A Hyperelastic Bounding Surface Plasticity Model for Unsaturated Granular Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Development
2.1. Effective Stress Definition
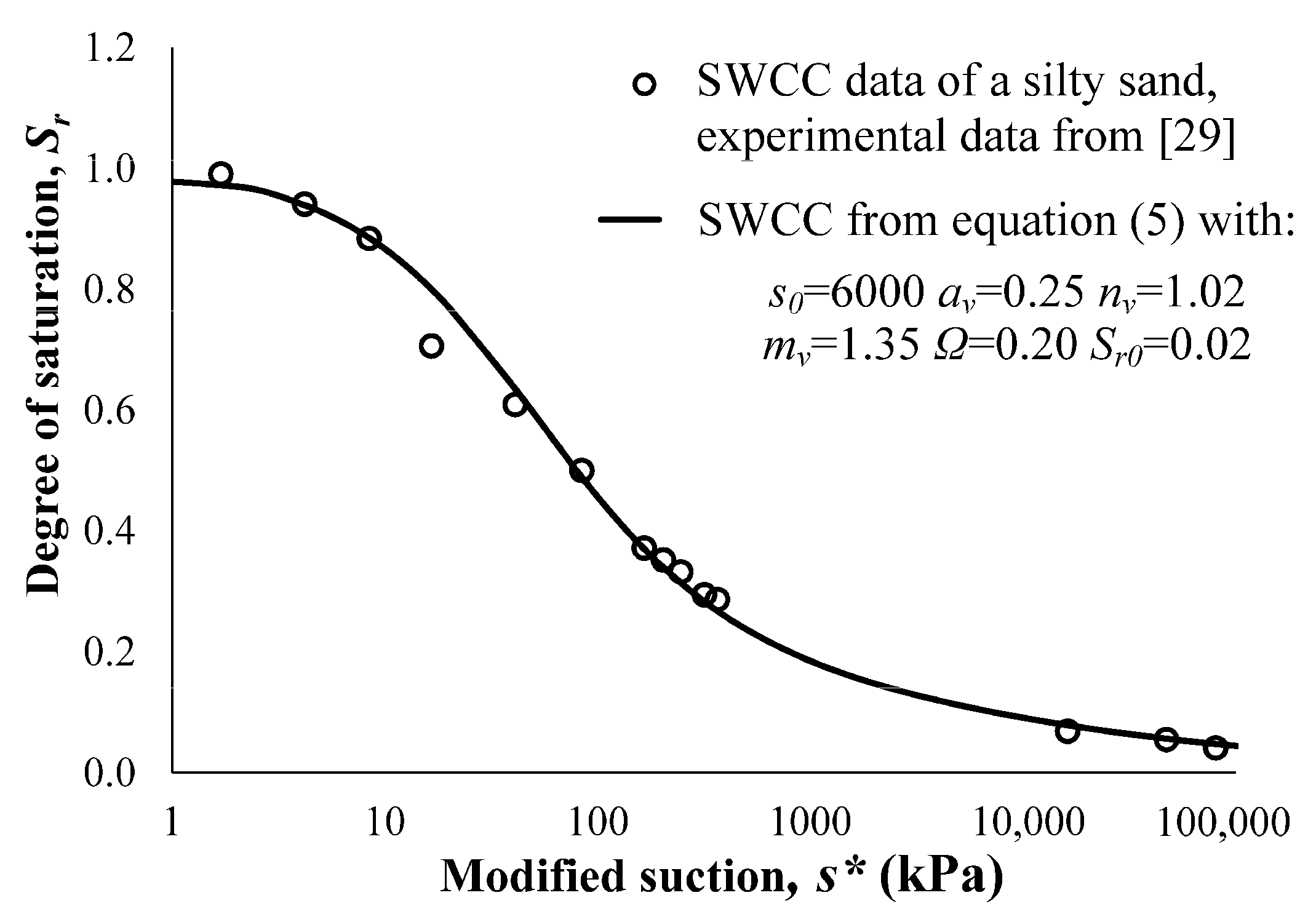
2.2. The Idealization of the Soil Water Characteristic Curve (SWCC)
2.3. Strain Decomposition
2.4. Definition of the Elastic Response
2.5. Definition of the Bounding Surface
2.6. Definition of the Dilatancy Surface
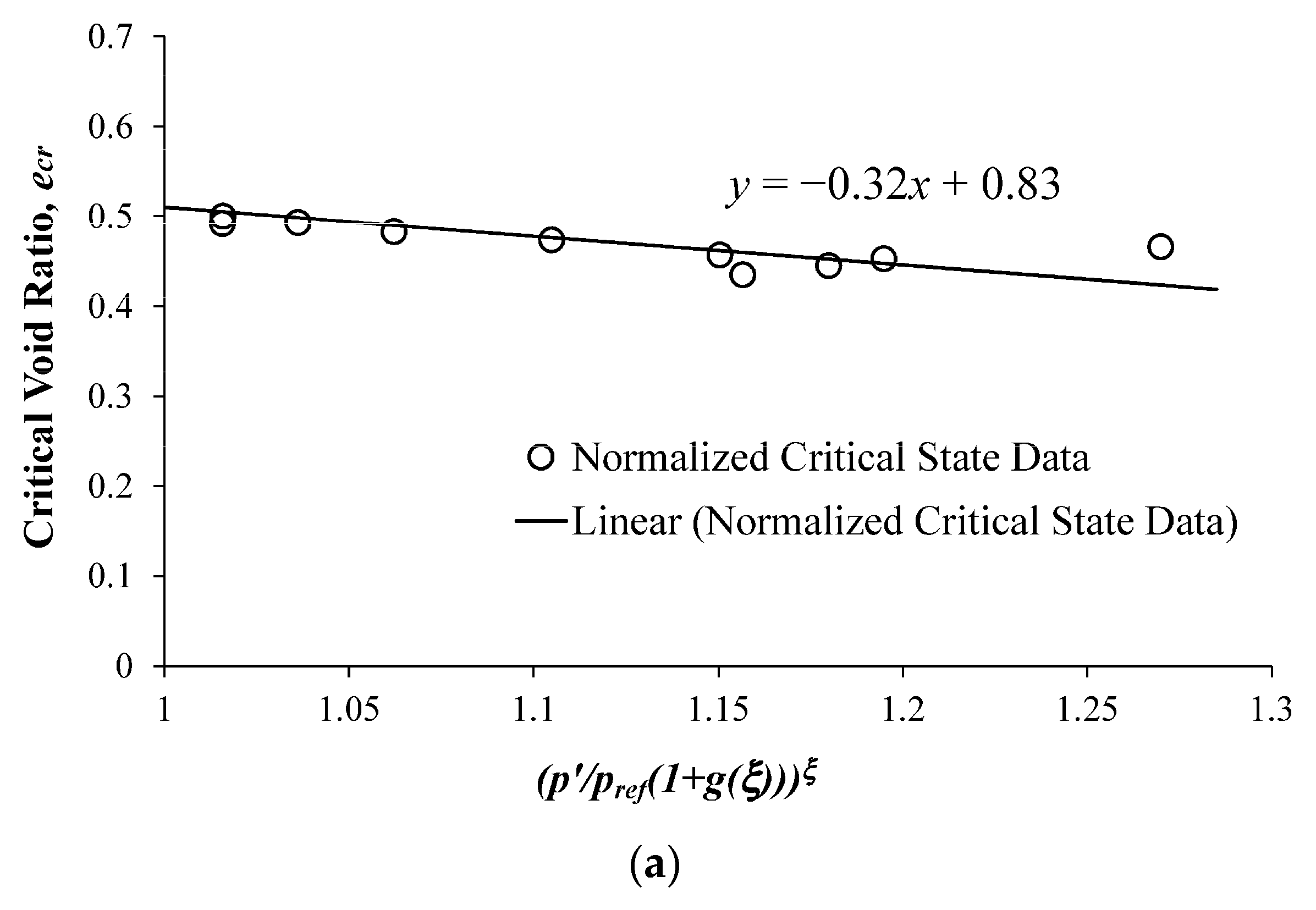
2.7. Definition of the Critical State Void Ratio
2.8. Definition of the Flow Rule, Hardening Rule, and Dilatancy Function
3. Determination of Model Parameters
3.1. Elastic Parameters
3.2. Critical State Related Parameters
3.3. Parameters Controlling State-Dependency
3.4. Dilatancy Parameter
3.5. Hardening Parameters
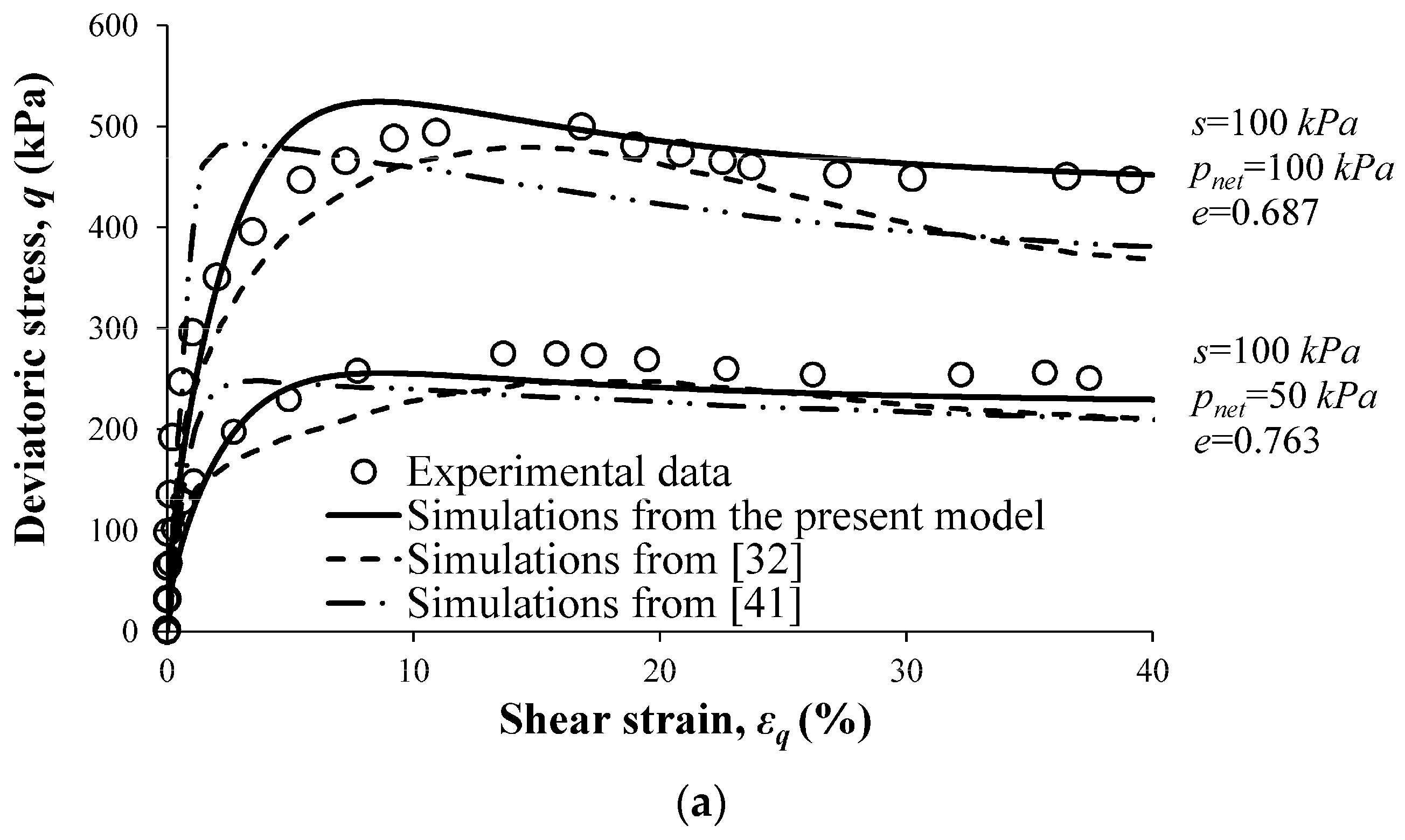
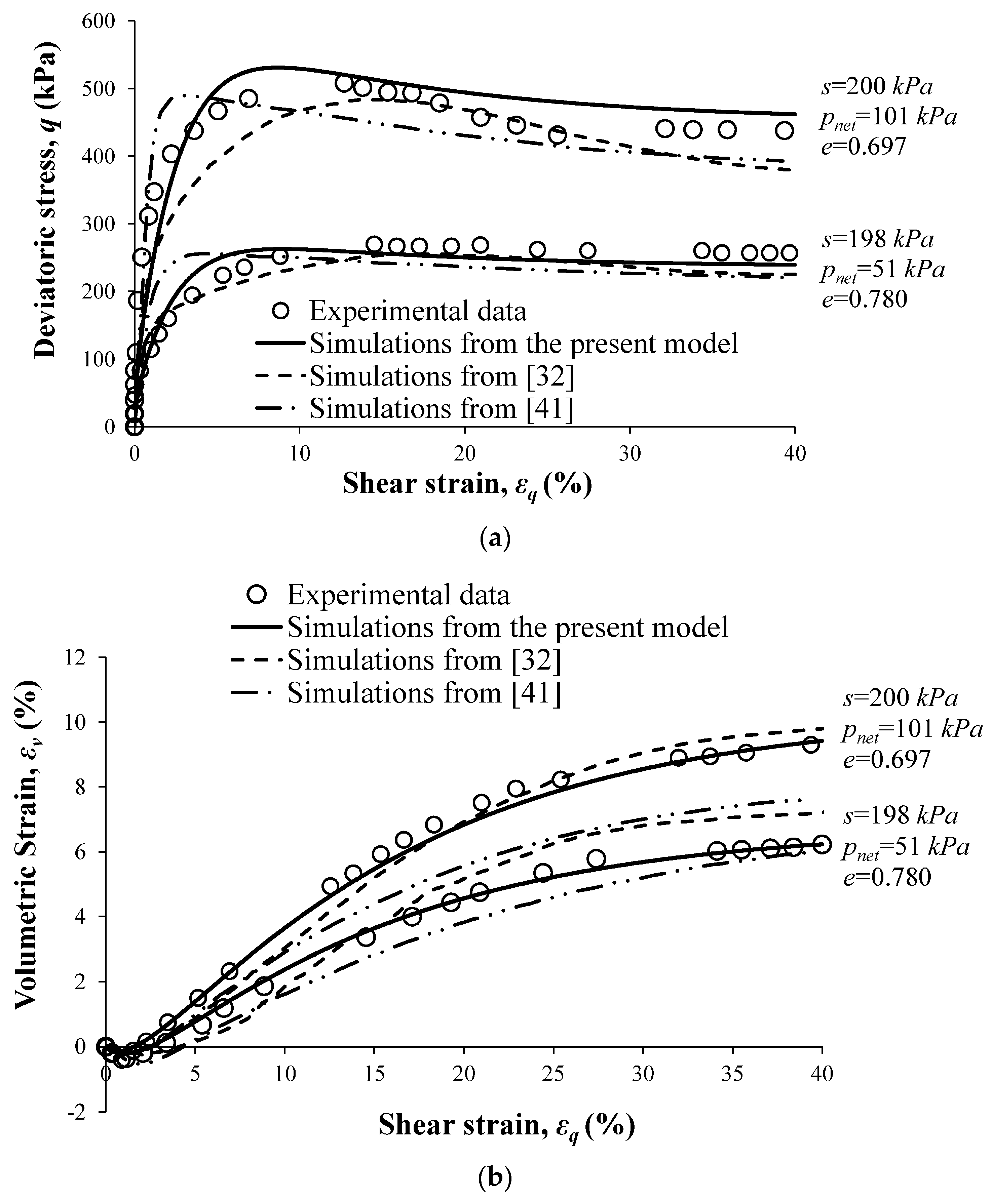
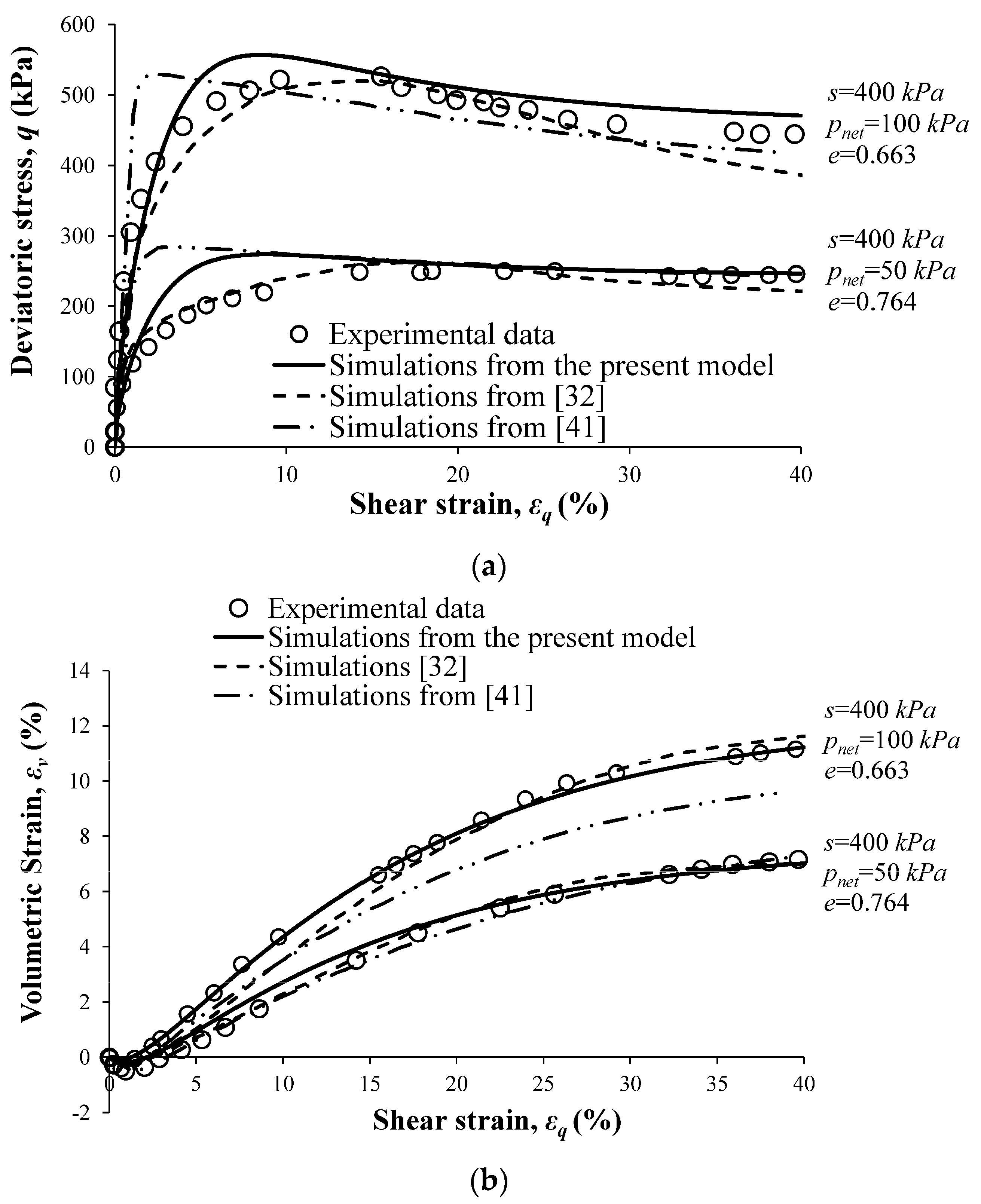
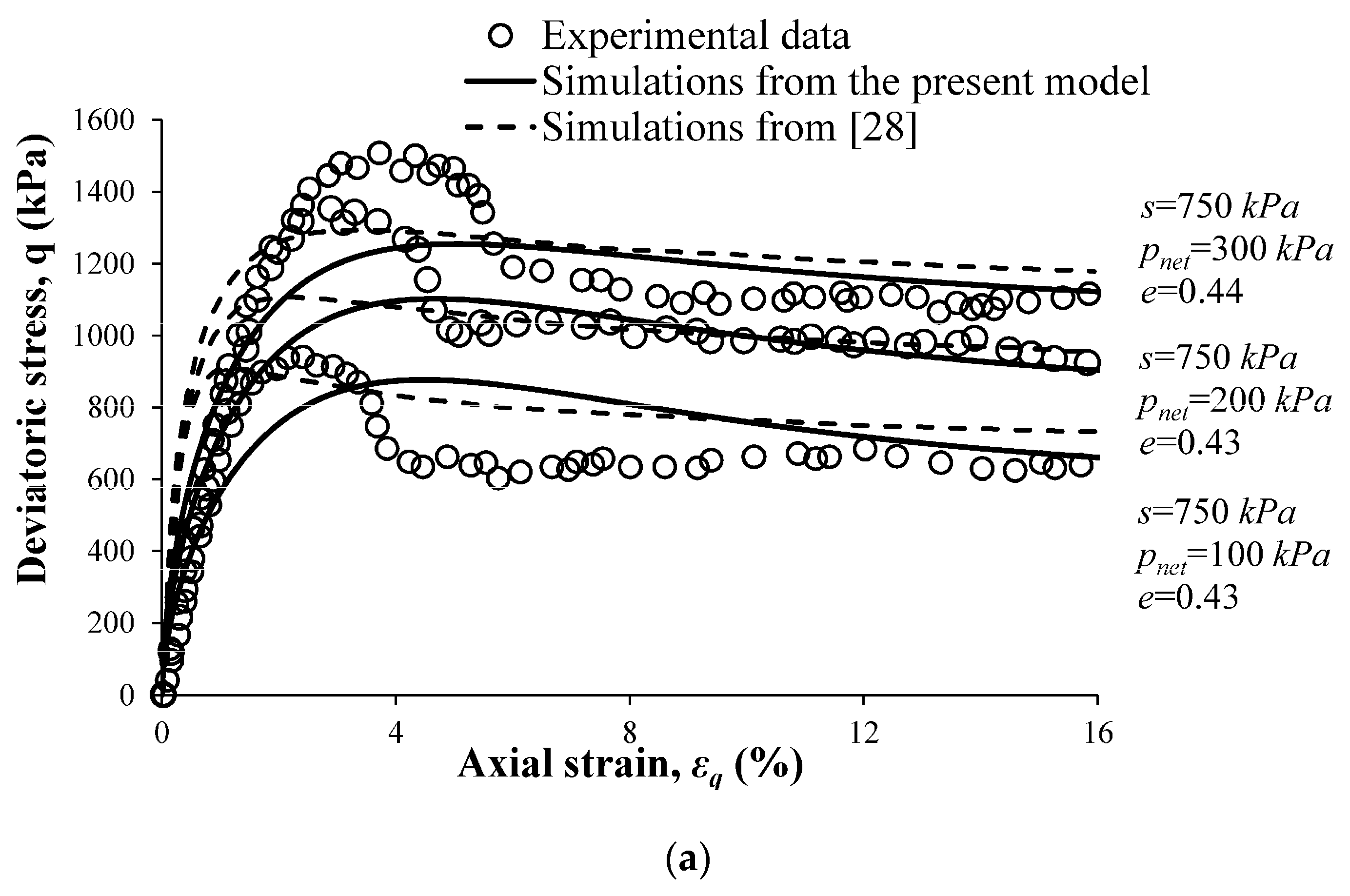
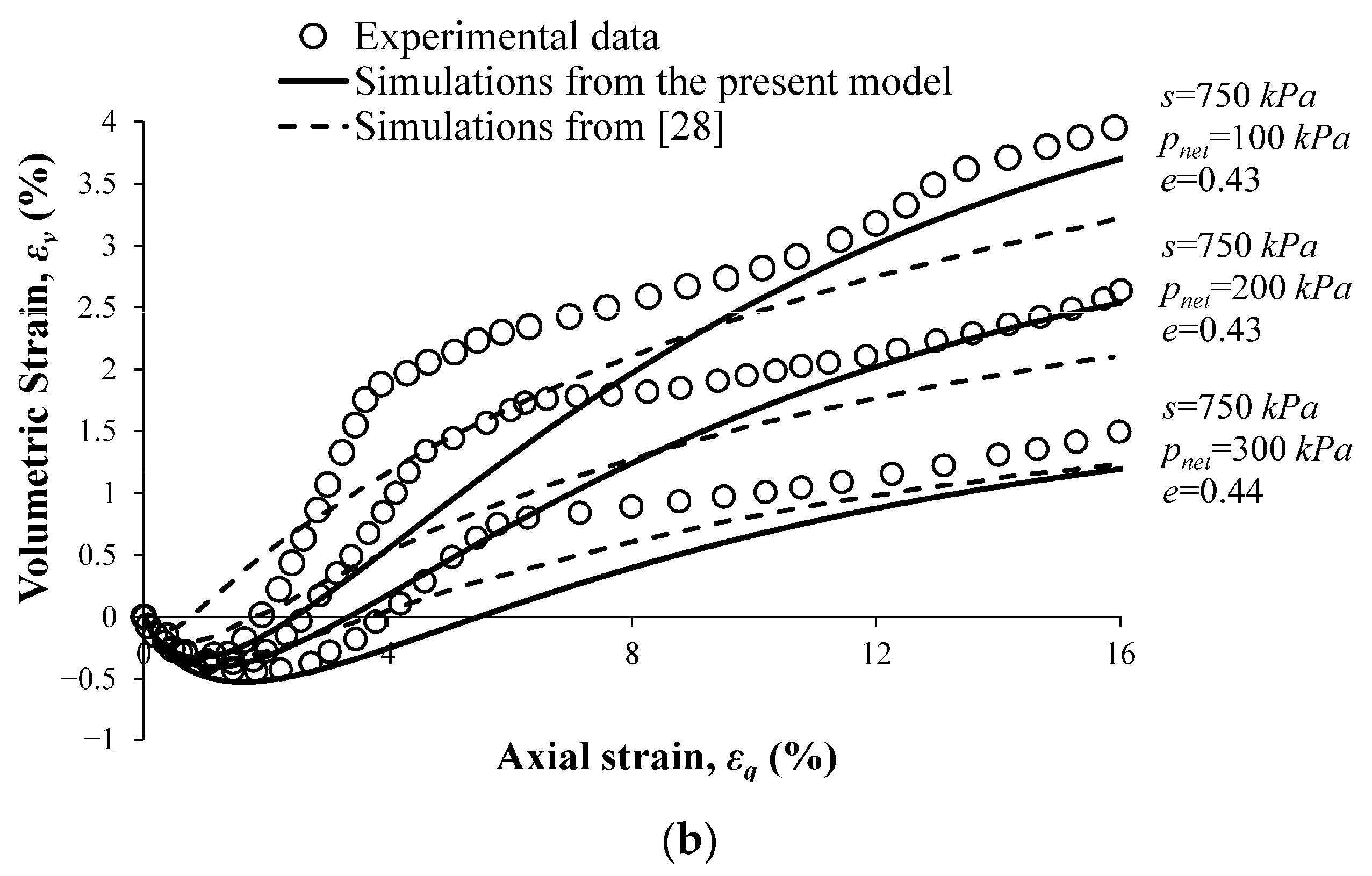
4. Assessment of Predictive Capabilities
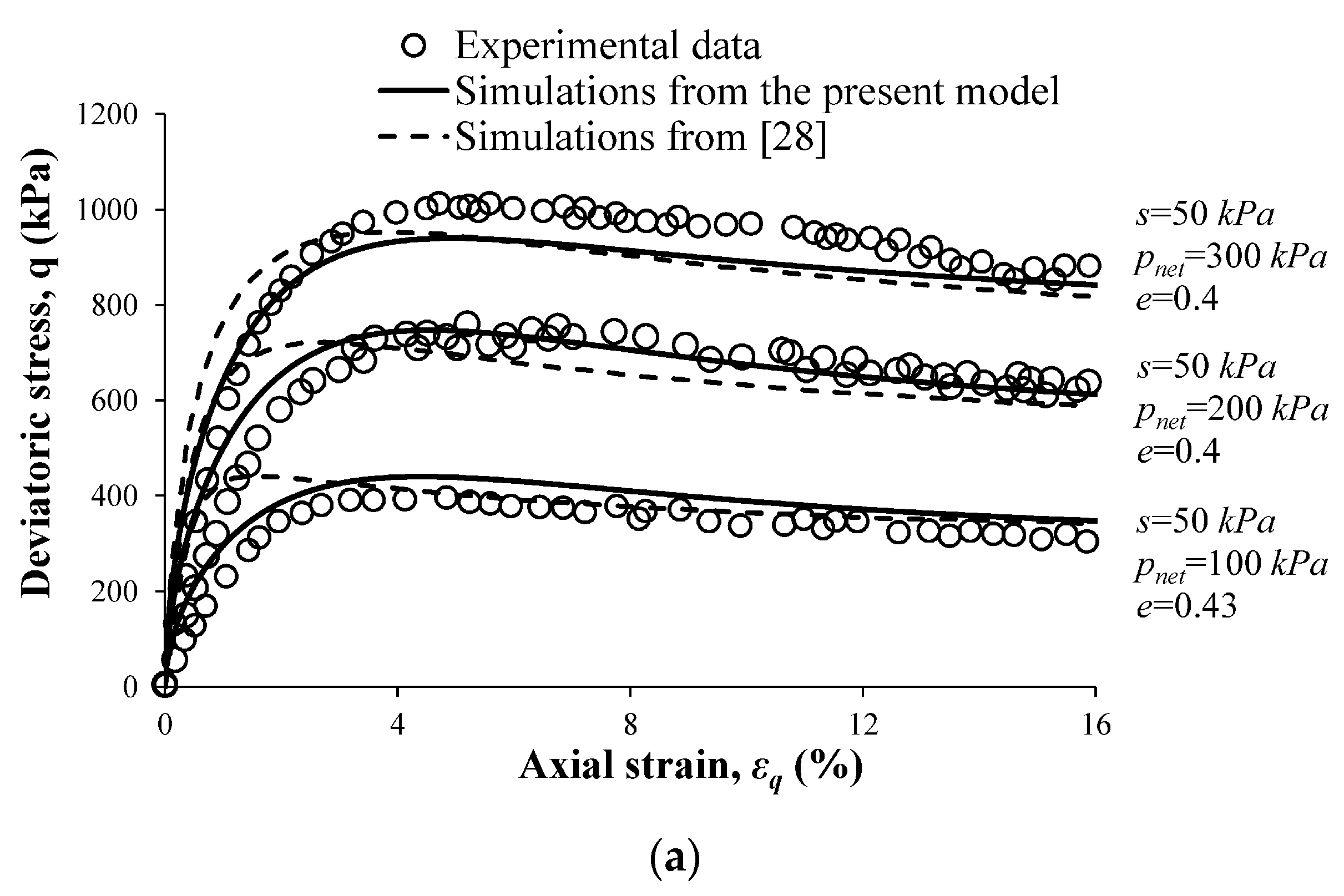
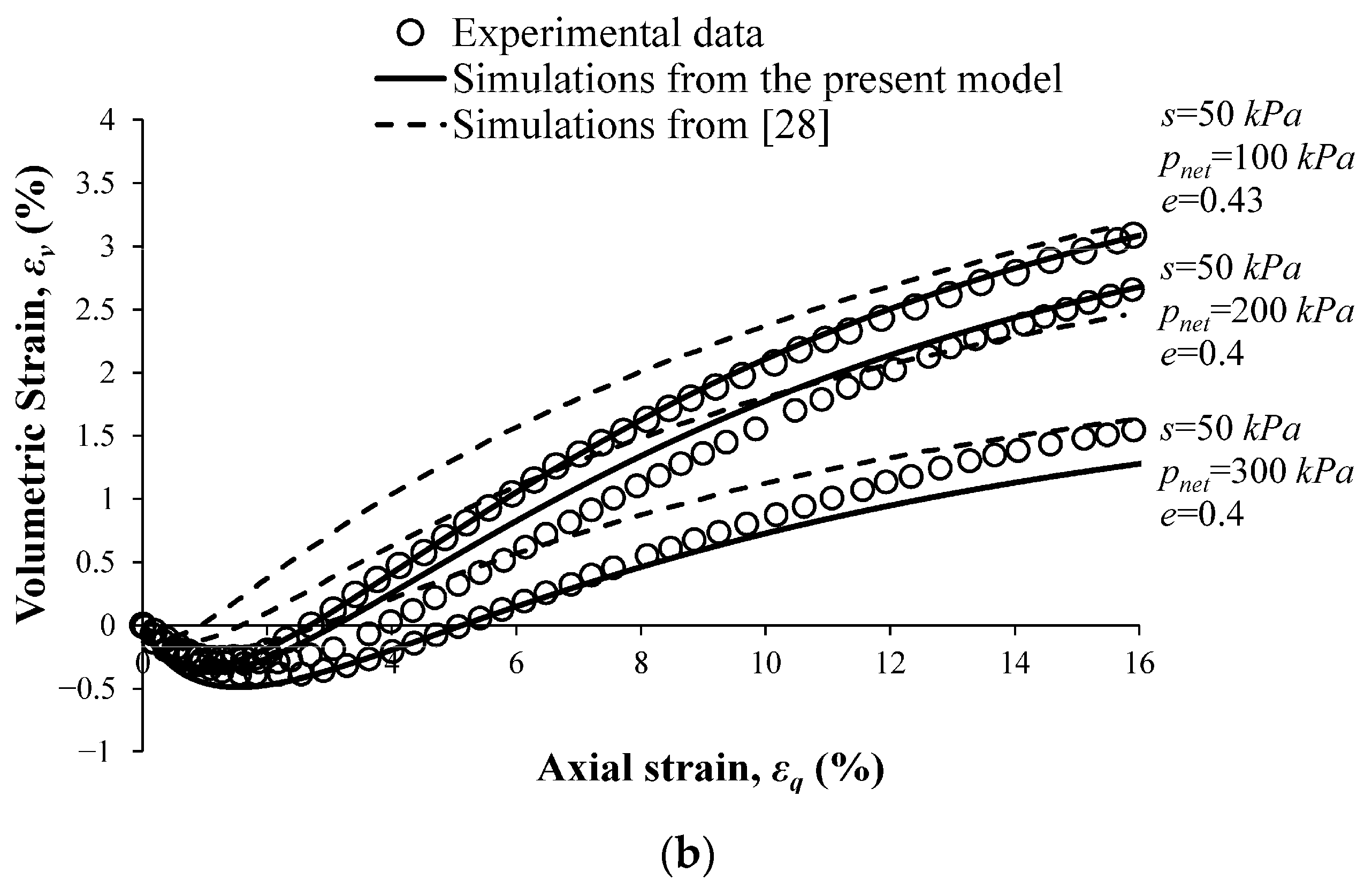
4.1. Simulation of the Behavior of Clean Sand
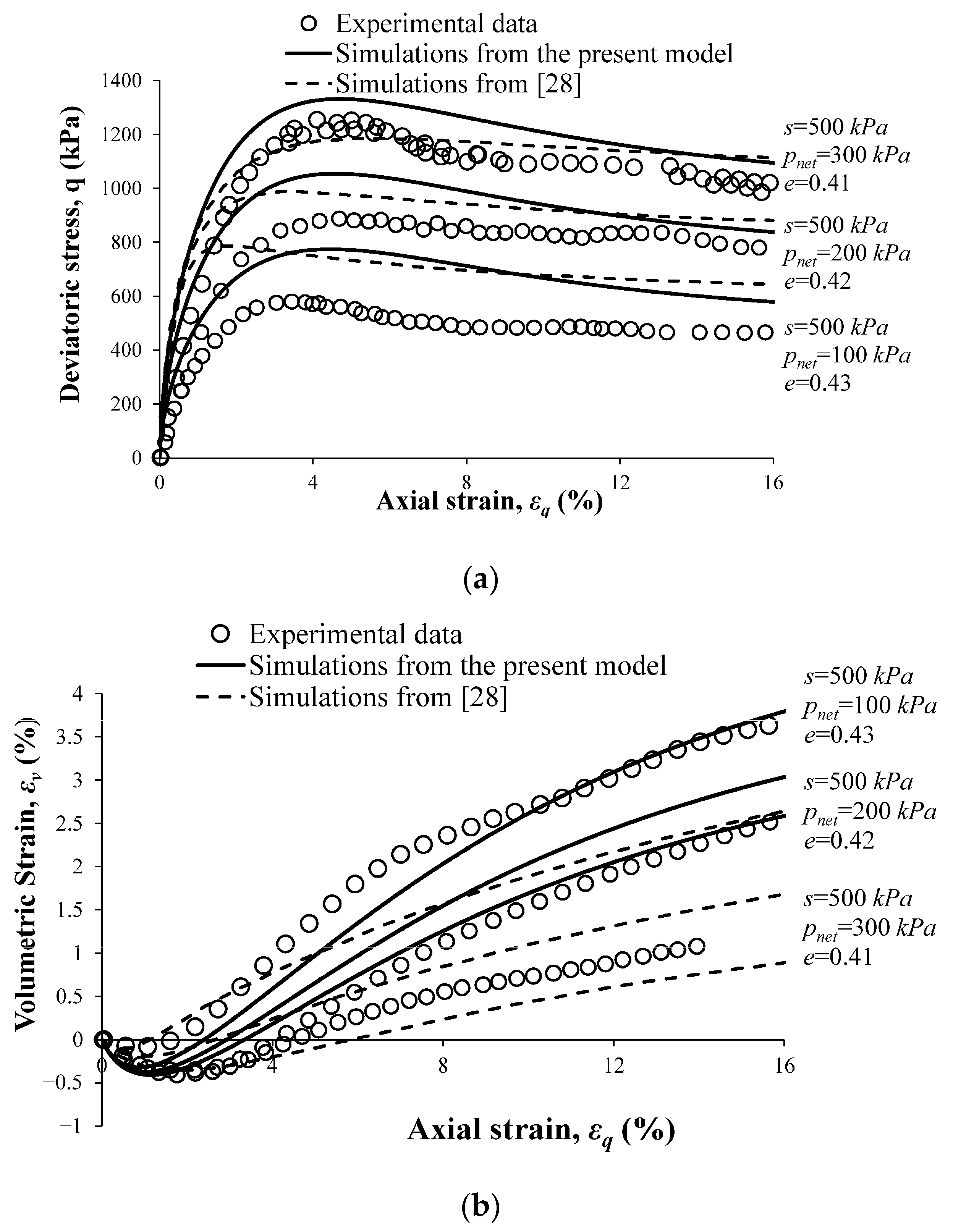
4.2. Simulation of the Behavior of a Silty Sand
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wray, W.K.; Meyer, K.T. Expansive Clay Soil—A Widespread and Costly GeoHazard. Geo-Strat.—Geo Inst. ASCE 2004, 5, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, E.E.; Gens, A.; Josa, A. A constitutive model for partially saturated soils. Géotechnique 1990, 40, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, K.H.; Burland, J. On the Generalized Stress-Strain Behavior of Wet Clay; Heyman, J., Leckie, F., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1968; pp. 535–609. [Google Scholar]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Widger, R.A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1978, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Morgenstern, N.R. Stress state variables for unsaturated soils. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. 