Abstract
This study evaluated the applicability of natural zeolite for the removal of the NH-forms in the enzyme-mediated calcite precipitation technique. The natural zeolite of mordenite was added to prepared grouting solutions composed of urea and urease and mixed thoroughly using a rotation table for the mixing times of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 h. Then, the concentrations of evolving NH-forms in the solutions were measured. The effects of the presence of zeolite on the amount and the mineralogical substance of the precipitated minerals were also evaluated by X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopy analyses. Sand samples were treated with the grouting solutions containing zeolite, and the improvement in strength was assessed. It was found that utilizing zeolite in grouting solutions can reduce the concentration of NH-forms. A significant reduction in the concentration of NH-forms was obtained. The addition of 10 g natural zeolite/L solution, combined with the 2-h mixing time, resulted in removal efficiencies of 75% and 45% in reagent concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mol/L, respectively. Mechanical test results showed that the grouting solutions also brought about a significant improvement in the soil strength. A precipitated material, comprising 9% of the sand mass, was produced by three pore volume (PV) injections of the grouting materials, which showed an unconfined compressive strength of 300 kPa.
1. Introduction
Calcite precipitation techniques have been proposed as the alternative method for improving the engineering properties of soil [1,2,3,4]. Enzyme-mediated calcite precipitation (EMCP) may be one of the promising methods [4,5,6,7,8]. The unconfined compressive strength of treated sand ranging from 200 kPa to 1.6 MPa, depending upon the amount of precipitated calcite can be achieved, and the permeability of the improved samples can be reduced by more than one order of magnitude [4,5,9]. In this technique, an enzyme of urease is employed to dissociate the urea into ammonium and carbonate ions. The produced carbonate ions are precipitated as calcium carbonate crystals in the presence of calcium ions [10]. The reactions of the urea hydrolysis and the calcite formation are shown in Equations (1)–(5).
The EMCP technique produces ammonia and ammonium as the byproduct of urea hydrolysis (see Equations (1) and (2)). The hydration of ammonia gas increases the pH, and hence, promotes the calcination process (see Equation (2)) [11,12]. However, ammoniums are poisonous at high concentrations, and their toxicity may contaminate the soil [13,14]. For example, in Japan, wastewater should not contain an ammonium concentration more than 100 g/L [15]. Hence, the removal of ammonia and ammonium without compromising the applicability of EMCP as a soil-improvement technique is a great challenge in terms of developing an environmentally friendly soil improvement method.
Several methods for ammonium removal, such as nitrification, ammonia stripping, chemical precipitation, and ion exchange, have been proposed as potential methods [16,17]. The ion exchange method uses an absorbent of natural zeolite and has been confirmed as a promising technique for ammonia removal [17,18,19,20,21,22]. The use of natural zeolite for ammonia removal is considered to be a competitive and effective method [23,24,25,26]. Natural zeolite has a unique structure, large internal cavities, and entry channels [17]. It is proved to have high cation exchange capacity, cation selectivity, higher void volume, and a great affinity for ammonium (NH4+) and other cations [18,27,28,29]. It is also low in cost and independent of temperature [18,19,22,27]. The general formula for natural zeolite is . M+ and M2+ are exchangeable cations (i.e., Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and/or Ba2+). Al and Si are known as structural cations which develop the framework of the structure with O [22,30]. The ion-exchange behavior of natural zeolite depends on several factors: the framework structure, the ion size, the shape, the charge density of the anionic framework, the ionic charge, and the concentration of the external electrolyte solution [24]. The rate of the ion exchange process using zeolite can be increased by the intensity of the mixed solution and by the augmentation of the concentration and temperature of the solution [30].
In this study, the applicability of natural zeolite as an ammonia and ammonium removal method in the EMCP technique was evaluated. The natural zeolite of mordenite was used in the preparation of grouting materials. It was added and mixed thoroughly for several mixing times, and the evolution of the total ammonia and ammonium concentration was evaluated. The effects of the utilization of natural zeolite on the EMCP parameters (i.e., the precipitated amount, the pH, the mineralogy of the precipitated minerals, and the improved strength of the treated sand) were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zeolite
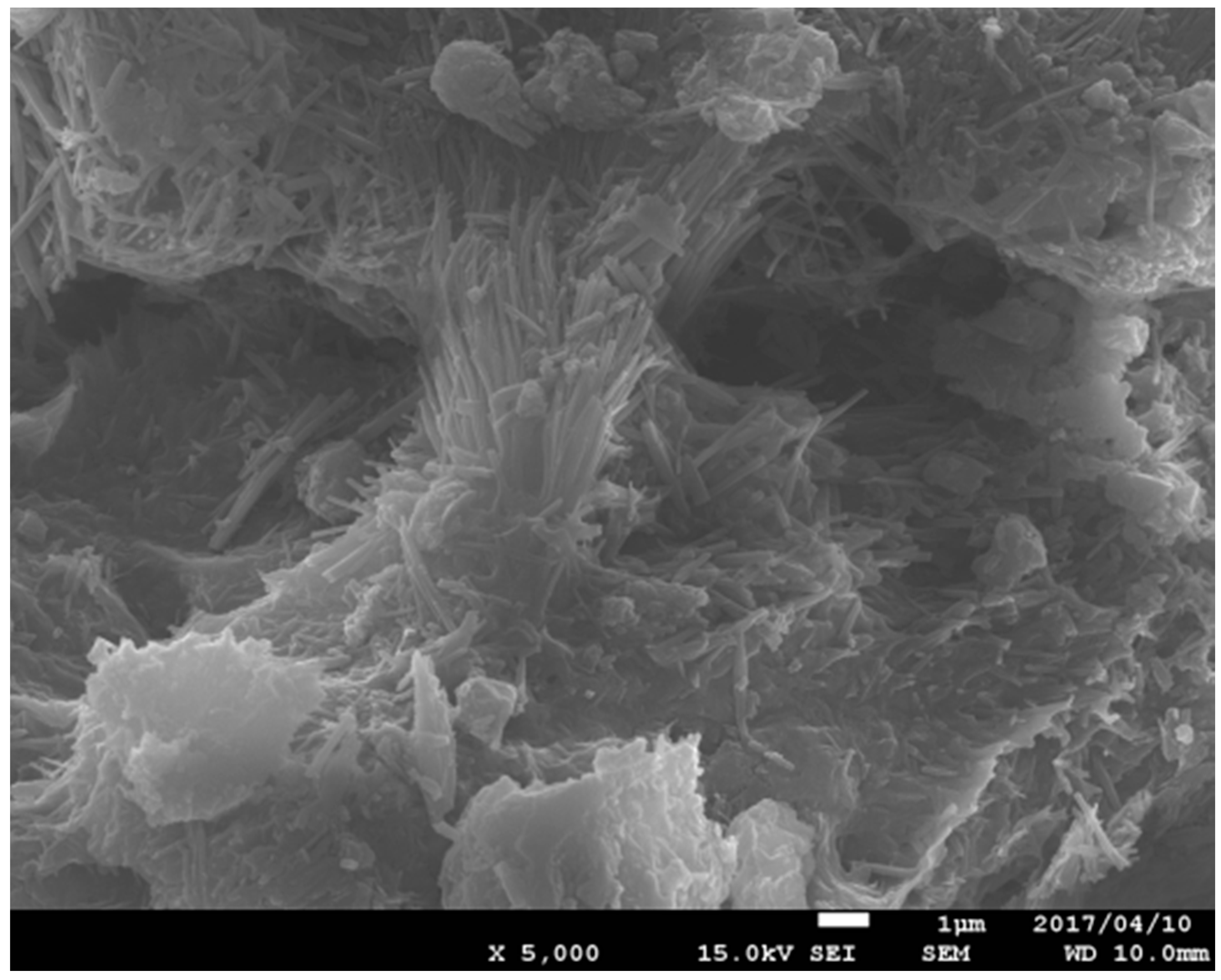
The natural zeolite of mordenite from Izumo, Shimane Prefecture, Japan, with grain sizes of 0.25–1.00 mm, was obtained from Sinkou Sunrise Co., Ltd. (Matsue, Japan). The mineral composition and the morphology of mordenite are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1, respectively.

Table 1.
Mineral composition of natural zeolite of mordenite [31].
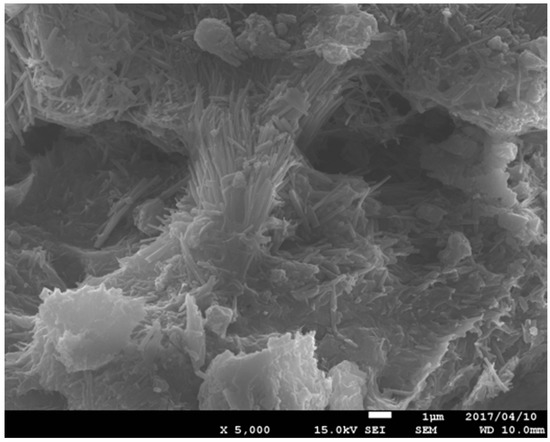

Figure 1.
Morphology of natural zeolite of mordenite.
