Abstract
In this paper, we present a systematic GIS-based approach for producing updated, upscaled, unified and reevaluated maps for the Ionian Islands of Greece, which is an area of great geological interest. In particular, Cephalonia and Lefkada are two islands with an increased and intense seismicity. Therefore, a common GIS geodatabase was produced for handling the geoinformation of the area. New upscaled (scale 1:50,000) geotechnical and seismotectonic maps of these islands were produced based on older ones. On the other hand, the corresponding maps of the islands, based on the categories of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8, were produced in an effort to correlate them. Beyond that, all the available isoseismal maps of the earthquakes that hit the Ionian Islands were gathered in an effort to evaluate them and to find possible correlations with the other types of maps. Based on the correlation results, the consideration of the Vs30 parameter in the Greek antiseismic code is proposed for a better categorization of the geological formations.
1. Introduction
The Ionian Islands are located in Western Greece, in the Ionian Sea. From north to south, the sequence of islands is Corfu, Paxoi, Lefkada, Cephalonia, Ithaki and Zakynthos. More specifically, the well-known Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ) is located at the western side of Lefkada and Cephalonia, on the northwestern end of the Hellenic subduction arc. This is the reason for the high seismicity on the islands of Cephalonia and Lefkada. Several disastrous earthquakes have been generated in the past on the Ionian Islands [1,2,3,4], causing casualties and building damage mainly to Cephalonia and Lefkada [5,6,7,8,9,10,11].
For these reasons, the existing cartographic data of the Ionian Islands were gathered, combined and evaluated in order to improve the management of the seismic hazard of these areas. Therefore, creating a set of updated, improved and accumulated maps for these areas is considered to be crucial and important. For this reason, several kinds of maps can be found in the literature, e.g., in [12,13,14,15,16]. In this paper, though, we focus on the production of specific types of maps such as geotechnical maps, seismotectonic maps and those according to the classification of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8. All of these maps, along with the geological ones, have been presented in a unified form [17,18,19] in order to have a common reference across all the Ionian Islands.
2. Presenting the Maps
In this section, all the produced sets of maps for the Ionian Islands are presented. Four maps of each map category were created as follows: one for the islands of Corfu and Paxoi, one for Lefkada, one for the islands of Cephalonia and Ithaki and one more for Zakynthos.
All the produced maps are GIS-based and were created in the ArcPro environment including both raster and vector data. The raster data concern the topographical relief of all the Ionian Islands and consist of digital elevation models (DEM) and hillshade reliefs with a 5 m resolution, derived from topographical maps with a scale of 1:5000. Furthermore, the existing geological maps (1:50,000 scale) had to be digitized, since they were in paper format. Some improvements were also made due to the field observations of the authors after having visited several areas of the islands. Using this procedure, the respective fields in the database were created, including the code names of the geological formations and their detailed descriptions as they appear in the original maps. Afterwards, two new fields were created, corresponding to the unified code names and descriptions that allow for the production of unified digital geological maps.
Apart from the prementioned detailed descriptions of the geological formations, additional quantitative fields for the corresponding P-wave velocity and density values were added. Therefore, essential database associations were made, leading to the addition of two more fields that are essential for the production of new, upscaled and improved geotechnical and seismotectonic maps. Their classification is based on existing maps with a scale of 1:500,000. Moreover, completely new maps of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8 were produced based on the two corresponding geodatabase fields. Finally, all the retrieved isoseismal maps were digitized.
2.1. Geological Setting of the Ionian Islands
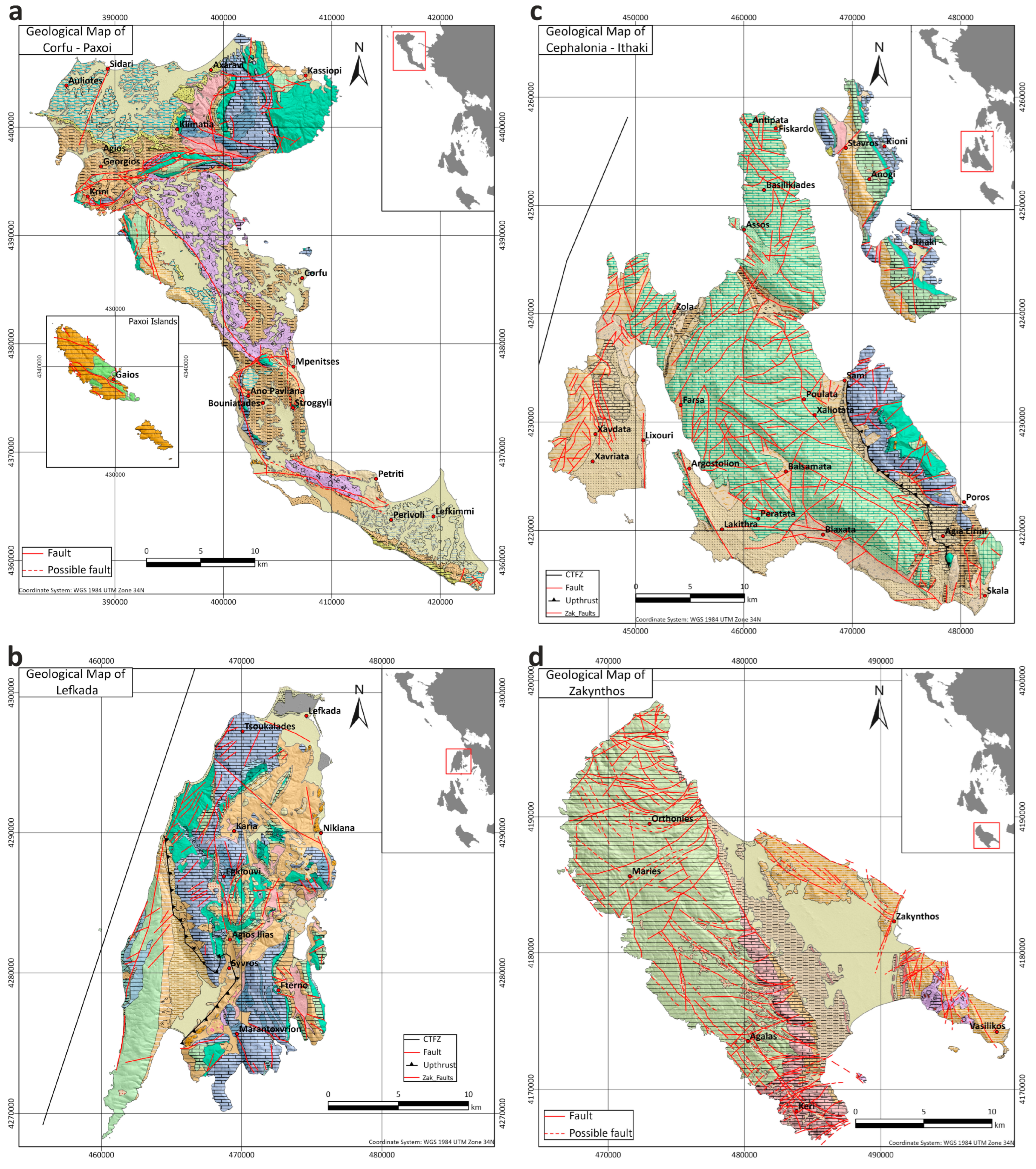
The islands of Corfu and Paxoi (Figure 1a) are mainly covered by post-alpine geological formations, as shown in Figure 1a, based on geological mapping from IGME [20,21,22]. The alpine formations of the Ionian unit dominate throughout the island, comprising a carbonate series, which starts with the typical Triassic formation of limestones with Cardita, followed by Triassic breccia and gypsum. The Triassic formations are overlaid by Jurassic–Eocene formations of limestones and shales.

