Elemental Geochemistry on Paleoenvironment Reconstruction: Proxies on Miocene-Pliocene of Marine to Fluvial Sediment in Serpong, Banten, Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
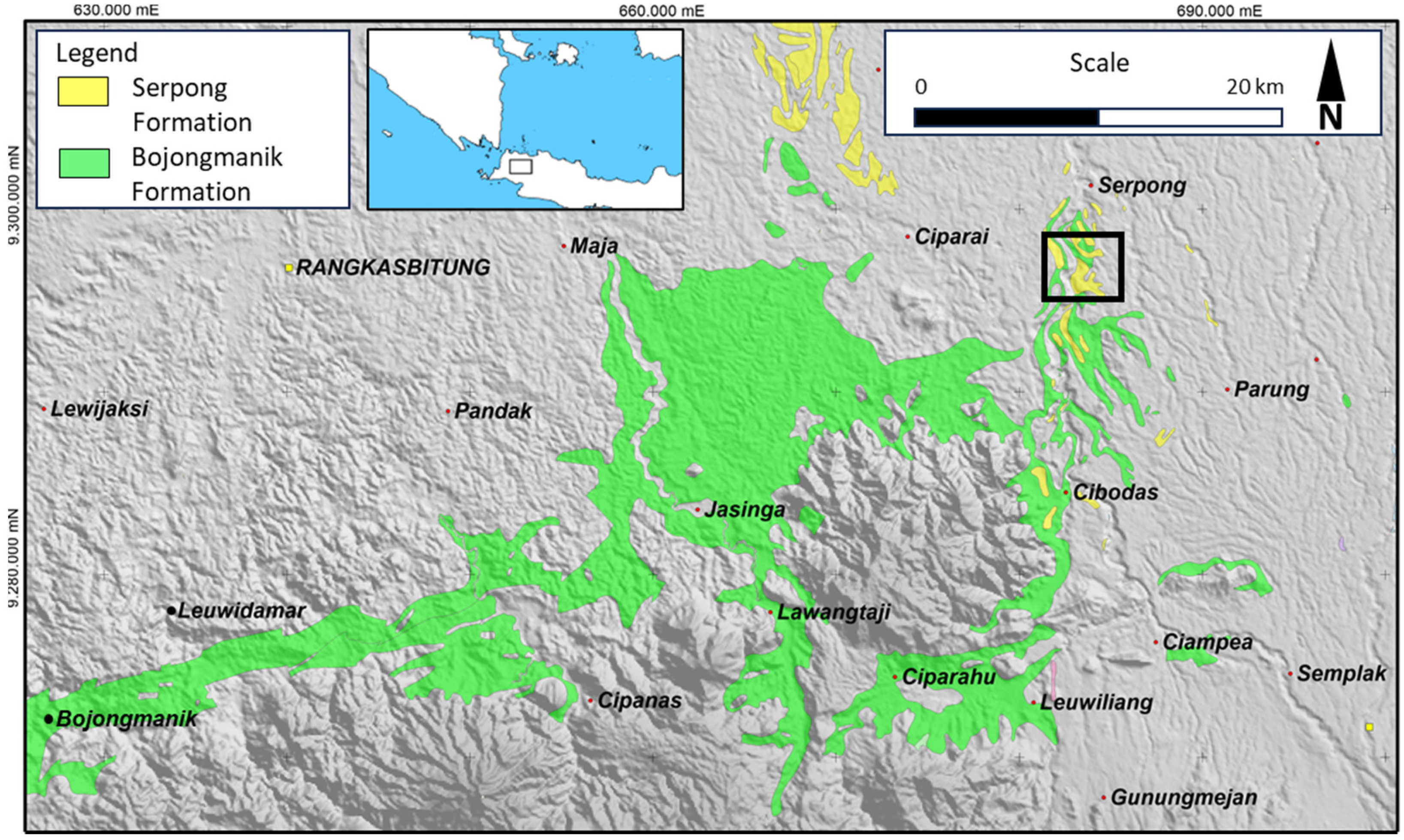
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
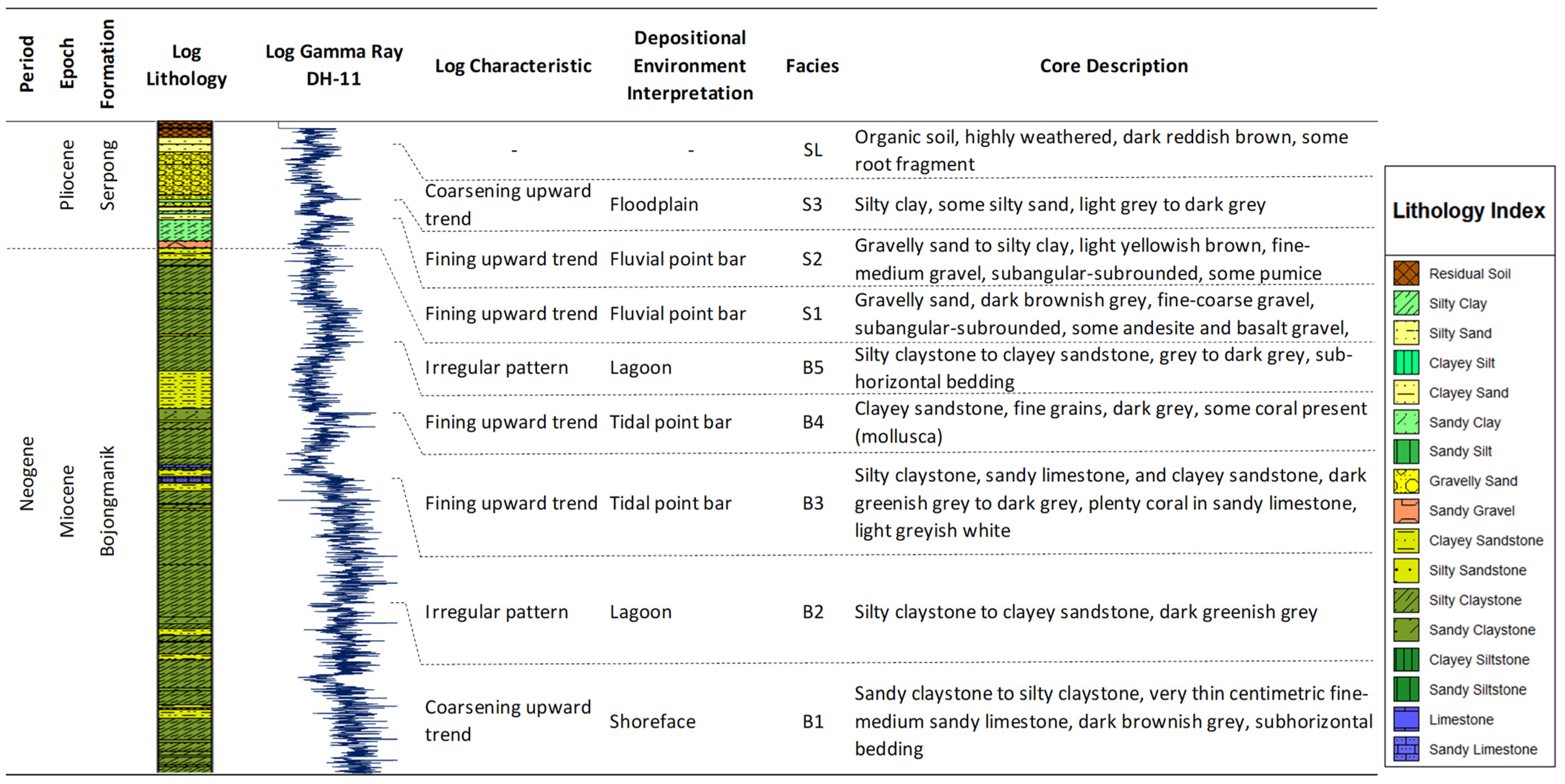
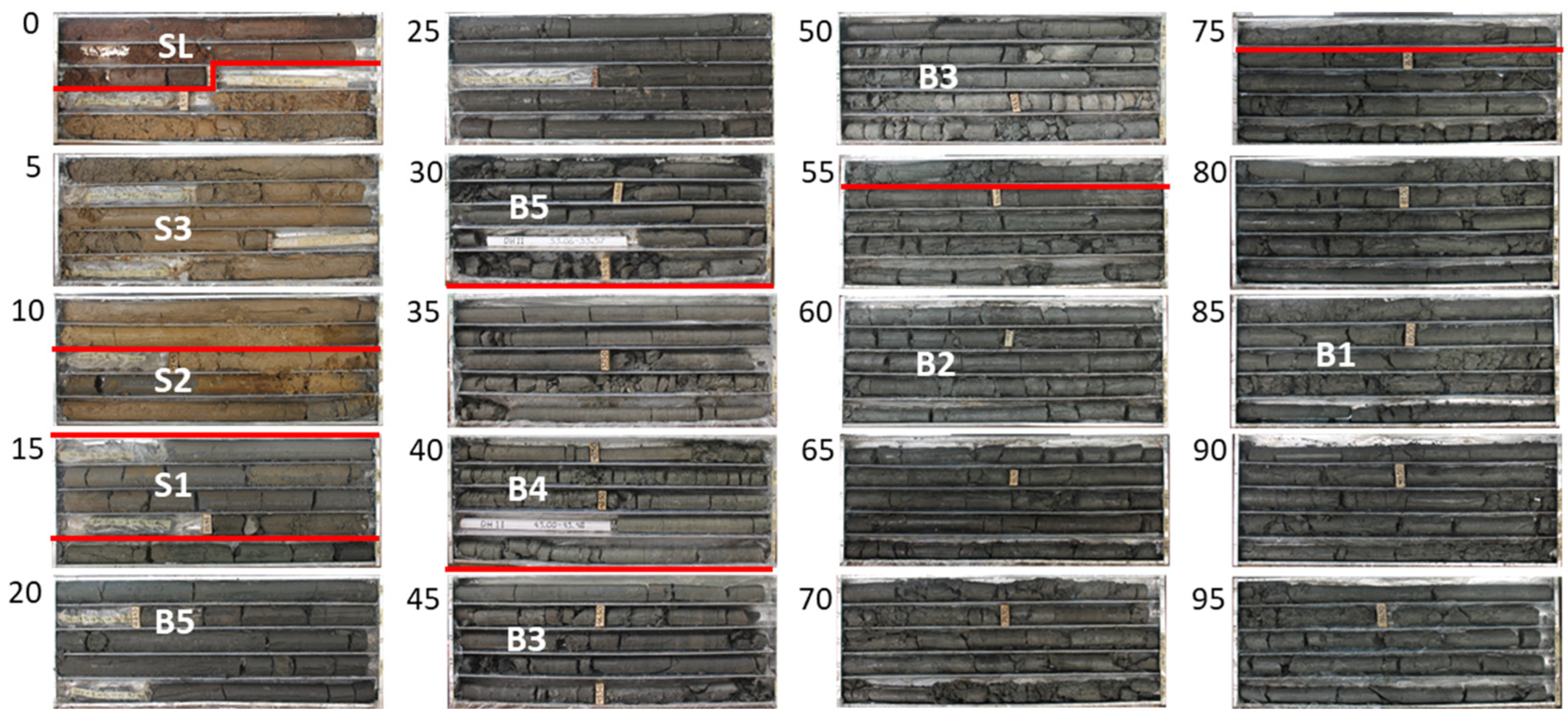
4.1. GR-Log Facies Analysis
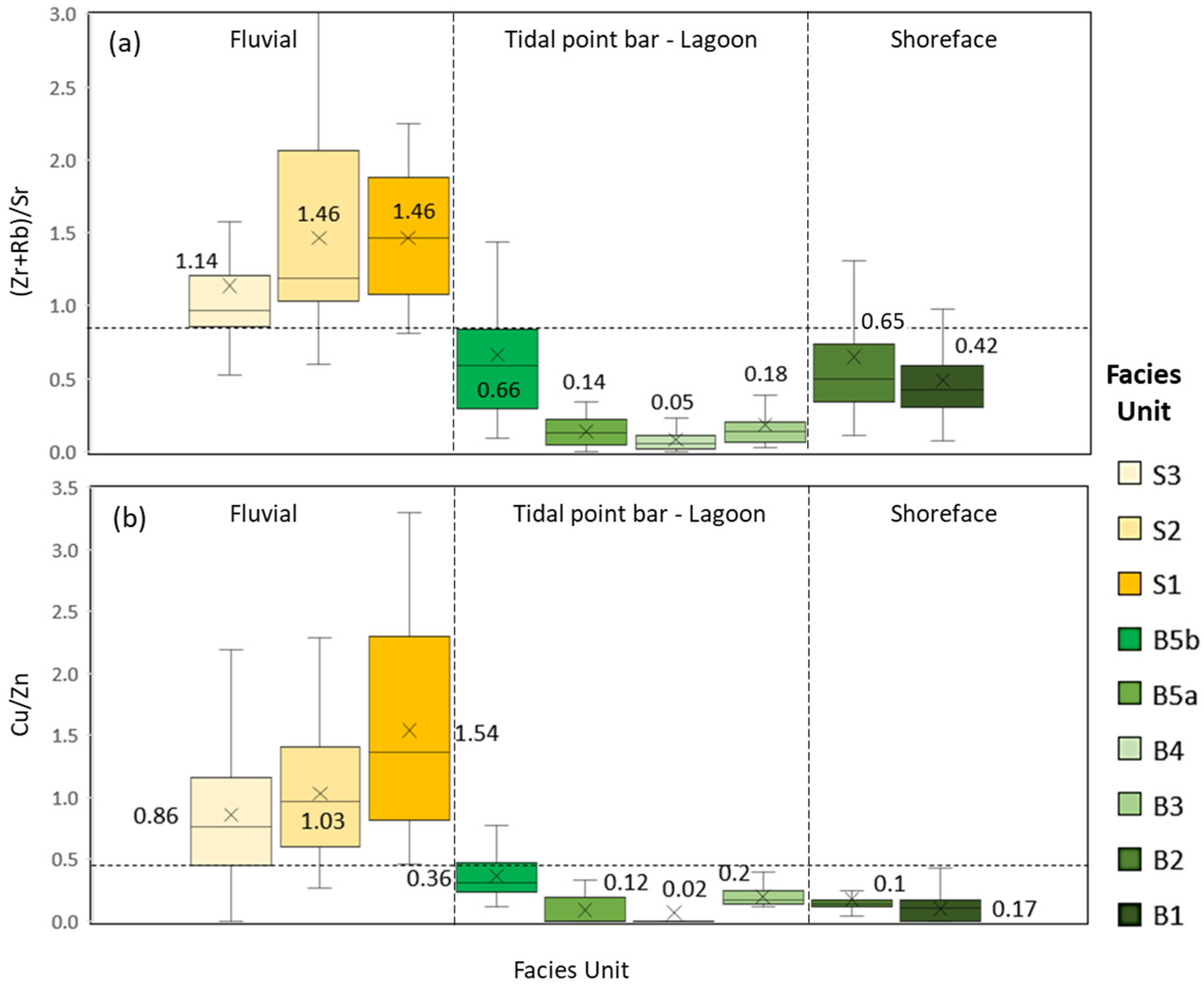
4.2. Geochemistry Paleoenvironment Analysis
4.2.1. Correlation of GR and Elemental Geochemistry
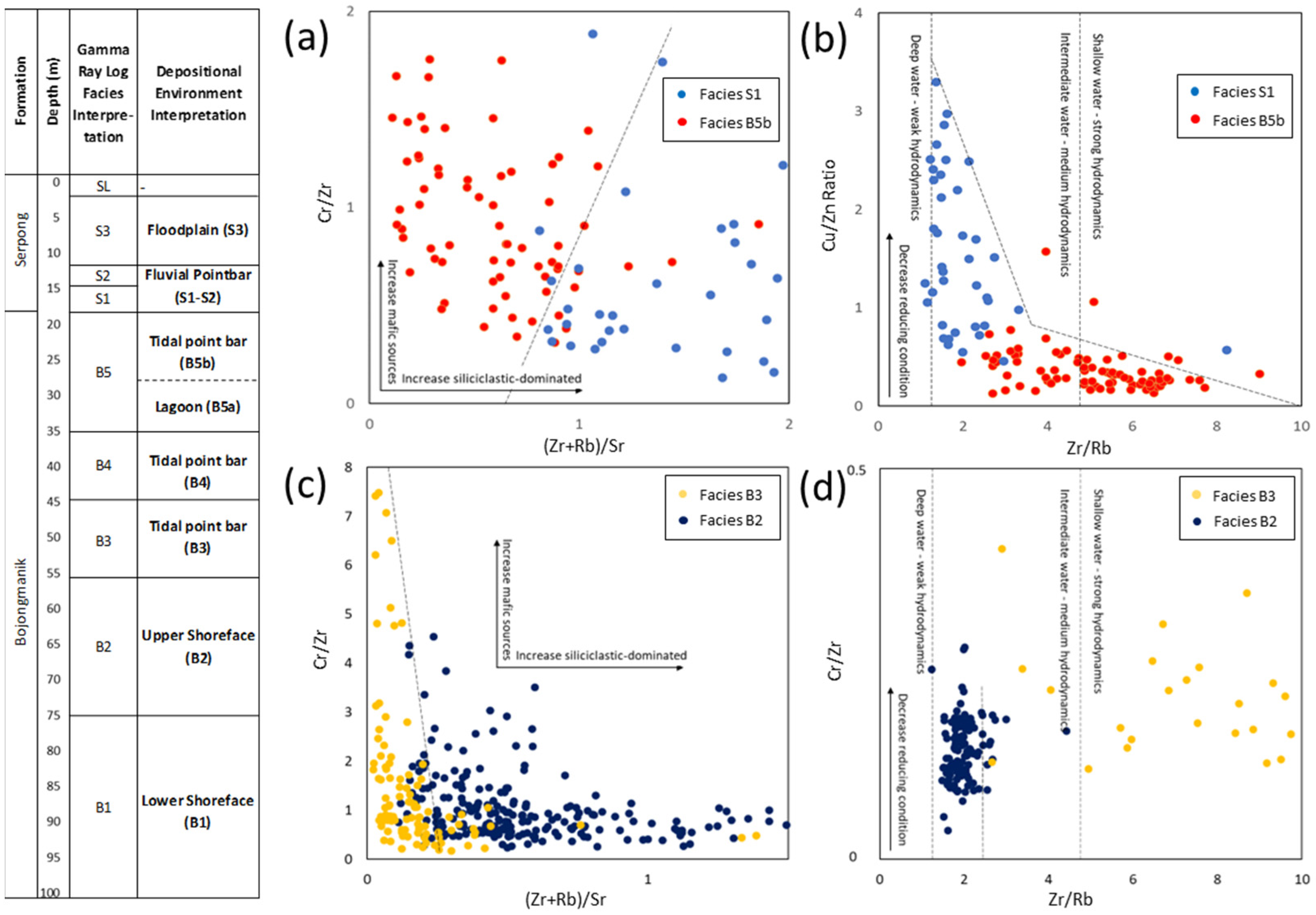
4.2.2. Paleoenvironment Analysis Based on Elemental Affinity
4.2.3. Paleoenvironment Analysis Based on Elemental Ratio
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoga, K.E.; Syahrulyati, T. Winantris Umur dan Lingkungan Purba Satuan Batupasir Sisipan Batulempung Formasi Bojongmanik Berdasarkan Data Palinologi. Padjadjaran Geosci. J. 2020, 4, 376–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayatullah, A.Y.; Sihombing, F.M.H. Microfacies and Diagenesis of Limestone in Bojongmanik Formation in the Western Endut Mountain Area, Lebak Regency, Banten Province Based on Petrographical Analysis Methods. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 830, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangga, A.D.; Mayasari, E.D.; Wiwik, E. Analisis Diagenesa dan Identifikasi Batugamping Formasi Bojongmanik daerah Cigudeg, Bogor, Jawa Barat. In Proceedings of the Seminar Nasional AVoER XI 2019, Palembang, Indonesia, 22–23 October 2019; pp. 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Syahrulyati, T.; Isnaniawardhani, V.; Rosana, M.F.; Winantris, W. Bojongmanik Formation Sedimentation Mechanism in the Middle to Late Miocene (N9-N17) in the Rangkasbitung Basin. Sci. Contrib. Oil Gas 2020, 43, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnaniawardhani, V.; Rivaldy, M.; Ismawan; Sophian, R.I.; Andyastiya, A.S. The Miocene (25.2–5.6 million years ago) climate changes recorded by foraminifera and nannofossils assemblages in Bogor Basin, Western Java. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 575, 012222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syaeful, H.; Muhammad, A.G. Interpretation of Depositional Environment of Rock Formation using Electrofacies Analysis in Pupiptek Site, Serpong. Eksplorium 2017, 38, 29–42. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martodjojo, S. Evolution of Bogor Basin, West Java; ITB Bandung: Bandung, Indonesia, 2003. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- Syahrulyati, T.; Isnaniawardhani, V.; Fatimah, M. The Environmental Construction of the Bojongmanik Formation in the Rangkasbitung Basin. Int. J. Innov. Creat. Chang. 2020, 12, 504–520. [Google Scholar]
- Abdurrokhim; Ito, M. The role of slump scars in slope channel initiation: A case study from the Miocene Jatiluhur Formation in the Bogor Trough, West Java. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 73, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, B.; Hall, R. Cretaceous to Late Miocene stratigraphic and tectonic evolution of West Java. In Proceedings of the Indonesian Petroleum Association, Jakarta, Indonesia, 14–16 May 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliastuti, Y.; Syaeful, H.; Syahbana, A.J.; Alhakim, E.E.; Sembiring, T.M. One dimensional seismic response analysis at the non-commercial nuclear reactor site, Serpong—Indonesia. Rud. Geol. Naft. Zb. 2021, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkandi, T.; Sidarto; Agustiyanto, D.; Hadiwidjojo, M. Geologic Map of Jakarta and Kepulauan Seribu Quadrangles, Jawa; GRDC: Bandung, Indonesia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Delinom, R.M.; Assegaf, A.; Abidin, H.Z.; Taniguchi, M.; Suherman, D.; Fajar, R.; Yulianto, E. The contribution of human activities to subsurface environment degradation in Greater Jakarta Area, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 3129–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnington, D.W.; Spooner, I.S.; Mallory, M.L.; White, C.E.; Gagnon, G.A. Evaluating the utility of elemental measurements obtained from factory-calibrated field-portable X-Ray fluorescence units for aquatic sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshmand, N.; Goodfellow, S.; Esmaeili, K.; Ordóñez Calderón, J.C. Rock Type Classification Based on Petrophysical, Geochemical, and Core Imaging Data Using Machine and Deep Learning Techniques. Appl. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 16, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, H.; Lentz, D.R.; Thorne, K.; Rogers, N. Application of portable X-ray and micro-X-ray fluorescence spectrometry to characterize alteration and mineralization within various gold deposits hosted in southern New Brunswick, Canada. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 229, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Li, B.; Lewis, K.; Godoy, M.; Paulette, L.; Weindorf, D.C. Determination of base saturation percentage in agricultural soils via portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. Geoderma 2019, 338, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillian, C.D.; Burnett, J.S.; Oweidi, A.; Gharib, R. Geochemical characterization of Jordanian basalts using portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and sourcing of the Amman Theater Statue. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 46, 103720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barago, N.; Pavoni, E.; Floreani, F.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Lenaz, D.; Larese Filon, F.; Covelli, S. Portable X-ray Fluorescence (pXRF) as a Tool for Environmental Characterisation and Management of Mining Wastes: Benefits and Limits. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercovici, A.; Cui, Y.; Forel, M.B.; Yu, J.; Vajda, V. Terrestrial paleoenvironment characterization across the Permian-Triassic boundary in South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 98, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravansari, R.; Wilson, S.C.; Tighe, M. Portable X-ray fluorescence for environmental assessment of soils: Not just a point and shoot method. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNulty, B.A.; Fox, N.; Berry, R.F.; Gemmell, J.B. Lithological discrimination of altered volcanic rocks based on systematic portable X-ray fluorescence analysis of drill core at the Myra Falls VHMS deposit, Canada. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 193, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemière, B. A review of pXRF (field portable X-ray fluorescence) applications for applied geochemistry. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 188, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Richard, F.; Kassim, A.M.; Tekin, Y.; Mouazen, A.M. Fusion of Gamma-rays and portable X-ray fluorescence spectral data to measure extractable potassium in soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momta, P.S.; Odigi, M.I. Reconstruction of the Depositional Setting of Tortonian Sediments in the Yowi Field, Shallow Offshore Niger Delta, Using Wireline Logs. Am. J. Geosci. 2016, 6, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, A.; Ahmed, S.; Hussain, S. Sedimentary facies interpretation of Gamma Ray (GR) log as basic well logs in Central and Lower Indus Basin of Pakistan. Geod. Geodyn. 2016, 7, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliva, R.G. Aquifer Characterization Techniques; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9783319321370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslin, A.; Esterle, J.S. Electrofacies analysis for coal lithotype profiling based on high-resolution wireline log data. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Wang, H. Coordinated analysis of county geological environment carrying capacity and sustainable development under remote sensing interpretation combined with integrated model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.A.; Bălc, R.; Humphrey, J.D.; Amao, A.O.; Kaminski, M.A.; Alzayer, Y.; Duque, F. Changes in paleoenvironmental conditions during the Late Jurassic of the western Neo-Tethys: Calcareous nannofossils and geochemistry. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2022, 173, 102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M. Paleoenvironment-driven organic matter accumulation in lacustrine shale mixed with shell bioclasts: A case study from the Jurassic Da’anzhai member, Sichuan Basin (China). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omietimi, E.J.; Lenhardt, N.; Yang, R.; Götz, A.E.; Bumby, A.J. Sedimentary geochemistry of Late Cretaceous-Paleocene deposits at the southwestern margin of the Anambra Basin (Nigeria): Implications for paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2022, 600, 111059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, D.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, S.; Pan, S. Sedimentology and geochemistry of Carboniferous-Permian marine-continental transitional shales in the eastern Ordos Basin, North China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 571, 110389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.J.; Huang, Z.L.; Chen, X.; Li, X.N.; Liu, J.T. Paleoenvironment and organic matter enrichment of the Carboniferous volcanic-related source rocks in the Malang Sag, Santanghu Basin, NW China. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Bao, Z.; Munnecke, A.; Liu, W.; Harrison, G.W.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Lu, K.; et al. Paleoenvironment of the Lower-Middle Cambrian Evaporite Series in the Tarim Basin and Its Impact on the Organic Matter Enrichment of Shallow Water Source Rocks. Minerals 2021, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, I.M. Paleoenvironmental changes across the Paleocene–Eocene boundary in West Central Sinai, Egypt: Geochemical proxies. Swiss J. Geosci. 2020, 113, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermaelen, N.; Vanacker, V.; Clapuyt, F.; Christl, M.; Beerten, K. Reconstructing the depositional history of Pleistocene fluvial deposits based on grain size, elemental geochemistry and in-situ 10Be data. Geomorphology 2022, 402, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerner, M.; Berner, U.; Erdmann, M.; Barth, T. Geochemical characterization of the depositional environment of Paleocene and Eocene sediments of the Tertiary Central Basin of Svalbard. Chem. Geol. 2020, 542, 119587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, T.J.; Liu, J. A re-assessment of elemental proxies for paleoredox analysis. Chem. Geol. 2020, 540, 119549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Barnes, C.R. Late Ordovician (Katian) conodont community analysis and anoxic shallow water origin of organic-rich black shales, Red Head Rapids Formation, Southampton Island, Canadian Arctic. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2022, 592, 110896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, C.; Poulton, S.W.; Beckmann, B.; Küster, K.; Wagner, T.; Kasten, S. Redox sensitivity of P cycling during marine black shale formation: Dynamics of sulfidic and anoxic, non-sulfidic bottom waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 3703–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dypvik, H.; Harris, N.B. Geochemical facies analysis of fine-grained siliciclastics using Th/U, Zr/Rb and (Zr + Rb)/Sr ratios. Chem. Geol. 2001, 181, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.R.L. Late Quaternary Niger Delta and adjacent areas: Sedimentary environments and lithofacies. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1965, 49, 547–600. [Google Scholar]


| Paleoclimate | Paleosalinity | Paleoredox | Paleo-Hydrodynamics | Sediment Provenance | Siliciclastic-Dominated | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry and hot | Sr/Cu >5 | Marine | Sr/Ba > 0.5 | Anoxic | Cu/Zn < 0.21 | Weak/ Deepwater | Zr/Rb < 1.25, low Fe/Mn | Mafic sources | High Cr/Zr | Increase siliciclastic | High (Zr + Rb)/Sr |
| Brackish | Sr/Ba 0.2–0.5 | Weak anoxic | Cu/Zn 0.21–0.38 | Intermediate | Zr/Rb 1.25–4.76 | ||||||
| Warm and humid | Sr/Cu 1–5 | Transition | Cu/Zn 0.38–0.5 | Felsic sources | Low Cr/Zr | Increase carbonate | Low (Zr + Rb)/Sr | ||||
| Terres-trial | Sr/Ba < 0.2 | Weak oxic | Cu/Zn 0.5–0.63 | Strong/Shallow water | Zr/Rb > 4.76, high Fe/Mn | ||||||
| Oxic | Cu/Zn > 0.63 | ||||||||||
| S (ppm) | K (ppm) | Ca (ppm) | Ti (ppm) | V (ppm) | Cr (ppm) | Mn (ppm) | Fe (ppm) | Ni (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | Zn (ppm) | As (ppm) | Rb (ppm) | Sr (ppm) | Y (ppm) | Zr (ppm) | Nb (ppm) | Ba (ppm) | Pb (ppm) | GR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S (ppm) | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||
