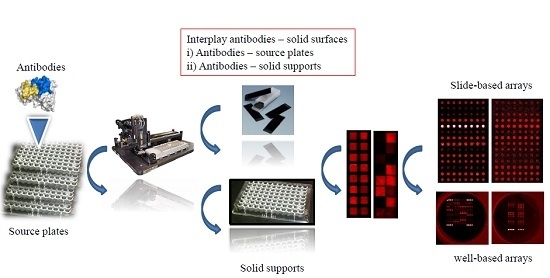
Evaluation of Solid Supports for Slide- and Well-Based Recombinant Antibody Microarrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surfaces
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Samples
2.4. Microarray Production and Processing
2.5. Antibody Footprint
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Source Plates
3.2. Slide-Based Solid Supports: Surface Fouling
3.3. Slide-Based Solid Supports: Surface Fouling and Spot Properties
3.4. Slide-Based Solid Supports: Reproducibility, Sensitivity and Dynamic Range
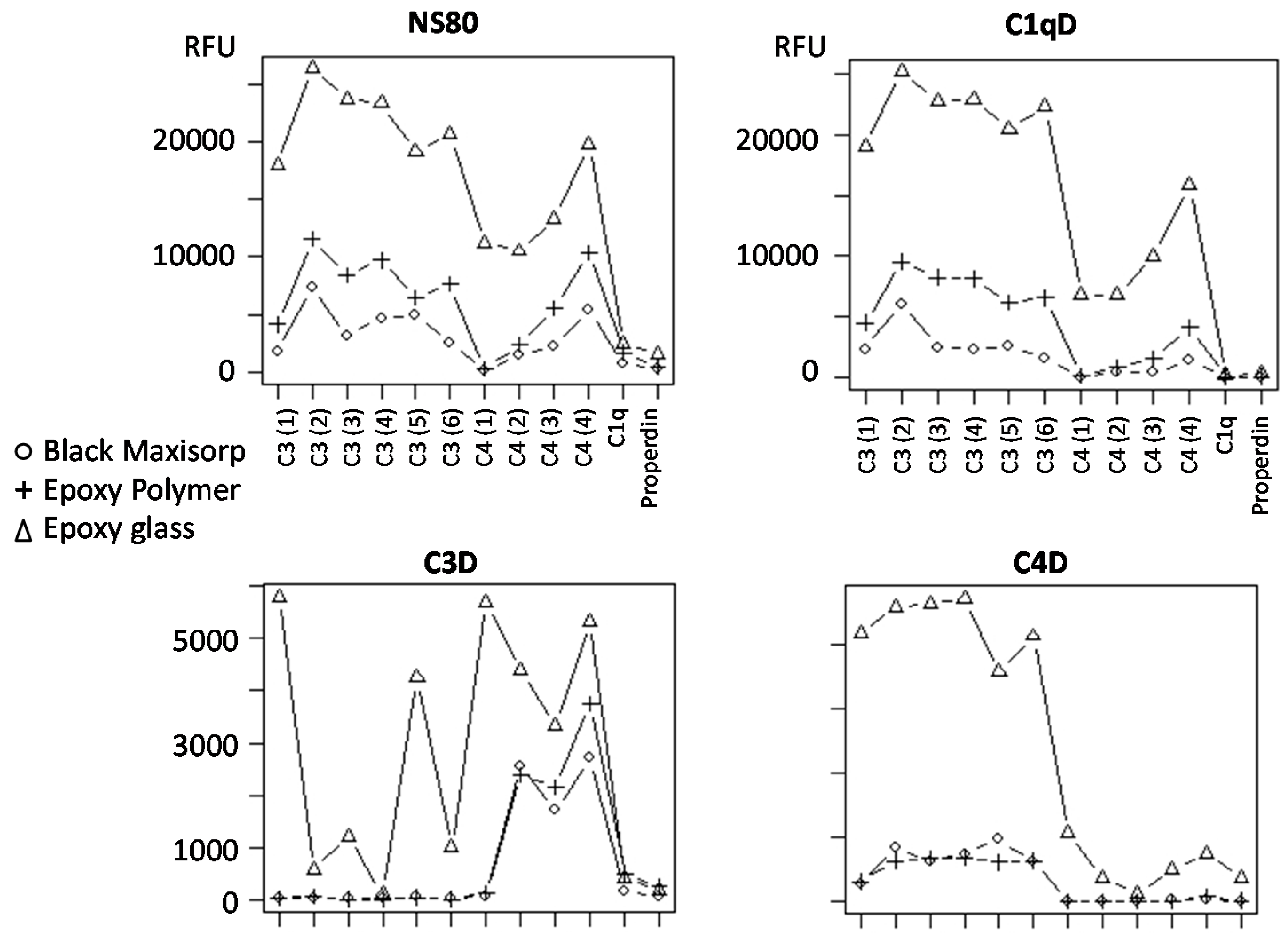
3.5. Slide-Based Solid Supports: Specificity and Stability
3.6. Slide-Based Solid Supports: Semi-Automatic Array Handling
3.7. Well-Based Solid Supports: Surface and LED/CCD Plate Scanner
3.8. Well-Based Solid Supports: Confocal LS Slide/Plate Scanner
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ayoglu, B.; Haggmark, A.; Neiman, M.; Igel, U.; Uhlen, M.; Schwenk, J.M.; Nilsson, P. Systematic antibody and antigen-based proteomic profiling with microarrays. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 11, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Carbayo, M. Antibody microarrays as tools for biomarker discovery. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 785, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. High-throughput proteomics using antibody microarrays: An update. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 7, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingvarsson, J.; Larsson, A.; Sjoholm, A.G.; Truedsson, L.; Jansson, B.; Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Design of recombinant antibody microarrays for serum protein profiling: Targeting of complement proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3527–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingren, C.; Ingvarsson, J.; Dexlin, L.; Szul, D.; Borrebaeck, C.A. Design of recombinant antibody microarrays for complex proteome analysis: Choice of sample labeling-tag and solid support. Proteomics 2007, 7, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Antibody array generation and use. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1131, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steinhauer, C.; Ressine, A.; Marko-Varga, G.; Laurell, T.; Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Biocompatibility of surfaces for antibody microarrays: Design of macroporous silicon substrates. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 341, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusnezow, W.; Hoheisel, J.D. Solid supports for microarray immunoassays. J. Mol. Recognit. 2003, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seurynck-Servoss, S.L.; White, A.M.; Baird, C.L.; Rodland, K.D.; Zangar, R.C. Evaluation of surface chemistries for antibody microarrays. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 371, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenendt, P.; Glokler, J.; Sobek, J.; Lehrach, H.; Cahill, D.J. Next generation of protein microarray support materials: Evaluation for protein and antibody microarray applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1009, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angenendt, P.; Glokler, J.; Murphy, D.; Lehrach, H.; Cahill, D.J. Toward optimized antibody microarrays: A comparison of current microarray support materials. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 309, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnezow, W.; Jacob, A.; Walijew, A.; Diehl, F.; Hoheisel, J.D. Antibody microarrays: An evaluation of production parameters. Proteomics 2003, 3, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, S.; Laforte, V.; Lo, P.S.; Li, H.; Juncker, D. Evaluating mixtures of 14 hygroscopic additives to improve antibody microarray performance. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8451–8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Design of high-density antibody microarrays for disease proteomics: Key technological issues. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Xie, Z.; Qian, J.; Blackshaw, S.; Zhu, H. Functional protein microarray technology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusnezow, W.; Banzon, V.; Schroder, C.; Schaal, R.; Hoheisel, J.D.; Ruffer, S.; Luft, P.; Duschl, A.; Syagailo, Y.V. Antibody microarray-based profiling of complex specimens: Systematic evaluation of labeling strategies. Proteomics 2007, 7, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piehler, J.; Brecht, A.; Geckeler, K.E.; Gauglitz, G. Surface modification for direct immunoprobes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1996, 11, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.G.; McQuary, P.; Mongan, A.; Gangadharan, R.; Brignac, S.; Eggers, M. High-throughput microarray-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Biotechniques 1999, 27, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matson, R.S.; Milton, R.C.; Cress, M.C.; Chan, T.S.; Rampal, J.B. Printing low density protein arrays in microplates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 381, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ingvarsson, J.; Wingren, C.; Carlsson, A.; Ellmark, P.; Wahren, B.; Engstrom, G.; Harmenberg, U.; Krogh, M.; Peterson, C.; Borrebaeck, C.A. Detection of pancreatic cancer using antibody microarray-based serum protein profiling. Proteomics 2008, 8, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.; Wingren, C.; Ingvarsson, J.; Ellmark, P.; Baldertorp, B.; Ferno, M.; Olsson, H.; Borrebaeck, C.A. Serum proteome profiling of metastatic breast cancer using recombinant antibody microarrays. Eur J. Cancer 2008, 44, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitelegg, N.R.; Rees, A.R. WAM: an improved algorithm for modelling antibodies on the WEB. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Recombinant antibodies for the generation of antibody arrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 785, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixit, C.K.; Vashist, S.K.; MacCraith, B.D.; O’Kennedy, R. Evaluation of apparent non-specific protein loss due to adsorption on sample tube surfaces and/or altered immunogenicity. Analyst 2011, 136, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillman, B.A.; Tonkinson, J.L. Fast slides: A novel surface for microarrays. Biotechniques 2000, 29, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kukar, T.; Eckenrode, S.; Gu, Y.; Lian, W.; Megginson, M.; She, J.X.; Wu, D. Protein microarrays to detect protein-protein interactions using red and green fluorescent proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 306, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, T.O.; Schrenk, M.; Hopfl, P.; Kroger, K.; Chowdhury, U.; Stoll, D.; Schorner, D.; Durr, M.; Herick, K.; Rupp, S.; et al. A microarray enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for autoimmune diagnostics. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoz-Gurpide, J.; Wang, H.; Misek, D.E.; Brichory, F.; Hanash, S.M. Protein based microarrays: A tool for probing the proteome of cancer cells and tissues. Proteomics 2001, 1, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paweletz, C.P.; Charboneau, L.; Bichsel, V.E.; Simone, N.L.; Chen, T.; Gillespie, J.W.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Roth, M.J.; Petricoin, I.E.; Liotta, L.A. Reverse phase protein microarrays which capture disease progression show activation of pro-survival pathways at the cancer invasion front. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piehler, J.; Brecht, A.; Valiokas, R.; Liedberg, B.; Gauglitz, G. A high-density poly(ethylene glycol) polymer brush for immobilization on glass-type surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, C.; Wingren, C.; Khan, F.; He, M.; Taussig, M.J.; Borrebaeck, C.A. Improved affinity coupling for antibody microarrays: Engineering of double-(His)6-tagged single framework recombinant antibody fragments. Proteomics 2006, 6, 4227–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, M.D.; Van Arsdell, S.W.; Murphy, K.P.; Orencole, S.F.; Burns, C. Array-based ELISAS for high-throughput analysis of human cytokines. Biotechniques 2001, 31, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiese, R.; Belosludtsev, Y.; Powdrill, T.; Thompson, P.; Hogan, M. Simultaneous multianalyte ELISA performed on a microarray platform. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liew, M.; Groll, M.C.; Thompson, J.E.; Call, S.L.; Moser, J.E.; Hoopes, J.D.; Voelkerding, K.; Wittwer, C.; Spendlove, R.S. Validating a custom multiplex ELISA against individual commercial immunoassays using clinical samples. Biotechniques 2007, 42, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backen, A.C.; Cummings, J.; Mitchell, C.; Jayson, G.; Ward, T.H.; Dive, C. “Fit-for-purpose” validation of searchlight multiplex ELISA of angiogenesis for clinical trial use. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 342, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.E. Solid supports in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and other solid-phase immunoassays. Methods 2000, 22, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Source Plate | CV-Value | Maximum Signal Difference (1) |
|---|---|---|
| PP/black/NUNC (2) | 3% | 11% |
| PP/clear/Genetix (3) | 6% | 20% |
| PP/clear/ABgene (4) | 7% | 36% |
| PS/clear/Genetix (5) | 5% | 19% |
| PS/clear/NUNC (6) | 8% | 26% |
| PS, NBS-treated/clear/Corning (7) | 8% | 55% |
| PS/black/PerkinElmer (8) | 10% | 30% |
| PS, NBS-treated/white/Corning (9) | 16% | 55% |
