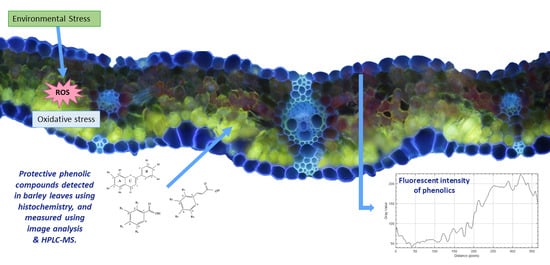
Light and CO2 Modulate the Accumulation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in Barley Leaves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
2.2. Histochemical Detection of Phenolic Compounds
2.2.1. Microscopic Image Acquisition
2.2.2. Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Compounds Using Image Analysis
2.3. Targeted HPLC-HRMS Analysis of Contents of Phenolic Compounds
2.4. Chlorophyll and UV Screening Indices
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Localization of Phenolic Compounds within Leaf Cross-Sections
3.2. Target Analysis of Phenolic Compounds by HPLC-HRMS
3.3. Chlorophyll and UV Screening Indices
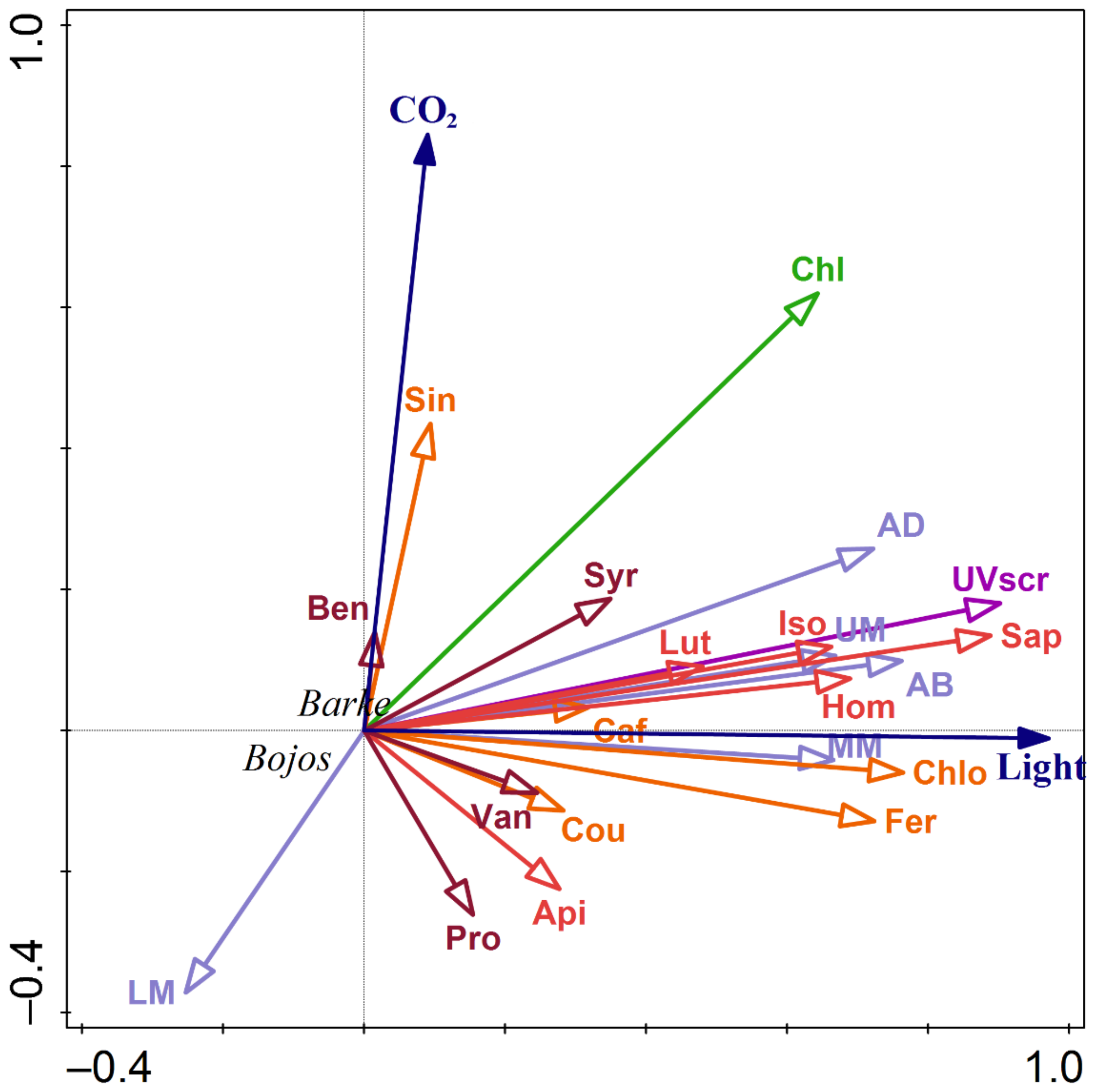
3.4. Relationships between Localization and Accumulation of PhCs in Leaves
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zohary, D.; Hopf, M. Domestication of Plants in the Old World; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 0198503563. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Crops/Regions/World List/Production Quantity for Barley; UN Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama, M.; Shibamoto, T. Flavonoids with potent antioxidant activity found in young green barley leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 60, 6260–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, B.K.; Ullrich, S.E. Barley for food: Characteristics, improvement, and renewed interest. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J. Estimating Demand for Agricultural Commodities to 2050; Report No. 3-16-10; Global Harvest Initiative: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano, D.; Ceccarelli, S.; Grando, S.; Romagosa, I.; Benbelkacem, A.; Akar, T.; Al-Yassin, A.; Pecchioni, N.; Francia, E.; Ronga, D. The impact of climate change on barley yield in the Mediterranean basin. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 106, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xiong, W.; Pan, J.; Ali, T.; Cui, Q.; Guan, D.; Meng, J.; Mueller, N.D.; Lin, E.; Davis, S.J. Decreases in global beer supply due to extreme drought and heat. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.A.; Hectors, K.; O′Brien, N.M.; Guisez, Y.; Potters, G. Plant stress and human health: Do human consumers benefit from UV-B acclimated crops? Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 449–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gara, L.; Locato, V.; Dipierro, S.; de Pinto, M.C. Redox homeostasis in plants. The challenge of living with endogenous oxygen production. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 173, S13–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyer, C.; Noctor, G. Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: A metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Lelandais, M.; Kunert, K.J. Photooxidative stress in plants. Physiol. Plant. 1994, 92, 696–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klem, K.; Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Rattanapichai, W.; Oravec, M.; Holub, P.; Veselá, B.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Urban, O. Distinct morphological, physiological, and biochemical responses to light quality in barley leaves and roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayez, K.A.; Bazaid, S.A. Improving drought and salinity tolerance in barley by application of salicylic acid and potassium nitrate. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2014, 13, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.J. Biochemical basis for the resistance of barley to aphids. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfanz, H.; Oppmann, B.; Wolf, P.; Lomsky, B. Detoxification of air pollutants in the presence of apoplastic phenols. Ishs Acta Hortic. 1994, 381, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A. Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, M.M.; Robberecht, R.; Flint, S.D. Internal filters: Prospects for UV-acclimation in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 1983, 58, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.; Miller, N.; Paganga, G. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Hu, T.X.; Zhu, D.Y. Structure-activity relationship of natural flavonoids in hydroxyl radical-scavenging effects. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002, 23, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Cuvelier, M.E.; Richard, H.; Berset, C. Comparison of the antioxidative activity of some acid-phenols: Structure-activity relationship. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agati, G.; Brunetti, C.; Di Ferdinando, M.; Ferrini, F.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Functional roles of flavonoids in photoprotection: New evidence, lessons from the past. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, I.; Alegre, L.; Van Breusegem, F.; Munné-Bosch, S. How relevant are flavonoids as antioxidants in plants? Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agati, G.; Azzarello, E.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: Location and functional significance. Plant Sci. 2012, 196, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, T.A.; Lees, H.A.; Lampi, M.A.; Enstone, D.; Brain, R.A.; Greenberg, B.M. Photosynthetic redox imbalance influences flavonoid biosynthesis in Lemma gibba. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hutzler, P.; Fischbach, R.; Heller, W.; Jungblut, T.P.; Reuber, S.; Schmitz, R.; Veit, M.; Weissenböck, G.; Schnitzler, J.P. Tissue localization of phenolic compounds in plants by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, P.; Bilger, W.; Weissenböck, G. Contribution of hydroxycinnamates and flavonoids to epidermal shielding of UV-A and UV-B radiation in developing rye primary leaves as assessed by ultraviolet-induced chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csepregi, K.; Neugart, S.; Schreiner, M.; Hideg, É. Comparative evaluation of total antioxidant capacities of plant polyphenols. Molecules 2016, 21, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agati, G.; Brunetti, C.; Fini, A.; Gori, A.; Guidi, L.; Landi, M.; Sebastiani, F.; Tattini, M. Are flavonoids effective antioxidants in plants? Twenty years of our investigation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Jaafar, H.Z.; Rahmat, A.; Rahman, Z.A. The relationship between phenolics and flavonoids production with total non structural carbohydrate and photosynthetic rate in Labisia pumila Benth. under high CO2 and nitrogen fertilization. Molecules 2011, 16, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.X.; Tiedemann, A.V. Light-dependent oxidative stress determines physiological leaf spot formation in barley. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, K.; Ač, A.; Holub, P.; Kováč, D.; Špunda, V.; Robson, T.M.; Urban, O. Interactive effects of PAR and UV radiation on the physiology, morphology and leaf optical properties of two barley varieties. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 75, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, I. Quality of malting barley grain in the Czech Republic, crop 2017. Kvasny Prumysl. 2018, 64, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofroň, P.; Skoblík, R.; Enge, J.; Sekora, M. Testing of malting barley—Variety bojos. Kvasny Prumysl. 2006, 52, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agrární Komora České Republiky. Ústrědní Kontrolní a Zkušební Ústav Zemědělsý: Obilniny 2018; Národní odrůový úřad: Brno, Czech Republic, 2018; ISBN 9788074011610. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas-Corraliza, M.G.; Rolo, V.; López-Díaz, M.L.; Moreno, G. Wheat and barley can increase grain yield in shade through acclimation of physiological and morphological traits in Mediterranean conditions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, M. The Chemistry of Lignin; Waverly Press: New York, NY, USA, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, R. Vanillin-hydrochloric acid as a histochemical test for tannin. Stain Technol. 