Figure 1.
(a) Geological map of Corfu–Paxoi, (b) geological map of Lefkada, (c) geological map of Cephalonia–Ithaki, (d) geological map of Zakynthos.
Regarding the post-alpine molassic formations above the Ionian unit, a sequence of marls alternating with breccia, conglomerates and sandstones can be observed. The base of the breccia is located at the lower horizons of the sequence, while a package of marls with interbedding sandstone and conglomerates overlies them. The sequence of marls continues with sandstones, breccia and conglomerates until the Pliocene. Alluvial deposits are placed in unconformity either on the Miocene layers or the Alpine formations.
On Lefkada Island (Figure 1b), the Ionian unit is considered the parautochthonous unit of the island, while the Paxoi unit is considered the relatively autochthonous one [23] because of a small horizontal displacement resulting from the alpine deformation phase. The Paxoi unit, covering the majority of the island’s western part, is structured by limestones, dolomitic limestones and dolomites, overlying the Miocene marls and sandstones. The Ionian unit on Lefkada Island is formed by the characteristic formation of Triassic breccia and gypsum, overlayed by series of dolomites, limestones and shales from the Triassic to the upper Eocene. The carbonate series is covered by flysch formations (U. Eocene–L. Miocene), followed by a series of transgressive molassic deposits of marls, conglomerates, sandstones and marly limestones. Post-alpine Quaternary deposits cover the geological formations of both units to a limited extent, mainly in the southwestern and northern parts of the island.
The islands of Cephalonia and Ithaki (Figure 1c) are structured by alpine formations of the Paxoi and Ionian geotectonic units and post-alpine Quaternary deposits overlying the alpine basement in unconformity. Based on the literature [24,25,26,27], the Paxoi unit dominates throughout Cephalonia Island and mainly comprises carbonate geological formations from the Triassic to middle Miocene. The carbonate formations are covered by a Miocene sequence of marls, sandstones and brecciated limestones. The island of Ithaki is mainly structured by the Ionian unit, except for a small part to the west where the Paxoi unit appears.
The Ionian unit is considered to be an allochthonous one and appears mostly on the western part of the island of Cephalonia, on top of the Paxoi unit. It is formed by Triassic Pantocrator limestones, while Jurassic–Eocene limestones and shales complete the carbonate series before the flysch formation that appears only on the island of Ithaki Island.
On Cephalonia Island (Figure 1c), the Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ) on its western coasts is responsible for the high seismicity of the area. This structure is one of the most active in Greece and is responsible for large earthquakes in the region, which have a significant impact on the population and infrastructure of Cephalonia and other Ionian Islands.
Zakynthos Island (Figure 1d) is mainly structured by the Paxoi unit, based on IGME mapping [28], which covers a high percentage of the island. It is over-thrusted by the Ionian unit, in a narrow area, at the eastern part of Zakynthos. On Zakynthos Island, the Paxoi unit starts with a carbonate series of upper Cretaceous–Oligocene limestones and marly limestones, overlayed by Miocene deposits of marls, sandstones and mudstones. The Ionian unit that appears in the eastern part of the island only consists of a Triassic succession of limestones, evaporites and breccia. The alpine formations, along with the overthrust line between the Paxoi and Ionian unit, are covered by post-alpine, Quaternary deposits of alluvial and coastal material.
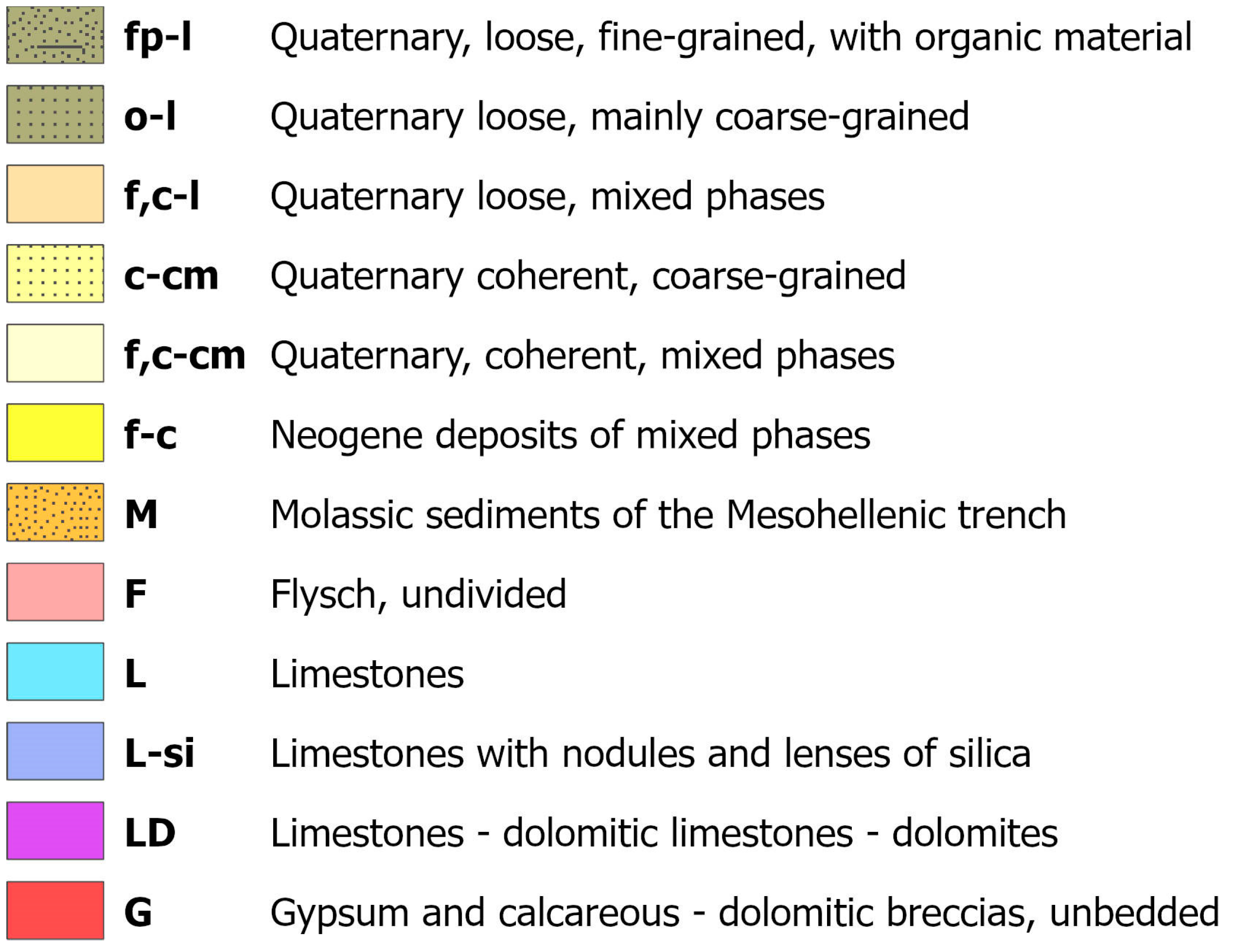
A common legend for all four islands was adopted and split into three parts, which are the post-alpine formations (Figure 2), the Ionian unit (Figure 3) and the Paxoi unit (Figure 4). It is the result of the unification of existing geological maps of the Ionian Islands published by different cartographers who provided different code names for practically the same formations, based on their detailed descriptions.

Figure 2.
Legend of post-alpine geological formations on the Ionian Islands.

Figure 3.
Legend of Ionian unit’s geological formations on the Ionian Islands.

Figure 4.
Legend of Paxoi unit’s geological formations on the Ionian Islands.
2.2. Geotechnical Maps of the Ionian Islands
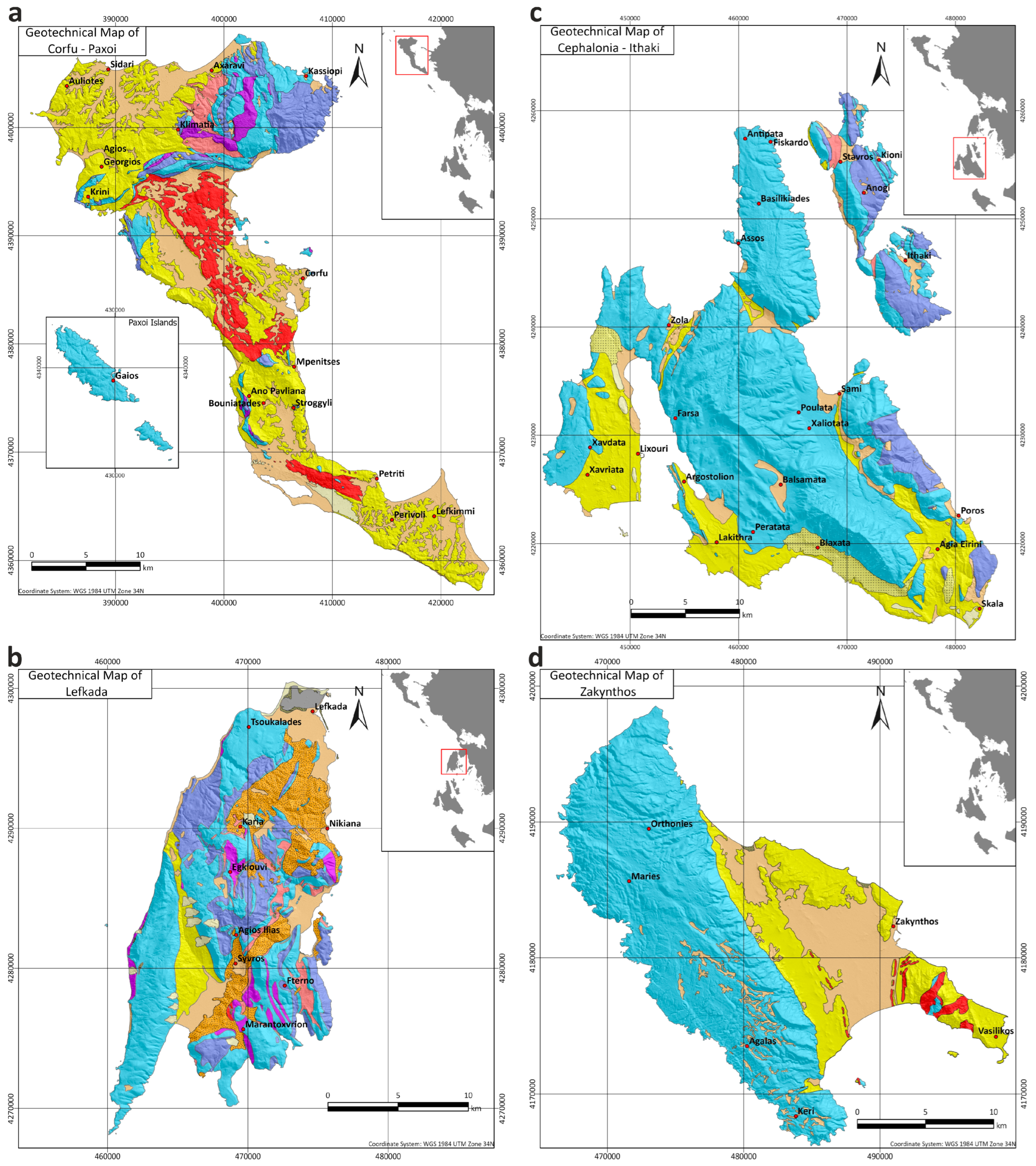
According to their physical and lithological characteristics, the geological formations of the Ionian Islands were correlated with different geotechnical categories based on the classification of the existing Engineering Map of Greece with a scale of 1:500,000 [29]. Figure 5 illustrates the geotechnical legend for the corresponding maps of the Ionian Islands (Figure 6), while in Table A1, their physical and mechanical properties are presented. The conversion of the geological formations to geotechnical units was carried out based on the digital geological maps and their detailed geological descriptions. Following the aforementioned procedure, we managed to upscale the existing map (1:500,000) to 1:50,000, which is similar to the scale of the corresponding geological maps. Therefore, four (4) geotechnical maps with a scale of 1:50,000 were produced (Figure 6) for the Ionian Islands.