1977, 103, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.J.; Sivakumar, V. An elasto-plastic critical state framework for unsaturated soil. Géotechnique 1995, 45, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Fredlund, D.G.; Gens, A. A new modelling approach for unsaturated soils using independent stress variables. Can. Geotech. J. 2008, 45, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.J.; Delage, P. Yielding and plastic behaviour of an unsaturated compacted silt. Géotechnique 1996, 46, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.R.; He, Y. Analysis of coupled heat moisture and air transfer in a deformable unsaturated soil. Géotechnique 1994, 44, 667–689. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, C.F.; Ng, C.W.W. A state-dependent elasto-plastic model for saturated and unsaturated soils. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 809–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gens, A.; Sánchez, M.; Sheng, D. On constitutive modelling of unsaturated soils. Acta Geotech. 2006, 1, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuth, M.; Laloui, L. Effective stress concept in unsaturated soils: Clarification and validation of a unified framework. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2008, 32, 771–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D. Review of fundamental principles in modelling unsaturated soil behaviour. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlsby, G.T. The work input to an unsaturated granular material. Géotechnique 1997, 47, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.W. The principle of effective stress. Tec. Ukebl. 1959, 39, 859–863. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, D.; Sloan, S.W.; Gens, A. A constitutive model for unsaturated soils: Thermomechanical and computational aspects. Comput. Mech. 2004, 33, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.a.; Sheng, D.; Sloan, S.W. Elastoplastic modelling of hydraulic and stress–strain behaviour of unsaturated soils. Mech. Mater. 2007, 39, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.A.; Sheng, D.C.; Cui, H.B.; Sloan, S.W. A density-dependent elastoplastic hydro-mechanical model for unsaturated compacted soils. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2007, 31, 1257–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loret, B.; Khalili, N. An effective stress elastic–plastic model for unsaturated porous media. Mech. Mater. 2002, 34, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.; Wong, H.; Dubujet, P.; Dangla, P. Adaptation of existing behaviour models to unsaturated states: Application to CJS model. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2005, 29, 1127–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzon, G.; Schrefler, B.A.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. Elastoplastic soil constitutive laws generalized to partially saturated states. Géotechnique 1996, 46, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ng, C.W.W.; Chen, R. A bounding surface plasticity model for unsaturated soil at small strains. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2015, 39, 1141–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Liu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Gallipoli, D. A constitutive model for unsaturated soils with consideration of inter-particle bonding. Comput. Geotech. 2014, 59, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanal, D.; Pastor, M.; Merodo, J.A.F. Generalized plasticity state parameter-based model for saturated and unsaturated soils. Part II: Unsaturated soil modeling. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2011, 35, 1899–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašín, D.; Khalili, N. Swelling phenomena and effective stress in compacted expansive clays. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 53, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.J.; Sharma, R.S.; Buisson, M.S.R. Coupling of hydraulic hysteresis and stress–strain behaviour in unsaturated soils. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.; Pouyan, H. A kinematic hardening based model for unsaturated soils considering different hydraulic conditions. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2016, 40, 2271–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.D.; Hoyos, L.R.; Morvan, M.; Puppala, A.J. Bounding surface-based modeling of compacted silty sand exhibiting suction dependent postpeak strain softening. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2018, 42, 1741–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.D.; Hoyos, L.R.; Puppala, A.J. Modeling Essential Elastoplastic Features of Compacted Silty Sand via Suction-Controlled Triaxial Testing. Int. J. Geomech. 2016, 16, D4016012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, M.; Manahiloh, K.N.; Kaliakin, V.N. A Bounding Surface Based Constitutive Model for Unsaturated Granular Soils. In Proceedings of the Geo-Congress 2019, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 24–27 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Santagiuliana, R.; Schrefler, B.A. Enhancing the Bolzon–Schrefler–Zienkiewicz Constitutive Model for Partially Saturated Soil. Transp. Porous Media 2006, 65, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.R.; Khalili, N. A unified bounding surface plasticity model for unsaturated soils. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2006, 30, 181–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, R.D. A Practical Two Surface Plasticity Theory. J. Appl. Mech. 1975, 42, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafalias, Y.F.; Popov, E.P. Cyclic loading for materials with a vanishing elastic region. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1977, 41, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliakin, V.N.; Dafalias, Y.F. Simplifications to the bounding surface model for cohesive soils. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1989, 13, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardet, J.P. Bounding Surface Plasticity Model for Sands. J. Eng. Mech. 1986, 112, 1198–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzari, M.T.; Dafalias, Y.F. A critical state two-surface plasticity model for sands. Géotechnique 1997, 47, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Dafalias, Y.F. Dilatancy for cohesionless soils. Géotechnique 2000, 50, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafalias, Y.F.; Manzari, M.T. Simple Plasticity Sand Model Accounting for Fabric Change Effects. J. Eng. Mech. 2004, 130, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliakin, V.N.; Nieto-Leal, A.; Mashayekhi, M. Modeling the Time- and Temperature-Dependent Response of Cohesive Soils in a Generalized Bounding Surface Framework. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotechnol. 2018, 5, 250–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvan, M.; Wong, H.; Branque, D. An unsaturated soil model with minimal number of parameters based on bounding surface plasticity. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2010, 34, 1512–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkari, A.; Golchin, A. On the influence of elastic-plastic coupling on sands response. Comput. Geotech. 2014, 55, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkari, A.; Karimi, A.; Fakharian, K.; Kaviani-Hamedani, F. Prediction of Undrained Behavior of Isotropically and Anisotropically Consolidated Firoozkuh Sand: Instability and Flow Liquefaction. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04017083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Z. Calibration of an elastoplastic model of sand liquefaction using the swarm intelligence with a multi-objective function. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schefler, B. The Finite Element Method in Soil Consolidation (with Applications to Surface Subsidence). Doctoral Dissertation, University College of Swansea, Swansea, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Maatouk, A.; Leroueil, S.; Rochelle, P.L. Yielding and critical state of a collapsible unsaturated silty soil. Géotechnique 1995, 45, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Xing, A. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 1994, 31, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, D.; Bruno, A.W.; D’onza, F.; Mancuso, C. A bounding surface hysteretic water retention model for deformable soils. Géotechnique 2015, 65, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W.; Wu, D.T. A closed-form equation for effective stress in unsaturated soil. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 2009WR008646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.R. Some steady state solutions of the unsaturated moisture flow equation with application to evaporation from a water table. Soil Sci. Am. 1958, 85, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdine, N.T. Relative permeability calculations from pore size distribution data. Trans. AIME 1952, 198, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, W.B. Studies in the physical properties of soils. V. The hysteresis effect in capillary properties and the modes of moisture distribution associated therewith. J. Agric. Sci. 1930, 20, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulovassilis, A. Hysteresis of pore water, an application of the concept of independent domains. J. Soil Sci. 1962, 93, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Pang, Y.W. Experimental investigation of soil–water characteristics of a volcanic soil. Can. Geotech. J. 2000, 37, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Pang, Y.W. Influence of stress state on soil–water characteristics and slope stability. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2000, 26, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanapalli, S.K.; Fredlund, D.G.; Pufahl, D.E. The influence of soil structure and stress history on the soil-water characteristics of a compacted till. Géotechnique 1999, 49, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, E.; Vaunat, J. Retention curves of deformable clays. In International Workshop on Unsaturated Soils: Experimental Evidence and Theoretical Approaches in Unsaturated Soils; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, V.A. A Critical State Framework for Unsaturated Soil. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, S.J. Inclusion of specific water volume within an elasto-plastic model for unsaturated soil. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, D.; Wheeler, S.J.; Karstunen, M. Modelling the variation of degree of saturation in a deformable unsaturated soil. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lytton, R.L. Discussion of “A new modelling approach for unsaturated soils using independent stress variables”. Can. Geotech. J. 2008, 45, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Fredlund, D.G.; Gens, A. Reply to the discussion by Zhang and Lytton on ‘A new modelling approach for unsaturated soils using independent stress variables’. Can. Geotech. 