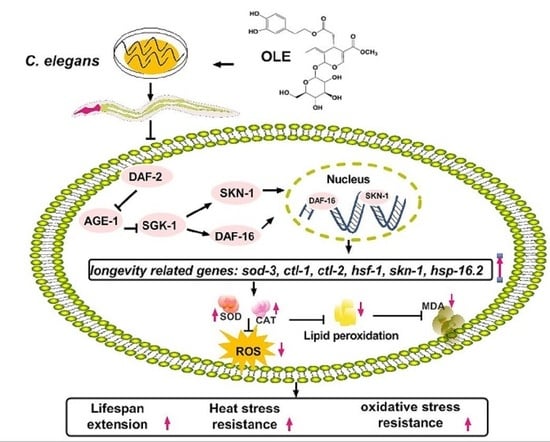
Oleuropein Enhances Stress Resistance and Extends Lifespan via Insulin/IGF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. C. elegans Strains and Maintenance
2.3. Lifespan Assay
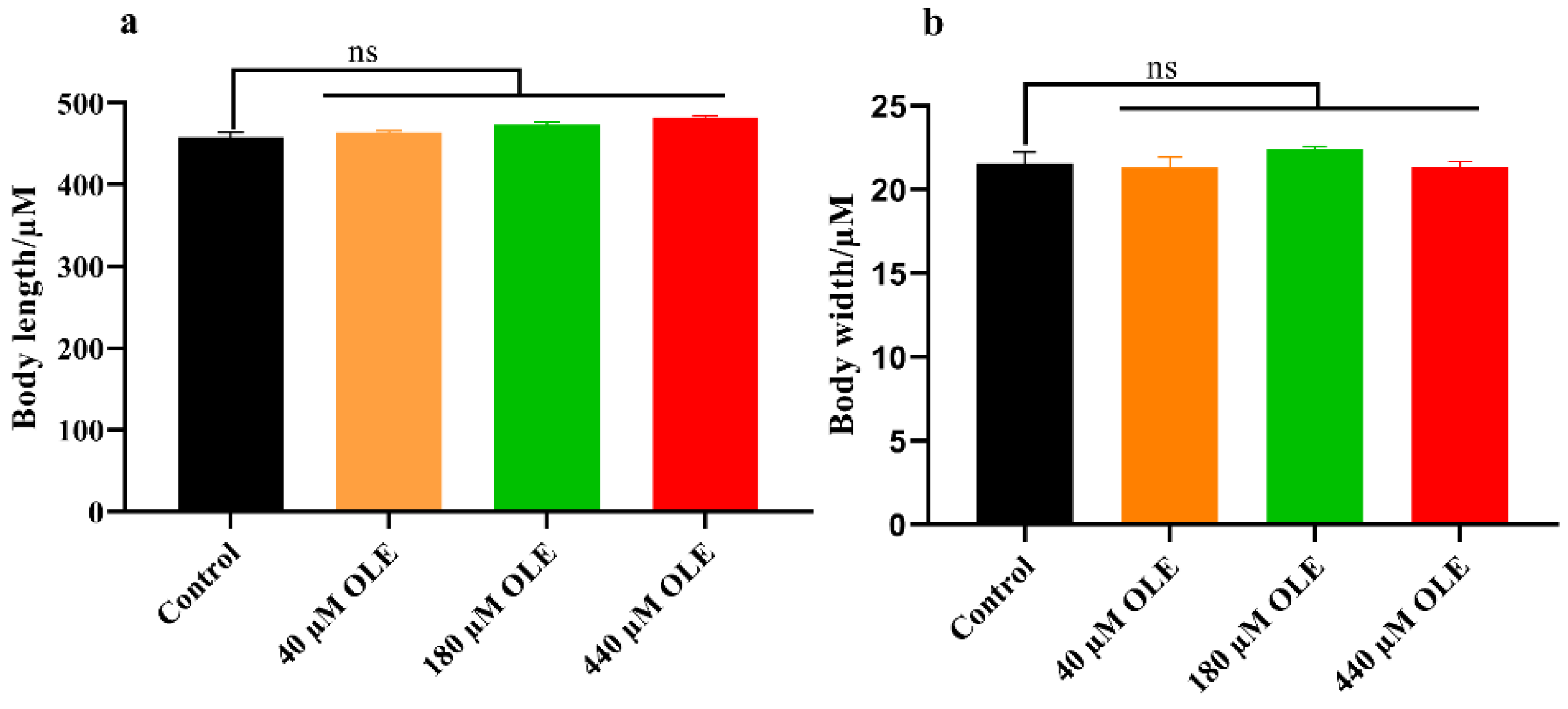
2.4. Body Length and Width Measurements
2.5. Heat Stress Assay
2.6. Oxidative Stress Assay
2.7. Measurement of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.8. Quantification sod-3p::GFP Expression
2.9. Quantification hsp-16.2p::GFP Expression
2.10. DAF-16::GFP Localization Assay
2.11. Analysis of Genes Expression by qRT-PCR
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
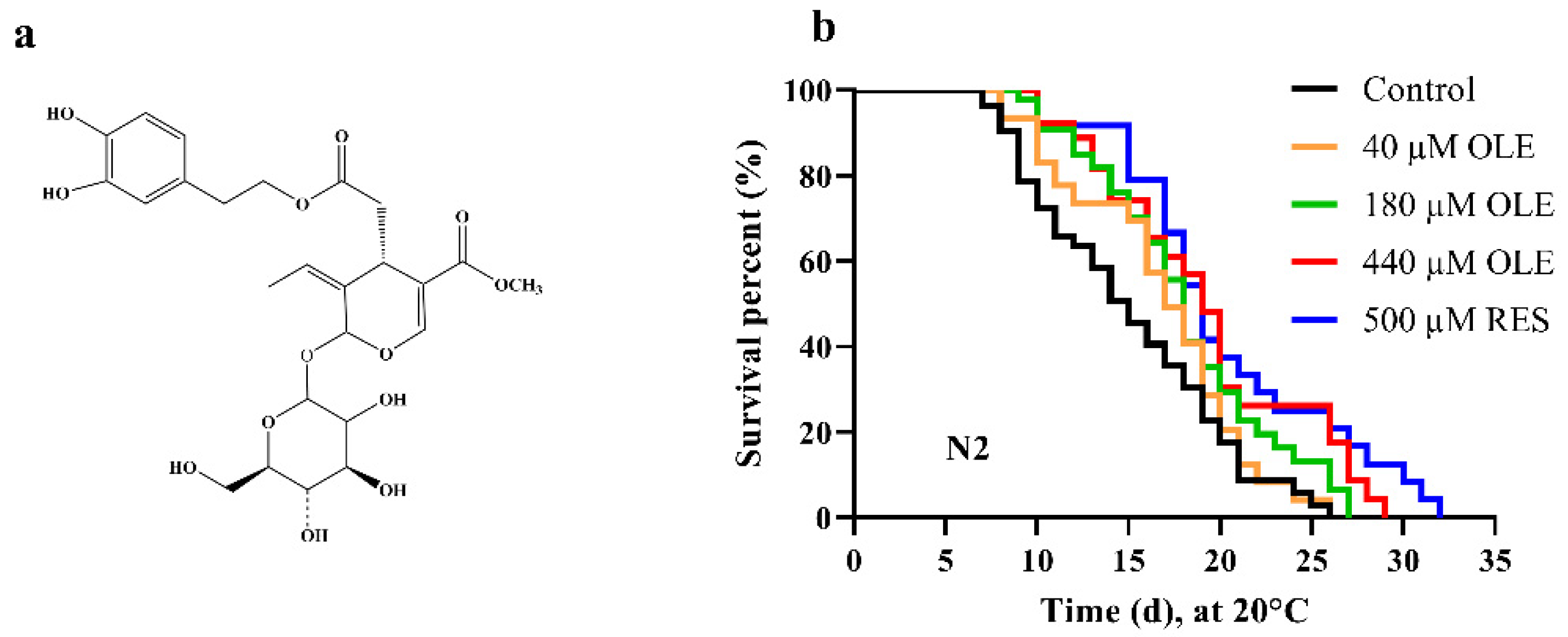
3.1. OLE Extends C. elegans Lifespan
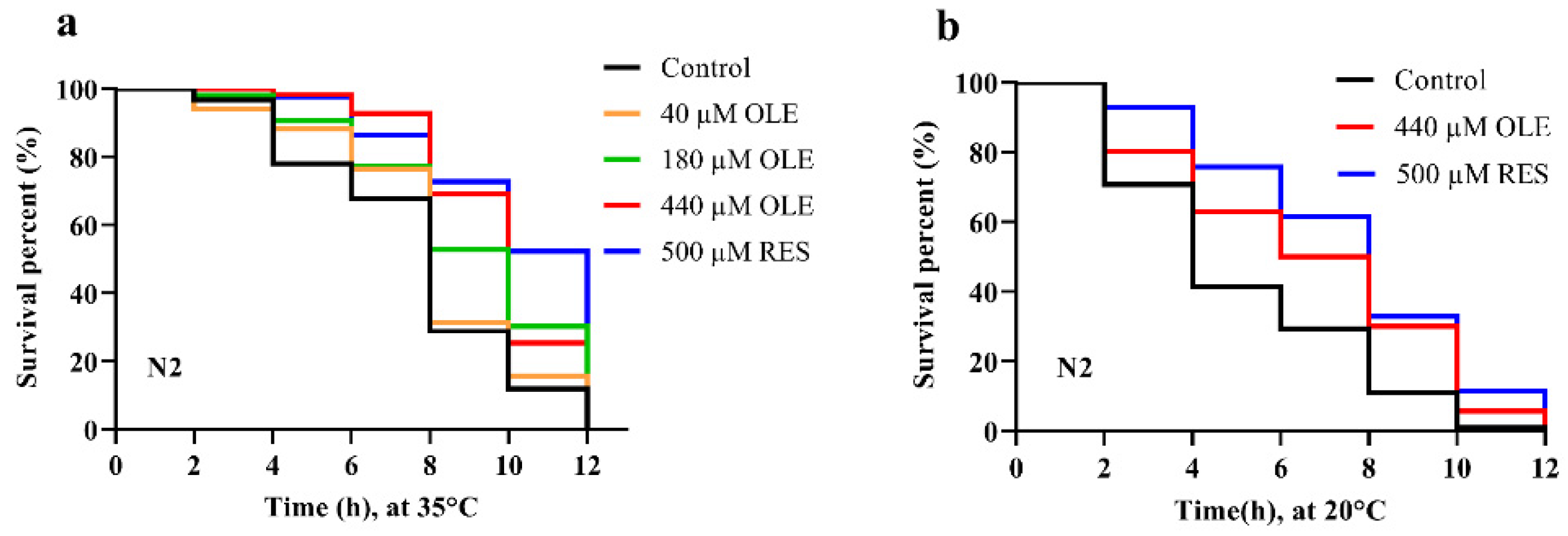
3.2. OLE Enhances Resistance of C. elegans against Heat and Oxidative Stress
3.3. OLE Reduces the MDA Content and Enhances Antioxidant Enzymes Activities
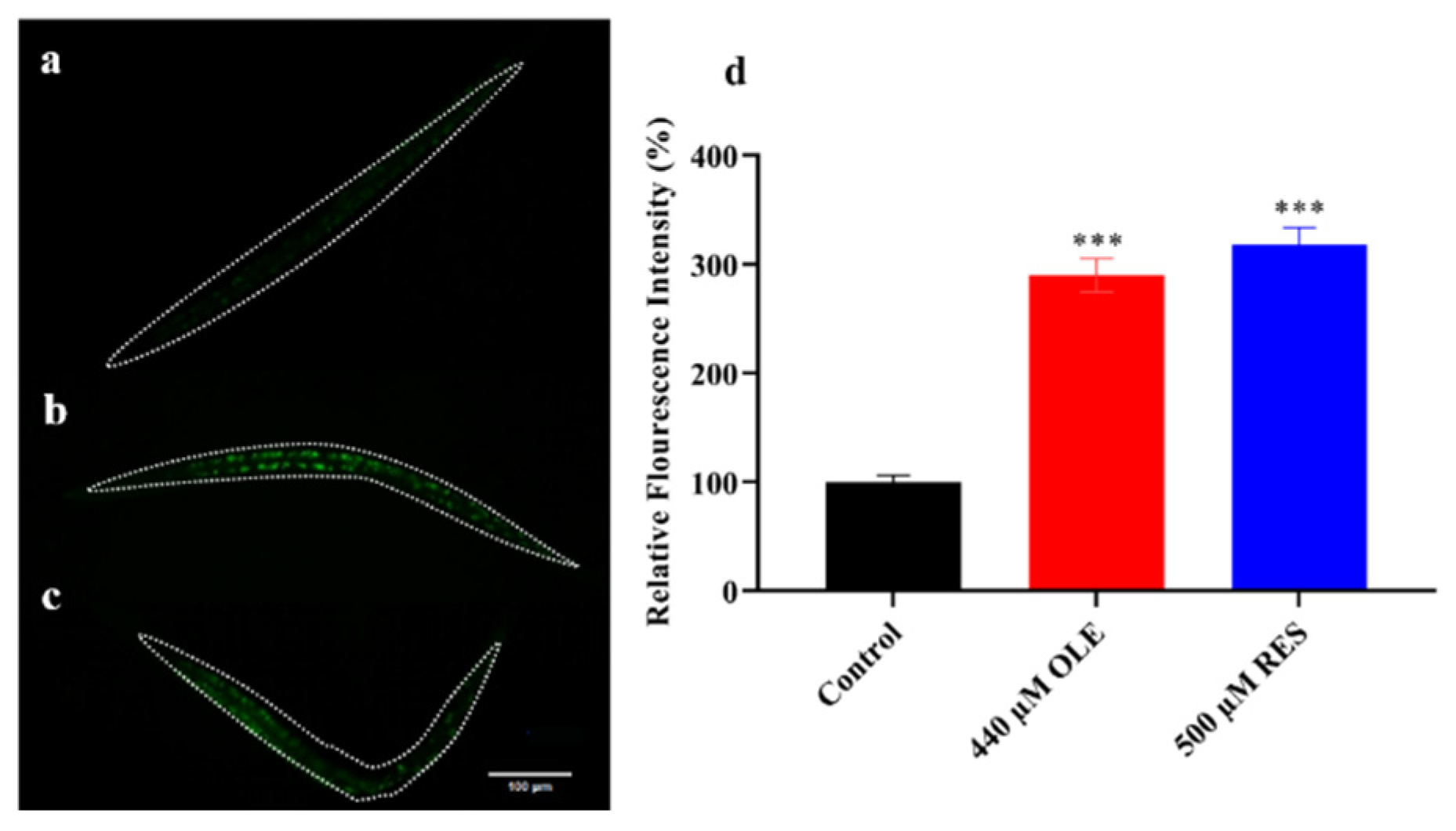
3.4. OLE Increases Expression of sod-3p::GFP in C. elegans
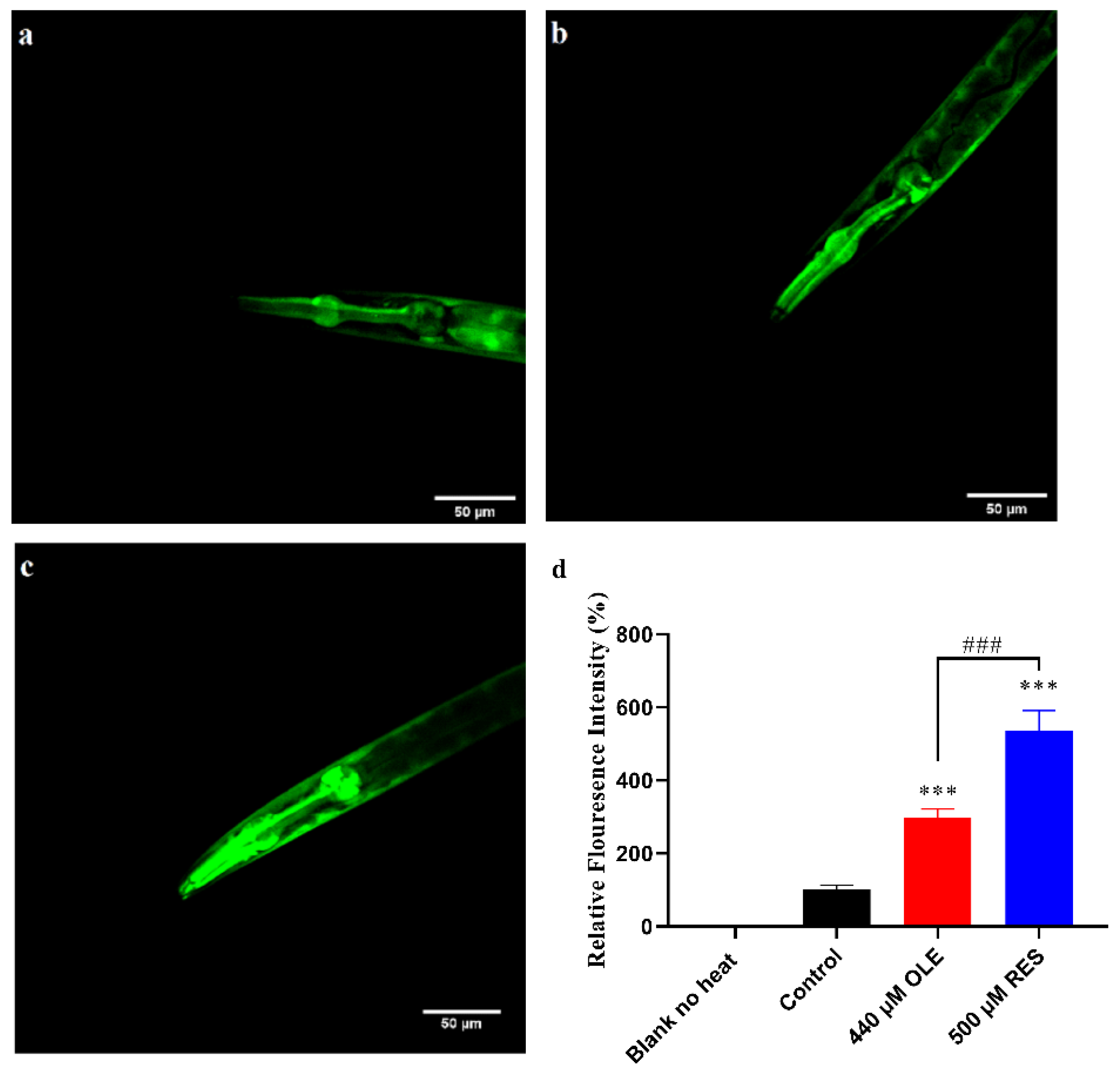
3.5. OLE Strengthens the Expression of hsp-16.2p::GFP in C. elegans
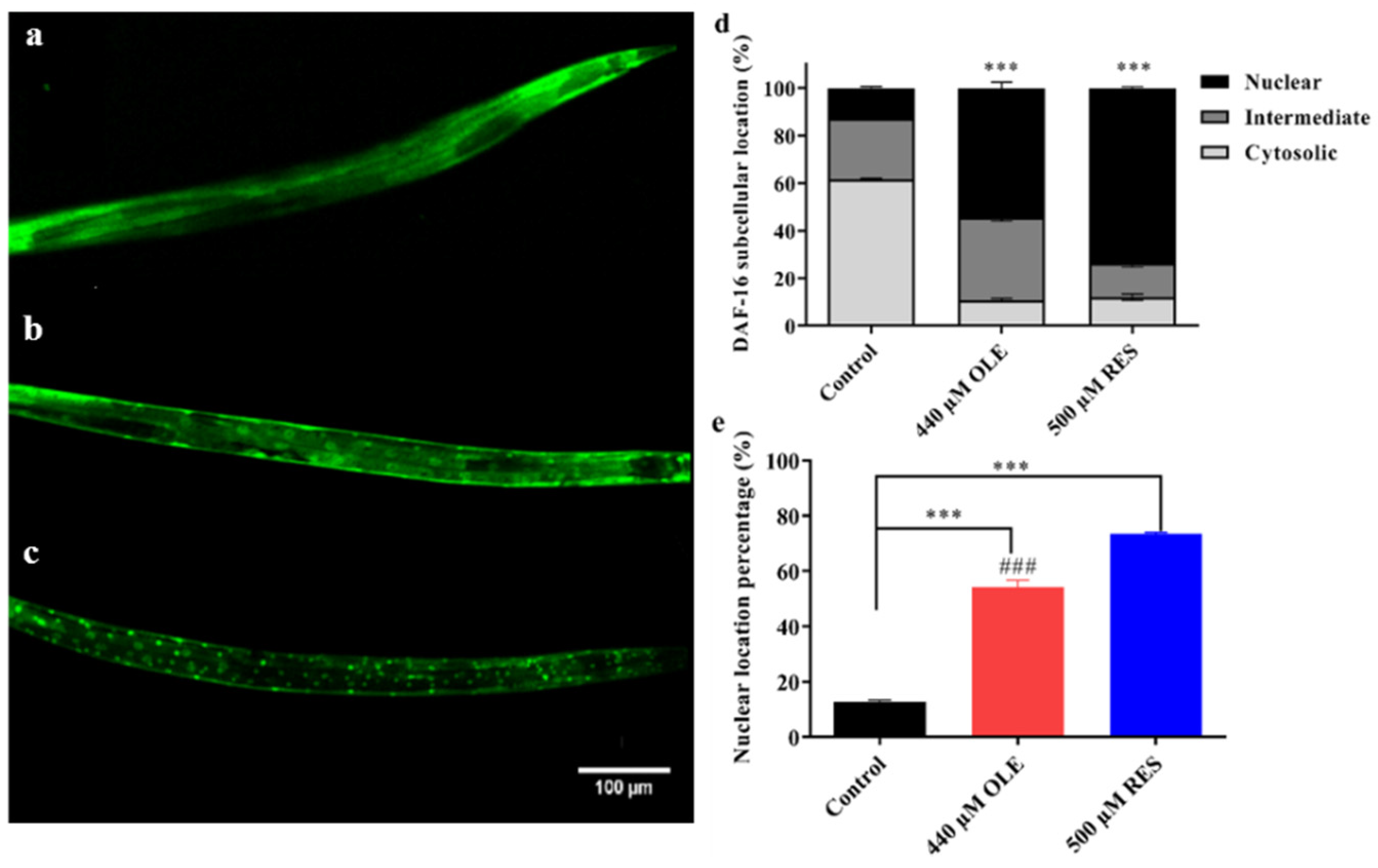
3.6. OLE Promotes Nuclear Translocation of DAF-16
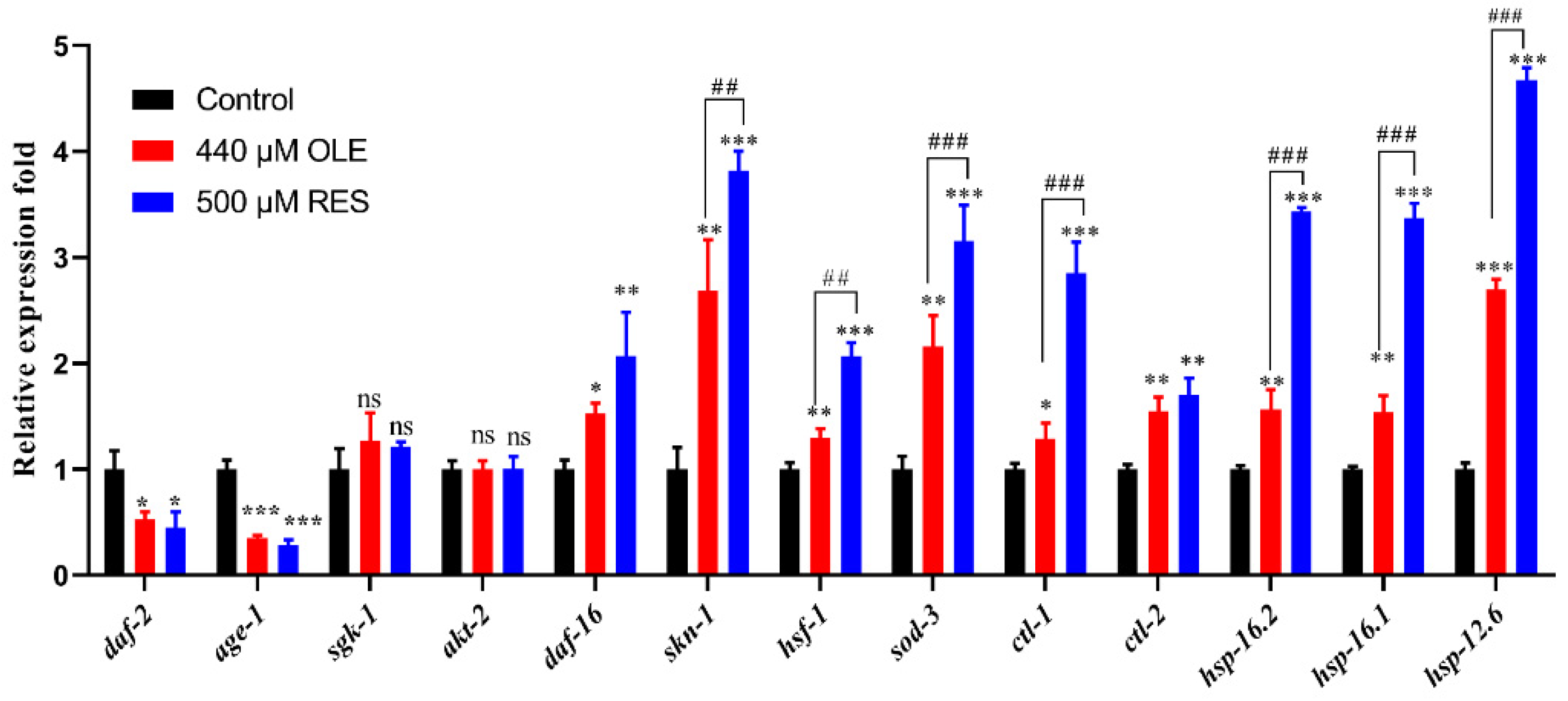
3.7. OLE Extends Healthspan of C. elegans via IIS Pathway and SKN-1/Nrf2 Transcription Factor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayes, J.; Allen, P.; Brunton, N.; O’Grady, M.; Kerry, J. Phenolic composition and in vitro antioxidant capacity of four commercial phytochemical products: Olive leaf extract (Olea europaea L.), lutein, sesamol and ellagic acid. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaivits, E.; Termentzi, A.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Fokialakis, N.; Topakas, E. Enzymatic tailoring of oleuropein from Olea europaea leaves and product identification by HRMS/MS spectrometry. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 253, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, S.H. Oleuropein in olive and its pharmacological effects. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menendez, J.A.; Joven, J.; Aragonès, G.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Camps, J.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Cufí, S.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; et al. Xenohormetic and anti-aging activity of secoiridoid polyphenols present in extra virgin olive oil. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rigacci, S. Olive Oil Phenols as Promising Multi-targeting Agents against Alzheimer’s Disease. In Natural Compounds as Therapeutic Agents for Amyloidogenic Diseases; Vassallo, N., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 863, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, S.; Fereshteh, M.; Mansooreh, S. Antioxidant role of oleuropein on midbrain and dopaminergic neurons of substantia nigra in aged rats oleuropein ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress in mice. Iran. Biomed. J. 2014, 18, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Metin, O.; Ayla, O.; Musa, K.; Oguz, M.; Hasan, O.; Abdulsamed, K.; Mahmut, K. Oleuropein ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress in mice. J. Trace Elem. Med. Bio. 2016, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Daitoku, H.; Fukamizu, A. FOXO transcription factors in the regulatory networks of longevity. J. Biochem. 2007, 141, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangjan, C.; Rangsinth, P.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wink, M.; Tencomnao, T. Glochidion zeylanicum leaf extracts exhibit lifespan extending and oxidative stress resistance properties in Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-16/FoxO and SKN-1/Nrf-2 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2019, 64, 153061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Huang, Y.; Liao, J.; Yang, R.; Zhou, L.; Ding, C. Panax notoginseng polysaccharide increases stress resistance and extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 45, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, M.; Chondrogianni, N.; Chinou, I.; Rivett, A.J.; Gonos, E.S. The Olive Constituent Oleuropein Exhibits Proteasome Stimulatory Properties In Vitro and Confers Life Span Extension of Human Embryonic Fibroblasts. Rejuv. Res. 2007, 10, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Foster, A.L.; Vantipalli, M.C.; White, M.P.; Sampayo, J.N.; Gill, M.S.; Olsen, A.; Lithgow, G.J. Compounds that confer thermal stress resistance and extended lifespan. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lithgow, G.J.; Walker, G.A. Stress resistance as a determinate of C. elegans lifespan. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendler, M.; Riedinger, C.; Schlotterer, A.; Volk, N.; Fleming, T.; Herzig, S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Morcos, M. Reduction in ins-7 gene expression in non-neuronal cells of high glucose exposed Caenorhabditis elegans protects from reactive metabolites, preserves neuronal structure and head motility, and prolongs lifespan. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2016, 31, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suthammarak, W.; Somerlot, B.H.; Opheim, E.; Sedensky, M.; Morgan, P.G. Novel interactions between mitochondrial superoxide dismutases and the electron transport chain. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McElwee, J.; Bubb, K.; Thomas, J.H. Transcriptional outputs of the Caenorhabditis elegans forkhead protein DAF-16. Aging Cell 2003, 2, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cañuelo, A.; Gilbert-Lopez, B.; Liñán, P.J.P.; Martínez-Lara, E.; Siles, E.; Miranda-Vizuete, A. Tyrosol, a main phenol present in extra virgin olive oil, increases lifespan and stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2012, 133, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhong, Q.; Kuang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Effects on longevity extension and mechanism of action of carnosic acid in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Li, J.; Rao, Y.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y. Gengnianchun Extends the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via the Insulin/IGF-1 Signalling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Guo, J.; Huo, C.; Wang, M.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Oleuropein improves mitochondrial function to attenuate oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2 pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.H.; Vranas, K.; Lucke, M.; Inoue, H.; Hisamoto, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Blackwell, T.K. Regulation of the Caenorhabditis elegans oxidative stress defense protein SKN-1 by glycogen synthase kinase-3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16275–16280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tullet, J.M.; Hertweck, M.; An, J.H.; Baker, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Liu, S.; Oliveira, R.P.; Baumeister, R.; Blackwell, T.K. Direct Inhibition of the Longevity-Promoting Factor SKN-1 by Insulin-like Signaling in C. elegans. Cell 2008, 132, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carranza, A.D.V.; Saragusti, A.; Chiabrando, G.A.; Carrari, F.; Asis, R. Effects of chlorogenic acid on thermal stress tolerance in C. elegans via HIF-1, HSF-1 and autophagy. Phytomedicine 2020, 66, 153132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Su, Z.; Xiao, J.; Lv, M.