Figure 5.
Legend for geotechnical maps of the Ionian Islands (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
(a) Geotechnical map of Corfu–Paxoi, (b) geotechnical map of Lefkada, (c) geotechnical map of Cephalonia–Ithaki, (d) geotechnical map of Zakynthos.
Based on the produced geotechnical map of Corfu and Paxoi (Figure 6a), it seems that a high percentage of the land of Corfu Island is covered by Neogene and Quaternary deposits of mixed and loose phases. On the other hand, the northeastern part of the island is dominated by undivided flysch and limestones in cases with silica and dolomitic limestones/dolomites. At the central part of the island, gypsum and dolomitic breccias formations are observed, along with a limited development on the southern part of the island. Finally, the whole island of Paxoi is structured with limestones.
Regarding the island of Lefkada, the geotechnical map (Figure 6b) reveals a high percentage of alpine formations, mainly limestones, which, in some cases, are observed with silica or dolomitic limestones/dolomites. These types of geotechnical formations structure the biggest part of the island, especially in the western and southern parts. Molassic sediments, along with Neogene and Quaternary deposits of mixed phases, cover the northern and central parts of Lefkada Island.
It is obvious that the island of Cephalonia (Figure 6c) is mainly structured by limestones, apart from the southern part and the peninsula of Lixouri, where Neogene and Quaternary deposits of mixed phases dominate. Ithaki Island is also structured by limestones with silica, while there are also minor areas of undivided flysch.
Finally, on Zakynthos Island (Figure 6d), limestones dominate throughout the western part of the island, while the eastern part is structured with Neogene and Quaternary deposits of mixed phases. Gypsum and dolomitic breccia formations are found in small-scale appearances in the southeastern part of the island.
2.3. Seismotectonic Maps of the Ionian Islands
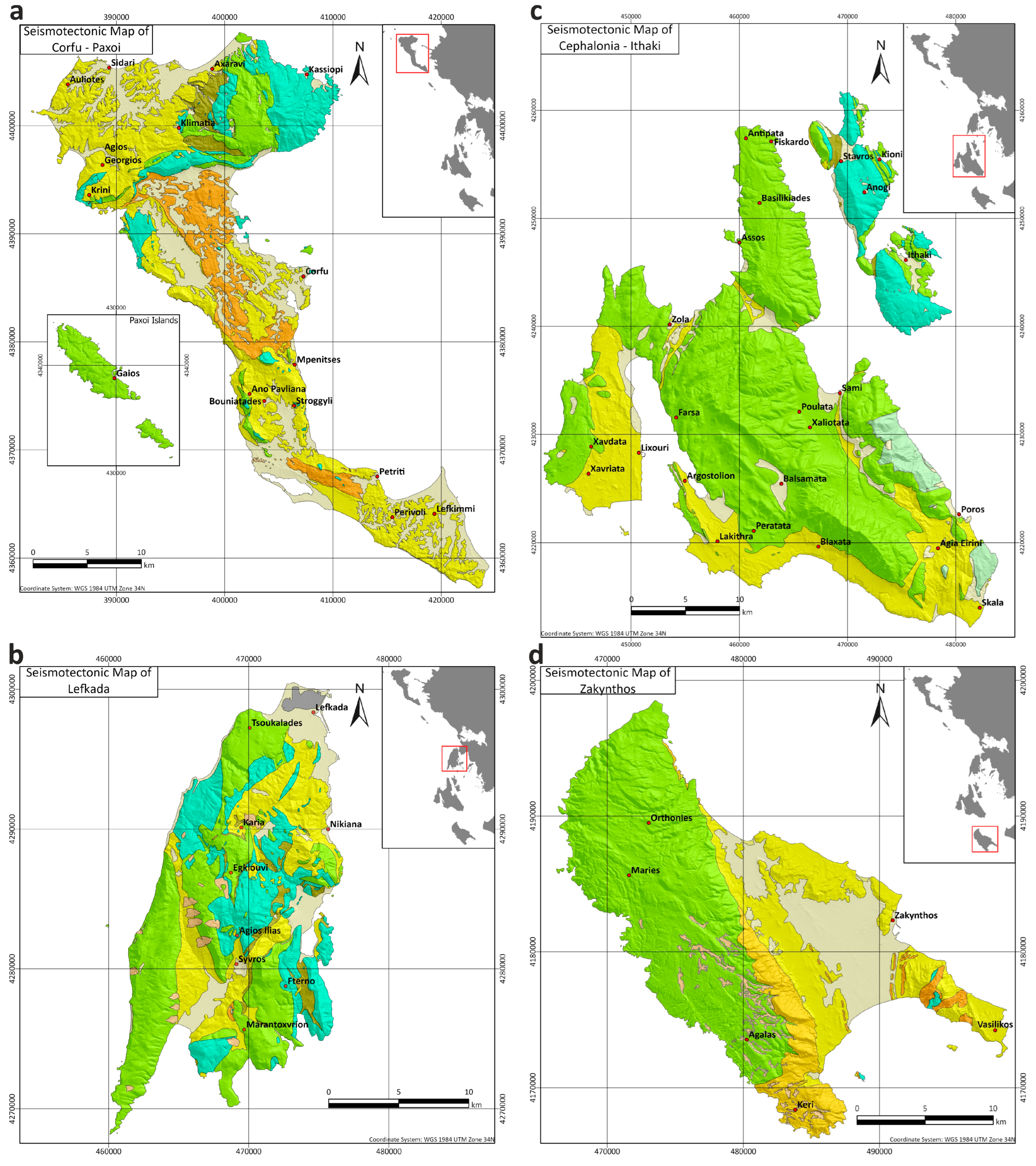
A third set of maps regarding the Ionian Islands comprises upscaled seismotectonic maps of the Ionian Islands with a scale of 1:50,000 (Figure 7). They originate from the seismotectonic map of Greece with a scale of 1:500,000 [30], based on the combination of existing faults and seismicity, in combination with geological maps with a scale of 1:50,000. Practically, in [30], the geological formations are grouped according to their P-wave velocity and density values, which are adapted in our upscaled seismotectonic maps (Figure 7). Their common legend is presented in Figure 8.

Figure 7.
(a) Seismotectonic map of Corfu–Paxoi, (b) seismotectonic map of Lefkada, (c) seismotectonic map of Cephalonia–Ithaki, (d) seismotectonic map of Zakynthos.

