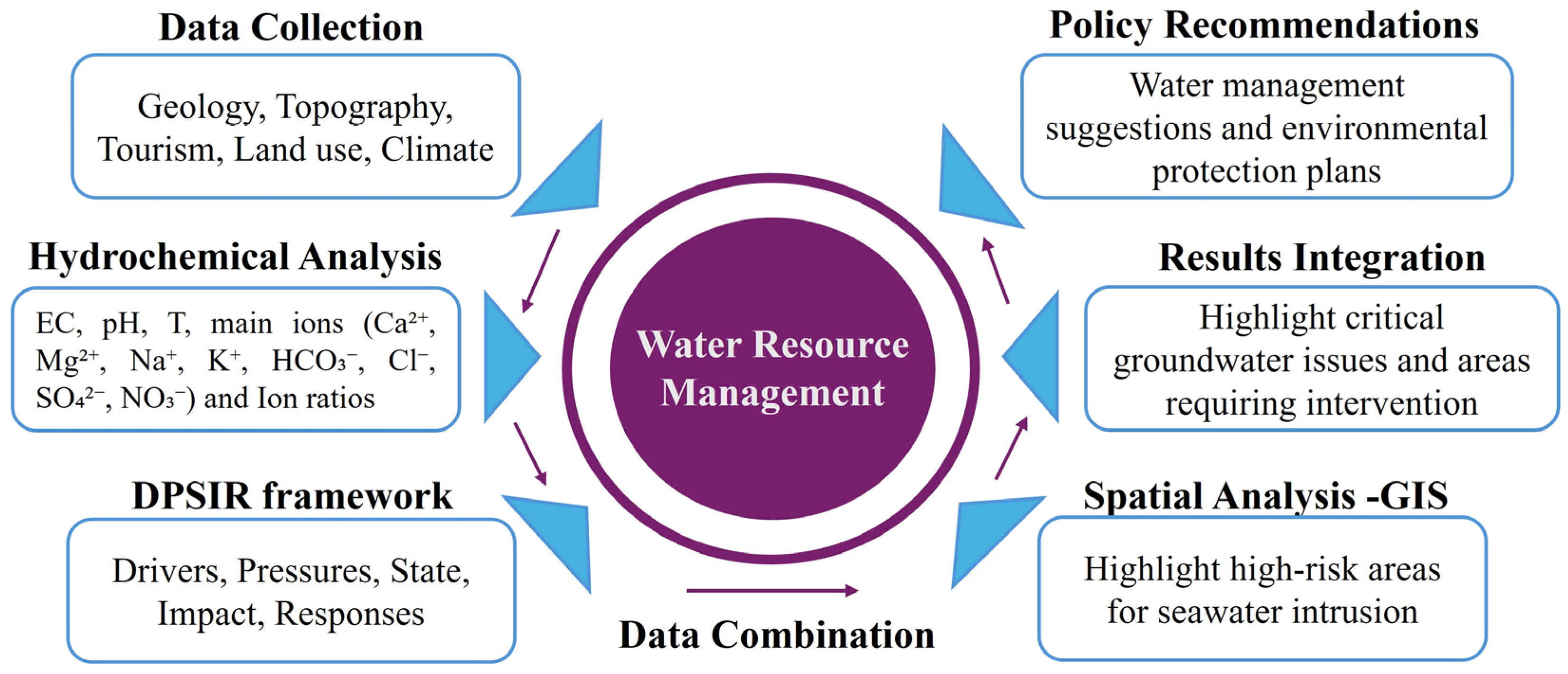
Coupling Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response–Management Framework with Hydrochemical Data for Groundwater Management on Sithonia Peninsula, Greece †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
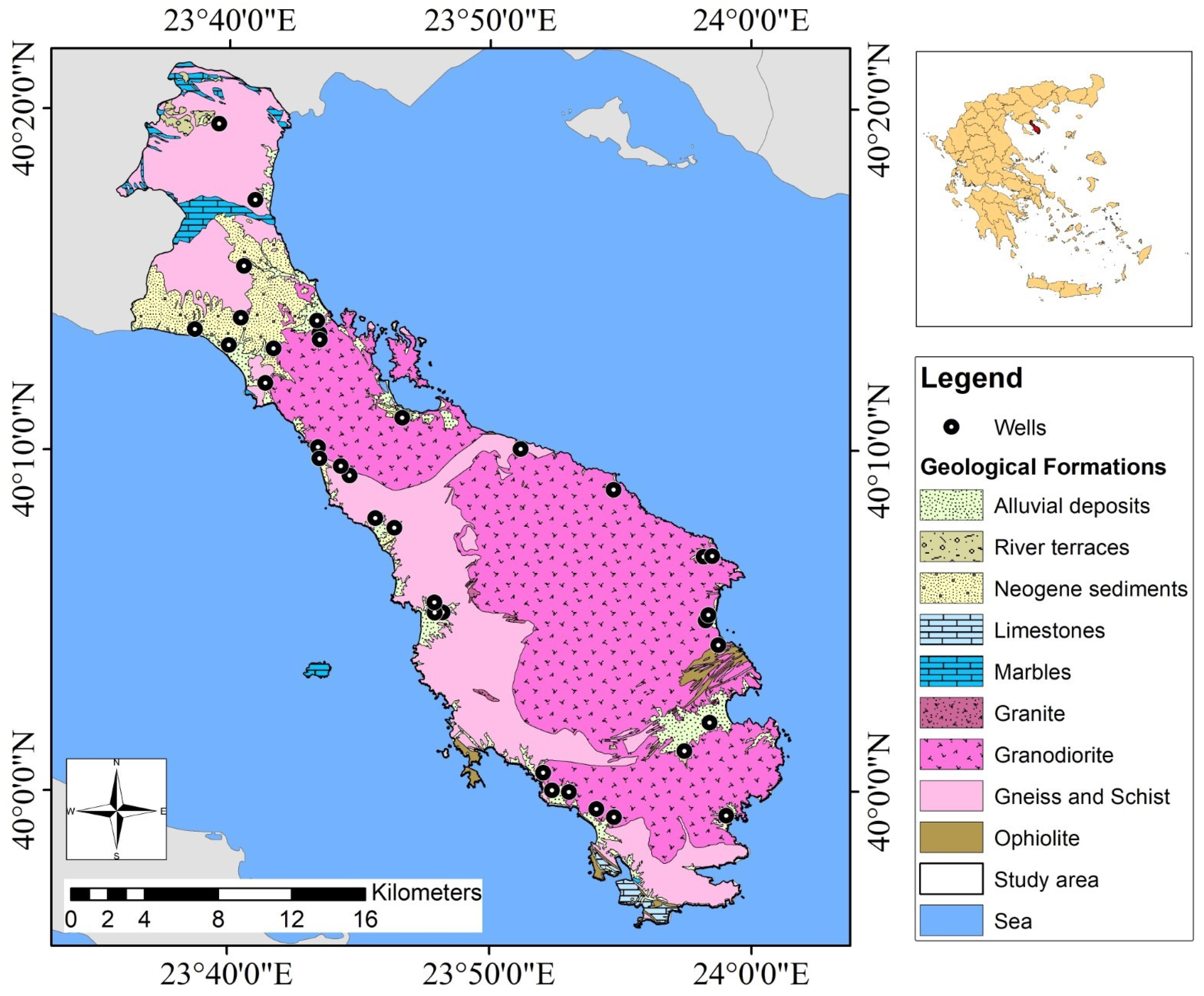
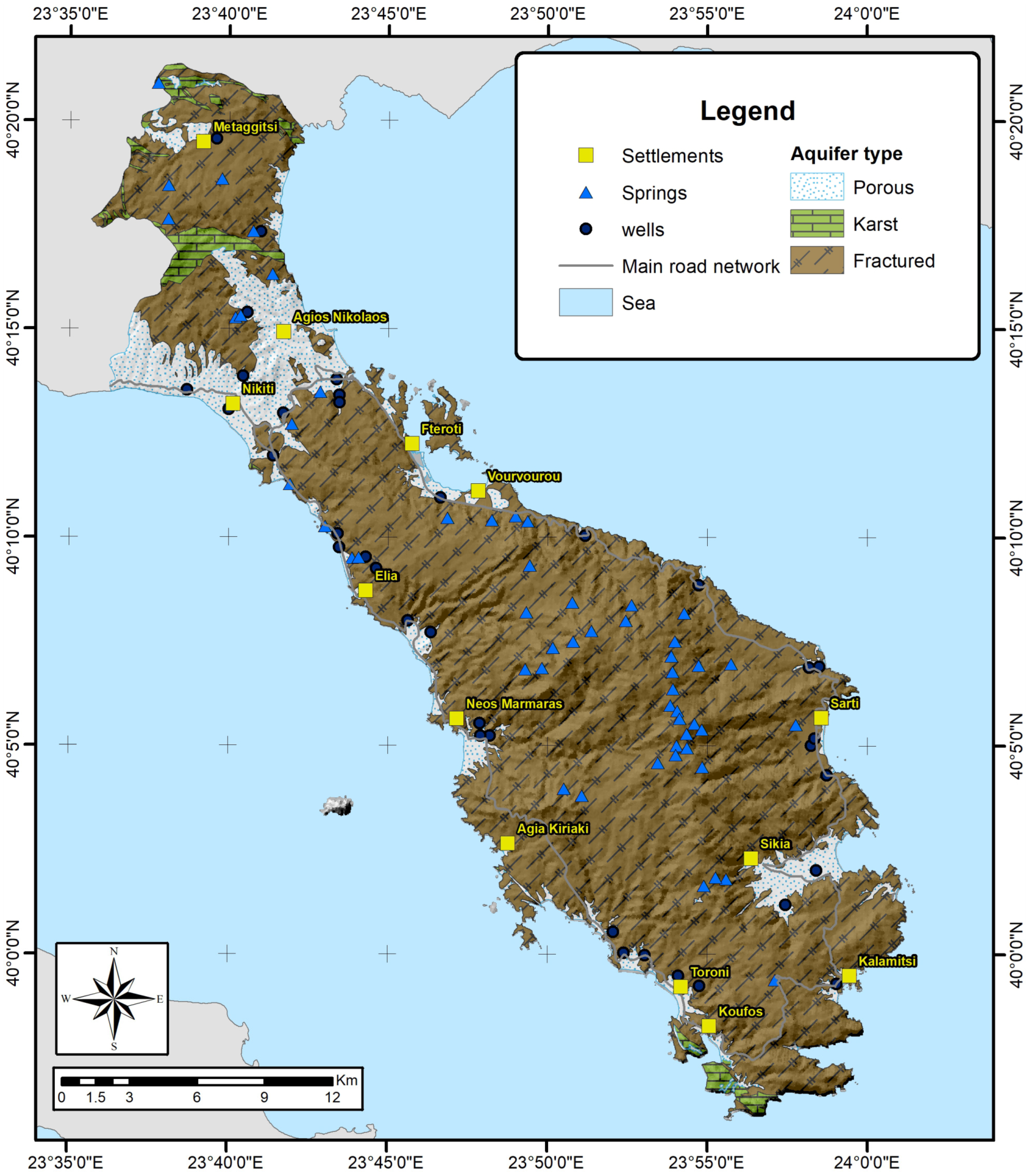
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
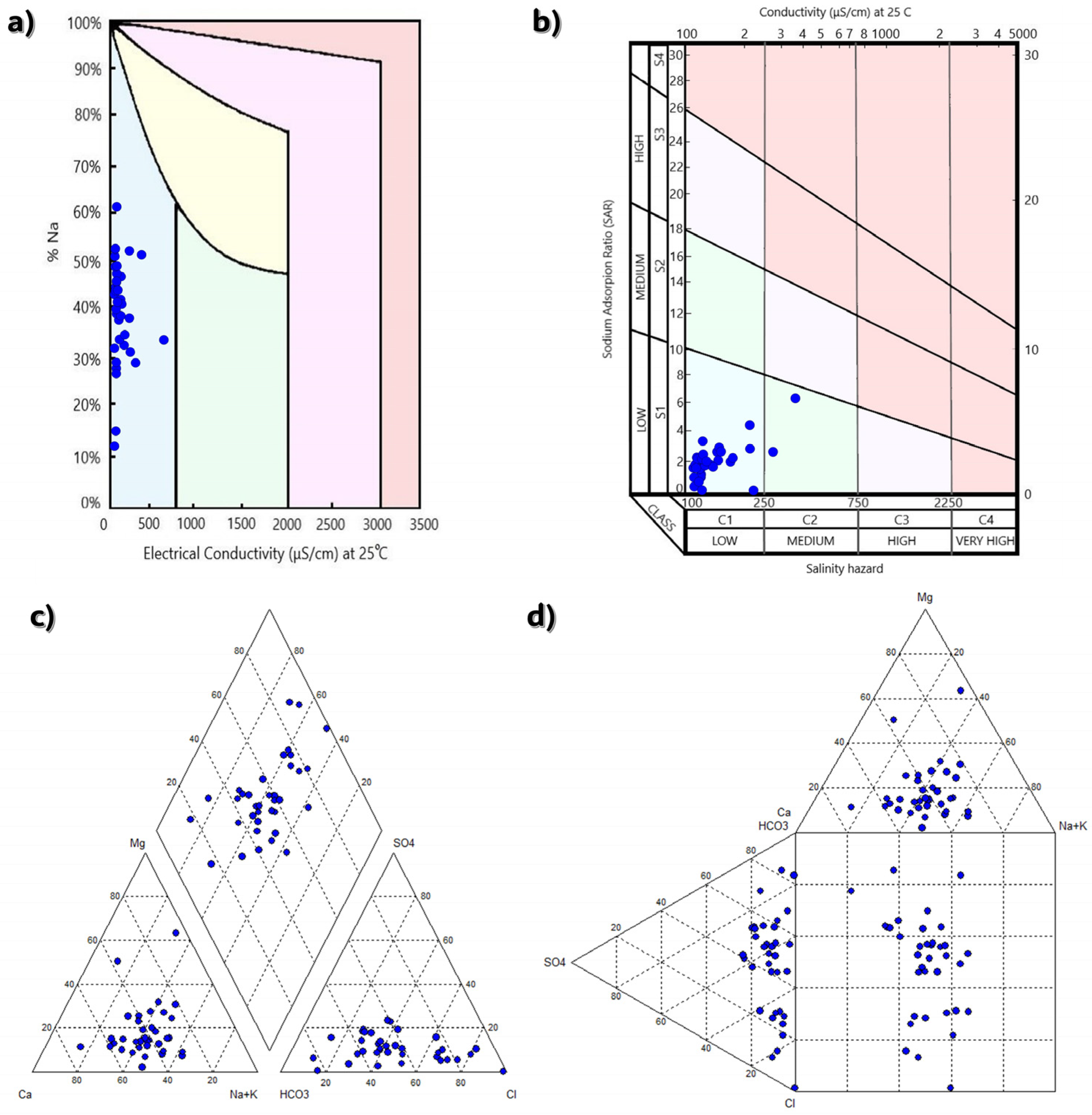