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Carnosol improved lifespan and healthspan by promoting antioxidant capacity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5958043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.-Z.; Yu, Y.-T.; Lin, H.-R.; Liao, D.-C.; Cui, X.-H.; Wang, H.-B. Lonicera japonica extends lifespan and healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.H. Cardioprotective and neuroprotective roles of oleuropein in olive. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, A.-J.; Zheng, S.; Huang, X.-B.; Xing, T.-K.; Wu, G.-S.; Sun, H.-Y.; Qi, S.-H.; Luo, H.-R. Current perspective in the discovery of anti-aging agents from natural products. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2017, 7, 335–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, C.T. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in C. elegans. WormBook 2013, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackwell, T.K.; Steinbaugh, M.J.; Hourihan, J.M.; Ewald, C.Y.; Isik, M. SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Gene Accession Number | Gene | Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Gene ID: 179535 | act-1 F | 5’-CCAGGAATTGCTGATCGTATGCAGAA-3’ |
| Gene ID: 179535 | act-1 R | 5’-TGGAGAGGGAAGCGAGGATAGA-3’ |
| Gene ID: 175410 | daf-2 F | 5’-GGATAAAGGCGAATCAAAGTGTC-3’ |
| Gene ID: 175410 | daf-2 R | 5’-CGATACACTTTCCCTTGTGATAGAC-3’ |
| Gene ID: 174762 | age-1 F | 5’-CCTGAACCGACTGCCAATC-3’ |
| Gene ID: 174762 | age-1 R | 5’-GTGCTTGACGAGATATGTGTATTG-3’ |