Figure 8.
Legend for seismotectonic maps of the Ionian Islands (Figure 7).
In some cases, geophysical measurements were taken into account [31] in order to calibrate the original data. A great part of Corfu and Lefkada towns were covered with geophysical measurements in [31], investigating the majority of existing geological formations. For the estimation of the VP wave velocity, 2D seismic refraction tomography (SRT) was implemented by the authors and was presented recently in [31]. Moreover, the density calculation of the selected geological formations was also carried out through laboratory measurements [31]. The above-mentioned values of the seismic velocities and densities were used for the comparison with the ones provided by the seismotectonic map of Greece [30] and their re-evaluation.
The produced seismotectonic map of Corfu and Paxoi (Figure 7a) highlights the appearance of medium to high velocity (Vp = 1800–3500 m/s) and density (ρ = 2.2–2.7 gr/cm3) formations on the north central and northeastern part of Corfu Island, derived by the existence of alpine geological formations. The majority of the surface of Corfu Island is covered with formations of lower P-wave velocities and densities that generally correspond to Neogene and Quaternary deposits. On Paxoi, which mainly consists of limestones of the Paxoi unit, high P-wave velocities and densities are observed.
The seismotectonic map of Lefkada Island (Figure 7b) reveals a high percentage of coverage by formations of high P-wave velocity (3500–4500 m/s) and density (2.6–2.9 gr/cm3) values due to the development of alpine formations of the Ionian and Paxoi units. Moreover, lower VP velocities (1800–3500 m/s) and densities (2.2–2.6 gr/cm3) are observed in the central south, northern and northeastern parts of Lefkada Island.
On Cephalonia and Ithaki (Figure 7c), most of the geological formations are categorized as Ki and KPA-KPa classes (Figure 8). They correspond to limestone and dolomite formations of the Ionian and Paxoi units, identified with high P-wave velocity (3500–4500 m/s) and density (2.6–2.9 gr/cm3) values. The remaining parts of Cephalonia, especially the southern part, are covered with formations of low VP velocity (1800–3500 m/s) and density values (2.2–2.6 gr/cm3).
The northern and eastern parts of the island of Zakynthos are categorized in the KPA-KPa category (Figure 7d), which signifies high P-wave velocity (3500–4500 m/s) and density (2.6–2.9 gr/cm3) values. The rest of the island’s surface is covered with formations of lower VP (1800–3500 m/s) and density (2.2–2.6 gr/cm3) values that correspond to the post-alpine deposits of Zakynthos Island (Figure 7d).
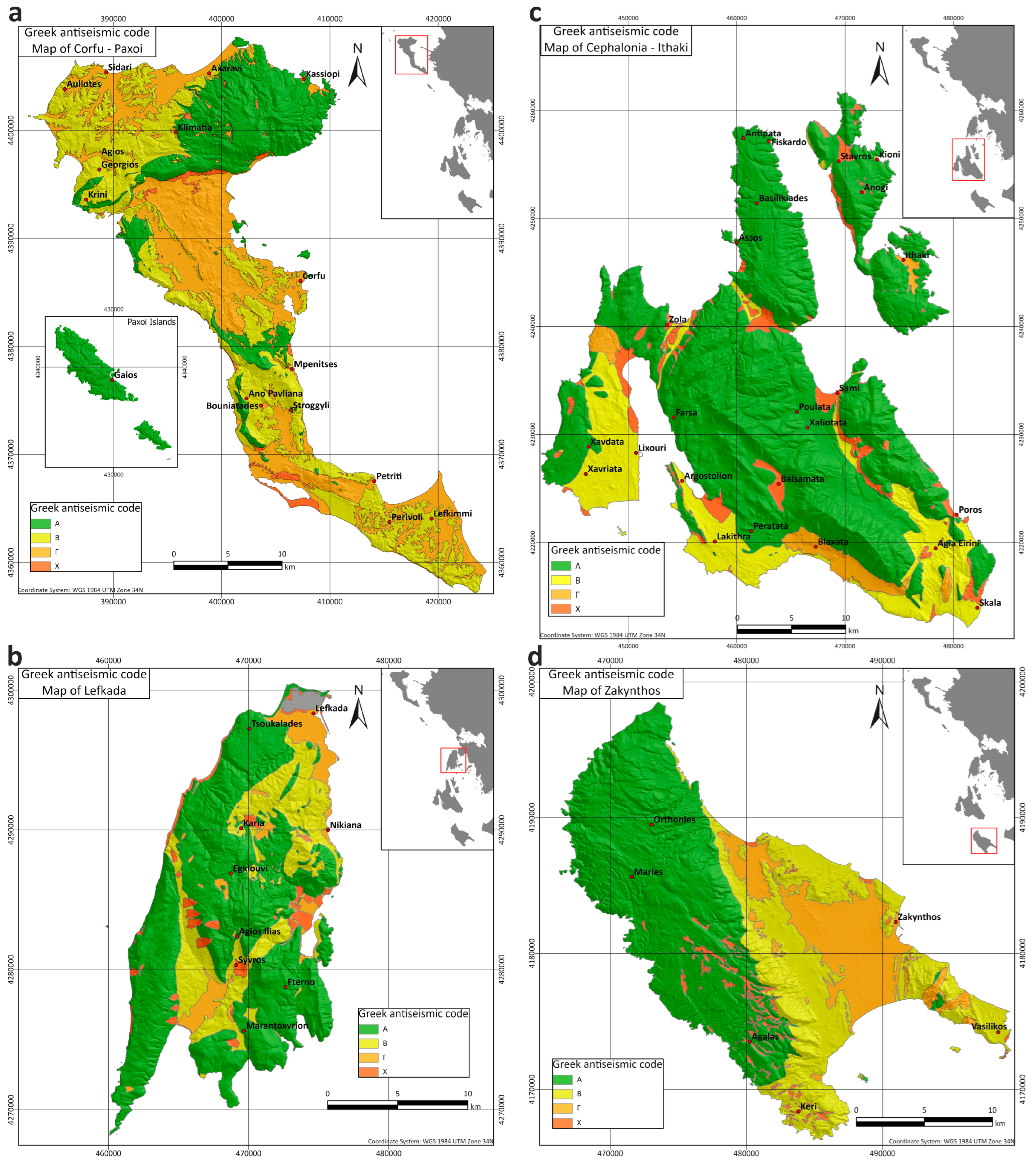
2.4. Maps of Greek Antiseismic Code
The fourth type of maps of the Ionian Islands concerns the Greek antiseismic code [32], which takes into consideration the ground acceleration, the building type and the soil classification. The antiseismic code provides the necessary guidelines for the appropriate building structures in order to have the essential antiseismic protection in Greece. Each country’s antiseismic code, which is revised and updated whenever it is necessary, contains a set of rules that define the minimum requirements for the design of seismic structures. The first Greek antiseismic code was drawn up in 1959. In 1984, it was supplemented with additional articles, and its application began in 1985. In 1995, the new Greek antiseismic code came into exclusive application. In 2003, the Seismic Hazard Zone Map was modified, including three (3) seismic hazard zones instead of the older four (4) ones [32]. The first zone corresponds to acceleration values of up to 0.16 g, the second one is for acceleration values between 0.16 and 0.24 g and the third one is for values between 0.24 g and 0.36 g.
The new antiseismic code also includes the classification of soil types, as presented in Table 1. Taking into consideration this type of categorization, all the geological formations of the Ionian Islands were matched to class in the unified GIS geodatabase in order to produce the set of maps of the Greek antiseismic code, as they are illustrated in Figure 9.

Table 1.
Soil classification based on Greek antiseismic code [32].

Figure 9.
Map for the classification of Greek antiseismic code [32] of (a) Corfu–Paxoi, (b) Lefkada, (c) Cephalonia–Ithaki and (d) Zakynthos.
Based on the Greek antiseismic code, the geological formations of Corfu and Paxoi (Figure 9a) are categorized into four (4) corresponding soil classes (A, B, Γ and X). The dominating soil classes are Β and Γ, but the northeastern part of Corfu and Paxoi are almost dedicated to class A.
Regarding the island of Lefkada (Figure 9b), the categorization of the geological formations also involves all four categories (A, B, Γ and X). A high percentage of the island formations are categorized as class A, which corresponds to the alpine formations that prevail. In the south central and northeastern part of the island, the formations are categorized as B and Γ. In some cases, where the coastal formations and scree are presented in steep slopes, we can also observe soil class X.
The geological formations of Cephalonia and Ithaki are categorized into three (3) soil classes regarding the Greek antiseismic code (Figure 9c). As both islands are mainly structured with rocky alpine formations, class A is mostly present. The class Γ is located in the southern part of Cephalonia Island. Finally, class X corresponds to coastal formations and loose formations that are present in steep slopes, like on the island of Lefkada.
The geological formations of Zakynthos Island (Figure 9d) are also divided into four soil classes (A, B, Γ and X). At the eastern part of the island, the geological formations are mainly rocky alpine, corresponding to soil class A. At the central and southern parts of Zakynthos, soil class B is mainly present, while on the rest of the island, soil classes Γ and X prevail.
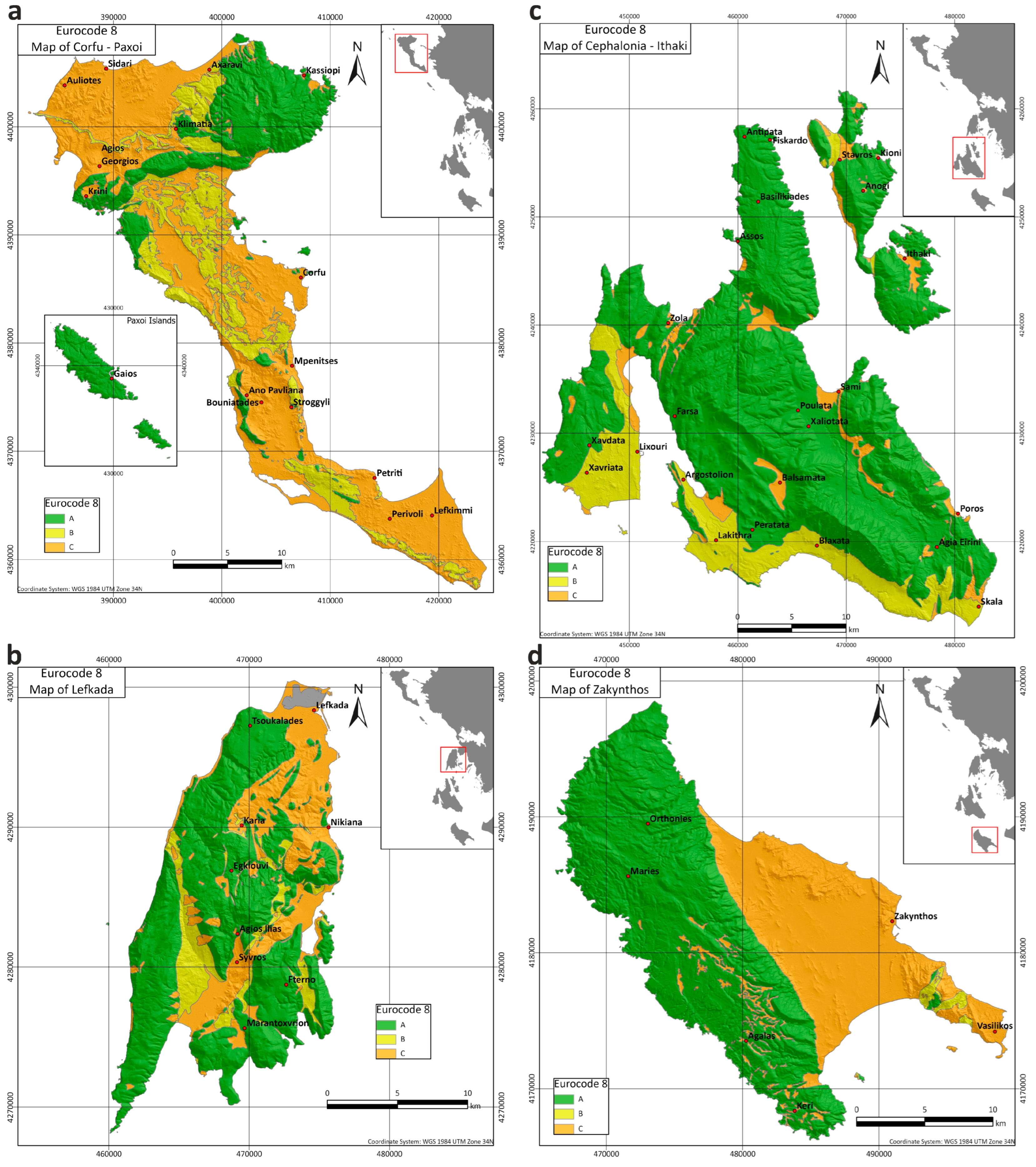
2.5. Eurocode 8 Maps of the Ionian Islands
A final set of maps for the Ionian Islands was produced regarding their categorization for Eurocode 8 [33] (Figure 10). According to the European Committee for Standardization’s Eurocode 8 (EC 8), as presented in Table 2, the VS30 values are used for the classification of the ground type. These VS30 values were calculated with the contribution of geophysical measurements and, more specifically, the Multi Analysis Surface Waves (MASW), which were carried out at selected geological formations of Corfu and Lefkada [31]. This procedure was proven to be really useful for the categorization of all the formations of the Ionian Islands.

