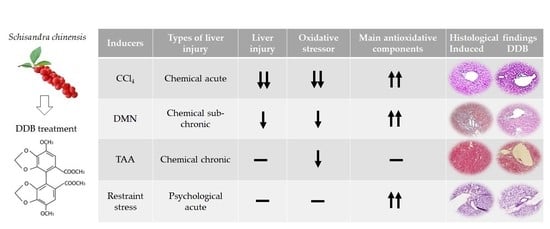
Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidative and Hepatoprotective Activities of Dimethyl Diphenyl Bicarboxylate in Four Animal Models of Hepatic Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Serum Aminotransferase Determination
2.3. Hepatic Tissue Preparation for Hepatic Oxidative Stress-Related Parameter Determination
2.4. Hepatic Total Reactive Oxygen Species Determination
2.5. Hepatic Lipid Peroxidation Determination
2.6. Hepatic Glutathione and Glutathione Peroxidase and Glutathione Reductase Determination
2.7. Hepatic Superoxide Dismutase Determination
2.8. Hepatic Catalase Determination
2.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of the Serum Aminotransferases and AST to ALT Ratio in Four Liver Injury Models
3.2. Comparison of Hepatic ROS Activity and Lipid Peroxidation in Four Liver Injury Models
3.3. Comparison of Hepatic GSH System in Four Hepatic Injury Models
3.4. Comparison of Hepatic SOD and Catalase in Four Hepatic Injury Models
3.5. Comparison of Liver Histopathological Change in Four Hepatic Injury Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cichoż-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, C.; Huang, W.; Yu, X. Mitochondrial stress response in drug-induced liver injury. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, O.; Arnau, A.; Pareja, M.; Poch, E.; Ramirez, I.; Soley, M. Acute stress-induced tissue injury in mice: Differences between emotional and social stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2002, 7, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Animal models of drug-induced liver injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, E.; Gumuslu, S. Immobilization stress in rat tissues: Alterations in protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 144, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Oh, D.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Son, T.G.; Yuk, D.Y.; Jung, Y.S. Silymarin Prevents Restraint Stress-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Reducing Inflammatory Response. Molecules 2016, 21, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, D.B.; Budhathoki, P.; Sedhai, Y.R.; Adhikari, A.; Poudel, A.; Aryal, B.; Baniya, R. N-acetyl cysteine versus standard of care for non-acetaminophen induced acute liver injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hepatol 2021, 24, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas-Grajales, S.; Muriel, P. Antioxidants in liver health. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 6, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arauz, J.; Ramos-Tovar, E.; Muriel, P. Redox state and methods to evaluate oxidative stress in liver damage: From bench to bedside. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, K.G.; Wang, J.H.; Shin, J.W.; Lee, D.S.; Son, C.G. A traditional formula, Chunggan extract, attenuates thioacetamide-induced hepatofibrosis via GSH system in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surai, P.F. Silymarin as a Natural Antioxidant: An Overview of the Current Evidence and Perspectives. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 204–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Zobeiri, M.; Parvizi, F.; El-Senduny, F.F.; Marmouzi, I.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Naseri, R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M. Curcumin in Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Cellular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Clinical Perspective. Nutrients 2018, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Bernatoniene, J. Antioxidant Effects of Schisandra chinensis Fruits and Their Active Constituents. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Z.; Song, X.; Xu, C.; Cui, Z.; Xiang, L. Evidence of anti-inflammatory activity of Schizandrin A in animal models of acute inflammation. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Cao, Y.; He, R.; Han, N.; Liu, Z.; Miao, L.; Yin, J. Schizandrin, an antioxidant lignan from Schisandra chinensis, ameliorates Abeta1-42-induced memory impairment in mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 721721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ip, S.P.; Yiu, H.Y.; Ko, K.M. Differential effect of schisandrin B and dimethyl diphenyl bicarboxylate (DDB) on hepatic mitochondrial glutathione redox status in carbon tetrachloride intoxicated mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2000, 205, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G. Effect of diphenyl dimethyl bicarboxylate on concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.W.