Automated and Multiplexed Soft Lithography for the Production of Low-Density DNA Microarrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
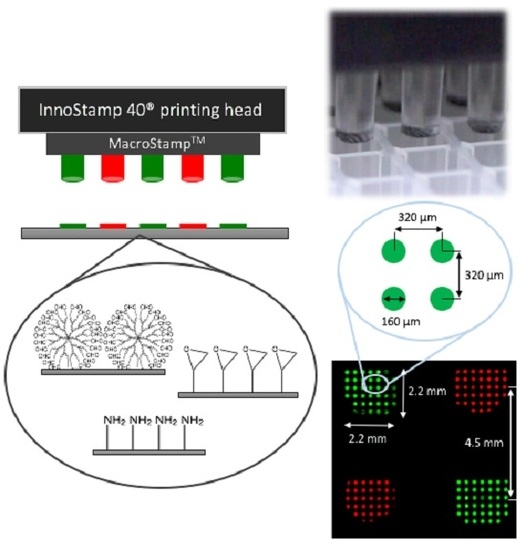
2.1. InnoStamp 40® for Multiplexed Printing of Biomolecules Using MacroStampTM
- Loading of the magnetic MacroStampTM (Figure 2) and aligning with the microtiter plate;
- Inking (1 min) by immersion of the magnetic MacroStampTM in the microtiter plate containing oligonucleotides to be deposited at the appropriate concentrations;
- Drying (30 s) of the MacroStampTM using a turbine (100 UA);
- Printing of oligonucleotides (1 min): MacroStampTM is automatically aligned and brought into contact with glass slides allowing the transfer of oligonucleotides and the one step microarray fabrication.
2.2. Preparation of the Magnetic MacroStampTM
2.3. Fabrication and Processing of the Microarrays
2.4. Hybridization
2.5. Data Acquisition and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Features of the InnoStamp 40® for Automated and Multiplexed Microcontact Printing
3.2. MacroStampTM Reusability and Reliability
3.3. Immobilization Efficiency
3.4. Sensitivity Response of Arrays Made by Microcontact Printing and by Mechanical Spotting
3.5. Effect of the Surface Chemistry on Probe Accessibility and Hybridization Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pirrung, M.C. How to make a DNA chip. Angew. Chem. 2002, 41, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D.; Blum, L.J. DNA biosensors and microarrays. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissler, M.; Roy, E.; Deneault, J.S.; Arbour, M.; Diaz-Quijada, G.A.; Nantel, A.; Veres, T. Stretching the stamp: A flexible approach to the fabrication of miniaturized DNA arrays. Small 2009, 5, 2514–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.A.; Benes, V.; Kern, D.P.; Hörber, H.; Bernard, A. Microcontact printing of DNA molecules. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, D.J.; Dong, H.; Byrne, M.C.; Follettie, M.T.; Gallo, M.V.; Chee, M.S.; Mittmann, M.; Wang, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Horton, H.; et al. Expression monitoring by hybridization to high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaita, K.; Wang, Y.; Mirkin, C.A. Applications of dip-pen nanolithography. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Gasson, S.; Green, R.D.; Yue, Y.J.; Nelson, C.; Blattner, F.; Sussman, M.R.; Cerrina, F. Maskless fabrication of light-directed oligonucleotide microarrays using a digital micromirror array. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalon, D.; Smith, S.J.; Brown, P.O. A DNA microarray system for analyzing complex DNA samples using two-color fluorescent probe hybridization. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, A.; Gunther, R.; Schwienhorst, A.; Doring, M.; Lindemann, B.F. Accurate high-speed liquid handling of very small biological samples. Biotechniques 1993, 15, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fodor, S.P.; Read, J.L.; Pirrung, M.C.; Stryer, L.; Lu, A.T.; Solas, D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science 1991, 251, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipshutz, R.J.; Fodor, S.P.; Gingeras, T.R.; Lockhart, D.J. High density synthetic oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.R.; Mao, M.; Jones, A.R.; Burchard, J.; Marton, M.J.; Shannon, K.W.; Lefkowitz, S.M.; Ziman, M.; Schelter, J.M.; Meyer, M.R.; et al. Expression profiling using microarrays fabricated by an ink-jet oligonucleotide synthesizer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolber, P.K.; Collins, P.J.; Lucas, A.B.; de Witte, A.; Shannon, K.W. The agilent in situ-synthesized microarray platform. Method Enzymol. 2006, 410, 28–57. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, J.C.; Kawasaki, E.S. Microarrays: The use of oligonucleotides and cdna for the analysis of gene expression. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Biebuyck, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterning self-assembled monolayers—Applications in materials science. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1498–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Whitesides, G.M. Features of gold having micrometer to centimeter dimensions can be formed through a combination of stamping with an elastomeric stamp and an alkanethiol ink followed by chemical etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.; Delamarche, E.; Schmid, H.; Michel, B.; Bosshard, H.R.; Biebuyck, H. Printing patterns of proteins. Langmuir 1998, 14, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.S.; Takayama, S.; Ostuni, E.; Ingber, D.E.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterning proteins and cells using soft lithography. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskuhl, J.; Brinkmann, J.; jonkheijm, P. Advances in contact printing technologies of carbohydrate, peptide and protein arrays. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, T.; Ravoo, B.J. Stamps, inks and substrates: Polymers in microcontact printing. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, J.P.; Bernard, A.; Bietsch, A.; Michel, B.; Bosshard, H.R.; Delamarche, E. Fabricating arrays of single protein molecules on glass using microcontact printing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 108, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricoult, S.G.; Nezhad, A.S.; Knapp-Mohammady, M.; Kennedy, T.E.; Juncker, D. Humidified microcontact printing of proteins: Universal patterning of proteins on both low and high energy surfaces. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12002–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, S.A.; Chen, C.S. Microcontact printing: A tool to pattern. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Taylor, P.; Ersoz, M.; Fletcher, P.D.I.; Paunov, V.N. Microcontact printing of DNA-surfactant arrays on solid substrates. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozkiewicz, D.I.; Brugman, W.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Ravoo, B.J.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Dendrimer-mediated transfer printing of DNA and RNA microarrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11593–11599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, C.; le Berre, V.; Casimirius, S.; Trevisiol, E.; Francois, J.; Vieu, C. Direct microcontact printing of oligonucleotides for biochip applications. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thibault, C.; Severac, C.; Mingotaud, A.F.; Vieu, C.; Mauzac, M. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) contamination in microcontact printing and its influence on patterning oligonucleotides. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10706–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalo, H.; Cau, J.C.; Thibault, C.; Marsaud, N.; Severac, C.; Vieu, C. Microscale multiple biomolecules printing in one step using a PDMS macrostamp. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 1428–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisiol, E.; le Berre-Anton, V.; Leclaire, J.; Pratviel, G.; Caminade, A.M.; Majoral, J.P.; Francois, J.M.; Meunier, B. Dendrislides, dendrichips: A simple chemical functionalization of glass slides with phosphorus dendrimers as an effective means for the preparation of biochips. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau, J.C.; Lafforgue, L.; Nogues, M.; Lagraulet, A.; Paveau, V. Magnetic field assisted microcontact printing: A new concept of fully automated and calibrated process. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 110, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent compatibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavachari, N.; Bao, Y.P.; Li, G.; Xie, X.; Muller, U.R. Reduction of autofluorescence on DNA microarrays and slide surfaces by treatment with sodium borohydride. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 312, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, V.; Trevisiol, E.; Dagkessamanskaia, A.; Sokol, S.; Caminade, A.M.; Majoral, J.P.; Meunier, B.; Francois, J. Dendrimeric coating of glass slides for sensitive DNA microarrays analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimse, S.B.; Song, K.; Sonawane, M.D.; Sayyed, D.R.; Kim, T. Immobilization techniques for microarray: Challenges and applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 22208–22229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbulovic-Nad, I.; Lucente, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wheeler, A.R.; Bussmann, M. Bio-microarray fabrication techniques—A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2006, 26, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.N.; Grainger, D.W. Biophysical properties of nucleic acids at surfaces relevant to microarray performance. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 436–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Marangoni effect reverses coffee-ring depositions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7090–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, V.; Graves, D.J.; Fortina, P.; McKenzie, S.E. Adsorption and surface diffusion of DNA oligonucleotides at liquid/solid interfaces. Langmuir 1997, 13, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.W.; Heaton, R.J.; Georgiadis, R.M. The effect of surface probe density on DNA hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchepinov, M.S.; Case-Green, S.C.; Southern, E.M. Steric factors influencing hybridisation of nucleic acids to oligonucleotide arrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fredonnet, J.; Foncy, J.; Cau, J.-C.; Séverac, C.; François, J.M.; Trévisiol, E. Automated and Multiplexed Soft Lithography for the Production of Low-Density DNA Microarrays. Microarrays 2016, 5, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5040025
Fredonnet J, Foncy J, Cau J-C, Séverac C, François JM, Trévisiol E. Automated and Multiplexed Soft Lithography for the Production of Low-Density DNA Microarrays. Microarrays. 2016; 5(4):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleFredonnet, Julie, Julie Foncy, Jean-Christophe Cau, Childérick Séverac, Jean Marie François, and Emmanuelle Trévisiol. 2016. "Automated and Multiplexed Soft Lithography for the Production of Low-Density DNA Microarrays" Microarrays 5, no. 4: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5040025
APA StyleFredonnet, J., Foncy, J., Cau, J.-C., Séverac, C., François, J. M., & Trévisiol, E. (2016). Automated and Multiplexed Soft Lithography for the Production of Low-Density DNA Microarrays. Microarrays, 5(4), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5040025