| K (ppm) | −0.40 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ca (ppm) | 0.13 | −0.44 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| Ti (ppm) | −0.15 | 0.25 | −0.44 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| V (ppm) | 0.74 | −0.12 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| Cr (ppm) | 0.85 | −0.26 | 0.42 | −0.16 | 0.75 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Mn (ppm) | −0.03 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| Fe (ppm) | 0.14 | −0.07 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Ni (ppm) | −0.12 | 0.26 | −0.08 | 0.28 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| Cu (ppm) | −0.19 | 0.13 | −0.03 | −0.08 | −0.21 | −0.19 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Zn (ppm) | −0.09 | 0.15 | −0.18 | 0.38 | −0.04 | −0.11 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| As (ppm) | 0.11 | 0.18 | −0.09 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.13 | −0.06 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Rb (ppm) | −0.08 | 0.81 | −0.38 | 0.38 | 0.12 | −0.04 | 0.23 | −0.13 | 0.33 | −0.02 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Sr (ppm) | 0.17 | −0.39 | 0.27 | −0.34 | 0.32 | 0.12 | −0.03 | −0.17 | −0.05 | −0.14 | −0.19 | −0.19 | −0.35 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Y (ppm) | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.12 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.13 | −0.12 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.16 | −0.11 | 1.00 | |||||
| Zr (ppm) | −0.05 | 0.12 | −0.37 | 0.40 | −0.09 | −0.13 | 0.02 | −0.07 | 0.06 | −0.04 | 0.10 | −0.03 | 0.17 | −0.29 | 0.09 | 1.00 | ||||
| Nb (ppm) | 0.04 | 0.05 | −0.05 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 0.16 | −0.12 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 1.00 | |||
| Ba (ppm) | −0.42 | 0.20 | −0.14 | −0.23 | −0.40 | −0.36 | −0.05 | −0.10 | −0.14 | 0.27 | −0.05 | −0.07 | 0.01 | −0.06 | −0.24 | 0.11 | −0.08 | 1.00 | ||