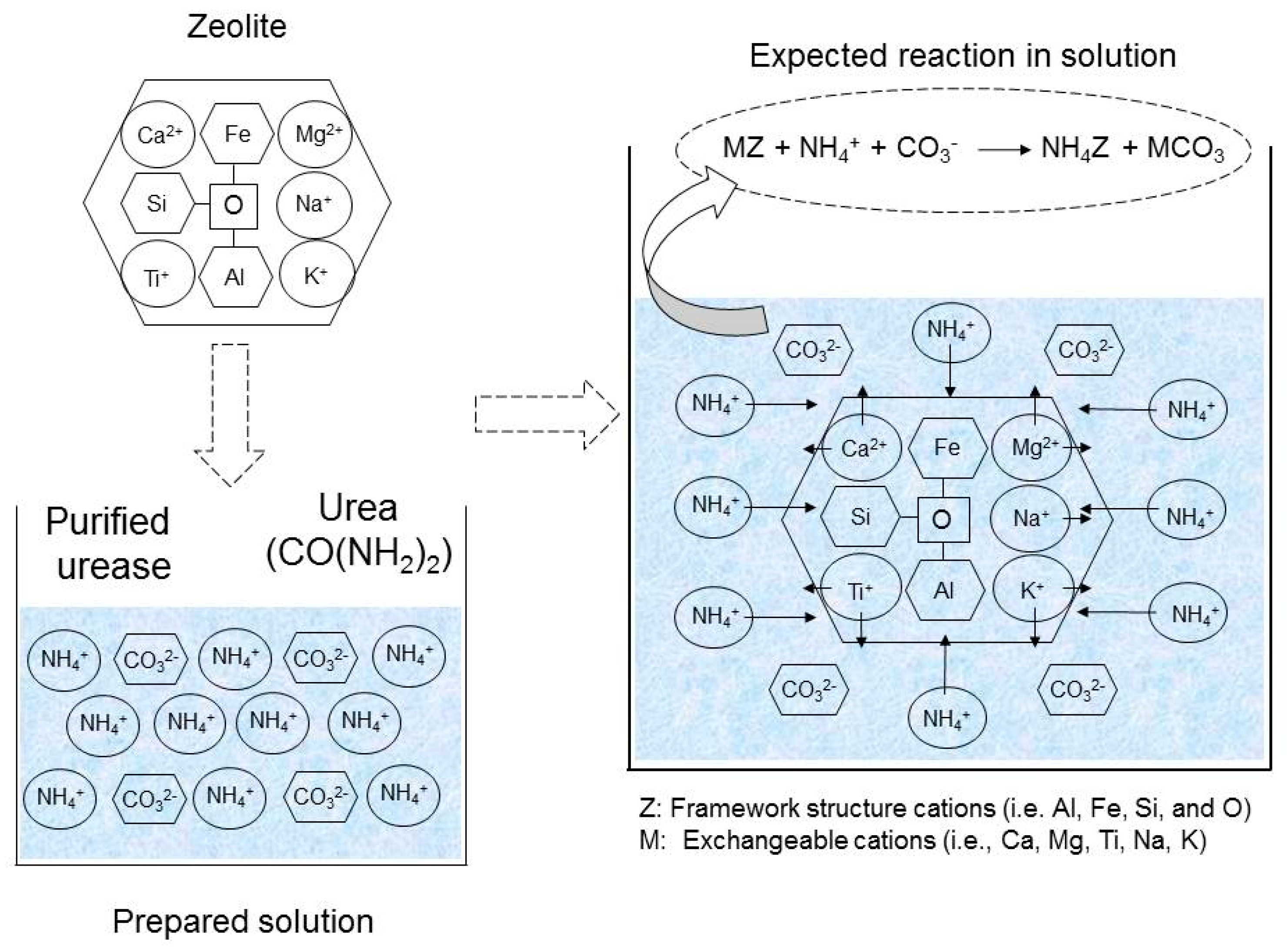
The addition of natural zeolite to the grouting solution is expected to cause the adsorption of the produced ammonium ions [32]. Exchangeable cations from the zeolite may also be released into the system and bound with the carbonate ions. The expected mechanism of the ion exchange process and the reaction are illustrated in Figure 2.
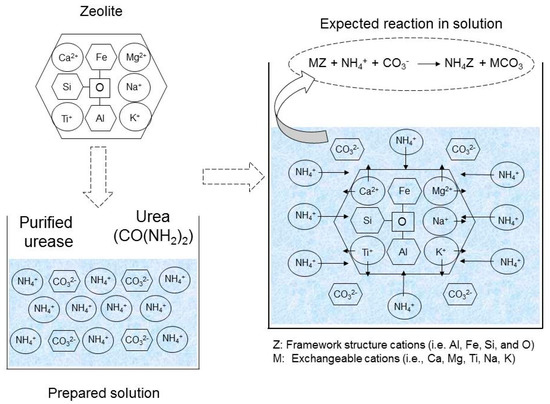
Figure 2.
Expected mechanism of ion exchange process and the reaction in the presence of zeolite.
2.2. Grouting Materials
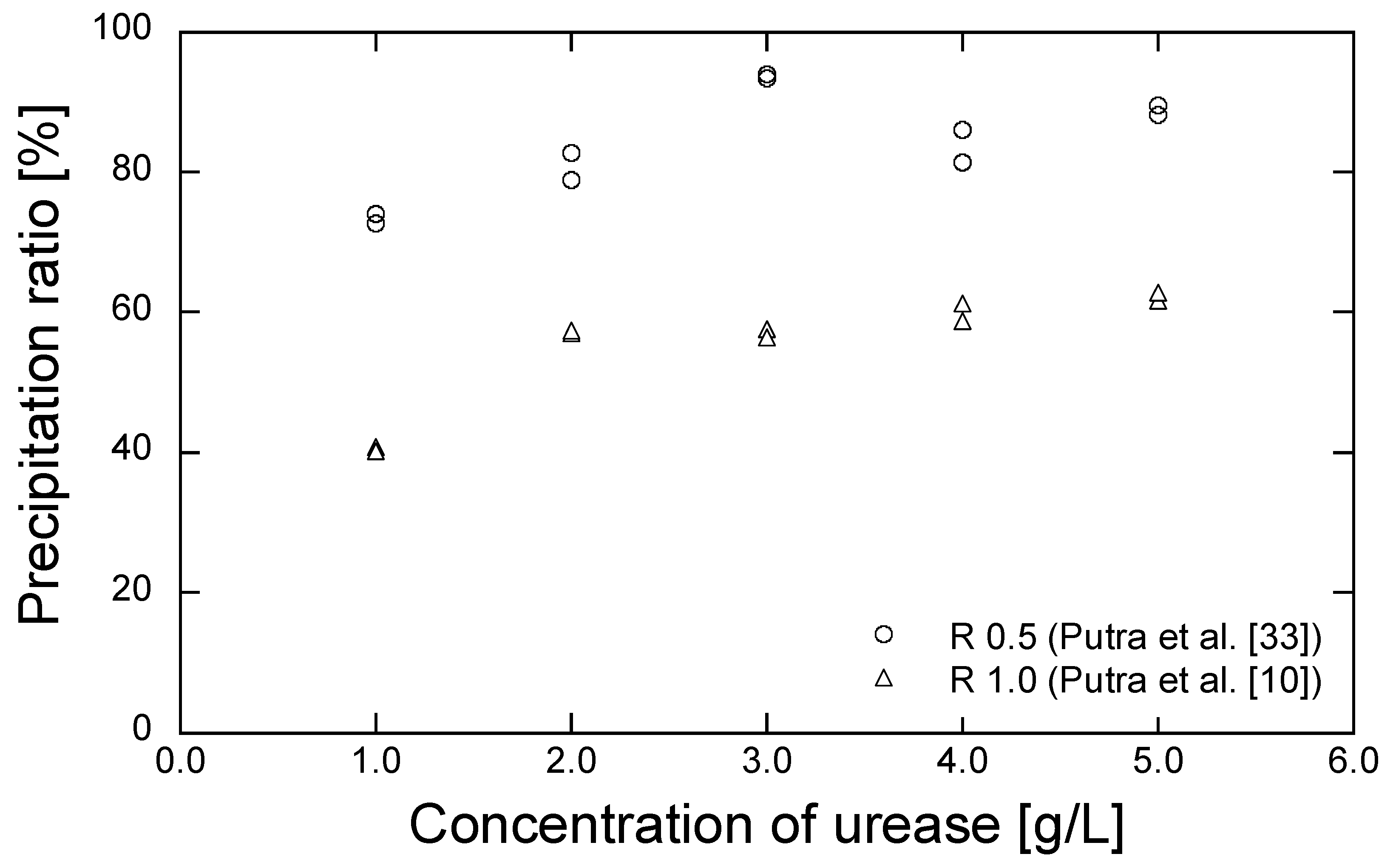
The grouting materials adopted for the EMCP technique are composed of urea, CaCl2, and urease. In this study, the urea and CaCl2 were obtained from Kanto Chemical (Tokyo, Japan), while the enzyme urease (020-83242, Kishida Chemical, Osaka, Japan) with the urease activity of 2950 U/g, was purified from jack bean meal. The precipitated amount, corresponding to the different combinations of reagent and urease concentrations, were evaluated in our previous work [10,33]. Urease with concentrations of 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 g/L were used to dissociate the 0.5 and 1.0 mol/L of urea in the mixed solution of the reagent composed of urea-CaCl2. The test tube results are shown as a precipitation ratio: the ratio of the actual mass of precipitated minerals to the theoretical mass of the maximum precipitation of CaCO3 in a solution of 30 mL, in Figure 3 [10,33]. The reagent concentration of 0.5 mol/L produced a higher precipitation ratio than that of 1.0 mol/L. A precipitation ratio of 70% was obtained with the urease concentration of 1.0 g/L. With the reagent concentration of 1.0 mol/L, the precipitated ratio increased when 2.0 g/L of urease were added. However, a further increase in urease concentration had no significant impact on the precipitation ratio. Hence, urease concentrations of 1.0 and 2.0 g/L were selected to dissociate the reagents with concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mol/L, respectively. The conditions of the selected grouting materials are shown in Table 2.