Figure 10.
Map for the classification of Eurocode 8 [33] of (a) Corfu–Paxoi, (b) Lefkada, (c) Cephalonia–Ithaki and (d) Zakynthos.

Table 2.
Ground type classification based on Eurocode 8 [33].
In Figure 10a, three ground types (A, B and C) of Eurocode 8 are discriminated on Corfu and Paxoi. The ground type A formations, with the highest VS30 values (>800 m/s), are concentrated at the central, northern and northeastern parts of Corfu Island. They also appear across the whole Paxoi Island (Figure 10a). On the other hand, ground type C (180–360 m/s) seems to dominate at the remaining part of the island, along with several areas of ground type B (360–800 m/s), which are mostly located at the central part of the island of Corfu.
On Lefkada Island (Figure 10b), the geological formations are categorized into three ground types of Eurocode 8 (A, B and C). The greater part of the island belongs to category A (>800 m/s), while the rest of the island, which is structured with post-alpine formations, is categorized as ground types B (360–800 m/s) and C (180–360 m/s), depending on their internal structure and cohesion.
The rocky alpine formations of Cephalonia and Ithaki (Figure 10c) present high Vs30 values (>800 m/s), and thus, are categorized in ground type A of Eurocode 8. Ground types B and C are located at the southern part of Cephalonia Island and in small-scale appearances on Ithaki Island, corresponding to loose alpine (flysch) and post-alpine formations.
Finally, on Zakynthos Island (Figure 10d), the dominating ground types of Eurocode 8 are A (>800 m/s) and C (180–360 m/s). Ground type A is primarily found at the western part of the island, while ground type C is constrained at the eastern part, where post-alpine formations are present.
3. Results—Discussion
3.1. Isoseismal Maps—Macroseismic Data
As we have already mentioned, the Ionian Islands, especially Cephalonia and Lefkada, are known for their severe earthquakes that cause infrastructure damage and human casualties. Two of the most common intensity scales are the EMS98 and the ESI. The EMS98 scale [34] classifies residential buildings into six vulnerability classes and evaluates their damage distribution in five classes, which account for the damage level of both the main structural and non-structural components. Based on the assessment of the damage caused to the infrastructures and buildings, we can produce the corresponding isoseismal map of the area, illustrating the damage distribution from an earthquake. On the other hand, the ESI scale [35] is based on earthquake effects on the natural environment, including geological, hydrological and geomorphological features. Normally, an EMS98 isoseismal map can be obtained only in terrestrial areas where buildings and infrastructures exist, and therefore, their damage can be recorded. For areas such as the Ionian Islands, the collection of these types of data might be tricky due to the nature of the geomorphology of an island and the existence of the sea.
From the inquiry of the literature, we found almost 35 isoseismal maps or the essential macroseismic data, allowing for the creation of isoseismal maps from different events and/or researchers. Unfortunately, those data mainly refer to the islands of Cephalonia and Lefkada, due to their vicinity with the Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ). In particular, for the island of Cephalonia, recent intensity maps showing the earthquakes of 2014 were retrieved (scaled either using EMS98 or ESI) [36,37]. Additionally, the author of [38] presents isoseismal maps from two historical earthquakes in 1741 and 1767.
Regarding the island of Lefkada, the isoseismal maps of two seismic events were found. A first map for the 1948 earthquake is presented by the authors of [39]. On the other hand, the earthquake of 2015 led to the production of isoseismal maps (of both scales EMS98 and ESI) from several researchers [40,41,42,43]. Regarding the island of Zakynthos, the authors of [44] provide an evaluation of all the major historical and recent earthquakes felt on Zakynthos Island, based on the ESI scale. Finally, only one isoseismal map for the earthquake of 1975 [45] was retrieved from the literature, regarding the island of Corfu.
Several other published isoseismal maps were also found [7,46,47,48,49,50]. Unfortunately, they could not provide adequate data in order to correlate them with the new geotechnical maps, since they were quite rough and simplified. Beyond that, the EMS98 maps were preferred due to their direct association with infrastructure damage. Finally, the authors of [51] used the macroseismic intensities of the Ionian Islands for their hazard analysis.
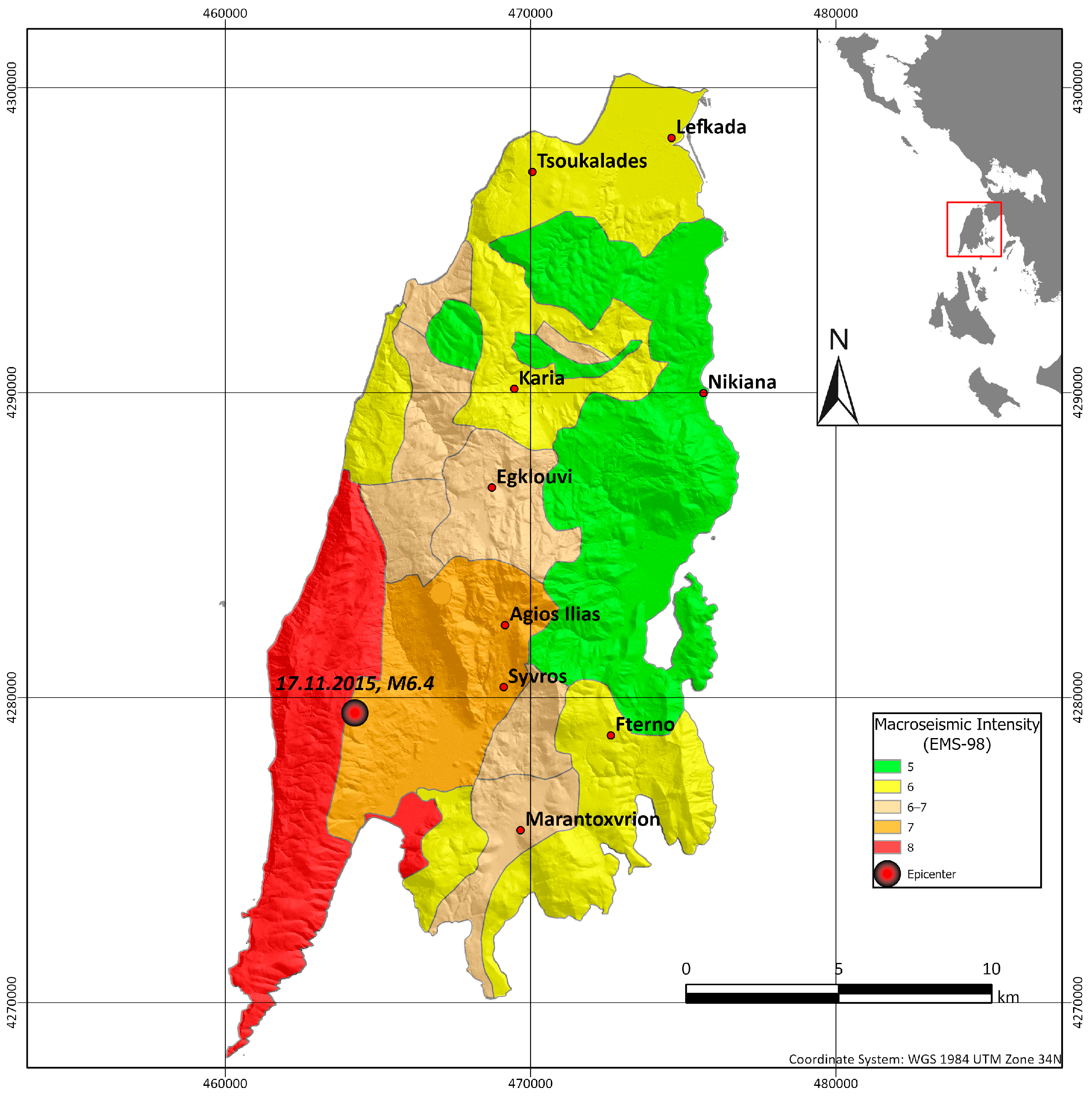
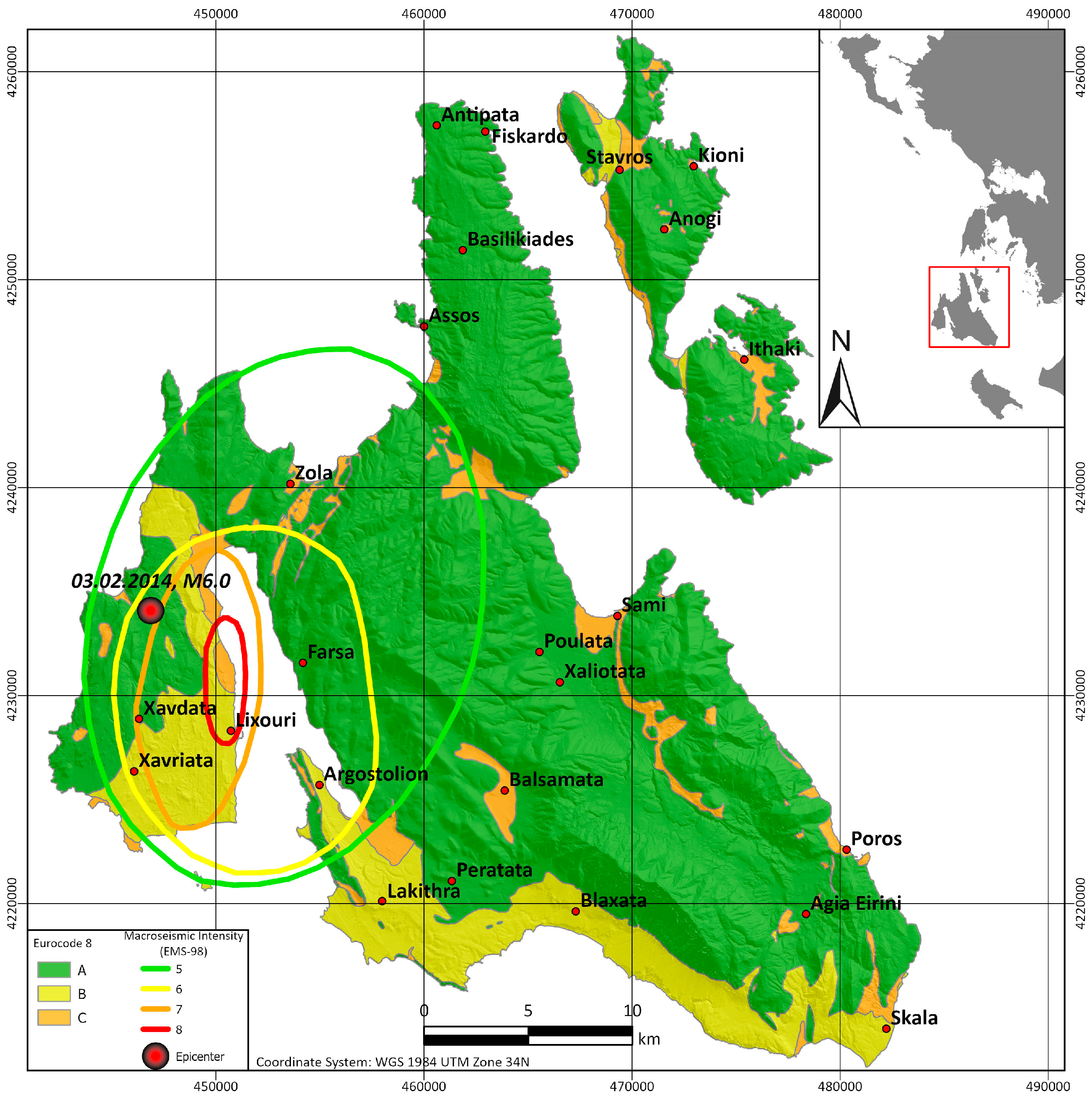
In Figure 11, one retrieved isoseismal map of Lefkada Island is illustrated, presented with polygons and not contours. A similar approach of a polygonal isoseismal map was also produced for the Mw = 6.2 Richter earthquake, on 14 August 2003 [41,42]. Moreover, in Figure 12, an isoseismal map from the latest severe earthquakes on Cephalonia Island [47] is presented, revealing its impact on the western part of the island and mostly on the Lixouri peninsula.