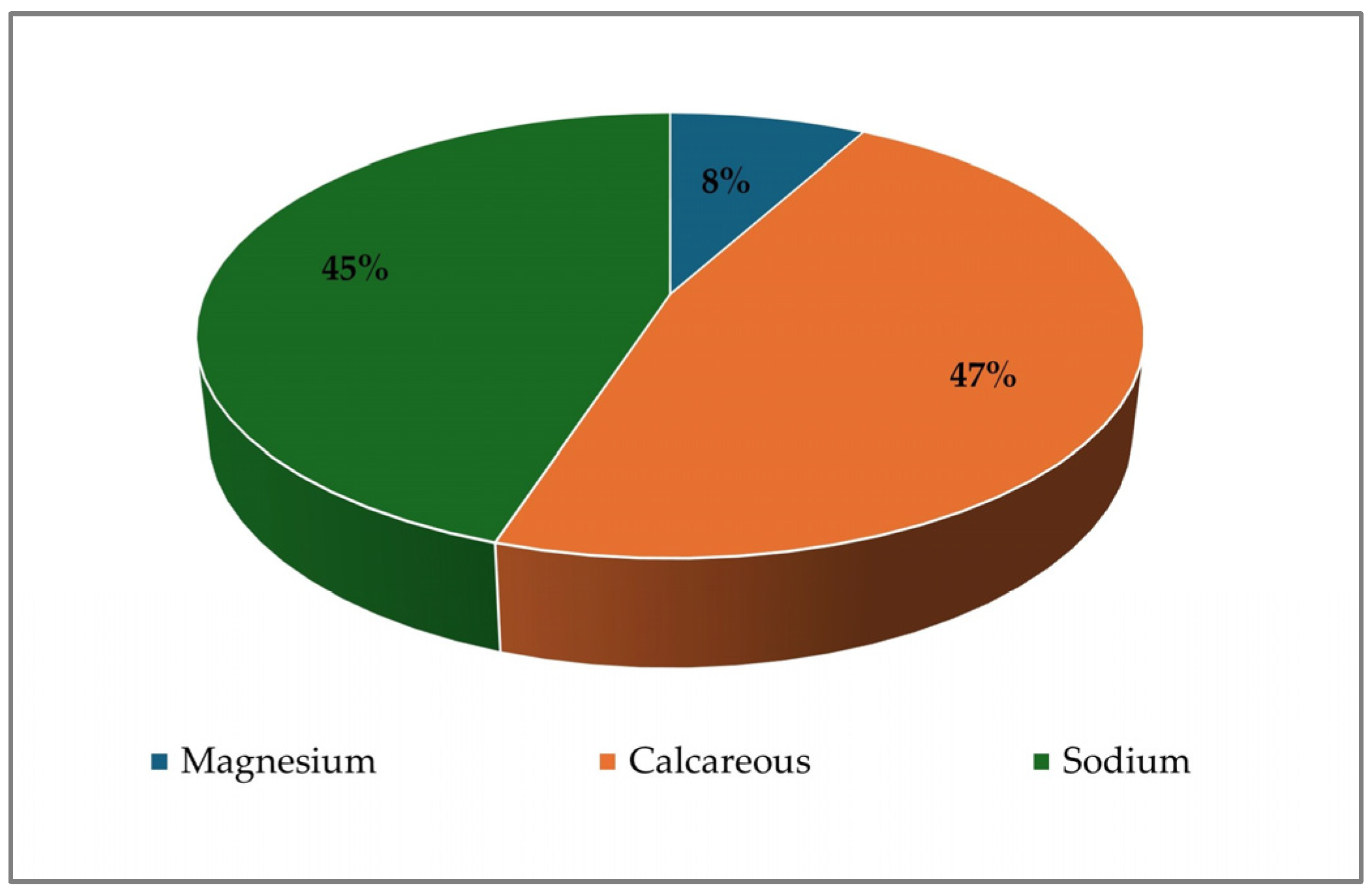
4.1. Groundwater Quality
4.2. DPSIR
4.2.1. Protected Areas
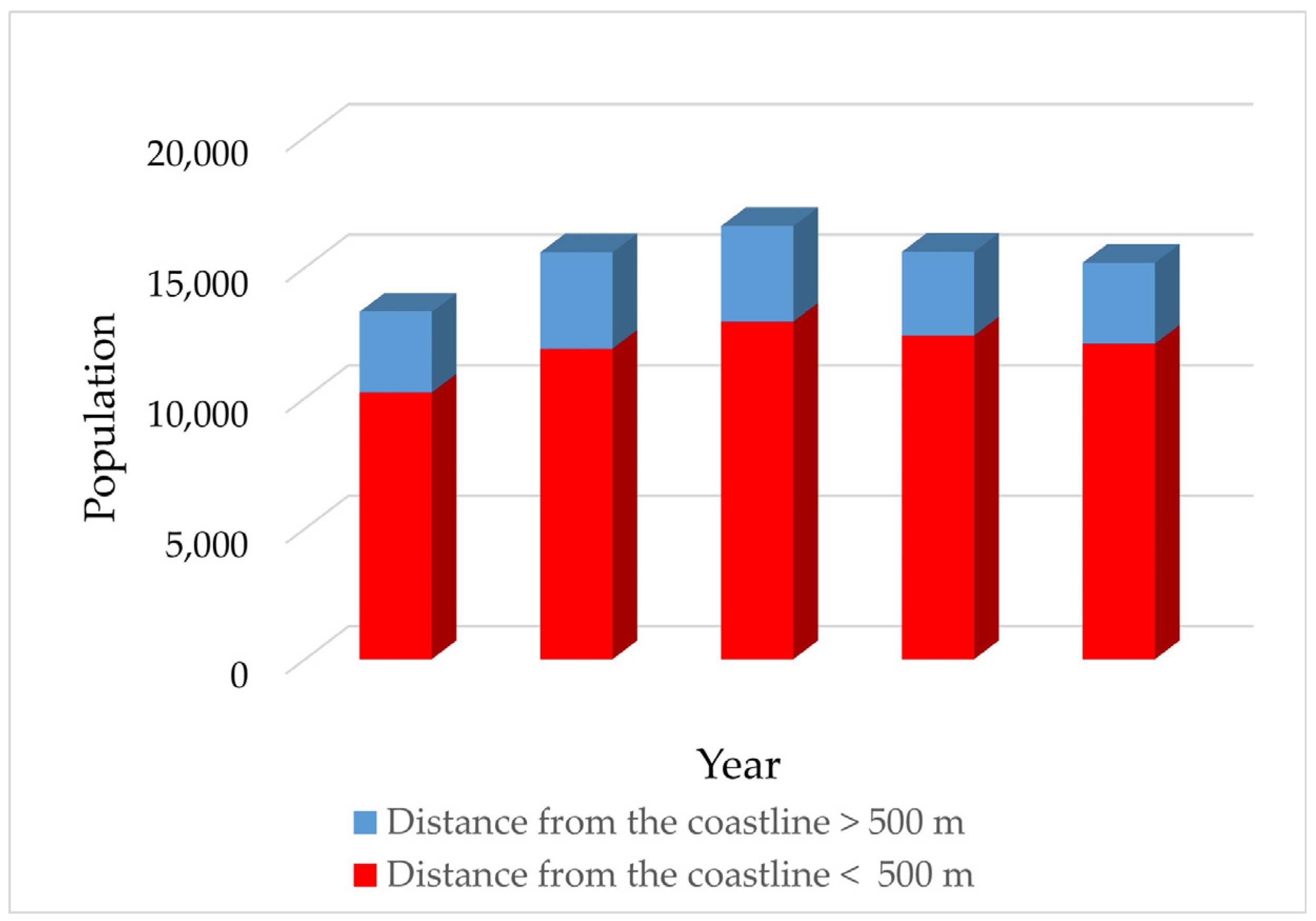
4.2.2. Urban Development
4.2.3. Tourism
4.2.4. Climate
4.2.5. Topography of the Area
4.2.6. Geology
4.2.7. Agricultural and Livestock Activity
4.2.8. Industrial Activity
4.3. Hydrochemical Analysis and DPSIR Framework
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- ▪