2008, 45, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, I.F.; Houlsby, G.T. Application of thermomechanical principles to the modelling of geotechnical materials. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1997, 453, 1975–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, G.; Hueckel, T. Nonassociated and coupled flow rules of elastoplasticity for rock-like materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1979, 16, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchin, A.; Lashkari, A. A critical state sand model with elastic–plastic coupling. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 2807–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M.J.; Lashkari, A. Sand instability under constant shear drained stress path. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 150, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einav, I.; Puzrin, A.M. Pressure-Dependent Elasticity and Energy Conservation in Elastoplastic Models for Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Been, K.; Jefferies, M.G. A state parameter for sands. Géotechnique 1985, 35, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, B.O.; Richart, F.E. Elastic Wave Velocities in Granular Soils. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1963, 89, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Wang, Y. Linear Representation of Steady-State Line for Sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1998, 124, 1215–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkari, A.; Yaghtin, M.S. Sand flow liquefaction instability under shear–volume coupled strain paths. Géotechnique 2018, 68, 1002–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, D.; Gens, A.; Sharma, R.; Vaunat, J. An elasto-plastic model for unsaturated soil incorporating the effects of suction and degree of saturation on mechanical behaviour. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.R. On the Capillary Forces in an Ideal Soil; Correction of Formulae Given by W. B. Haines. J. Agric. Sci. 1926, 16, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkari, A.; Kadivar, M. A constitutive model for unsaturated soil–structure interfaces. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2016, 40, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