1975, 50, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, R. Chelates of diarylboric acids with aliphatic oxyalkylamines as reagents for the detection of oxyphenyl-benzo-γ-pyrones. Die Nat. 1957, 44, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valette, C.; Andary, C.; Geiger, J.P.; Sarah, J.L.; Nicole, M. Histochemical and cytochemical investigations of phenols in roots of banana infected by the burrowing nematode Radopholus similis. Phytopathology 1998, 88, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Schweiger, J. Cell wall bound ferulic acid, the major substance of the blue-green fluorescence emission of plants. J. Plant Physiol. 1998, 152, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechtová, J.; Kubínová, Z.; Soukup, A.; Janáček, J. Image analysis: Basic procedures for description of plant structures. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1080, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agati, G.; Cerovic, Z.G.; Pinelli, P.; Tattini, M. Light-induced accumulation of ortho-dihydroxylated flavonoids as non-destructively monitored by chlorophyll fluorescence excitation techniques. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 73, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulas, Y.; Cerovic, Z.G.; Cartelat, A.; Moya, I. Dualex: A new instrument for field measurements of epidermal ultraviolet absorbance by chlorophyll fluorescence. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 4488–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smilauer, P.; Lepš, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using Canoco 5, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Day, T.A.; Martin, G.; Vogelmann, T.C. Penetration of UV-B radiation in foliage: Evidence that the epidermis behaves as a non-uniform filter. Plant Cell Environ. 1993, 16, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClendon, J.H.; Fukshanksky, L. On the interpretation of absorption spectra of leaves—II. The non-absorbed ray of the sieve effect and the mean optical pathlength in the remainder of the leaf. Photochem. Photobiol. 1990, 51, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, C.A.; Pfündel, E.E. Origins of non-linear and dissimilar relationships between epidermal UV absorbance and UV absorbance of extracted phenolics in leaves of grapevine and barley. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 25, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Neumann, E.K.; Ge, J.; Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Li, P.; Sweedler, J.V. Interrogation of spatial metabolome of Ginkgo biloba with high-resolution matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Zidorn, C.; Kasprzycka, M.; Zyna Szymczak, G.; Szewczyk, K. Phenolic acid content, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of four Kalanchoë species. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 25, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrazdina, G.; Wagner, G. Metabolic pathways as enzyme complexes: Evidence for the synthesis of phenylpropanoids and flavonoids on membrane associated enzyme complexes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1985, 237, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, D.J.; Wurms, K.V.; Labbé, C.; Bélanger, R.R. Synthesis of C-glycosyl flavonoid phytoalexins as a site-specific response to fungal penetration in cucumber. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 63, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Hoerner, R.; Weissenböck, G. Contribution of phenolic compounds to the UV-B screening capacity of developing barley primary leaves in relation to DNA damage and repair under elevated UV-B levels. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarakshina, M.M.; Ivanov, B.N.; Naydov, I.A.; Hillier, W.; Badger, M.R.; Krieger-Liszkay, A. Production and diffusion of chloroplastic H2O2 and its implication to signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dixon, R.A. MATE transporters facilitate vacuolar uptake of epicatechin 3j-O-glucoside for proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in medicago truncatula and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2323–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tattini, M.; Galardi, C.; Pinelli, P.; Massai, R.; Remorini, D.; Agati, G. Differential accumulation of flavonoids and hydroxycinnamates in leaves of Ligustrum vulgare under excess light and drought stress. New Phytol. 