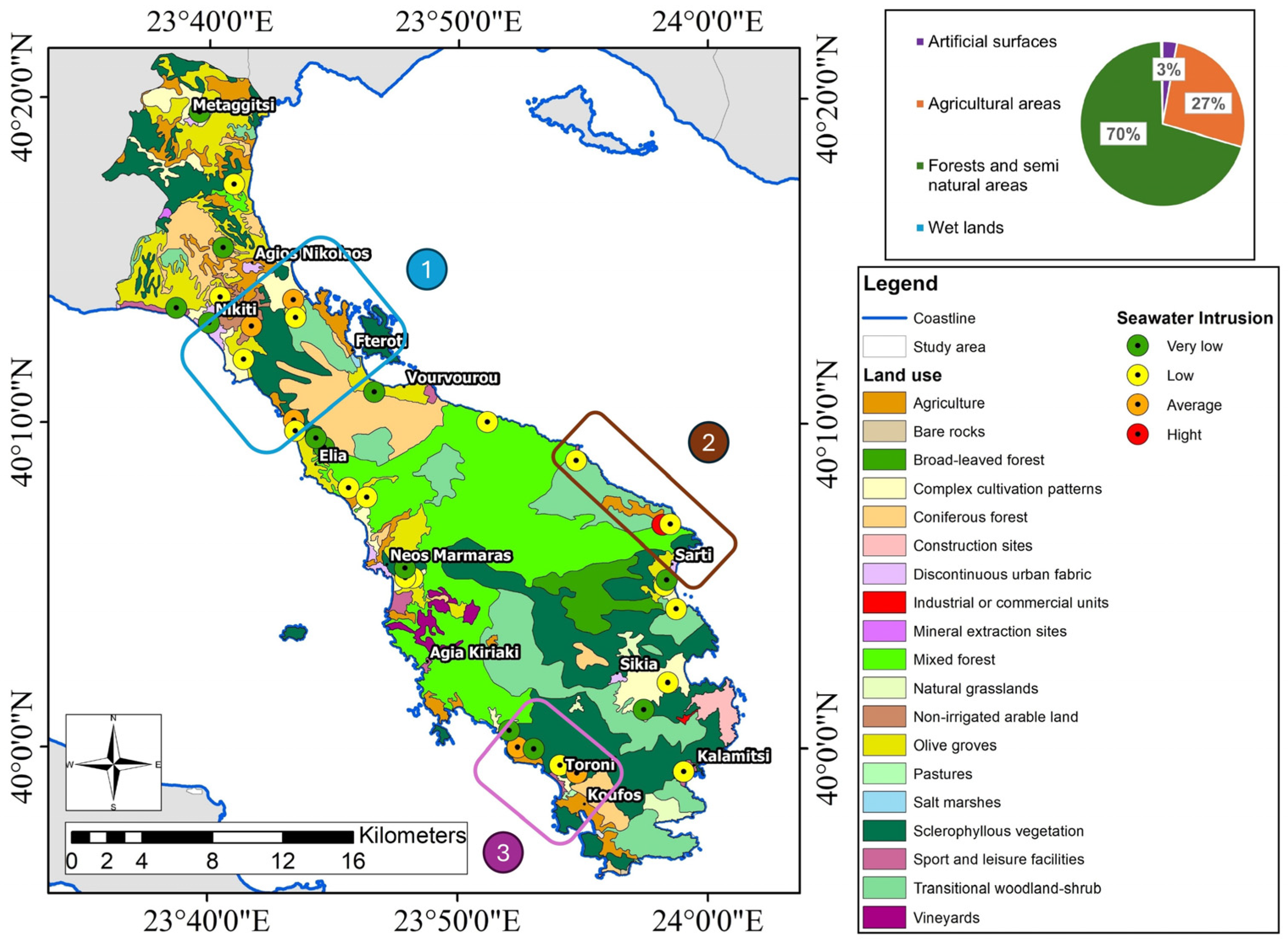
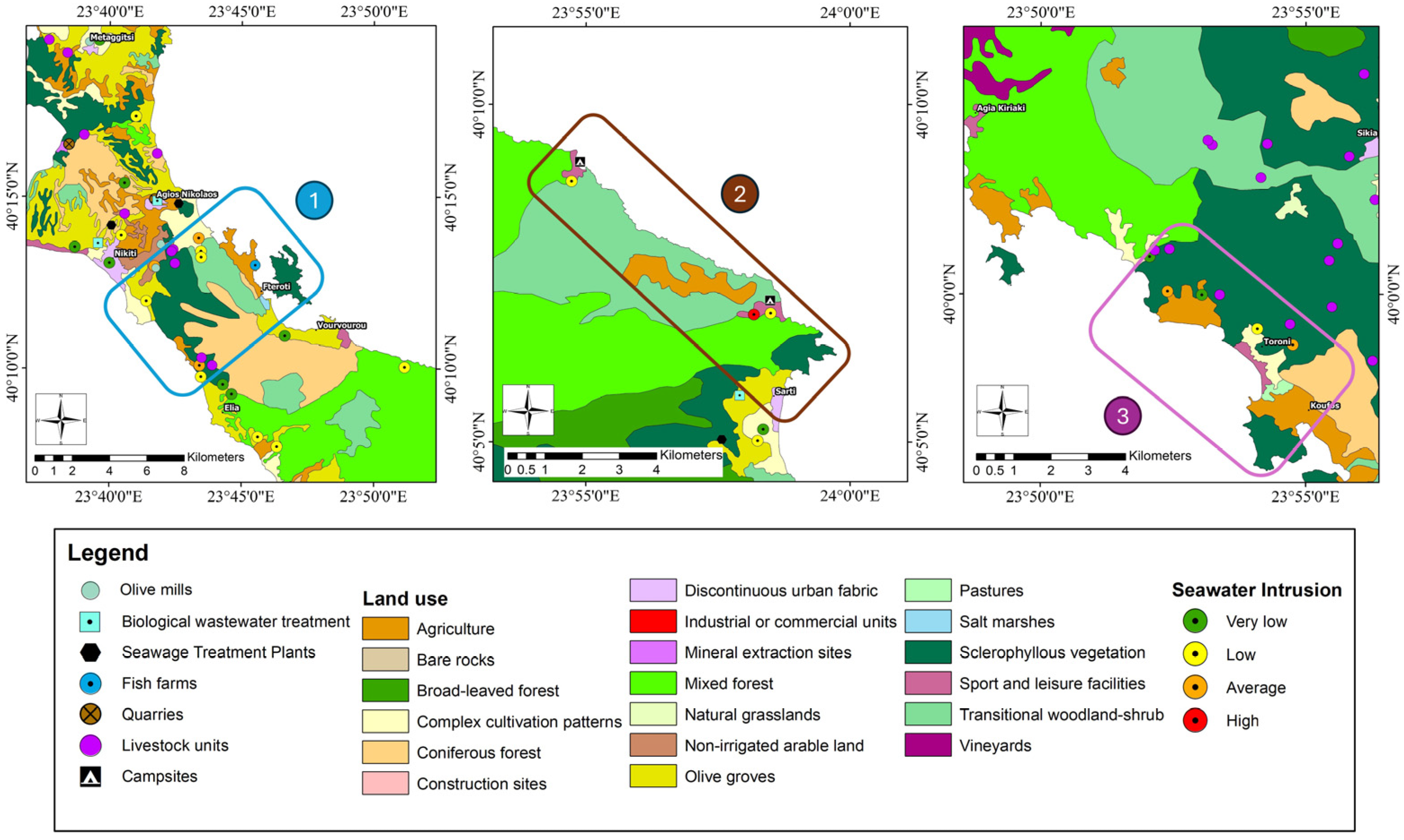
- The main pressures in the study area are the geological regime, the presence of biological wastewater treatments, illegal dumpsites, olive mills, tourism, and livestock activities.
- ▪
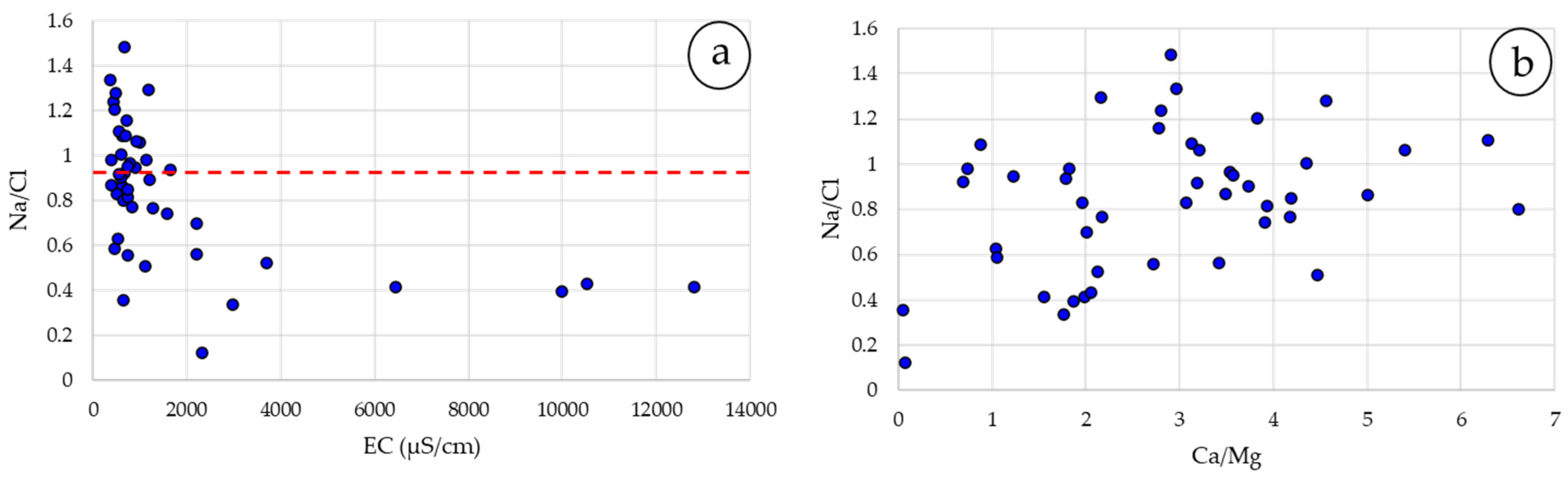
- Na+/Cl− and Cl−/SO42− ion ratios range from 0.12 to 1.48 and 0.91 to 186.58, respectively, and indicate the seawater intrusion phenomenon.
- ▪
- These ion ratios indicate a high possibility of seawater intrusion in three areas of the coastal zone. The main pressures in Area 1 are geological formations. In Area 2, tourism is the main driver, and in Area 3, livestock units, tourist accommodations, and hotels affect groundwater systems.
- ▪
- Water obtained from boreholes is limited in the fractured rock aquifer of Sithonia due to the site’s hydrogeological regime. Therefore, the borehole network must be extended in order to ensure water security.
- Establishing a monitoring network to record hydrometeorological parameters and expand the groundwater monitoring network in collaboration with key stakeholders.
- Developing biological wastewater treatment systems, wastewater treatment plants, and proper olive mill wastewater management to prevent surface water degradation in the study area.