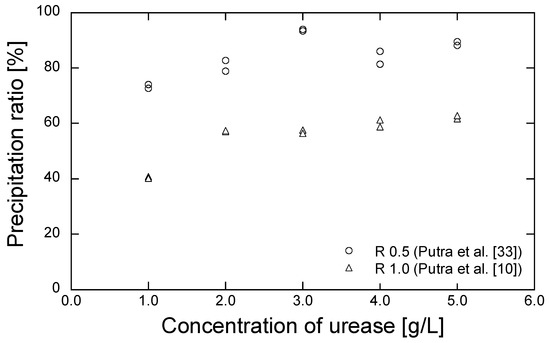
Figure 3.
Precipitation ratio results for several concentrations of urease [10,33].

Table 2.
Selected grouting materials.
2.3. Experimental Procedures
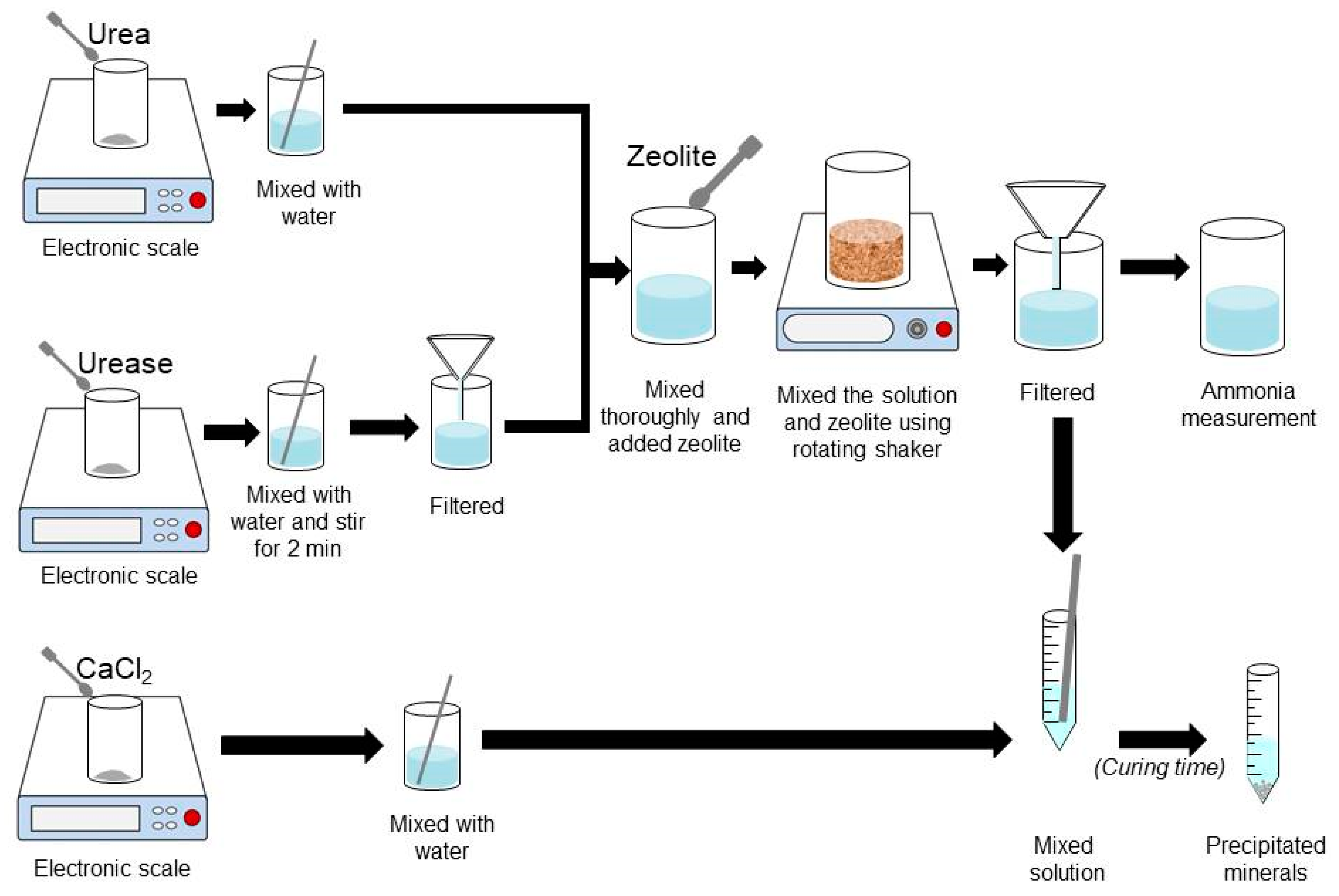
The sample preparation procedure, developed by Putra et al. [34], was adopted in this work. Urea was mixed thoroughly with distilled water. Urease, with concentrations of 1.0 and 2.0 g/L, were then mixed into the distilled water for 2 mins and filtered using filter paper (pore size of 11 μm) to remove the undissolved particles of urease. The purified urease solution was mixed thoroughly with the urea solution in a total solution of 75 mL. Various concentrations of natural zeolite were added to the prepared solutions composed of urea-urease and stirred together for the mixing times of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 h. In this work, the maximum mixing time was set to be 2 h because gel-like precipitation formed when the CaCl2 solution was added to the filtered solutions if the mixing time was greater than 2 h. After the mixing process (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 h after stirring), the solution composed of urea, urease, and zeolite was filtered using filter paper (pore size of 11 μm) to remove the zeolite.
In the present study, the ammonia ion selective electrode (i.e., ammonium ion meter TiN9001K-SR, TOKO Chemical Laboratories Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used to measure the total concentration of produced ammonia and ammonium ion in grouting solution. Ammonia selective electrodes are gas-sensing electrodes, which can evaluate the concentration of NH4+ based on measured NH3 and pH. Therefore, the grouting solution containing both of ammonia and ammonium, and all the ammonium were converted to ammonia by pH adjusting. “NH-forms” is used to express the total of ammonia (i.e., the existing NH3 and converted NH3 from NH4+) in the solution. The experimental procedure for the sample preparation and NH-forms measurement are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
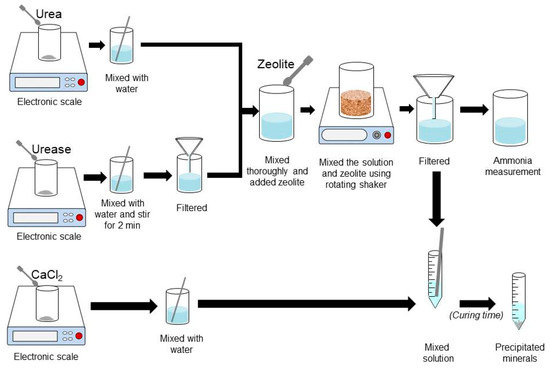
Figure 4.
Procedure for sample preparation for NH-forms measurement and precipitation tests.