Figure 11.
Isoseismal map of Lefkada Island regarding the Mw = 6.4 Richter earthquake of 17 November 2015 based on [41].

Figure 12.
Isoseismal map of Cephalonia Island regarding the Mw = 6.0 Richter earthquake of 3 February 2014 based on [47], compared with the corresponding Eurocode 8 map of the island.
An effort was made to correlate the data of all isoseismal maps with the corresponding maps for the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8. Unfortunately, it was not possible to identify some kind of similarity pattern for the island of Lefkada by associating the retrieved isoseismal maps with the corresponding Greek antiseismic code (Figure 9b) and Eurocode 8 (Figure 10b) maps. One possible reason for this could be that the damage distribution of an earthquake is also controlled by the location of its epicenter and its characteristics, which do not remain stable for each seismic event. On the other hand, for the island of Cephalonia, an association between the isoseismal map of the 3 February 2014 earthquake [47] and the Eurocode 8 map can be observed in Figure 12. More specifically, the maximum intensities (7–8) seem to have been recorded mainly on zones B and C of the Eurocode 8 map.
3.2. Groups of Formations
The production of the aforementioned maps of the Ionian Islands (Section 2) provides valuable information regarding the classification of all their existing geological formations. In Table 3, all the geological formations of these islands are grouped based on the similarities οf their geological characteristics (Figure 1), but also based on their geotechnical classification (Figure 6), their seismotectonic class (Figure 7) and their Greek antiseismic code (Figure 9) and Eurocode 8 (Figure 10) maps.

Table 3.
Classification of the geological formations of the Ionian Islands.
3.3. Correlation of Greek Antiseismic Code and Eurocode Maps
As far as the island of Corfu is concerned, the class A formations of the Greek antiseismic code (Figure 9a) mainly correspond to the formations of the respective class A of the Eurocode 8 map (Figure 10a). A part of Eurocode 8’s class A formations includes formations of the Greek antiseismic code class B. The formations of class B Greek antiseismic code, in general, correspond to Eurocode’s class C. Regarding Paxoi Island, the formations belong to class A both for the Eurocode and Greek antiseismic code maps.
Quite the same correlation is observed on Lefkada Island, as the formations of the primary category A of the Greek antiseismic code (Figure 9b) seem to belong to class A for Eurocode 8 (Figure 10b). On the other hand, the formations of class B regarding the Greek antiseismic code are separated into two different categories, classes B and C, regarding Eurocode 8 categorization. Furthermore, the formations of category C for Eurocode 8 seem to correspond to the X class of the Greek antiseismic code on Lefkada Island (Figure 9b).
These associations are also observed on the islands of Cephalonia and Ithaki (Figure 9c and Figure 10c). One difference is observed, with the formations of class B of the Greek antiseismic code, at the southeastern and western parts of Cephalonia, corresponding to class A of Eurocode 8. This kind of correlation can also be observed on Corfu Island.
Finally, for the island of Zakynthos, the correspondence of class A formations of Eurocode 8 to class A of the Greek antiseismic code is once again observed. Furthermore, the majority of all other classes of the Greek antiseismic code (B, Γ and X), as shown in Figure 9d, are practically mutually presented as Eurocode 8 class C formations in Figure 10d.
In Table 4, all the associations among the categories of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8 were grouped, while in Table 3, all the corresponding categorizations can be found in detail. In general, we can say that all types of carbonate formations belong to class A of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8. Flysch, though, belongs to class A of the Greek antiseismic code, but belongs to class B of Eurocode 8. The formations of class B of the Greek antiseismic code including marly limestones or intercalations of limestones turn into class A of Eurocode 8, but when sandstones exist, they are also characterized as class B of Eurocode 8. Furthermore, formations that were classified as category Γ of the Greek antiseismic code can refer to class B of Eurocode 8, if breccia or conglomerates are involved, or remain as class C if they have evaporites/gypsum or even alluvial deposits. Finally, all formations of category X of the Greek antiseismic code are classified as category C of Eurocode 8.