2004, 163, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gitz, D.C.; McClure, J.W. Effects of UV-B on flavonoids, ferulic add, growth and photosynthesis in barley primary leaves. Physiol. Plant. 1995, 93, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuber, S.; Bornman, J.F.; Weissenböck, G. Phenylpropanoid compounds in primary leaf tissues of rye (Secale cereale). Light response of their metabolism and the possible role in UV-B protection. Physiol. Plant. 1996, 97, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knogge, W.; Weissenböck, G. Tissue-distribution of secondary phenolic biosynthesis in developing primary leaves of Avena sativa L. Planta 1986, 167, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerdjieva, S.I.; Sheffield, E.; Phoenix, G.K.; Gwynn-Jones, D.; Callaghan, T.V.; Johnson, G.N. Contrasting strategies for UV-B screening in sub-Arctic dwarf shrubs. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, L. Autofluorescence in plants. Molecules 2020, 25, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.J.; Hartley, R.D. Phenolic constituents of the cell walls of monocotyledons. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1980, 8, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, P.A.; Vapaavuori, E.; Julkunen-Tiitto, R. Accumulation of phenolic compounds in birch leaves is changed by elevated carbon dioxide and ozone. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1305–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.L.; Radzikowska, D.; Ivanišová, E.; Szwengiel, A.; Kačániová, M.; Sawinska, Z. Influence of abiotic stress factors on the antioxidant properties and polyphenols profile composition of green barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattini, M.; Guidi, L.; Morassi-Bonzi, L.; Pinelli, P.; Remorini, D.; DeglÍnnocenti, E.; Giordano, C.; Massai, R.; Agati, G. On the role of flavonoids in the integrated mechanisms of response of Ligustrum vulgare and Phillyrea latifolia to high solar radiation. New Phytol. 2005, 167, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, S.G.; Logan, B.A. Energy dissipation and radical scavenging by the plant phenylpropanoid pathway. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2000, 355, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, R.J.; Ascencio, J.M.; Legrand, M. Polar ice evidence that atmospheric CO2 20,000 yr BP was 50% of present. Nature 1980, 284, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Cerling, T.E. Atmospheric CO2 and the ratio of intercellular to ambient CO2 concentrations in plants. Tree Physiol. 1995, 15, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Leuzinger, S.; Körner, C. Moving beyond photosynthesis: From carbon source to sink-driven vegetation modeling. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacio, S.; Hoch, G.; Sala, A.; Körner, C.; Millard, P. Dies carbon storage limit tree growth? New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafar, H.Z.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Karimi, E. Phenolics and flavonoids compounds, phenylanine ammonia lyase and antioxidant activity responses to elevated CO2 in Labisia pumila (Myrisinaceae). Molecules 2012, 17, 6331–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhotáková, Z.; Urban, O.; Dubánková, M.; Cvikrová, M.; Tomášková, I.; Kubínová, L.; Zvára, K.; Marek, M.V.; Albrechtová, J. The impact of long-term CO2 enrichment on sun and shade needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies): Photosynthetic performance, needle anatomy and phenolics accumulation. Plant Sci. 2012, 188–189, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Peñuelas, J.; Estiarte, M.; Kimball, B.A.; Idso, S.B.; Pinter, P.J.; Wall, G.W.; Garcia, R.L.; Hansaker, D.J.; LaMorte, R.L.; Hendrix, D.L. Variety of responses of plant phenolic concentration to CO2 enrichment. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Poorter, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Poorter, L.; Wright, I.J.; Villar, R. Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA): A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Cui, J.; Fu, Y.; Liu, H. Effect of different light intensity on physiology, antioxidant capacity and photosynthetic characteristics on wheat seedlings under high CO2 concentration in a closed artificial ecosystem. Photosynth. Res. 2020, 144, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holub, P.; Nezval, J.; Štroch, M.; Špunda, V.; Urban, O.; Jansen, M.A.; Klem, K. Induction of phenolic compounds by UV and PAR is modulated by leaf ontogeny and barley genotype. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepacka, J.; Gujska, E.; Michalak, J. Phenolic compounds as cultivar- and variety-distinguishing factors in some plant products. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, D.; Mitchella, A.; Hampson, J.; McPherson, A. The induction of systemic resistance in barley to powdery mildew infection using salicylates and various phenolic acids. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1993, 122, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, G. (Ed.) The Oxford Companion to Beer; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; ISBN 0195367138. [Google Scholar]








| df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Var | 1 | 10.09 | 0.002 |
| [CO2] | 2 | 7.85 | <0.001 |
| Light | 1 | 266.23 | <0.001 |
| Loc | 4 | 147.23 | <0.001 |
| Var × [CO2] | 2 | 8.82 | <0.001 |
| Var × Light | 1 | 2.01 | 0.157 |
| [CO2] × Light | 2 | 15.15 | <0.001 |
| Var × Loc | 4 | 3.00 | 0.019 |
| [CO2] × Loc | 8 | 5.92 | <0.001 |
| Light × Loc | 4 | 44.58 | <0.001 |
| Var × [CO2] × Light | 2 | 1.67 | 0.189 |
| Var × [CO2] × Loc | 8 | 2.33 | 0.019 |
| Var × Light × Loc | 4 | 0.17 | 0.955 |
| [CO2] × Light × Loc | 8 | 2.12 | 0.034 |
| Var × [CO2] × Light × Loc | 8 | 0.24 | 0.982 |
| Hydroxybenzoic Acids | Hydroxycinnamic Acids | Flavones | Chlorophyll Index | UV Screening Index | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| Var | 1 | 167.03 | <0.001 | 140.09 | <0.001 | 0.02 | 0.895 | 44.94 | <0.001 | 223.92 | <0.001 |
| [CO2] | 2 | 7.73 | 0.001 | 5.21 | 0.008 | 15.28 | <0.001 | 73.39 | <0.001 | 62.87 | <0.001 |
| Light | 1 | 56.98 | <0.001 | 198.83 | <0.001 | 325.94 | <0.001 | 160.55 | <0.001 | 1517.14 | <0.001 |
| Var × [CO2] | 2 | 11.15 | <0.001 | 1.21 | 0.305 | 1.22 | 0.302 | 0.43 | 0.653 | 6.72 | 0.002 |
| Var × Light | 1 | 44.61 | <0.001 | 23.16 | <0.001 | 4.43 | 0.040 | 0.74 | 0.394 | 14.83 | <0.001 |
| [CO2]× Light | 2 | 5.72 | 0.005 | 2.22 | 0.117 | 8.05 | <0.001 | 1.49 | 0.234 | 16.13 | <0.001 |
| Var × [CO2] × Light | 2 | 8.67 | <0.001 | 0.58 | 0.562 | 2.35 | 0.104 | 2.40 | 0.099 | 0.53 | 0.592 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hunt, L.; Klem, K.; Lhotáková, Z.; Vosolsobě, S.; Oravec, M.; Urban, O.; Špunda, V.; Albrechtová, J. Light and CO2 Modulate the Accumulation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in Barley Leaves. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030385
Hunt L, Klem K, Lhotáková Z, Vosolsobě S, Oravec M, Urban O, Špunda V, Albrechtová J. Light and CO2 Modulate the Accumulation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in Barley Leaves. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(3):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030385
Chicago/Turabian StyleHunt, Lena, Karel Klem, Zuzana Lhotáková, Stanislav Vosolsobě, Michal Oravec, Otmar Urban, Vladimír Špunda, and Jana Albrechtová. 2021. "Light and CO2 Modulate the Accumulation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in Barley Leaves" Antioxidants 10, no. 3: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030385
APA StyleHunt, L., Klem, K., Lhotáková, Z., Vosolsobě, S., Oravec, M., Urban, O., Špunda, V., & Albrechtová, J. (2021). Light and CO2 Modulate the Accumulation and Localization of Phenolic Compounds in Barley Leaves. Antioxidants, 10(3), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030385