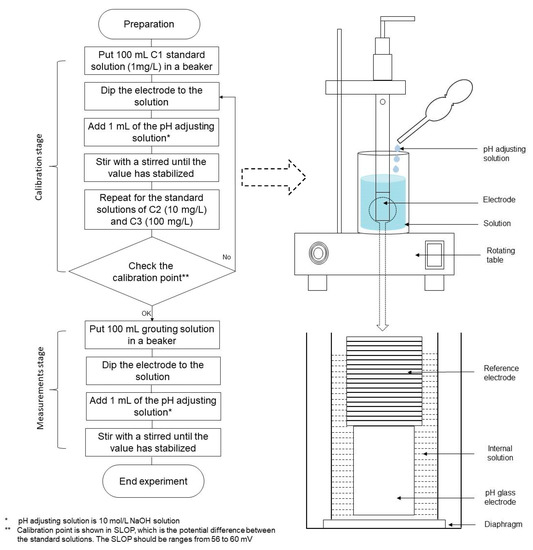
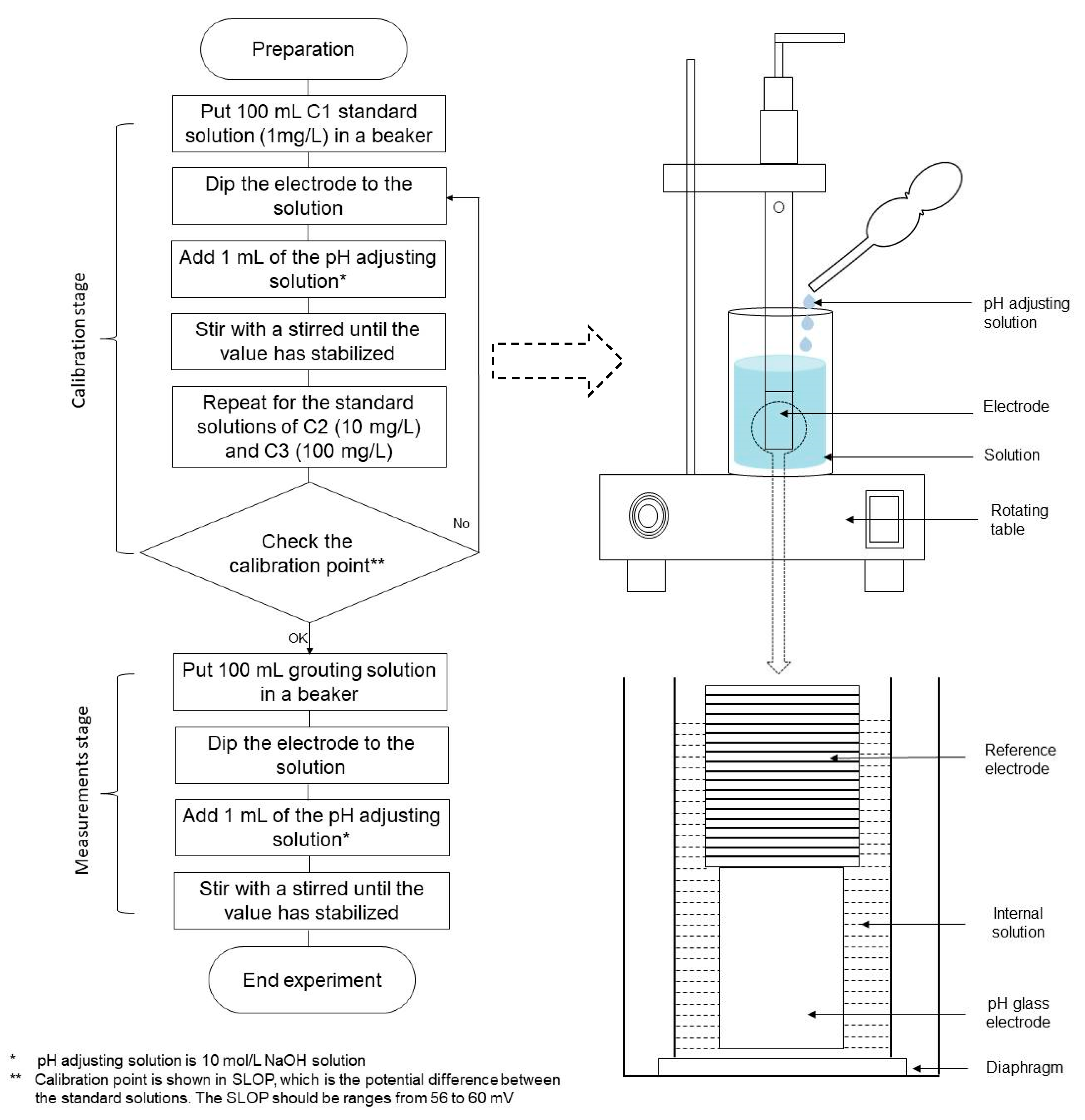
Figure 5.
Experimental procedure and setup for NH-forms measurement [35].
In this work, three-point calibration was conducted with the standard solutions containing the fixed amount of ammonium ions mixed within distilled water, namely, C1 (1 mg/L), C2 (10 mg/L), and C3 (100 mg/L). In the measurement stage, all the grouting solutions were diluted 10–100 times to make the concentrations measurable by the ammonium ion meter. Prior to the measurements, the pH of each grouting solution was adjusted to 11 or more by adding the pH adjusting solution (i.e., 10 mol/L NaOH). Hence, ammonium ions (NH4+) in the solution are converted to the ammonia gas (NH3), as shown in the Equation (2) [35]. When the electrode is immersed in the solution, ammonia gas passes through the hydrophobic diaphragm and the internal solution. The equilibrium of the reaction is expressed in Equation (6).
When the concentration of ammonium ions in the internal solution is assumed to remain constant, Equation (6) can be change to Equation (7).
Equation (7) shows the proportional correlation between the concentration of ammonia gas and hydroxide ion (pH). By using this correlation, ammonia electrode in the device measure the concentration of ammonium ions indirectly by adopting the pH electrode as the internal electrode [35].
The pH measurements were also performed to observe the evolution of the pH during the precipitation process. The evolving pH was measured using a pH meter (LAQUAact D-73, Horiba Scientific, Ltd., Kyoto, Japan). NH-forms and pH measurements were also performed for grouting solutions without zeolite. Precipitation tests were conducted to evaluate the effect of the presence of the zeolite during the sample preparation on the amount of precipitated minerals. Calcium chloride was mixed with distilled water and added to the filtered grouting solution. Two identical tests were conducted for each condition to check the reproducibility. The experimental conditions for the NH-forms measurements and the precipitation tests are shown in Table 3. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses were also conducted evaluate the effect of the utilization of natural zeolite on the mineralogy of the precipitated materials.

Table 3.
Experimental conditions for NH-forms measurement and precipitation tests.
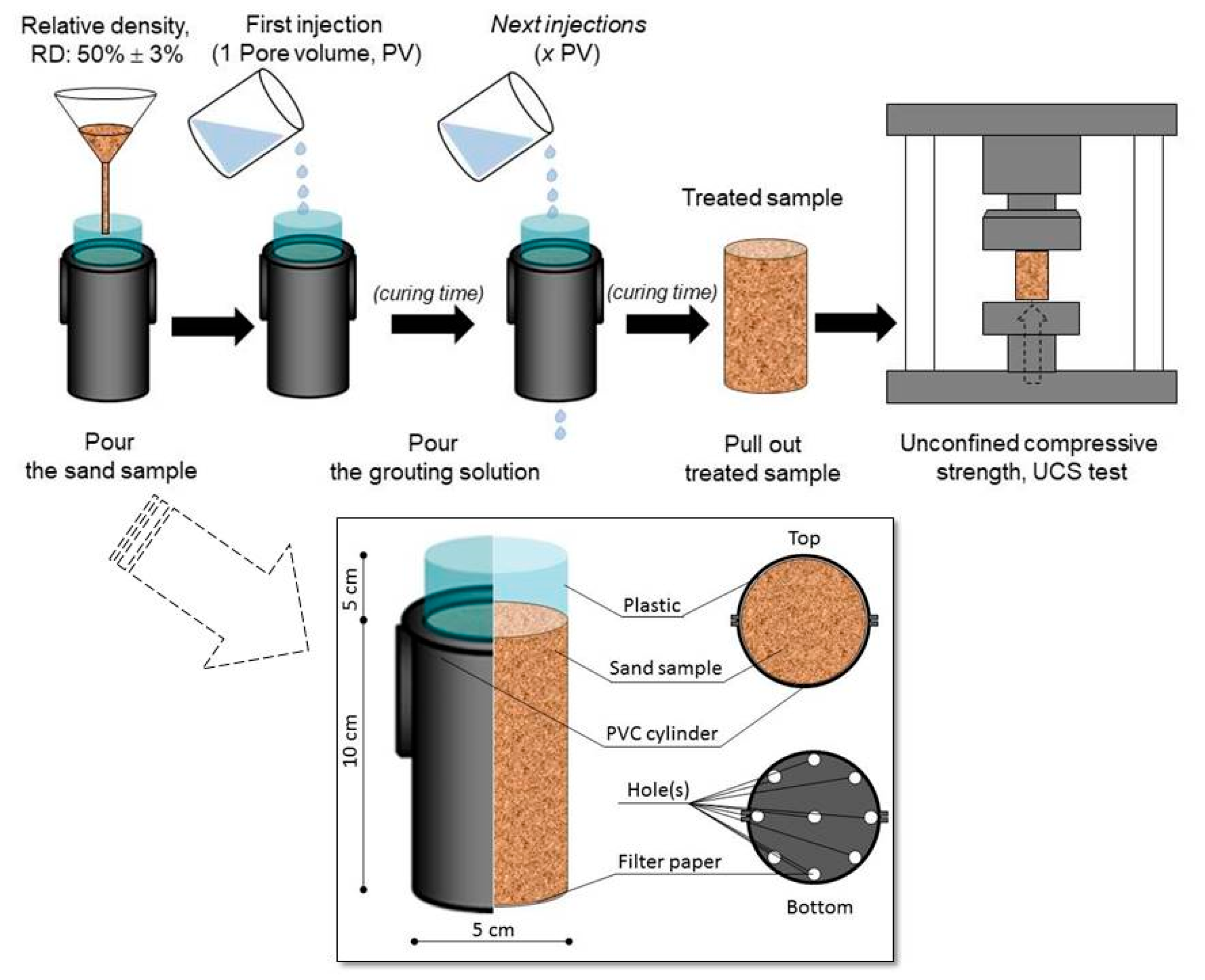
Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) tests were performed to evaluate the applicability of the grouting materials for improving the soil strength. The experimental procedures developed by Putra et al. [10] were followed in this work. Sand specimens of silica sand with emax, emin, coefficient of uniformity (CU), and specific gravities (Gs) of 0.899, 0.549, 1.550, and 2.653, respectively, were used in this study. The PVC cylinders with 5 cm in diameter and 10 cm in height were prepared, and 300 g of sand was poured into the cylinders to obtain a relative density, RD of 50%. The fixed volume of the solution composed of calcium chloride and filtered solution (urea-urease after the addition of zeolite) were injected into the prepared sand samples. The procedure of PVC cylinder test is shown in Figure 6 [10]. The injected volume was controlled by the number of pore volumes (PVs), the amount of one PV being ~75 mL. The sand samples were treated with one to three PVs for a three-day curing time. The acid leaching method was used to evaluate the amount of precipitated calcite within the sand samples [4,5,34,36]. Finally, by comparing the relation between the precipitated amount and the UCS obtained in this study, with those obtained from the literature, the effects of the utilization of zeolite during the sample preparation in the EMCP technique were evaluated.