- Establishing a landfill site to improve local waste management services, particularly during the summer tourism season.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gössling, S. Global Environmental Consequences of Tourism. Glob. Environ. Change. 2002, 12, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water Management: Current and Future Challenges and Research Directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drius, M.; Bongiorni, L.; Depellegrin, D.; Menegon, S.; Pugnetti, A.; Stifter, S. Tackling Challenges for Mediterranean Sustainable Coastal Tourism: An Ecosystem Service Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulos, N.; Liargovas, P.; Stavroyiannis, S.; Makris, I.; Apostolopoulos, S.; Petropoulos, D.; Anastasopoulou, E. Sustaining Rural Areas, Rural Tourism Enterprises and EU Development Policies: A Multi-Layer Conceptualisation of the Obstacles in Greece. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.U.; Heuzard, A.G.; Le, T.X.H.; Zhao, J.; Yin, R.; Shang, C.; Fan, C. The Impacts of Climate Change on Groundwater Quality: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N. A Critical Review of Water Resources in Greece: The Key Role of Agricultural Adaptation to Climate-Water Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulelis, P.P.; Proutsos, N.; Solomou, A.D.; Avramidou, E.V.; Malliarou, E.; Athanasiou, M.; Xanthopoulos, G.; Petrakis, P.V. Effects of Climate Change on Greek Forests: A Review. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Karakatsanis, D.; Ntona, M.M.; Polydoropoulos, K.; Zavridou, E.; Voudouri, K.A.; Busico, G.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Patsialis, T.; Perdikaki, M.; et al. Groundwater Depletion. Are Environmentally Friendly Energy Recharge Dams a Solution? Water 2024, 16, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tham, J. The Impact of Environmental Regulation, Environment, Social and Government Performance, and Technological Innovation on Enterprise Resilience under a Green Recovery. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Qin, J.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, P. The DPSIR Model-Based Sustainability Assessment of Urban Water Resources: A Comparative Study of Zhuhai and Macao. Water 2024, 16, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscherning, K.; Helming, K.; Krippner, B.; Sieber, S.; Paloma, S.G.Y. Does Research Applying the DPSIR Framework Support Decision Making? Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.R.; Wingard, P.M.; Yorty, S.C.; Thompson, M.C.; Jensen, N.K.; Roberson, J. Applying DPSIR to Sustainable Development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2007, 14, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, B.; Anderberg, S.; Olsson, L. Structuring Problems in Sustainability Science: The Multi-Level DPSIR Framework. Geoforum 2010, 41, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimidis, K.; Andrikakou, P.; Kallioras, A.; Pliakas, F. The DPSIR Approach to Groundwater Management for Sustainable Development in Coastal Areas: The Case of Nea Peramos Aquifer System, Kavala, Greece. Water Util. J. 2017, 16, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dzoga, M.; Simatele, D.M.; Munga, C.; Yonge, S. Application of the DPSIR Framework to Coastal and Marine Fisheries Management in Kenya. Ocean Sci. J. 2020, 55, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, S. Assessment of Groundwater Sustainability and Management Plan Formulations through the Integration of Hydrogeological, Environmental, Social, Economic and Policy Indices. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Pinillos, F.J.; Chica Ruiz, J.A. Coastal Management and Climate Change on the Island and the Sea of Chiloé (Chile): An Evaluation of Policies, Regulations, and Instruments. Environ. Sci. Policy 2024, 156, 103758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, R.; Yang, W. Framework System of Marine Sustainable Development Assessment Based on Systematic Review. Mar. Policy 2023, 154, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shen, J.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Wan, Y. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of the High–Quality Development of Urbanization and Water Resource Coupling in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, W.; Jiang, E.; Yuan, L.; Qu, B.; Degefu, D.M.; Ramsey, T.S. Evaluation and Prediction of Water Security Levels in Northwest China Based on the DPSIR Model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, J.; Elliott, M.; Mazik, K.; Papadopoulou, K.-N.; Smith, C.J. DPSIR—Two Decades of Trying to Develop a Unifying Framework for Marine Environmental Management? Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, R.; Zhou, L.; Bosompem Boadi, E.; Nsiah, T.; Ayamba, E.; Minkah, A.Y.; Asante, H. The Causal Link Between Anthropogenic Activities, Water Pollution and Health-Related Quality of Life from Residents’ Perspective: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelble, C.R.; Loomis, D.K.; Lovelace, S.; Nuttle, W.K.; Ortner, P.B.; Fletcher, P.; Cook, G.S.; Lorenz, J.J.; Boyer, J.N. The EBM-DPSER Conceptual Model: Integrating Ecosystem Services into the DPSIR Framework. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, R.E.; Riley, C. Socio-Economic Indicators and Integrated Coastal Management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2003, 46, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. DPSIR Framework and Sustainable Approaches of Brine Management from Seawater Desalination Plants in Qatar. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxim, L.; Spangenberg, J.H.; O’Connor, M. An Analysis of Risks for Biodiversity under the DPSIR Framework. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, E.; Weterings, R. Environmental Indicators: Typology and Overview; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lalande, N.; Cernesson, F.; Decherf, A.; Tournoud, M.-G. Implementing the DPSIR Framework to Link Water Quality of Rivers to Land Use: Methodological Issues and Preliminary Field Test. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kagalou, I.; Leonardos, I.; Anastasiadou, C.; Neofytou, C. The DPSIR Approach for an Integrated River Management Framework. A Preliminary Application on a Mediterranean Site (Kalamas River-NW Greece). Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1677–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svarstad, H.; Petersen, L.K.; Rothman, D.; Siepel, H.; Wätzold, F. Discursive Biases of the Environmental Research Framework DPSIR. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, P.; Geng, Q.; Xu, L. Sustainability Assessment of Regional Water Resources under the DPSIR Framework. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M. The Role of the DPSIR Approach and Conceptual Models in Marine Environmental Management: An Example for Offshore Wind Power. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, iii–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Jeunesse, I.; Rounsevell, M.; Vanclooster, M. Delivering a Decision Support System Tool to a River Contract: A Way to Implement the Participatory Approach Principle at the Catchment Scale? Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmir, M.; Javadi, S.; Moridi, A.; Neshat, A.; Razdar, B. A New Combined Framework for Sustainable Development Using the DPSIR Approach and Numerical Modeling. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, S. Evaluation of Mountain Case Studies by Means of Sustainability Variables. Mt. Res. Dev. (MRED) 2004, 24, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheren, P.A.G.M.; Kroeze, C.; Janssen, F.J.J.G.; Hordijk, L.; Ptasinski, K.J. Integrated Water Pollution Assessment of the Ebrié Lagoon, Ivory Coast, West Africa. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, I.P.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Shackley, S.; Harrison, P.A.; Nicholls, R.J.; Berry, P.M.; Audsley, E. A Regional, Multi-Sectoral and Integrated Assessment Of The Impacts Of Climate And Socio-Economic Change In The UK. Clim. Change. 2005, 71, 9–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Fonseca, F.; Santiago, A.; Rodrigues, D. Sustainability Indicators Model Applied to Waste Management in Brazil Using the DPSIR Framework. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Broadcasting on internet of Water DPSIR Indicators. Experiment on the Nestos Delta, Greece. Glob. Nest J. 2013, 5, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikidis, N.T. The Environmental State of Rivers in the Balkans—A Review within the DPSIR Framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2501–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgis, A.P.; Skourtos, M.S.; Kapsimalis, V.; Kontogianni, A.D.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Pagou, K.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Drakopoulou, P.; Zanou, B.; Karamanos, H.; et al. An Integrated Approach to Watershed Management within the DPSIR Framework: Axios River Catchment and Thermaikos Gulf. Reg. Environ. Change. 2005, 5, 138–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntona, M.M.; Busico, G.; Mastrocicco, M.; Kazakis, N. Coupling SWAT and DPSIR Models for Groundwater Management in Mediterranean Catchments. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.Y.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Approaches to Achieve Sustainable Use and Management of Groundwater Resources in Qatar: A Review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Linking DPSIR Model and Water Quality Indices to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals in Groundwater Resources. Hydrology 2021, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Census Results. 2022. Available online: https://elstat-outsourcers.statistics.gr/census_results_2022_en.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Results of the Population-Housing Census of 5 April 1981; Hellenic Statistical Authority: Athens, Greece, 1994; Volume 1, p. A59. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Nimfopoulos, M.; Katirtzoglou, C.; Polya, D.; Veranis, N.; Anagnostaras, I. Quality and Pollution of Surface and Groundwaters in the Chalkidiki District, Macedonia, N. Greece. In Proceedings of the 6th Hydrogeological Congress of the Geological Society of Greece, Xanthi, Greece, 8–10 November 2002; Volume I, pp. 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Christofides, G.; Pe-Piper, G.; Koroneos, A.; Papadopoulou, L. Geochemistry of Beach Sands from Sithonia Peninsula (Chalkidiki, Northern Greece). Min. Pet. 2015, 109, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geological Institute of Mineral and Metallurgical Research (IGME). Hydrogeological Study of Epanomi-Moudania, Kassandra, Ormylia, and Sithonia Aquifer Systems in the Central Macedonia, Water District (YD10); Technical Report 2B; Geological Institute of Mineral and Metallurgical Research (IGME): Athens, Greece, 2010. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). CORINE Land Cover (CLC)—European Union, Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. European Environment Agency. 2018. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cov (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Management Plan of the River Basins of Central Macedonia River Basin District (2024). 2nd Revision of Development of the River Basin Management Plans of the River Basins of West Macedonia and Central Macedonia River Basin Districts According to the Specifications of the WFD 2000/60/EC, Applying the Greek Law 3199/2003 and the Greek PD 51/2007. Available online: https://wfdver.ypeka.gr/en/management-plans-en/approved-management-plans-en/ (accessed on 9 January 2025). (In Greek).