| Format | Name | Surface Chemistry | Surface Geometry a | Binding Chemistry | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slides | Nexterion H | NHSb polymer | 3D | Covalent | Schott |
| Nexterion P | Hydrophilic NHS polymer | 3D | Covalent | Schott | |
| GAPS II | Aminopropylsilane | 2D | Ionic | Corning | |
| NHS glass | NHS glass | 3D | Covalent | PolyAn | |
| NHS polymer | NHS polymer | 3D | Covalent | PolyAn | |
| Epoxy glass | Epoxy glass | 3D | Covalent | PolyAn | |
| Epoxy polymer | Epoxy polymer | 3D | Covalent | PolyAn | |
| FAST | Nitrocellulose | 3D | Adsorption | Whatman | |
| SuperProtein | Hydrophobic polymer | 2D | Adsorption | Arrayit | |
| Silane-Prep | Aminoalkylsilane glass | 2D | Ionic | Sigma | |
| Black MaxiSorp | Hydrophilic polymer | 2D | Adsorption | NUNC | |
| Clear MaxiSorp* | Hydrophilic polymer | 2D | Adsorption | NUNC | |
| 96-well plates | Clear MaxiSorp | Hydrophilic polymer | 2D | Adsorption | NUNC |
| SciPLEXPLATE | Polystyrene | 2D | Adsorption | Scienion | |
| Costar | Polystyrene | 2D | Adsorption | Corning |
| Slide | Blocking Solution | Background Intensity (1) | Background Homogeneity (2) | Spot Intensity (3) | Spot Size (μm) | Spot Morphology (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black MaxiSorp | 5% (w/v) milk PBS | 500 | + + + | 11,600 | 125–140 | + + |
| Epoxy glass | 0.5% (v/v) Tween-20 PBS | 800 | − − | 30,900 | 130–140 | + |
| Epoxy polymer | 0.5% (v/v) Tween-20 PBS | 250 | + | 14,700 | 130–150 | + + + |
| GAPSII | 5% (w/v) BSA PBS | 1100 | − − − | 6300 | 150–160 | + + |
| Nexterion H | 1% (w/v) milk TBS | 200 | + | 8900 | 60–120 | − − |
| Nexterion P | 5% (w/v) BSA PBS | 150 | + + | 5300 | 60–170 | − − − |
| NHS glass | 0.5% (v/v) Tween-20 PBS | 350 | − | 13,900 | 70–160 | + |
| NHS polymer | 1% (w/v) milk TBS | 300 | − | 1400 | 60–160 | + + |
| Silane-Prep | 1% (w/v) BSA PBS | 700 | − − − | 3700 | 160–170 | − |
| Array Features | Epoxy Glass | Epoxy Polymer | Black MaxiSorp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spot-to-spot | 4.7 ± 7.7 | 4.1 ± 5.2 | 3.3 ± 3.0 |
| Array-to-array | 26.4 ± 15.0 | 19.5 ± 6.5 | 3.6 ± 0.6 |
| Slide-to-slide | 34.3 ± 11.6 | 29.0 ± 15.7 | 12.2 ± 3.6 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerdtsson, A.S.; Dexlin-Mellby, L.; Delfani, P.; Berglund, E.; Borrebaeck, C.A.K.; Wingren, C. Evaluation of Solid Supports for Slide- and Well-Based Recombinant Antibody Microarrays. Microarrays 2016, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5020016
Gerdtsson AS, Dexlin-Mellby L, Delfani P, Berglund E, Borrebaeck CAK, Wingren C. Evaluation of Solid Supports for Slide- and Well-Based Recombinant Antibody Microarrays. Microarrays. 2016; 5(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerdtsson, Anna S., Linda Dexlin-Mellby, Payam Delfani, Erica Berglund, Carl A. K. Borrebaeck, and Christer Wingren. 2016. "Evaluation of Solid Supports for Slide- and Well-Based Recombinant Antibody Microarrays" Microarrays 5, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5020016
APA StyleGerdtsson, A. S., Dexlin-Mellby, L., Delfani, P., Berglund, E., Borrebaeck, C. A. K., & Wingren, C. (2016). Evaluation of Solid Supports for Slide- and Well-Based Recombinant Antibody Microarrays. Microarrays, 5(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5020016