| Gene ID: 181524 | akt-2 F | 5′-ACATTCAGCGAAGCACGAACA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 181524 | akt-2 R | 5′-TACATGACCACTCCGACTCCC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 172981 | daf-16 F | 5′-TCGTCGTCTCGTGTTTCTCCA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 172981 | daf-16 R | 5′-TTCCATAGGCACCCGGTAGTG-3′ |
| Gene ID: 181697 | sgk-1 F | 5′-CACCGACTTTGGGCTCTGTAA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 181697 | sgk-1 R | 5′-CTTGAGACGAAGTGGCTGGTT-3′ |
| Gene ID: 177343 | skn-1 F | 5′-AGTGTCGGCGTTCCAGATTTC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 177343 | skn-1 R | 5′-GTCGACGAATCTTGCGAATCA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 173078 | hsf-1 F | 5′-TTGACGACGACAAGCTTCCAGT-3′ |
| Gene ID: 173078 | hsf-1 R | 5′-AAAGCTTGCACCAGAATCATCCC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 181748 | sod-3 F | 5′-CTAAGGATGGTGGAGAACCTTCA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 181748 | sod-3 R | 5′-CGCGCTTAATAGTGTCCATCAG-3′ |
| Gene ID: 178659 | hsp-16.2 F | 5′-CTGCAGAATCTCTCCATCTGAGTC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 178659 | hsp-16.2 R | 5′-AGATTCGAAGCAACTGCACC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 259738 | ctl-1 F | 5′-TTTCAACGGTCGCTGGAGAA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 259738 | ctl-1 R | 5′-AGTCTGTGGATTGCGCTTCA-3′ |
| Gene ID: 175085 | ctl-2 F | 5′-TTCGCTGAGGTTGAACAATCCG-3′ |
