.E.; Holum, K.G., Lapin, H., Eds.; University Press of Maryland: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 111–131. [Google Scholar]
- ‘Ad, U.; Arbel, Y.; Gendelman, P. Caesarea, Area LL. 2018; Hadashot Arkheologiyot: Excavations and Surveys in Israel/חדשות ארכיאולוגיות חפירות וסקרים בישראל. [Google Scholar]
- Ambraseys, N.N. Earthquakes in the Mediterranean and Middle East, A Multidisciplinary Study of Seismicity up to 1900; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Amiran, D.; Arieh, E.; Turcotte, T. Earthquakes in Israel and Adjacent Areas: Macroseismic Observations since 100 B.C.E. Isr. Explor. J. 1994, 44, 260–305. [Google Scholar]
- Mart, Y.; Perecman, I. Neotectonic Activity in Caesarea, the Mediterranean Coast of Central Israel. Tectonophysics 1996, 254, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlfelder, R.L. Byzantine Coin Finds from the Sea: A Glimpse of Caesarea Maritima’s Later History. In Harbour Archaeology; Raban, A., Ed.; BAR International Series: Oxford, UK, 1985; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Stieglitz, R. Stratonos Pyrgos–MigdalSar–Sebastos: History and Archaeology. In Caesarea Maritima–Retrospective after Two Millennia; Raban, A., Holum, K.G., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 593–608. [Google Scholar]
- Raban, A. The Inner Harbour Basin of Caesarea; Archaeological Evidence for Its Gradual Demise. In Caesarea Maritima: A Retrospective after Two Millennia; Raban, A., Holum, K.G., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 21, pp. 628–666. [Google Scholar]
- Raban, A. The Harbour of Sebastos (Caesarea Maritima) in Its Roman Mediterranean Context By; BAR Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, S.; Hartal, M.; Hazan, N.; Lev, L.; Stein, M. Archaeology, History, and Geology of the A.D. 749 Earthquake, Dead Sea Transform. Geology 2003, 31, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, N.; Katz, O.; Dray, Y.; Gonen, I.; Marco, S. Estimating Location and Size of Historical Earthquake by Combining Archaeology and Geology in Umm-El-Qanatir, Dead Sea Transform. Nat. Hazards 2009, 50, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, M.F.; Katz, O.; Hillman, A.; Livio, F.; Amit, R.; Michetti, A.M. The Mid-Eighth Century CE Surface Faulting along the Dead Sea Fault at Tiberias (Sea of Galilee, Israel). Tectonics 2020, 39, e2020TC006186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, G.W. The potential for earthquake damage to Temple II architecture at Roman Omrit. In The Roman Temple Complex at Horvat Omrit: Interim Report; Overman, J.A., Schowalter, D., Eds.; British Archaeological Reports: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Namdar, L.; Gadot, Y.; Mavronanos, G.; Gross, B.; Sapir-Hen, L. Frozen in time: Caprine pen from an early Islamic earthquake complex in Tel Beth Shemesh. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 45, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalit, A. Diferential earthquake footprints on the masonry styles at Qal’at al-Subayba (Nimrod fortress) support the theory of its ancient origin. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, S. Stone weathering in the monastic building complex on Mountain of St Aaron in Petra, Jordan. Master’s Thesis, Department of Archaeology, University of Helsinki Institute for Cultural Studies, Helsinki, Finland, 2008; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, J.I.; Reinhardt, E.G.; Goodman, B.N. Magnetic Detection of Ship Ballast Deposits and Anchorage Sites in King Herod’s Roman Harbour, Caesarea Maritima, Israel. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raban, A. The Harbours of Caesarea Maritima. Results of the Caesarea Ancient Harbour Excavation Project, 1980–1985, 491st ed.; Raban, A., Ed.; BAR: Oxford, UK, 1989; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Roskin, J.; Sivan, D.; Shtienberg, G.; Roskin, E.; Porat, N.; Bookman, R. Natural and Human Controls of the Holocene Evolution of the Beach, Aeolian Sand and Dunes of Caesarea (Israel). Aeolian Res. 2015, 19, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtienberg, G.; Dix, J.K.; Roskin, J.; Waldmann, N.; Bookman, R.; Bialik, O.M.; Porat, N.; Taha, N.; Sivan, D. New Perspectives on Coastal Landscape Reconstruction during the Late Quaternary: A Test Case from Central Israel. Palaeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2017, 468, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskin, J.; Taxel, I. “He Who Revives Dead Land”: Groundwater