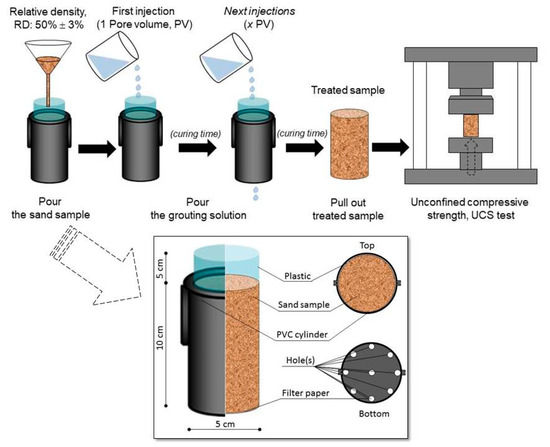
Figure 6.
Procedure of PVC cylinder tests [10].
3. Results and Discussion
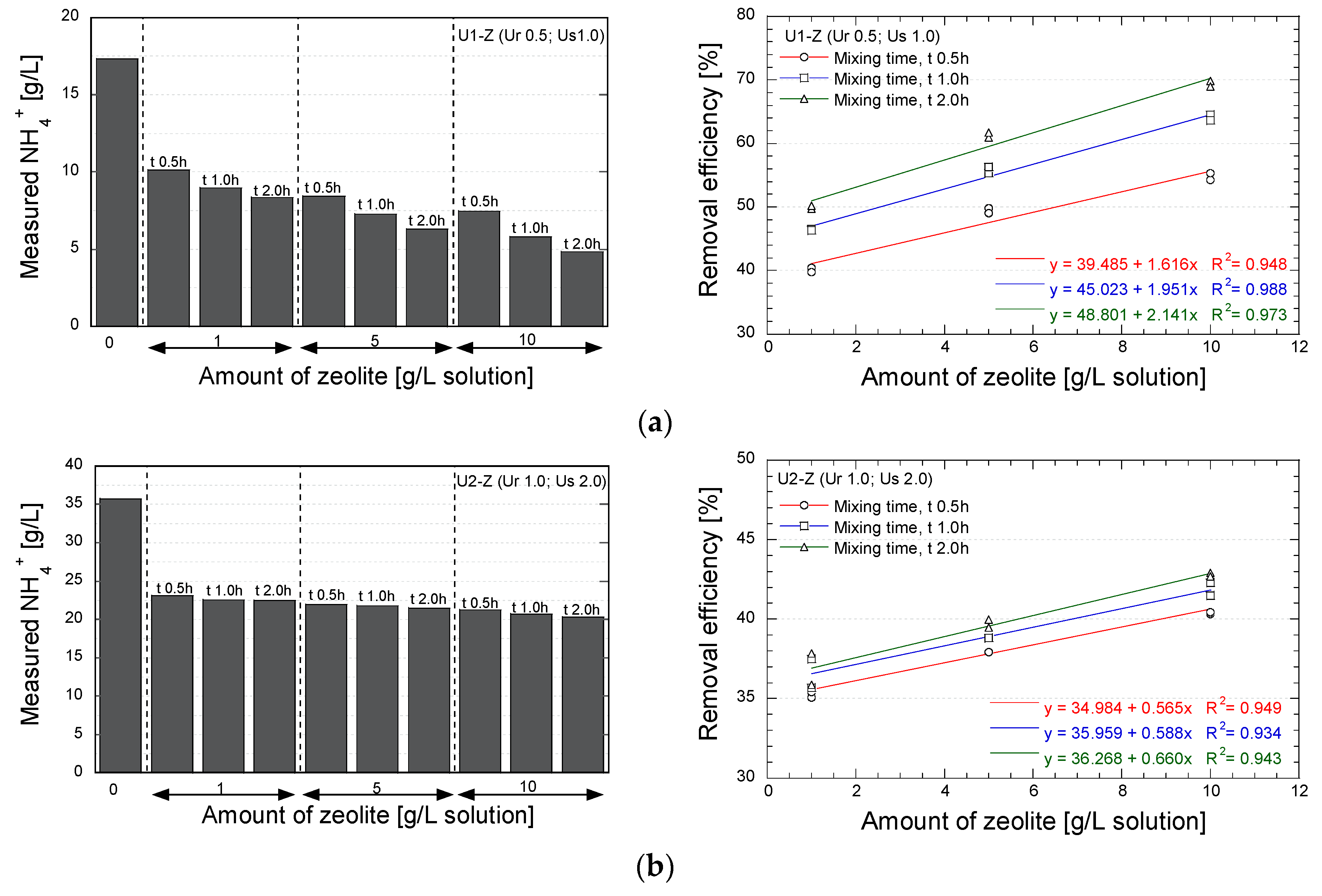
The applicability of natural zeolite for reducing the concentration of NH-forms in the EMCP technique was evaluated. The measurements were conducted after the concentration NH-forms became stable (i.e., when the maximum values were obtained), which were 24 and 48 h after the mixing process for the urea concentration of 0.5 and 1.0 mol/L, respectively. Figure 7 shows the final concentration and the removal efficiency of NH-forms for several concentrations of zeolite and several mixing times.
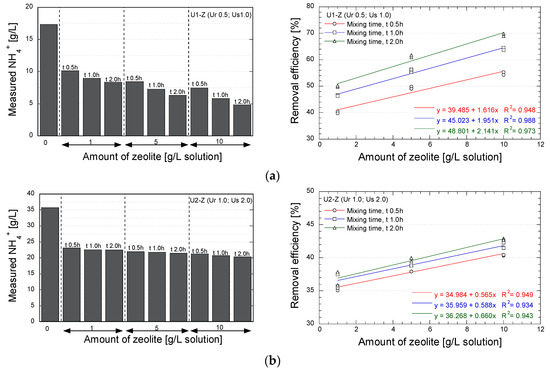
Figure 7.
Results of NH-forms measurements; (a) Urea 0.5 mol/L; urease 1.0 g/L; (b) Urea 1.0 mol/L; urease 2.0 g/L.
As is apparent, the utilization of zeolite significantly reduced the NH-forms. In case U1-Z (Figure 7a), with reagent and urease concentrations of 0.5 mol/L and 1.0 g/L, respectively, a removal efficiency of 75% of the maximum theoretical concentration was obtained by mixing 10 g zeolite/L solution for 2.0 h. The concentration of zeolite and the mixing time were found to significantly affect the decrease in NH-forms. In case U2-Z (Figure 7b), which produced more NH-forms, the application of zeolite brought about the NH-forms removal of 45% of the maximum theoretical concentration. In this case, the mixing time had no significant effect on the removal efficacy of the zeolite. The relation between the removal efficiency and the concentration of zeolite indicated that the effectivity of the natural zeolite to remove NH-forms could be increased by increasing the amount of zeolite, notably in the lower concentration of urea-urease.