| Pb (ppm) | 0.03 | 0.23 | −0.19 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.31 | −0.11 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 0.32 | −0.13 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.24 | −0.19 | 1.00 | |
| GR | 0.23 | 0.25 | −0.23 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.27 | −0.32 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.51 | −0.16 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.22 | −0.50 | 0.34 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syaeful, H.; Bakhri, S.; Muljana, B.; Sumaryanto, A.; Sukadana, I.G.; Pratama, H.A.; Muhammad, A.G.; Ngadenin; Indrastomo, F.D.; Ciputra, R.C.; et al. Elemental Geochemistry on Paleoenvironment Reconstruction: Proxies on Miocene-Pliocene of Marine to Fluvial Sediment in Serpong, Banten, Indonesia. Geosciences 2024, 14, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14070189
Syaeful H, Bakhri S, Muljana B, Sumaryanto A, Sukadana IG, Pratama HA, Muhammad AG, Ngadenin, Indrastomo FD, Ciputra RC, et al. Elemental Geochemistry on Paleoenvironment Reconstruction: Proxies on Miocene-Pliocene of Marine to Fluvial Sediment in Serpong, Banten, Indonesia. Geosciences. 2024; 14(7):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14070189
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyaeful, Heri, Syaiful Bakhri, Budi Muljana, Agus Sumaryanto, I. Gde Sukadana, Hendra Adhi Pratama, Adi Gunawan Muhammad, Ngadenin, Frederikus Dian Indrastomo, Roni Cahya Ciputra, and et al. 2024. "Elemental Geochemistry on Paleoenvironment Reconstruction: Proxies on Miocene-Pliocene of Marine to Fluvial Sediment in Serpong, Banten, Indonesia" Geosciences 14, no. 7: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14070189
APA StyleSyaeful, H., Bakhri, S., Muljana, B., Sumaryanto, A., Sukadana, I. G., Pratama, H. A., Muhammad, A. G., Ngadenin, Indrastomo, F. D., Ciputra, R. C., Widodo, S., Madyaningarum, N., Santosa, P., Burhannudinnur, M., & Zakaria, Z. (2024). Elemental Geochemistry on Paleoenvironment Reconstruction: Proxies on Miocene-Pliocene of Marine to Fluvial Sediment in Serpong, Banten, Indonesia. Geosciences, 14(7), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences14070189