Harvesting Agroecosystems in Sand along the Southeastern Mediterranean Coast since Early Medieval Times. Med. Geosc. Rev. 2021, 3, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, L.I.; Netzer, E. Excavations at Caesarea Maritima 1975, 1976, 1979-Preliminary Report; The Institute of Archaeology: Jerusalem, Israel, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Stabler, J.; Holum, K.; Stanley, F.H., Jr.; Risser, M.; Iamim, A. The Warehouse Quarter (Area LL) and the Temple Platform (Area TP), 1996–2000 and 2002 Seasons. In Caesarea Reports and Studies: Excavations 1995–2007 within the Old City and the Ancient Harbor; Holum, K., Stabler, J., Reinhardt, E., Eds.; BAR International Series: Oxford, UK, 2008; Volume 1784, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bronk Ramsey, C. Bayesian Analysis of Radiocarbon Dates. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, T.J.; Blaauw, M.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, B.C.; Reimer, P.J.; Scott, M. The IntCal20 Approach to Radiocarbon Calibration Curve Construction: A New Methodology Using Bayesian Splines and Errors-in-Variables. Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 821–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curve (0-55 Cal KBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel, G.; Levy, G.J.; Mingelgrin, U.; Singer, M.J. Critical Evaluation of the Use of Laser Diffraction for Particle-Size Distribution Analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buurman, P.; Pape, T.; Muggler, C.C. Laser Grain-Size Determination in Soil Genetic Studies 1. Practical Problems. Soil Sci. 1997, 162, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. Particle Size Distribution Analysis of Sand-Sized Particles by Laser Diffraction: An Experimental Investigation of Instrument Sensitivity and the Effects of Particle Shape. Sedimentology 2006, 53, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman-Coulter. Coulter LS Series: Product Manual; Beckman Coulter: Miami, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C. Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld, J.; Alve, E.; Geslin, E.; Jorissen, F.; Korsun, S.; Spezzaferri, S.; Abramovich, S.; Almogi-Labin, A.; du Chatelet, E.A.; Barras, C.; et al. The FOBIMO (FOraminiferal BIo-MOnitoring) Initiative-Towards a Standardised Protocol for Soft-Bottom Benthic Foraminiferal Monitoring Studies. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2012, 94, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon-Parry, K.D. Scanning Electron Microscopy: An Introduction. III-Vs Rev. 2000, 13, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, L.; Greenbaum, N.; Yu, L.P.; Bookman, R.; Roskin, J. High-Resolution Portable-OSL Analysis of Vegetated Linear Dune Construction in the Margins of the Northwestern Negev Dunefield (Israel) during the Late Quaternary. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyikwa, K.; Telfer, M.; Baker, I.; Knight, C. Core Drilling of Quaternary Sediments for Luminescence Dating Using the Dormer Drillmite TM. Anc. TL 2011, 29, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, D.C.W.; Murphy, S. Using Simple Portable OSL Measurements and Laboratory Characterisation to Help Understand Complex and Heterogeneous Sediment Sequences for Luminescence Dating. Quat. Geochronol. 2010, 5, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Salinas, E.; Bishop, P.; Sanderson, D.C.; Zamorano, J.J. Interpreting Luminescence Data from a Portable OSL Reader: Three Case Studies in Fluvial Settings. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2011, 36, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, Y. Sedimentological Aspects of the Israel and Sinai Mediterranean Coasts; Coastal Education & Research Foundation, Inc: Jerusalem, Israel, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zviely, D.; Kit, E.; Rosen, B.; Galili, E.; Klein, M. Shoreline Migration and Beach-Nearshore Sand Balance over the Last 200 Years in Haifa Bay (SE Mediterranean). Geo-Mar Lett 2009, 29, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, T.; Crouvi, O. Sediment Flux Dynamics over the Shallow (25 m Depth) Shelf of the Mediterranean Sea along the Israeli Coast. Mar. Geol. 2018, 406, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitan, M.; Zviely, D. Sand Beach Nourishment: Experience from the Mediterranean Coast of Israel. J. Mar. Sci.Eng. 2020, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Mushkin, A. Characteristics of sea-cliff erosion induced by a strong winter storm in the eastern Mediterranean. Quat. Res. 2013, 80, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandy, O.L.; Arnal, R.E. Concepts of Foraminiferal Paleocology. Bull. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. 1960, 44, 1921–1923. [Google Scholar]