Table 4.
Associations of Greek antiseismic code [32] and Eurocode 8 [33] classifications on the Ionian Islands.
Overall, it is considered that the Greek antiseismic code is insufficient due to the fact that it is mainly based on the soil type, and its classification is somehow qualitative. On the other hand, the classification of Eurocode 8 takes into account the Vs30 values, which can also be determined via geophysical measurements. Therefore, as already stated by other researchers [52,53,54], Eurocode 8 seems to provide better classification for engineering purposes, or alternatively, the Greek antiseismic code can be improved by embedding elements of Eurocode 8, such as Vs30.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, an organized effort to gather, digitize (in GIS environment) and update valuable information regarding the cartographic data of the Ionian Islands was carried out. Existing maps, such as seismotectonic and geotechnical ones, were upscaled from 1:500,000 to 1:50,000 for these islands, and simultaneously re-evaluated. Additionally, new sets of maps were also produced based on the classification of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8.
Beyond this, we tried to unify all the geological formations of the Ionian Islands in a geodatabase and adapt a common categorization, given the fact that most of them can be observed on more than one island even though they are symbolized differently on older paper maps.
As already mentioned, during the procedure for the production of upscaled and updated seismotectonic maps, a comparison/calibration of the density and Vp values for several formations was carried out between the existing data of the IGME maps [30] and recently acquired geophysical data, which are presented in detail in [31]. The density values were almost identical, while the Vp seismic velocities were observed to have slight differences. More specifically, the velocities provided in [30] were vaguely higher, which is probably due to the fact that the values in [31] were collected near the surface.
Finally, some associations for the classifications of the Greek antiseismic code and Eurocode 8 were identified for specific types of geological formations. For that reason, it seems that information from both classifications is valuable, and Vs30 values should also be embedded somehow in the categorization of the Greek antiseismic code. Finally, only for the island of Cephalonia, similar patterns were determined between the Eurocode 8 map and existing isoseismal map.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D.A., N.V. and E.V.; methodology, J.D.A., C.F. and E.V.; software, I.-K.G., C.F. and E.V.; validation, S.D., I.-K.G., C.F. and E.V.; investigation, S.D., I.-K.G., C.F. and E.V.; resources, J.D.A. and N.V.; data curation, S.D., I.-K.G., C.F. and E.V.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D. and I.-K.G.; writing—review and editing, J.D.A., S.D., C.F., E.V. and N.V.; visualization, S.D. and I.-K.G.; supervision, J.D.A., C.F., E.V. and N.V.; project administration, J.D.A. and N.V.; funding acquisition, N.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the project “Telemachus Innovative Seismic Risk Management Operational System of the Ionian islands” (MIS 5007986), which is part of the Regional Operational Program “Ionian islands 2014 2020” and is co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) (National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF) 2014 20).
Data Availability Statement
All data were retrieved from the existing literature.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Petras A for his contribution to the data acquisition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Physical and mechanical properties of the geotechnical categories observed on the Ionian Islands, based on the legend data of the original Engineering Map of Greece with a scale of 1:500,000 [29].
Table A1.
Physical and mechanical properties of the geotechnical categories observed on the Ionian Islands, based on the legend data of the original Engineering Map of Greece with a scale of 1:500,000 [29].
| Geotechnical Category [21] | Yb (g/cm3) | LL (%) | PL (%) | Cohesion (Kg/cm2) | Friction Angle (o) | qu (kg/cm2) | Cs (kg/cm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shear Tests (cs) | Triaxial Tests (ct) | Shear Tests (φs) | Triaxial Tests (φt) | ||||||
| fp-l | 1.3–2.25 | 20–65 | 12–25 | 0.03–0.9 | 0.04–1.8 | 18–38 | 15–32 | 0.2–3.5 | 0.2–4.0 |
| o-l | 2.0–2.4 | 17–40 | 13–25 | 0.0–0.5 | 0.0–0.5 | 25–50 | - | 0.3–2.5 | 0.2–0.5 |
| f,c-l | 1.8–2.2 | 20–46 | 8–30 | - | 0.2–0.5 | - | 15–35 | 0.5–3.5 | - |
| c-cm | 2.1–2.8 | - | - | - | 2.0–30 | - | 35–65 | 2–150 | - |
| f,c-cm | 1.8–2.8 | 30–70 | 14–40 | 0.4–2.0 | 0.4–50 | 18–52 | 10–70 | 0.3–550 | 0.16–0.2 |
| f-c | 1.8–2.8 | 27–67 | 19–33 | 0.03–25 | 0.05–75 | 20–50 | 15–40 | 1–25 | 0.15–0.2 |
| M | 1.8–2.2 | 25–60 | 16–35 | - | 0.03–70 | - | 14–43 | 2–550 | 0.13–0.2 |
| G | 1.7–2.3 | - | - | 10–150 | 25–35 | 10–200 | - | ||
| F | 1.7–2.8 | 25–35 | 16–21 | 6–200 | - | 20–45 | - | 65–700 | - |
| L | 2.5–2.7 | - | - | - | 100–300 | 25–45 | 30–45 | 300–1200 | - |
| L-si | 2.5–2.7 | - | - | - | 100–300 | 30–45 | 200–1700 | - | |
| LD | 2.6–2.8 | - | - | - | 100–300 | - | 27–45 | 350–1800 | - |
Yb: Bulk density; LL: Liquid limit; PL: Plastic limit; cs: Cohesion from shear tests; ct: Cohesion from triaxial tests; φs: Angle of friction from shear tests; φt: Angle of friction from triaxial tests; qu: Uniaxial compressive strength; Cs: Compression index.
References
- Sakkas, V.; Kapetanidis, V.; Kaviris, G.; Spingos, I.; Mavroulis, S.; Diakakis, M.; Alexopoulos, J.D.; Kazantzidou-Firtinidou, D.; Kassaras, I.; Dilalos, S.; et al. Seismological and Ground Deformation Study of the Ionian Islands (W. Greece) during 2014–2018, a Period of Intense Seismic Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazachos, B.C.; Papazachou, C.B. The Earthquakes of Greece; Ziti Editions: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2003; 286p. [Google Scholar]
- Kouskouna, V.; Makropoulos, K. Historical earthquake investigations in Greece. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 47, 723–731. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2122/792 (accessed on 20 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Makropoulos, K.; Kaviris, G.; Kouskouna, V. An updated and extended earthquake catalogue for Greece and adjacent areas since 1900. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, G.; Pavlides, S. Using the INQUA scale for the assessment of intensity: Case study of the 2003 Lefkada (Ionian Islands), Greece earthquake. Quat. Int. 2007, 173, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakostas, V.; Papadimitriou, E.; Mesimeri, M.; Gkarlaouni, C.; Paradisopoulou, P. The 2014 Kefalonia doublet (Mw 6.1 and Mw 6.0), central Ionian Islands, Greece: Seismotectonic implications along the Kefalonia transform fault zone. Acta Geophys. 2015, 63, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Karastathis, V.K.; Koukouvelas, I.; Sachpazi, M.; Baskoutas, I.; Chouliaras, G.; Agalos, A.; Daskalaki, E.; Minadakis, G.; Moshou, A.; et al. The Cephalonia, Ionian Sea (Greece), sequence of strong earthquakes of January-February 2014: A first report. Res. Geophys. 2014, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoulidis, N.; Karakostas, C.; Lekidis, V.; Makra, K.; Margaris, B.; Morfidis, K.; Papaioannou, C.; Rovithis, E.; Salonikios, T.; Savvaidis, A. The Cephalonia, Greece, January 26 (M6. 1) and February 3, 2014 (M6. 0) earthquakes: Near-fault ground motion and effects on soil and structures. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 14, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakostas, C.; Lekidis, V.; Makarios, T.; Salonikios, T.; Sous, I.; Demosthenous, M. Seismic response of structures and infrastructure facilities during the Lefkada, Greece earthquake of 14/8/2003. Eng. Struct. 2005, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Diakakis, M.; Kranis, H.; Vassilakis, E.; Kapetanidis, V.; Spingos, I.; Kaviris, G.; Skourtsos, E.; Voulgaris, N.; Lekkas, E. Inventory of historical and recent earthquake-triggered landslides and assessment of related susceptibility by GIS-based analytic hierarchy process: The case of Cephalonia (Ionian Islands, Western Greece). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoyanni, T.; Sakellariou, M.; Baskoutas, J.; Christodoulou, N. Evaluation of active faulting and earthquake secondary effects in Lefkada Island, Ionian Sea, Greece: An overview. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Graña, A.; Goy, J.L.; Zazo, C.; Yenes, M. Engineering geology maps for planning and management of natural parks:“Las Batuecas-Sierra de Francia” and “Quilamas”(Central Spanish System, Salamanca, Spain). Geosciences 2013, 3, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, G.; Fabbrocino, S.; Fabbrocino, G.; Lanzano, G.; Santucci de Magistris, F.; Silvestri, F. A geolithological approach to seismic site classification: An application to the Molise Region (Italy). Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 15, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.C.; Sousa, M.L.; Carvalho, A. Seismic zonation for Portuguese national annex of Eurocode 8. In Proceedings of the 14WCEE, Beijing, China, 12–17 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zuquette, L.V.; Pejon, O.J.; dos Santos Collares, J.Q. Engineering geological mapping developed in the Fortaleza metropolitan region, State of Ceara, Brazil. Eng. Geol. 2004, 71, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumurdjanov, N.; Milutinovic, Z.; Salic, R. Seismotectonic model backing the PSHA and seismic zoning of Republic of Macedonia for National Annex to MKS EN 1998-1:2012 Eurocode 8. J. Seismol. 2020, 24, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasiano, A.; Bartoccini, U.; Nardi, F. Geospatial data homogenization and processing for integrated assessment of urban and natural resources and risks. A pilot case for Lazio Region (Italy). In Proceedings of the 57th ISOCARP World Planning Congress 57th ISOCARP World Planning Congress Planning Unlocked: New Times, Better Places, Stronger Communities, Doha, Qatar, 28 October–11 November 2021; pp. 1330–1338, ISOCARP. [Google Scholar]