| Gene ID: 175085 | ctl-2 R | 5′-GTTGCTGATTGTCATAAGCCATTGC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 179286 | hsp-16.1 F | 5′-GTCACTTTACCACTATTTCCGTCCAGCTCAACGTTC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 179286 | hsp-16.1 R | 5′-CAACGGGCGCTTGCTGAATTGGAATAGATCTTCC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 177778 | hsp-12.6 F | 5′-GTGATGGCTGACGAAGGAAC-3′ |
| Gene ID: 177778 | hsp-12.6 R | 5′-GGGAGGAAGTTATGGGCTTC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, T.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Li, T.; Ding, C. Oleuropein Enhances Stress Resistance and Extends Lifespan via Insulin/IGF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111697
Feng S, Zhang C, Chen T, Zhou L, Huang Y, Yuan M, Li T, Ding C. Oleuropein Enhances Stress Resistance and Extends Lifespan via Insulin/IGF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(11):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111697
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Shiling, Chunyan Zhang, Tao Chen, Lijun Zhou, Yan Huang, Ming Yuan, Tian Li, and Chunbang Ding. 2021. "Oleuropein Enhances Stress Resistance and Extends Lifespan via Insulin/IGF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans" Antioxidants 10, no. 11: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111697
APA StyleFeng, S., Zhang, C., Chen, T., Zhou, L., Huang, Y., Yuan, M., Li, T., & Ding, C. (2021). Oleuropein Enhances Stress Resistance and Extends Lifespan via Insulin/IGF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants, 10(11), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111697