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, S.G. The anti-fibrogenic effect of a pharmaceutical composition of [5-(2-pyrazinyl)-4-methyl-1,2-dithiol-3-thione] (oltipraz) and dimethyl-4,4′-dimethoxy-5,6,5′,6′-dimethylene dioxybiphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylate (DDB). Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2002, 25, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, H.S.; Goertz, C.; Fritts, M.; Jonas, W.B. Natural products and chronic hepatitis C virus. Liver Int. 2007, 27, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, D.G.; Ahn, D.S. A study on the efficacy and safety of dipheny-dimethyl-dicarboxylate in patients with chronic liver disease. Korean J. Hepatol. 1996, 2, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, R.; Hockenjos, B.; Blum, H.E. DDB treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1732–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.; Tahir, R.A.; Santoso, W.D.; Soemarno; Sumaryono; Noer, H.M.; Liu, G. Effectiveness of the analogue of natural Schisandrin C (HpPro) in treatment of liver diseases: An experience in Indonesian patients. Chin. Med. J. 1998, 111, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shankar, K.; Mehendale, H.M. Oxidative Stress. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 735–737. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, I.; Morishita, Y.; Imai, K.; Nakamura, M.; Nakachi, K.; Hayashi, T. High-throughput spectrophotometric assay of reactive oxygen species in serum. Mutat. Res. 2007, 631, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Shin, J.W.; Son, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Son, C.G. Antifibrotic effects of CGX, a traditional herbal formula, and its mechanisms in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-M.; Kim, H.-G.; Choi, M.-K.; Lee, J.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Wang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Son, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Son, C.-G. Aqueous extract of Artemisia iwayomogi Kitamura attenuates cholestatic liver fibrosis in a rat model of bile duct ligation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, C.R.; Salzman, J.A.; Elsayed, N.M.; Omaye, S.T.; Korte, D.W., Jr. Automated assays for superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione reductase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 184, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meyer, C.; Xu, C.; Weng, H.; Hellerbrand, C.; ten Dijke, P.; Dooley, S. Animal models of chronic liver diseases. Am. J Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G449–G468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vento, S.; Cainelli, F. Acute liver failure. Lancet 2020, 395, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, D.V.; Rosen, H.R. Abnormal findings on liver function tests. Interpreting results to narrow the diagnosis and establish a prognosis. Postgrad. Med. 2000, 107, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, D.E. Special considerations in interpreting liver function tests. Am. Fam. Physician. 1999, 59, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rej, R. Aminotransferases in disease. Clin. Lab. Med. 1989, 9, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanji, A.A.; French, S.W.; Mendenhall, C.L. Serum aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase ratio in human and experimental alcoholic liver disease: Relationship to histologic changes. Enzyme 1989, 41, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C. Laboratory Animal Medicine; Seoul University Press: Seoul, Korea, 1989; pp. 502–512. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Tan, F.; Yi, R.; Mu, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z. Effects of Lactobacillus on Mice with Diabetes Induced by High-Fat Diet with Streptozotocin (STZ). Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutzman, R.; Wall, H.; Vinegar, A. Toxic Hazards Research Unit, 1989; Annual report; NSI Technology Services Corporation: Dayton, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, L.W.; Boll, M.; Stampfl, A. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: Carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2003, 33, 105–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, G.; Calcutt, M.W.; Nagy, L.D.; Guengerich, F.P. Oxidation of methyl and ethyl nitrosamines by cytochrome P450 2E1 and 2B1. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9995–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Panahi, Y.; Sahraei, H.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. The impact of stress on body function: A review. EXCLI J 2017, 16, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipes, I.G.; el Sisi, A.E.; Sim, W.W.; Mobley, S.A.; Earnest, D.L. Reactive oxygen species in the progression of CCl4-induced liver injury. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1991, 283, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.-Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, S.-H.; Son, C.-G. A literature review for the mechanisms of stress-induced liver injury. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poli, G.; Albano, E.; Dianzani, M.U. The role of lipid peroxidation in liver damage. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1987, 45, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beshbishy, H.A. The effect of dimethyl dimethoxy biphenyl dicarboxylate (DDB) against tamoxifen-induced liver injury in rats: DDB use is curative or protective. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 38, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, H.Y.; Ha, K.; Koh, H.; Shin, I.; Suh, T. Effects of biphenyldimethyl dicarboxylate (DDB) on the lipid peroxidation, oxygen free radical scavenging enzymes activities and hepatic functions in ethanol-induced hepatotoxic rats. Korean J. Pharmacol. 1994, 30, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Duygu, F.; Karsen, H.; Aksoy, N.; Taskin, A. Relationship of Oxidative Stress in Hepatitis B Infection Activity with HBV DNA and Fibrosis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2012, 32, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, H.; Thompson, D.C.; Shertzer, H.G.; Nebert, D.W.; Vasiliou, V. Glutathione defense mechanism in liver injury: Insights from animal models. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ACMT Position Statement: Duration of Intravenous Acetylcysteine Therapy Following Acetaminophen Overdose. J. Med. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 126–127. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, D.; Hanawa, N.; Saberi, B.; Kaplowitz, N. Mechanisms of liver injury. III. Role of glutathione redox status in liver injury. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G1–G7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weydert, C.J.; Cullen, J.J. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, K.; Marcus, C.B.; Huffman, K.; Kruk, H.; Malfroy, B.; Doctrow, S.R. Synthetic combined superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics are protective as a delayed treatment in a rat stroke model: A key role for reactive oxygen species in ischemic brain injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Y.; Doctrow, S.R.; Tocco, G.; Baudry, M. EUK-134, a synthetic superoxide dismutase and catalase mimetic, prevents oxidative stress and attenuates kainate-induced neuropathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9897–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Y.Q. Diphenyl Dimethyl Bicarboxylate in the Treatment of Viral Hepatitis, Adjuvant or Curative? Gastroenterol. Res. 2008, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Model Type | Acute Liver Injury | Subchronic Liver Injury | Chronic Liver Injury | Psychological Acute Liver Injury | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Nor | CCl4 | DDB | Nor | DMN | DDB | Nor | TAA | DDB | Nor | Stress | DDB |
| Animal | BALB/c mice (8 in each group) | SD rats (8 in each group) | SD rats (8 in each group) | BALB/c mice (8 in each group) | ||||||||
| Inducer (Frequency) | − | CCl4 (0.2% in olive oil, ip, single) | − | DMN (10 mg/kg, ip, thrice/week, 3 weeks) | − | TAA (200 mg/kg, ip, twice/week, 14 weeks) | − | Restraint (6 h of immobilization, single) | ||||
| DDB (Dosage) | − | − | 100 mg/kg (q.d., 4 days) | − | − | 25 mg/kg (q.d., 3 weeks) | − | − | 5 mg/kg (q.d., 14 weeks) | − | − | 50 mg/kg (q.d., 5 days) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-J.; Son, C.-G. Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidative and Hepatoprotective Activities of Dimethyl Diphenyl Bicarboxylate in Four Animal Models of Hepatic Injury. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101508
Wang J-H, Hwang S-J, Son C-G. Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidative and Hepatoprotective Activities of Dimethyl Diphenyl Bicarboxylate in Four Animal Models of Hepatic Injury. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(10):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101508
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing-Hua, Seung-Ju Hwang, and Chang-Gue Son. 2021. "Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidative and Hepatoprotective Activities of Dimethyl Diphenyl Bicarboxylate in Four Animal Models of Hepatic Injury" Antioxidants 10, no. 10: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101508
APA StyleWang, J.-H., Hwang, S.-J., & Son, C.-G. (2021). Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidative and Hepatoprotective Activities of Dimethyl Diphenyl Bicarboxylate in Four Animal Models of Hepatic Injury. Antioxidants, 10(10), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101508