- Smiraglia, D.; Capotorti, G.; Guida, D.; Mollo, B.; Siervo, V.; Blasi, C. Land units map of Italy. J. Maps 2013, 9, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, T.; Merz, C.; van Gasselt, S.; Steidl, J. GIS-based modeling of a complex hydrogeological setting in the younger Pleistocene of NE-Germany. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2016, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016. PSC2016-928. [Google Scholar]
- Savoyat, E.; Monopoli, D.; Pinel, C. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet North Corfu, Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Maragkoudaki, N.; Savoyat, E.; Monopoli, D. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet South Corfu, Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, L.J.; Dainelli, L.; Temple, P.G. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet Paxi, Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Bornovas, I. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet Lefkas, Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- British Petroleum, C.; Bergmann, H.; Braune, K.; Dremel, G.; Hatzopoulos, E.; Hug, F.; Uliczny, E.; Migkiros, G. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet Cephalonia Island (Northern Part), Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- British Petroleum, C.; Bergmann, H.; Braune, K.; Dremel, G.; Hatzopoulos, E.; Hug, F.; Uliczny, E.; Migkiros, G. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet Cephalonia Island (Southern Part), Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Stavropoulos, A. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet Ithaki-Atokos Islands, Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bourli, N.; Kokkaliari, M.; Dimopoulos, N.; Iliopoulos, I.; Zoumpouli, E.; Iliopoulos, G.; Zelilidis, A. Comparison between siliceous concretions from the Ionian basin and the Apulian platform margins (Pre-Apulian zone), western Greece: Implication of differential diagenesis on nodules evolution. Minerals 2021, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, L.J.; Temple, P.G. Geological Map of Greece, Sheet Zakynthos Island, Scale 1:50,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Andronopoulos, B.; Rozos, D.; Kynigalaki, M.; Koukis, G.; Tzitziras, A.; Pogiatzi, E.; Apostolidis, E. Engineering Geological Map of Greece, Scale 1:500,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mouyiaris, N.; Andronopoulos, V.; Eleftheriou, A.; Kynigalaki, M.; Koukis, G.; Rondoyanni, T.; Mettos, A.; Katsikatsos, G.; Perissoratis, C.; Drakopoulos, J.; et al. Seismotectonic Map of Greece with Seismogeological Data, Scale 1:500,000; Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration: Athens, Greece, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulos, J.D.; Voulgaris, N.; Dilalos, S.; Gkosios, V.; Giannopoulos, I.K.; Mitsika, G.S.; Vassilakis, E.; Sakkas, V.; Kaviris, G. Near-Surface Geophysical Characterization of Lithologies in Corfu and Lefkada Towns (Ionian Islands, Greece). Geosciences 2022, 12, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAK2003; Greek Seismic Code. EPPO: Athens, Greece, 2003. (In Greek)
- EN-1998-1; Eurocode 8, “Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance”, Part 1: General Rules, Seismic Actions and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Grünthal, G. European Macroseismic Scale 1998. (EMS-98). In Cahiers du Centre Européen de Géodynamique et de Séismologie 15; Centre Européen de Géodynamique et de Séismologie: Luxembourg, 1998; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Reicherter, K.; Michetti, A.M.; Barroso, P.S. Palaeoseismology: Historical and prehistorical records of earthquake ground effects for seismic hazard assessment. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2009, 316, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.L.; Mavroulis, S.D. Earthquake environmental effects and ESI 2007 seismic intensities of the early 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, western Greece) earthquakes (January 26 and February 3, Mw 6.0). Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 1517–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, G.; Valkaniotis, S.; Ganas, A. Evaluation of the macroseismic intensities triggered by the January/February 2014 Cephalonia, (Greece) earthquakes based on ESI-07 scale and their comparison to 1867 historical event. Quat. Int. 2017, 451, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaperdas, V. Catalogue of Historical Earthquakes and Macroseismic Intensities Database of Greece in 18th Century. Master’s Thesis, National Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2016; 153p. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulos, G. Die Seismizitat der Insel Leukas. Gerlands Beitr. Stur Geophys. 1950, 62, 27–38. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Papathanassiou, G.; Valkaniotis, S.; Ganas, A.; Grendas, N.; Kollia, E. The November 17th, 2015 Lefkada (Greece) strike-slip earthquake: Field mapping of generated failures and assessment of macroseismic intensity ESI-07. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidou-Firtinidou, D.; Kassaras, I.; Tonna, S.; Ganas, A.; Vintzileou, E.; Chesi, C. Τhe November 2015 Mw6. In 4 earthquake effects in Lefkas Island. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Natural Hazards Infrastructure, Chania, Greece, 18–21 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kassaras, I.; Kazantzidou-Firtinidou, D.; Ganas, A.; Tonna, S.; Pomonis, A.; Karakostas, C.; Papadatou-Giannopoulou, C.; Psarris, D.; Lekkas, E.; Makropoulos, K. On the Lefkas (Ionian Sea) November 17, 2015 Mw= 6.5 Earthquake Macroseismic Effects. J. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 24, 1913–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Carydis, P.; Alexoudi, V. The 17 November 2015 Mw 6.4 Lefkas (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) Earthquake: Impact on Environment and Buildings. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 2109–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Stanota, E.S.; Lekkas, E. Evaluation of environmental seismic intensities of all known historical and recent earthquakes felt in Zakynthos Island, Greece using the Environmental Seismic Intensity (ESI 2007) scale. Quat. Int. 2019, 532, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleytheriou, A.; Monopolis, D. Macroseismic Observations of the May 1975 Earthquakes of Corfu Island; Institute of Geological Mineral Research: Athens, Greece, 1975. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Critikos, N. L’ile de Leucade et sismes du 23 et du 27 Novembre 1914. Annales de l’observatoire d’ Athenes 1916, 7, 62–81. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulis, S.; Alexoudi, V.; Grambas, A.; Lekkas, E.; Carydis, P. The January-February 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) earthquake sequence: Damage pattern on buildings. In Proceedings of the 16th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Santiago, Chile, 9–13 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schenková, Z.; Kalogeras, I.; Schenk, V.; Pichl, R.; Kourouzidis, M.; Stavrakakis, G. Atlas of Isoseismal Maps of Selected Greek Earthquakes (1956-2003); Joint Publication of the Institute of Geodynamics of the National Observatory of Athens and the Institute of Rock Structure and Mechanics of the Czech Academy of Sciences: Athens, Greece, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianaki, K.; Kouskouna, V.; Rossetto, T. Intensity EMS-98 for early-mid 20th century damaging earthquakes in Greece. In Proceedings of the Vienna Congress on Recent Advances in Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, Vienna, Austria, 28–30 August 2013; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Shebalin, N.V.; Kárnik, V.; Hadjievski, D. Atlas of Isoseismals. Part III. UNDP/UNESCO; Survey of the Seismicity of the Balkan Region: Skopje, Republic of Macedonia, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Sakkas, G.; Kouskouna, V.; Makropoulos, K. Seismic hazard analysis in the Ionian Islands using macroseismic intensities. Hell. J. Geosci. 2010, 45, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Pitilakis, K.; Riga, E.; Roumelioti, Z. The urgent need for an improvement of the Greek seismic code based on a new seismic hazard map for Europe and a new site classification system. In A. Anagnostopoulos, 50 Years of Service at the National Technical University of Athens; Kavvadas, M., Ed.; National Technical University of Athens: Athens, Greece, 2016; pp. 437–461. [Google Scholar]
- Κaviris, G.; Zymvragakis, A.; Bonatis, P.; Sakkas, G.; Kouskouna, V.; Voulgaris, N. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment for the Broader Messinia (SW Greece) Region. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2022, 179, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khose, V.N.; Singh, Y.; Lang, D.H. A comparative study of design base shear for RC buildings in selected seismic design codes. Earthq. Spectra 2012, 28, 1047–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).