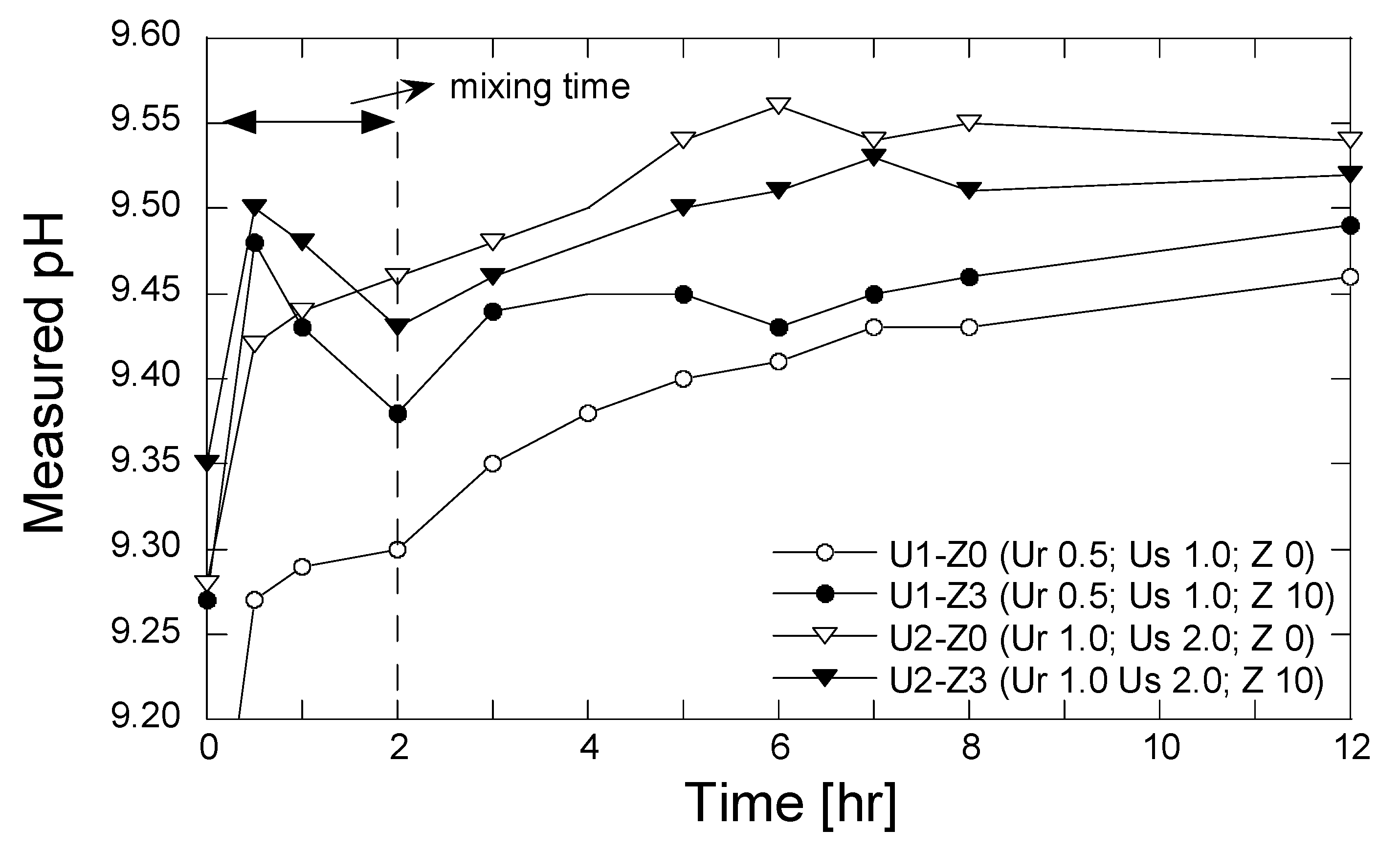
The measurements of pH were conducted for the grouting solutions that were treated by the zeolite 10 g/L solution with a mixing time 2.0 h. The evolving pH of the grouting solution without the zeolite treatment was also conducted to evaluate the effect of zeolite on the pH change. The evolving pH was measured 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, and 12.0 h after the grouting solution was prepared. The results of the pH measurement are shown in Figure 8.
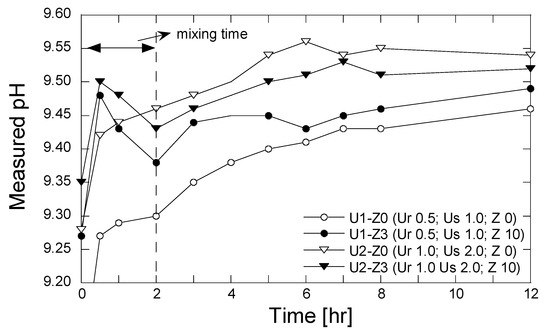
Figure 8.
Evolution of pH with time.
As is apparent, the pH increased rapidly after 0.5 hr. The presence of zeolite during the mixing process resulted in a higher pH of the solution. The increase in pH may be attributed to the effects of both the production of ammonium occurring after the urea hydrolysis and the releasing of OH− ions from the zeolite structure. The existence of alkali and alkaline metal (K, Na, Ca, and Mg) in zeolite form hydroxide ions when dissolved in water [37]. In contrast, the pH decreased during the period of 0.5–2.0 h, which may be attributed to the convolved phenomena of ion exchange and secondary mineral precipitation. After the mixing process was finished and the zeolite was taken out, the measured pH again increased and approached the steady state. In comparison to the measured pH of the grouting solution without zeolite, the pH increased gradually with time from the beginning. The increase in pH is attributed likely to the production of the ammonium and OH− ions (see Equation (2)).
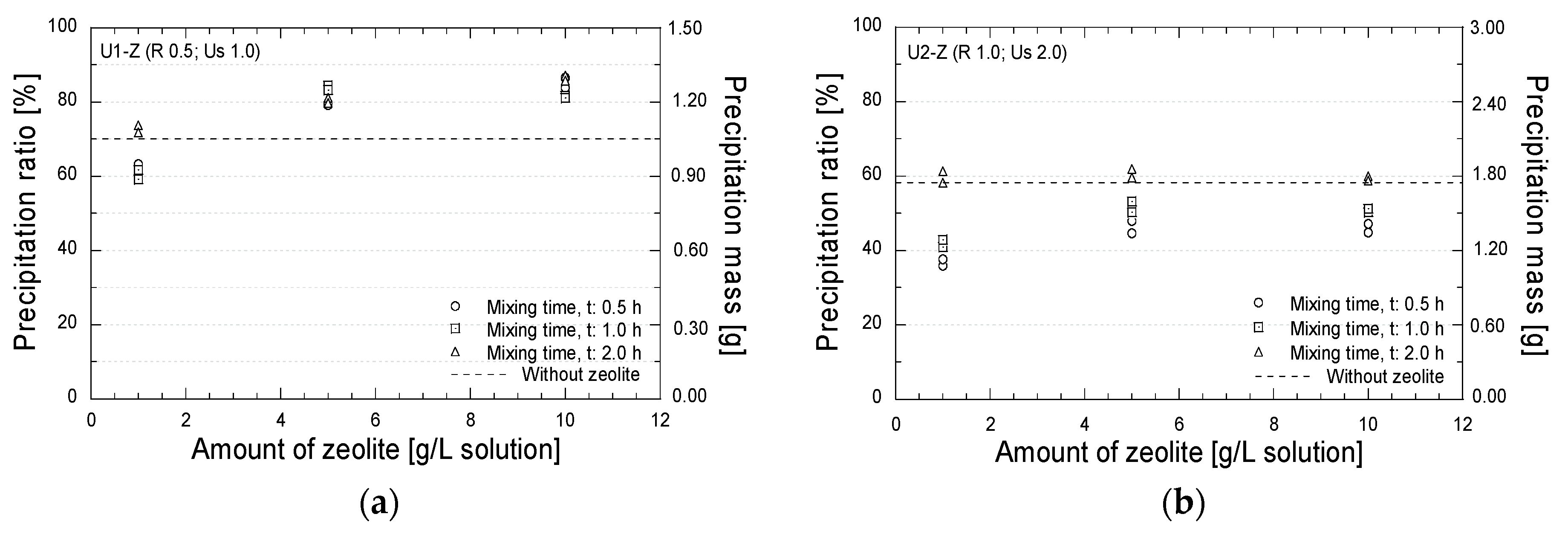
Test tube experiments were also conducted to evaluate the effect of the presence of zeolite during the mixing process on the amount and the mineralogy of the precipitated minerals. Figure 9 shows the relation between the precipitated amounts and the amount of zeolite with the different mixing times. In case U1 (Figure 9a), with the reagent and urease concentrations of 0.5 mol/L and 1.0 g/L, respectively, a higher precipitation amount than that without zeolite (dashed line) was obtained. A precipitated ratio of 80% was achieved by the addition of zeolite of 5 and 10 g/L solution. The increase in the precipitated amount might have been caused by the ion exchange process. The free calcium and magnesium ions from the zeolite might have been bound to the carbonate ions obtained from the urea hydrolysis; hence, the precipitated amount further increased (see Figure 2). In case U2 (Figure 9b), the addition of zeolite with the mixing times of 0.5 and 1.0 h decreased the precipitation amount. However, when the mixing time was increased to 2.0 h, the similar precipitated amounts with that without zeolite were obtained. The longer mixing time might have allowed the ion exchange process and have promoted reactions between potentially exchangeable cations released from zeolite (i.e., Ca2+ and Mg2+) and the carbonate ions.
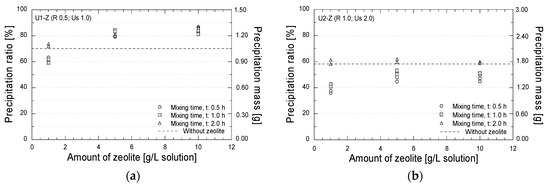
Figure 9.
Precipitation test results; (a) Reagent 0.5 mol/L; urease 1.0 g/L; (b) Reagent 1.0 mol/L; urease 2.0 g/L.