- Buzas, M.A.; Gibson, T.G. Species Diversity: Benthonic Foraminifera in Western North Atlantic. Science 1969, 163, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, B.P.; Engelhart, S.E.; Kemp, A.C.; Sawai, Y. Microfossils in tidal settings as indicators of sea-level change, paleoearthquakes, tsunamis, and tropical cyclones. Treatise Geomorphol. 2013, 14, 292–314. [Google Scholar]
- Mamo, B.; Strotz, L.; Dominey-Howes, D. Tsunami sediments and their foraminiferal assemblages. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 96, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.B.; Medioli, F.S.; Schafer, C.T. Monitoring in Coastal Environments Using Foraminifera and Thecamoebian Indicators; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, R.; Le, S.; Ho, S.L.; Bassetti, M.; Lin, I.; Lin, H.; Chang, Y.; Jiann, K.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; et al. Planktic-benthic foraminifera ratio (%P) as a tool for the reconstruction of paleobathymetry and geohazard: A case study from Taiwan. Mar. Geo. 2022, 453, 106922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnaim-Katav, S.; Hyams-Kaphzan, O.; Milker, Y.; Almogi-Labin, A. Bathymetric zonation of modern shelf benthic foraminifera in the Levantine Basin, eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Sea. Res. 2015, 99, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almogi-Labin, A.; Ashckenazi-Polivoda, S.; Edelman-Furstenberg, Y.; Benjamin, C. Anoxia-dysoxia at the sediment-water interface of the southern Tethys in the late Cretaceous: Mishash Formation, southern Israel. In Anoxia: Evidence for Eukaryote Survival and Paleontological Strategies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Avnaim-Katav, S.; Almogi-Labin, A.; Sandler, A.; Sivan, D. Benthic foraminifera as palaeoenvironmental indicators during the last million years in the eastern Mediterranean inner shelf. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 386, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, E.G.; Patterson, R.T.; Schroeder-Adams, C.J. Geoarchaeology of the Ancient Harbor Site of Caesarea Maritima, Israel; Evidence from Sedimentology and Paleoecology of Benthic Foraminifera. J. Foraminifer. Res. 1994, 24, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, E.G.; Raban, A. Destruction of Herod the Great’s Harbor at Caesarea Maritima, Israel–Geoarchaeological Evidence. Geology 1999, 27, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.G.; Shi, S. Tsunami Deposits. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2000, 157, 875–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, G.; Chough, S.K.; Shiki, T. Depositional Events and Their Records—An Introduction. Sediment. Geol. 1996, 104, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayama, F.; Shigeno, K.; Satake, K.; Shimokawa, K.; Koitabashi, S.; Miyasaka, S.; Ishii, M. Sedimentary Differences between the 1993 Hokkaido-Nansei-Oki Tsunami and the 1959 Miyakojima Typhoon at Taisei, Southwestern Hokkaido, Northern Japan. Sediment. Geol. 2000, 135, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.; McFadgen, B.G.; Chagué-Goff, C. Sedimentary Differences between the 2002 Easter Storm and the 15th-Century Okoropunga Tsunami, Southeastern North Island, New Zealand. Mar. Geol. 2004, 204, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.; Horton, B.P.; Evelpidou, N.; Cahill, N.; Spada, G.; Sivan, D. Can We Detect Centennial Sea-Level Variations over the Last Three Thousand Years in Israeli Archaeological Records? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 210, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lario, J.; Bardají, T.; Silva, P.G.; Zazo, C.; Goy, J.L. Improving the Coastal Record of Tsunamis in the ESI-07 Scale: Tsunami Environmental Effects Scale (TEE-16 Scale). Geol. Acta 2016, 14, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsidik; Benazir; Luthfi, M.; Suppasri, A.; Comfort, L.K. The 22 December 2018 Mount Anak Krakatau Volcanogenic Tsunami on Sunda Strait Coasts, Indonesia: Tsunami and Damage Characteristics. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, P.S.; Aswan, A.; Maryunani, K.A.; Yulianto, E.; Nugroho, S.H.; Setiawan, V. Post-Event Field Survey of the 22 December 2018 Anak Krakatau Tsunami. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 2477–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynett, P.J.; Borrero, J.C.; Weiss, R.; Son, S.; Greer, D.; Renteria, W. Observations and Modeling of Tsunami-Induced Currents in Ports and Harbors. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 327–328, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, N.Z.; Salem, E.M.; El Shahat, A.M.; Habib, A.F.; Ahamed, A.E.; El Hakim, B.A. Seismicity of Gulf of Aqaba before and after Aqaba 95 Quake. In Proceedings of the Egyptian Geological Survey Cenn Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 15–20 March 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Frucht, E.; Salamon, A.; Gal, E.; Ginat, H.; Grigorovitch, M.; Tov, R.S.; Ward, S. A Fresh View of the Tsunami Generated by the Dead Sea Transform, 1995 Mw 7.2 Nuweiba Earthquake, along the Gulf of Elat–Aqaba. Seism. Res. Lett. 2019, 90, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaythwaite, J.W. Design of Marine Facilities for the Berthing, Mooring, and Repair of Vessels; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-7844-0726-4. [Google Scholar]
- Okal, E.A.; Fritz, H.M.; Raad, P.E.; Synolakis, C.; Al-Shijbi, Y.; Al-Saifi, M. Oman Field Survey after the December 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami. Earthq. Spectra 2006, 22, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holum, K.G.; Stabler, J.A.; Reinhardt, E.G. Caesarea Reports and Studies: Excavations 1995-2007 within the Old City and the Ancient Harbor; Holum, K.G., Stabler, J.A., Reinhardt, E.G., Eds.; Archaeo Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shalem, N. Seismic Tidal Waves (Tsunamis) in the Eastern Mediterranean. Soc. Explor. Eretz Isr. 1956, 20, 159–170. (In Hebrew) [Google Scholar]
- Tsafrir, Y.; Foerster, G. The Dating of the ‘Earthquake of the Sabbatical Year’ of 749 C.E. in Palestine. Bull. Sch. Orient. African Stud. 1992, 55, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, G.I.; Goodman-Tchernov, B.N.; Porat, N. OSL Over-Dispersion: A Pilot Study for the Characterisation of Extreme Events in the Shallow Marine Realm. Sediment. Geol. 2018, 378, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T.; Goto, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Goff, J. Dating Tsunami Deposits: Present Knowledge and Challenges. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, A.L.; Cupper, M.L.; Jankaew, K.; Sawai, Y. Indian Ocean Tsunami Recurrence from Optical Dating of Tsunami Sand Sheets in Thailand. Mar. Geol. 2012, 295–298, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey Martinez, J.; Cartwright, J.; Hall, B. 3D seismic interpretation of slump complexes: Examples from the continental margin of Israel. Basin Res. 2005, 17, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Reuven, E.; Aharonov, E. Submarine Landslides and Fault Scarps along the Eastern Mediterranean Israeli Continental-Slope. Mar. Geol. 2015, 369, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, A.; Rockwell, T.; Guidoboni, E.; Comastri, A. A Critical Evaluation of Tsunami Records Reported for the Levant Coast from the Second Millennium BCE to the Present. Isr. J. Earth-Sci. 2011, 58, 327–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, M.; Satake, K. Possible Sources of the Tsunami Observed in the Northwestern Indian Ocean Following the 2013 September 24 Mw 7.7 Pakistan Inland Earthquake. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 199, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Heidarzadeh, M.; Satake, K.; Mulia, I.E.; Yamada, M. A tsunami warning system based on offshore bottom pressure gauges and data assimilation for Crete Island in the Eastern Mediterranean Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB020293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiyanto, W.; Santoso, P.B.; Hsiao, S.C.; Imananta, R.T. Post-Event Field Survey of 28 September 2018 Sulawesi Earthquake and Tsunami. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldon, J.; Rosen, A. Society and Environment in the East Mediterranean ca 300-1800 CE. Problems of Resilience, Adaptation and Transformation. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldon, J.; Mordechai, L.; Newfield, T.P.; Chase, A.F.; Izdebski, A.; Guzowski, P.; Labuhn, I.; Roberts, N. History Meets Palaeoscience: Consilience and Collaboration in Studying Past Societal Responses to Environmental Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3210–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izdebski, A.; Mordechai, L.; White, S. The Social Burden of Resilience: A Historical Perspective. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bavel, B.; Curtis, D.R.; Dijkman, J.; Hannaford, M.; de Keyzer, M.; van Onacker, E.; Soens, T. Disasters and History. The Vulnerability and Resilience of Past Societies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Holum, K.G. Caesarea in Palestine: Shaping the Early Islamic Town. In Le Proche-Orient de Justinien aux abbassides. Peuplement et dynamiques spatiales (Turnhout); Borrut, A., Debié, M., Papaconstantinou, A., Pieri, D., Sodini, J.P., Eds.; Brepols Publishers: Turnhout, Belgium, 2011; pp. 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb, D. Qaysariyah as an Early Islamic Settlement; Holum, K.G., Lapin, H., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Avni, G. The Byzantine-Islamic Transition in Palestine: An Archaeological Approach, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mesqui, J. Césarée Maritime. Ville Fortifiée Du Proche-Orient: Paris, French, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, C. Framing the Early Middle Ages: Europe and the Mediterranean 400–800; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley, A. Early Islamic Syria: An Archaeological Appraisal; Gerald Duckworth & Co. Ltd: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, H. The Prophet and the Age of the Caliphates. The Islamic Near East from the Sixth to the Eleventh Centuries, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Raban, A.; Toueg, R.; Yankelevitz, S.; Arnon, Y. Land Excavations in the Inner Harbour (1993–1994). In Caesarea Papers 2; Holum, K., Raban, A., Patrich, J., Eds.; Journal of Roman Archaeology Supplementary Series: Portsmouth, UK, 1999; Volume 35, pp. 198–224. [Google Scholar]






| Sample Category | Color | Photo | Sampling Locations | # Samples | Avg Mean (µm) | Avg Mode (µm) | Avg Median (µm) | Avg σ | Forams (#/cc) | Pristine Forams (#/cc) | TOC (%) | IC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anomalous |  | Cores C1,C2 | 43 | 256 | 218 | 225 | 124 | 1097 | 14 | 0.01 | 2.42 | |
| Mixed Contact |  | Core C1 | 6 | 281 | 210 | 221 | 231 | 968 | 7 | 0.04 | 3.38 | |
| Archaeological Deposit |  | Cores C1, C2 | 59 | 350 | 558 | 241 | 326 | 231 | 1 | 0.4 | 5.34 | |
| Umayyad Floor |  | Core C1 | 7 | 575 | 864 | 414 | 509 | 358 | 0 | X | X | |
| Upper Baulk |  | Southern Baulk section | 13 | 448 | 527 | 304 | 369 | 244 | 2 | X | X | |
| Lower Baulk |  | Southern Baulk section | 6 | 253 | 223 | 227 | 119 | 1298 | 10 | X | X | |
| Nearshore |  | offshore Aqueduct Beach, and Sdot Yam | 5 | 226 | 210 | 212 | 80 | 977 | 42 | 0.02 | 1.98 | |
| Dune |  | Michmoret dunes, Aqueduct sand ramp | 5 | 243 | 228 | 233 | 67 | 283 | 3 | 0 | 1.33 | |
| Storm | within Crusader Moat | 2 | 271 | 223 | 237 | 127 | 495 | 7 | X | X | ||
| Hamra |  | offshore Aqueduct Beach | 3 | 216 | 210 | 202 | 86 | 37 | 0 | X | X |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Everhardt, C.J., IV; Dey, H.W.; ‘Ad, U.; Sharvit, J.; Gendelman, P.; Roskin, J.; Robins, L.; Jaijel, R.; Barkai, O.; Goodman-Tchernov, B.N. Earthquake, Fire, and Water: Destruction Sequence Identified in an 8th Century Early Islamic Harbor Warehouse in Caesarea, Israel. Geosciences 2023, 13, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13040108
Everhardt CJ IV, Dey HW, ‘Ad U, Sharvit J, Gendelman P, Roskin J, Robins L, Jaijel R, Barkai O, Goodman-Tchernov BN. Earthquake, Fire, and Water: Destruction Sequence Identified in an 8th Century Early Islamic Harbor Warehouse in Caesarea, Israel. Geosciences. 2023; 13(4):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13040108
Chicago/Turabian StyleEverhardt, Charles J., IV, Hendrik W. Dey, Uzi ‘Ad, Jacob Sharvit, Peter Gendelman, Joel Roskin, Lotem Robins, Roy Jaijel, Ofra Barkai, and Beverly N. Goodman-Tchernov. 2023. "Earthquake, Fire, and Water: Destruction Sequence Identified in an 8th Century Early Islamic Harbor Warehouse in Caesarea, Israel" Geosciences 13, no. 4: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13040108
APA StyleEverhardt, C. J., IV, Dey, H. W., ‘Ad, U., Sharvit, J., Gendelman, P., Roskin, J., Robins, L., Jaijel, R., Barkai, O., & Goodman-Tchernov, B. N. (2023). Earthquake, Fire, and Water: Destruction Sequence Identified in an 8th Century Early Islamic Harbor Warehouse in Caesarea, Israel. Geosciences, 13(4), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13040108