- Hellenic Survey of Geology & Mineral Exploration (HSGME). Geological Map of Greece, Scale 1:50,000, Sheets: Arnea and Sithonia; Hellenic Survey of Geology & Mineral Exploration (HSGME): Athens, Greece, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Parastatidou, E. Water Resources and DPSIR Framework. The Case of Sithonia, Chalkidiki Prefecture. Master’s Thesis, Democritus University of Thrace, Xanthi, Greece, 2021. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Ntona, M.M.; Chalikakis, K.; Busico, G.; Mastrocicco, M.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Kazakis, N. Application of Judgmental Sampling Approach for the Monitoring of Groundwater Quality and Quantity Evolution in Mediterranean Catchments. Water 2023, 15, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliaka, C.; Gkiougkis, I.; Karasogiannidis, D.; Angelidis, P.; Kallioras, A.; Pliakas, F.-K. Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability to Seawater Intrusion Using GALDIT, SITE and SIVI Methods in Laspias River Coastal Aquifer System, NE Greece. Water 2024, 16, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veranis, N.; Christidis, C. Hard Rock Aquifers of Central and Eastern Chalkidiki, Region of Central Macedonia, Northern Greece. In Proceedings of the 10th International Hydrogeological Congress, Thessaloniki, Greece, 8–13 September 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Geological Institute of Mineral and Metallurgical Research (IGME). Recording and Evaluation of Hydrogeological Characteristics of Groundwater and Aquifer Systems in Greece (Project Code: 7.3.2.1). In Subproject 4: Water Balances of Basins, Monitoring Water Quality, and Protection Measures for Central Macedonia (YD09, YD10, YD11 West); Geological Institute of Mineral and Metallurgical Research (IGME): Athens, Greece, 2009. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Elango, L.; Kannan, R. Chapter 11 Rock—Water Interaction and Its Control on Chemical Composition of Groundwater. In Developments in Environmental Science; Sarkar, D., Datta, R., Hannigan, R., Eds.; Concepts and Applications in Environmental Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment and Energy. Special Secretariat for Water National Water Monitoring Network. Available online: http://Nmwn.Ypeka.Gr/?Q=en (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Bouzourra, H.; Bouhlila, R.; Elango, L.; Slama, F.; Ouslati, N. Characterization of Mechanisms and Processes of Groundwater Salinization in Irrigated Coastal Area Using Statistics, GIS, and Hydrogeochemical Investigations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2643–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-92-4-004506-4. [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumar, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Srinivas, Y.; Selvam, S.; Kaliraj, S.; Magesh, N.S.; Venkatramanan, S. Hydrogeochemical Processes Controlling the Groundwater Salinity in the Coastal Aquifers of Southern Tamil Nadu, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodossiou, N.; Latinopoulos, P. A Management Framework for the Efficient Use of Surface Water Resources in Sithonia Peninsula (Greece). Glob. Int. J. 2001, 3, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Parastatidou, E.; Voudouris, K.; Kazakis, N. Determination of Site Suitability for a Sanitary Landfill Using GIS and Boolean Logic: The Case of the Regional Unit of Chalkidiki, Northern Greece. Environments 2024, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Ministry of Tourism. Empower Mediterranean for Smart Tourism (SMARTMED). Tableau Public. Available online: https://public.tableau.com/app/profile/hellenic.ministry.of.tourism/viz/Final_GR/sheet0_1 (accessed on 6 January 2025). (In Greek).