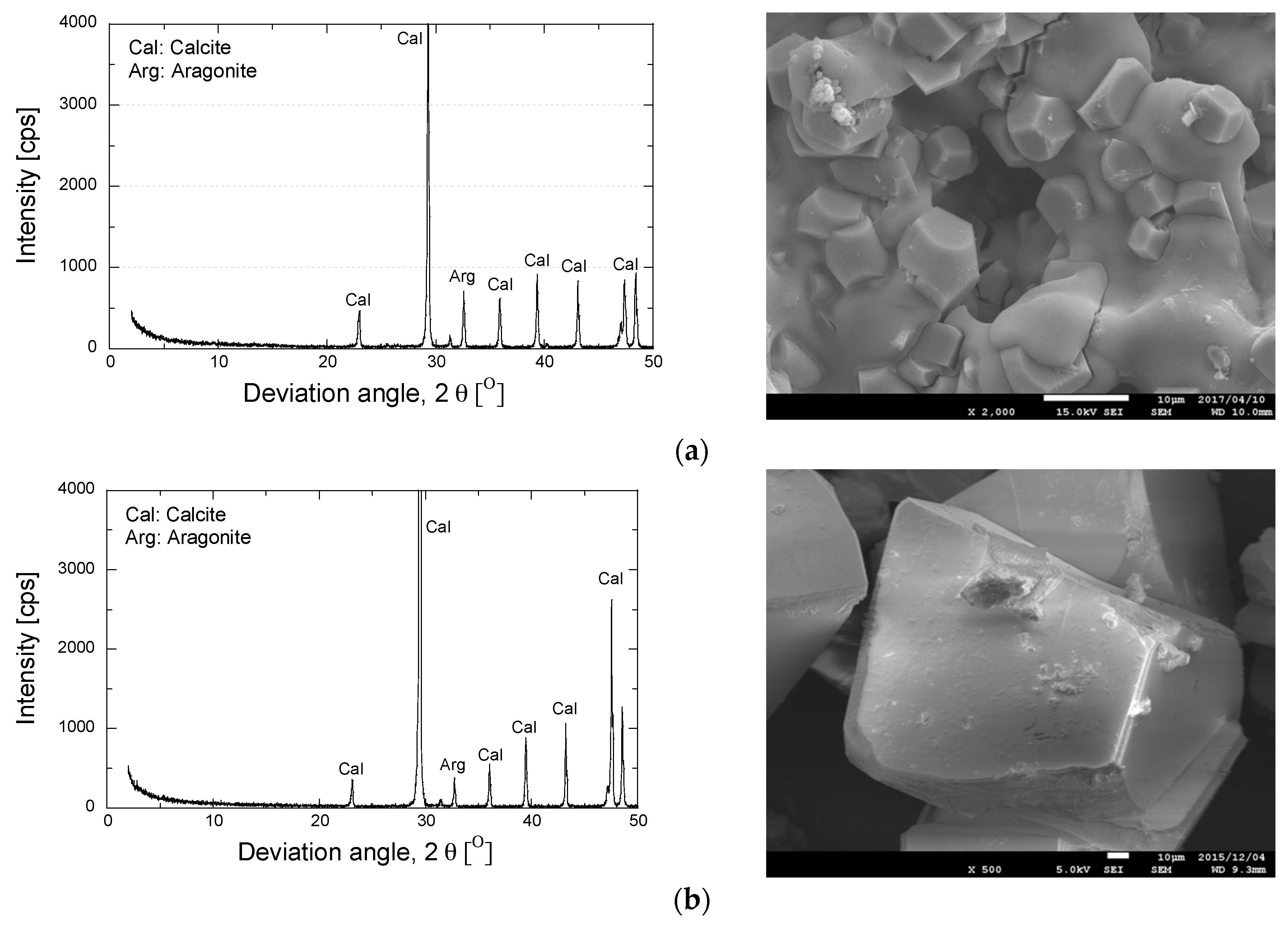
XRD and SEM analyses were performed to evaluate the effect of the utilization of zeolite in the preparation of the grouting solution on the resulting minerals and the shapes of the precipitated materials. Figure 10 shows the XRD pattern and the SEM image for the precipitated materials.
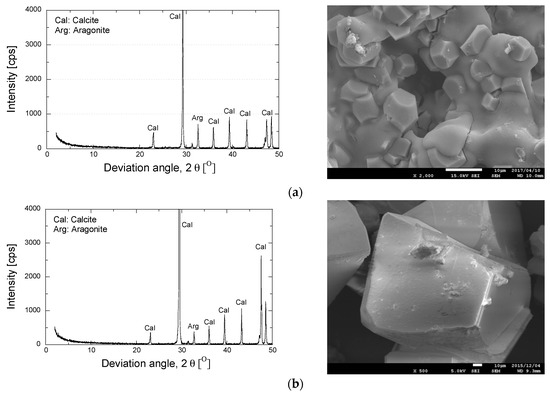
Figure 10.
Results of mineralogy and morphology analyses of precipitated minerals. (a)Treated solution; (b)EMCP crystal/non-treated solution [34].
As is apparent, the use of zeolite has no significant effect on the mineralogical substance. Similar XRD patterns were obtained in both cases (a) and (b). Moreover, the presence of zeolite in the grouting solution was found to modify the shape of the precipitated materials. The agglomeration form was obtained in addition to the rhombohedral crystal. The utilization of zeolite also reduced the crystal size of the precipitated materials. The release of exchangeable cations of zeolite (e.g., Mg2+) might have contributed to the evolution of the crystal form. As reported by Putra et al. [34], the substitution of magnesium promoted the agglomeration formation and significantly reduced the crystal size of the precipitated minerals [34].
The improvement in strength of the treated sand was also evaluated through UCS tests. The selected zeolite concentration of 10 g/L was added to the grouting solution and mixed for a mixing time of 2.0 h. The experimental conditions for the UCS tests are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Experimental conditions for unconfined compressive strength (UCS) tests.
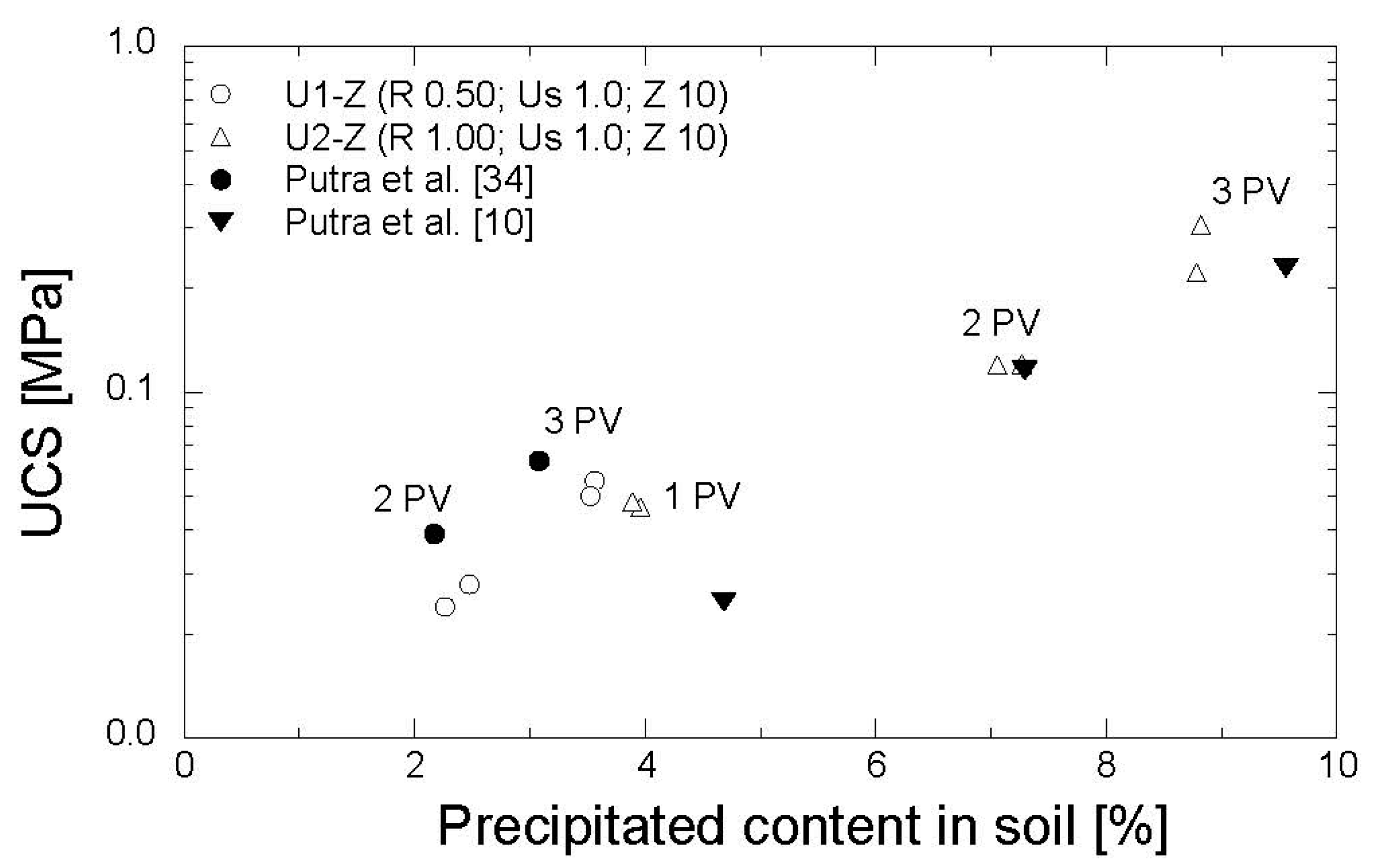
The results of the UCS tests are shown in Figure 11. The precipitated amounts, ranging from 2.2–8.8% of the soil mass and corresponding to the strength of 24–305 kPa, were obtained by one to three PV injections. In comparison to the previous studies, in which the EMCP technique was conducted without zeolite [10,34], the precipitated amount and the strength obtained in this work were relatively similar. With a low concentration of reagents (R = 0.5 mol/L), the strength derived from Putra et al. [34] was slightly higher than that obtained in this study. Moreover, in the reagent concentration of 1.0 mol/L, the strength gained in this study was slightly greater than that obtained in Putra et al. [10]. The results confirmed that the utilization of zeolite during the preparation of grouting materials in the EMCP technique has no significant impact on the strength of treated soil.