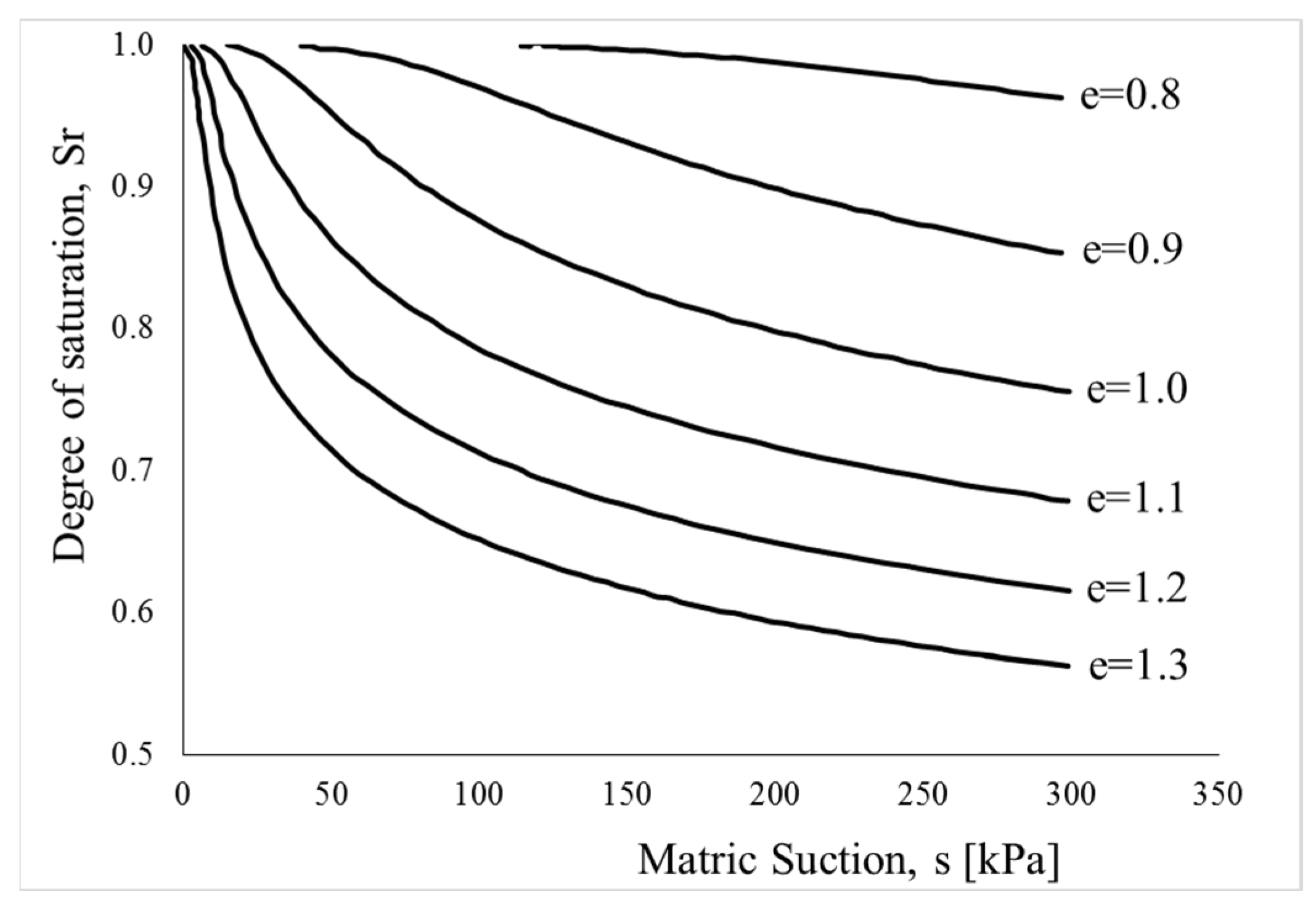

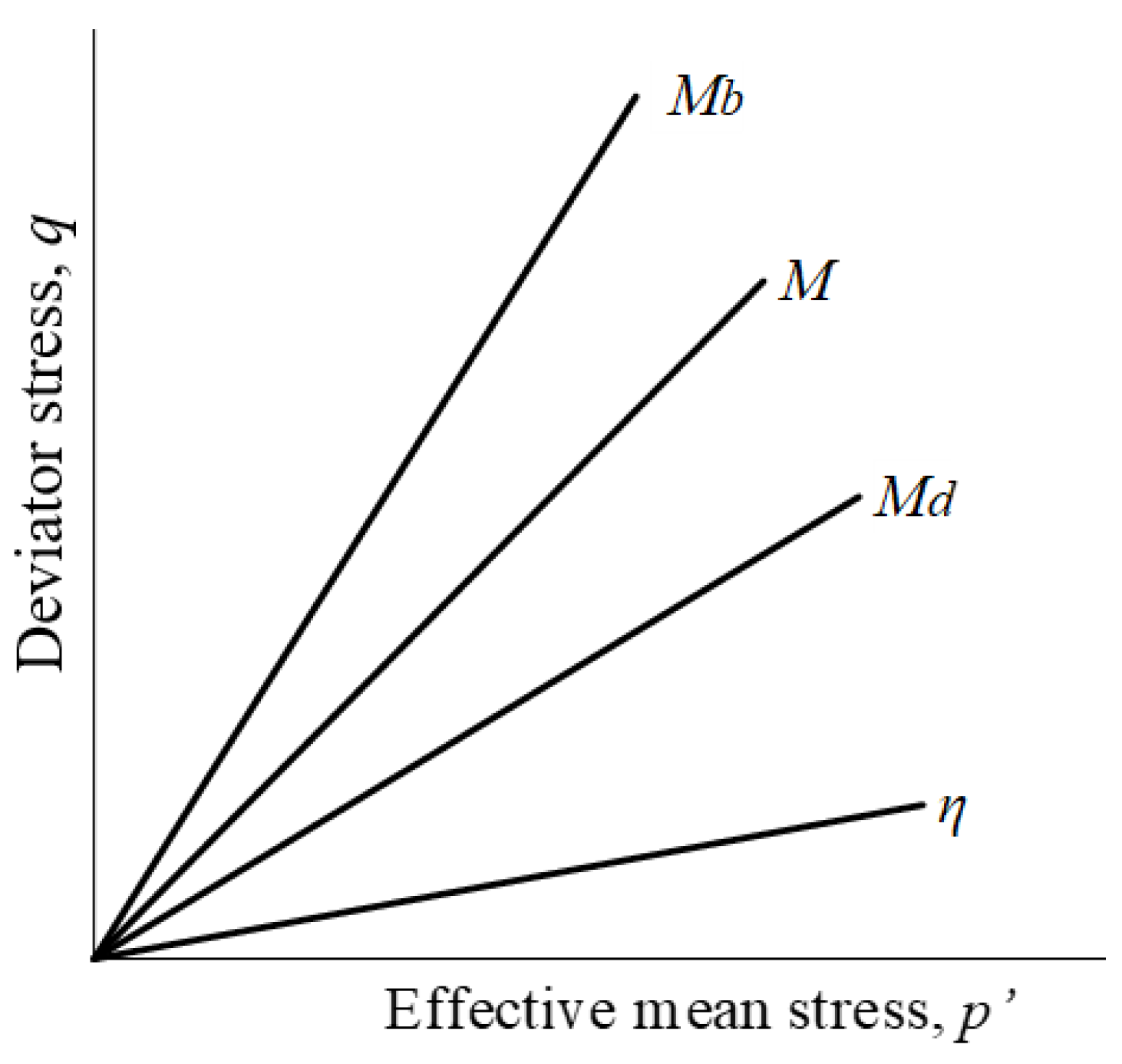

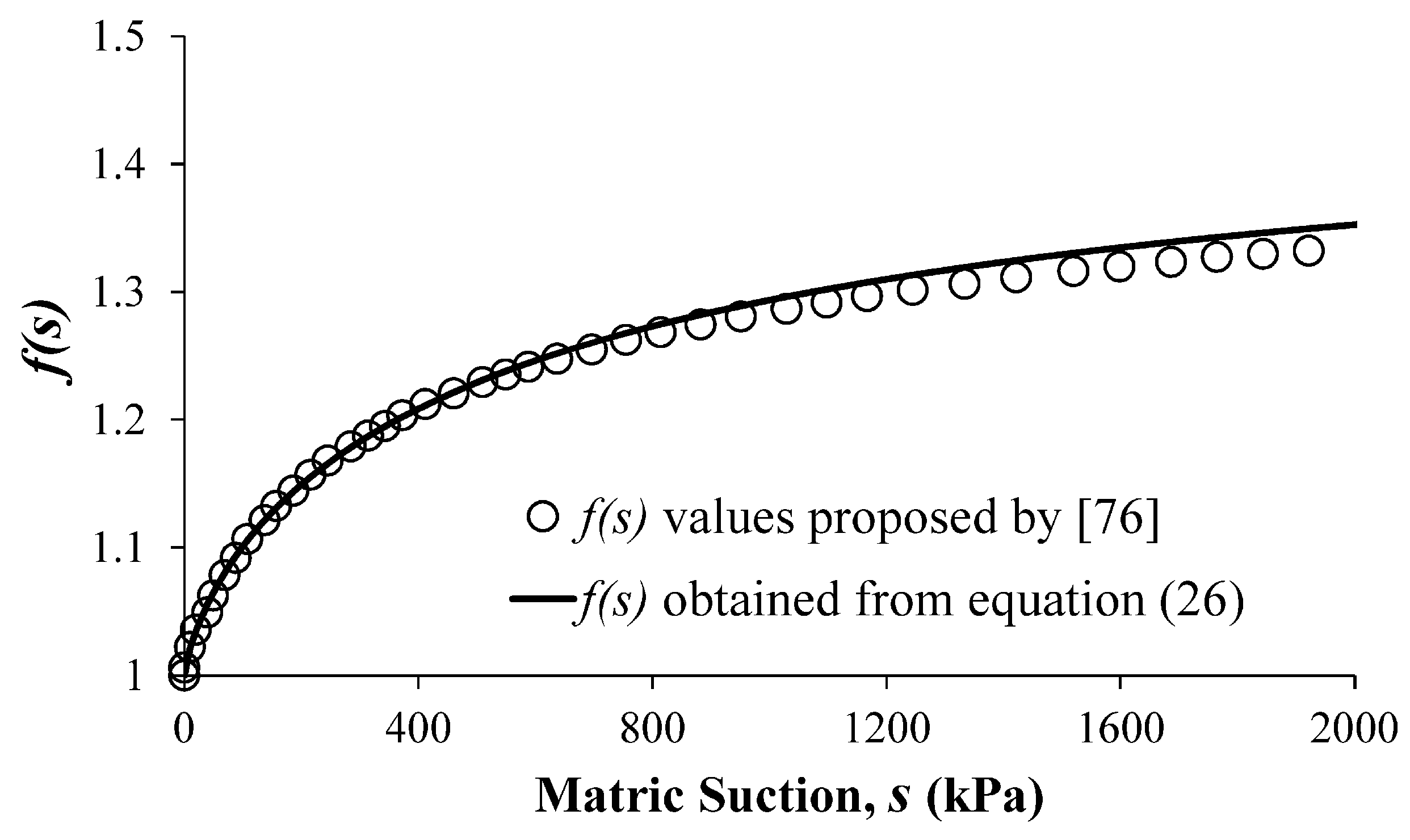
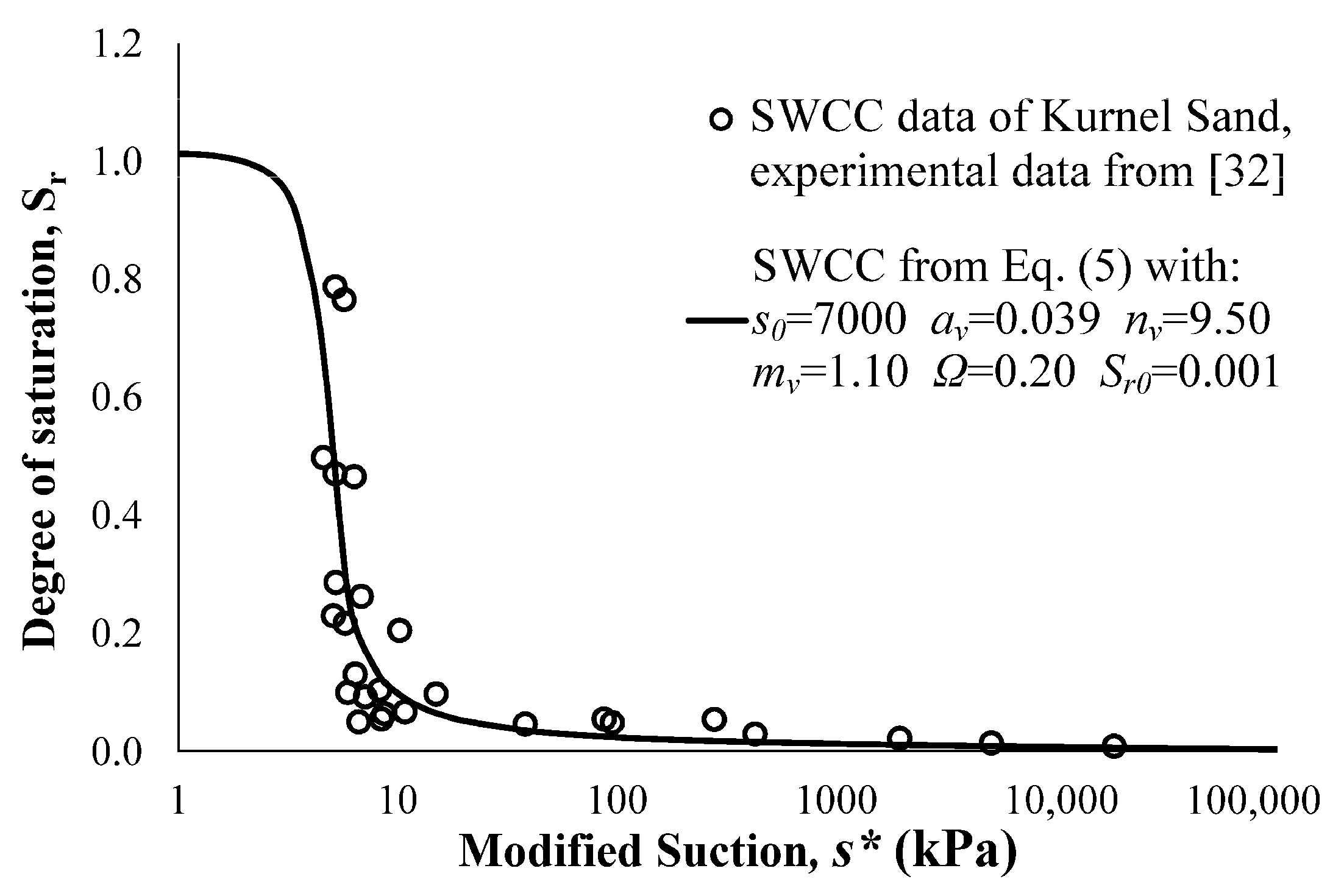





| Total strain rate | |||
| Elastic + Plastic | |||
| Reversible elastic + Coupled (Irreversible) elastic + Plastic | |||
| Reversible elastic + Coupled (Irreversible) | |||
| Parameter Category | Elastic | Critical State | State | Dilatancy | Hardening | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | K0 | G0 | e0 | λ | a | b | ζ | Mc | nb | nd | Ad | h0 | ch |
| Value | 250 | 200 | 1.422 | 0.508 | 0 | 0 | 0.07 | 1.77 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 0.35 | 95 | 0.1 |
| Parameter Category | Elastic | Critical State | State | Dilatancy | Hardening | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Symbol | K0 | G0 | e0 | λ | a | b | ζ | Mc | nb | nd | Ad | h0 | ch |
| Value | 250 | 200 | 0.83 | 0.32 | 0.57 | 1.73 | 1.18 | 1.33 | 4.4 | 0.75 | 0.6 | 105 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadivar, M.; Manahiloh, K.N.; Kaliakin, V.N. A Hyperelastic Bounding Surface Plasticity Model for Unsaturated Granular Soils. Geosciences 2024, 14, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14060148
Kadivar M, Manahiloh KN, Kaliakin VN. A Hyperelastic Bounding Surface Plasticity Model for Unsaturated Granular Soils. Geosciences. 2024; 14(6):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14060148
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadivar, Mehdi, Kalehiwot Nega Manahiloh, and Victor N. Kaliakin. 2024. "A Hyperelastic Bounding Surface Plasticity Model for Unsaturated Granular Soils" Geosciences 14, no. 6: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14060148
APA StyleKadivar, M., Manahiloh, K. N., & Kaliakin, V. N. (2024). A Hyperelastic Bounding Surface Plasticity Model for Unsaturated Granular Soils. Geosciences, 14(6), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14060148