- El Jeitany, J.; Pacetti, T.; Caporali, E. Evaluating Climate Change Effects on Hydrological Functionality and Water-Related Ecosystem Services. Ecohydrology 2024, 17, e2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffault, J.; Curt, T.; Moron, V.; Trigo, R.M.; Mouillot, F.; Koutsias, N.; Pimont, F.; Martin-StPaul, N.; Barbero, R.; Dupuy, J.-L.; et al. Increased likelihood of heat-induced large wildfires in the Mediterranean Basin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copernicus Emergency Management Service. EFFIS Current Situation Viewer [Internet]. Available online: https://forest-fire.emergency.copernicus.eu/apps/effis_current_situation/ (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Navarro, N. Community Perceptions of Tourism Impacts on Coastal Protected Areas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Chong, X.; Bao, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, S. Fuzzy Comprehensive Assessment Method Based on the Entropy Weight Method and Its Application in the Water Environmental Safety Evaluation of the Heshangshan Drinking Water Source Area, Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Water 2017, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitivattananon, V.; Srinonil, S. Enhancing Coastal Areas Governance for Sustainable Tourism in the Context of Urbanization and Climate Change in Eastern Thailand. Adv. Clim. Change. Res. 2019, 10, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godschalk, D.R. Coastal Zone Management. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Merchán-Sanmartín, B.; Caicedo-Potosí, J.; Bitar, J.B.; Berrezueta, E.; Carrión-Mero, P. A Systematic Review of Coastal Zone Integrated Waste Management for Sustainability Strategies. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Jiang, W.; Hua, T.; Zhao, W. The Research Priorities of Resources and Environmental Sciences. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enemark, T.; Peeters, L.J.M.; Mallants, D.; Batelaan, O. Hydrogeological Conceptual Model Building and Testing: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convertino, M.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Kiker, G.A.; Perz, S.G. Design of Optimal Ecosystem Monitoring Networks: Hotspot Detection and Biodiversity Patterns. Stoch Environ. Res. Risk Assess 2015, 29, 1085–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzafou, A.; Panagopoulos, Y.; Dimitriou, E. Designing the National Network for Automatic Monitoring of Water Quality Parameters in Greece. Water 2019, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebben, M.L.; Werner, A.D.; Graf, T. Seawater Intrusion in Fractured Coastal Aquifers: A Preliminary Numerical Investigation Using a Fractured Henry Problem. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 85, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciopinto, C.; Palmiotta, D. A New Method to Infer Advancement of Saline Front in Coastal Groundwater Systems by 3D: The Case of Bari (Southern Italy) Fractured Aquifer. Computation 2016, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrikaki, O.; Kazakis, N.; Voudouris, K. Vulnerability Map: A Useful Tool for Groundwater Protection: An Example from Mouriki Basin, North Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 2516–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Kazakis, N.; Busico, G.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Voudouris, K. Limitations of GALDIT to Map Seawater Intrusion Vulnerability in a Highly Touristic Coastal Area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 191, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Huang, X.; Cui, X.; Liang, X.; Su, J.; Jin, M. Characterizing the water–rock interactions and groundwater flow processes in the Paleozoic to Cenozoic strata aquifer systems with contrasting mineralogy at basin scale: Qingyi river, east China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625A, 129991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarrah, N.; Walraevens, K. Groundwater Overexploitation and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Areas of Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Water 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getsinger, A.; Rushmer, T.; Jackson, M.D.; Baker, D. Generating High Mg-numbers and Chemical Diversity in Tonalite-Trondhjemite-Granodiorite (TTG) Magmas during Melting and Melt Segregation in the Continental Crust. J. Petrol. 2009, 50, 1935–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gari, S.R.; Newton, A.; Icely, J.D. A Review of the Application and Evolution of the DPSIR Framework with an Emphasis on Coastal Social-Ecological Systems. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 103, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jago-on, K.A.B.; Kaneko, S.; Fujikura, R.; Fujiwara, A.; Imai, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Zhang, J.; Tanikawa, H.; Tanaka, K.; Lee, B.; et al. Urbanization and Subsurface Environmental Issues: An Attempt at DPSIR Model Application in Asian Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3089–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, E.D.; Evans, D.M.; Atkins, J.P. Investigating the impacts of climate change on ecosystem services in UK agro-ecosystems: An application of the DPSIR framework. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Cao, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, B.; Teng, Y.; Li, X. Elevated Fe and Mn Concentrations in Groundwater in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China, and the Factors and Mechanisms Involved. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophare, A.M.; Lamsoge, B.R.; Katpatal, Y.B.; Nawale, V.P. Impact of over-exploitation on groundwater quality: A case study from WR-2 Watershed, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 1541–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammadova, L.; Negri, S. Understanding the impacts of overexploitation on the Salento aquifer: A Comprehensive review through well data analysis. Sustain. Futures 2024, 7, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, A.; Cayuela, M.L.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. An overview on olive mill wastes and their valorisation methods. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumb, A.; Sharma, T.C.; Bibeault, J.-F. A Review of Genesis and Evolution of Water Quality Index (WQI) and Some Future Directions. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2011, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Frostell, B. The DPSIR Framework and a Pressure-Oriented Water Quality Monitoring Approach to Ecological River Restoration. Water 2012, 4, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.; Fernández Escalante, E.; Megdal, S.B.; Massmann, G. Managed Aquifer Recharge for Water Resilience. Water 2020, 12, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelpidou, N.; Cartalis, C.; Karkani, A.; Saitis, G.; Philippopoulos, K.; Spyrou, E. A GIS-Based Assessment of Flood Hazard through Track Records over the 1886–2022 Period in Greece. Climate 2023, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Cui, P.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, B. Analysis of Regional River Blocking by Debris Flows in Response to Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Alexander, D. Integrated Flood Risk Assessment of River Basins: Application in the Dadu River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Omar, P.J.; Shekhar, S.; Gupta, S. Study of acidic air pollutant (SO2 and NO2) tolerance of microalgae with sodium bicarbonate as growth stimulant. AQUA—Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2023, 72, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tian, D.; Yan, F. Effectiveness of Entropy Weight Method in Decision-Making. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 1–5, 3564835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.; Carrasco, A.R.; Vila-Concejo, A.; Ferreira, Ó.; Dias, J.A. A Coastal Management Program for Channels Located in Backbarrier Systems. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2007, 50, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Li, L.; Yu, H.; Jin, R.; Zhu, W. Ecological Security Evaluation of Wetlands in Changbai Mountain Area Based on DPSIRM Model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| pH | T (°C) | EC (μS/cm) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | 8.4 | 19.8 | 6450 | 400.8 | 163.0 | 420.0 | 256.0 | 453.9 | 1453.9 | 257.0 | 16.9 |
| Min. | 6.9 | 16.9 | 358 | 5.3 | 3.36 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 28.0 | 13.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Mean | 7.6 | 19.2 | 663 | 51.4 | 11.4 | 54.5 | 3.0 | 182.5 | 93.6 | 33.4 | 3.0 |
| SD | 0.4 | 0.70 | 119 | 80.1 | 37.9 | 91.8 | 50.9 | 106.6 | 324.7 | 50.4 | 3.3 |
| Mg2+/Ca2+ | Na+/K+ | Na+/Cl− | Cl−/SO42− | (Ca2+ + Mg2+)/(Na+ + K+) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | 19.98 | 97.82 | 1.48 | 186.58 | 7.05 |
| Min. | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.91 | 0.61 |
| Mean | 0.35 | 27.90 | 0.90 | 3.80 | 1.38 |
| SD | 3.88 | 24.33 | 0.30 | 30.50 | 1.23 |
| Driving Force | Pressure | State | Impact | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protected areas |
|
|
|
|
| Urbandevelopment |
|
|
|
|
| Tourism |
|
|
|
|
| Climate variation |
|
|
|
|
| Topography |
|
|
|
|
| Geology |
|
|
|
|
| Agricultural and livestock activities |
|
|
|
|
| Industrial activity |
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parastatidou, E.; Ntona, M.M.; Kazakis, N.; Pliakas, F.-K. Coupling Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response–Management Framework with Hydrochemical Data for Groundwater Management on Sithonia Peninsula, Greece. Geosciences 2025, 15, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15010024
Parastatidou E, Ntona MM, Kazakis N, Pliakas F-K. Coupling Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response–Management Framework with Hydrochemical Data for Groundwater Management on Sithonia Peninsula, Greece. Geosciences. 2025; 15(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleParastatidou, Eleni, Maria Margarita Ntona, Nerantzis Kazakis, and Fotios-Konstantinos Pliakas. 2025. "Coupling Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response–Management Framework with Hydrochemical Data for Groundwater Management on Sithonia Peninsula, Greece" Geosciences 15, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15010024
APA StyleParastatidou, E., Ntona, M. M., Kazakis, N., & Pliakas, F.-K. (2025). Coupling Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response–Management Framework with Hydrochemical Data for Groundwater Management on Sithonia Peninsula, Greece. Geosciences, 15(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15010024