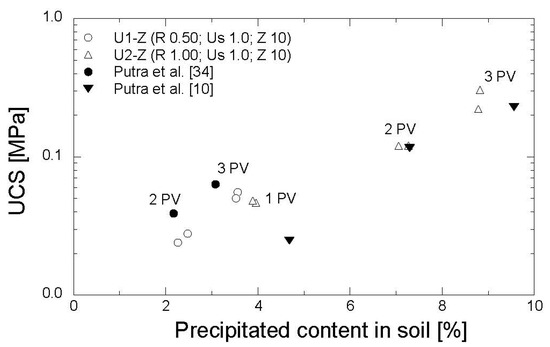
Figure 11.
Evolution of strength with precipitated amount.
4. Conclusions
The applicability of the ion exchange method using natural zeolite to remove the NH-forms in the EMCP technique has been evaluated. The natural zeolite of mordenite was added to grouting solutions composed of urea-urease and mixed thoroughly for different mixing times. The effects of the utilization of natural zeolite in the preparation of grouting materials on the EMCP parameters, such as the precipitated amount, the pH, the mineralogy, and the improvement in the strength of the treated soil were also evaluated.
The utilization of natural zeolite in the preparation of grouting materials brought about a significant effect on the NH-forms concentration. The NH-forms measurements showed that the use of 10 g zeolite/L solution with a 2-h mixing time could reduce the concentration of NH-forms by 75% and 45% of the maximum theoretical concentration in urea concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mol/L, respectively. XRD analysis indicated that the presence of zeolite had no significant impact on the mineralogy of the precipitated minerals. However, the utilization of zeolite in the EMCP technique promoted the agglomeration form of the precipitated materials. Mechanical test results showed that the grouting solutions brought about a significant improvement in the soil strength. A precipitated material of 9% of the sand mass was produced by three PV injections of grouting materials, which showed the unconfined compressive strength of 300 kPa. The results of this study have indicated that the application of natural zeolite of mordenite in the EMCP technique may be viable as an environmentally friendly soil improvement method.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partly supported by a research grant from the Penta-Ocean Construction Co., Ltd. Their support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author Contributions
Heriansyah Putra performed all the experiments and analyzed the data. Hideaki Yasuhara supervised this work, partly conducted the experiments, and analyzed the data. Naoki Kinoshita suggested how to proceed this work and partly conducted the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Martinez, B.C.; DeJong, J.T.; Ginn, T.R.; Montoya, B.M.; Barkouki, T.H.; Hunt, C.; Tanyu, B.; Major, D. Experimental Optimization of Microbial-Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Soil Improvement. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJong, J.T.; Mortensen, B.M.; Martinez, B.C.; Nelson, D.C. Bio-mediated soil improvement. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Paassen, L.A.; Daza, C.M.; Staal, M.; Sorokin, D.Y.; van der Zon, W.; van Loosdrecht, C.M. Potential soil reinforcement by biological denitrification. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, H.; Neupane, D.; Hayashi, K.; Okamura, M. Experiments and predictions of physical properties of sand cemented by enzymatically-induced carbonate precipitation. Soils Found. 2012, 52, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, D.; Yasuhara, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Unno, T. Applicability of Enzymatic Calcium Carbonate Precipitation as a Soil-Strengthening Technique. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Ishihara, M.; Tamura, K. Degree of Saturation and Liquefaction Resistances of Sand Improved with Sand Compaction Pile. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Stabnikov, V. Construction Biotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavazanjian, E.; Hamdan, N. Enzyme Induced Carbonate Precipitation (EICP) Columns for Ground Improvement. In IFCEE 2015; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2015; pp. 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, H.; Yasuhara, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Hirata, A. Application of magnesium to improve uniform distribution of precipitated minerals in 1-m column specimens. Geomech. Eng. 2017, 12, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, H.; Yasuhara, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Hirata, A. Optimization of Enzyme-Mediated Calcite Precipitation as a Soil-Improvement Technique: The Effect of Aragonite and Gypsum on the Mechanical Properties of Treated Sand. Crystals 2017, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.C.; Ferris, F.G. The coprecipitation of Sr into calcite precipitates induced by bacterial ureolysis in artificial groundwater: Temperature and kinetic dependence. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 4199–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.; Stehmeier, L.; Kantzas, A.; Mourits, F. Bacteriogenic mineral plugging. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1996, 35, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fu, Q.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Achal, V.; Kawasaki, S. Bio-grout based on microbially induced sand solidification by means of asparaginase activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soon, N.W.; Lee, L.M.; Khun, T.C.; Ling, H.S. Factors Affecting Improvement in Engineering Properties of Residual Soil through Microbial-Induced Calcite Precipitation. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 4014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment of Japan. Water Pollution Control Law; Ministry of the Environment of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 1970.
- Lin, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Lu, X. Removal of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater by microwave radiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, H.A.; Abdel-Rahim, M.; Lotfy, A.M.; Abdelaty, B.S.; Sallam, G.M. The Applicability of Activated Carbon, Natural Zeolites, and Probiotics (EM®) and Its Effects on Ammonia Removal Efficiency and Fry Performance of European Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, C.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y. The Mechanism and Performance of Zeolites for Ammonia Removal in the Zeolite Packed Electrolysis Reactor. Electrochemistry 2014, 82, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, T.C.; Weatherley, L.R. Ammonia removal from wastewater by ion exchange in the presence of organic contaminants. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, D.; Koc, Y.; Turan, M.; Armagan, B. Removal of ammonium ion from aqueous solution using natural Turkish clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltali, K.; Sari, A.; Aydin, M. Removal of ammonium ion from aqueous solution by natural Turkish (Yildizeli) zeolite for environmental quality. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Chung, Y.C.; Shin, H.S.; Son, D.H. Enhanced ammonia nitrogen removal using consistent biological regeneration and ammonium exchange of zeolite in modified SBR process. Water Res. 2004, 38, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kmiya, Y.; Okuhara, T. Removal of low-concentration ammonia in water by ion-exchange using Na-mordenite. Water Res. 2007, 41, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; An, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Mai, S. Study on zeolite enhanced contact-adsorption regeneration-stabilization process for nitrogen removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari-Hosseini, Z.; Kazemiyan, E.; Tayebee, R.; Shenavaei-Zare, T. Optimization of ammonia removal by natural zeolite from aqueous solution using response surface methodology. Hem. Ind. 2016, 70, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Tanner, C.C. Ammonium removal from wastewaters using natural New Zealand zeolites. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1998, 41, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozic, M.; Cerjan-Stefanovic, S.; Kurajica, S.; Vancina, V.; Hodzic, E. Ammoniacal nitrogen removal from water by treatmenre with clays and zeolites. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, K.; Zabukovec Logar, N.; Šiljeg, M.; Farkas, A. Natural Zeolites in Water Treatment—How Effective is Their Use. In Water Treat; Elshorbagy, W., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitachi. Analysis Report of Zeolite; Hitachi: Yasugi, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahim, M. Sustainable Use of Natural Zeolites in Aquaculture: A Short Review. Oceanogr. Fish. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, H.; Yasuhara, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Neupane, D. Optimization of Calcite Precipitation as a Soil Improvement Technique. In Proceedings of the 2nd Makassar International Conference on Civil Engineering, Makassar, Indonesia, 11–12 August 2015; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, H.; Yasuhara, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Neupane, D.; Lu, C.-W. Effect of Magnesium as Substitute Material in Enzyme-Mediated Calcite Precipitation for Soil-Improvement Technique. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko Chemical Laboratories, Handy Ion Meter TiN-9001 Instruction Manual, 2010; Toko Chemical Laboratories Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2010.
- Yasuhara, H.; Hayashi, K.; Okamura, M. Evolution in Mechanical and Hydraulic Properties of Calcite-Cemented Sand Mediated by Biocatalyst. In Geo-Frontiers 2011 ©; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; pp. 3984–3992. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.K.W.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The effect of ionic contaminants on the early-age properties of alkali-activated fly ash-based cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).